Ap Psychology unit 1
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Nature
genes and hereditary factor
Nutue
Environmental variables
Heredity
the genetic passing of characteristics between generations
Environment
All non-genetic influences on behavior- prenatal nutrition
Genes
segments of DNA that provide us the “biological instructions for life”
Genetic predisposition
increased chance of developing a given trait based on genetic makeup
Psychological genetic predisposition
mental health disorders and personality
Biological genetic predisposition
eye color, height, lifespan, hair texture
Medical genetic predisposition
heart disease, asthma and cancer
Behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior
the presence of a gene does not guarantee the expression of that trait
in many cases, genes are “turned on” by the environment
a gene many remain “silent” without the appropriate environment influence
What environmental factors might affect gene expression?
prenatal environment, socialization, nutrition, stimulation, traumatic experiences
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influence of gene expression that occur with DNA change
Interaction
the effect of one factor (environment) depends on another factor (heredity)
Twin studies
are one of the best ways to study the nature vs nurture questions
Fraternal twins
genetically close as siblings, shared a fetal environment, developed from two different eggs
Identical twins
genetically identical, one egg split into two
Evolutionary perspective
explores how natural selection affects the expression of behavior and mental process to increase survival and reproductive success.
Natural selection
organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce more successfully than others
Eugenics (good + genics :genes)
-selectively mating people with “desirable “ traits
-aims to reduce human suffering by “breeding out” disease, disabilities and “undesirable” characteristics from the human population
Nervous system
bodily system that sends messages back and forth between the brain and the body
involves the brain, spinal cord, and complex nerve
allows us to move, breathe, think
Central
brain & spinal cord
spinal cord is the “pathway” from the CNS to the PNS
Peripheral
sensory and motor neurons, regulates basic bodily functions, nerves
The peripheral NS sketal (somatic)
voluntary body movements
bodies, joints, muscles, tendons and ligaments
walk, run, dance and swim
The peripheral NS autonomic
involuntary process
control slandse muscles
HR, digestion, arousal, blood pressure
The Autonomic NS sympathetic
fight- or- flight
arouses body in stressful situations
delivers blood to parts to the body that need more oxygen to get out of a dangerous situation
the autonomic NS parasympathetic
-rest and digest
-calms the body to conserve energy
-relax and recover from flight or fight mode
Nerons
-smallest “building block” of the nervous system
-neuron sends and receives signals in order to communicate
-there are about 100 billion in the human body
-a single neuron could be connected to 10,000 others
sensory neurons
-also called afferent neurons
- receive information for sensory receptors
-send information to the brain to be processed
Motor neurons
-also called efferent neurons
-send information from the brain to the body
-tells our body how to move
Interneurons
-part of the CNS
-connect signals between sensory and motor neurons
Reflex arc
3 types of neurons work together in the spinal cord to control reflexes
Glial cells
type of brain cell
that support cells by providing structure, insulation, communication, and waste transport
Schwann cells
important type of glial cells
build myelin in the peripheral nervous system
Multiple sclerosis
chronic autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin, causing numbness, weakness, trouble walking and other motor difficulties
Neural transmission
electrical communication process between neurons is an electrical process
neurons are kind of like wires
Synaptic gap
space between the terminal button and dendrite of two neurons
Synapse
connection between two neurons
Resting potential
-a lot of the time, there is no electricity flowing through the neuron
-what that happens the neuron is “at rest”
-RP=-70mv
-this means the neurons is ready for an electrical change at anytime
Action Potential
+40 mv
when this happens the neutral impulse travels through the neuron
+55 mv threshold
level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
all or nothing law
when a neuron reaches the -55mv threshold, it will fire
neurons fire at one strength and intensity
there is no such thing as a strong action potential
Refractory period
time post-firing in which another action potential cannot occur while the neuron rests
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that travel across the synaptic gap between neurons
bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron to continue the message
Excitatory
stimulate neuron firing (fire more frequently and send messages faster)
Inhibtory
slow neuron firing (messages communicated more slowly)
Acetylcholine
excitatory NI that plays a role in learning, memory, attention, and triggers muscle contraction
oversupply- muscle spasm (muscles moving when you don’t want them to )
undersupply- Alzheimer’s diseases :progressive neurological disease that causes brain cell death, leading to problems with memory, thinking and behavior changes
Myasthenia gravis
the body makes antibodies that block/destroy receptor sites for ACH. Fewer receptor sites: muscles set fewer nerve signals making movement more difficult
Dopamine
excitatory and inhibitory NT- that is responsible for reward and pleasure. Influence movement, learning and attention
oversupply- schizophrenia (disorder associated with a loss of touch from reality)
undersupply- Parkinson Disease : loss of DA neurons causes tremors, slowed movements, muscle rigidity, and other movement changes
Schizophrenia symptoms
delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thinking
Positive symptoms
a behavior thought, or feeling that’s not typically present, adding something to a person’s experience
-hallucinations
-delusions
-disorganized thoughts
delusions of persection
someone is out to get you
Delusions of grandeur
especially impressive/important
Delusions of disorganized speech/behavior
word salad: incomprehensible speech or writing; a jungled mix of words and phares with no logical connection
Catatonia
Muscular rigidity, bizarre posture and reductor in movement
Negative symptoms
Decrease in or absence of typical behaviors, emotions, or thoughts
Flat affect
A noticeable lack of emotional expressions
Monotone voice
Minimal facial expressions
absences of body language
appears emotionally detached
causes of schizophrenia
Genetics- Neurochemical differences: high BA- structural brain differences: enlarged brain ventricles
Epigenetics
onset could be triggered by the environment- exposer to virus in utero- Trama or abuse
Antipsychotics
The most effective medication for treating schizophrenia by blocking dopamine receptors
Tardive dyskinesia
neurological side effects of antipsychotics
Endorphins
inhibitory opiate- like NTS linked to pain control and reward. They relieve stress and help improve mood.
oversupply- inadequate pain response
undersupply- linked to addiction
Gaba
inhibitory NT that regulated the sleep-wake cycle
most prevalent inhibitory NT
oversupply- sleep disorders; dysfunctional Gaba release is associated with insomnia
Glutemate
excitatory NT that is the basis for learning and long-term memory
most abundant excitatory NT
oversupply- migraines and seizures: too much glutamate can overstimulate neurons
undersupply- very rare and specific problems, but can cause general problems with concentration, sleep, and fatigue
Norepinephrine
excitatory NT associate with the autonomic NS (fight or flight response)
oversupply- anxiety: increased HR and BP, irritability, stress and insomnia
undersupply- depressive symptoms: low mood, low motivation, lack of energy, trouble concentrating
Serotonin
inhibitory neurotransmitter that regulated mood (calming) also helps regulate appetite, sleep, and mood
exposure to AM sunlight boosts production of serotonin and melatonin
oversupply- hallucinations; seeing or hearing things that others do not, intense happiness, elation
undersupply- depressive symptoms :low mood, low motivation, lack of energy, trouble concentrating
NTS are always being released, it’s not just one at a time and there is a overlap, but here the main difference between “happy” NTS
Depressive disorders
a category of mental health disorders marked by persistent low mood, loss of interest, worthlessness, fatigue, etc.
Major depressive disorder symptoms
persistent low mood or anhedonia ( loss of interest in pleasures)
symptoms
problems with memory or concentration
anger/irritability
5+ symptoms for 2+ weeks cause impaired functioning
Persistent depressive disorder
-depressed mood days for 2+ years, plus 2 of the following
symptoms- low self esteem, insomnia or hypersomnia, overeating
symptoms have not stopped for more than 2 months with no time
Causes of depressive disorders
genetics, neurochemistry, ability status, stress, trauma,
Treating depressive disorders
biological, psychological and lifestyle changes
Antidepressants
increase availability of serotonin & norepinephrine
selective serotonin- lexapro
selective norepinephrine- cymbalta
must taper on and off
side effects- weight gain, dizziness, hypertension
Effectiveness of antidepressants
-20-40 out of people who take antidepressants noticed symptoms improvement in 6-8 weeks
-40-60 out of 100 people who took an antidepressant noticed symptom notice improvement in 6-8 weeks
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
an non invasive technique that use a magnetic field to influence brain activity in a specific area, potentially treating conditions like treatment- resistant depression by stimulating neurons through electromagnetic induction
Biological treatments :depressive disorders
electro conclusive therapy
a brief electric shock is deliberately induced in the brain to produce a seizure, primarily used to treat severe treatment resistant depression or other Psychiatic disorders that have responded to other therapeutic
Stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up bodily functions.
mainly associated with dopamine
increases alertness and energy
increase BP and HR
feelings of euphoria
Type of stimulants- Caffeine
increased alertness
Type of stimulants- Nicotine
relaxation and pleasure
Type of stimulants- Amphetamines
energetic and “euphoric high”
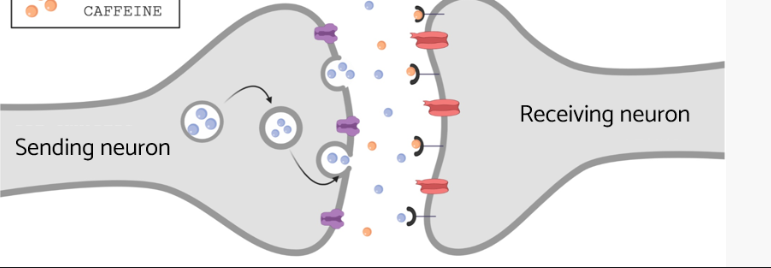
What happens in the brain when you drink coffee?
Caffeine is an adenosine receptor antagonist
Psychological dependence
psychological need for a drug like a craving and restlessness
Tolerance
diminishing effect of a substance with regular use
Dependence
is different from misuse or addiction
Misuse
pattern of substance use interfering with one’s daily life regardless of physical symptoms
Addicton
compulsive drug use or behaviors despite harmful consequences, interfering with a person’s life, often characterized by physical symptoms
Imparied control
use in larger amounts or for longer periods of time than intended and excessive time spent using drugs
Social impairment
failure to fulfill major obligations
Risky use
recurrent use in physically hazardous situations
pharmacological
tolerance and withdrawal
Reasons why people use substances
to feel good, to do better, to explore, and to feel better
Why do people misuse substances?
Biological, psychological, and social culture