Unit 7: RNA, Protein Synthesis, Mutations, Cloning, and Stem Cells
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
RNA
type of nucleic acid that is used during protein synthesis
Differences in RNA and DNA
RNA: ribose, single-stranded, and uracil
DNA: deoxyribose, double-helix, and thymine
How many types of RNA are there, and what are they called?
3; mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
mRNA
copy of a single gene in DNA
tRNA
adds amino acids and complementary bases to mRNA
rRNA
ribosome that reads mRNA
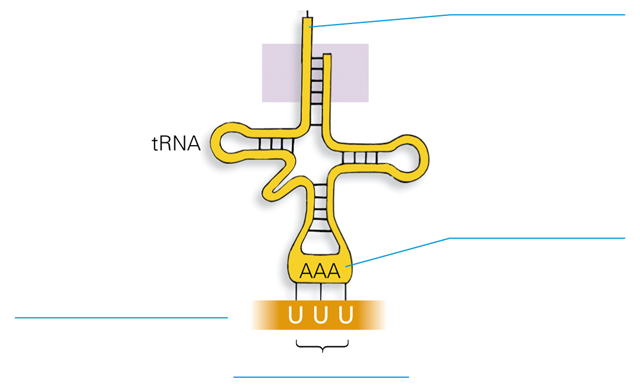
What type of RNA is this?
tRNA
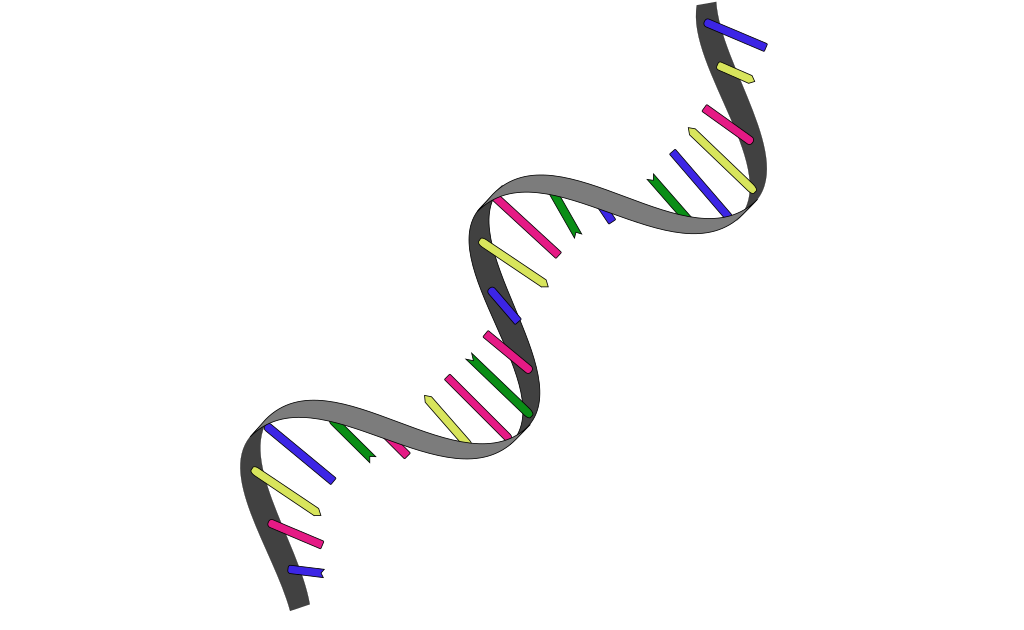
What type of RNA is this?
mRNA
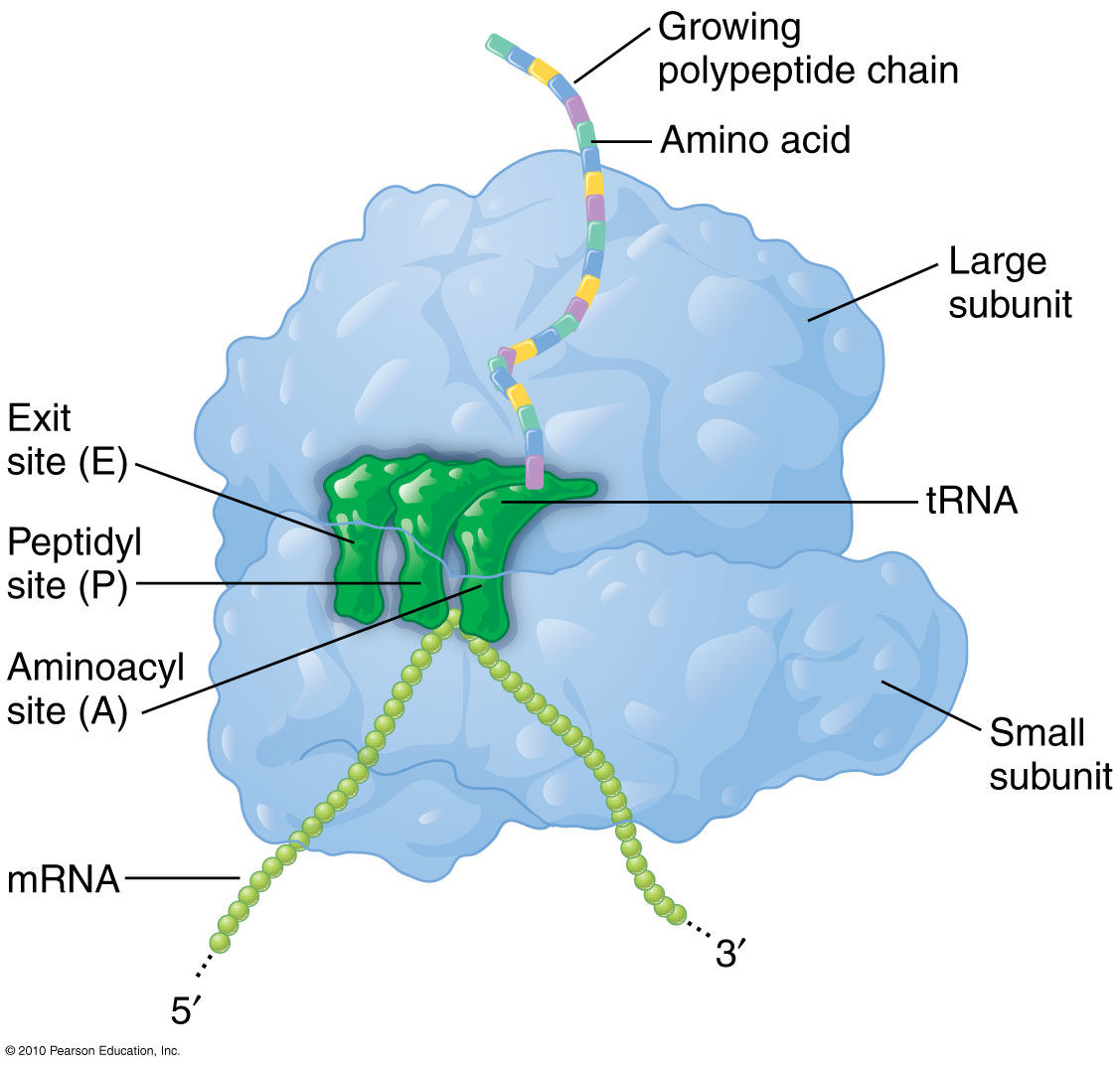
What type of RNA is this?
rRNA
What is the first step in protein synthesis and where does it take place?
Transcription in the nucleus
What is made in transcription?
mRNA
What is a codon and what does it code for?
A codon is three base long sequences that code for amino acids
What RNA type are codons found on?
mRNA
RNA Polymerase (what does it do, when does it do it)
temporarily unwinds DNA and adds complementary bases to mRNA during transcription
Promoter
TATA box that RNA binds to that indicates the start of the sequence
Terminator
stops transcription
What three things occur to the mRNA during mRNA processing?
MgCap is added, Poly-A-Tail is added, introns are removed and exons combine
What is the second step of protein synthesis and where does it occur?
mRNA processing in the nucleus
What is the third step of protein synthesis and where does it occur?
Translation in the cytoplasam
What do you make in translation?
Polypeptides/ Amino Acid Chains
What types of RNA are involved in translation?
All types! mRNA is used as the template of translation. tRNA adds the amino acids to the ribosomes. rRNA is the ribosome (E.P.A.)
In rRNA what does EPA stand for?
E- amino acids chain exits
P- polypeptide bond forms
A- new amino acids are added
What is an anti-codon and what type of RNA is it found on?
It adds the complementary codons on mRNA. It is found on tRNA.
What is the start codon and its amino acid?
Start codon: AUG
Amino Acid: Met.
How many stop codons are there?
3
Mutation?
Any mistake or change in the sequence of DNA
How do mutations occur?
DNA copying mistakes, radiation exposure, or infections from viruses
Mutagen
any chemical substitution that leads to a mutation
What are some examples of mutagens?
Chemicals and X-Rays
Point Mutation
One single base is being changed
How many types of Point Mutations are there
3
Point-Silence Mutation
One single base is changed however the amino acid doesn’t change
Point- Missense Mutation
one single base is changed and the amino acid changes
Point- Nonsense Mutation
One single base changes and it causes the sequence to prematurely stop
Frameshift Deletion
A base is deleted causing everything to move left
Frameshift Insertion
A base is added causing everything to move right
Chromosomal Nondisjunction
sister chromatids fail to separate properly
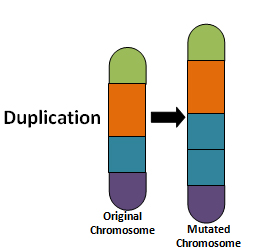
What type of chromosomal nondisjunction is this and what does this mean?
Duplicated Chromosomal Nondisjunction which means a base duplicated
What type of chromosomal nondisjunction is this and what does this mean?
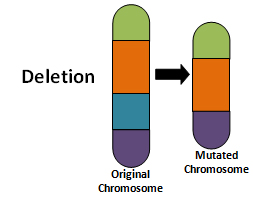
Deleted Chromosomal Nondisjunction which means a base is deleted
What type of chromosomal nondisjunction is this and what does this mean?
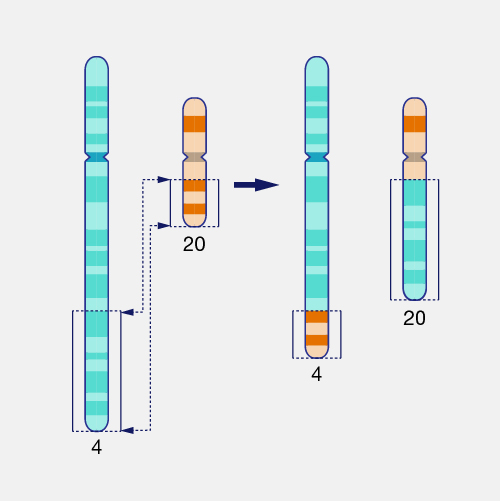
Translocation Chromosomal Nondisjunction which means two different chromosomes twisted on top of each other
What type of chromosomal nondisjunction is this and what does this mean?
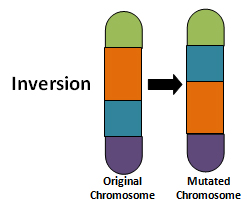
Inversion Chromosomal Nondisjunction which means two of the same chromosomes twisted on top of each other
What is the difference between reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning?
Reproductive cloning: clones/ reproduces and entire organism
Therapeutic cloning: clones one type of cell
What are STEM Cells?
Cells that can be turned into any type of cell.
What is the best source to obtain stem cells?
Embryonic
Why are embryonic cells better/ easier to work with than adult stem cells?
Easier to obtain and can change into what you want it to be
Pluripotent
can develop into every cell type, every tissue type, and every organ in a human body
What are some of the possible uses within the medical industry of STEM Cells?
Test new medications, repair cells or tissues that have been damaged by disease or injury, or Parkinson’s disease