BRAIN ANATOMY + SAGITTAL SECTION OF BRAIN STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONS
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
cerebral hemispheres
the two sections of the cortex on the left and right sides of the brain
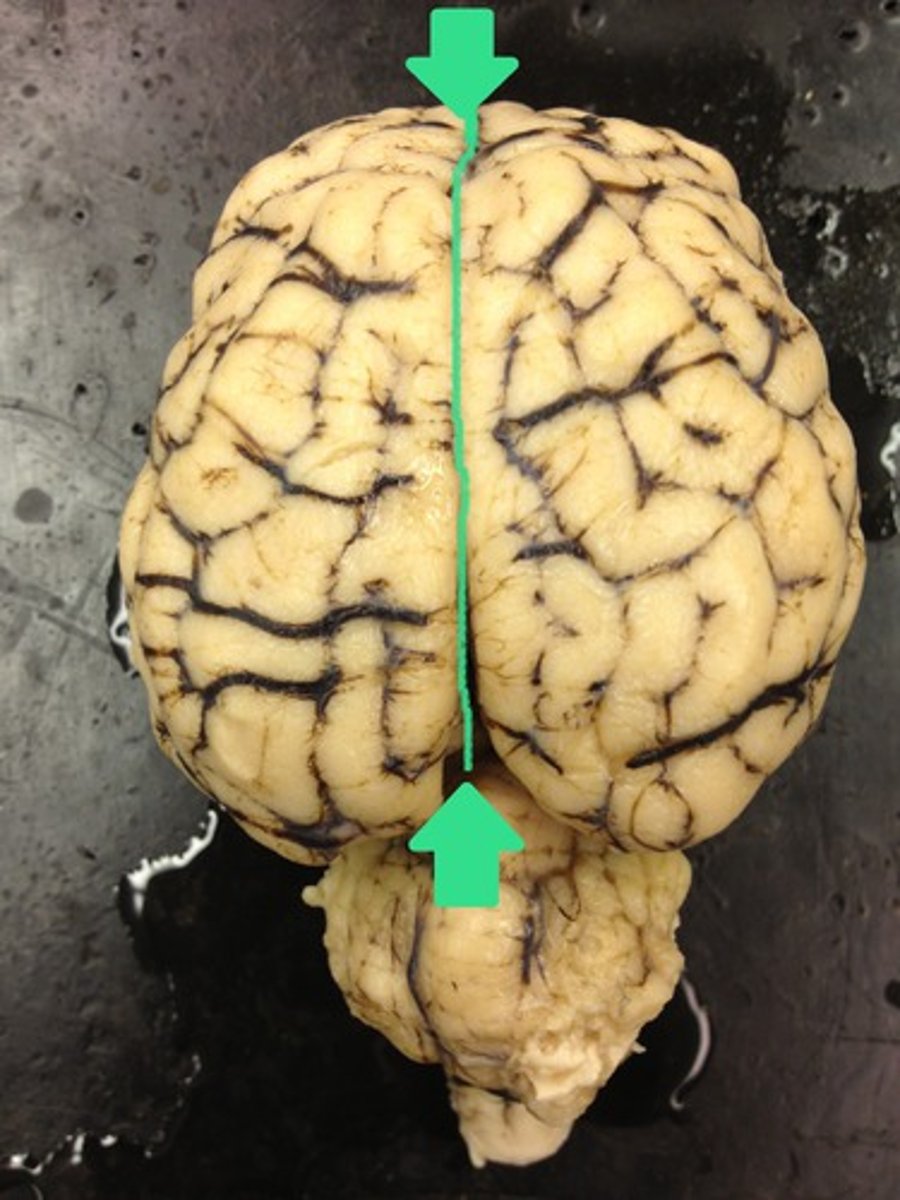
longitudinal fissure
separates left and right hemispheres of cerebrum
transverse cerebral fissure
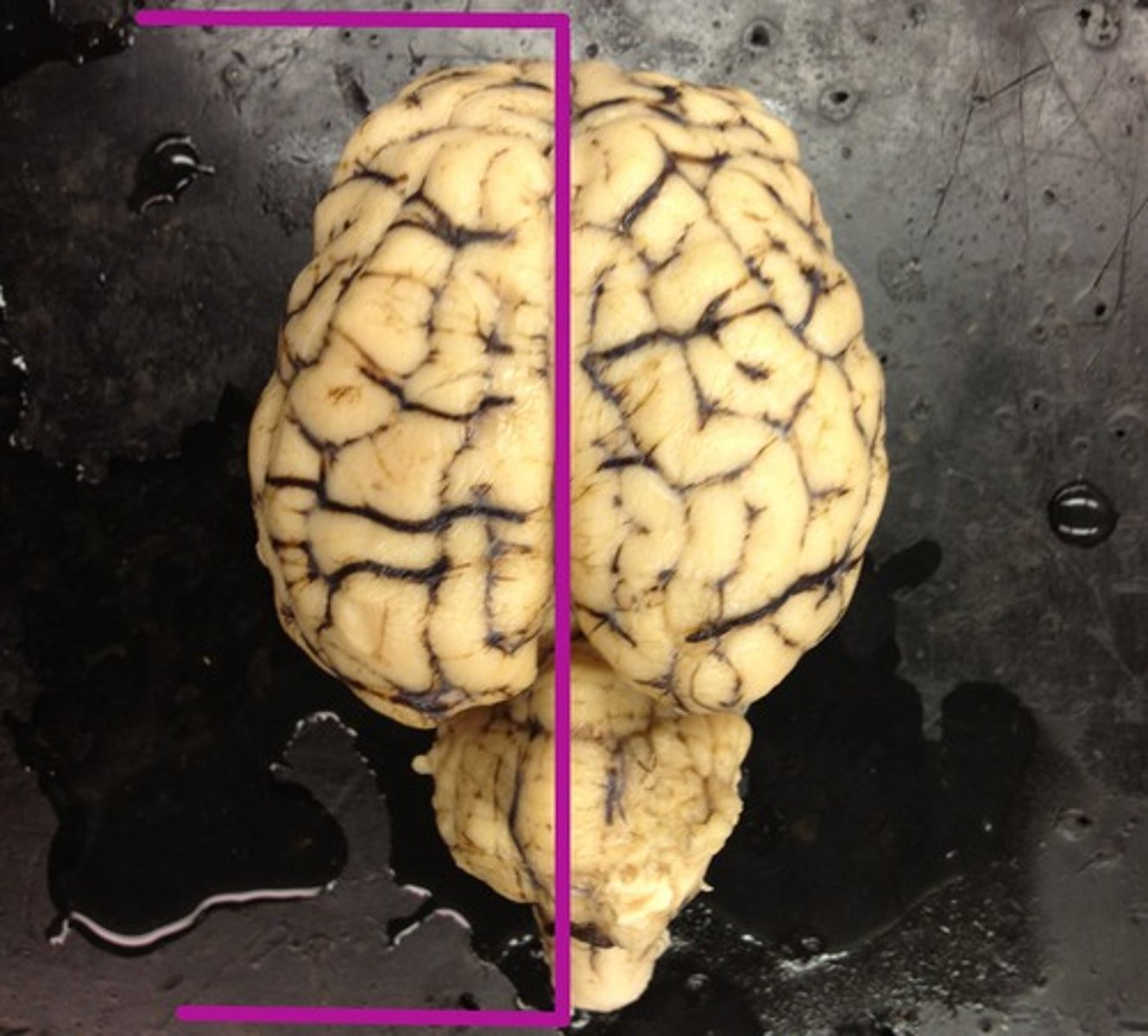
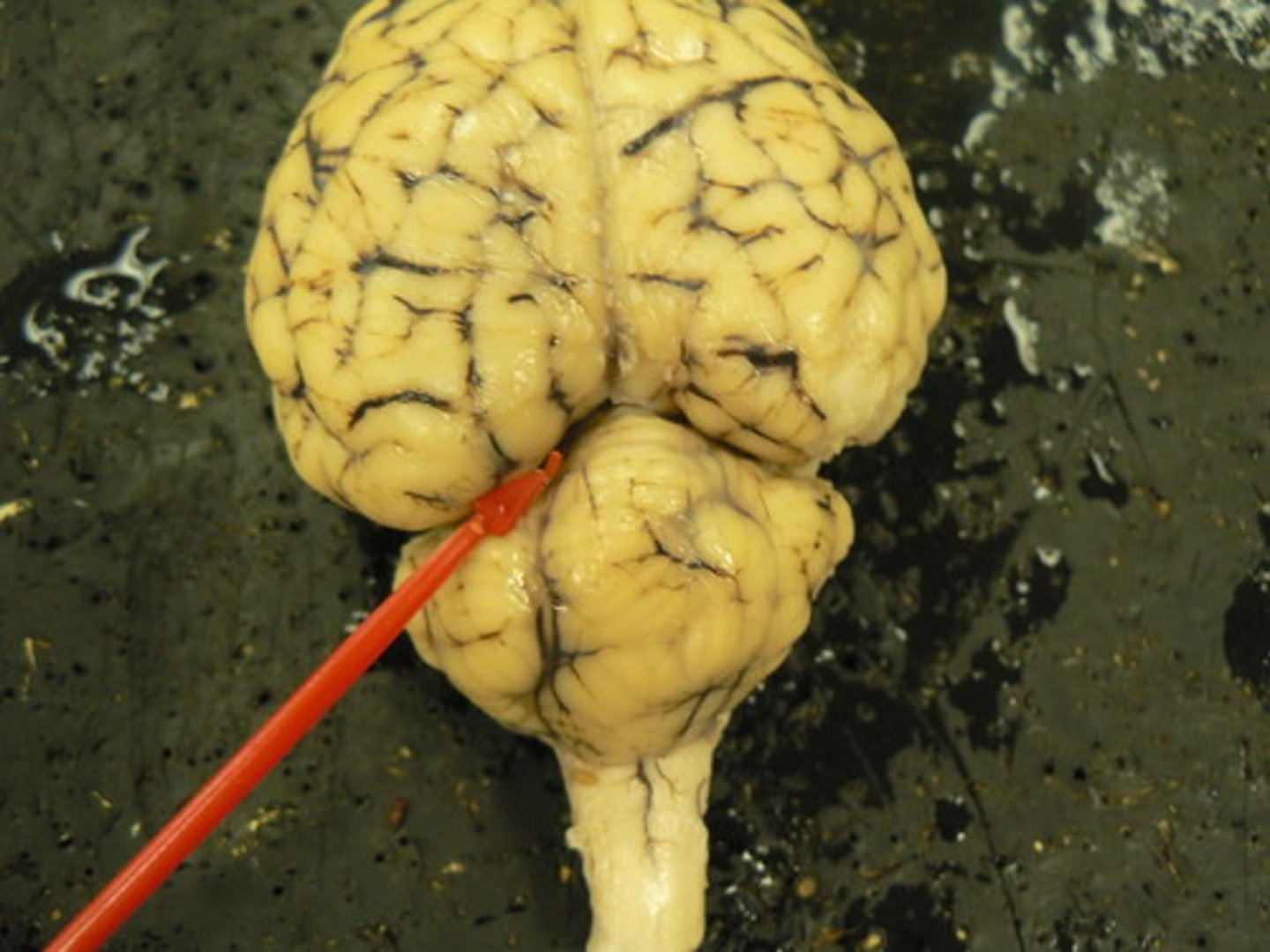
separates cerebrum and cerebellum
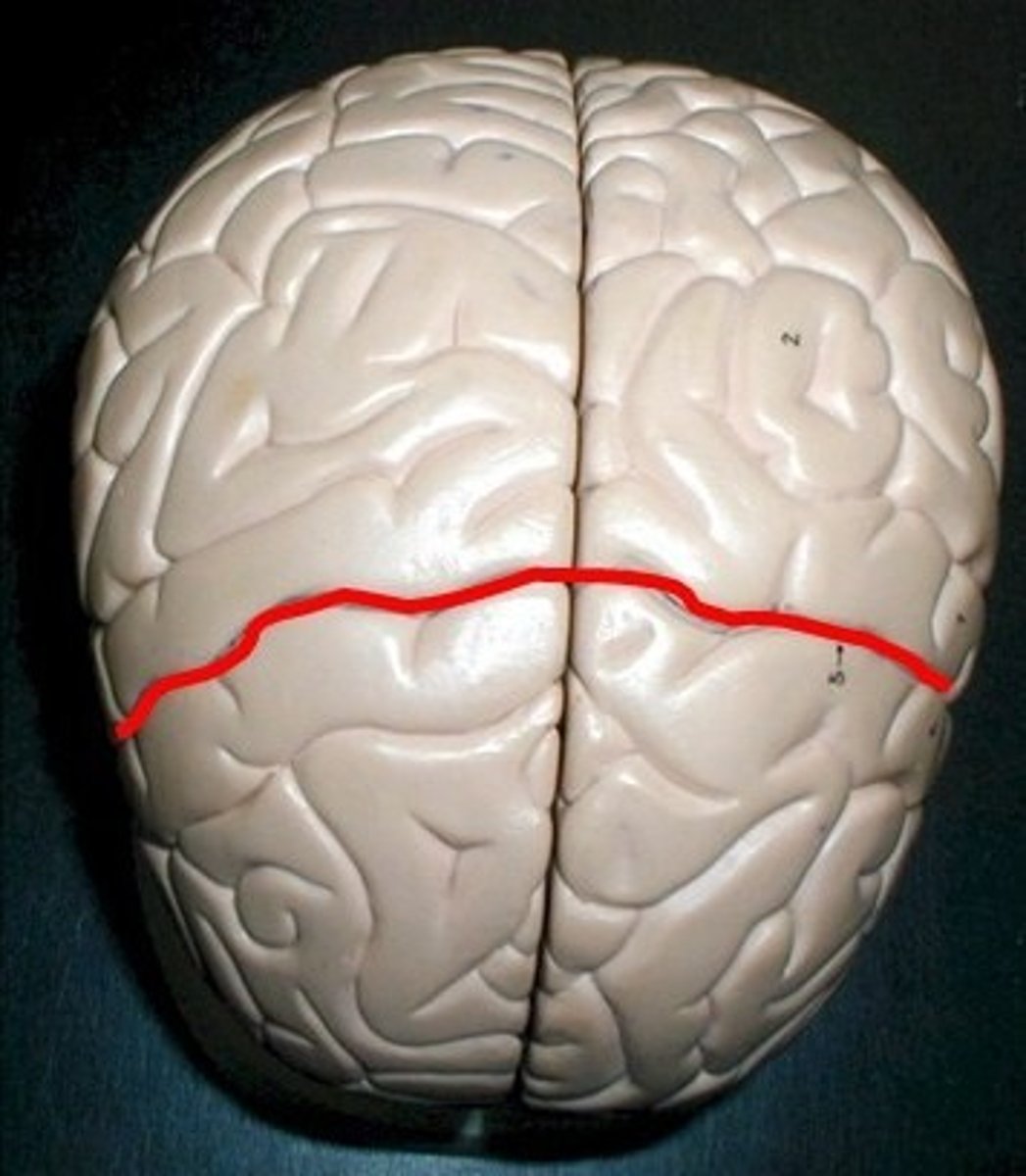
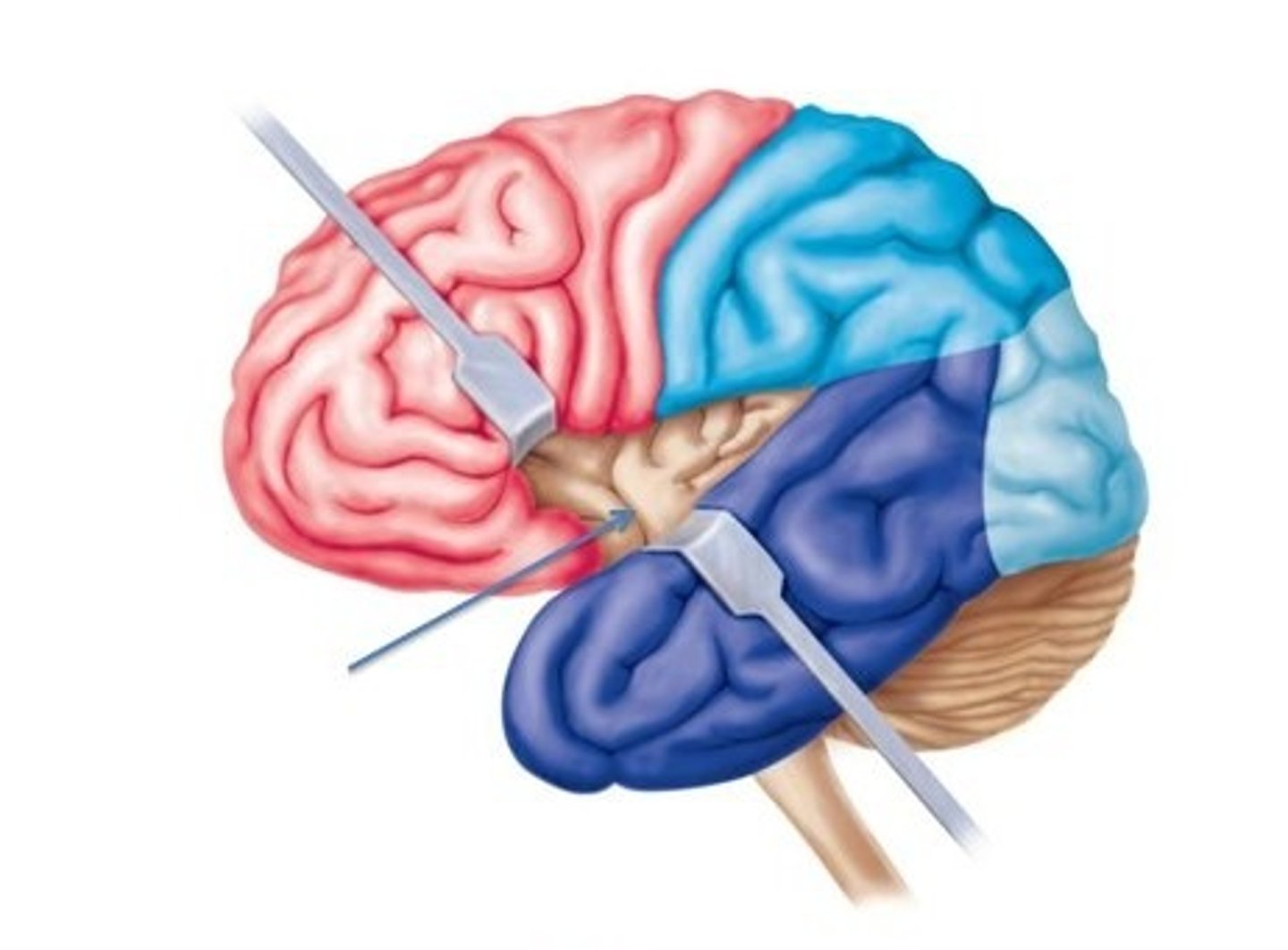
central sulcus
separates the frontal lobe from parietal lobes
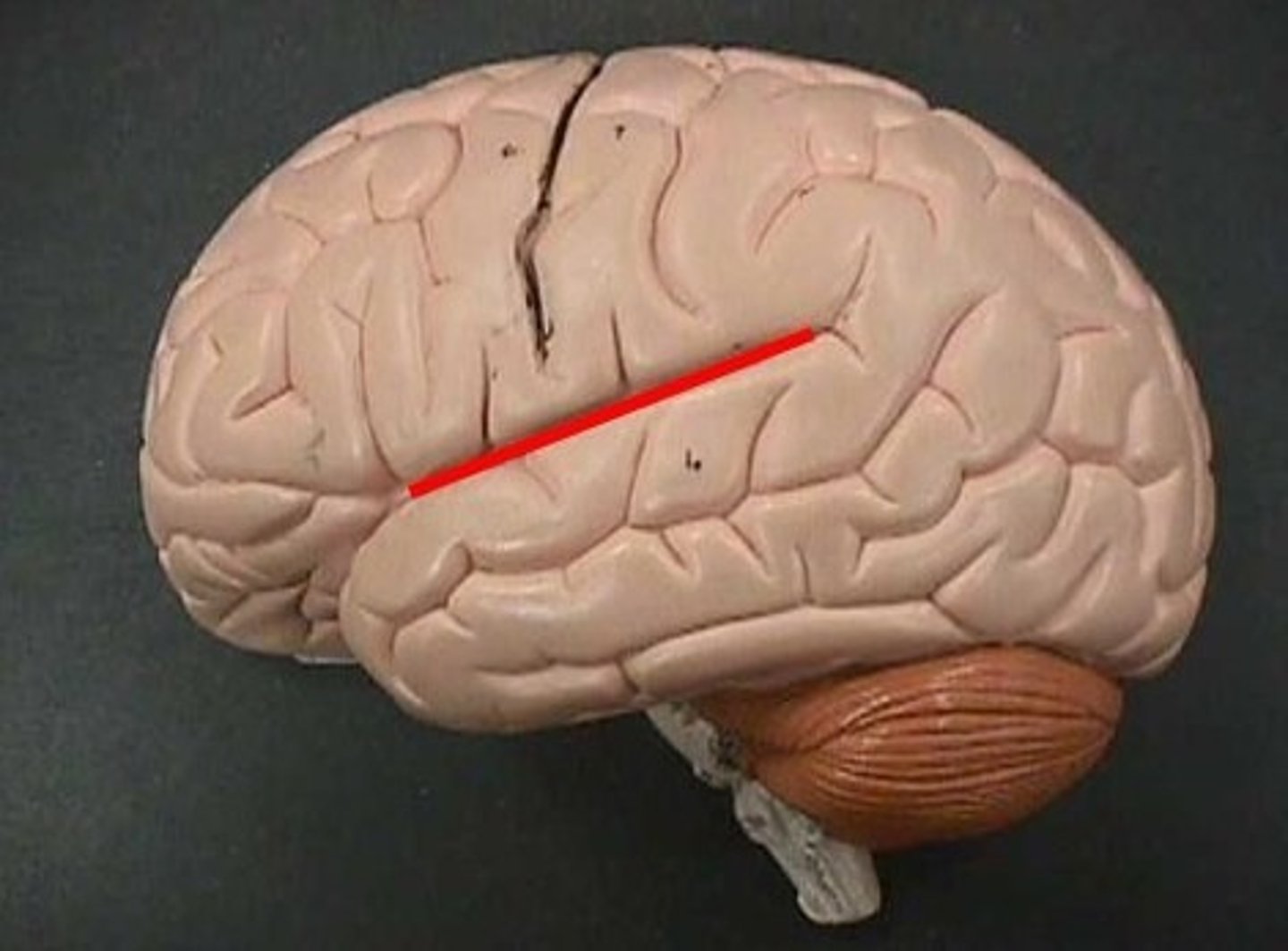
lateral sulcus
separates the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe and frontal lobe
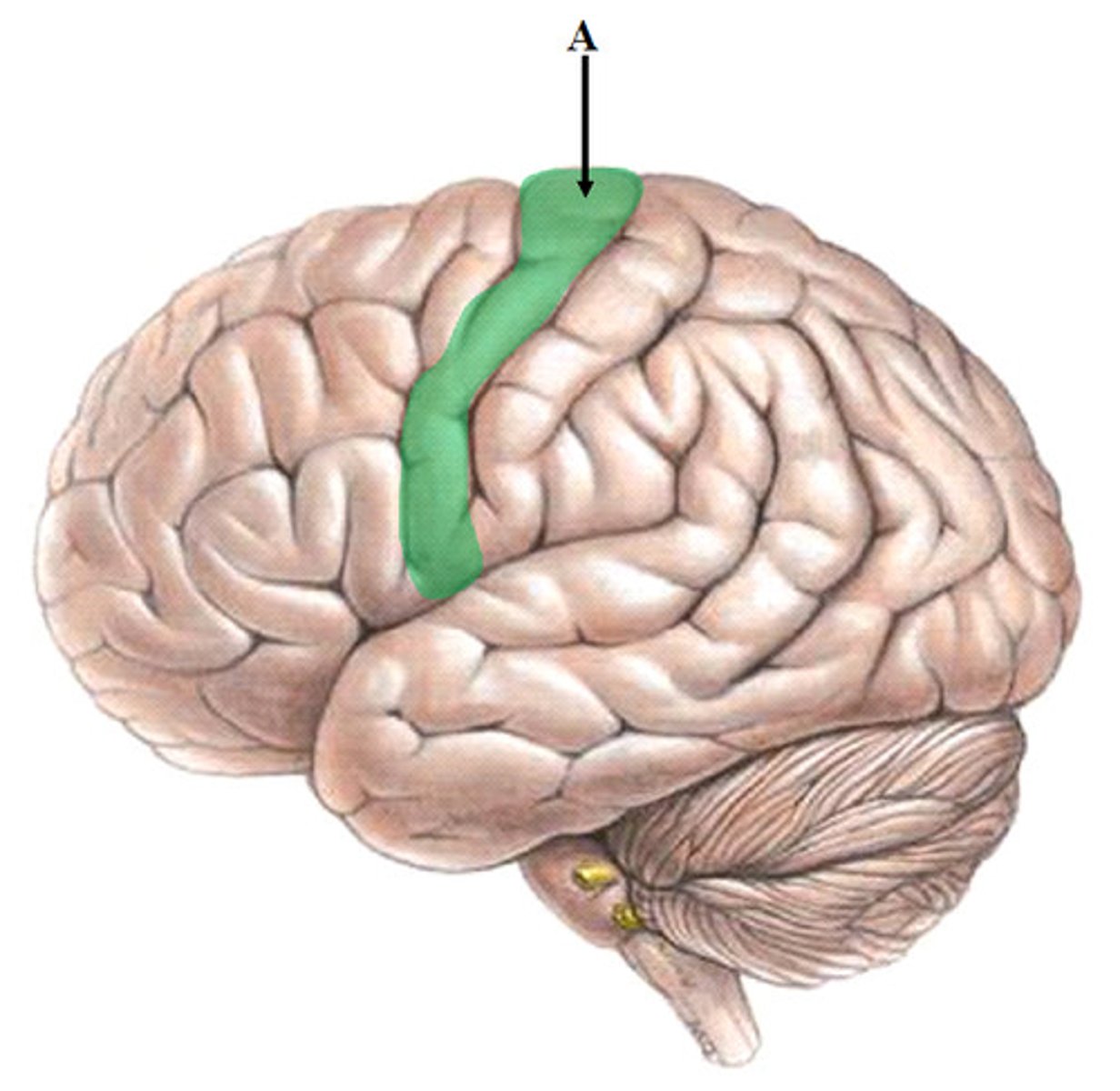
precentral gyrus
primary motor cortex
initiates + executes voluntary muscle movement
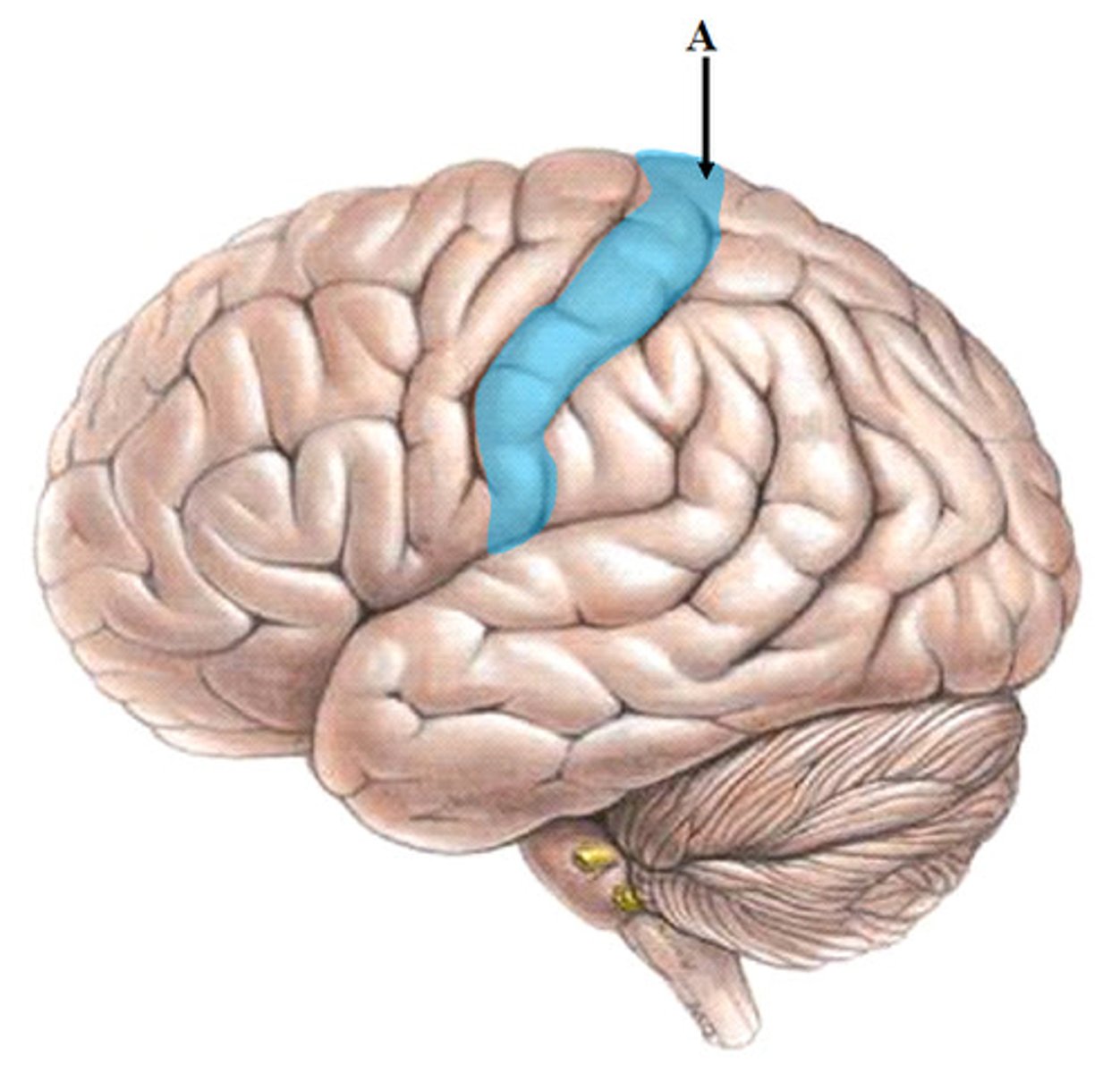
postcentral gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
receives somatosensory information
frontal lobe
- action lobe
- sending voluntary motor output
- communication
- executive functions: problem solving, planning, judgement, motivation, social behavior, decision making, memory, learning, reward, attention, personality.
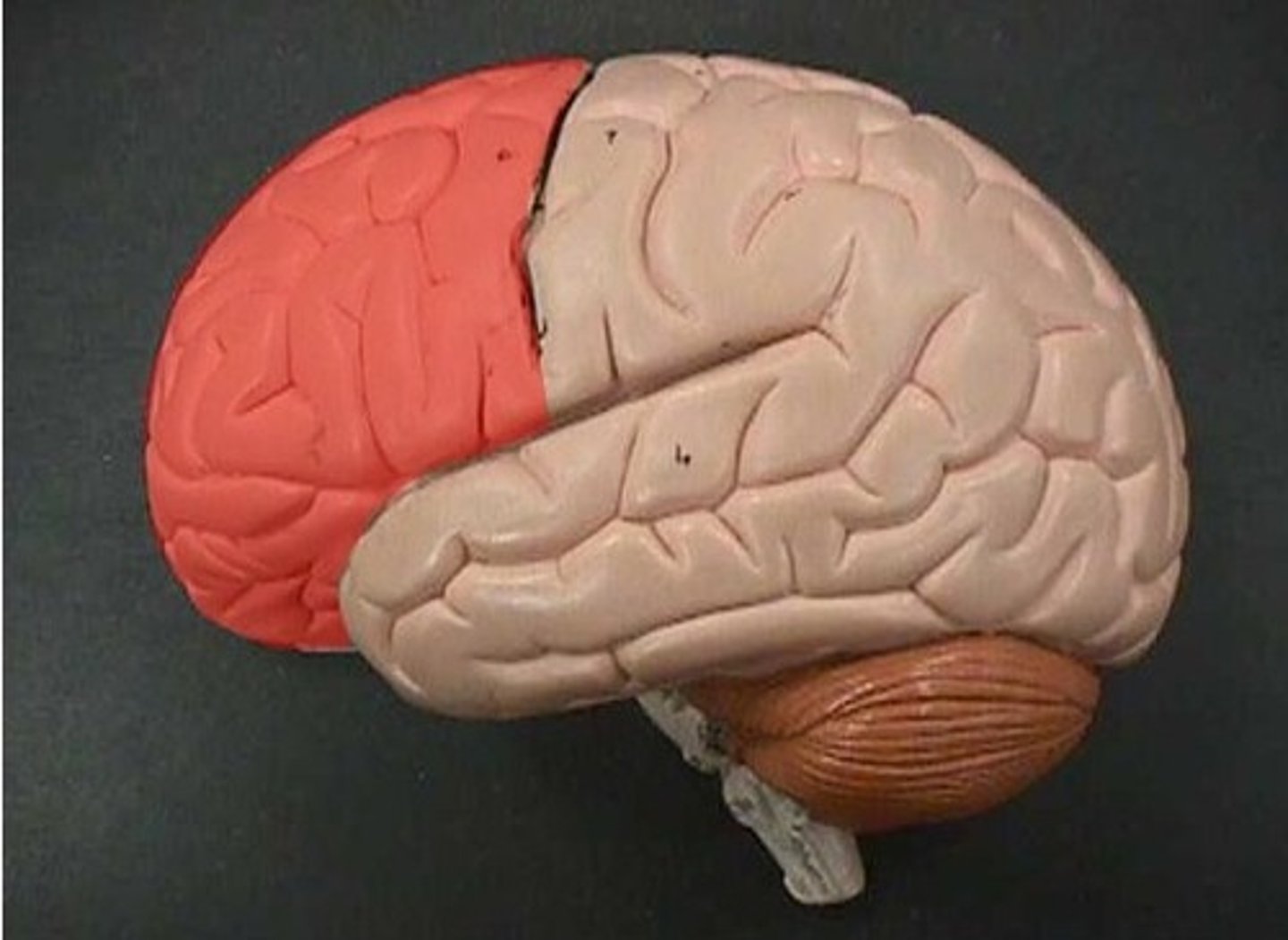
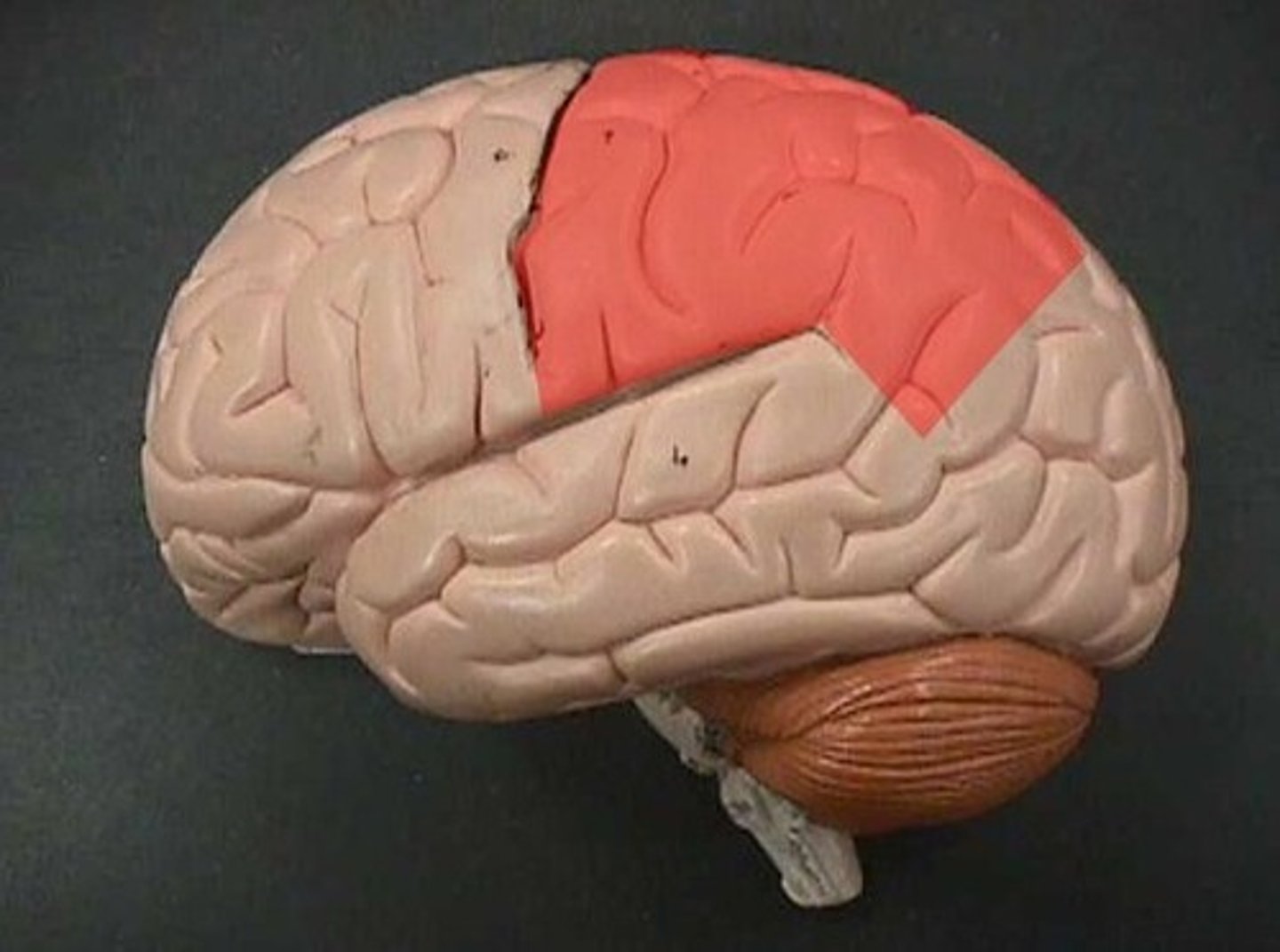
parietal lobe
processes somatosensory information:
- pain
-itch
-temperature
- touch
-pressure
-vibration
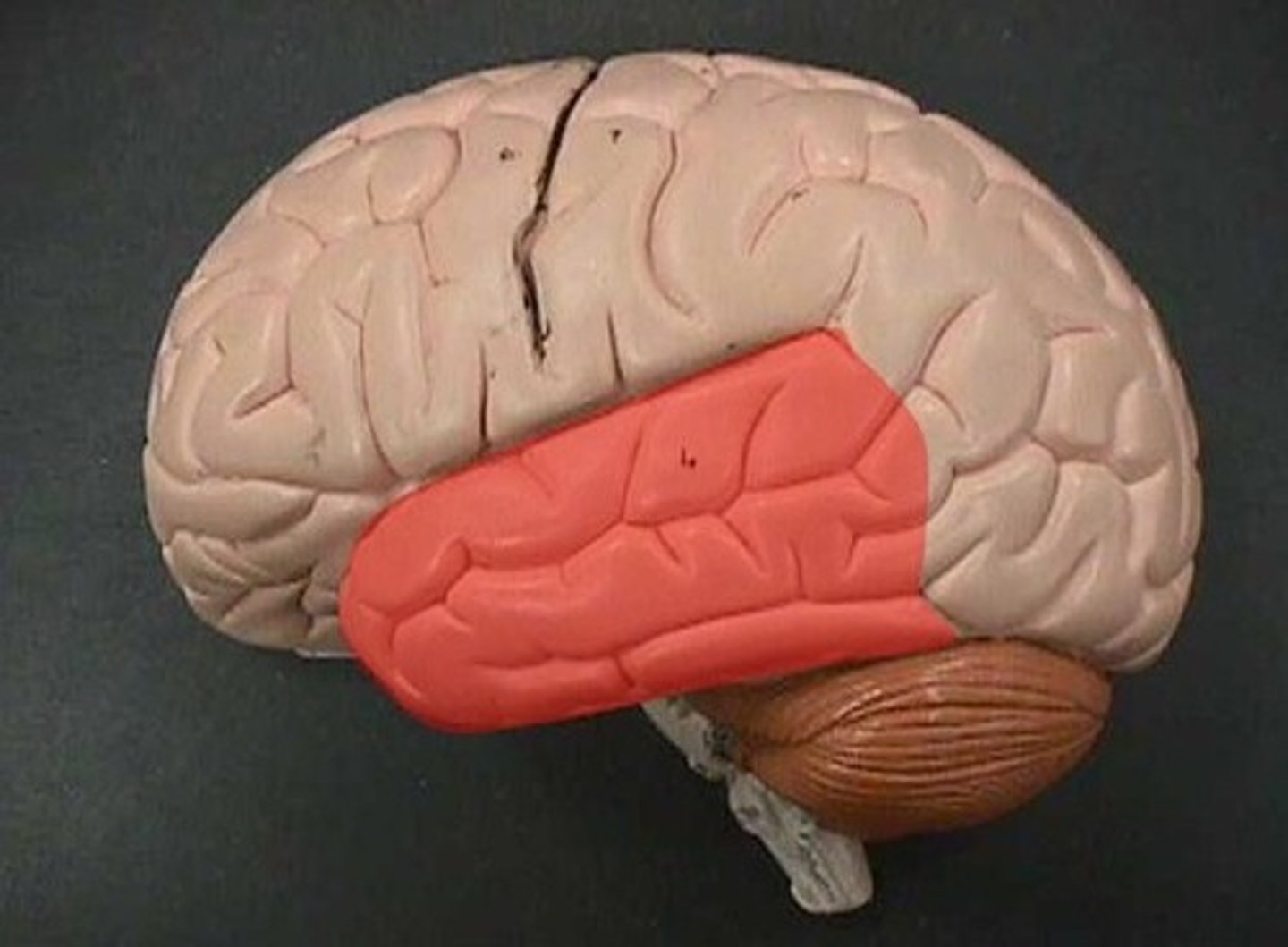
temporal lobe
processing incoming auditory + olfactory information (smell)
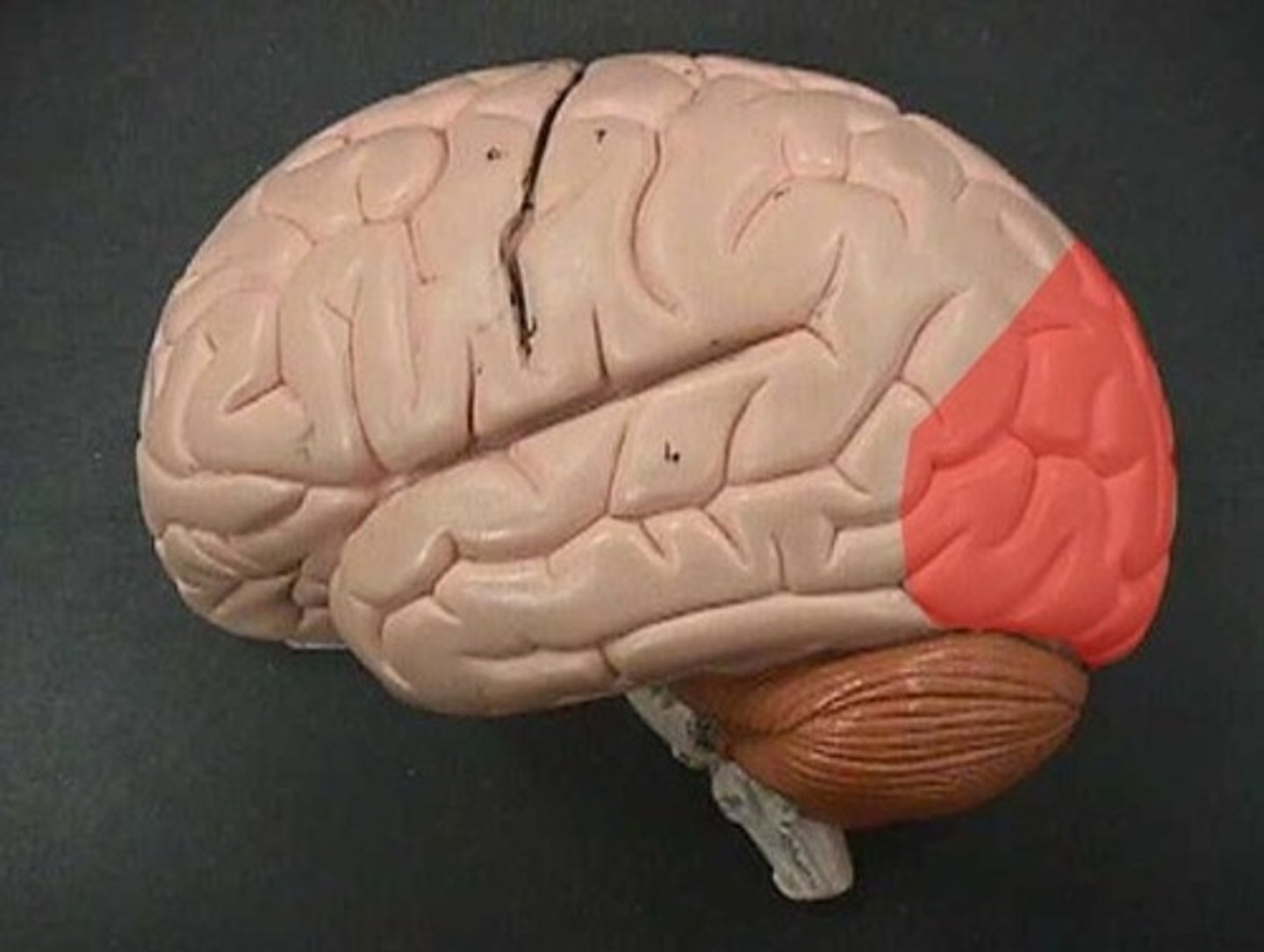
occipital lobe
- visual stimulus
- visual memory
insula
- gustatory (taste) information
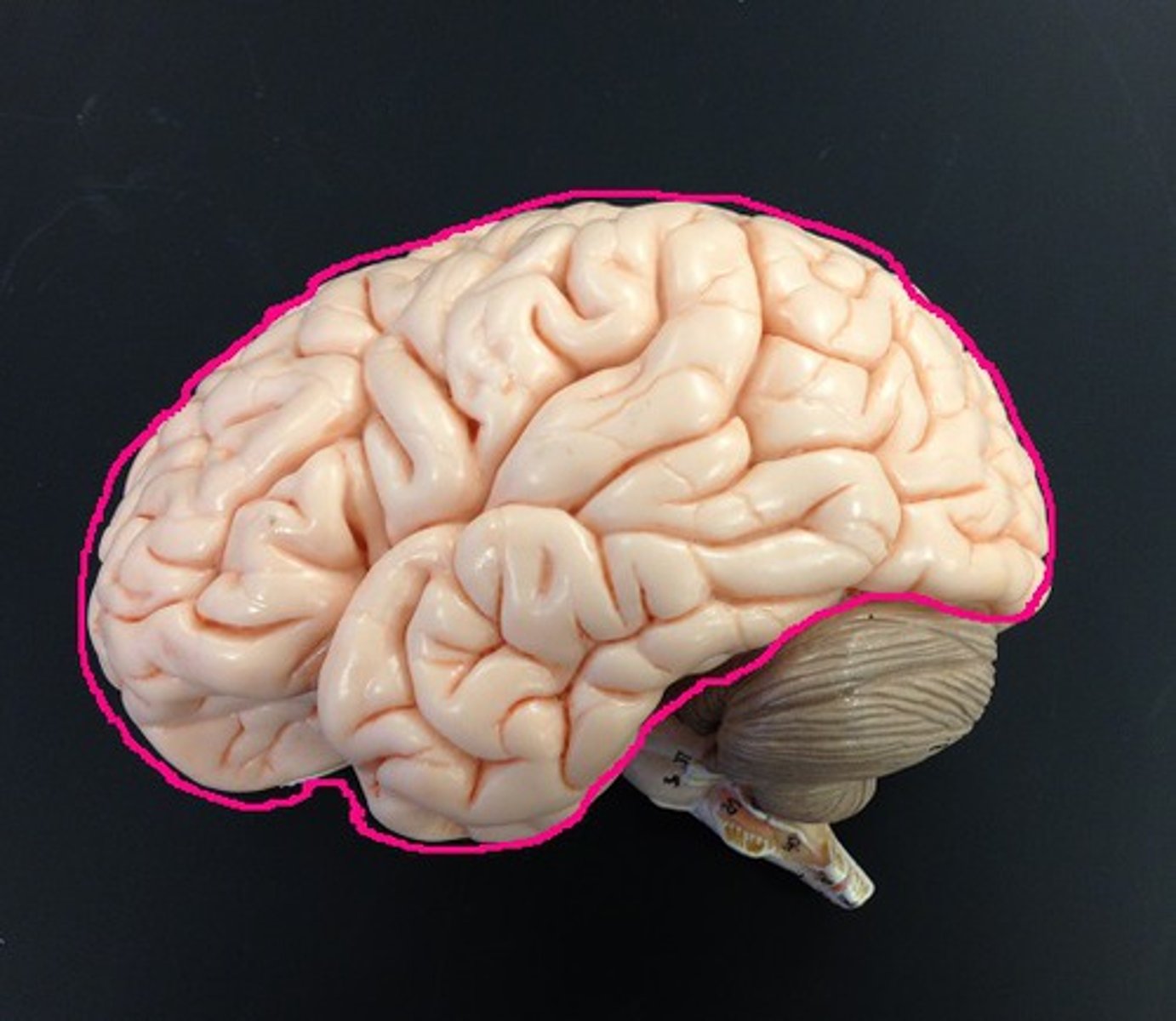
cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
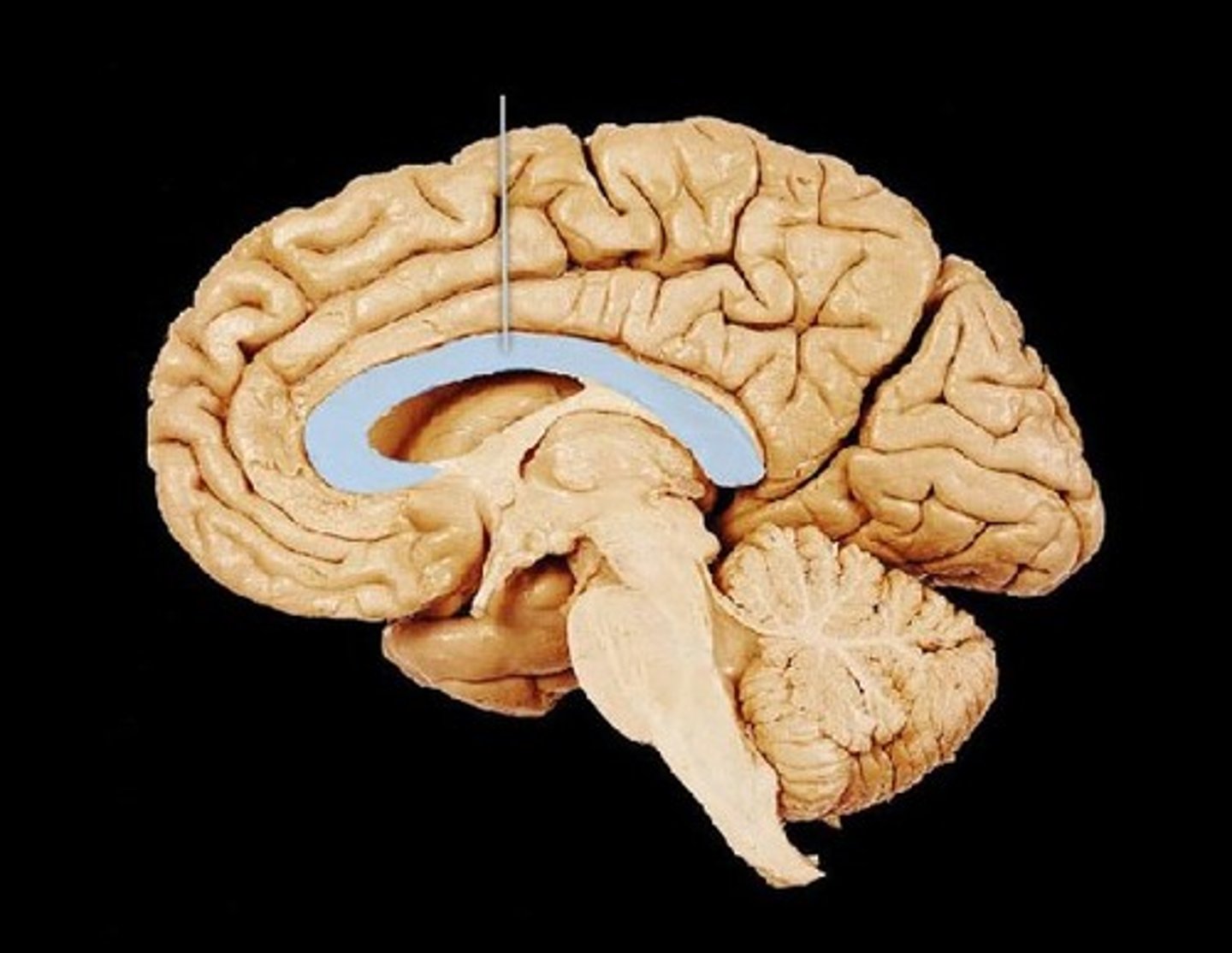
corpus callosum
commissure fibers tract that connect the left and right brain
anterior commissure
bundle of axons that connects the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex
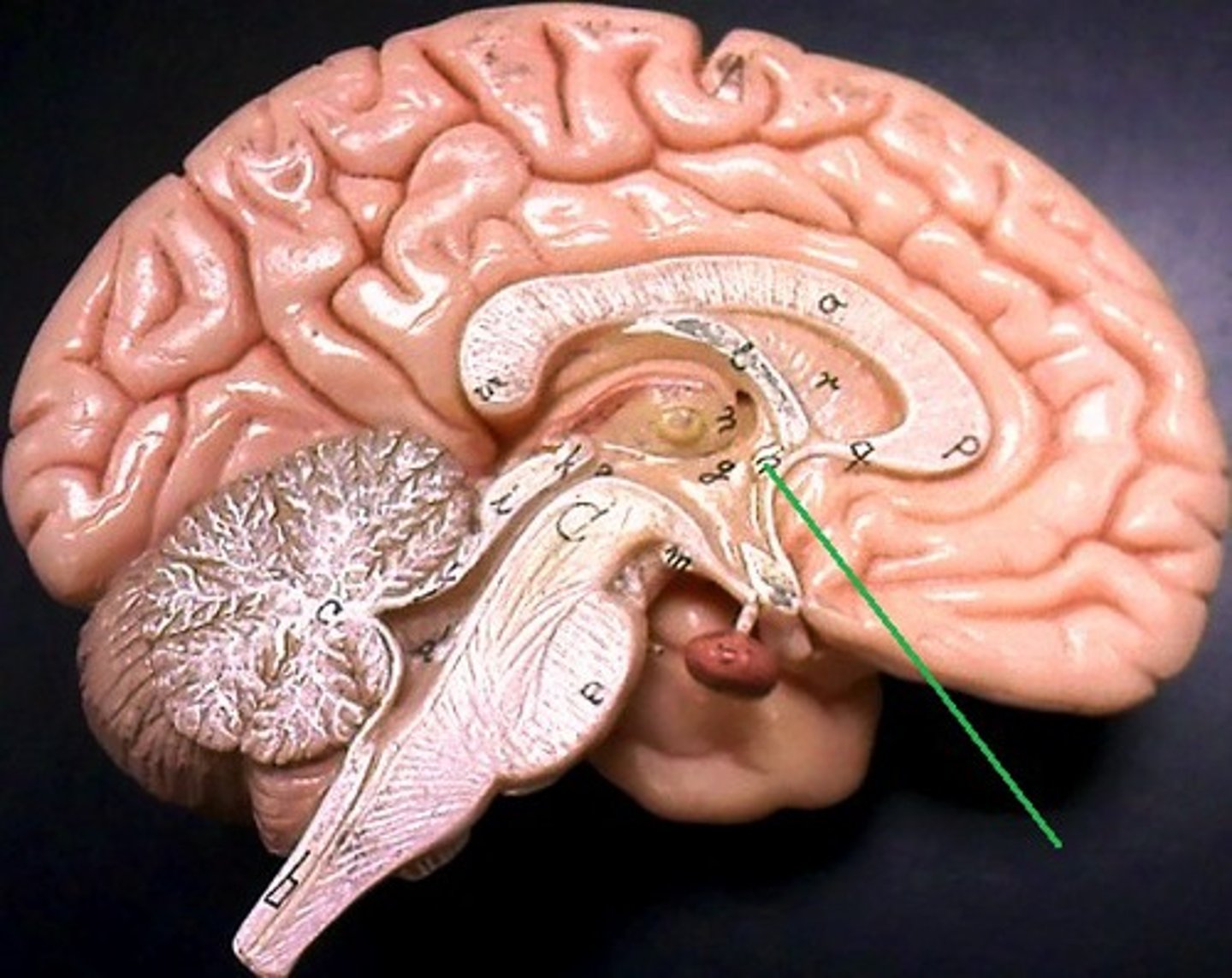
posterior commissure
between arytenoid cartilages
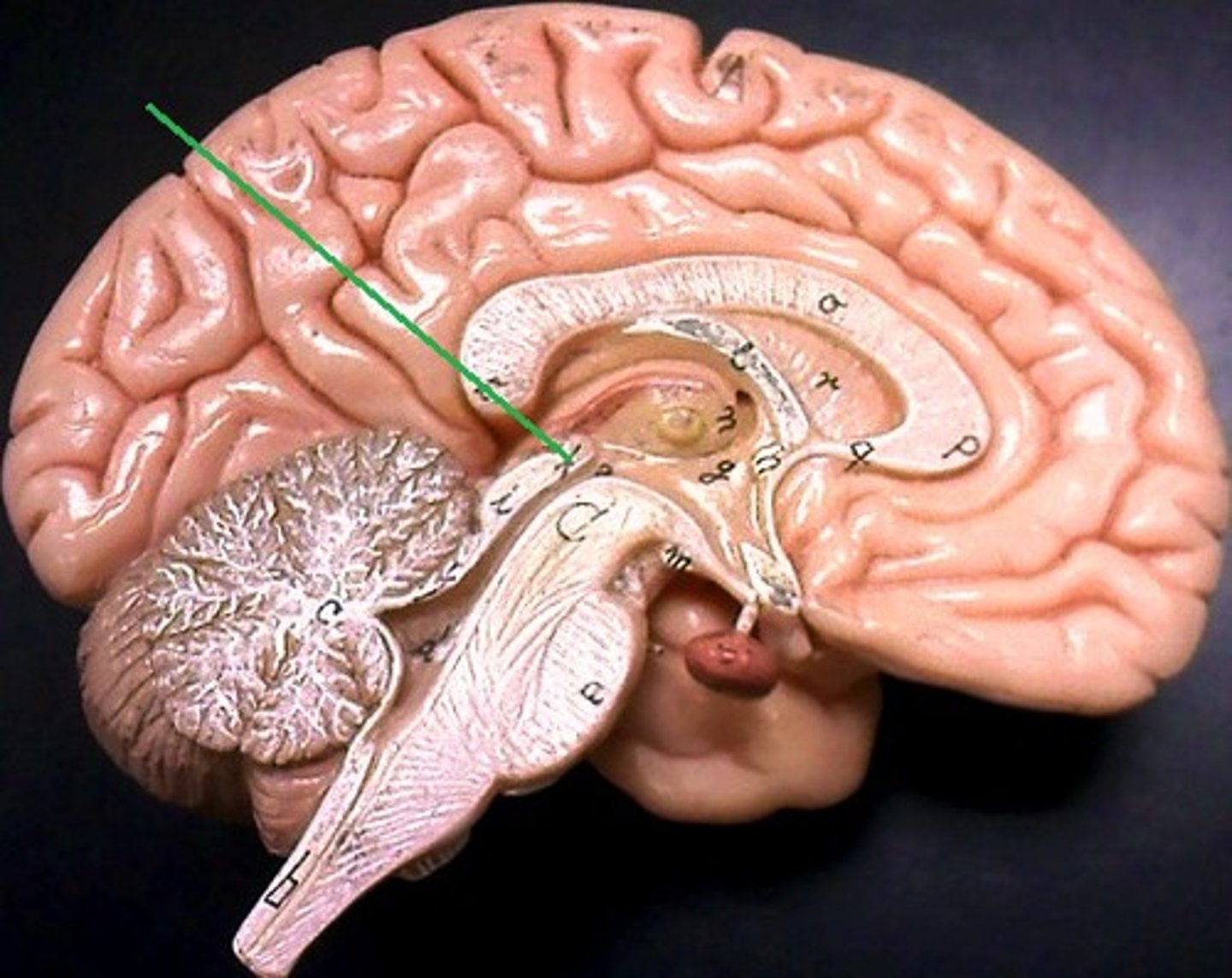
gray matter
- Includes cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, and limbic system
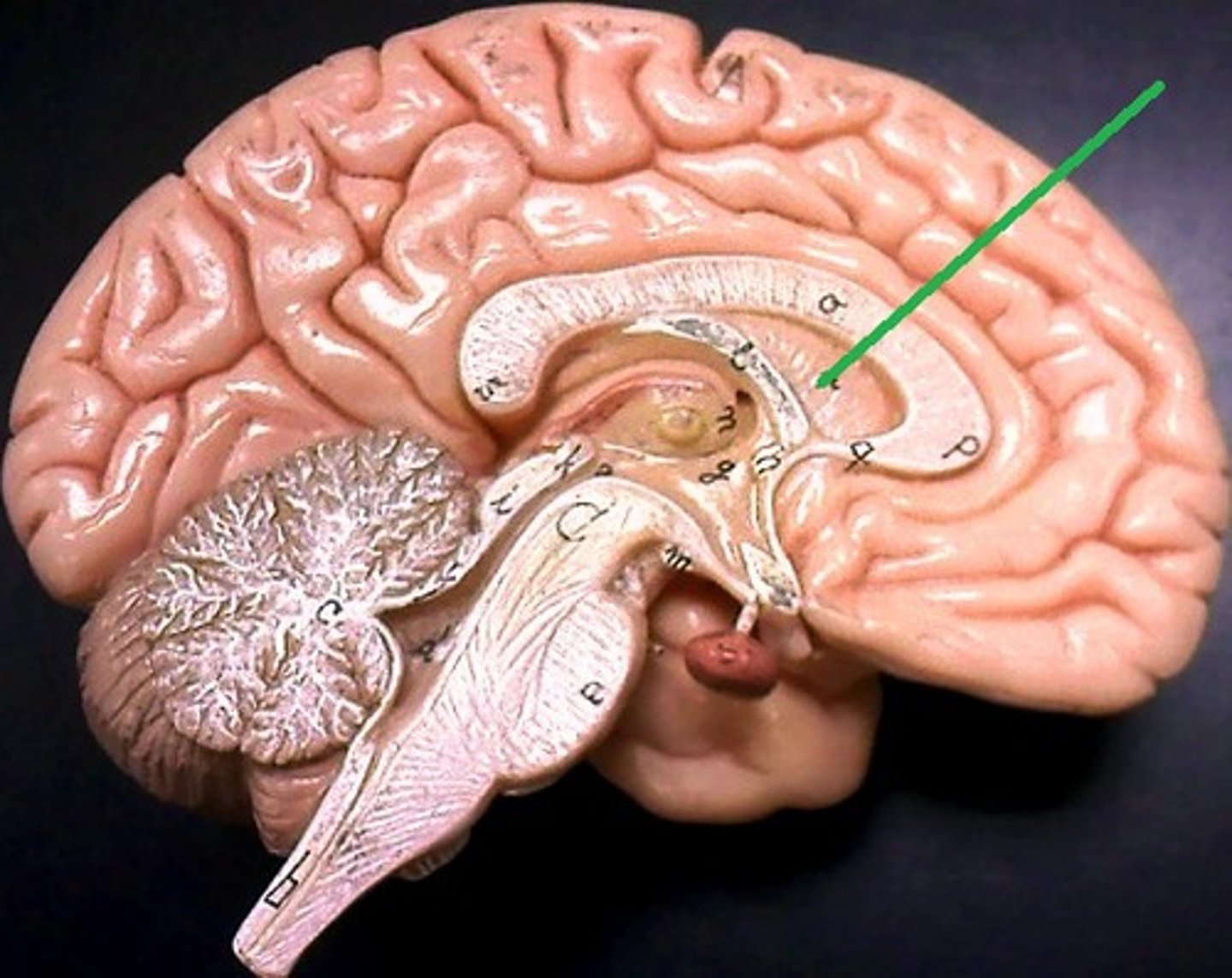
septum pellucidum
separates lateral ventricles
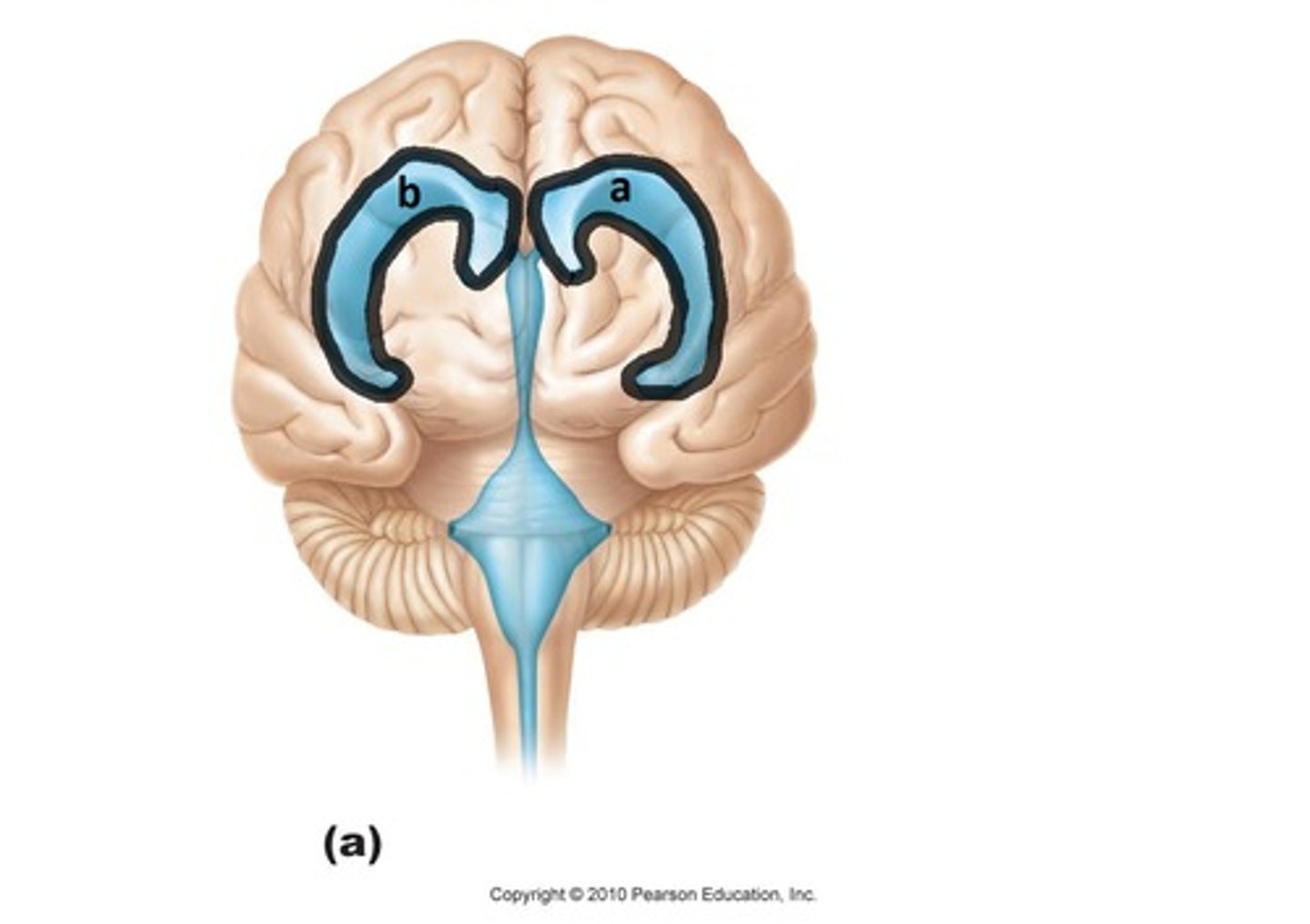
lateral ventricles
A set of paired ventricles lying within the cerebral hemispheres.
interventricular foramen
connects third ventricles to lateral ventricles
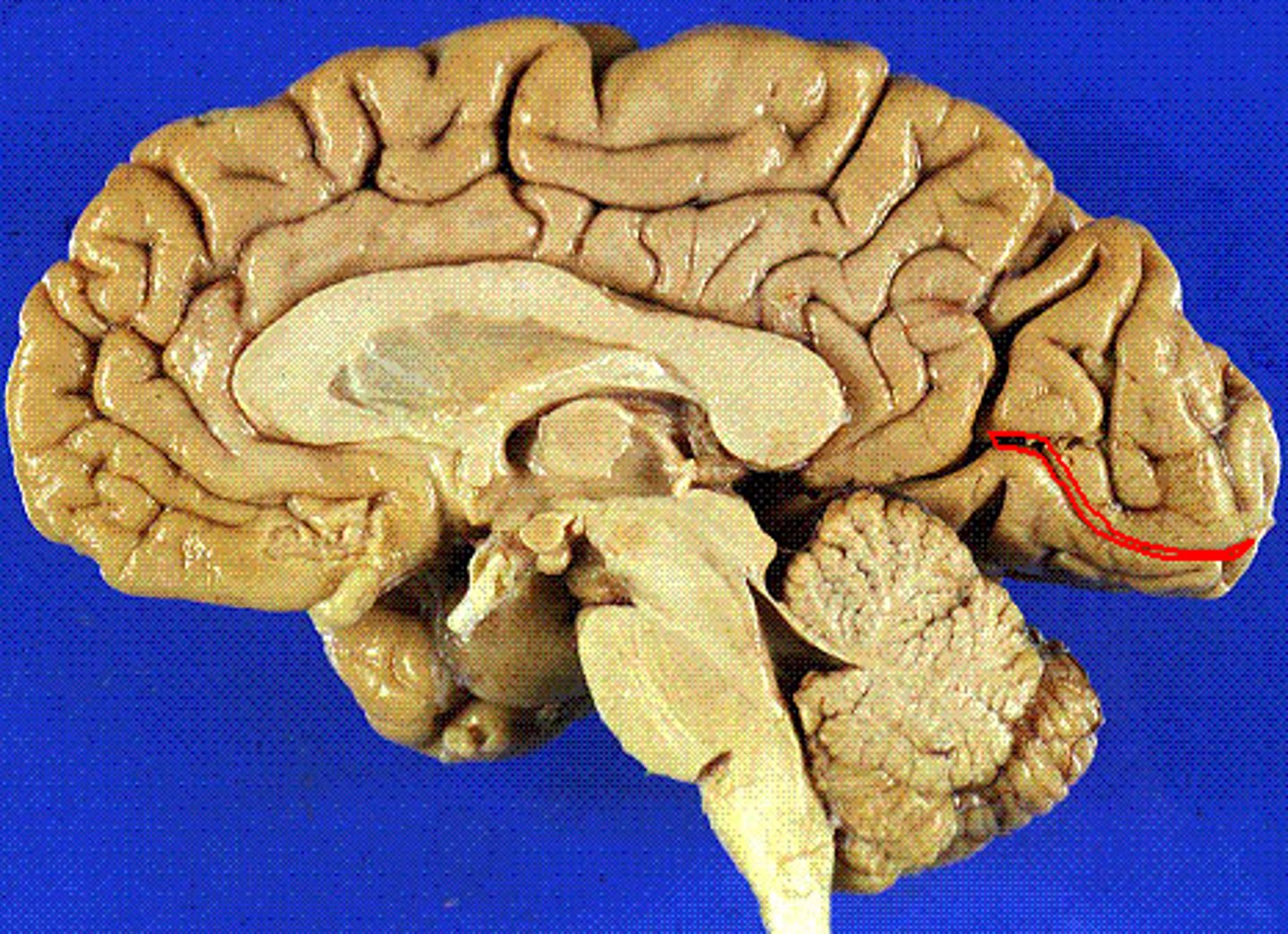
calcarine sulcus
- separates the occipital lobe into superior and inferior halves
- primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe
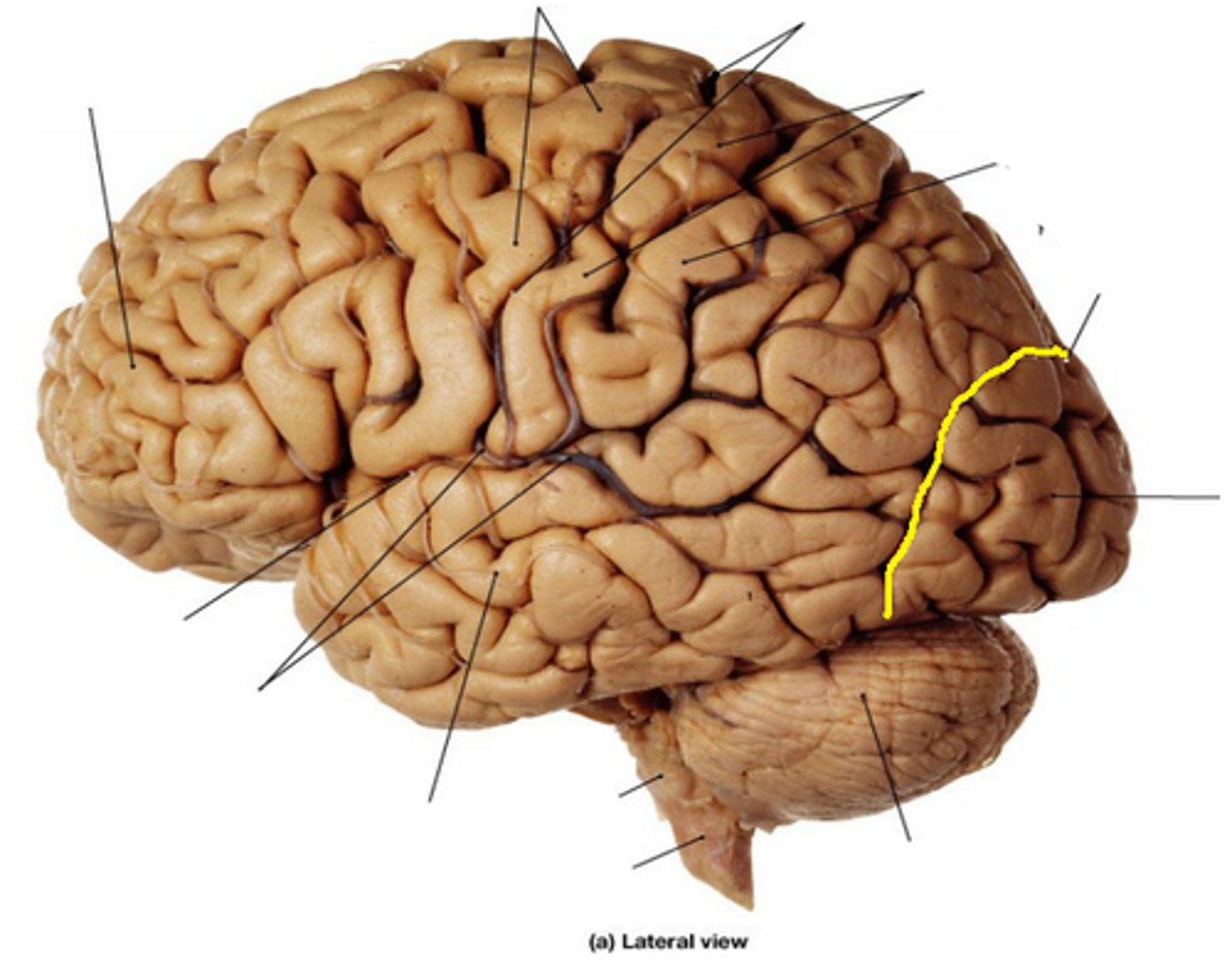
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates occipital and parietal lobes
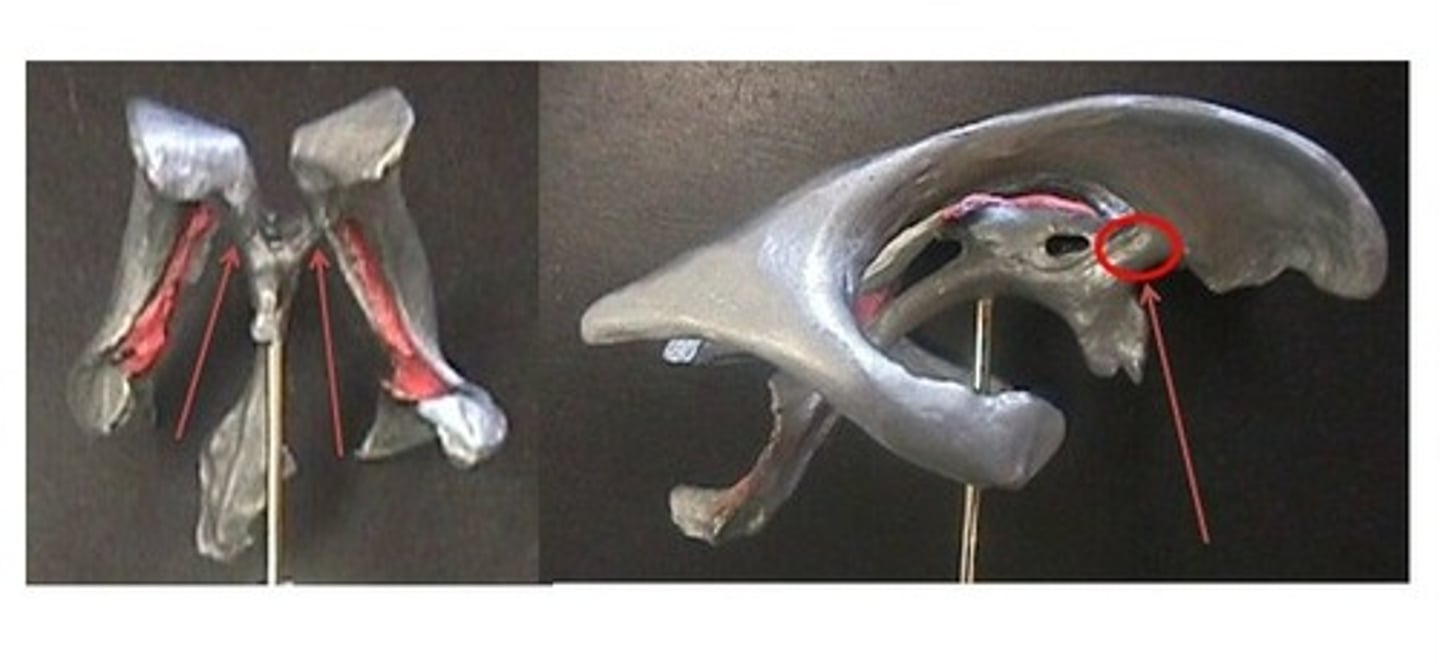
fornix
processing memory
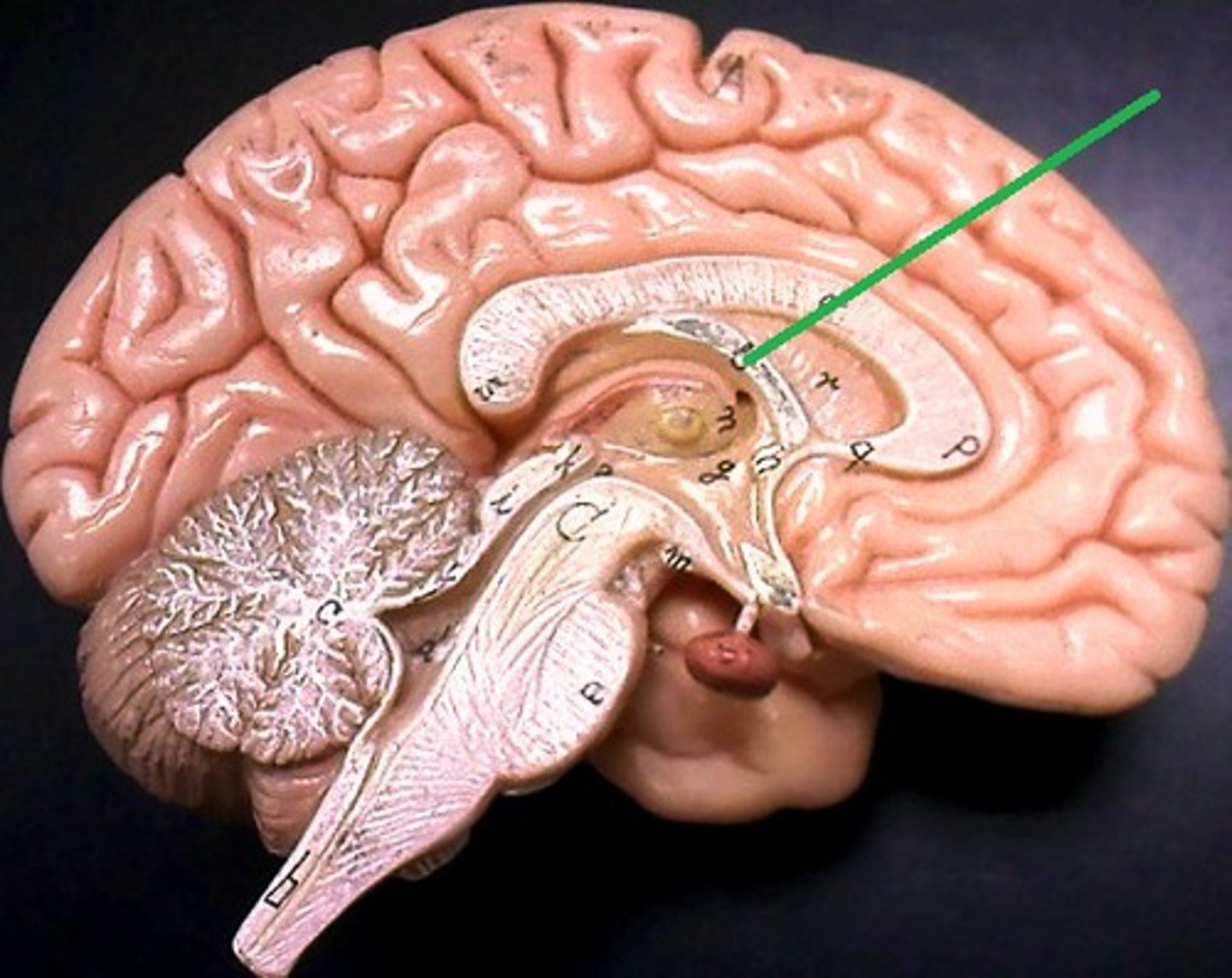
thalamus
gateway for sensory information
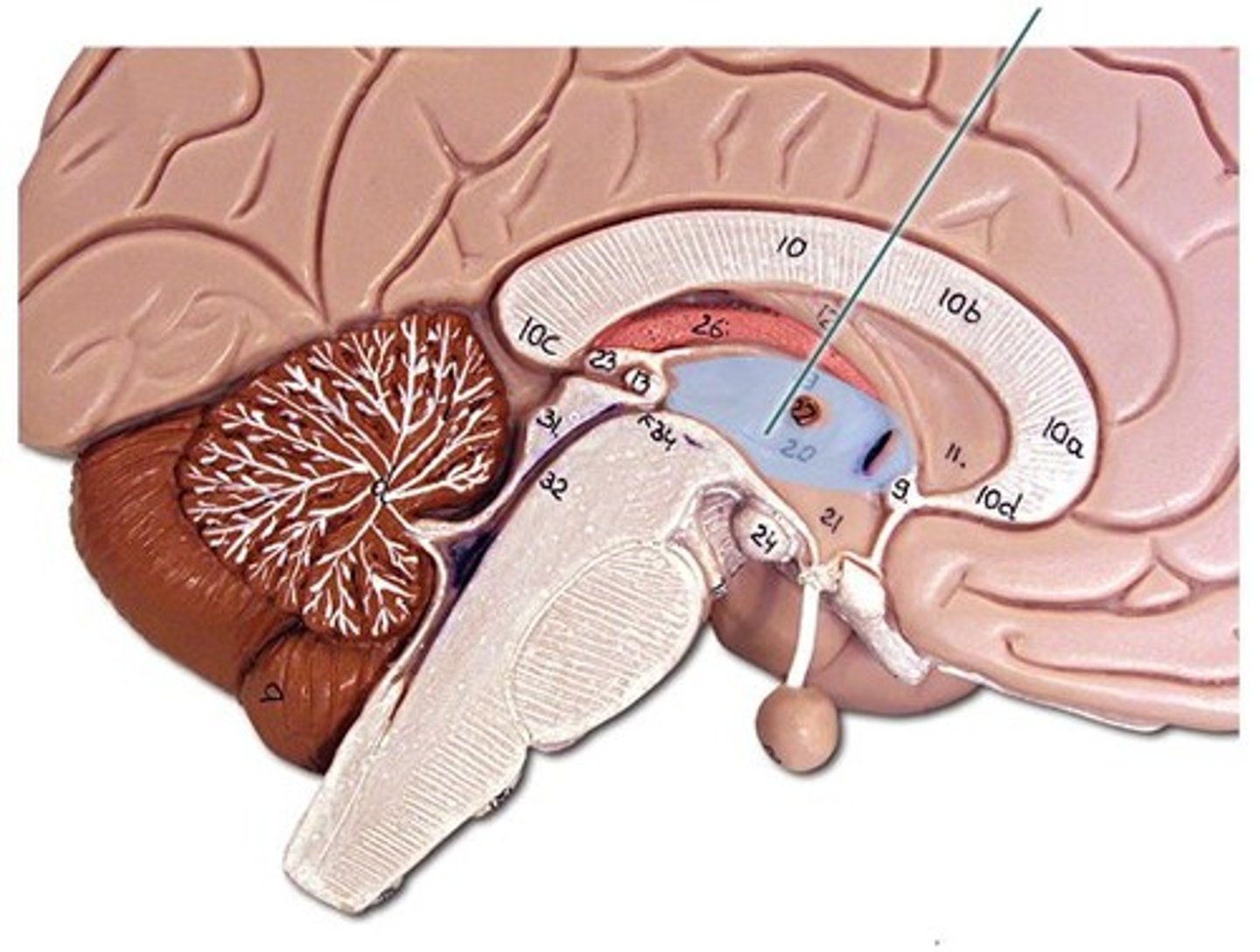
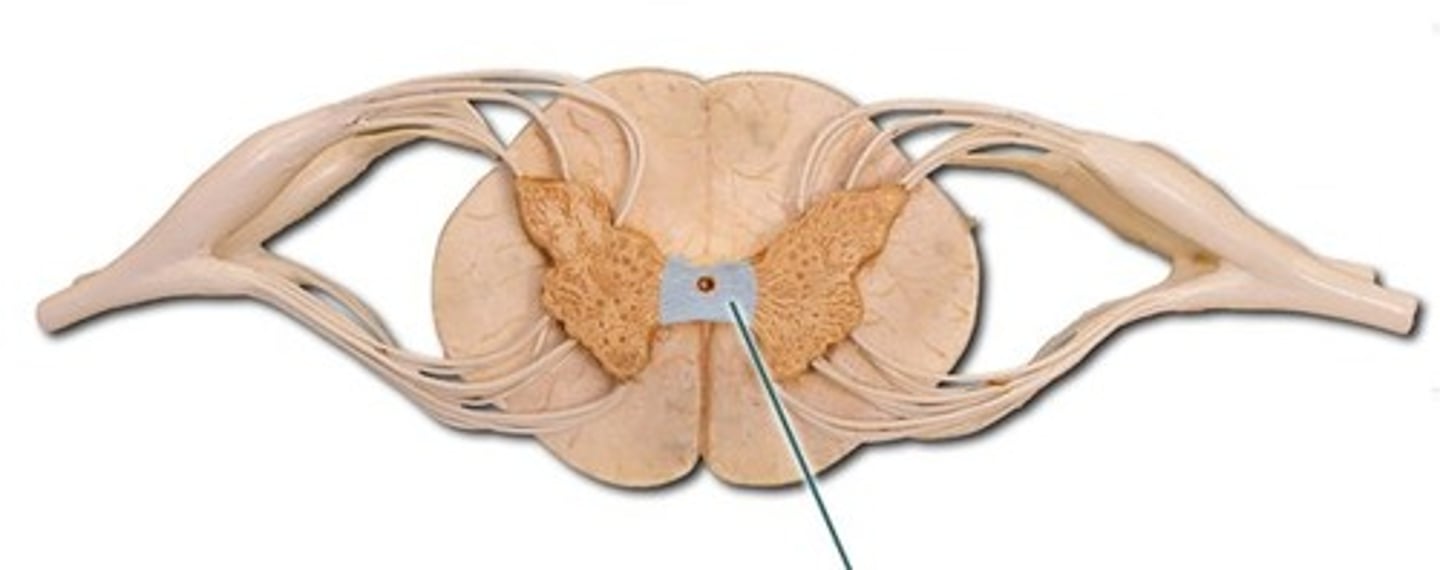
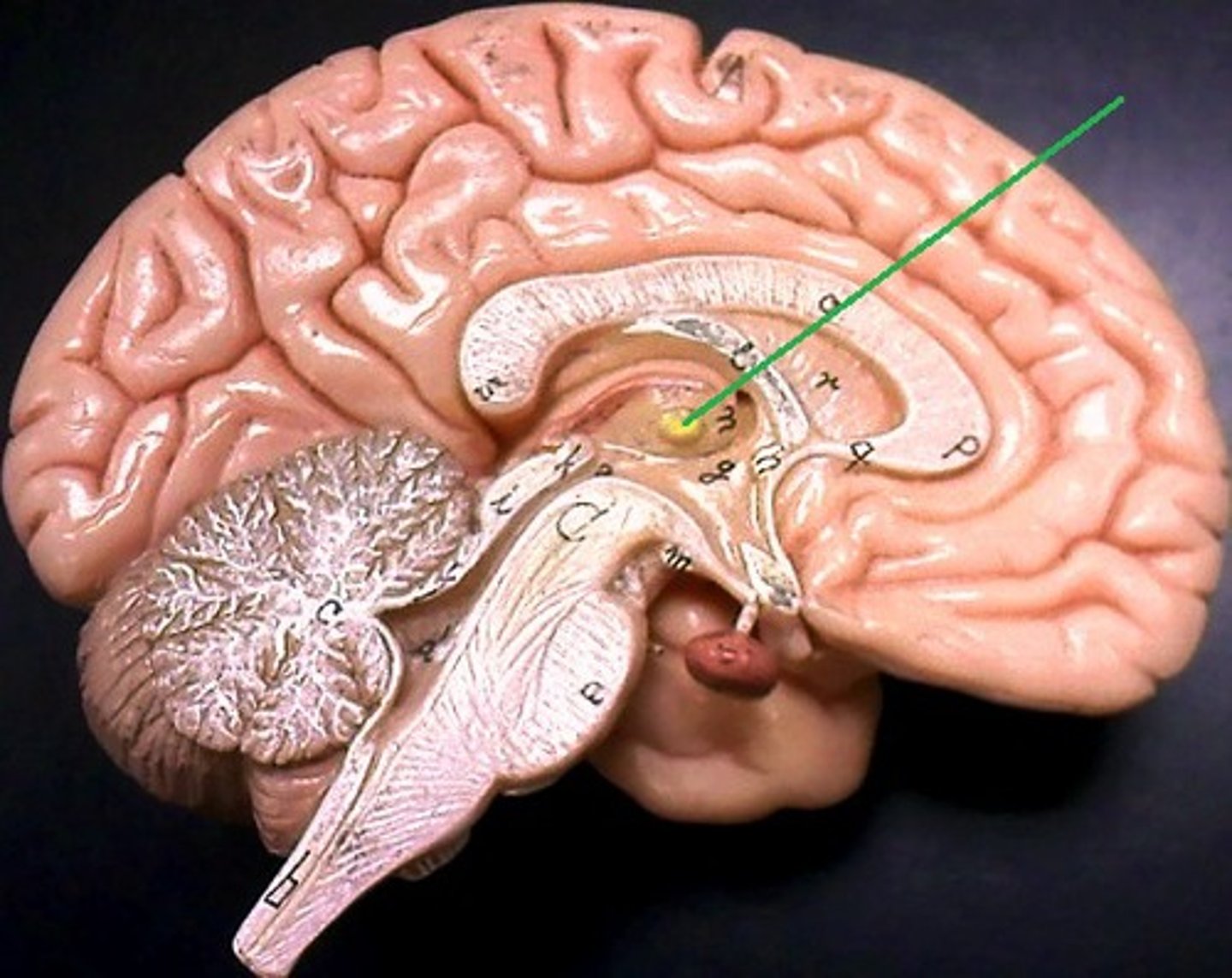
intermediate mass
commissure connecting R & L lobes of thalamus
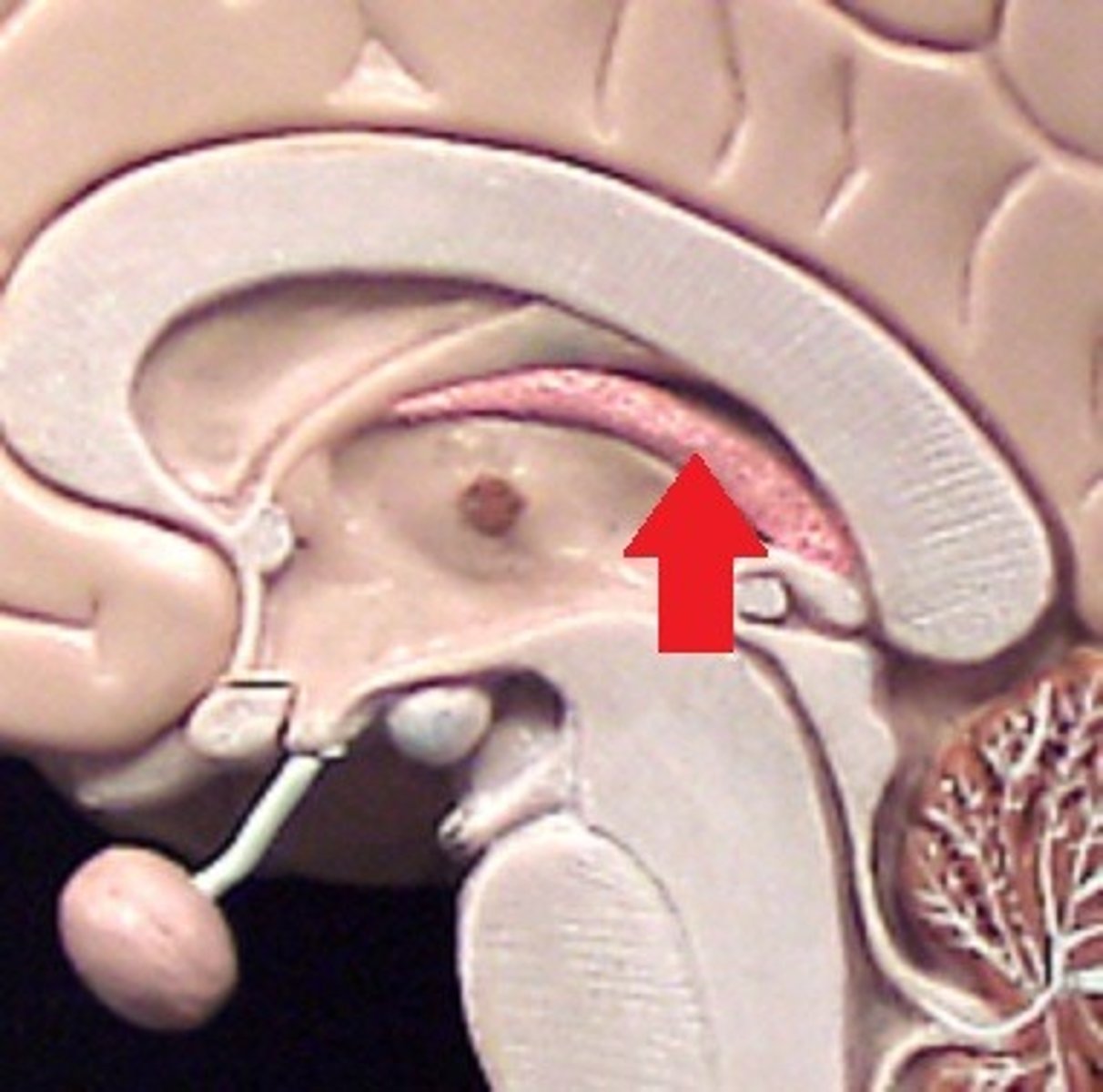
third ventricle
enclosed by the diencephalon
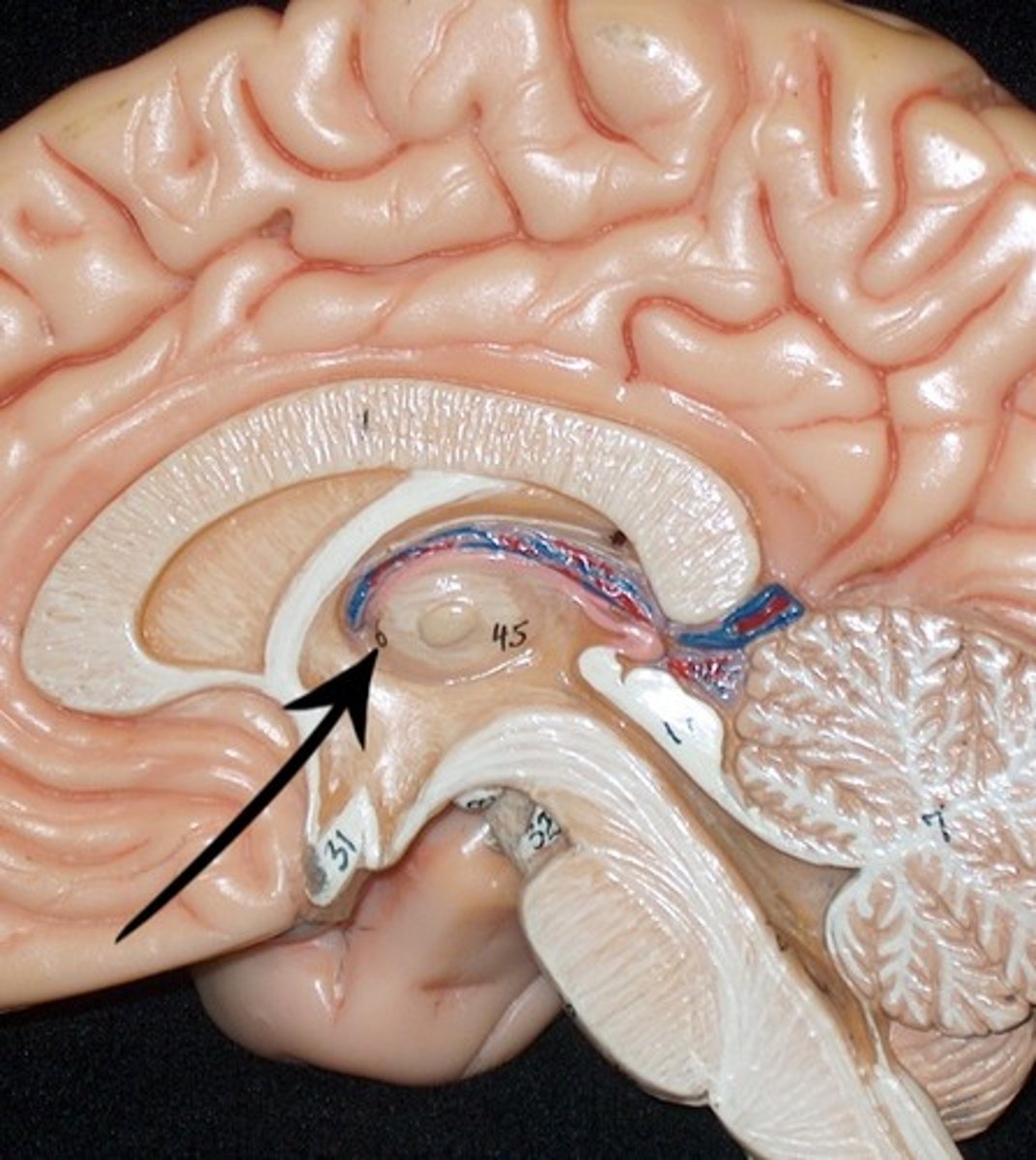
choroid plexus
- lined with ependymal cells that produce CSF
hypothalamus
- thirst + hunger
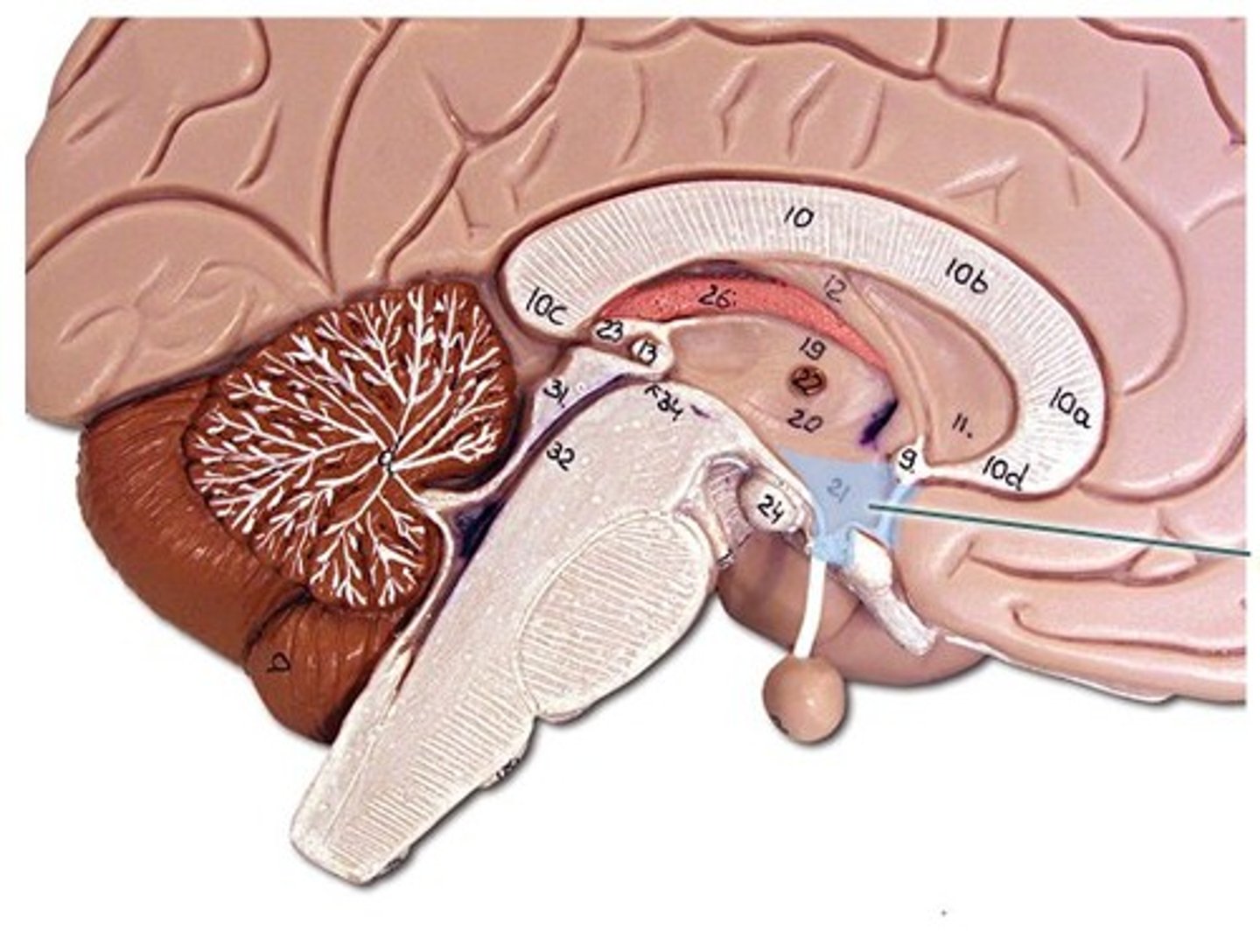
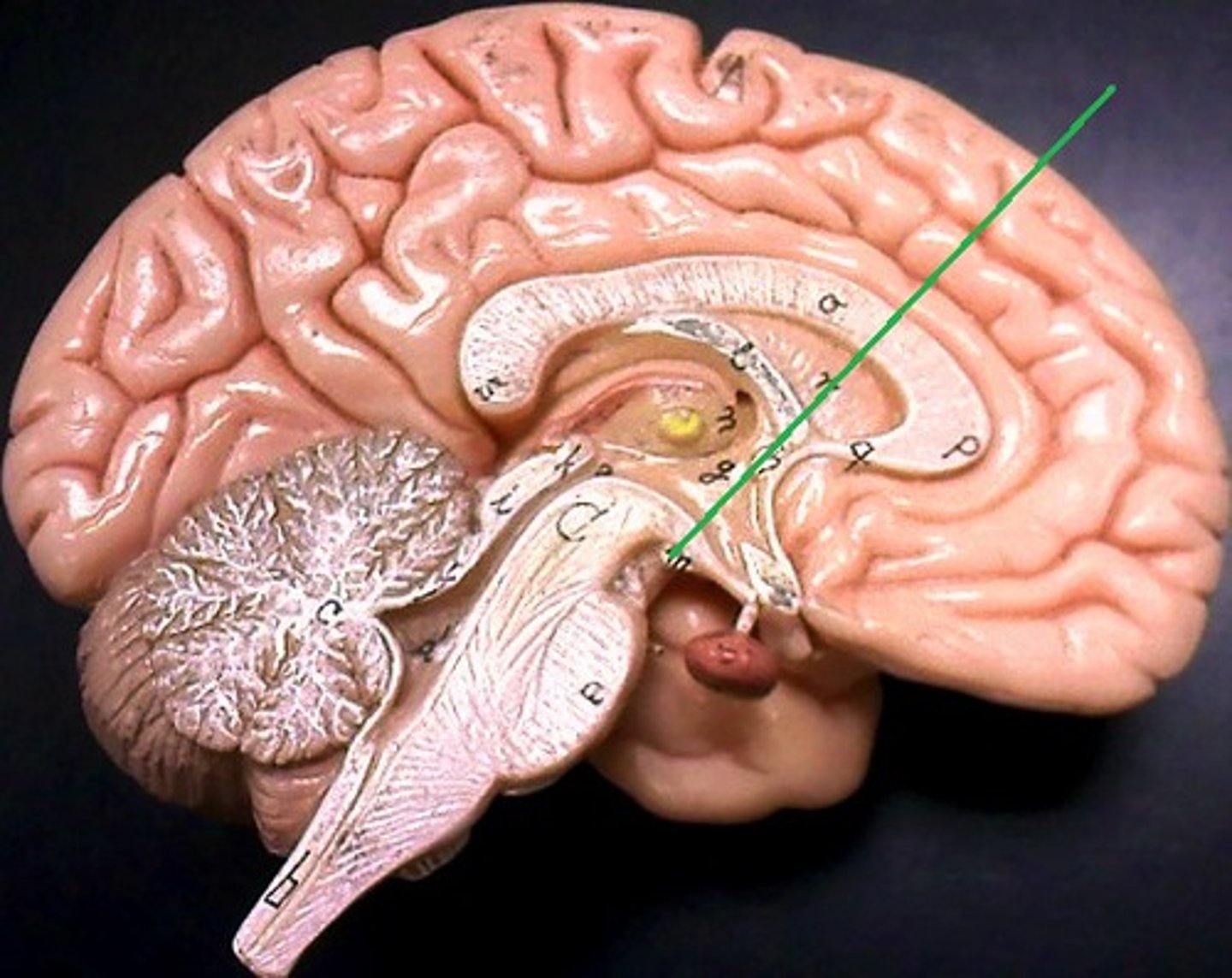
mammillary bodies
- relay stations for sending olfactory information to the temporal lobes
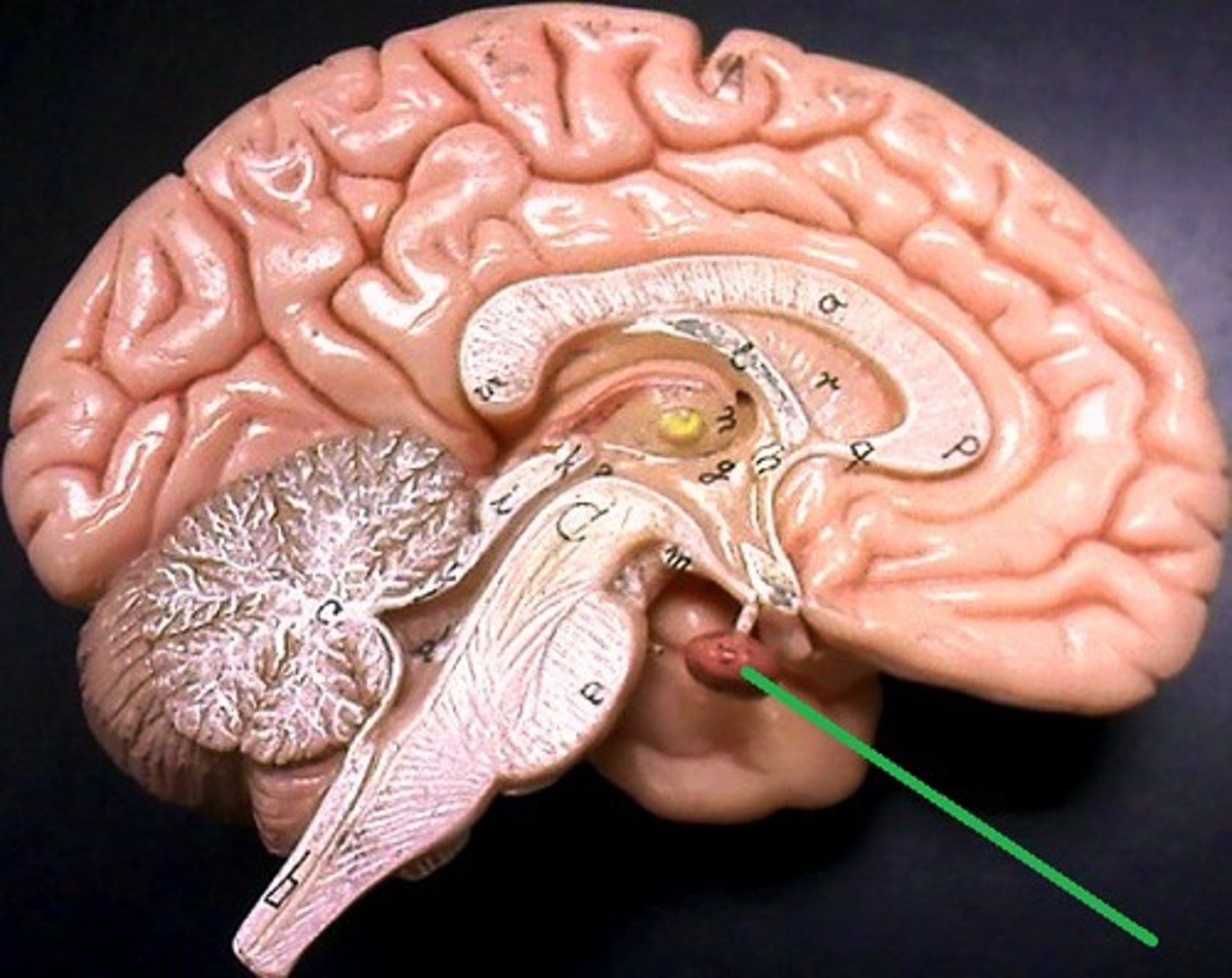
pituitary gland
regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
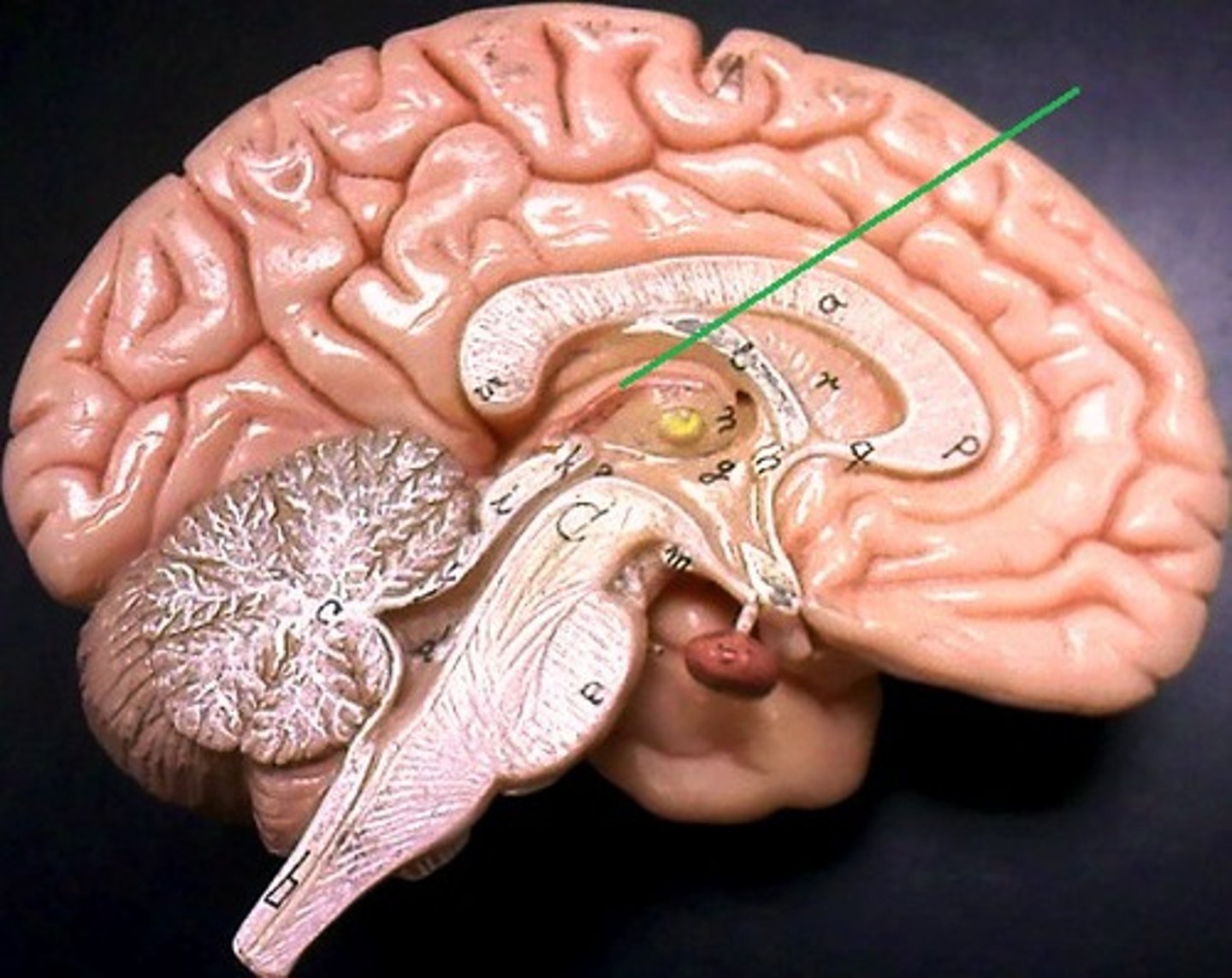
epithalamus
- contains pineal gland that secretes melatonin to regulate sleep-wake cycle
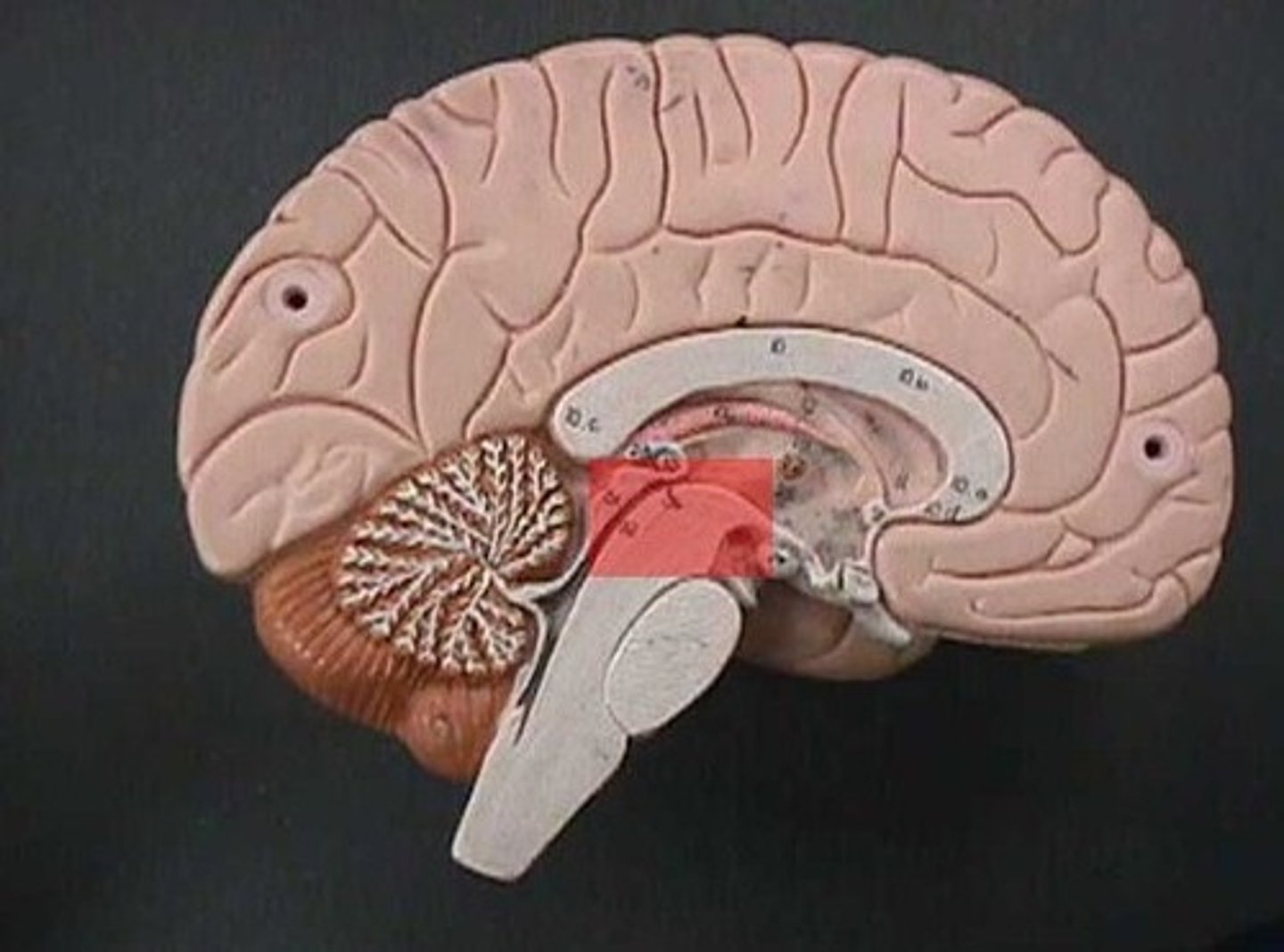
brain stem
- midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
- controls autonomic behaviors necessary for survival
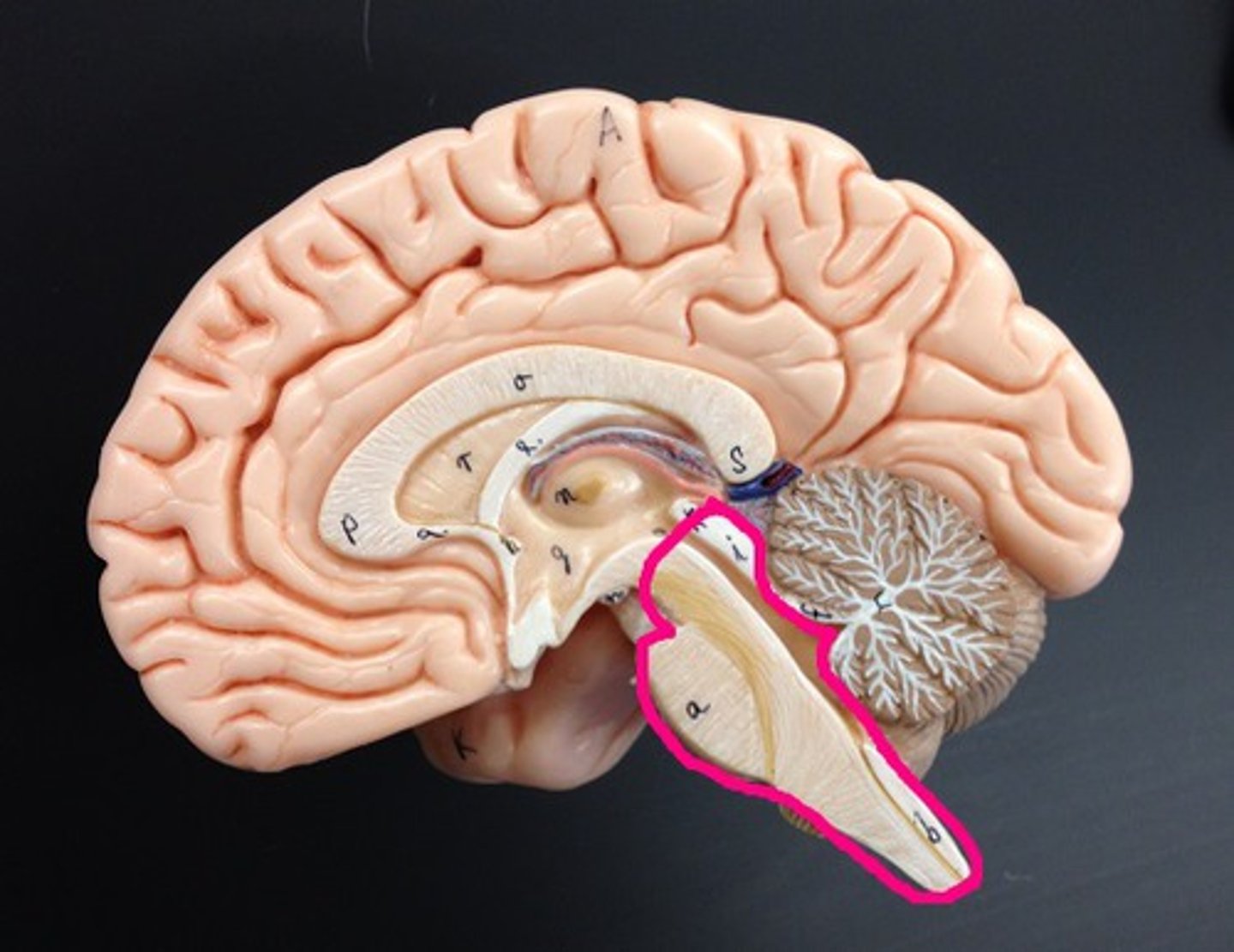
mid-brain
- processing motor movements
- hearing
- vision
cerebral punduncles
- balance + coordination
- assist in refining motor movements + posture maintenance
cerebral aqueduct
- allows CSF to flow from third ventricle to fourth ventricle
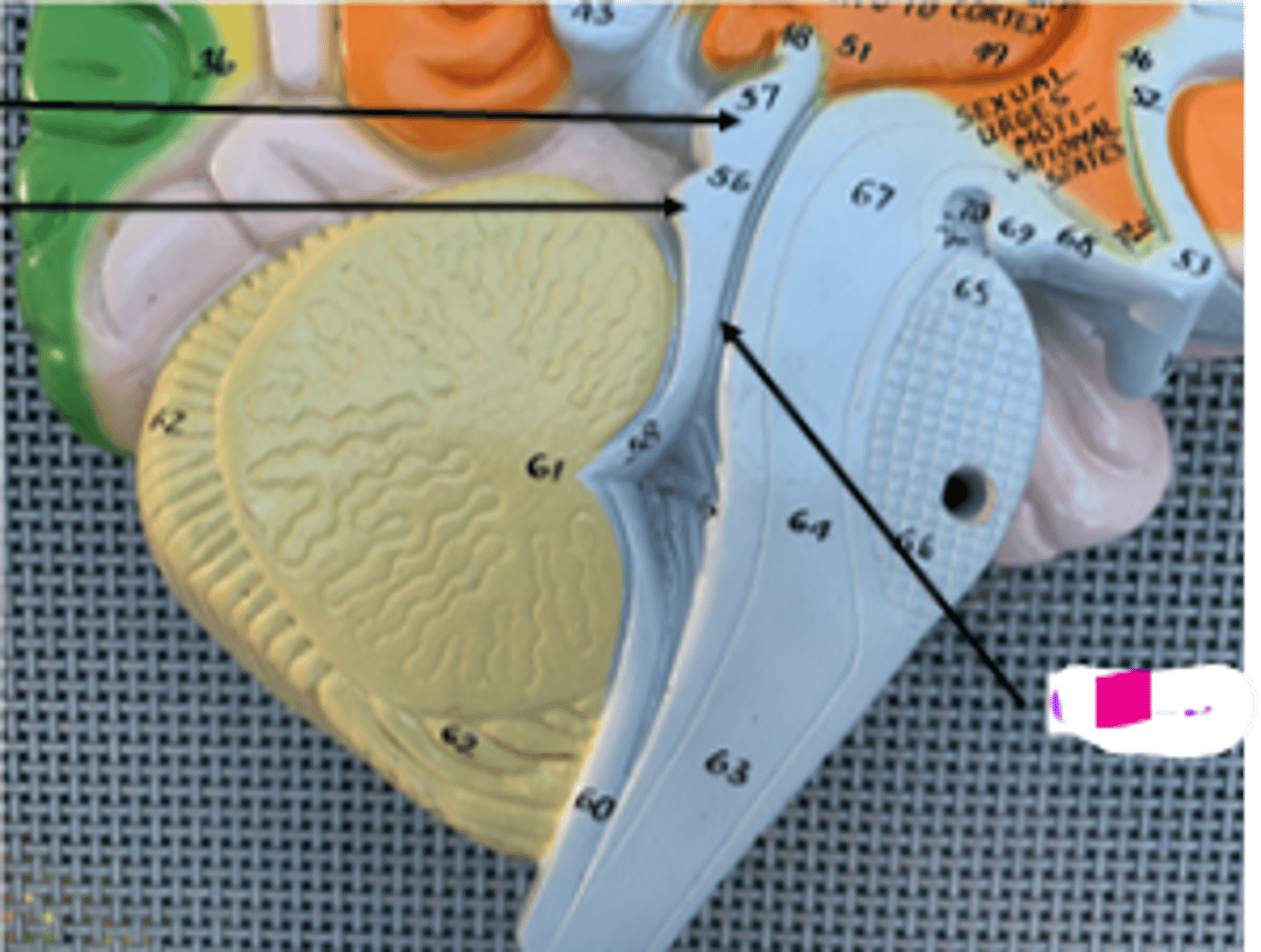
corpora quadrigemina
superior and inferior colliculi
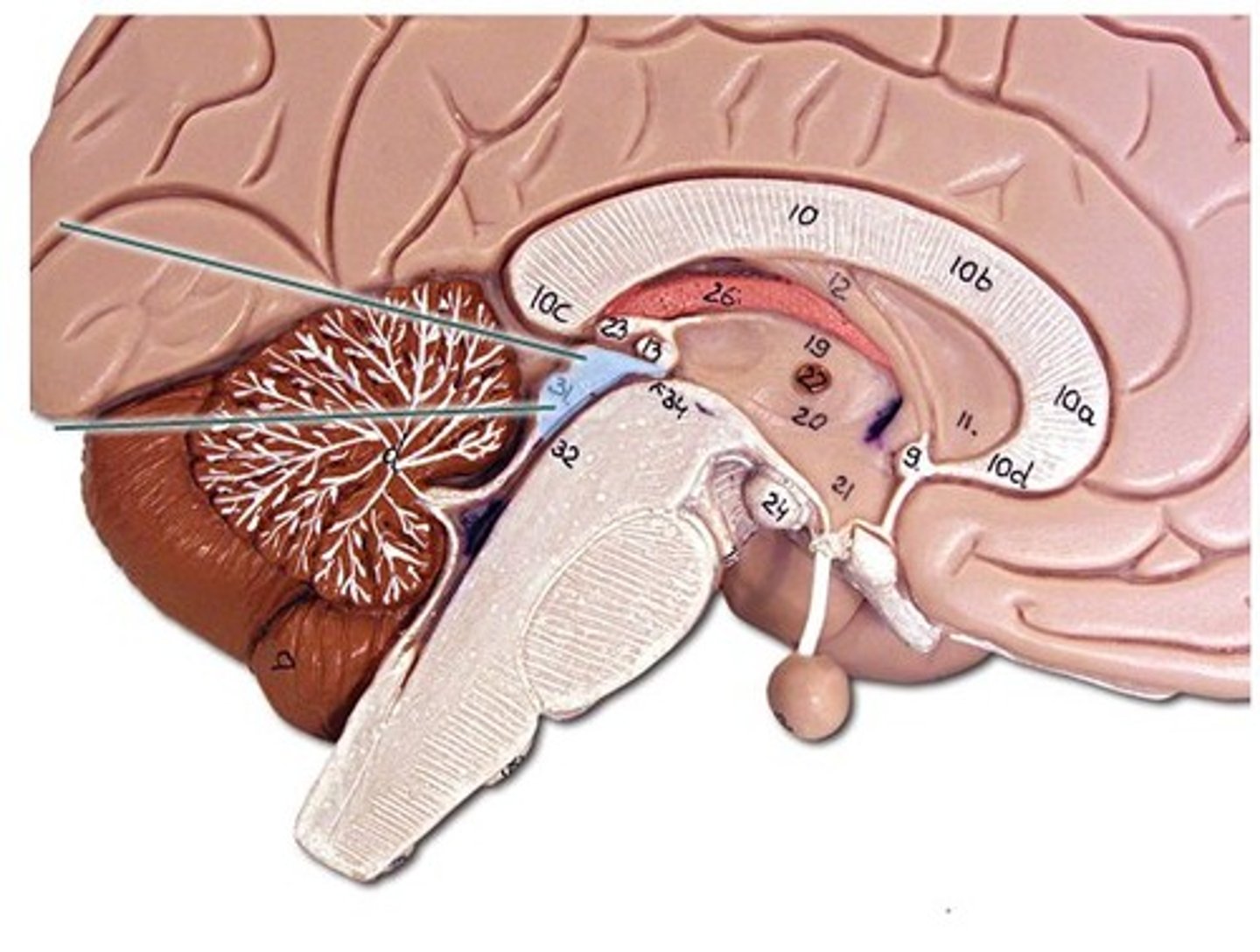
superior colliculus
movement of eyes
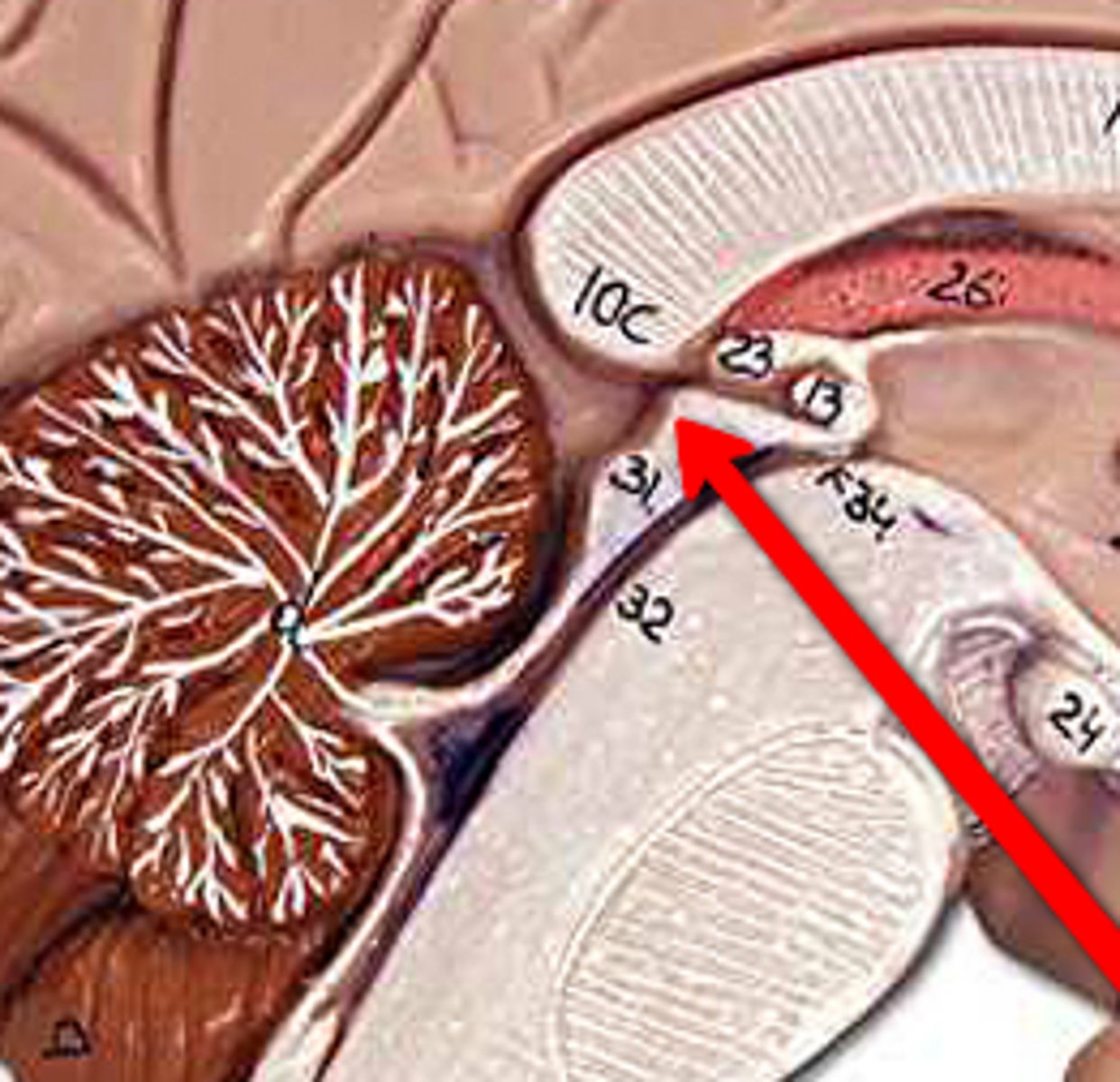
inferior colliculus
understanding sound
cingulate gyrus
- emotional memory
pons
regulation of respiration
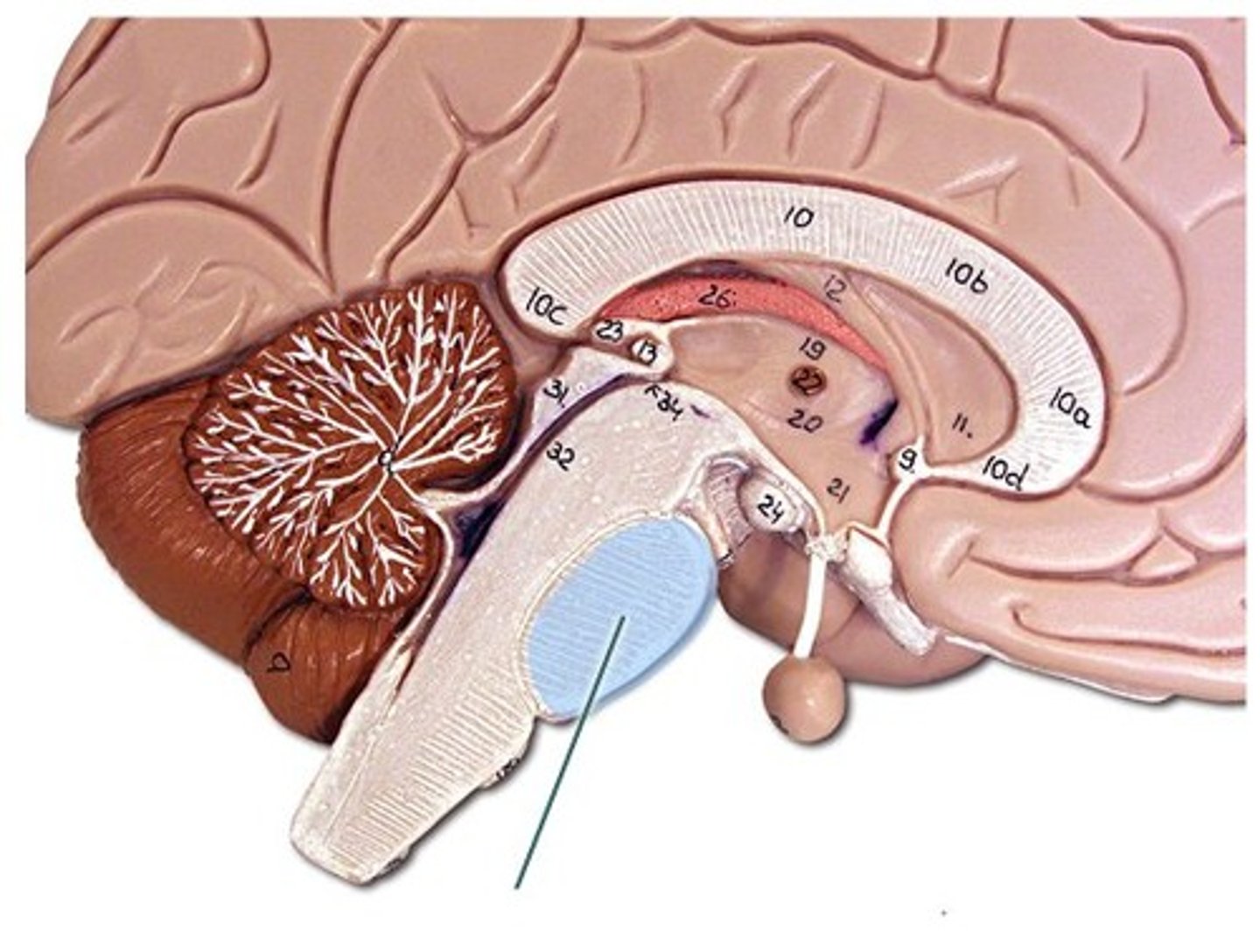
fourth ventricles
between brainstem and cerebellum
- produces CSF
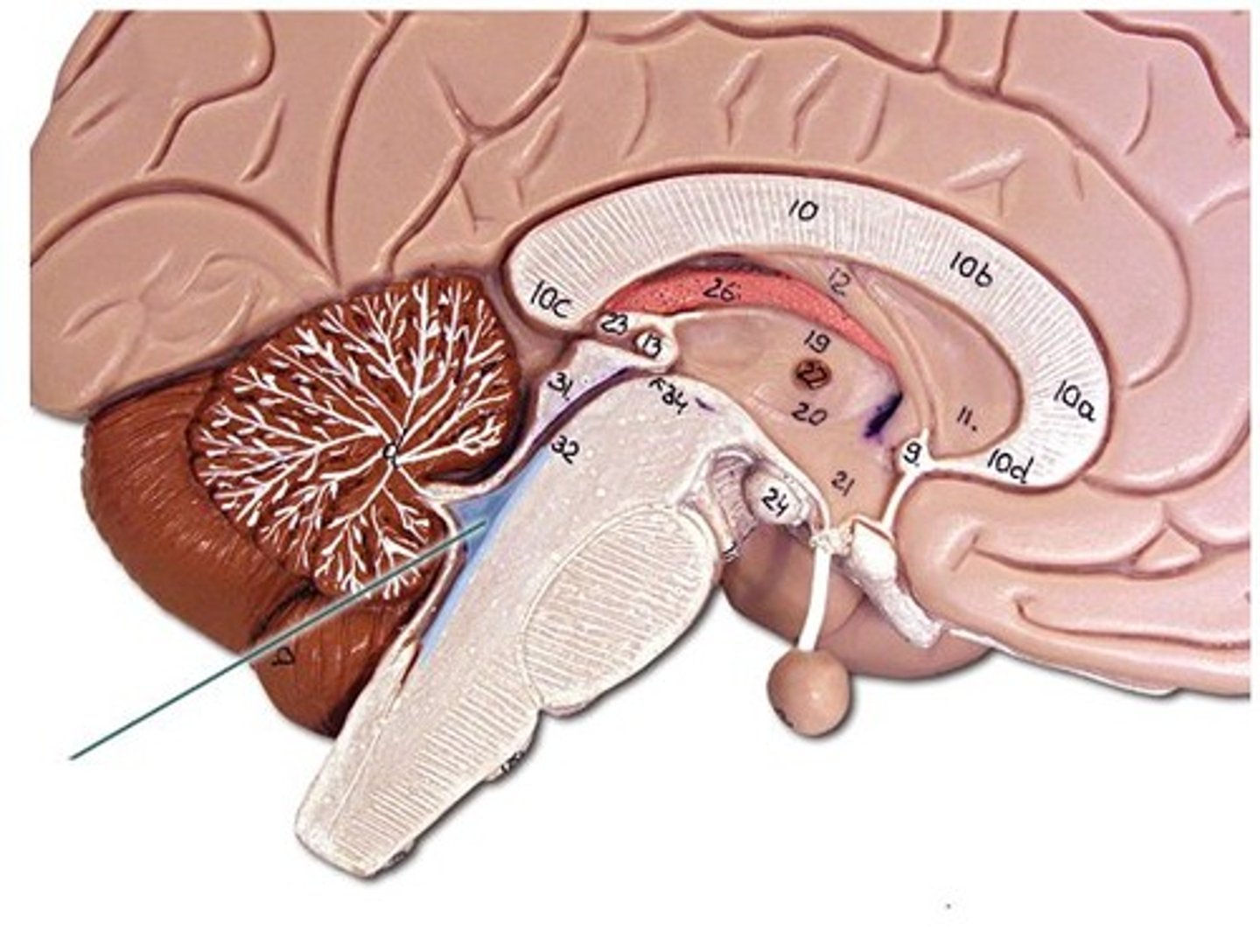
medulla oblongata
- regulation of heart rate
- vasodilation + vasoconstriction
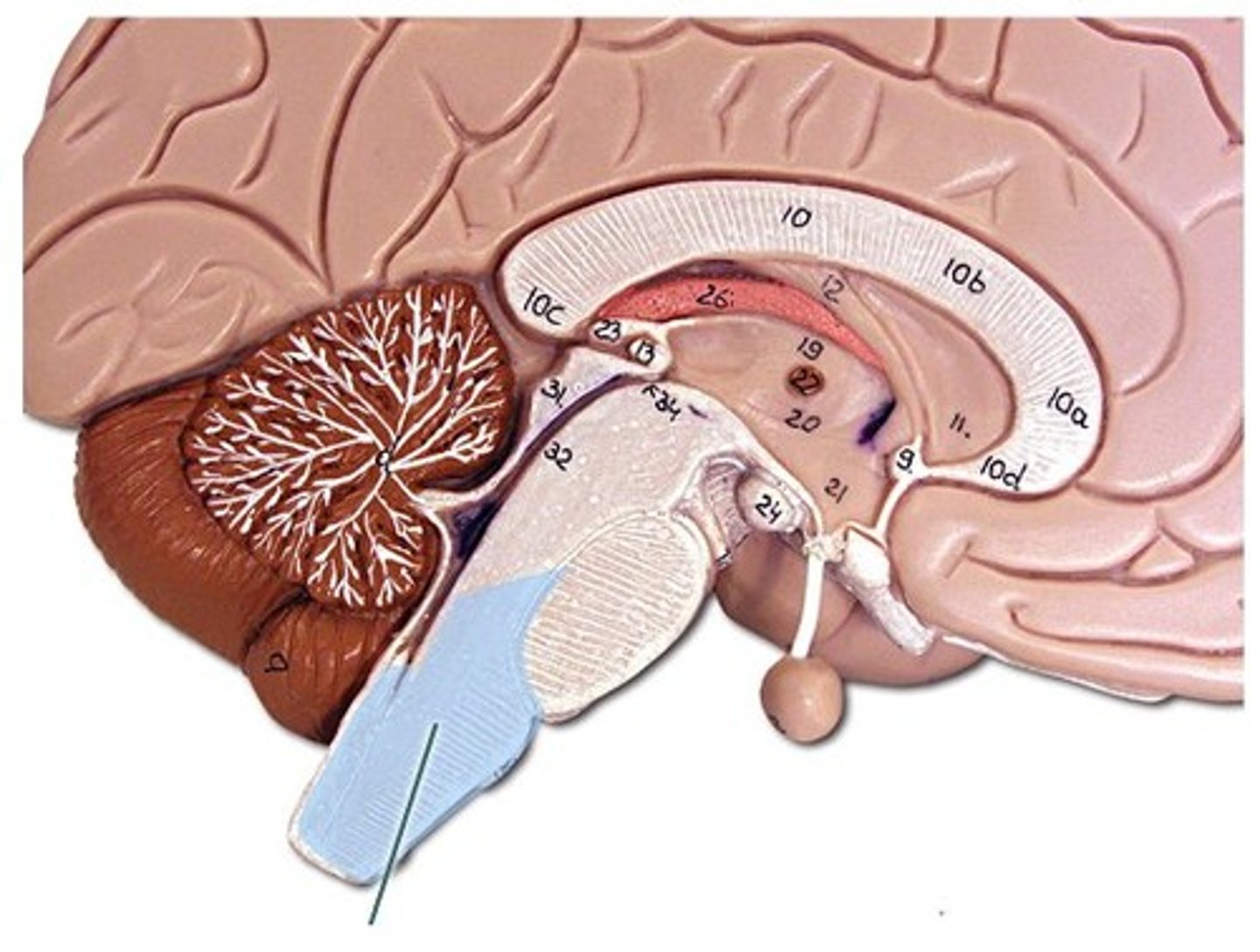
Cerebellum
- balance
- muscle coordination
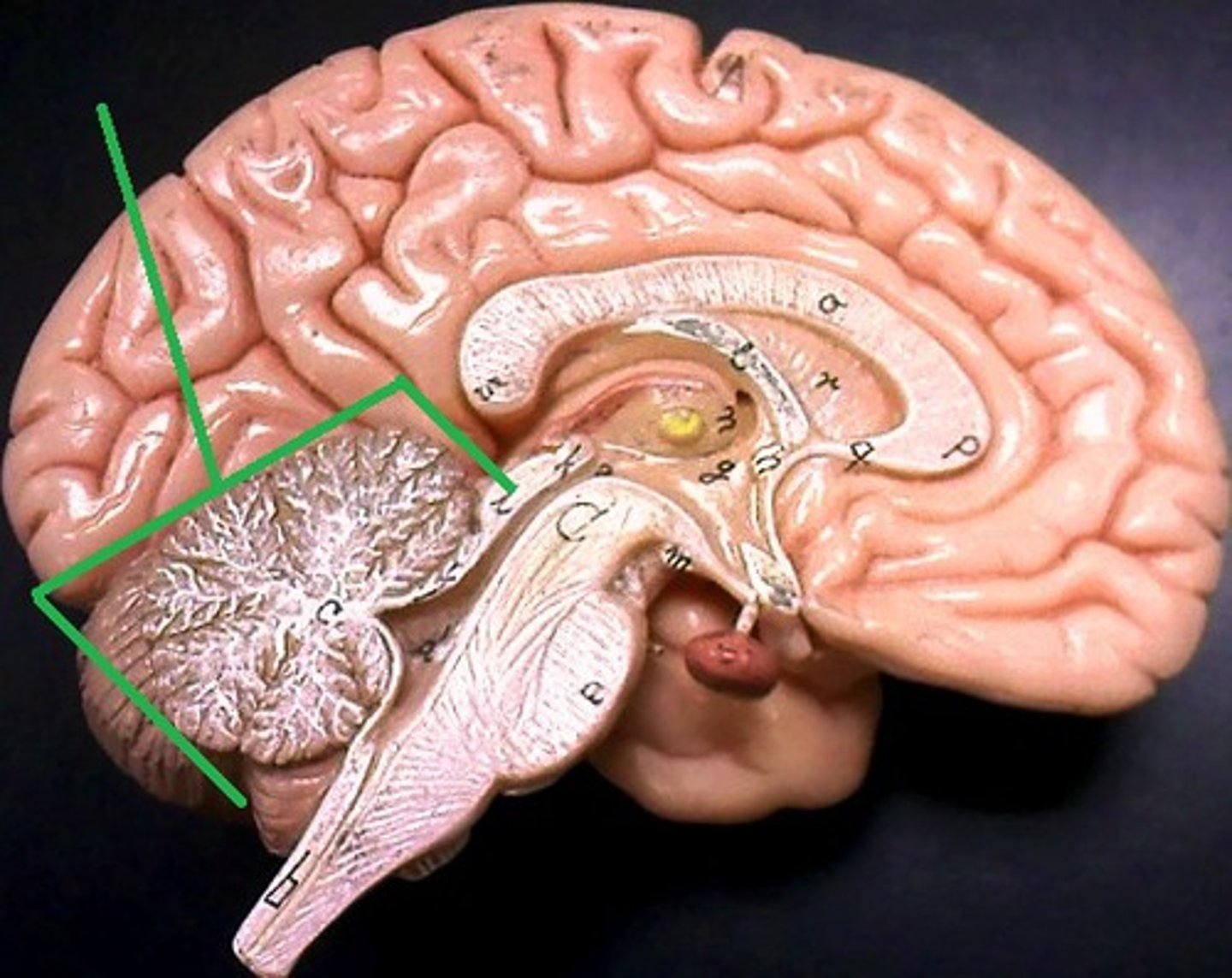
arbor vitae
white matter of the cerebellum
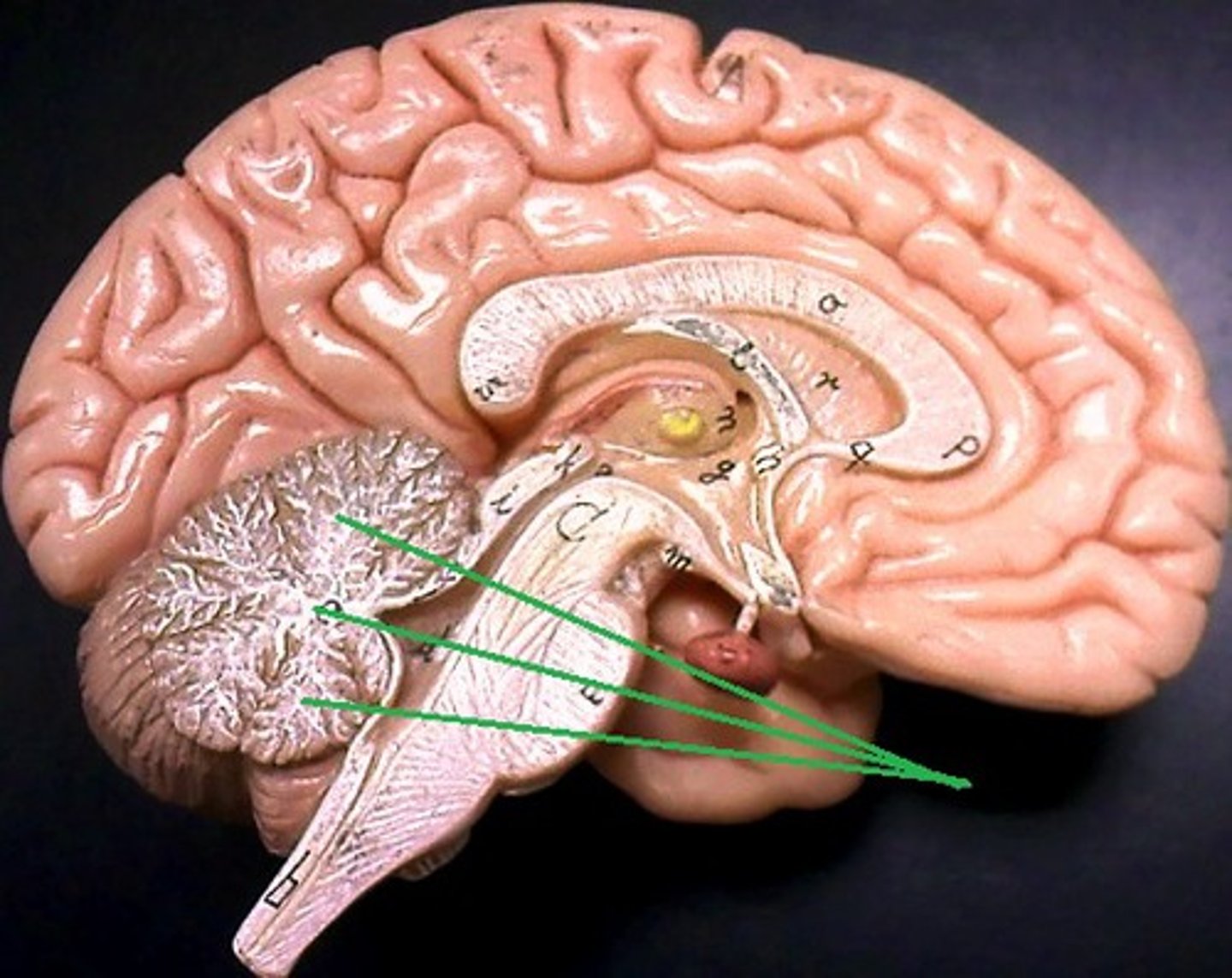
vermis
(worm-like structure) connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
follia + fissures
folds of cerebellum
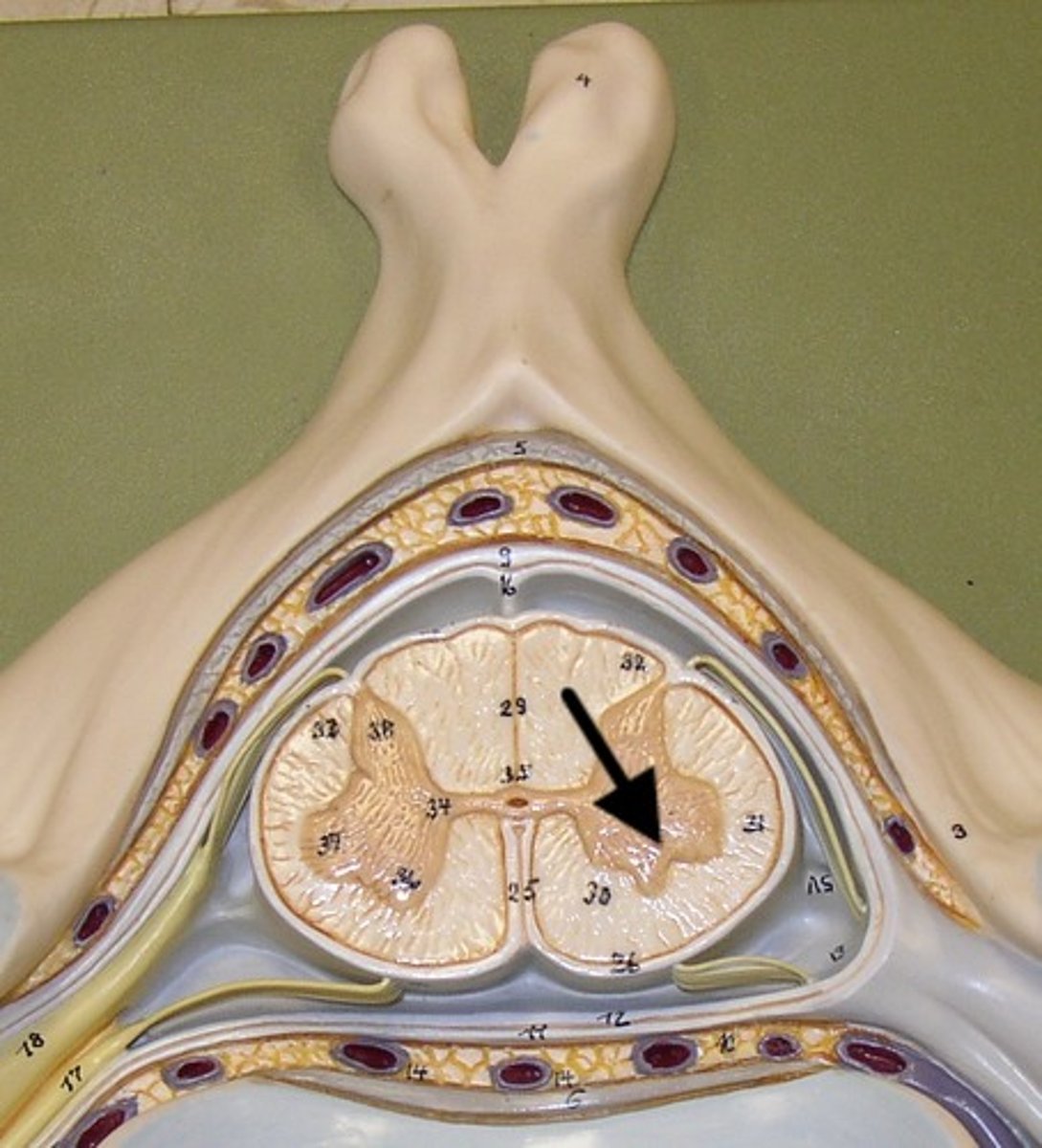
spinal cord
a major part of the central nervous system which conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain
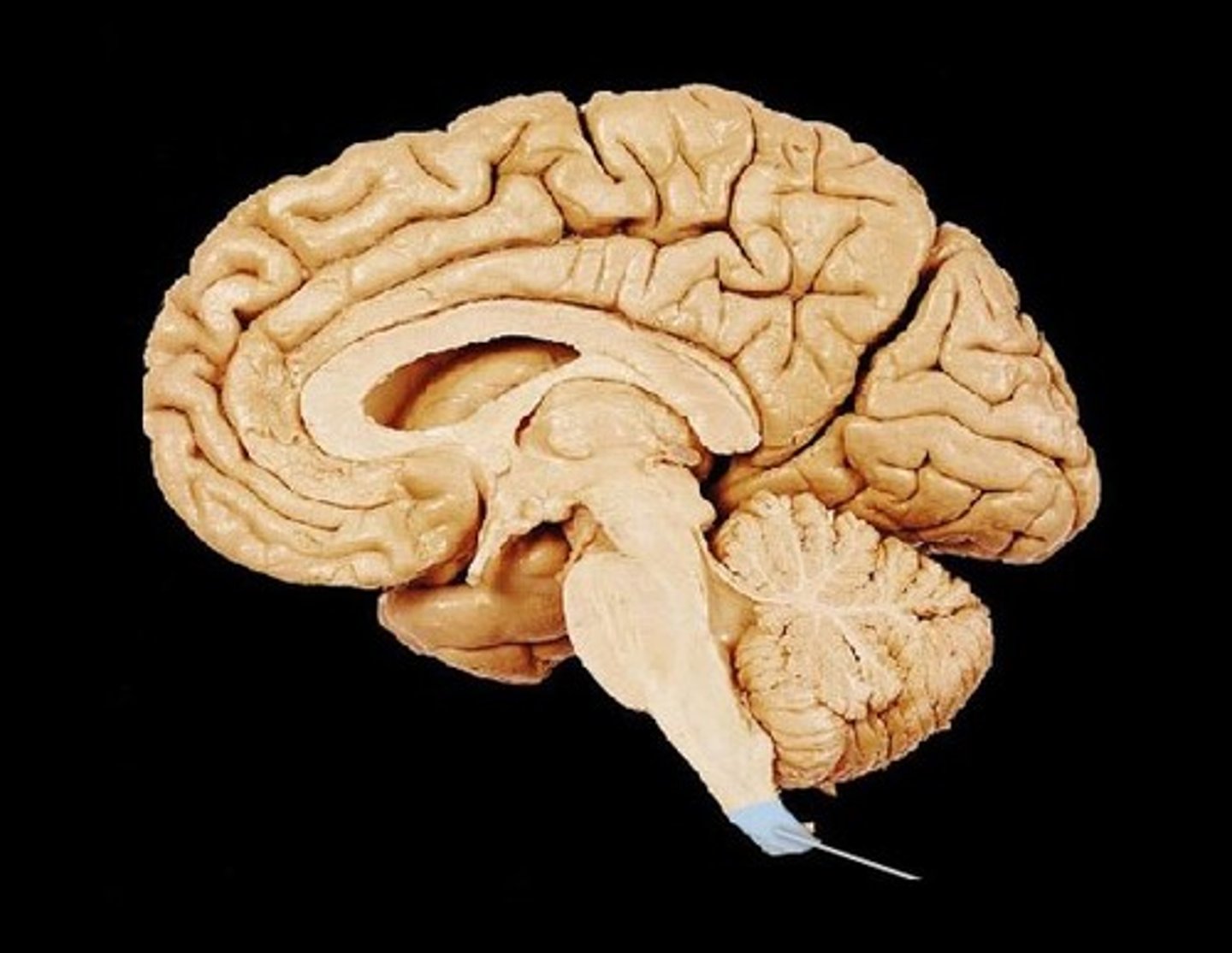
central canal
Where CSF is transported
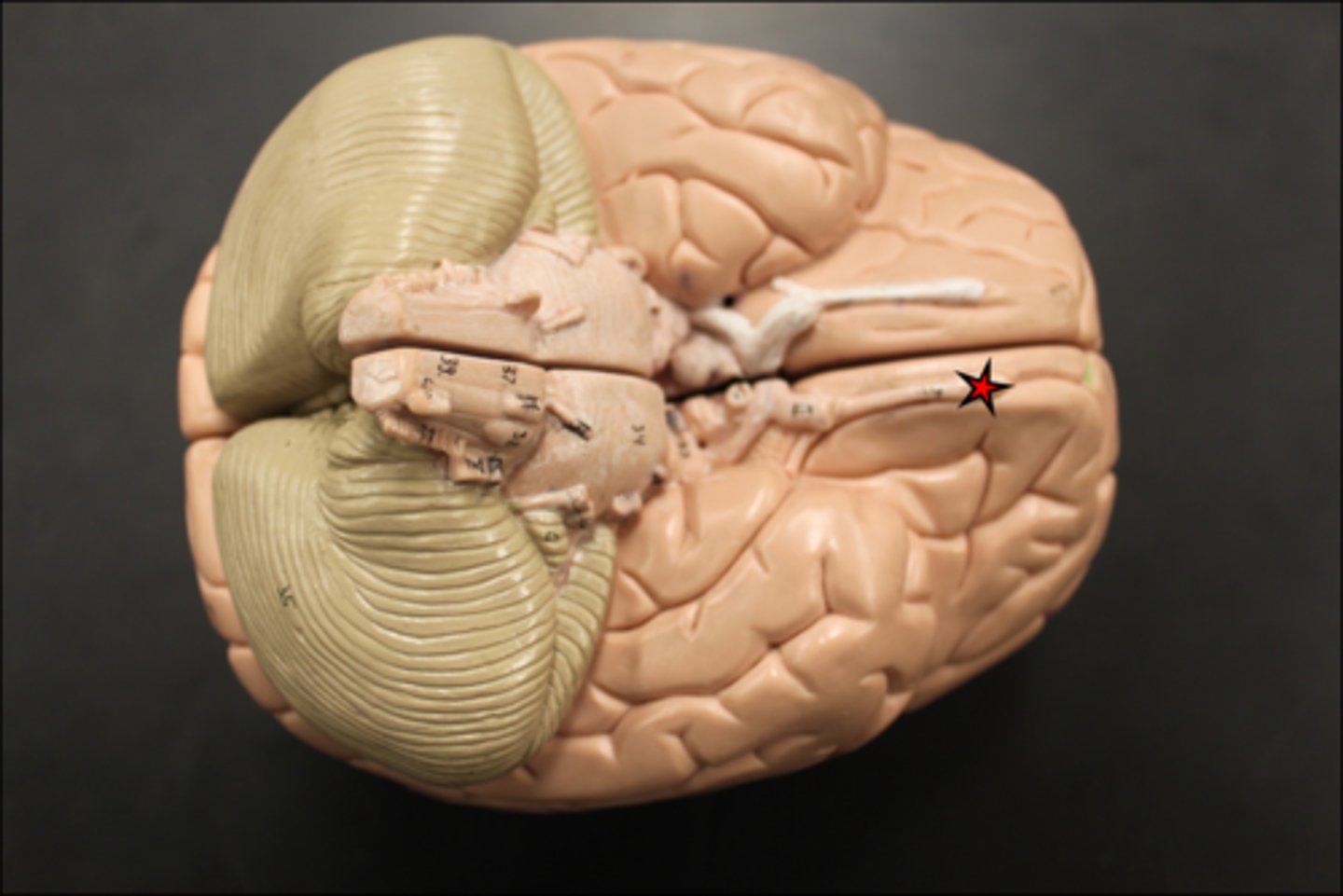
olfactory bulbs
olfactory receptor cells
optic chiasma
where optic nerves cross
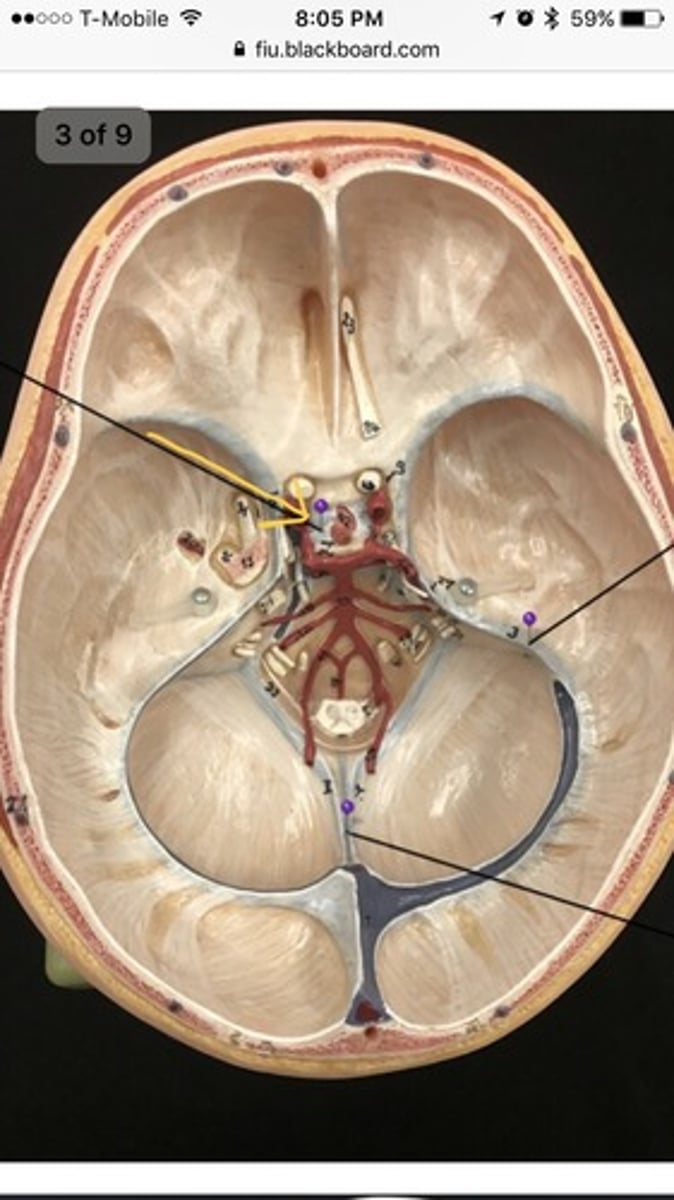
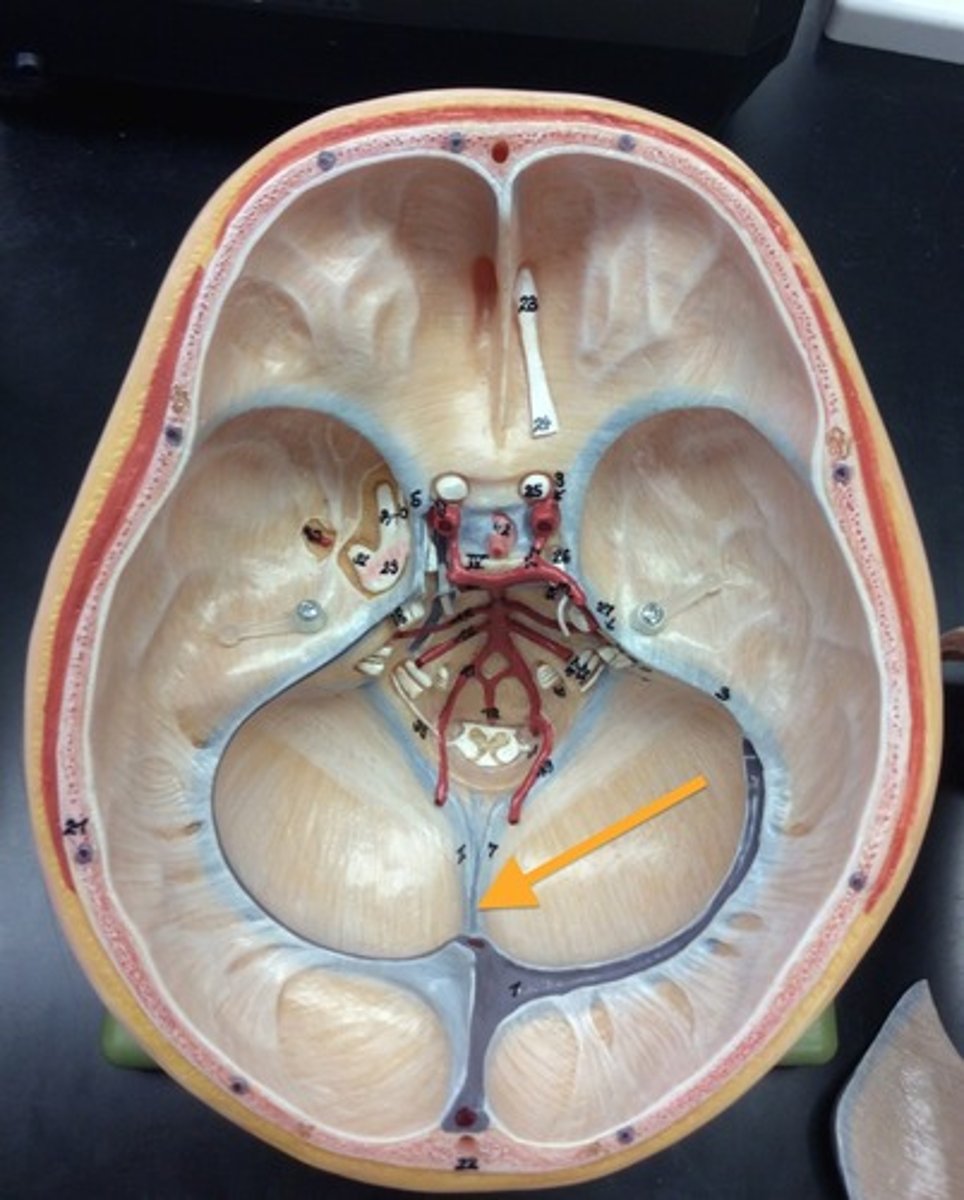
diaphragma sellae
a fold of Dura Mater that encases/ lines the sella turcica and pituitary gland
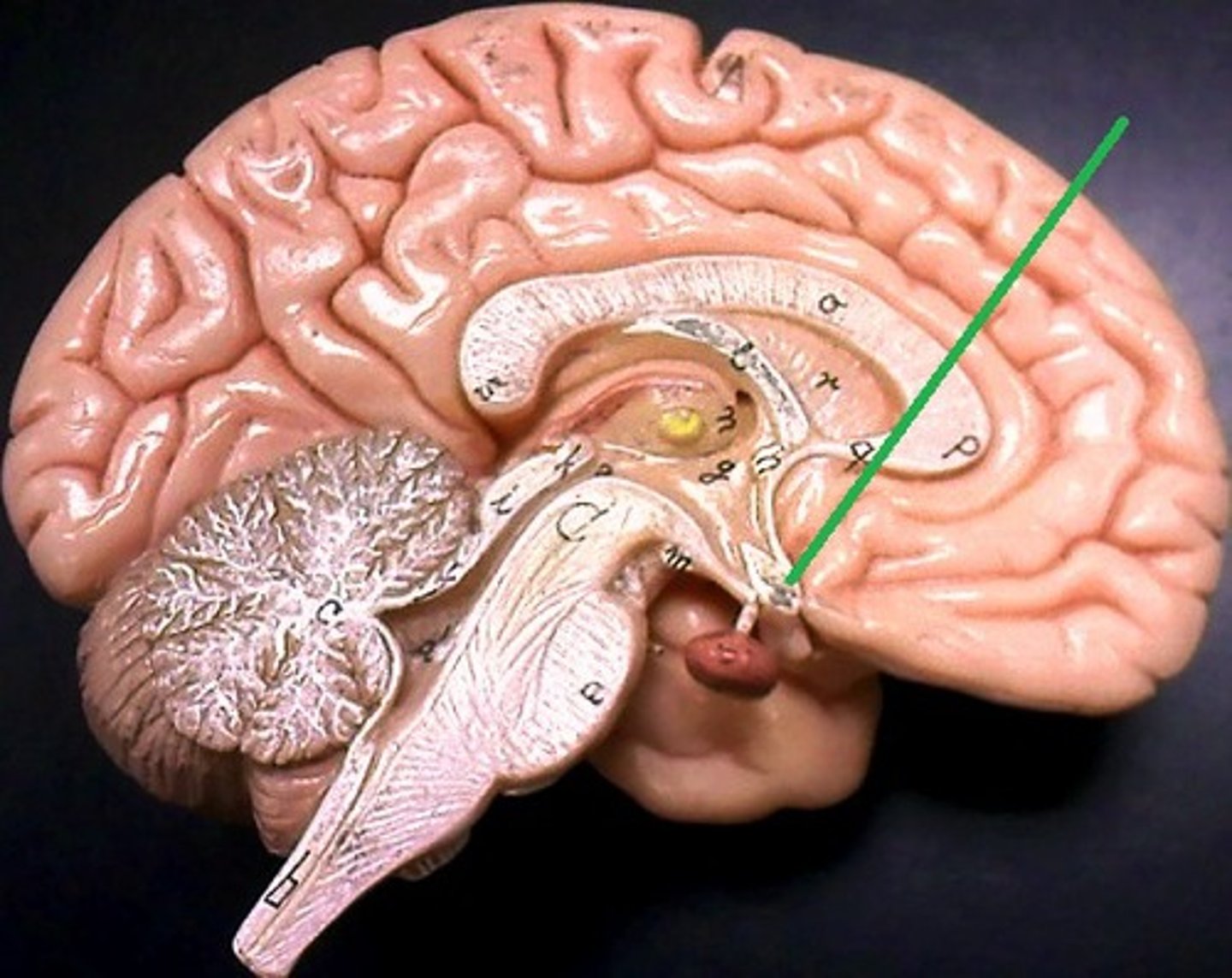
projection fibers
- tracts that connect cortex to other areas of CNS
- ex: internal capsule that connects brainstem to cerebral cortex
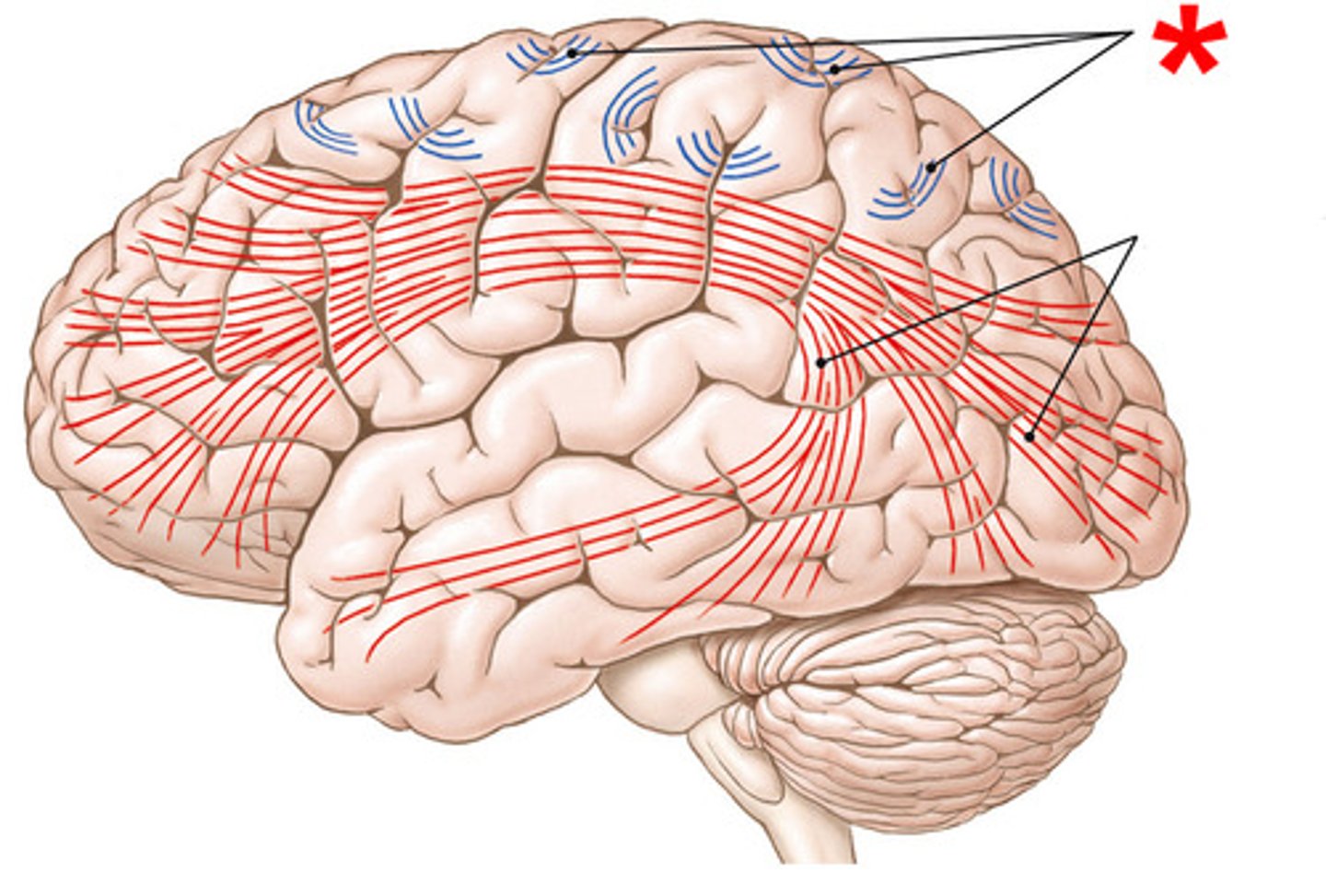
association fibers
- tracts that connect different areas of the brain
- ex: fornix + cingulate gyrus
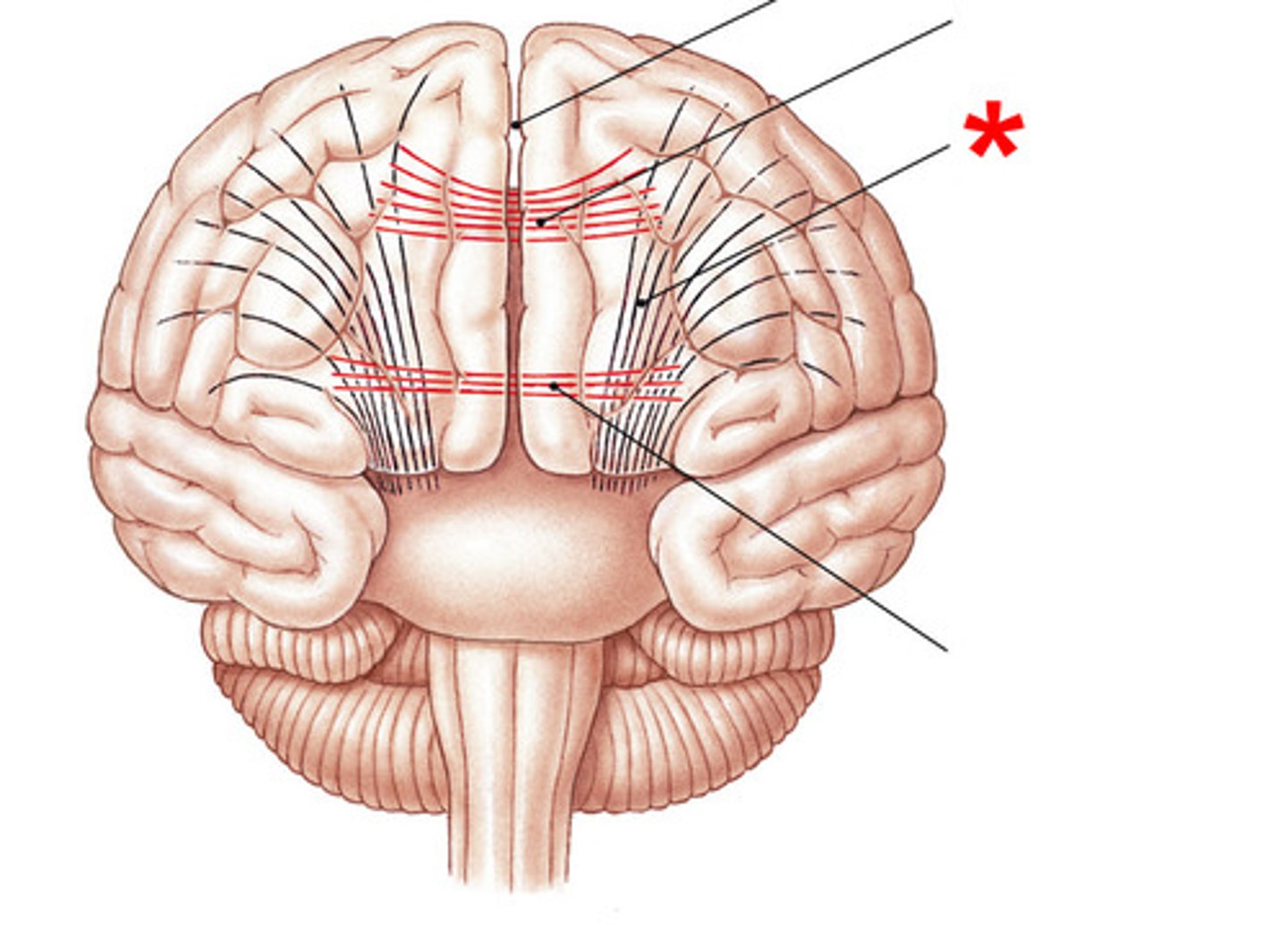
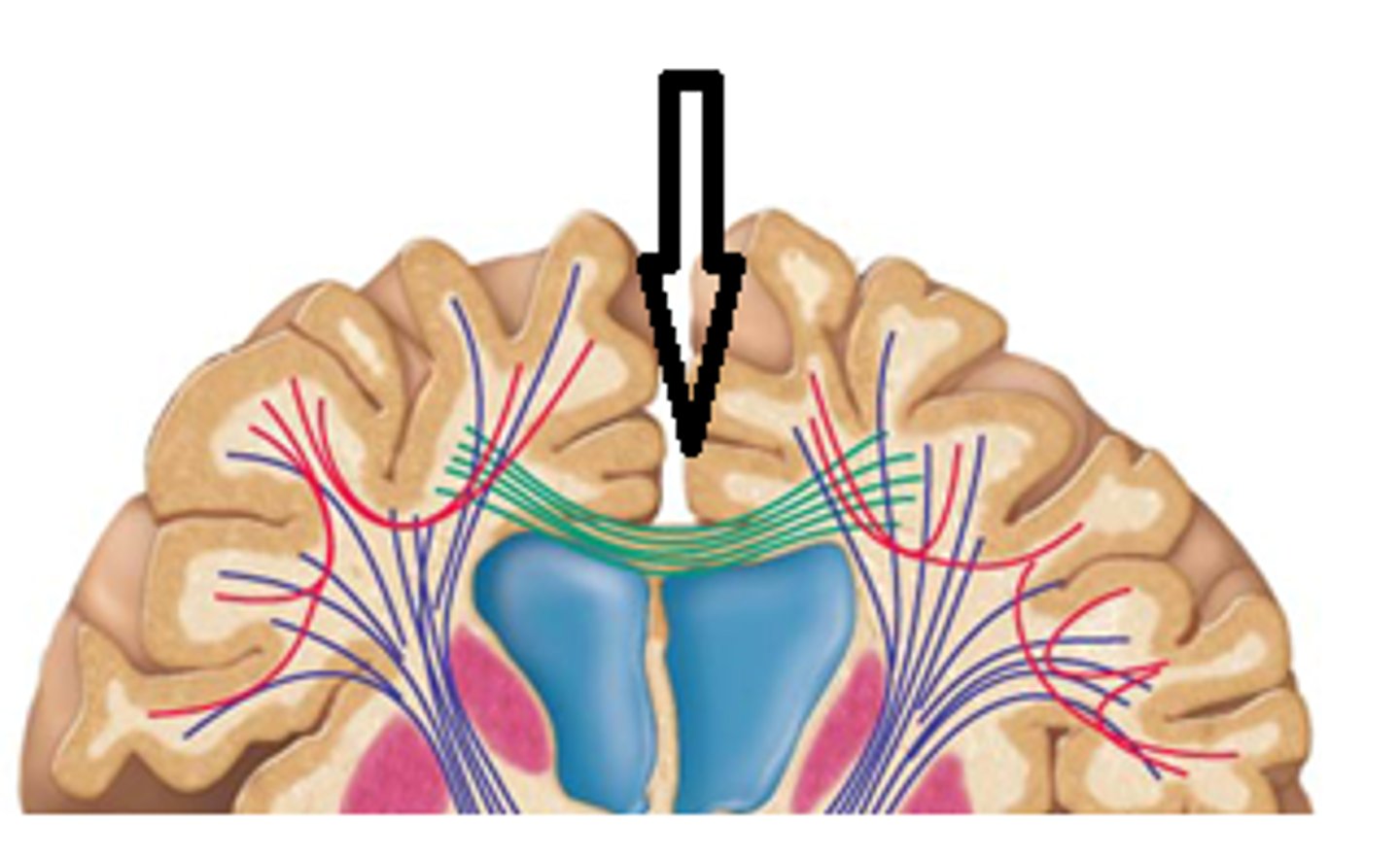
commissural fibers
- tracts that cross the midline of the brain
- corpus callosum
- anterior + posterior commissures
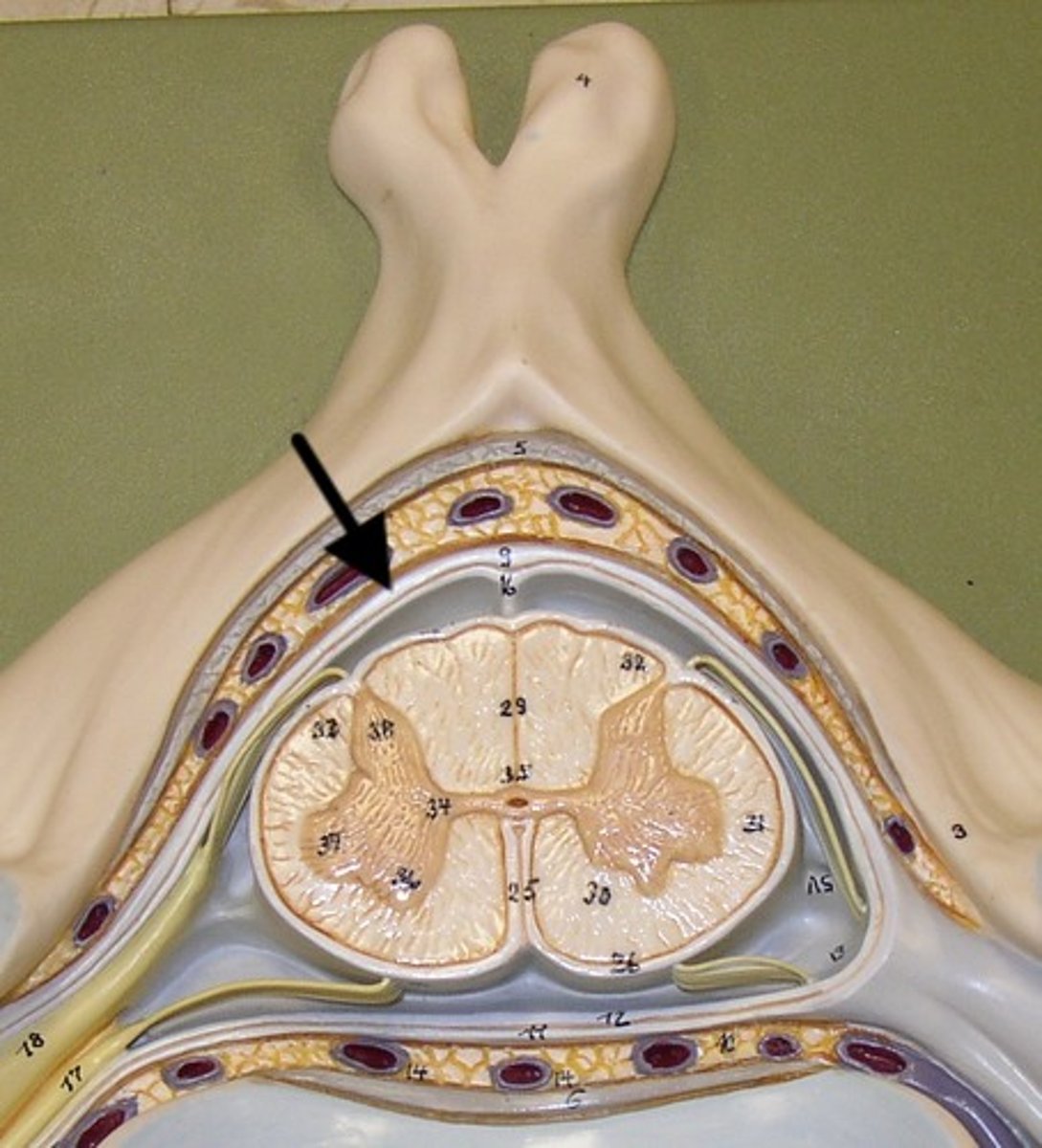
dura mater
tough layer of meninge
- protection
falx cerebri
separates cerebral hemispheres
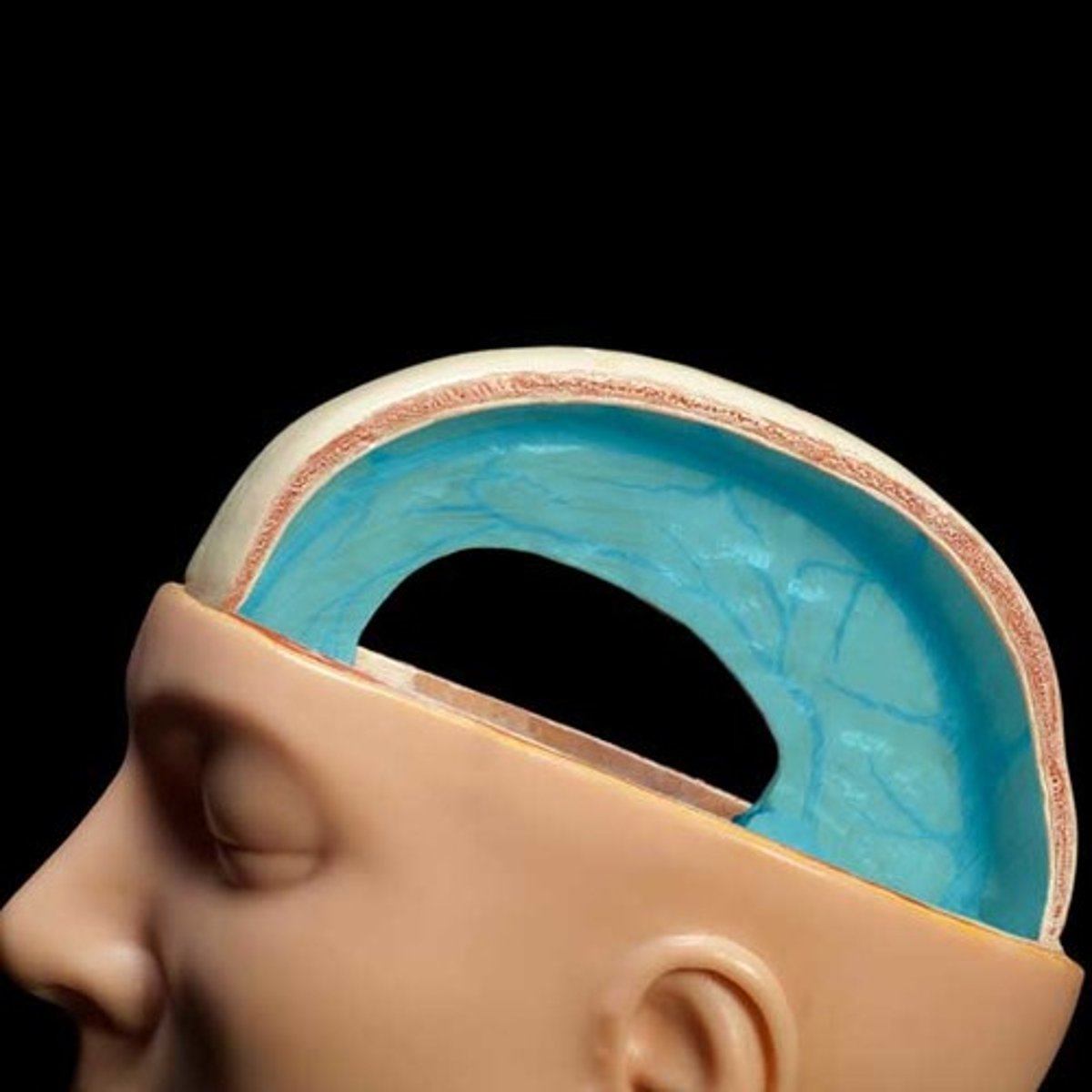
falx cerebelli
separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
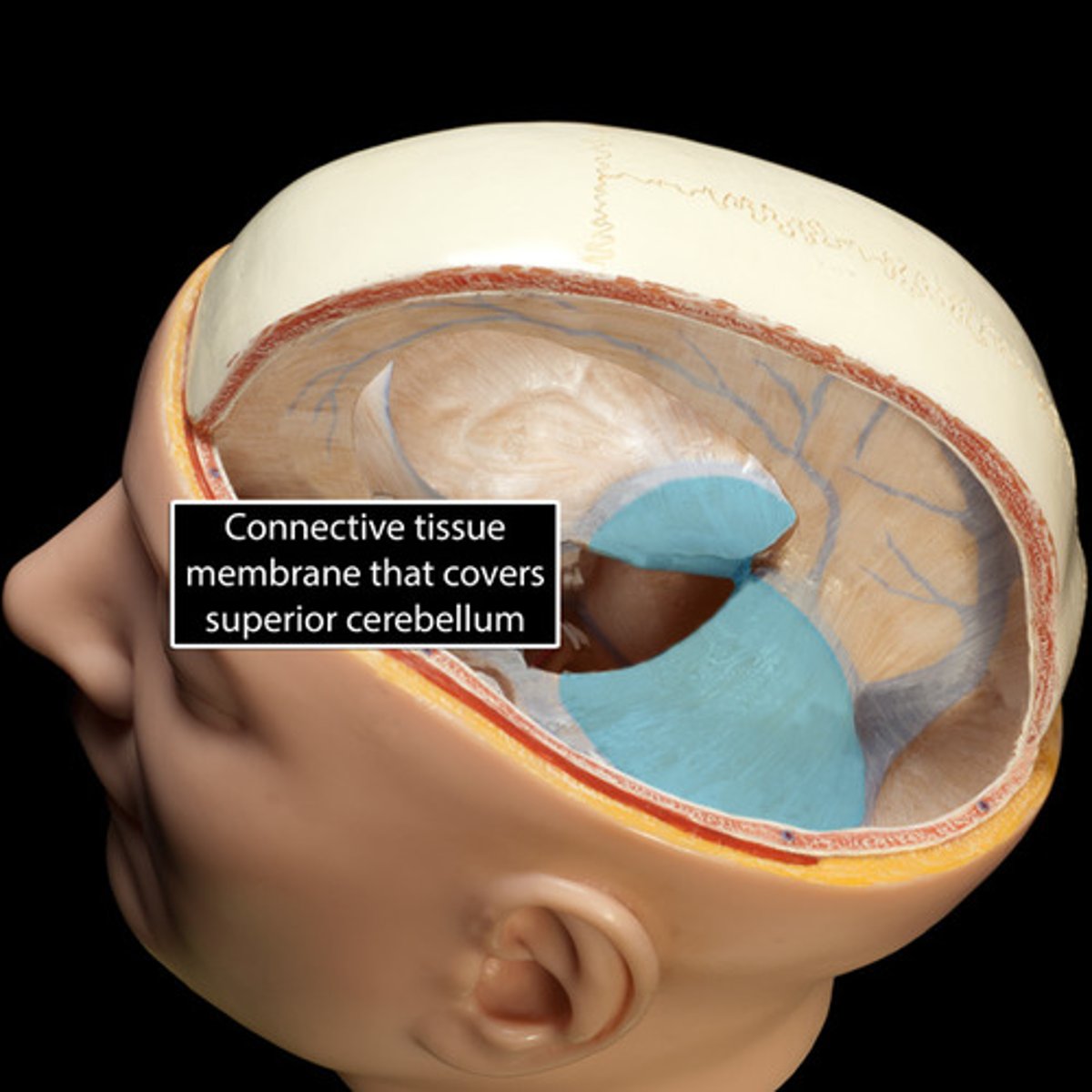
tentorium cerebelli
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
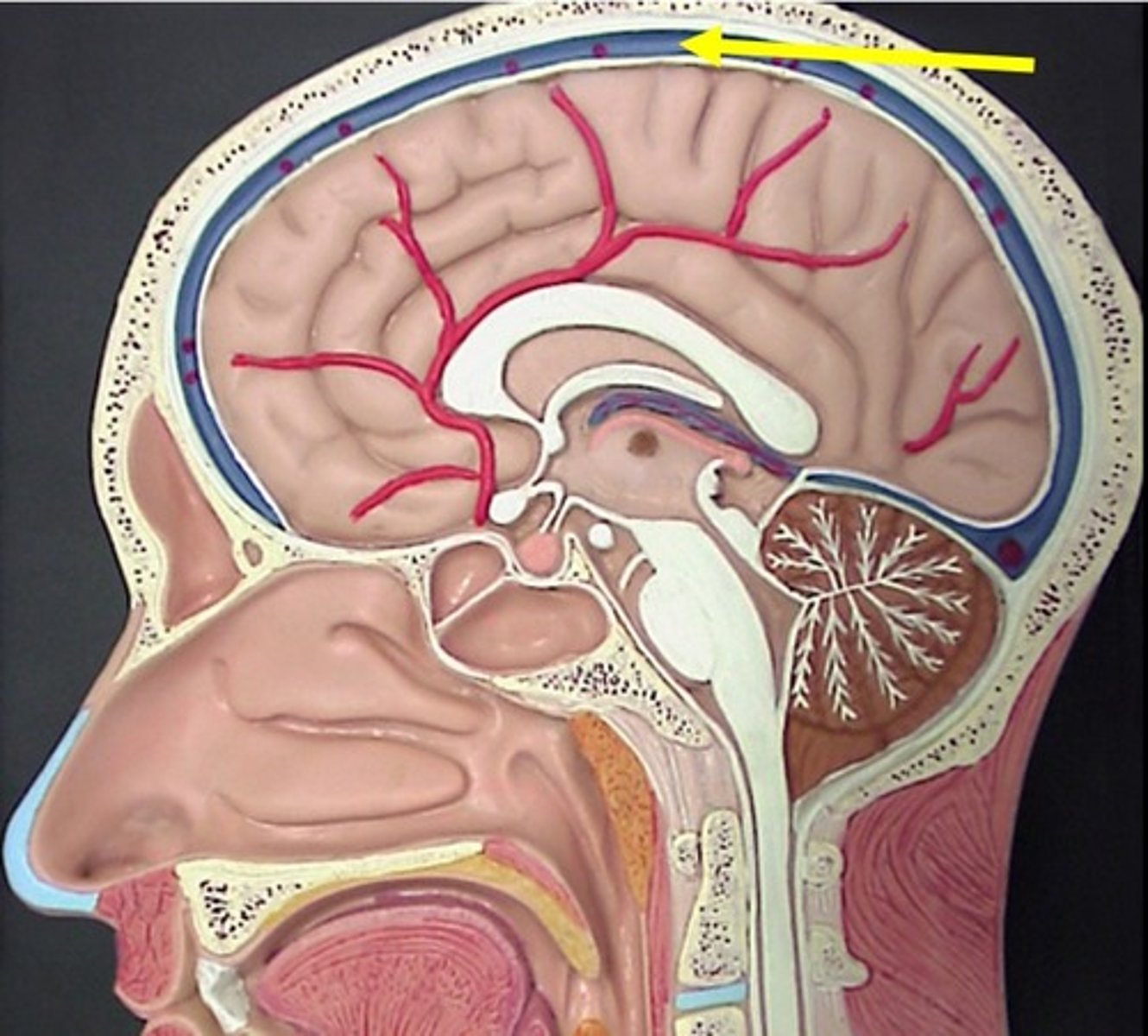
superior sagittal sinus
- blood vessels that returns blood to neck
inferior sagittal sinus
- blood vessels that returns blood to neck
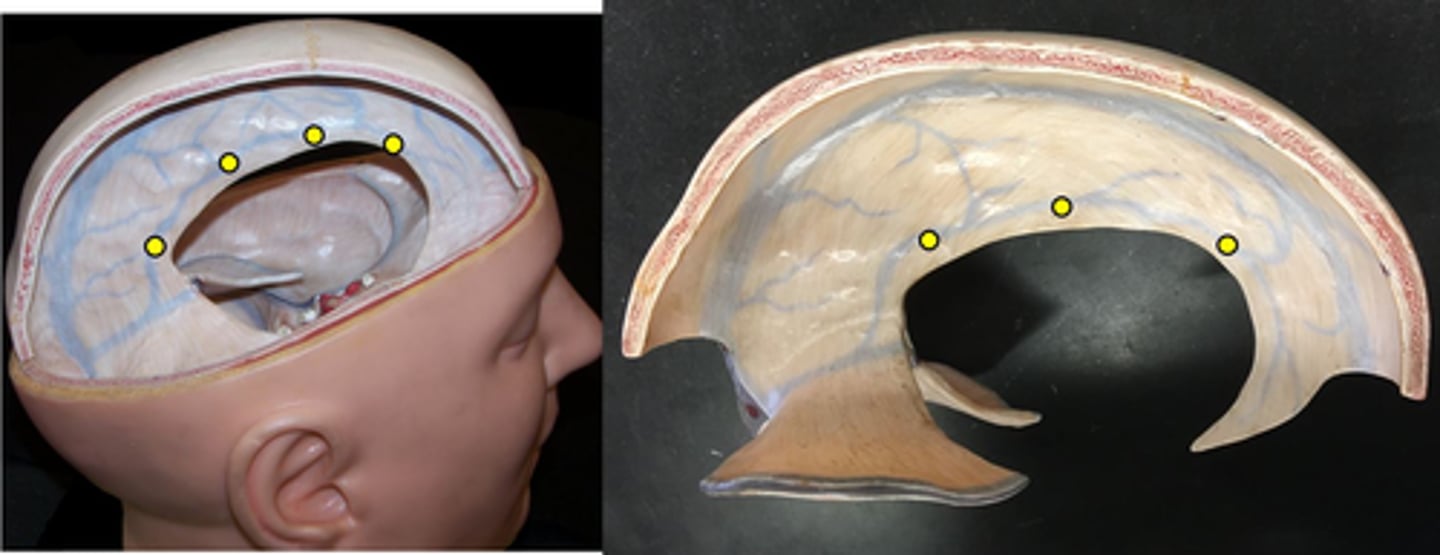
Arachnoid mater
Middle layer of meninges, web-like structure.
subdural space
space between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater, contains interstitial fluid
subarachnoid space
contains CSF from ependymal cells
arachnoid villi
- structures that return cerebrospinal fluid to the venous blood in the dural sinuses
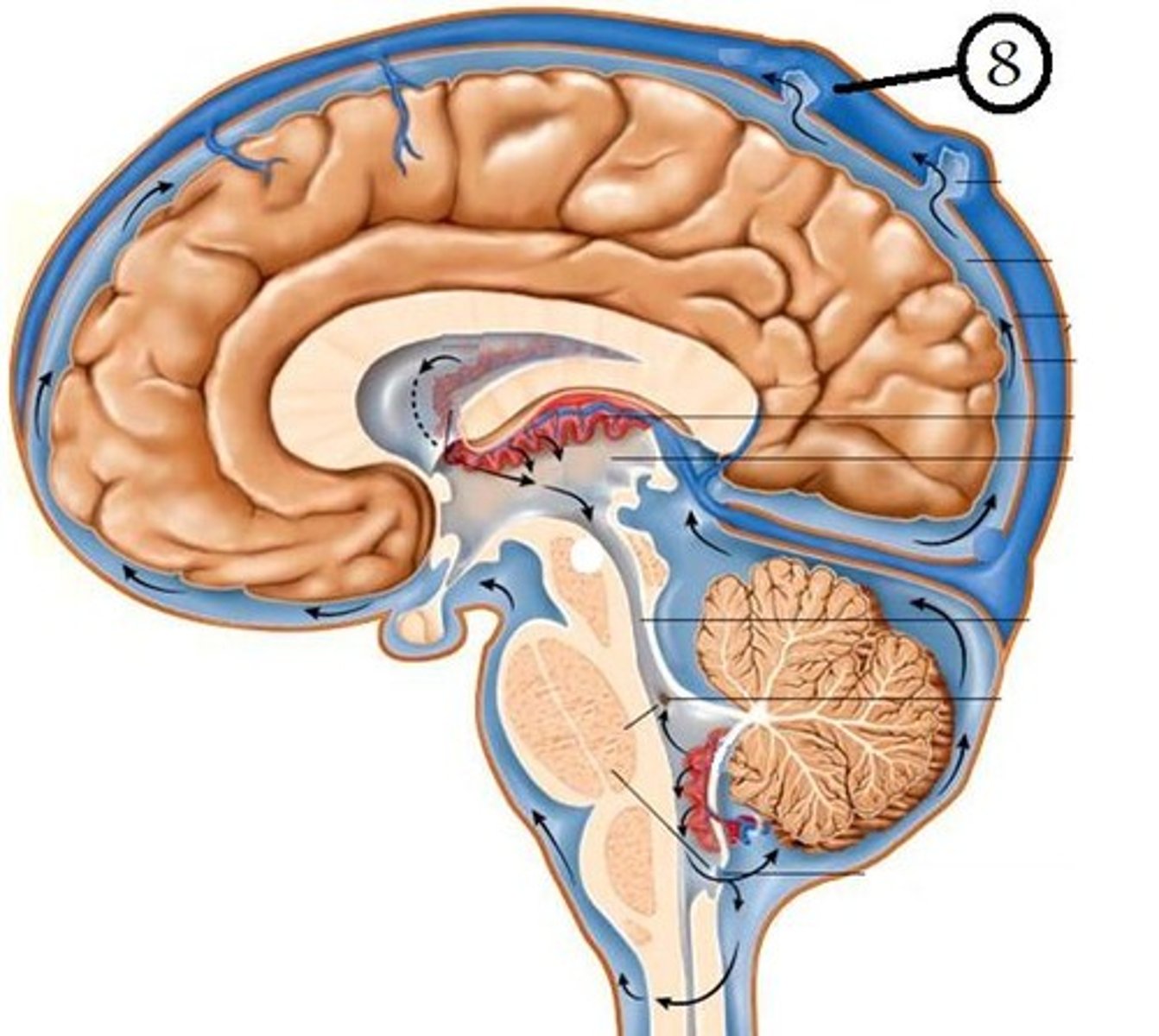
pia mater
- thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
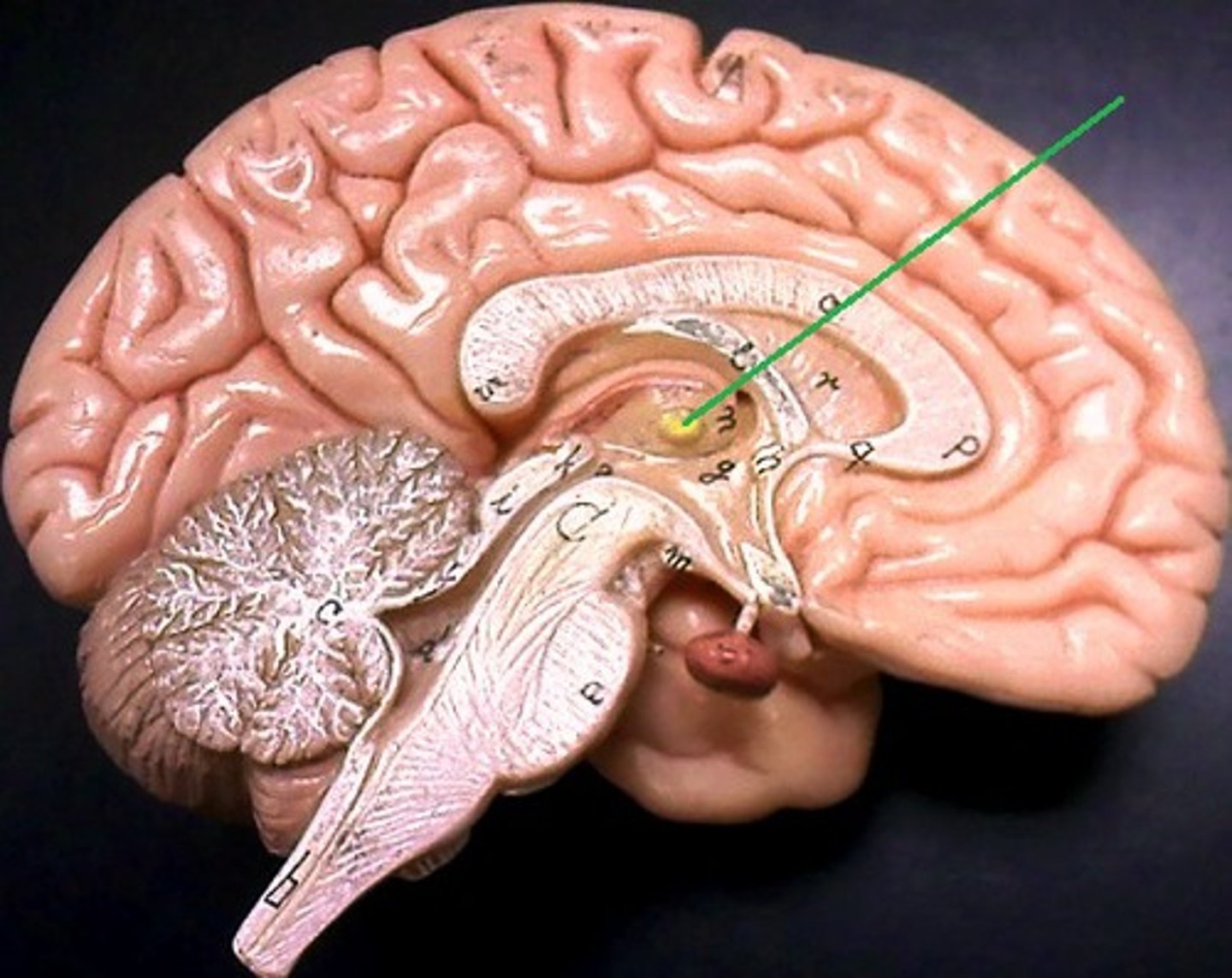
interthalamic adhesion
goes inside the 3rd ventricles
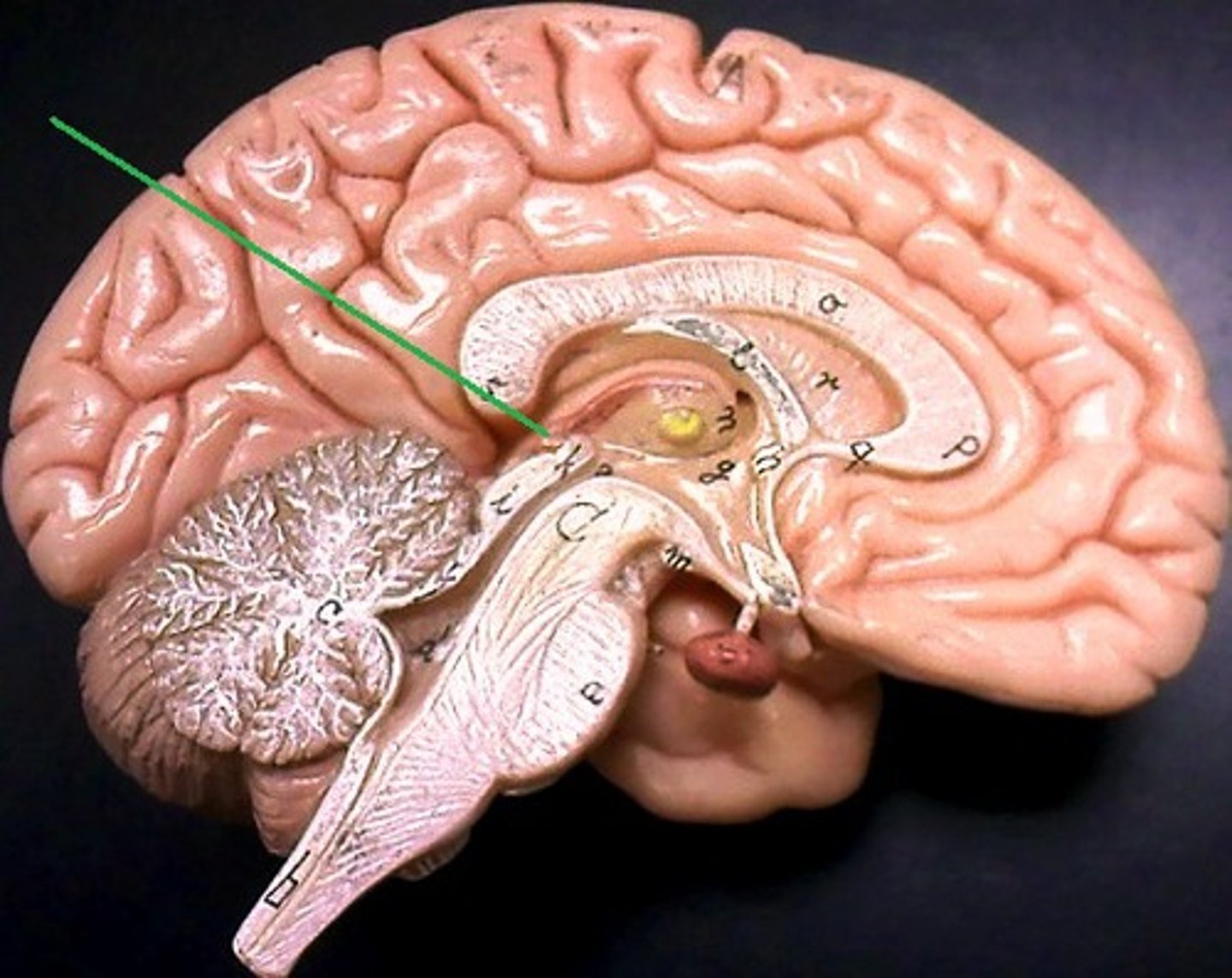
pineal gland
- secretes melatonin
- regulation of circadian rhythm
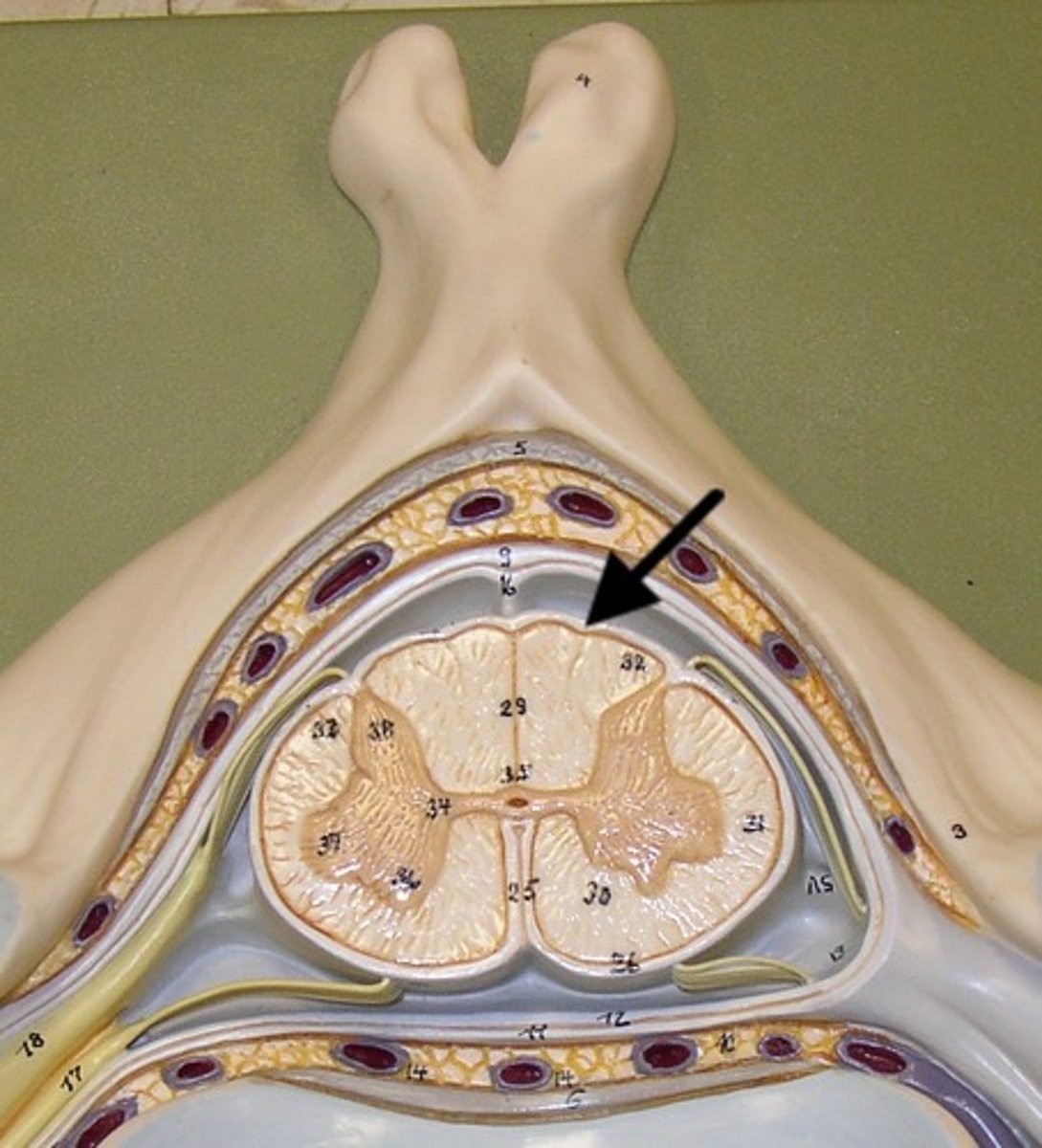
apertures (lateral + median)
holes that allow CSF to be transported to arachnoid vili
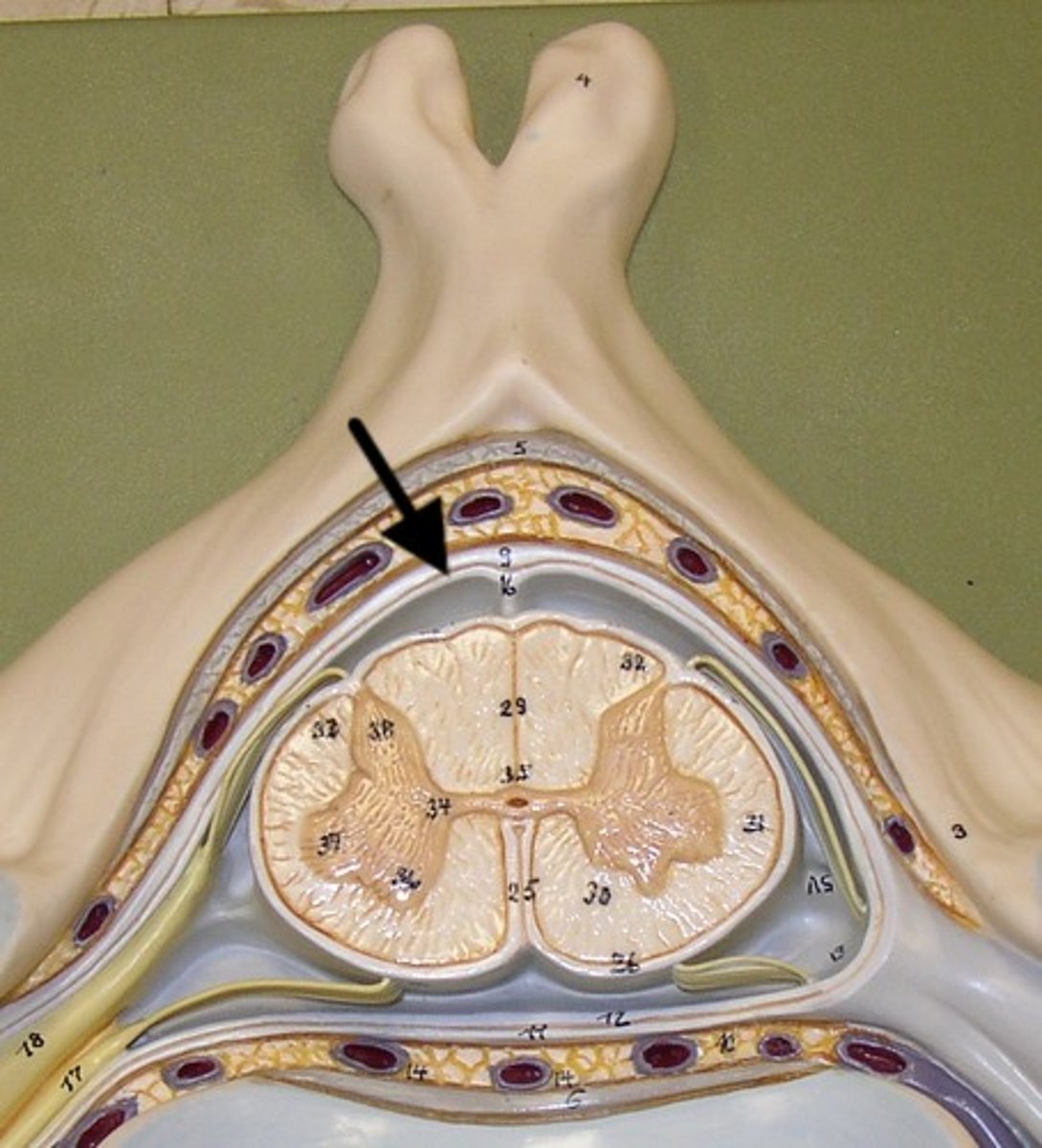
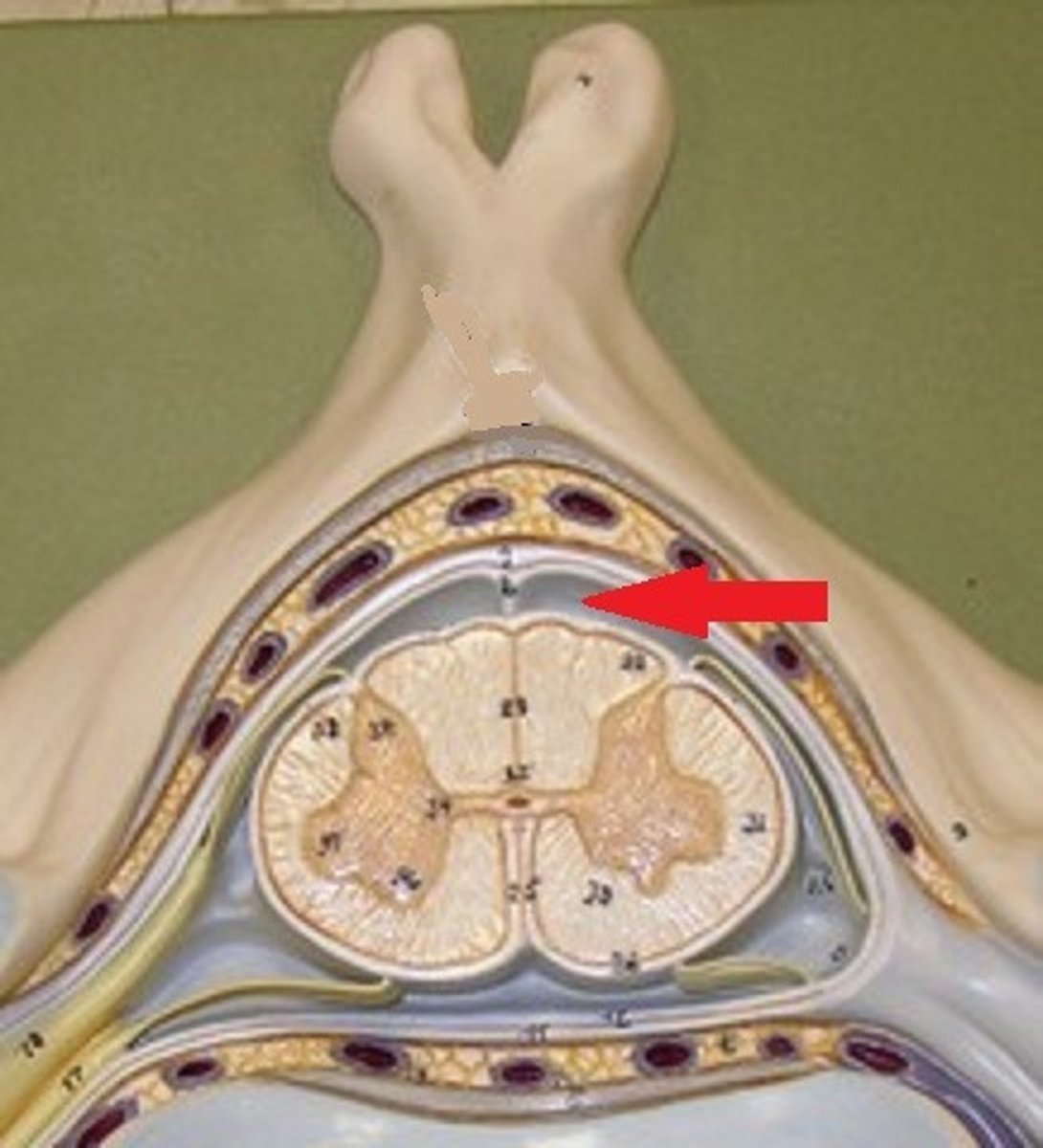
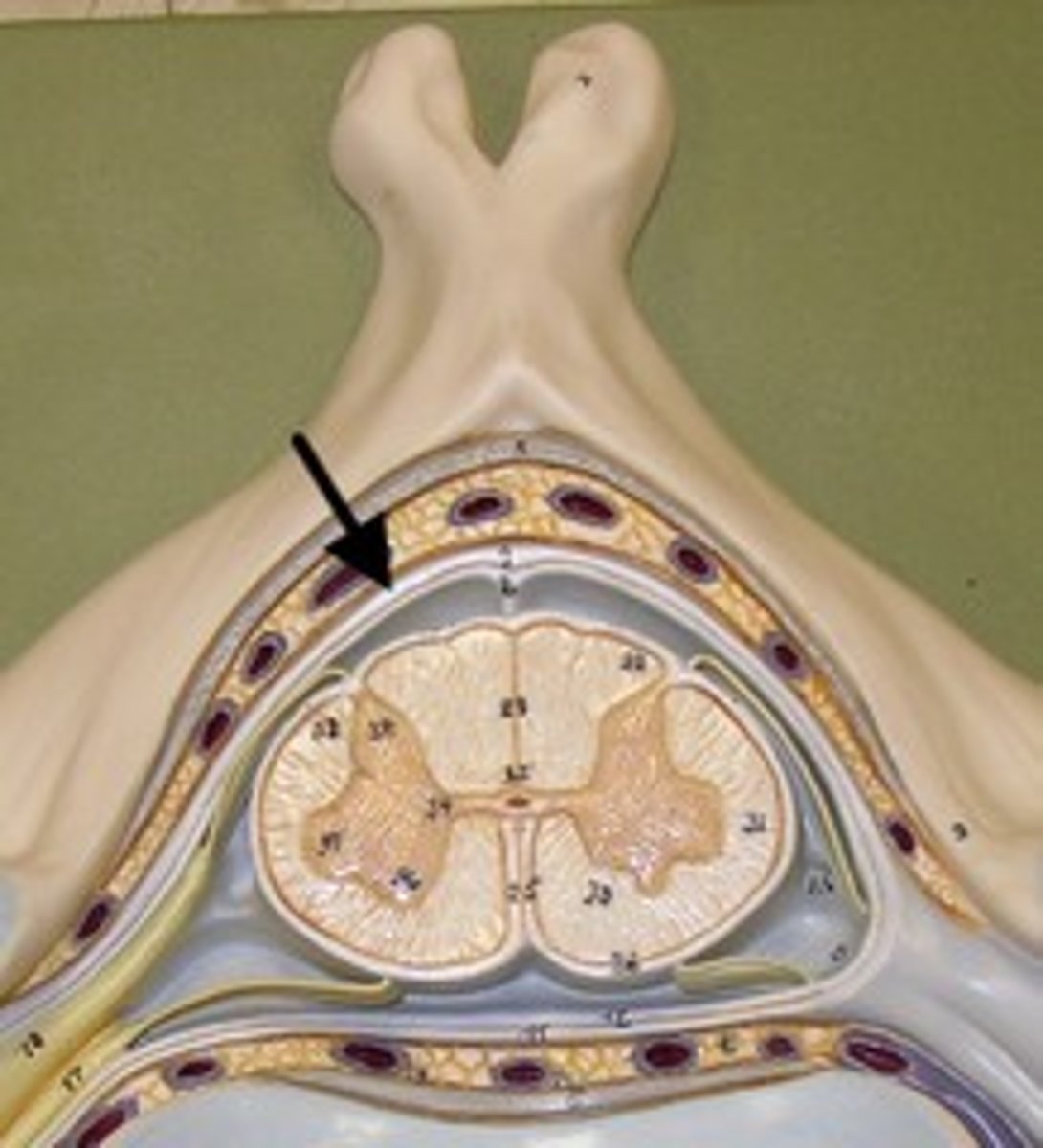
dural mater
tough mater closer to the bones that protects the spinal cord
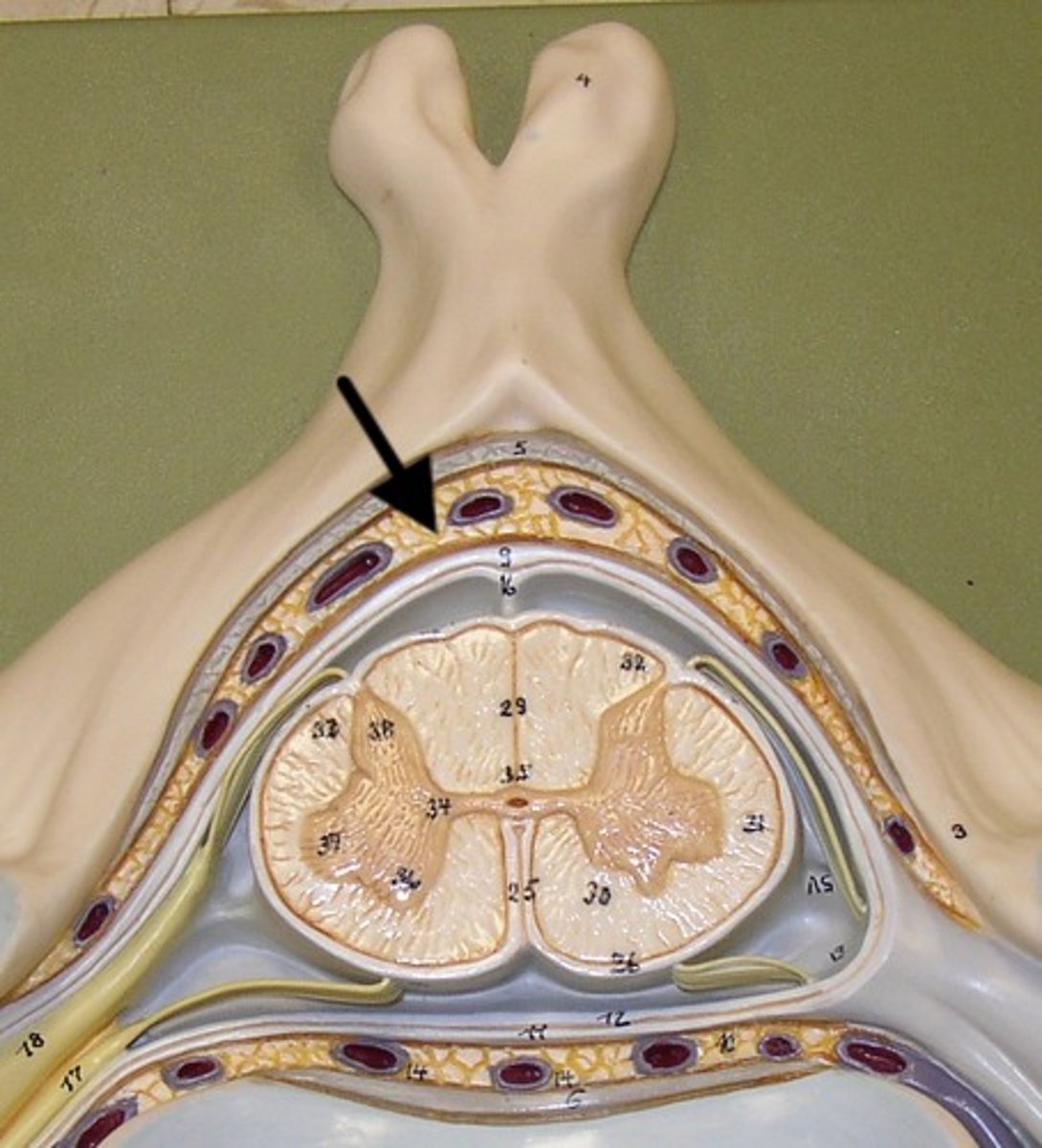
epidural space
fat + network of veins that protects and between dura mater + vertebrae
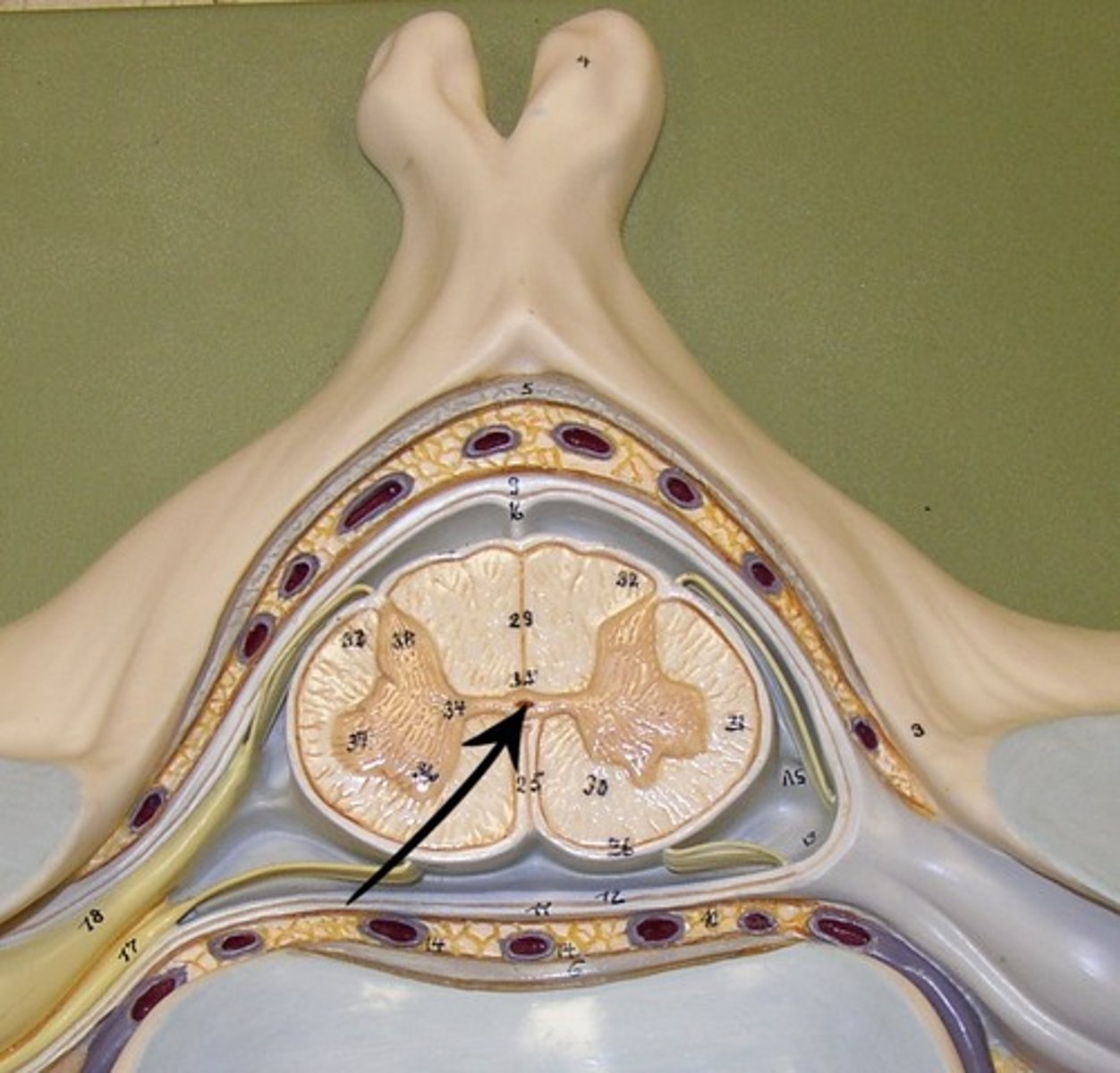
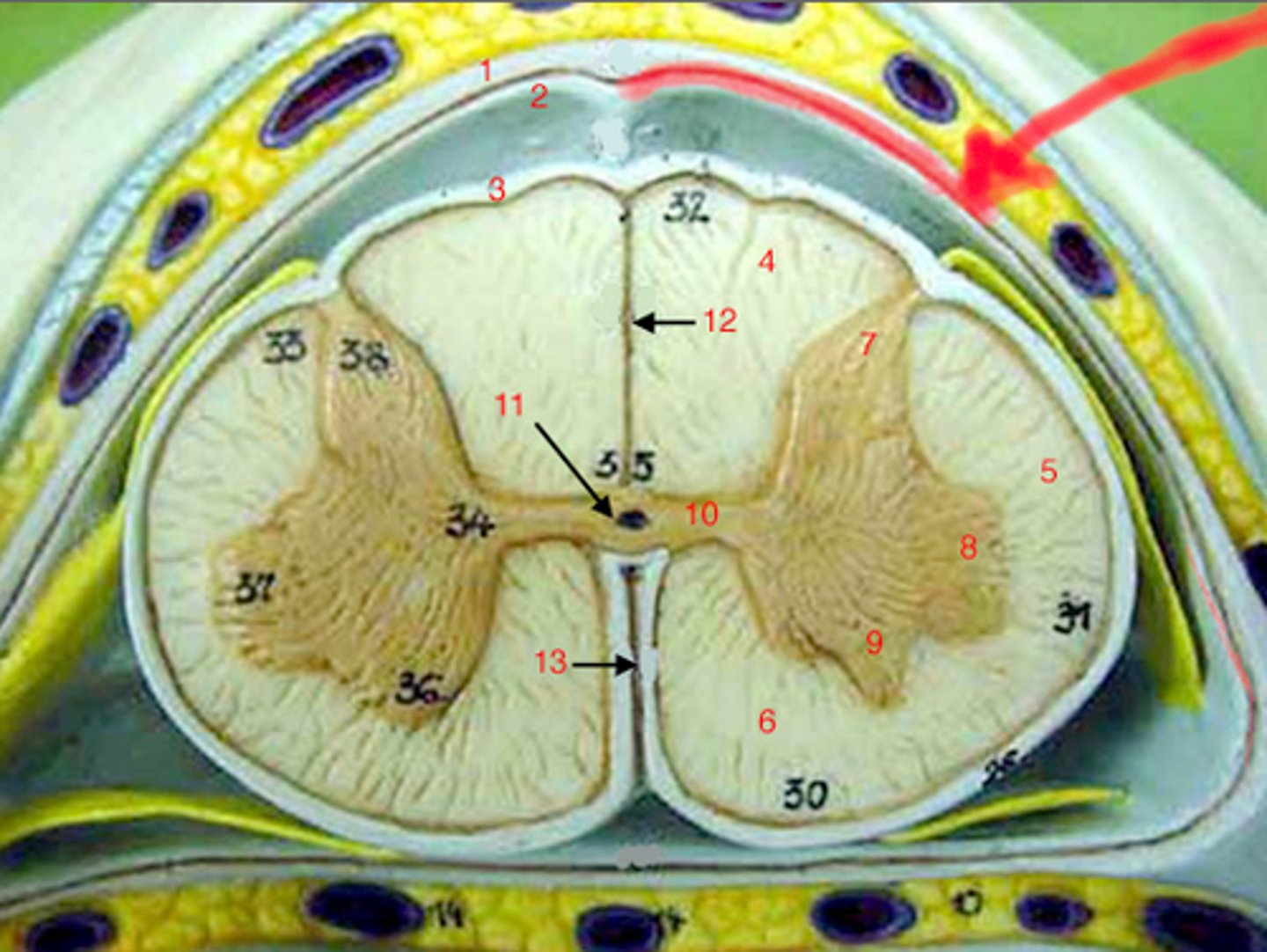
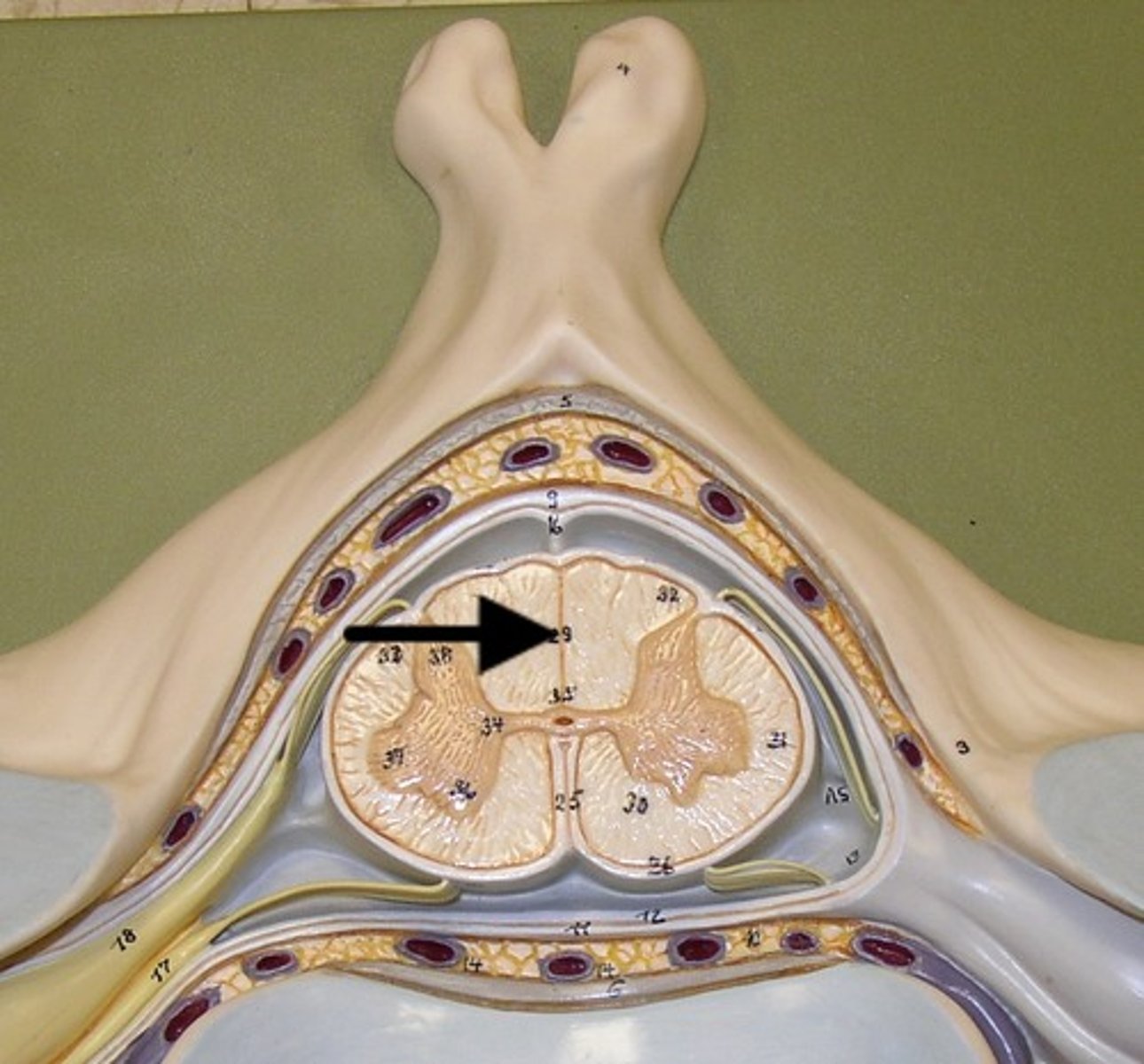
dorsal median sulcus
a depression that separates the posterior funiculi
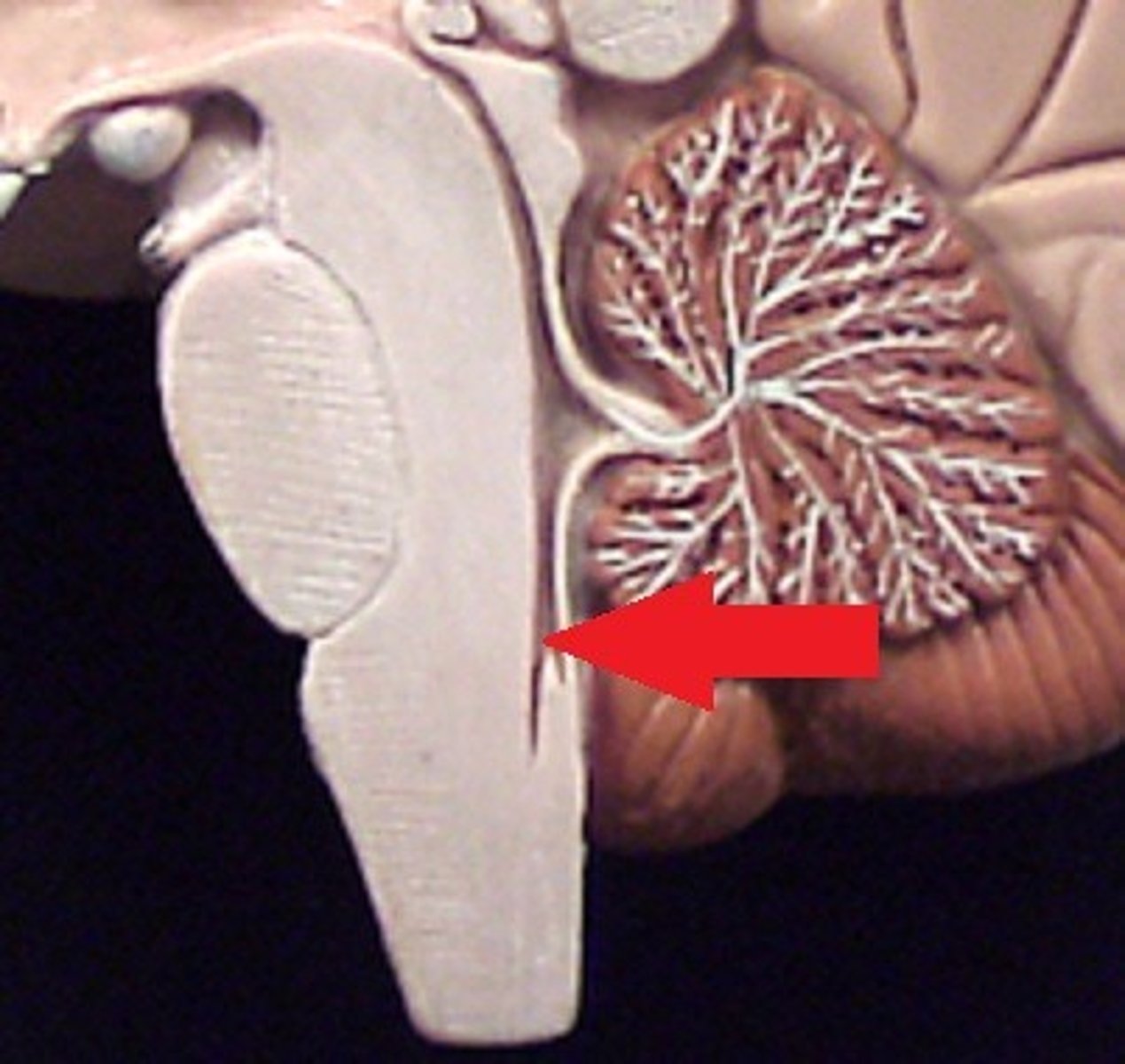
ventral median fissure
a deep groove that slightly separates the spinal cord
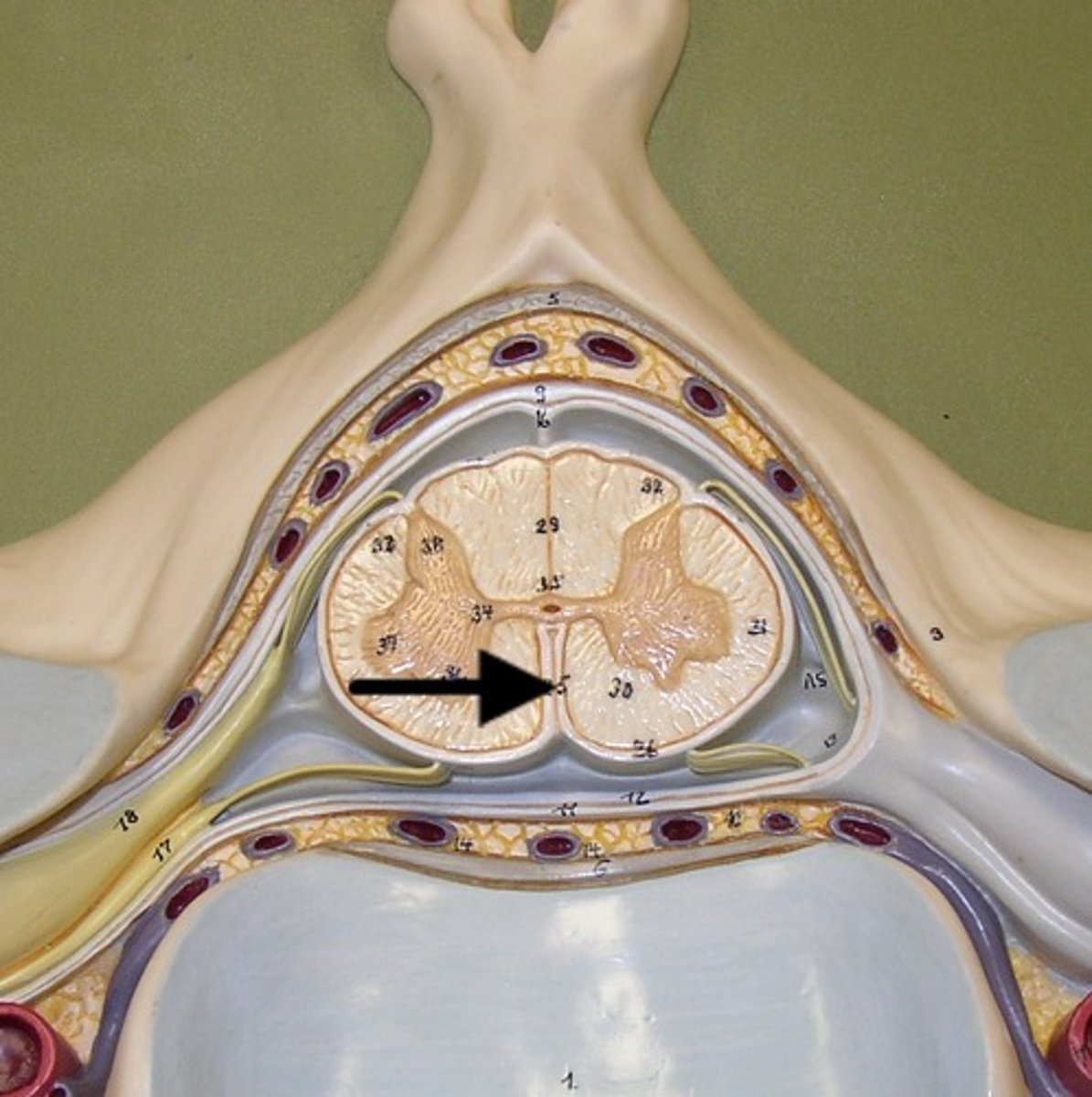
dorsal horn
hold somatosensory interneurons (somatic + visceral)
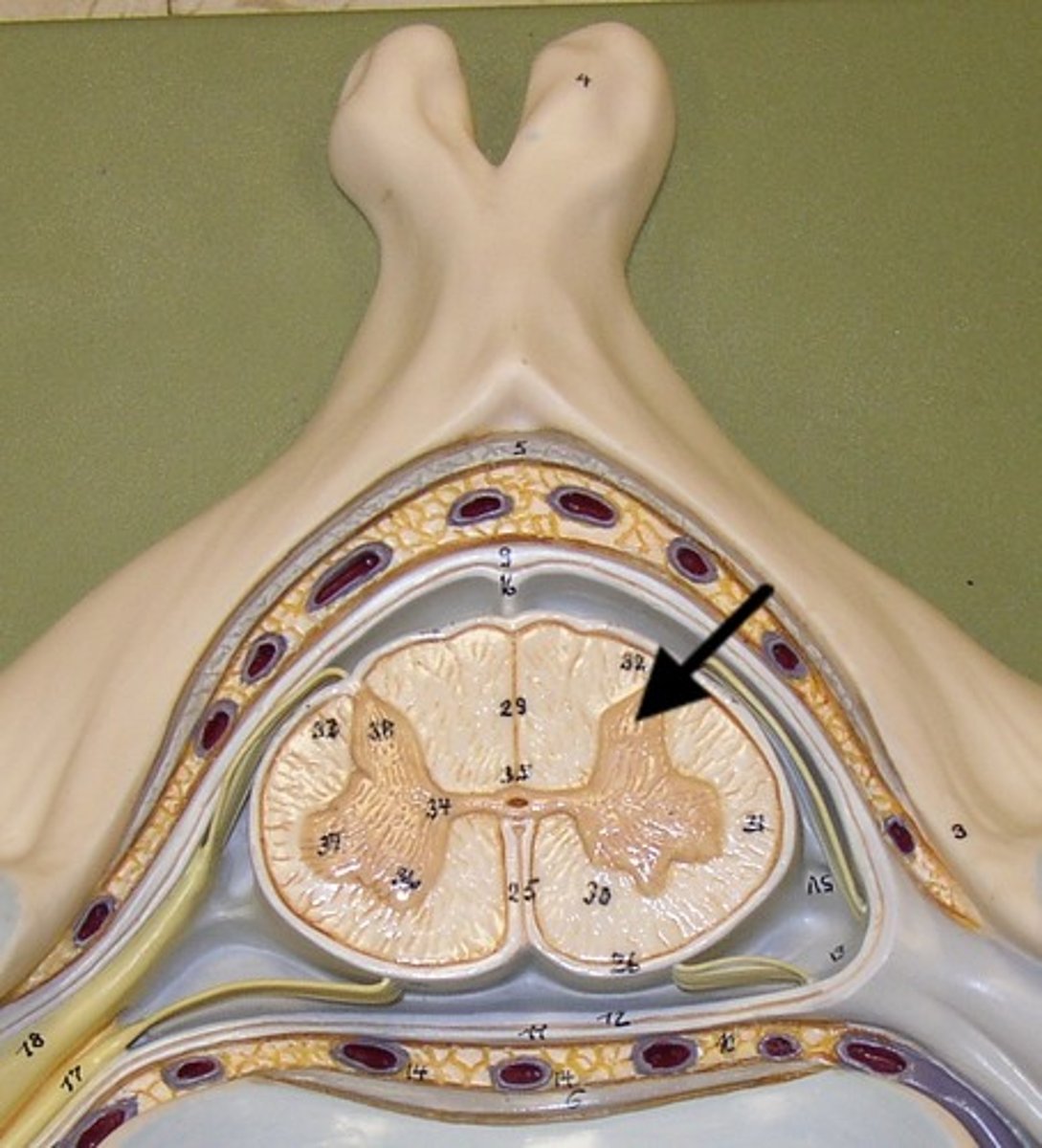
lateral horn
contains autonomic motor neurons to innervate cardiac + smooth muscle, CAN ONLY BE FOUND IN THE THORACIC + SUPERIOR LUMBAR SEGMENTS
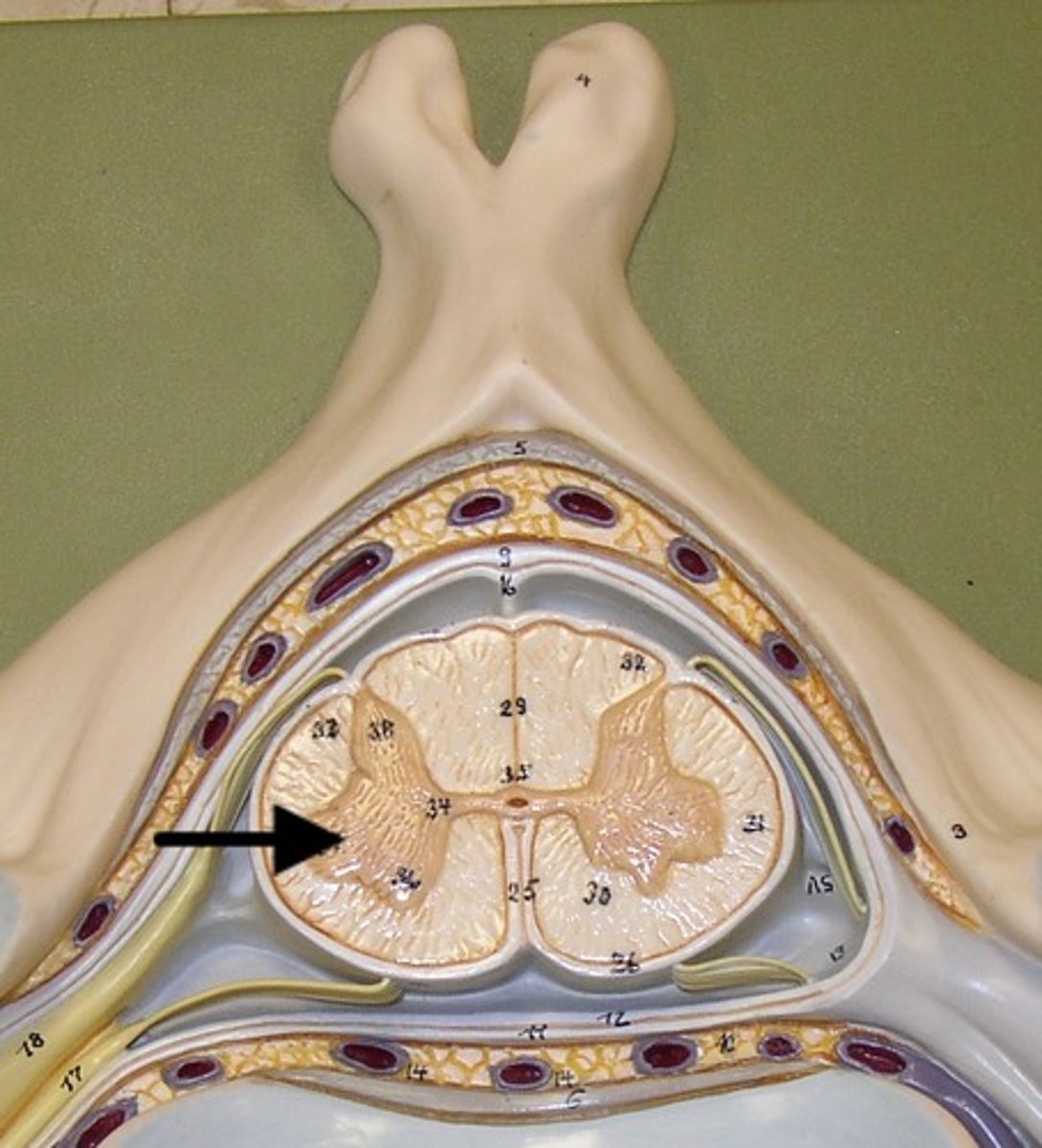
ventral horn
holds somatic motor neurons + responsible for innervating skeletal muscle
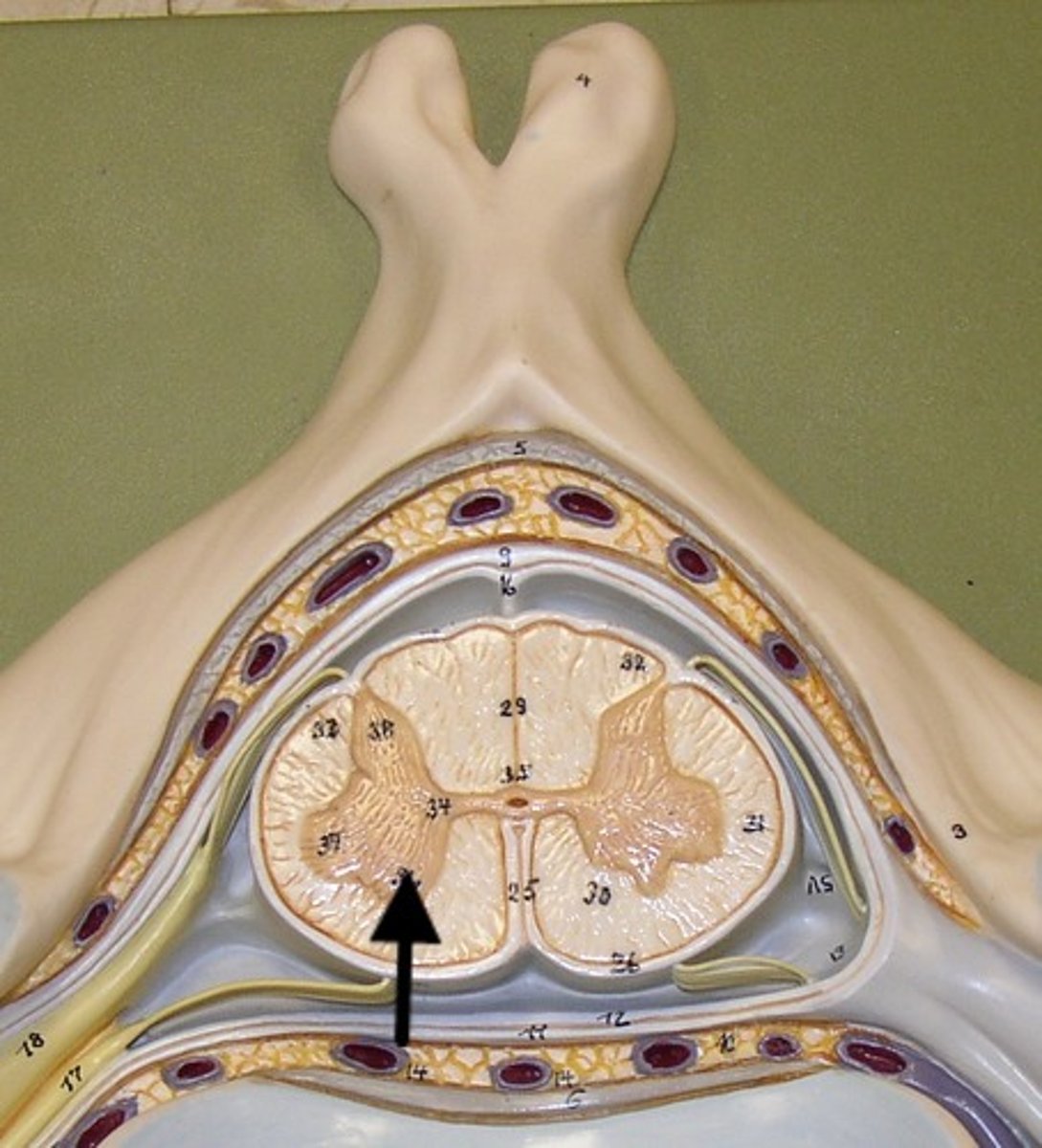
dorsal funiculus
white mater containing several fiber tracts/axons between the ventral horns posteriorly
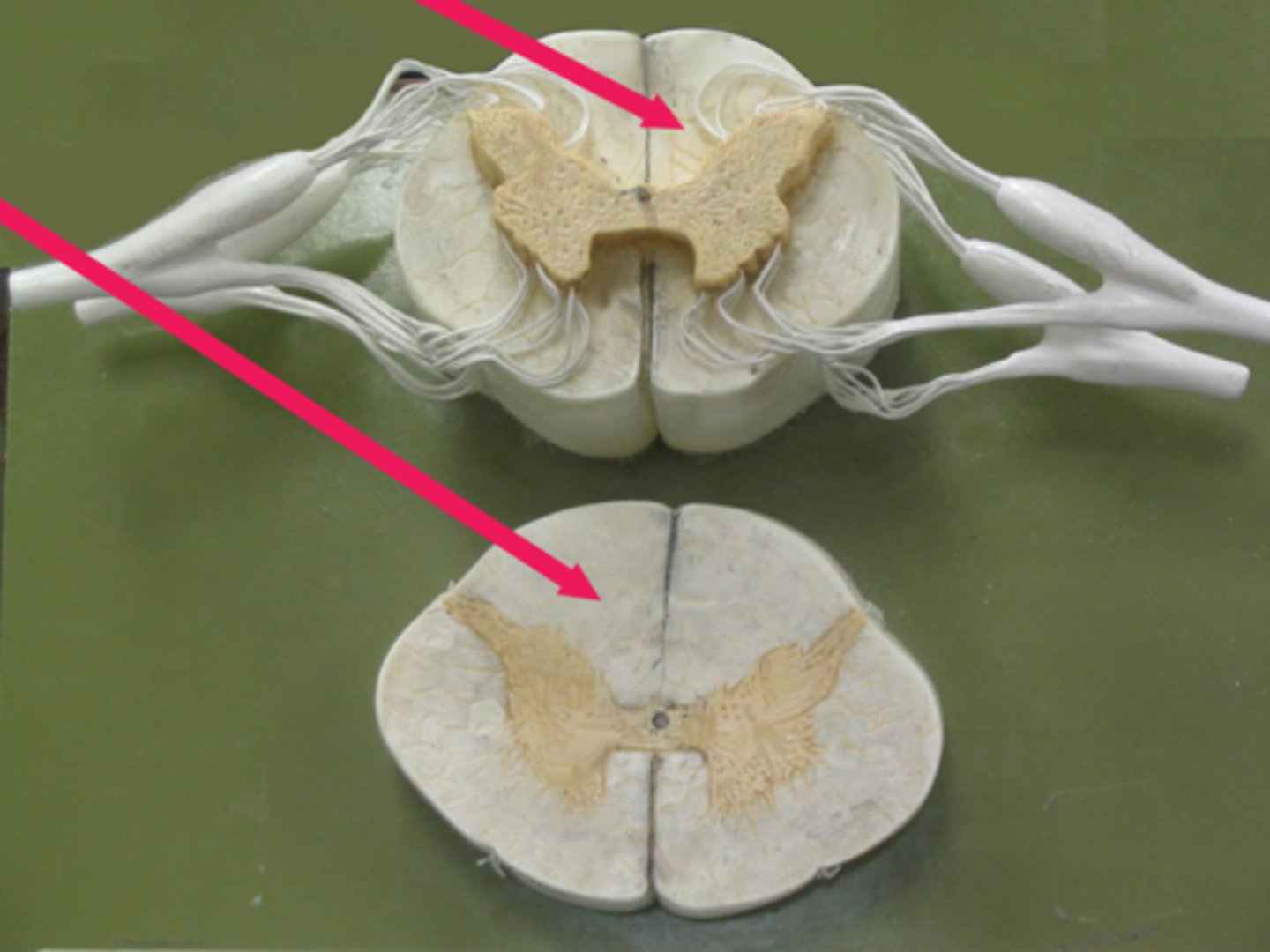
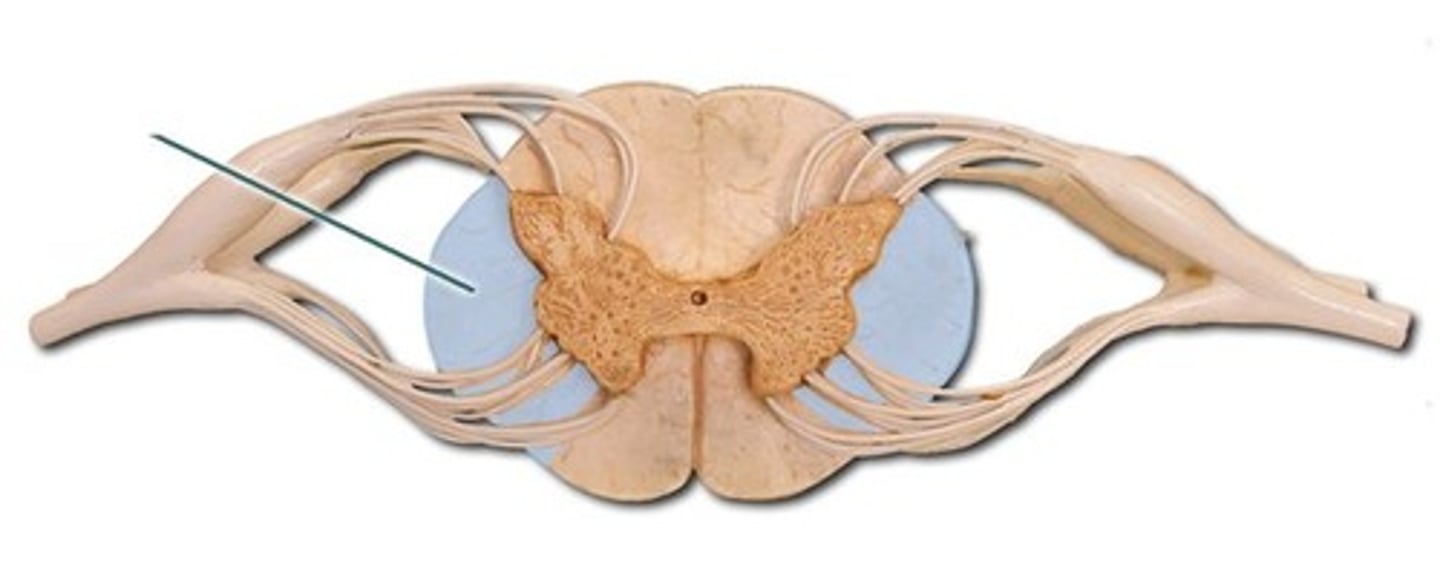
lateral funiculus
white matter containing several fibers tracts/ axons between the ventral + dorsal horn
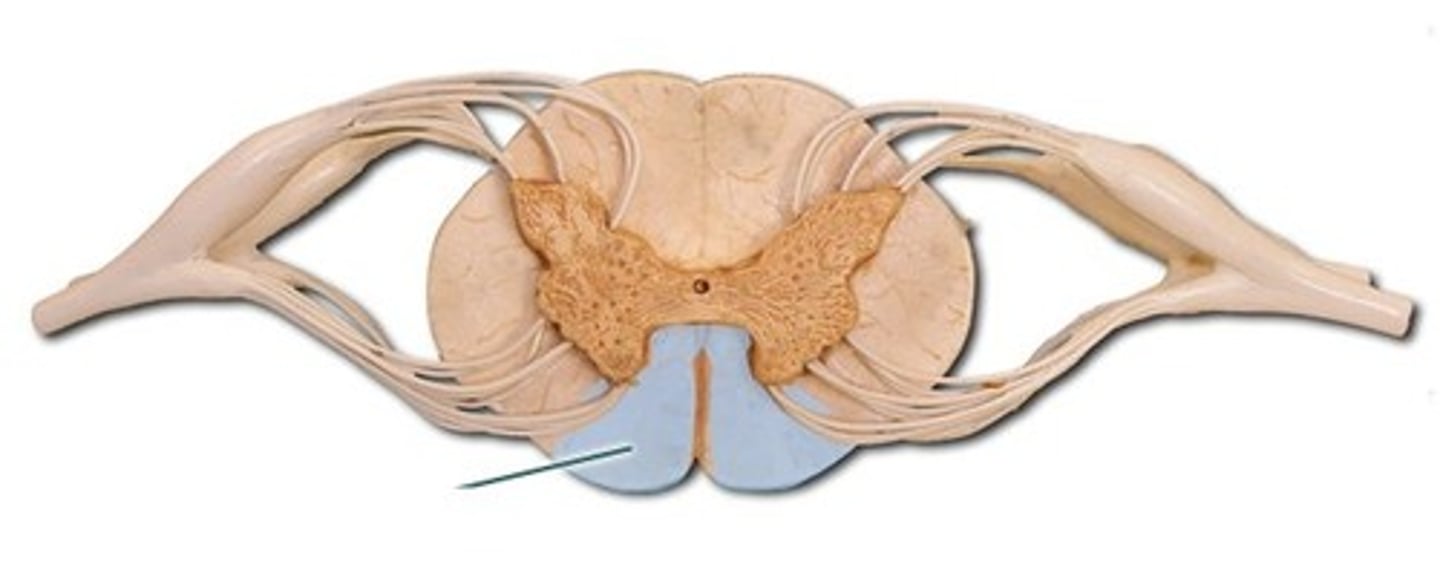
ventral funiculus
white matter containing several fiber tracts/axons between the ventral horns anteriorly
gray commissure
bridge of gray matter that connects masses of gray matter on either side allowing communication between both masses of gray matter