osmolarity and tonicity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Concentration
Number of solutes/volume
Always write units
Penetrating solute
Moves across membrane freely
Ex. Urea
Nonpenetrating solute
Water moves for equilibrium to be met
Ex. Ions na+ k+
Osmosis
Water moves to met equilibrium
Water moves from low to high solute concentration
Diffusion
Solute moves from high to low concentration
Partially penetrating
Freely enters membrane but can not leave
Ex. Glucose enters freely but cannot leave because it gets phosphorylated
Solute number
Moles
Osmoles
Concentration
Molarity: Moles/L or molars or M
Osmolarity: osmoles/L or osmoles or OsM
Osmolarity
Compares any 2 solutions
Describes solutions concentrations compared to each other
Diffusion to reach equilibrium
Can be Pen or Nonpen
Units are OsM
Tonicity
Describe solution compared to cell
Describe how solution affects behavior of cell (shrink or swell or nothing)
Osmosis to reach equilibrium
No penetrating matters
No units
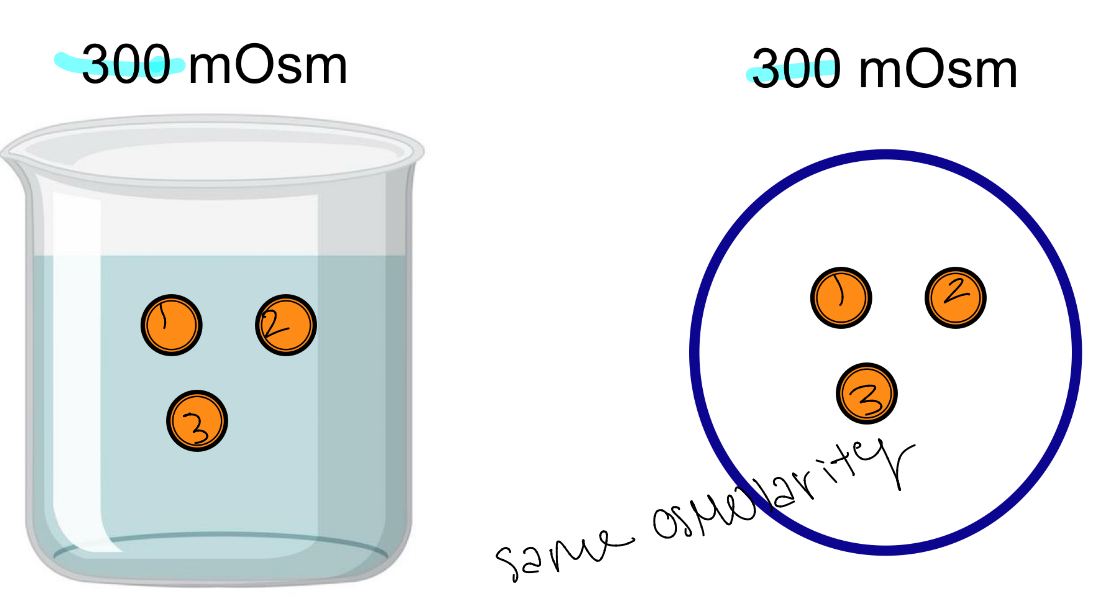
Isosmotic
Same Osmolarity
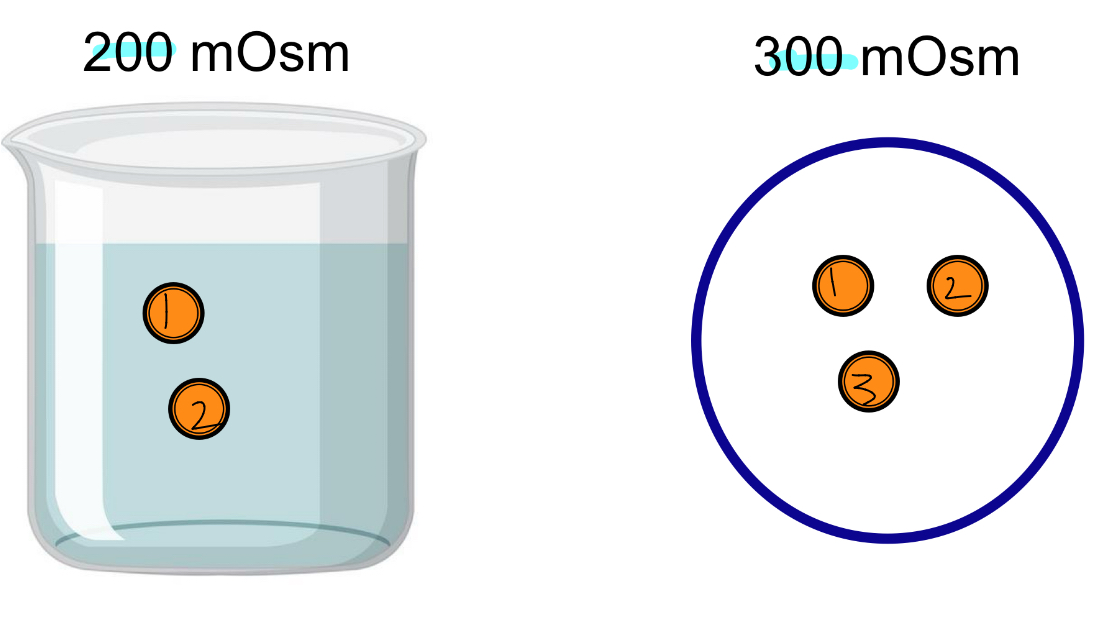
Hypoosmotic
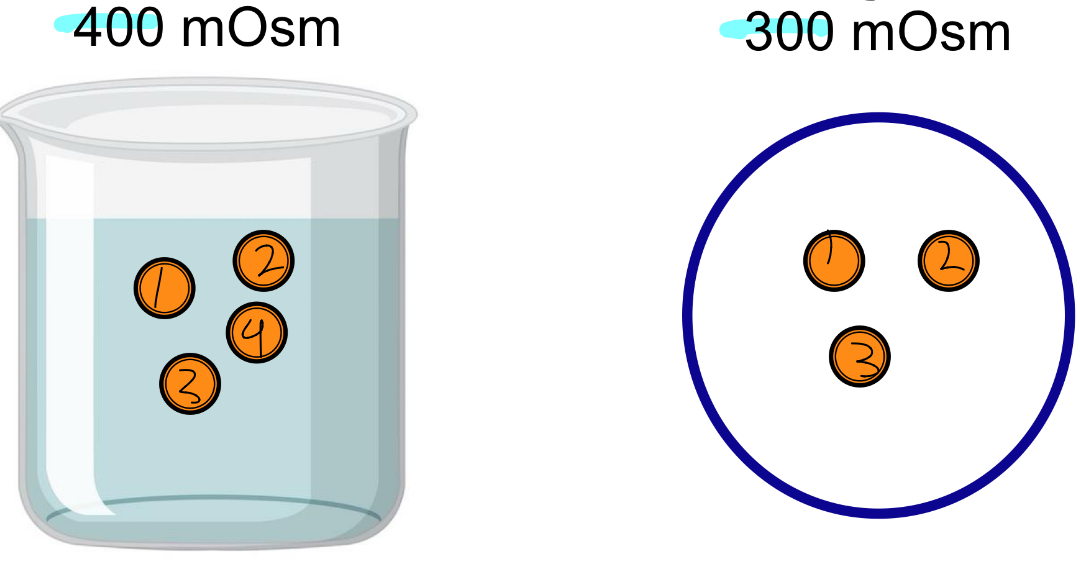
Hyperosmotic
Hypertonic
Water moves out of cell bc more NP outside
Cell shrinks/shrivels
Isotonic
No net movement of water bc equal NP
Normal cell
Hypotonic
Water moves into cell bcless NP outside
Cell swells and eventually bursts
Solute and volume of external solution are infinite to cell
Solute that leaves ECF into cell is replaced in the ECF
TBW
60% of body weight in kg
Intracellular 2/3
Extracellular 1/3
Plasma is 8% of TBW located in ECF and 25% of ECF
Interstitial fluid is 25% of TBW located in ECF
Markers
Indicate volumes of body compartments
Deuterium Oxide D2O Measures TBW
Insulin measures ECF
Evan’s blue measures plasma