Strengthening
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
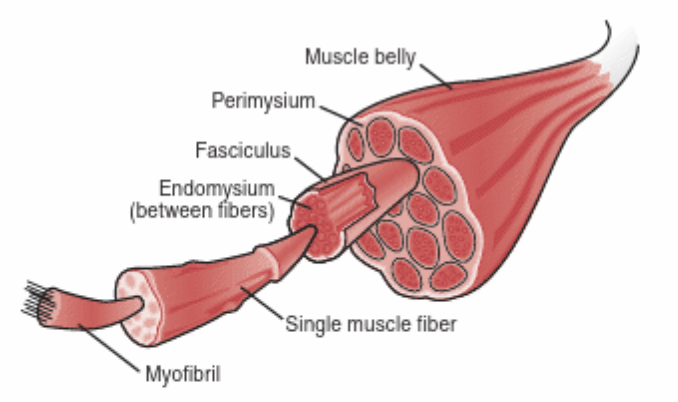
Muscle anatomy
Muscles are made up of fiber bundles called fascicles
have nuclei and are striated
each MF is composed of many sarcomeres (contractile unit)
Sarcomere structure
made up of two myofibrils: thin and thick filaments
Thin filament: actin, double stranded
Thick filament: myosin, single stranded w/ heads
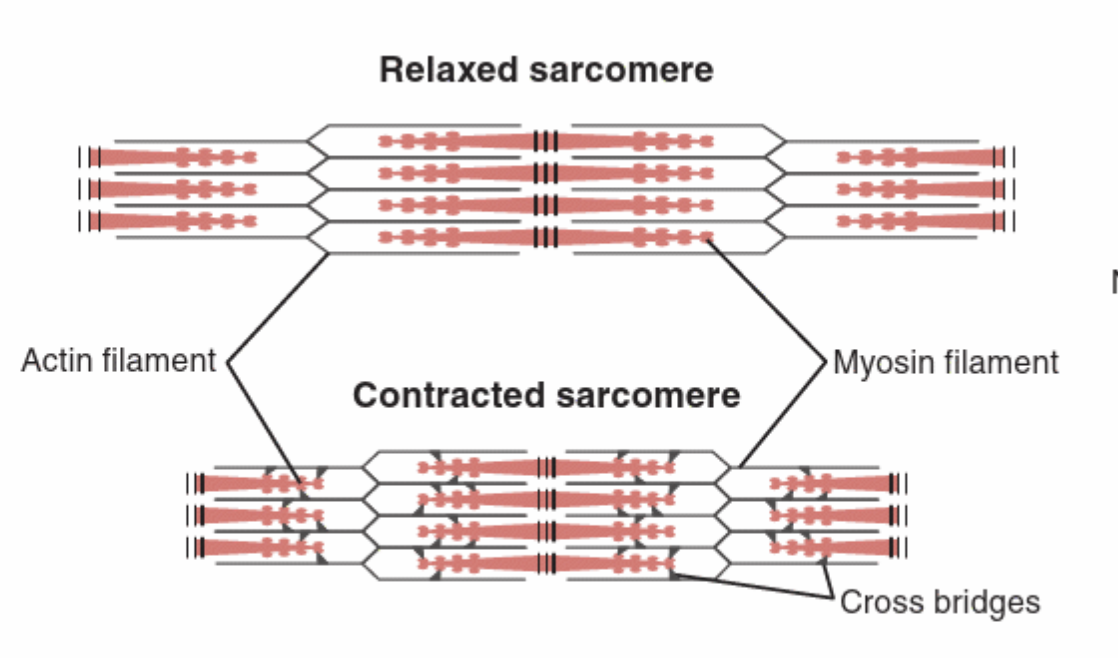
Muscle contraction- Sliding Filament Theory
Binding, sliding, binding, sliding
Myosin heads pull the actin filament inward, shortening the sarcomere→ actin slides on myosin
action potential reaches NM junction and triggers release of ACH→ causes release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Calcium binds with troponin on actin→ troponin rotates tropomyosin to expose site for myosin heads to attach
Muscle contraction: muscles
made up of multiple motor units, innervated by nerve fibers
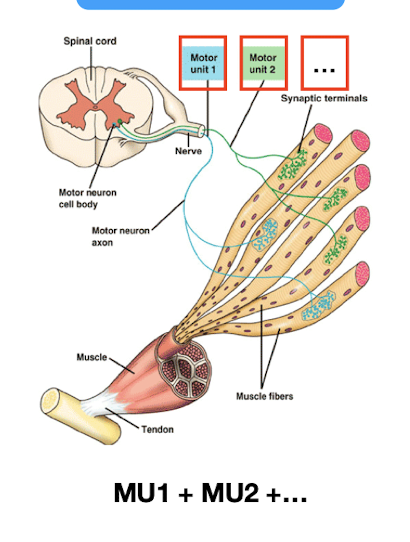
Muscle contraction: motor unit
1 motor neuron innervates many # of muscle fibers (4 to over 100)
Muscle contraction: Intrinsic muscle
Few muscle fibers innervated by 1 motor neuron
MF1+MF2+MF3+MF4
Muscle contraction: Extrinsic muscle
1 to >100 MF
Need to be activated more because bigger muscle
All or none principle
All muscle fibers innervated by a single MN contract at the same time or none contract at all
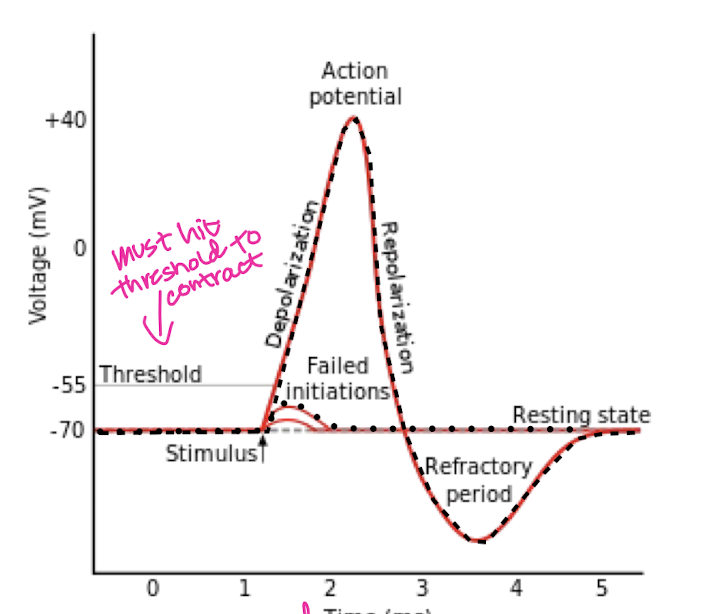
Slow twitch (type I) fiber
O2 for energy
increased resistance to fatigue
slow to reach max force
long lasting, low intensity
red color
endurance activities, posture
Oxidative (type IIa) fibers
O2 and glycogen for energy
some resistance to fatigue
quick muscle contractions
upper and lower extremities
power and endurance
white color
ex. 1 mile run, soccer, basketball
Glycolytic (type IIb) fibers
glycogen for energy
max force quick but easily fatigue
rapid and powerful contractions
upper and lower extremities
power activities
white color
ex. 100m sprint
What determines the type of fibers we have?
ratio of fibers varies
determined by genetics
everyone has all 3 but ratio is different depending on body type and training
Motor unit and Muscle fiber type
a motor unit has all 1 type of fiber, never a mix
between motor units of the same muscle there can be a mix
MU1 can have type 1 and MU2 can have type IIa
Can a muscle fiber become a different type?
the percentage of fiber type cannot be altered through resistance or endurance training
BUT type IIb (glycolytic) can become more efficient like type IIa (oxidative) through repeated endurance exercise
type IIa can become like IIb through power and strength training
^ but both are temporary
Muscle fiber type and Rehab
diff athletes need diff exercises→ know their needs and physical features
determine intensity and reps based on fiber/body type
Muscle performance
muscles ability to do work (force x distance)
strength, endurance, power
Strength
max force generation (single output/ 1 rep)
often includes external resistance
essential for injury prevention/normal functional movement
if decreased strength→ lead to dysfunction and decreased functional performance
To regain strength…
6-10 reps for 3+ sets
Endurance
repeated over an extended period
if increased strength → increased endurance
can improve endurance by increased reps and decreased weight
if decreased endurance→ decreased functional performance in ADL bc not using max force
to increase endurance…
10-15 reps for 3+ sets
<1 min rest b/t sets
Power
work in a given time
strength x distance/ time
if decreased power, decreased athletic performance
To increase power…
1-5 reps for 4+ sets
1-2 min rest b/t sets
Less reps but increased weight
Isometric contraction
contraction w/o length change
common in early rehab
only within pain free limits
Concentric contraction
muscle shortening contraction
use after some ROM recovery
Eccentric contraction
muscle lengthening contraction
use after some ROM recovery
Factors determining muscle performance
muscle hypertrophy
size of motor unit
NM efficiency
biomechanics
gravity
Cross-sectional area of muscle
area = L x W x Thickness
increased area = increased strength
more muscle fibers, more MN, more force
Atrophy
decreased muscle mass = decreased strength
inactivity due to injury/surgery (as little as 48 hrs)
size of muscle fibers shrink, you don’t loose # of them
Hypertrophy
exercise = increased area and strength of muscles
Factors: # and type of muscle fibers
increased # of MF = increased area = increased strength
increased type II = increased strength
number and type of MF are…
inherent
Neuromuscular system
nervous system + muscle causing movement of the body
Increasing motor units does what?
Increase MUs = increased fibers = increased strength
fire more MUs = more fibers involved in contraction = increased strength
Resistance Exercise does what
increased efficiency→ involve more MU during contraction
increased firing rate→ faster MUs, activate quicker
increased synchronization b/t MUs (one ends, another begins)
initial rehab (4-6 wks)
increased strength by increasing NM efficiency
Lever arm length
distance b/t joint and the force
longer lever arm = greater force needed
resistance far from joint→ harder to move→ more force
early rehab: resistance should be close to jt
Degree of force application
max force is in mid range
least force = end range (beginning/end)
Biomechanics: length tension relationship
physiologically shortened or lengthened muscles result in decreased force production capabilities and greater chance for dysfunction
Factors: age
Max strength gains occur in the early to mid twenties→ age 25 muscular force begins to decline 1% per year
can slow down curve through strength exercise
also decreased risk of future injuries
