Inheritance
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Entirety of an organism’s DNA called?
Genome
What is a gene?
A gene is a section of a molecule of DNA
What does one gene code for?
One amino acid
What do sequences of amino acids form?
different proteins
Some examples of different types of protein
Structural proteins
Enzymes
Hormones
What is DNA?
genetic material found in the nucleus of a cell. A polymer made up of two strands coiled around the make a double helix.
What are the complementary base pairs?
Adenine bonds with Thymine
Guanine bonds with cytosine
Why are base-pairing rules important?
essential for cell division and protein synthesis
structures formed when DNA supercoils?
Chromosomes
When are chromosomes visible?
Chromosomes are only visible during cell divison
How many pairs of chromosomes do human cells contain?
23 pairs
What is homologus pair?
consists of one chromosome from each parent
Main difference between DNA and RNA?
RNA single-stranded
DNA is double-stranded
Nitrogenous bases are found in RNA?
Adenine and uracil
guanine and cytosine
Structure of RNA?
Single polynucleotide strand with ribose sugars and phosphate groups.
2 main types of RNA molecules?
mRNA, tRNA
role of mRNA?
transcripts a copy of a gene that encodes a specific polypeptide.
role of tRNA?
tRNA molecules transport specific amino acids to the ribosome.
Stages of protein synthesis?
1- Transcription: DNA is transcribed to produce mRNA
2- Translation: mRNA is translated and an amino acid sequence is produced
Process of transcription?
Occurs in the nucleus
Enzyme- RNA polymerise unzips the DNA. Only one strand used a template.
mRNA contains information from the DNA and binds to the complementary nucleotides on the template strand. Adenine-uracil. Guyanine-cytosine.
Moves out of the pores of the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Process of translation?
Happens in the cytoplasm
mRNA binds to the ribosome
amino acids are brought to the ribosome through tRNA.
a second tRNA molecule attaches to the complementary codon and a peptide bond is formed between the two neighbouring amino acids.
This process continues until a ‘stop’ codon on the mRNA molecule is reached, acts as signal for translation to stop.
What is an allele
a variation of the same gene
significance of having different alleles?
differences in inherited charactersistics
Chracteristics you can see?
Phenotype
Combination of alleles that control each characteristic?
Genotype
Dominant allele?
only needs to be inherited from one parent for the characteristic to be present
Recessive allele?
Needs to be inherited from both parents to be present
homozygous?
two alleles of a gene are the same
hetrozygous?
two alleles of a gene are different
codominance?
when both alleles within a genotype are expressed in a phenotype (blood group)
Number of alleles that govern codominance?
3 alleles
polygenic characteristics?
characteristics controlled by more than one gene
polygenic characteristics in phenotype?
combinations of features (e.g. eye colour)
monohybrid inheritance?
characteristics are controlled by a single gene
genetic diagram used to determine monohybrid inheritance?
The punnett square
how are males and females represented in a family pedigree diagram?
males=squares, females=circles
what determines sex in humans?
by an entire chromosome pair
sex chromosomes for males and females?
XX=females XY=males
which chromosome determines the sex of the offspring
the male chromosome
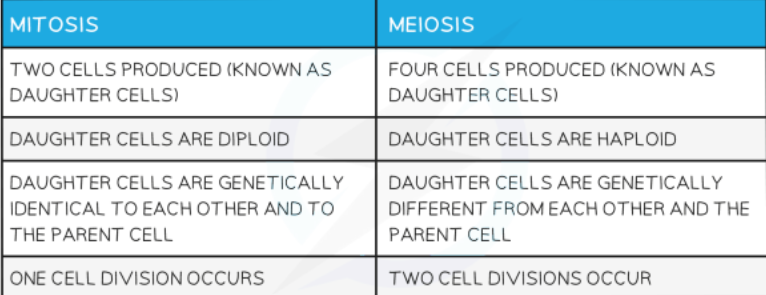
Mitosis?
nuclear division giving rise to genetically identical cells
mitosis is used for?
growth
repair of damaged tissues
replacement of cells
asexual reproduction
type of cells produced by mitosis?
diploid cells
process of mitosis?
chromosomes copy themselves, line up and then the cell divides.
Meiosis?
nuclear division that gives rise to genetically different cells
type of cells produced by meiosis?
Gametes (sex cells)
why is meiosis important?
for the production of gametes and increasing genetic variation
process of meiosis?
First division- chromosomes pair up along the centre of the cell and cell fibres will pull the pairs apart- each cell will have one chromosome pair.
Second division- chromosomes will line up along the centre of these cells, cell fibres will pull them apart
A total of 4 haploid daughter cells are produced.
comparisons between mitosis and meiosis
random fertilisation?
any male gamete can fuse with any female gamete.
creates genetic variation between zygotes.
example of genetic variation?
blood group
eye colour
gender
ability to roll tongue
free of attached ear lobes
role of meiosis in reproduction?
produces gametes necessary for sexual reproduction
diploid cell?
cell that contains two complete sets of chromosomes (2n)
haploid cell?
a cell that contains one complete set of chromosomes (n)
mutations?
rare random changes in the sequence of DNA bases
how do mutations affect proteins?
can lead to changes in the protein that the gene codes for. Most mutation do not alter the protein or only alter it slightly
causes of variation within a species?
differences in genes from random fertilisation of gametes
Environmental factors
A combination of both
Environmental variation?
Differences caused by external factors (climate, diet, lifestyle)
environmental factors affecting chracrteristcs?
accidents leading to scarring
weight gain poor diet and inactivity
language and accent influences by country of uprbrining
plant growth affected by light availability
discontinuous variation is usually caused by?
genetic variation alone
causes of continuous variation?
genetics and the environment
how can changes in DNA affect phenotype?
by altering the sequence of amino acids in a protein
3 ways a DNA sequence can change
insertion of a new base
deletion of a base
substitution of a base
what happens during an insertion mutation?
a new base is randomly inserted into the DNA sequence
effect of an insertion mutation on amino acids?
changes the amino acid coded for by the affected codon
what happens during a deletion mutation?
a base is randomly deleted from the DNA sequence
what happens during a substitution mutation?
it only changes the amino acid for the affected codon
how can mutations lead to new phenotypes?
creating new alleles that provide survival advantages
what is sickle cell anaemia an example of?
a harmful mutation that affects red blood cells
2 causes of mutations?
Gamma rays, x-rays and ultraviolet rays (radiation)
Chemical mutagens
What does Darwin’s theory state?
evolutionary change has occurred and that natural selection is the process that has driven this change.
Process of natural selection?
Individuals in a species show variation- caused by differences in genes
Individuals with characteristics that are advantageous in their environment have a higher chance of survival. ‘survival of the fittest’
Surviving individuals are more likely to reproduce and are more likely to pass on their advantageous alleles.
This is repeated over many generations and the advantageous characteristics become more common in the population
how can antibiotic resistance increase bacterial populations?
random mutation can give rise to a new bacterial allele that codes for antibiotic resistance
when a bacterial population is exposed to an antibiotic, individuals without the resistance allele die.
surviving bacteria are more likely to reproduce and pass on their resistance alleles to their offspring
This repeats over several generations and the frequency of the resistance allele increases. Results in an antibiotic resistant strain of bacteria.
what happens when a bacterial population becomes resistant to a particular antibiotic?
it can only be treated with the application of a different antibiotic; in some cases several antibiotics.
Antibiotic resistance therefore makes bacterial infections more difficult to control.