Cumulative AP Exam Study Guide
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Statistics
The science of collecting, analyzing, and drawing conclusions from data
Descriptive Statistics
Methods of organizing and summarizing statistics
Inferential Statistics
Making generalizations from a sample to the population
Population
An entire collection of individuals or objects
Sample
A subset of the population selected for study
Variable
Any characteristic whose value changes
Data
Observations on single or multi-variables
Categorical Variables (Qualitative)
Basic characteristics
Numerical Variables (Quantitative)
Measurements or observations of numerical data
Discrete Variables
Listable sets (counts)
Continuous Variables
Any value over an interval of values (measurements)
Univariate
One variable
Bivariate
Two variables
Multivariate
Many variables
Symmetrical Distribution
Data on which both sides are fairly the same shape and size (“Bell Curve”)
Uniform Distribution
Every class has an equal frequency (number) → “a rectangle”
Skewed Distribution
One side (tail) is longer than the other side. The skewness is in the direction that the tail points (left or right)
Bimodal Distribution
Data of two or more classes have large frequencies separated by another class between them (“double hump camel”)
How to describe numerical graphs
Shape - overall type (symmetrical, skewed right left, uniform, or bimodal)
Outliers - gaps, clusters, etc.
Center - middle of the data (mean, median, and mode)
Spread - refers to variability (range, standard deviation, and IQR)
Everything must be in context to the data and situation of the graph. When comparing two distributions – MUST use comparative language!
Parameter
Value of a population (typically unknown)
Statistic
A calculated value about a population from a sample(s)
Measures of Center
Median - the middle point of the data (50th percentile) when the data is in numerical order. If two values are present, then average them together.
Mean - μ is for a population (parameter) and x is for a sample (statistic).
Mode - occurs the most in the data. There can be more then one mode, or no mode at all if all data points occur once.
Variability
Allows statisticians to distinguish between usual and unusual occurrences
Measures of Spread (variability)
Range - a single value (Max-Min)
IQR - interquartile range (Q3 – Q1)
Standard deviation - σ for population (parameter) & s for sample (statistic) – measures the typical or average deviation of observations from the mean – sample standard deviation is divided by df = n-1
*Sum of the deviations from the mean is always zero!
Variance - standard deviation squared
Resistant
Not affected by outliers
Median
IQR
Non-Resistant
Mean
Range
Variance
Standard Deviation
Correlation Coefficient (r)
Least Squares Regression Line (LSRL)
Coefficient of Determination (r²)
Comparison of mean & median based on graph type
The mean is always pulled in the direction of the skew away from the median
Symmetrical
Mean and the median are the same value
Skewed Right
Mean is a larger value than the median
Skewed Left
The mean is smaller than the median
Trimmed Mean
Use a % to take observations away from the top and bottom of the ordered data. This possibly eliminates outliers
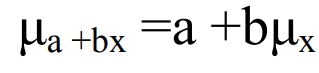
The mean is changed by both addition (subtract) & multiplication (division)
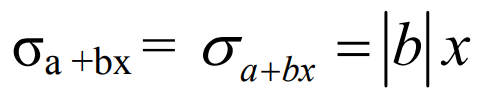
The standard deviation is changed by multiplication (division) ONLY
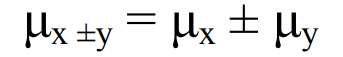
Just add or subtract the two (or more) means
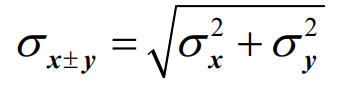
Always add the variances – X & Y MUST be independent
Z-Score
A standardized score. This tells you how many standard deviations from the mean an observation is. It creates a standard normal curve consisting of z-scores with a μ = 0 & σ = 1.
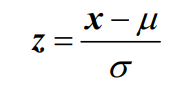
Normal Curve
Bell shaped and symmetrical curve.
As σ increases the curve flattens.
As σ decreases the curve thins.
Empirical Rule
(68-95-99.7) measures 1σ, 2σ, and 3σ on normal curves from a center of μ.
68% of the population is between -1σ and 1σ
95% of the population is between -2σ and 2σ
99.7% of the population is between -3σ and 3σ
Boxplots
Are for medium or large numerical data. It does not contain original observations.
Always use modified boxplots where the fences are 1.5 IQRs from the ends of the box (Q1 & Q3). Points outside the fence are considered outliers.
Whiskers extend to the smallest & largest observations within the fences.
5-Number Summary
Minimum
Q1 (1st Quartile – 25th Percentile)
Median
Q3 (3rd Quartile – 75th Percentile)
Maximum
Sample Space
Collection of all outcomes.
Event
Any sample of outcomes.
Complement
All outcomes not in the event.
Union
A or B, all the outcomes in both circles.
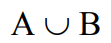
Intersection
A and B, happening in the middle of A and B.
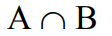
Mutually Exclusive (Disjoint)
A and B have no intersection. They cannot happen at the same time.
Independent
If knowing one event does not change the outcome of another
Experimental Probability
The number of success from an experiment divided by the total amount from the experiment.
Law of Large Numbers
As an experiment is repeated the experimental probability gets closer and closer to the true (theoretical) probability. The difference between the two probabilities will approach “0”.
Probability Rules
All values are 0 < P < 1.
Probability of sample space is 1.
P (at least 1 or more) = 1 – P (none)
Compliment of a Probability
P + (1 - P) = 1
Addition of Probabilities
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A & B)
Multiplication of Probabilities
P(A & B) = P(A) · P(B)
If a & B are independent
Conditional Probability
Takes into account a certain condition.
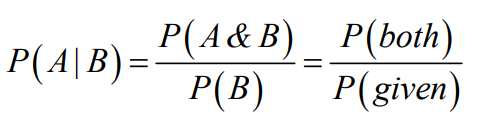
Correlation Coefficient (r)
A quantitative assessment of the strength and direction of a linear relationship. (use ρ (rho) for population parameter)
There is a strength, direction, linear association between x & y.
0 → no correlation
(0, ±0.5) → weak
[±0.5, ±0.8) → moderate
[±0.8, ±1] → strong
Least Squares Regression Line (LSRL)
A line of mathematical best fit. Minimizes the deviations (residuals) from the line. Used with bivariate data.
x is independent, the explanatory variable & y is dependent, the response variable
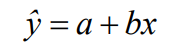
Residuals (error)
Vertical difference of a point from the LSRL. All residuals sum up to “0”.
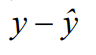
Residual Plot
Scatterplot of (x (or ˆy) , residual). No pattern indicates a linear relationship.
Coefficient of Determination (r²)
Gives the proportion of variation in y (response) that is explained by the relationship of (x, y). Never use the adjusted r².
Approximately r²% of the variation in y can be explained by the LSRL of x any y.
Slope (b)
For unit increase in x, then the y variable will increase/decrease slope amount.
Extrapolation
LRSL cannot be used to find values outside of the range of the original data.
Influential Points
Points that if removed significantly change the LSRL.
Outliers
Points with large residuals.
Census
A complete count of the population.
Why not to use a census?
Expensive
Impossible to do
If destructive sampling you get extinction
Sampling Frame
A list of everyone in the population.
SRS (Simple Random Sample)
One chooses so that each unit has an equal chance and every set of units has an equal chance of being selected.
Advantages: easy and unbiased.
Disadvantages: large σ² and must know population.
Stratified
Divide the population into homogeneous groups called strata, then SRS each strata.
Advantages: more precise than an SRS and cost reduced if strata already available.
Disadvantages: difficult to divide into groups, more complex formulas & must know population.
Systematic
Use a systematic approach (every 50th) after choosing randomly where to begin.
Advantages: unbiased, the sample is evenly distributed across population & don’t need to know population.
Disadvantages: a large σ² and can be confounded by trends.
Cluster Sample
Based on location. Select a random location and sample ALL at that location.
Advantages: cost is reduced, is unbiased & don’t need to know population.
Disadvantages: May not be representative of population and has complex formulas.
Random Digit Table
Each entry is equally likely and each digit is independent of the rest.
Random # Generator
Calculator or computer program
Bias
Error that favors a certain outcome, has to do with center of sampling distributions – if centered over true parameter then considered unbiased
Voluntary Response
People choose themselves to participate.
Convenience Sampling
Ask people who are easy, friendly, or comfortable asking.
Undercoverage
Some group(s) are left out of the selection process.