Unit 3.1 - Setting Marketing Objectives
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Marketing function
Provides the link between the customer and the business. Requires marketing managers to understand the nature of the market to know how est to convince customers to purchase from the business
A market
Where buyers and seller meet, involved a mutually beneficial transaction between buyers and sellers
Relationship marketing
Approach to marketing in which a company seeks to build long term connections with its customers by providing consistent satisfaction. Focus on customer retention rather than one off sales
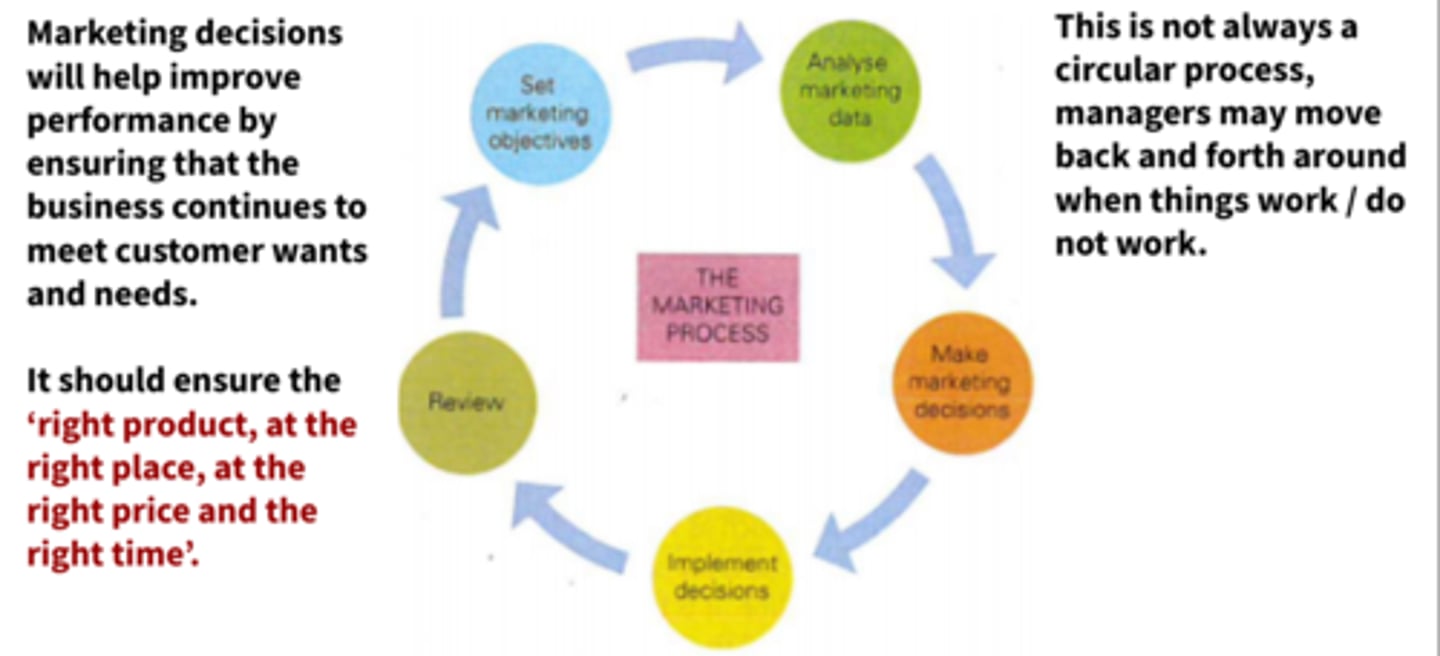
Process of marketing decision making
Set marketing objectives
Analyse marketing data
Make marketing decisions
Implement the decision
Review
The same as general decision making process but of course focused on functional area of marketing
Process of marketing decision making (diagram)
Business ethics
Refers to whether a business decision is perceived as morally right or wrong
How can business ensure its marketing is ethical
Ensure the product is as advertised
Avoid spamming customers
Ensure all information is factual
Avoid advertising for harmful products or producing them
Avoid aiming products at vulnerable people / children
Make all fees / prices clear
Avoid false advertising
Avoid misleading sales
Charge a fair price
Possible marketing objectives
- sales volume and sales value
- market size
- market and sales growth
- market share
- brand loyalty
Sales volume
The number of units sold by the business over a period of time i.e 50,000 pairs of shoes, 5 million tonnes of steel
Sales value
The monetary worth of sales made by a business over a period of time (how much customer have spent on the product) i.e £50,000 worth of sales
Sales growth
The increase in sales volume or value of sales over a given period of time i.e sales volume to increase by 5%
Sales growth formula
(Change in sales/original sales) x 100
i.e 2024 sales = £50,000 2025 sales = £60,000
Change from £50,000 to £60,000 = +£10,000
(£10,000/£50,000) x 100 = 20% change in sales value
Factors influencing possible rate of sales growth and target
- Overall market growth i.e higher market growth overall = likely higher growth target for business
- Current level of sales - easier to have higher increases in sales from a smaller amount
- Type of business
- Size of business
Market share
Measures the sales of one brand or business as a percentage of total market sales in a given period
Market share formula
(sales of product/total market sales) x 100
Why a business wants relatively high market share
- Relatively high sales and therefore possibly profit
- Relatively high outputs - may give the business power over suppliers
- Relatively high prominence in the market - raise the profile, strengthen the brand and make launching new products easier
Brand loyalty
Customers who return to use the business again - brand loyalty can be measured by customer retention
Benefits of creating a strong brand
- Increased customer loyalty - cheaper to retain customers then acquire new ones
- Charge a higher price
- Recognition for new product developments and launches
- Easier to gain distribution through retailers
- May attract publicity or endorsement making promotion cheaper
Internal influences on setting marketing objectives
- Overall strategy of the business (corporate objectives)
- The ambitions/attitudes of the managers
- The existing position of the business
- Finance
- The amount the business can produce - productive capacity
- The employees of the business - skill set
- Other functional areas
External influences on setting marketing objectives
PESTLE-C
Political/legal - i.e packaging, promotion or distribution restrictions, changes in trade blocks (EU)
Economic - Real incomes, globalisation, interest rates, employment
Social - Demographic changes, lifestyles, urbanisation, people beliefs and morals change, fashion and tastes
Technological - Communication, tracking customers, big data, reviews, social media, e-commerce
Competition - reacting to competitors promotion and pricing, more competition = more pressure
Globalisation
Increased interconnectedness and interdependence of world economies - for businesses this generally means increased trade between countries and internationalisation of businesses