S3.2.7 Isomerism
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
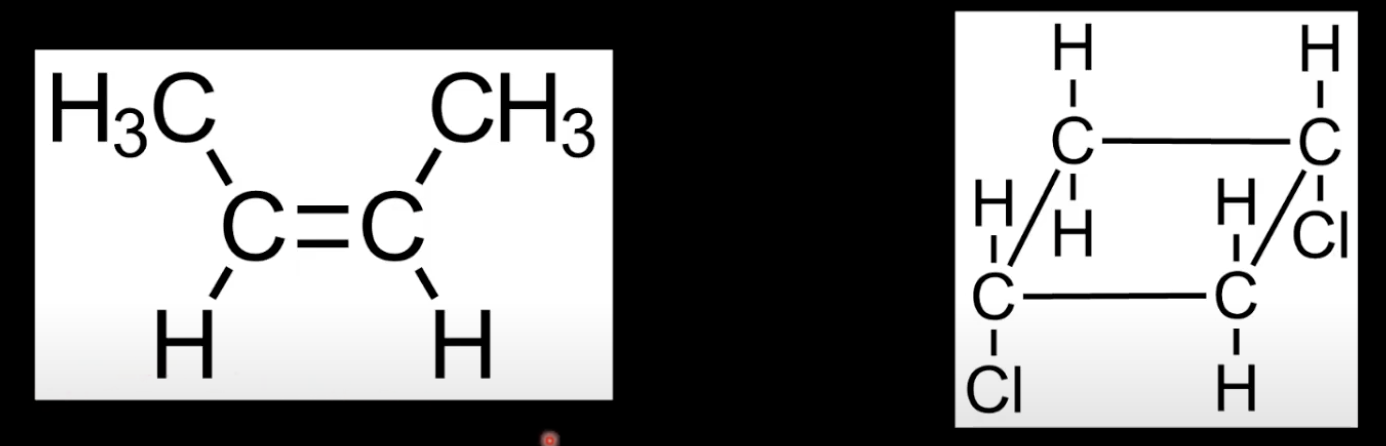
Arises from restricted rotation in double bonds or rings
Requires two different groups on each carbon of the C=C bond or ring structure.
When there are no cis-trans isomers
Only one carbon in the C=C bond has two different groups
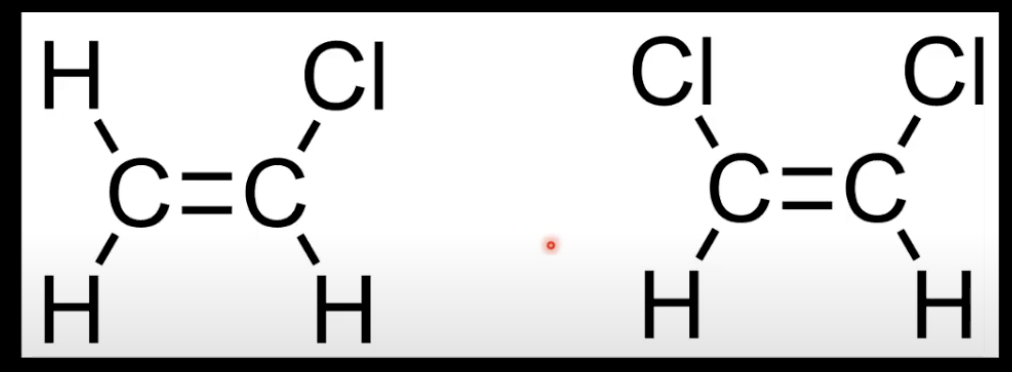
Cis-trans isomerism needs both carbons to be bonded to two different groups.
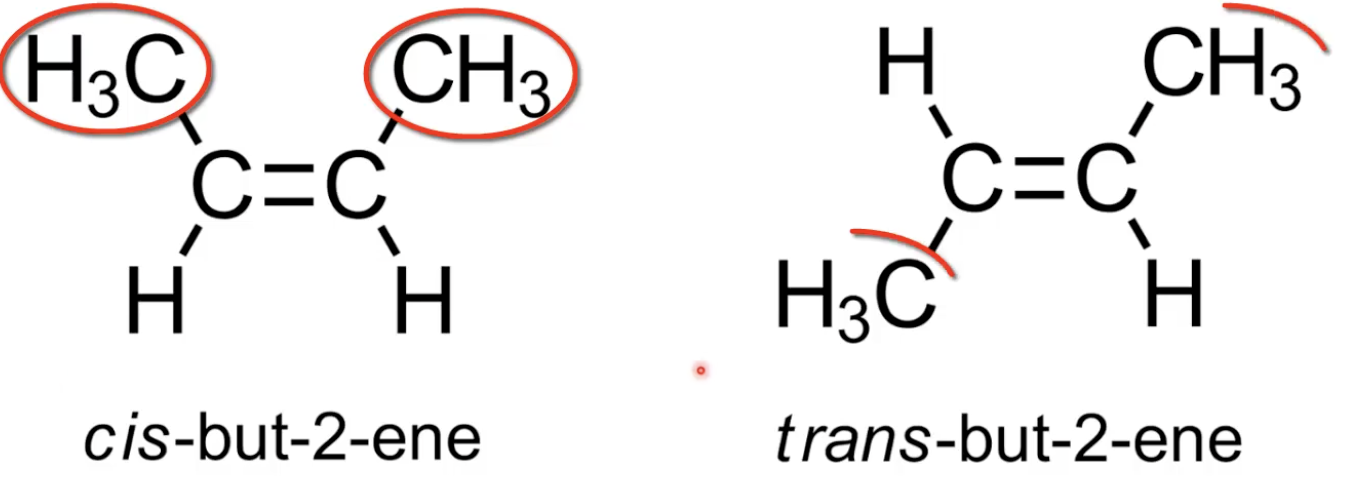
Cis has CH₃ groups on same side of C=C; trans has CH₃ groups on opposite sides
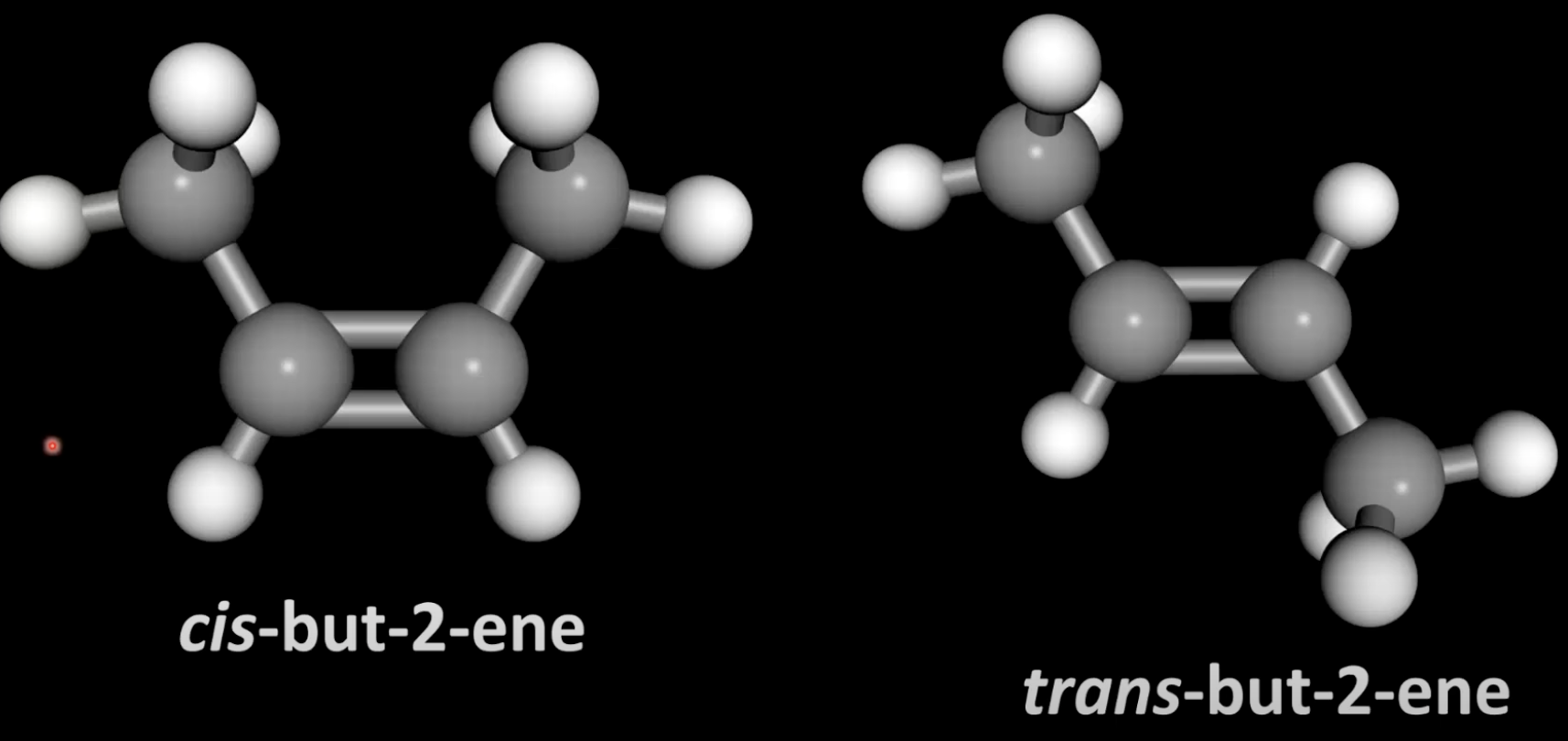
Caused by restricted rotation around the pi bond.
Cis shows CH₃ groups on same side in 3D; trans shows CH₃ groups on opposite sides
Affects polarity and boiling point.
Rotation restricted by ring
Different substituents can be on same side (cis) or opposite sides (trans) of the ring.
Cis has same substituents on same side of double bond
Trans has them on opposite sides
Occurs in unsymmetrical alkenes.
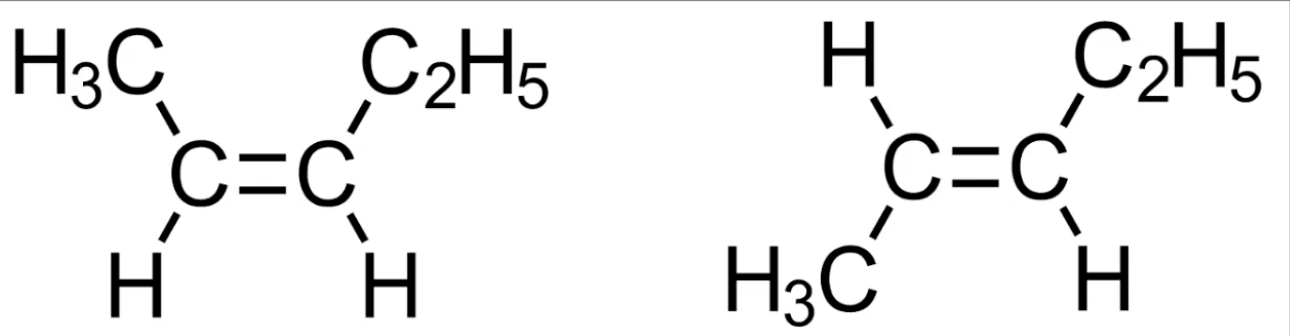
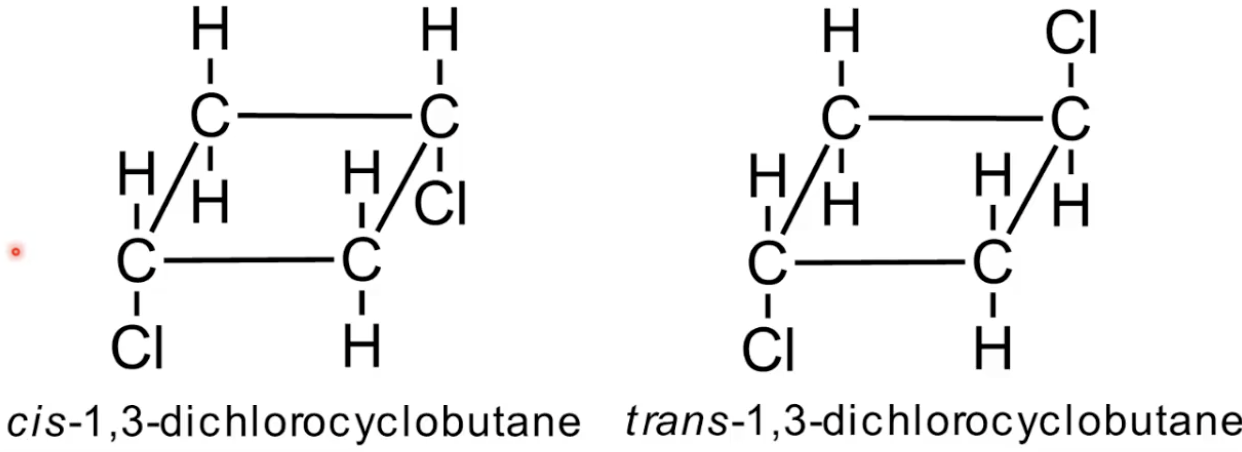
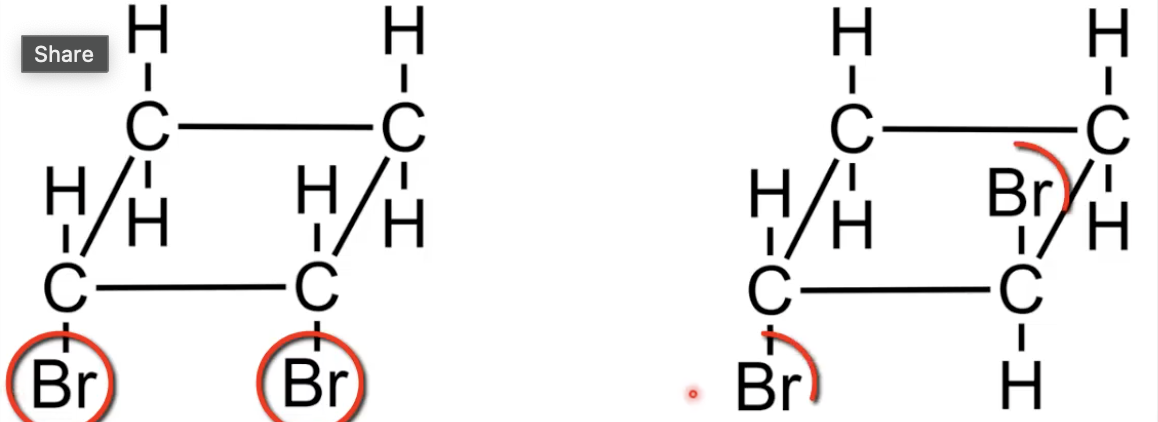
Cis has both Br on same face of the ring
Trans has Br on opposite faces
Classic cyclic isomer pair.
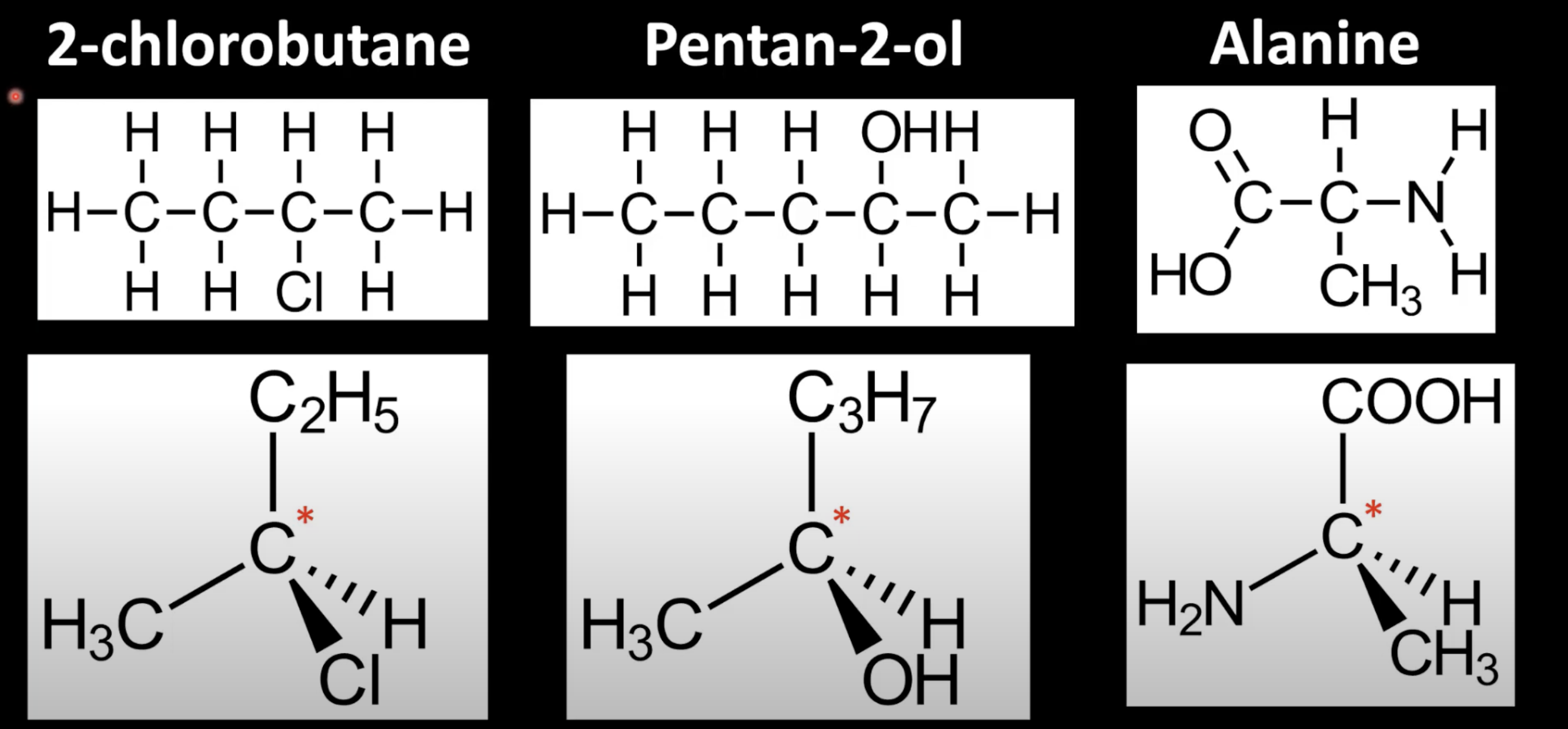
Occurs in chiral molecules with a carbon bonded to 4 different groups
Carbon is called a chiral center or asymmetric carbon.
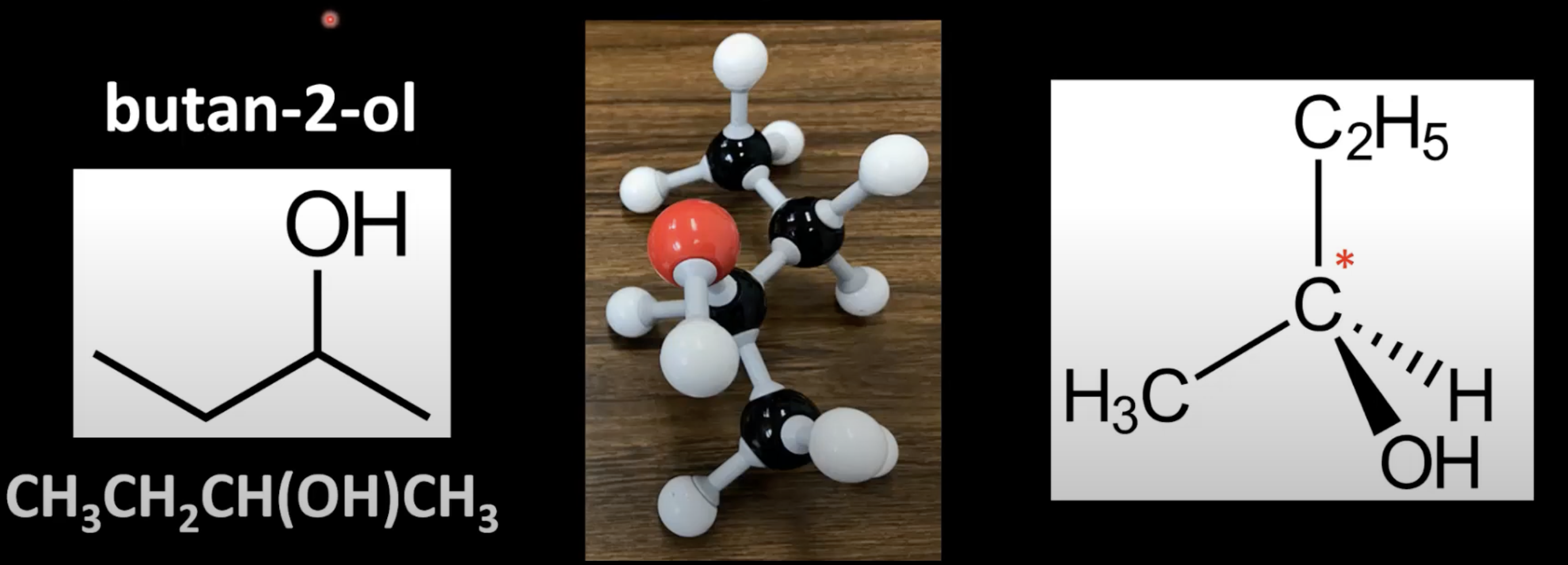

Carbon is bonded to CH3, OH, H, and C2H5 making it chiral
Creates two non-superimposable mirror images.
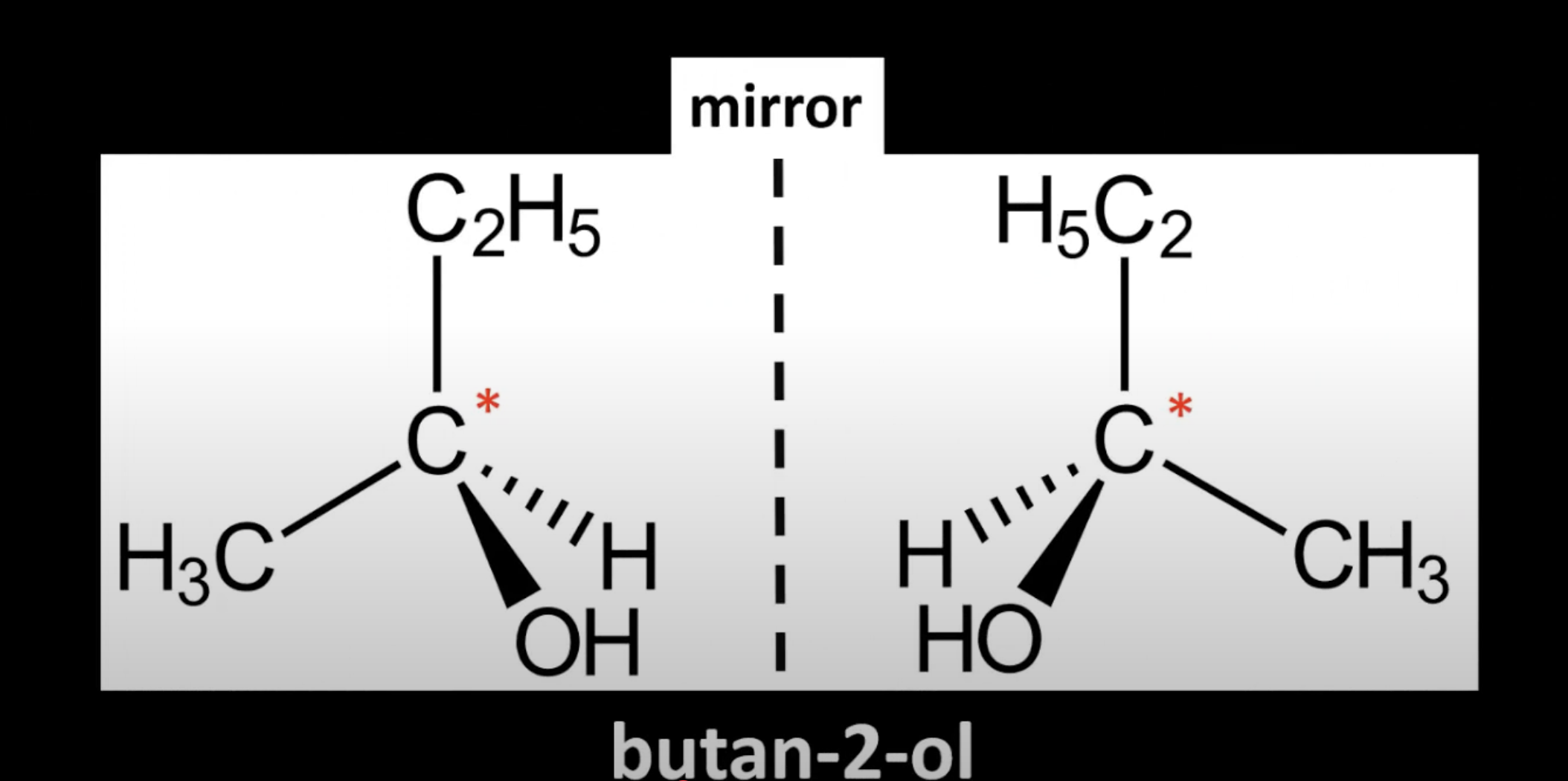
Non-superimposable mirror images of a chiral molecule
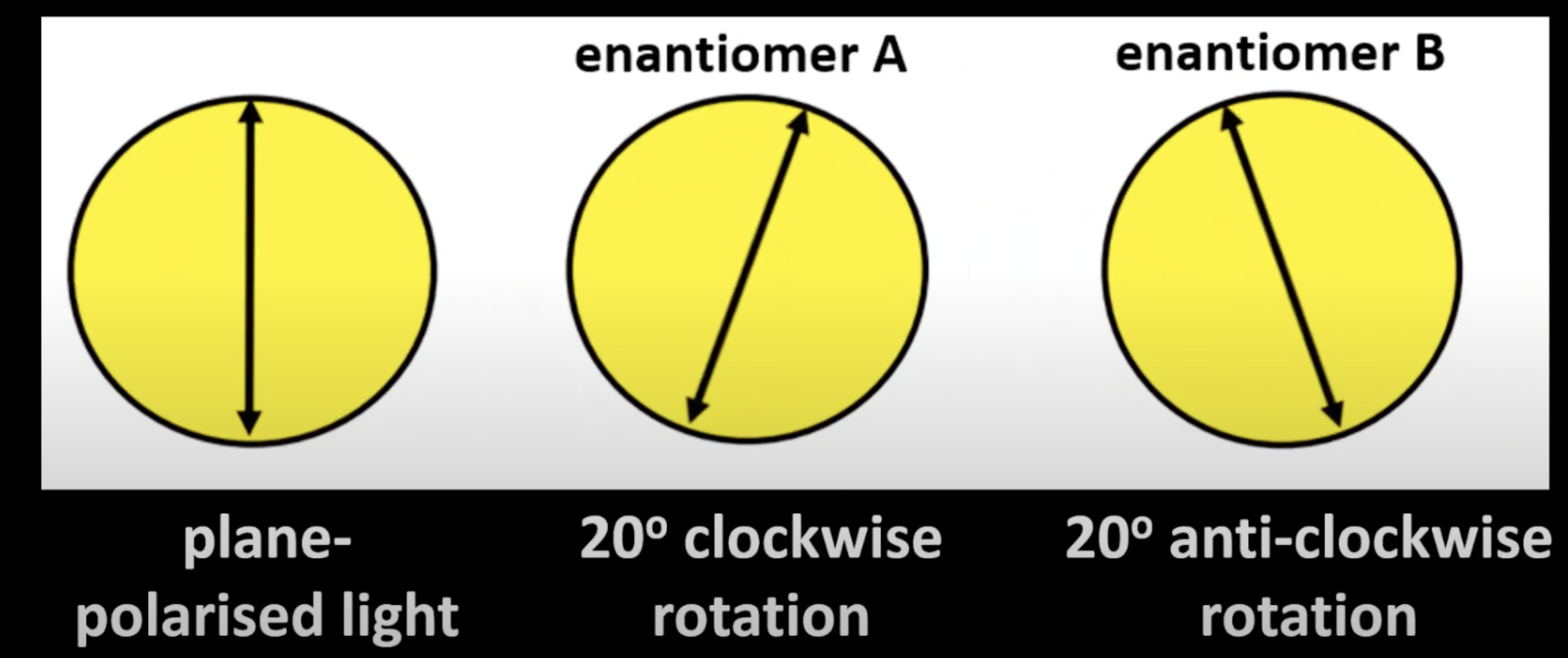
They differ in the direction they rotate plane-polarized light.
Same melting and boiling points
Differ only in how they rotate plane-polarized light (optically active).
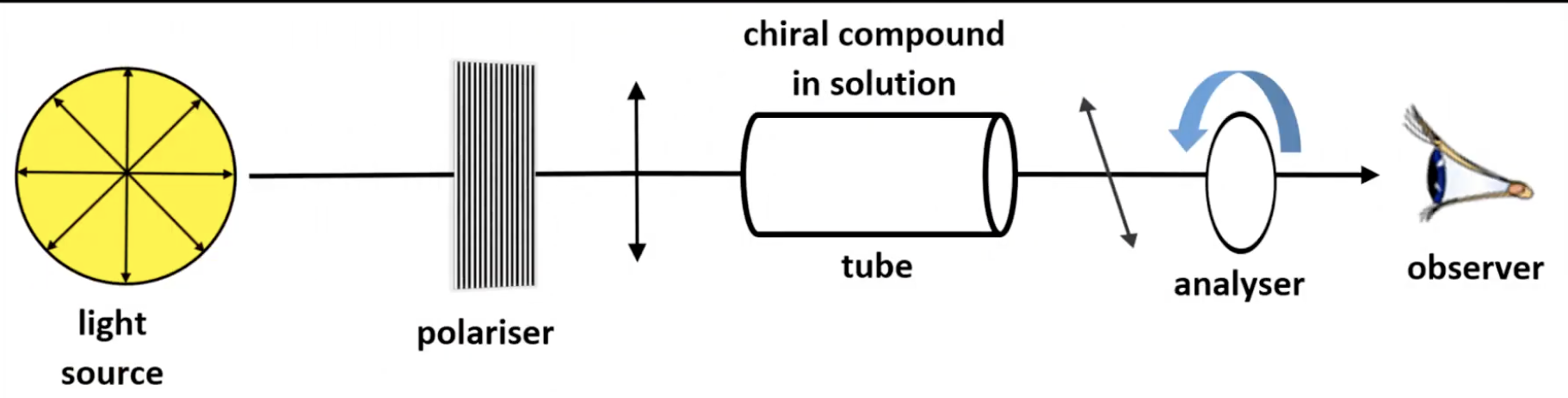
Light waves vibrating in one plane only
Produced by passing ordinary light through a polarizer.
Rotate plane-polarized light equally but in opposite directions
One clockwise (dextrorotatory), the other anti-clockwise (levorotatory).
Contains equal amounts of both enantiomers
Optically inactive as rotations cancel each other.