[CC LAB] L1: Pipetting
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
reconstituting controls and calibrators
preparing serum plasma dilutions
aliquoting specimens
what are pipettes used for (3)
Serologic pipettes
what pipette to use when the volume is 1-100mL
automated micropipettes or semi automated pipettes
what pipette to use when the volume is 1uL - 1mL
graduations
Lines marked on volume measuring devices that indicate volume.
meniscus
A curve formed by the surface of liquids confined in a narrow space, such as in a measuring device.
lower meniscus
which part of the meniscus will you read if clear & colorless fluid
upper meniscus
which part of the meniscus will you read if colored fluid
eye level
When reading the meniscus in the laboratory it should be ________ to avoid errors.
tolerance
How much error is allowed in the calibration or a measuring device.
accuracy
the _____ of the readings of the measurements is based on tolerance
lower tolerance limit (class A) because it reduce the range and more precised
which one is better? the higher tolerance limit or lower tolerance limit?
NIST - National Institute of Standards and Technology
ASTM - American Society for Testing and Materials
what are the organization groups responsible for the acceptance of pipettes
National Bureau of Standards (NBS)
NIST is also known as
ASTM E542
ASTM E969
Each pipette is calibrated in accordance with _______ and meets accuracy requirements of _________.
American Society for Testing and Technology
regardless of the design, most laboratory supplies must satisfy certain tolerances of
accuracy and fall into two classes of precision tolerance (Class A or Class B) as given by what organization?
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Including pipets, is manufactured and calibrated to deliver the most accurate volume of liquid.
Defined by
College of American Pathologists (CAP)
According to what organization? - Volumetric pipets must be of certified accuracy (Class A)
swift delivery
S in the label of pipette stands for?
caulfield
spectroline
safety bulb
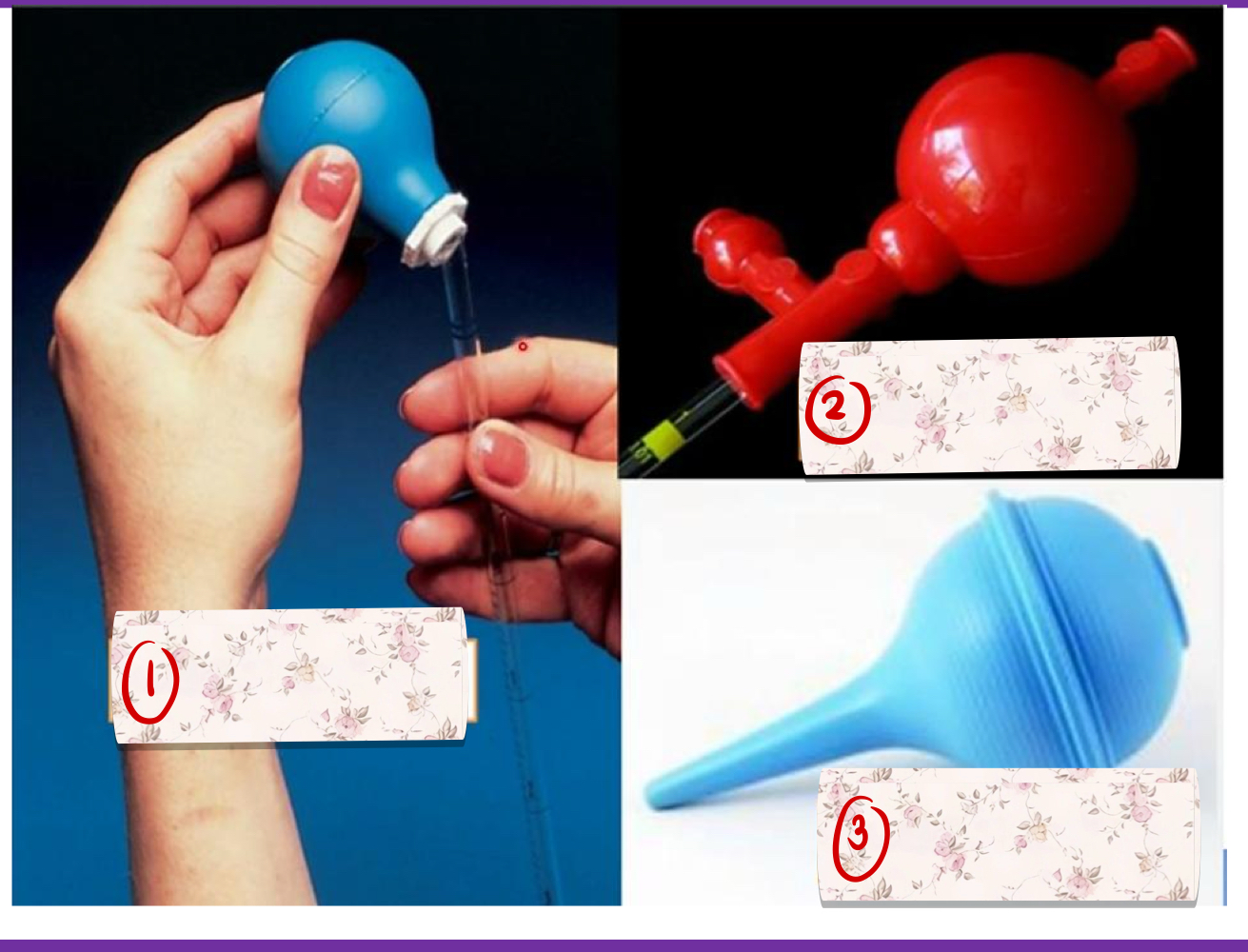
calibration Marks / Designs
Draining Characteristics
General Types / Categories
what are the 3 pipetting classifications?
To Contain (TC)
To Deliver (TD)
what are 2 types of calibration marks / designs?
Blow out
Self-Draining
what are 2 types of draining characteristics?
volumetric / transfer
measuring / graduated
what are 2 types of General types / categories
To Contain (TC)
hold or contains a particular volume but does not dispense the volume indicated
To Conta
Mercury
what is the calibrating medium of To Contain pipets
To Contain (TC)
micropipettes, long levy type, and sahli’s pipette are examples of what design
To Deliver (TD)
will dispense the volume indicated
gravity
To Deliver is designed to drain by ______
Distilled water
what is the calibrating medium of To Deliver (TD) pipet
To Deliver (TD)
Serological, Mohr pipette, Volumetric pipettes, Ostwald-Folin pipettes are examples of what pipet design?
blowout
Has 2 continuous rings located near the top of the
pipette or the area where we attach the pipette bulbs or
the safety bulbs for suction of the fluid.
blowout
The last drop of liquid should be expelled into the
receiving vessel through blowing out.
blowout
Serological and Ostwald-Folin pipettes are example of what draining characteristic
Self-draining
No ring markings located at the top of the pipettes. Draining is by gravity. what draining characteristic?
Self-Draining
Mohr pipette, Volumetric pipettes, Van Slyke pipettes are examples of what draining characteristic?
Volumetric / transfer pipets
Shaped like rolling pins with a large belly, one blunt end → the neck, one tapering end → the tip.
transfer pipette
what general type of pipet delivers only one exact volume, and they are used when a higher degree of accuracy is required
Transfer pipet
Used for preparation of standard solutions that are used (ex: in calibration)
measuring / graduated pipets
Long, cylindrical tubes drawn out to a tip and are calibrated in uniform fractional volume measurement.
measuring / graduated pipets
Mohr & Serologic Pipet are examples of what general type of pipet
measuring / graduated pipets
These pipettes can deliver multiple volumes, and are used when less accuracy of measurement is required
measuring / graduated pipets
Used for delivering of reagents or small amount of solvents, and however because of less accurate measurement for this pipet, this type of pipette should not be used for making standard solutions or quality control materials.
To deliver
Blowout
Measuring / graduated
serologic pipet
design -
draining characteristic -
general type -
To Deliver
Self-draining
Measuring / Graduated
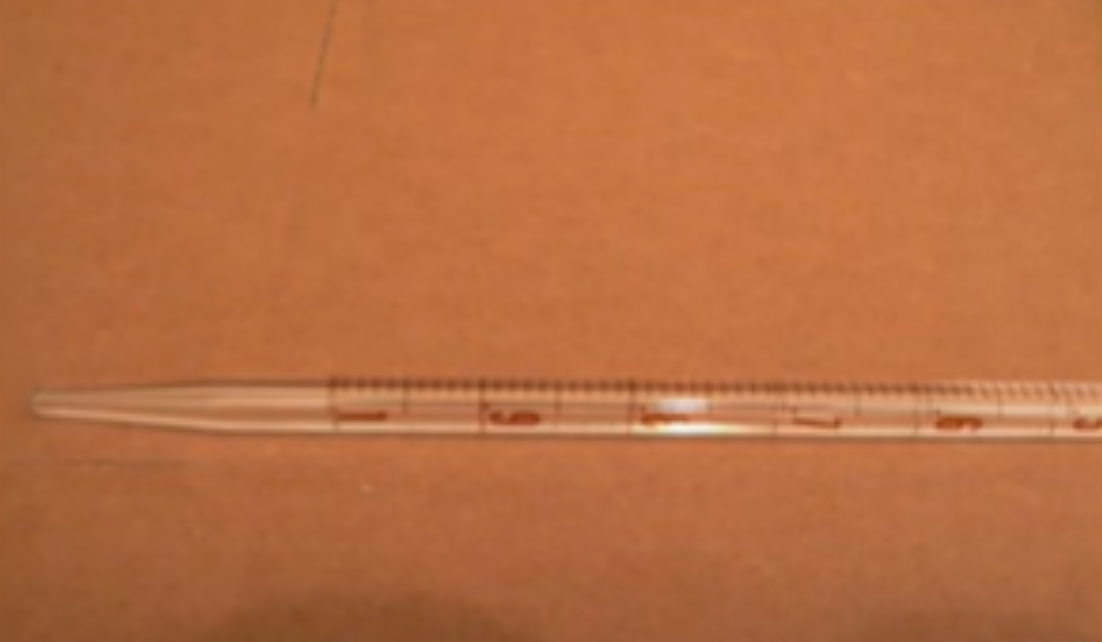
Mohr
design -
draining characteristic -
general type -
measuring / graduated
bacteriologic
general type -
measuring / graduated
ball, Kolmer, or Kahn
general type -
measuring / graduated
micropipette
general type -
To Deliver
Self-draining
Transfer / volumetric
volumetric
design -
draining characteristic -
general type -
To Deliver
Blowout
Transfer / volumetric
Ostwald-Folin
design -
draining characteristic -
general type -
Transfer / volumetric
Van Slyke Pipette
general type -
Transfer / volumetric
Sahli’s pipette
general type -
serologic pipette
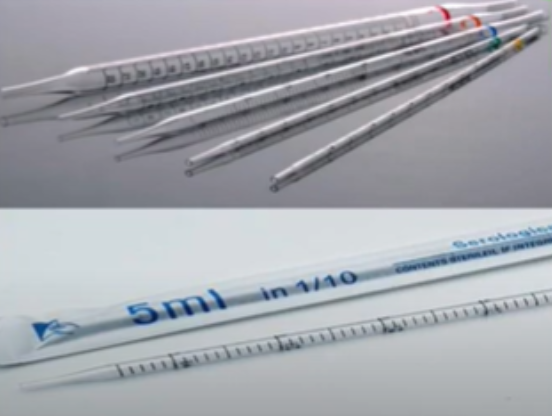

Mohr

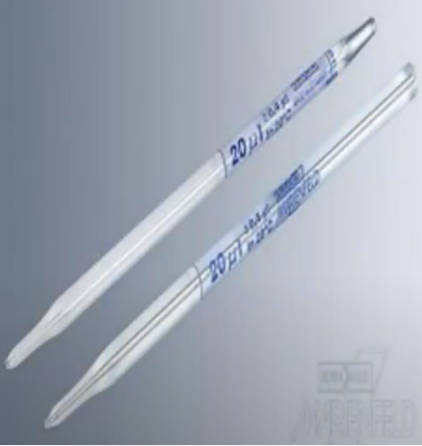
Micropipette
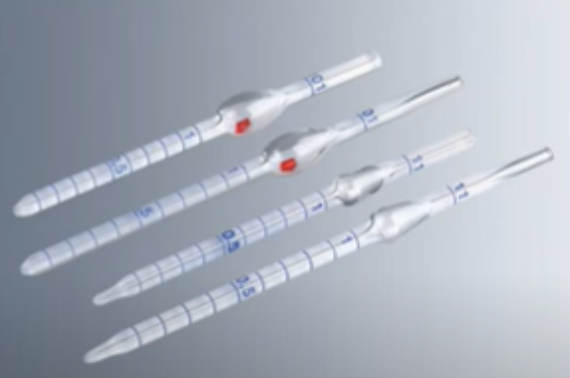
Micropipette
can only hold from 0.1 microliter to 1000 microliter (1mL = 1000 microliter)
Micropipette
o Sahli-Hellige pipette
o Lang-Levey pipette
o RBC and WBC pipettes
o Kirk and Overflow pipette
these are examples of ___ pipette
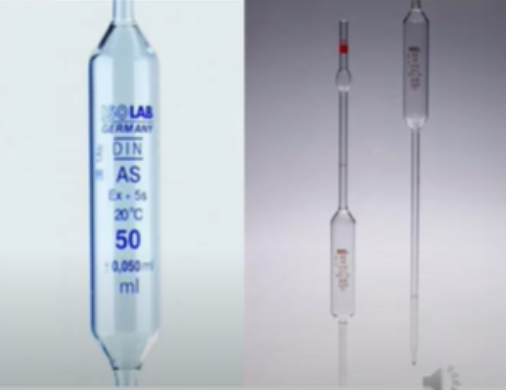
volumetric
used for non-viscous fluids
Volumetric
Have been used to add the diluent to a lyophilized control (freeze dried/powdered control) or to measure standards and controls.
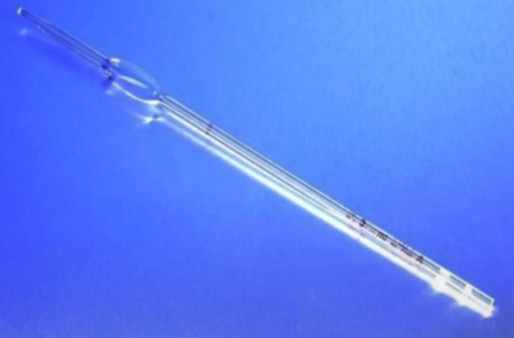
Ostwald-Folin
what transfer pipette - has the belly located at the center
Ostwald-Folin
the bulb is closer to the delivery tip, reducing the surface area in contact with the liquid
Ostwald-Folin
used for viscous fluids (whole blood, serum)
Van Slyke Pipette
Thick-walled capillary tubing with bulb in the center.
Sahli’s pipette
Can deliver 20 ul (microliters) of the aliquot.
Used in hematology, hemoglobin measurements and determination.
Volumetric pipette
Ostwald-Folin Pipette
Van Slyke Pipette

Sahli’s pipette

Mohr’s pipette

Volumetric pipette

Serologic pipette

Ostwald-Folin Pipette

Automated / Semi-automated micropipette
Lambda pipette / Dropping pipette

left - single channel
right - multichannel
what type of semi-automated pipette?
left -
right -
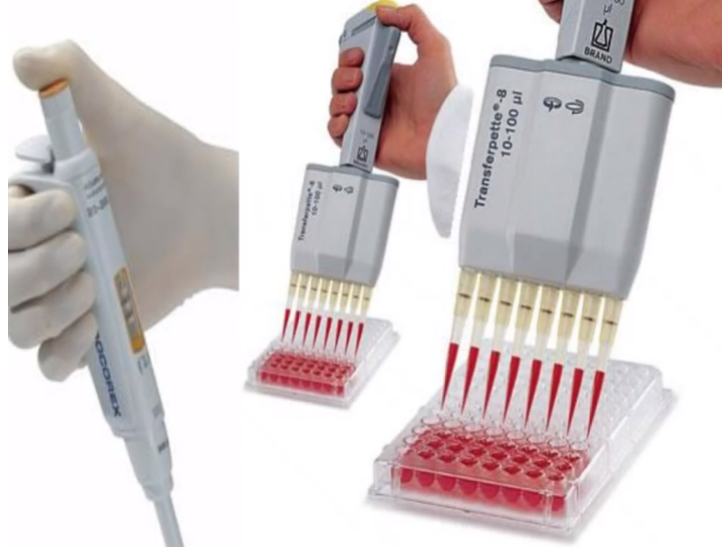
0.1uL to 1000uL
what volumes are used for semi-automated pipette?
semi-automated pipettes
offer more convenience and efficiency to pipetting. no pipetting bulb is required nor do pipettes have to be washed. only need to replace the pipetting tips every time you aspirate fluids.
propylene
what plastic tips are used in semi-automated pipette
semi-automated pipette
Advantages:
o Safety
o Stability
o Ease of use
o Increased precision
o Ability to save time
o Less cleaning required.
what pipette?
plunger
tip ejector button
friction ring
body
connecting nut
tip ejector
tip holder
tip cone
pipette tip
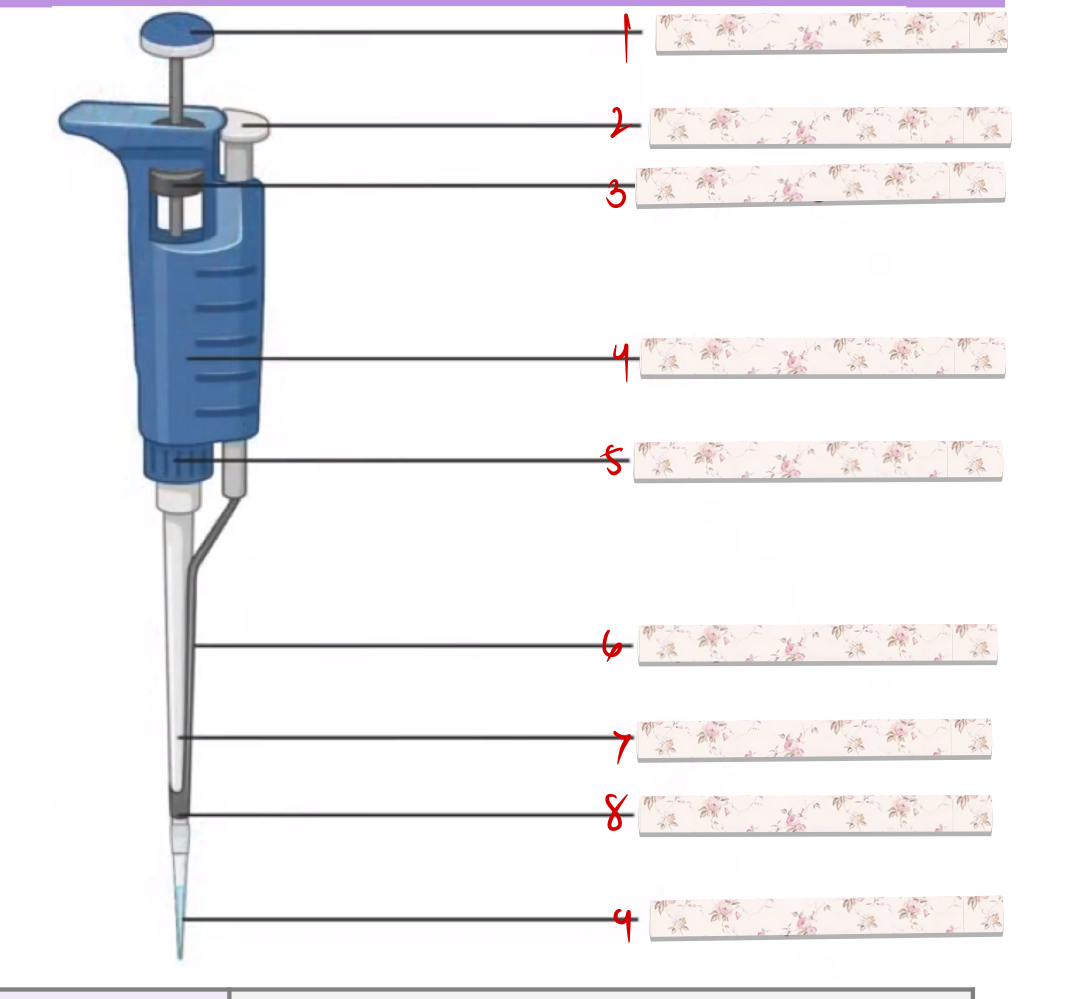
plunger
Press and release to aspirate, decant, or dispense the fluid.
tip ejector button
Used, by clicking or pushing, to discard the tip.
tip ejector
Once pushed, it will push the tip to discard.
tip cone
Where you attach the pipette tips.
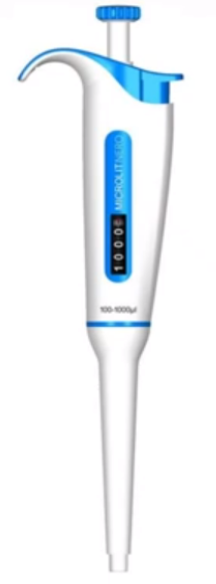
variable volume micropipette
● Change or adjust the volumes.
● From 100 to 1000 microliters (based in the picture.).
● Single channel micropipette
Fixed volume micropipette
● Can only give a fixed volume of micropipette.
● If it has 1000 microliters, it can only dispense 1000 microliters or 1 mL.
● There are also other types like 200 microliters, 20 microliters, 10 microliters, so on and so forth.
● Single channel micropipette
Multichannel micropipette
● Has a lot of tips.
● It can accommodate more than one pipet tips.

air displacement pipette
dispenser / dilutor pipette
positive displacement pipette
3 examples of mechanical or automatic pipettes
air displacement pipette
● Relies on the piston for suction creation (with the use of air) to draw the sample into a disposable tip.
● The most common principle applies.
dispenser / dilutor pipette
● Obtain the liquid from a common reservoir and dispense it repeatedly.
Positive displacement pipette
● Operates by mobbing the piston in the pipette tip or barrel, much like a hypodermic needle.
○ It suctions the fluid with the use of its piston in the pipette tip or barrel.
● Does not require a different tip for each use.
● Recommended for saline, water, and phosphate buffers.
● Not suitable for very dense liquids.