Primary Lymphoid organs: B and T cell development
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Where does adaptive immunity occur
lymphocytes are generated in the primary lymphoid organs
naive when leave primary lymphoid organ: have not yet encountered specific antigen
mature naive lymphocytes—encounter antigen and are activated and develop into an effector lymphocyte
T and B lymphocyte development and education
development: generate a functional B cell receptor (BCR) or T cell receptor (TCR)
education: tolerant to self antigens
create a collection of T and B lymphocytes with receptors specific for diverse antigens (gene arrangement)
primary lymph organs
bone marrow
thymus
intestine—ruminants and horses
secondary lymphoid organs
bone marrow
spleen
lymph nodes
salivary glands
resp. tract
mammary glands
intestine
urogenital system
hematopoietic cells are produced in
bone marrow
lymphocyte progenitor cells from bone marrow either
develop into B cells in bone marrow
migrate to the thymus to develop into T cells
site of B cell development is species specific
bone marrow—most species
ileal peyers patches—ruminants, horses
bursa—birds
continuous peyers patches
illeum
involutes by 15 months of age
primary lymphoid tissue for B cell development in ruminants, horses
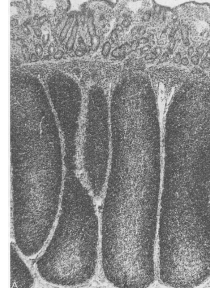
continuous peyers patches
discontinuous peyers patches
jejunum
life-long
secondary lymphoid tissue
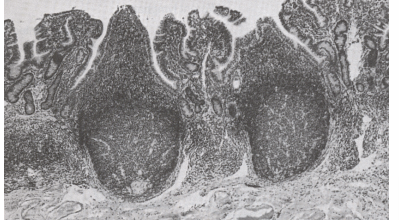
discontinuous peyers patches
thymus
epithelial outgrowth of third pharyngeal pouch
lymphoid progenitors from bone marrow migrate to thymus and become thymocytes
thymocytes mature to naive T lymphocytes
develop T cell receptor (TCR)
become MHC class restricted
educated (tolerized) to self antigen
most important step in life of a lymphocyte
development of the BCR or TCR
BCR/immunoglobulin structure
Fab=antigen binding regions consisting of variable regions (V) of amino acid (aa) structure
Fc region=constant (C) aa structure, determines isotype and primary function of immunoglobulin
membrane bound BCR are IgM isotype
T cell receptor
alpha and beta (Most numerous)
gamma and delta prevalent in ruminants
the hallmark of adaptive immunity is the
specificity of the immune response due to a diverse repertoire of unique BCR and TCR
gene arrangement—random selection of gene segments resulting in genetic diversity of BCR and TCR
occurs during lymphocyte development in primary lymphoid tissues
gene rearrangement occurs in each lymphocyte during development
it is random process like shuffling cards
segments of gene arrangement
v=variable gene segment
D=diversity gene
J=joining gene segment
V-D-J recombinase
enzymes need to recombine
RAG1 and RAG2 genes found only in lymphocytes—cleave DNA and protect dsDNA breaks from DNA repair mechanisms
central tolerance
process by which self-reactive lymphocytes are deleted or programmed to become unresponsive to self-antigen
immature B cells that bind self antigens with high affinity undergo
apoptosis and negative selection or
receptor editing of variable region genes
MHC I
CD8+ t cell
receptor binds
cytotoxic
MHC II
CD4+ T cell
receptor binds
helper
autoimmune regulator gene (AIRE)
controls expression of >400 tissue specific proteins
expressed by thymic medullary epithelial cells with MHC molecules
important for developing T cells to become self-tolerant
without bursa or ileal peyers patches
B cells constitute approximately 20% of circulating lymphocytes
total circulating lymphocyte pool slightly decrease
humoral immunity (antibody concentration) markedly decreased
absent or deteriorated thymus
no T cells in secondary lymphoid tissue
No T cells in circulation (60-70% circulating lymphocytes)
defective T-cell mediated immunity
SCID
severe combined immunodeficiency
cannot develop B or T cells