TExES - Listening, Theory, and Form
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This contains listening/theory terms that may be present on your TExES Music (177) exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Isochronous
All of the beats are the same length.
Non-isochronous
The beats are of different lengths.
Complex meter
Beats are simple and compound. (Take 5/4: This is usually grouped into 2+3 or 3+2, meaning it is frequently thought of as a duple division and a subsequent triple division, or vice versa).
“Call and response” is when one voice sings something, and another voice responds to it, often by echoing what was sung. Classical music has its own term for this; what is the classical synonym for “call and response”?
Antiphonal voicing.
Name the scale degrees present in an Italian augmented 6th chord.
Scale degrees 1, #4, b6
Name the scale degrees present in a French augmented 6th chord.
Scale degrees 1, 2, #4, b6
Name the scale degrees present in a German augmented 6th chord.
Scale degrees 1, b3, #4, b6.
Transposition: Alto Flute
In Concert C, Alto Flute is written in G. It sounds a P5 lower than concert pitch.
Transposition: English horn
English horn sounds P5 lower; write UP by P5
Transposition: French Horn (Horn in F)
French horn sounds P5 lower; write UP by P5
When composing in the style of the common practice period (Baroque-Romantic), the following types of contrapuntal motion may be used to approach fifths and octaves.
Contrary motion and oblique motion.
Which two tempi does “allegretto” fall between?
Andante (walking pace, 80-100) and Allegro (fast, around 120 bpm).
Trumpets read their music _____________ than concert pitch.
One whole step higher (i.e. Concert F = G, Concert C = D).
Which ancient civilizations saw the earliest framework of music theory?
Egypt, Greece, and Mesopotamia.
Jazz musicians often refer to the chord progression “I-IV-ii-V” by what name?
Rhythm changes
Trombone players are expected to read which clefs?
Bass clef, alto clef, treble clef
“Standing on the dominant”, or “dominant preparation”, is a feature of which technique in classical era composition?
Sonata development.
Contrasting form
The subsections of a piece begin with different thematic material.
Continuous form
The first subsection ends in a non-tonic key.
Heterophonic texture
Musical texture characterized by simultaneous performance of a single melodic line by 2+ musicians, with each performer adding slight variations, ornamentation, or embellishments. Common in some non-Western traditions.
Neighbor Tone (NT)
Non-chord tone that moves BY STEP from a chord tone and then returns to the original chord tone. Can be upper (UN) or lower (LN) and is typically found on an off-beat.
Appoggiatura
Non-chord tone that approaches BY LEAP (usually upward) and resolves by step (usually downward) to a consonant chord tone. Typically accented and occurs on a strong beat, creating dramatic effect.
Tonicization
Briefly emphasizing an extra-tonal area (often the dominant or subdominant of a related key) by preceding it with its own dominant-function chord. Temporary change of tonal center without fully modulating, e.g. D Major piece containing PAC in A Major (E7→A) at a phrase ending.
The Neapolitan chord in any key is a _____ _____ the tonic.
half-step; above
The Neapolitan chord frequently appears in music in which inversion?
1st inversion (N6)
Sonata Form
A musical form originating in the Classical Period comprised of three main parts, called the exposition, development, and recapitulation.
Exposition
Part one of the sonata form. Thematic material and home key are introduced; may be accompanied by similar or different thematic material in the dominant key.
Development
Part two of the sonata form. Tonality is unstable, but thematic material is still heard and embellished upon in this section.
Recapitulation
Part three of the sonata form. Opening thematic material comes back in full, and may include a coda.
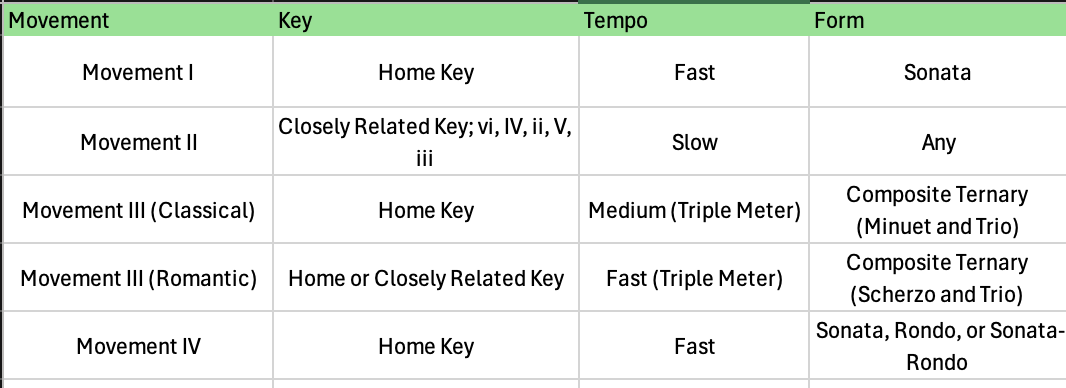
The image shows the standard model for four-movement _______, _______, and _______ from the Classical and Romantic Periods.
sonatas, symphonies, and string quartets
The following Roman numerals are considered closely related keys in relation to the tonic.
vi, IV, ii, V, iii
Ionian is the “modal name” for the major scale. Lydian contains which of the following altered scale degrees in relation to Ionian?
#4
Ionian is the “modal name” for the major scale. Mixolydian contains which of the following altered scale degrees in relation to Ionian?
b7
What is rondo form?
Rondo form consists of multiple unique sections. A section is introduced and is considered the ‘main theme’, and it returns after the presentation of each unique section. That could look like “ABACA” OR “ABACABA”.
Escape Tone (ET)
A non-chord tone that is approached by step and then skips in the opposite direction (lining up with the next chord).

In the key of G Major, the first chord can be analyzed as which of the following?
V(6/5) / vi

In the key of F Major, the first chord is a secondary dominant leading to which of the following chords?
G minor, the supertonic (in 1st inversion)
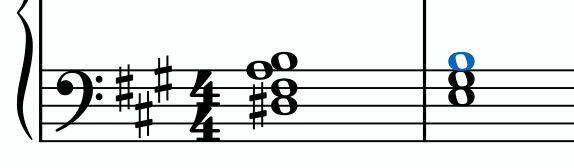
In the key of A Major, which of the following is an accurate Roman numeral analysis for the chords in the image? Disregard inversions.
V/V —> V
A tritone is equivalent to…
A diminished fifth
Retrograde
A melody is transformed by being put in reverse. Think “singing a melody backwards”.
Inversion
A melody is transformed by reversing the vertical direction of each interval
Retrograde Inversion
A melody is transformed by reversing BOTH the order of the pitches AND the vertical direction of each interval