BIOLOGY PAPER 1 ALL CONTENT
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Where is amylase produced?
Salivary glands, pancreas, small intestine
Where is protease produced?
Stomach (pepsin), pancreas, small intestine
Where is lipase produced?
Pancreas, small intestine
What does protease break down and into what?
Breaks down proteins into amino acids
What does lipase break down and into what?
Breaks down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids
What is the optimum pH for pepsin?
pH 2 (acidic)
What is the test for starch?
add Iodine solution using a pipet
turns blue-black if starch is present
What is the test for sugars?
Benedict’s solution: heat in water bath, turns green/yellow/brick red depending on sugar concentration
What is the test for proteins?
Biuret solution: turns from blue to purple if protein is present
What is the test for lipids?
Sudan III or ethanol test: red layer on top (Sudan III) or cloudy emulsion (ethanol) if lipids are present
Word equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Symbol equation for photosynthesis?
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Word equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in muscles?
Glucose → lactic acid
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants?
Glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
How are monoclonal antibodies made?
By combining a mouse B-lymphocyte
with a tumour cell
to make a hybridoma
that divides and produces identical antibodies
Why are monoclonal antibodies useful?
They are specific to one binding site on one antigen so can target specific cells or substances
How are monoclonal antibodies used in pregnancy tests?
They bind to the hormone hCG found in urine if pregnant
How are monoclonal antibodies used in cancer treatment?
They can deliver drugs directly to cancer cells
or block growth signals
How are monoclonal antibodies used in labs?
To locate specific molecules or measure levels of substances using markers
How does vaccination prevent illness?
It stimulates white blood cells to produce antibodies, leading to immunity
What is a double-blind trial?
Neither the patient nor the doctor knows who is receiving the drug or placebo, to prevent bias
Why must drugs be tested?
To ensure they are safe, effective, and have the correct dosage
What is a placebo and why is it used?
A dummy treatment used to compare effects in clinical trials
What causes antibiotic resistance?
Overuse and misuse of antibiotics, allowing resistant bacteria to survive and reproduce
What is transpiration?
The loss of water vapour from the leaves of a plant through the stomata
How do guard cells work?
They open and close stomata to control water loss and gas exchange
What are stomata?
Pores in the leaf that allow gas exchange
Why is the palisade layer good for photosynthesis?
It has many chloroplasts and is near the top of the leaf to receive maximum light
How does a vaccine lead to immunity?
White blood cells produce memory cells that respond faster to future infection
What is the function of the nucleus?
It contains genetic material that controls the activities of the cell.
What is the function of mitochondria?
They are the site of aerobic respiration, which releases energy.
Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; eukaryotic cells have both.
Why do root hair cells have a large surface area?
To increase the rate of absorption of water and mineral ions from the soil.
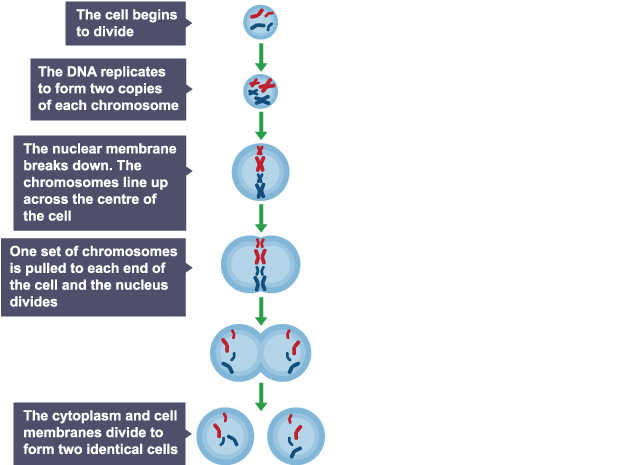
Describe the process of mitosis.
Mitosis is cell division that produces two identical daughter cells for growth and repair.
What is the purpose of stem cells?
Stem cells can differentiate into different types of cells and are used in development and repair.
Where are adult stem cells found?
In bone marrow.
What are the ethical issues surrounding stem cell use?
Some people object to the use of embryos, believing life begins at conception.
How is diffusion different from active transport?
Diffusion is passive; active transport requires energy to move substances against a concentration gradient.
Why does temperature affect diffusion?
Higher temperatures increase kinetic energy and speed up particle movement.
What is the function of enzymes?
To catalyse biological reactions by lowering activation energy.
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Each enzyme has an optimum pH; too high or too low denatures the enzyme.
What happens to an enzyme when it denatures?
The active site changes shape and can no longer bind to the substrate.
What does amylase do?
Breaks down starch into sugars.
Where is bile produced and what does it do?
Produced in the liver; neutralises stomach acid and emulsifies fats.
Name the four components of blood.
Red blood cells - carries o2 around the body
white blood cells - defending body against infection and disease
platelets - blood clotting
plasma - liquid transportation
What is the function of red blood cells?
Transport oxygen using haemoglobin.
How are arteries different from veins?
Arteries have thick muscular walls and carry blood away from the heart
Veins have valves and carry blood to the heart.
What is coronary heart disease?
A condition where the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart.
Describe how stents work.
Stents are tubes inserted into arteries to keep them open and improve blood flow.
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism that causes disease.
Name four types of pathogens.
Bacteria, viruses, fungi, protists.
How do viruses make you feel ill?
They reproduce inside cells, causing cell damage.
How does the body defend itself against pathogens?
Skin, mucus, stomach acid, white blood cells (phagocytosis, antibodies, antitoxins).
What is the purpose of vaccination?
To stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies without causing illness.
How do antibiotics work?
They kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Why don’t antibiotics work on viruses?
Viruses reproduce inside host cells, which antibiotics can't target without harming the host.
What is antibiotic resistance?
When bacteria evolve and are no longer killed by antibiotics.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Identical antibodies produced from a single clone of cells, used in medicine for diagnosis and treatment.
What is a placebo?
A substance with no therapeutic effect, used as a control in testing new drugs.
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Where does photosynthesis occur?
In the chloroplasts of plant cells.
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
Light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature.
Why is photosynthesis important?
It produces oxygen and glucose, essential for life on Earth.
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+ energy)
What is anaerobic respiration?
Respiration without oxygen, producing less energy.
How is lactic acid removed from muscles?
It is transported to the liver and broken down.
Why does heart rate increase during exercise?
To supply muscles with more oxygen and glucose for respiration.
What is metabolism?
The sum of all chemical reactions in the body.
Give an example of a metabolic reaction.
Converting glucose to starch in plants.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
It controls what enters and leaves the cell.
What are plasmids?
Small loops of DNA found in bacterial cells.
What is the role of chloroplasts?
To carry out photosynthesis using light energy.
What does the term 'cell differentiation' mean?
The process by which a cell changes to become specialized for its function.
Why is the electron microscope important in biology?
It allows higher magnification and resolution than a light microscope, revealing more detail.
What are the three stages of the cell cycle?
Interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
Give one use of therapeutic cloning.
It can be used to generate stem cells
that are genetically identical to the patient.
What is the function of xylem vessels?
To transport water and mineral ions from roots to leaves.
What is translocation?
The movement of sugars through phloem from sources to sinks.
How does the structure of alveoli help gas exchange?
Large surface area
thin walls
good blood supply increase diffusion efficiency.
What enzyme breaks down proteins?
Protease.
Why is the heart called a double circulatory system?
It has two circuits: one to the lungs and one to the rest of the body.
How do artificial pacemakers work?
They send electrical impulses to control heart rate.
What is cancer?
Uncontrolled cell division that forms a tumor, which can be benign or malignant.
How is measles spread?
Through droplets from coughs and sneezes.
What is malaria caused by?
A protist spread by mosquitoes.
Why is hygiene important in disease prevention?
It reduces the spread of pathogens.
What is herd immunity?
When enough of a population is vaccinated to stop the spread of a disease.
What is the first stage of drug testing?
Preclinical testing on cells, tissues, and animals.
How are monoclonal antibodies used in pregnancy tests?
They bind to the hormone hCG found in urine during pregnancy.
What is the inverse square law in photosynthesis?
Light intensity ∝ 1/distance², meaning light intensity decreases with distance squared.
How is glucose used by plants?
For respiration
making cellulose
making amino acids
storing as starch.
What is oxygen debt?
The extra oxygen needed after exercise to remove lactic acid and repay the deficit.
How does temperature affect respiration?
Higher temperatures increase enzyme activity up to an optimum; too high denatures enzymes.