Pathogens
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is a pathogen? Examples?
Anything that can cause a disease
Bacteria
Viruses
Fungi
Protozoa
Prions
Parasitic invertebrates
What is an disease? Infectious vs Non Infectious?
A disease is any condition that impairs the normal functioning of the body
Infectious disease-
Caused by a pathogen which can move between hosts
Non-infectious disease-
Not caused by pathogens therefore cannot be transferred between people E.g. genetic
Infectious disease main components? (Host, Parasite, Virulence)
Host (animal/plant) in or on which another organism parasitically lives
Parasite (Organism) that lives on or in another organism and causes it harm
Interference with normal body functions
Deprive host of vital nutrients
Virulence — the ability of a pathogen to cause disease
A measure of severity of disease
Virulent = extremely noxious, damaging, etc. Rapid and severe
Infectious diseases— how are they spread?
Infection must occur (the invasion of a host by a pathogen)
Can occur via:
Water droplets/spores in air
Water & food
Bodily fluids
Other animals
Types of diseases? (Inert, Virus, Vector)
Inert diseases — can survive for years without infecting hose (tetanus and anthrax)
Viruses — which need a host to survive & reproduce
Vector — moves from one host to another using another organism
What is an incubation period? & Why do pathogens need one
Time between infection & onset of symptoms
Pathogen needs time to divide many times to reach sufficient numbers to cause disease
Pathogen may need time to reach a particular organ/place in host
Pathogen may produce toxins (which can take time)
What are symptoms? How do symptoms help with diagnosis (+ Disease recovery)
Symptoms are effects the pathogen has on the body of the hose.
high temperature and rash develop in the measles
Diseases usually have characteristic symptoms that help doctors to diagnose the cause of the disease without isolating the pathogen
Disease recovery = when symptoms disappear
Terminology recap. Disease, Infectious disease, Infection, invasiveness, virulence & communicability

What is Koch’s Postulates? (1884-1890)
Koch developed four criteria to demonstrate that a specific disease is caused by a particular agent.
The specific agent must be associated with every case of the disease.
The agent must be isolated from a diseased host and grown in culture.
When the culture-grown agent is introduced into a healthy susceptible host, the agent must cause the same disease.
The same agent must again be isolated from the infected experimental host.
Phases of infectious disease?

How to classify infectious diseases? (Location, Timing, Duration, Geography)
+ By geography
Endemic/Enzootic - The constant presence of a disease or infectious agent within a given geographic area.
Epidemic/Epizootic - The occurrence in an area of a disease or illness in excess of what may be expected on the basis of past experience for a given population (in the case of a new disease, such as AIDS, any occurrence may be considered "epidemic").
Pandemic/Panzootic - A worldwide epidemic affecting an exceptionally high proportion of the global population.

Give an example of an infectious disease (Influenza)

How to transmit infectious diseases?
Direct physical contact
skin contact
bodily fluids
Indirect transmission
Formites (clothing & other infected objects)
Dust
Air
Water droplets
Food/water
Fecal matter
What is a reproductive rate?

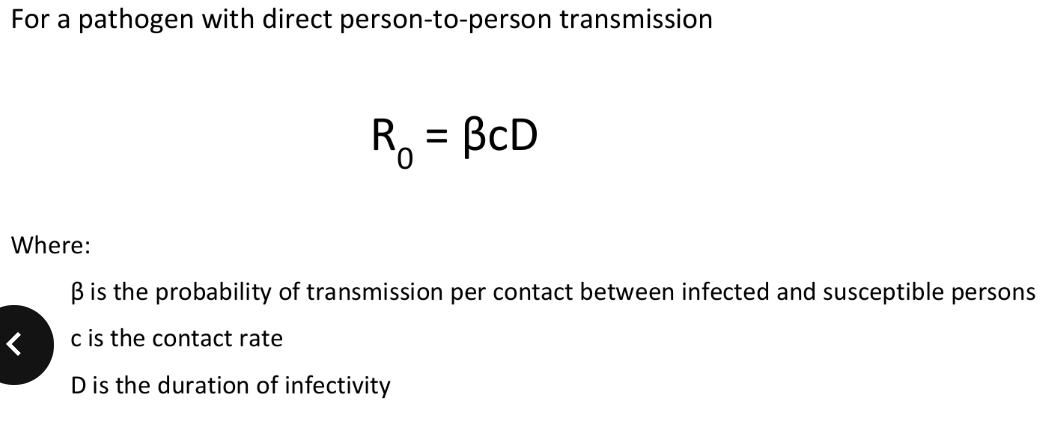
Formula for spread of infectious disease? & Assumptions?
Assumptions
Population is fixed (no entries/births or departures/deaths)
Latent period is zero
Infectious period = disease duration
After recovery, individuals are immune
People can be in one of three states
Susceptible to the infection (S)
Infected and infectious (I)
Recovered/immune (R*)
What is the chain of infection?
In order for disease to occur and spread from one individual to another, certain conditions must be met.
If any one condition is not met, the transmission of the disease will not happen.
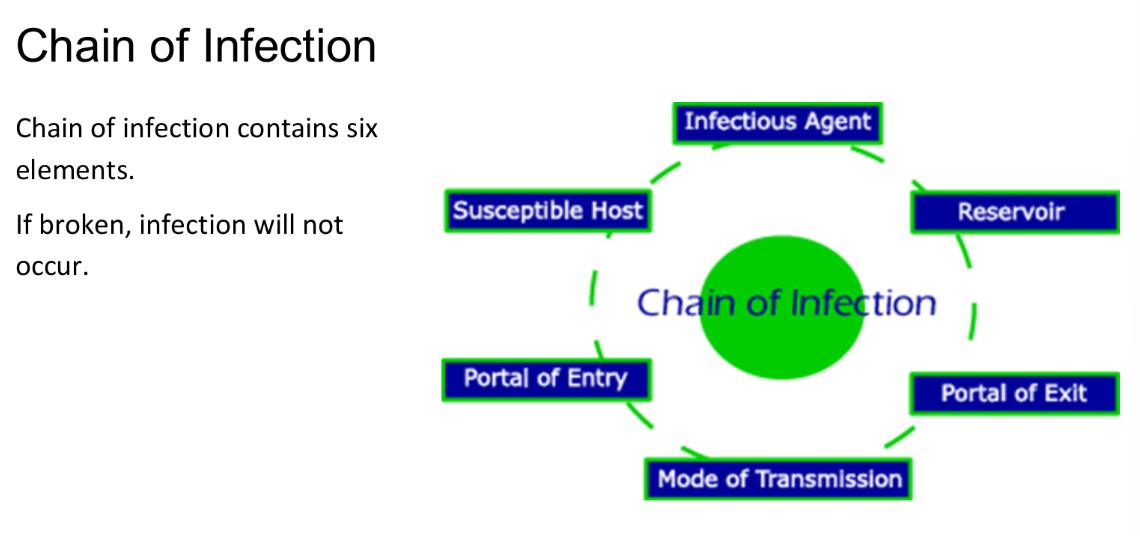
Explanation of chain of infection elements?
Infectious Agent – pathogen such as a bacteria or virus.
Reservoir – a place the pathogen can live.
Examples: human body, animals, the environment, fomites.
Fomites are objects contaminated with infectious material that contains pathogens.
Ex: doorknobs, bedpans, linens, instruments.
Portal of Exit – way to escape from the reservoir in which it has been growing.
Urine, Feces & Semen
Saliva, Mucous discharge (snot) & Tears
Respiratory & Gastrointestinal tract
Skin & Blood
Mode of Transmission – way in which it can be transmitted to another reservoir or host where it can live.
Can be through direct contact or airborne droplet.
Contaminated hands
Portal of Entry – way to enter the new reservoir or host.
Respiratory tract, mucous membranes, and gastrointestinal tract are common.
Damaged skin.
Susceptible Host – one that is capable of being infected.
Microorganisms must be present in large enough quantity to be virulent.
The host must be susceptible.
Individuals with an immunity to certain pathogens will not be susceptible.
What is a infectious disease case?
Case = person diagnosed as having a disease disorder injury or condition
Primary case = The first disease case in the population
Index case = the first disease case brought to attention of the epidemiologist
Secondary case = persons infected once a disease has been introduced to a population
Levels of diagnosis for cases
Suspect → Probable → Confirmed
Types of carriers & short definition?
Active carrier: Exposed/Harboring pathogen
Convalescent carrier: Harbor pathogen & In Recovery (Infectious)
Healthy (or Passive) carrier: Exposed to and harboring pathogen (Not ill/Not showing any symptoms)
Incubatory carrier: Exposed to and harbor pathogen, initial symptoms, ability to transmit a disease.
Intermittent carrier: Exposed to and habor pathogen, can spread disease.
Reasons why a disease can emerge/re-emerge
Appearance of a previously unknown agent
Evolution of a new infectious agent
Spread of an infectious agent to a new host
Spread of an infectious agent to new locations
Acquisition of resistance to anti-microbial drugs
Deliberate introduction to population
How to reduce spread of infectious disease?
Vaccines (immunisation)
Antimicrobial drugs
Good personal hygiene/sanitation (education)
Protection against mosquitoes
Quarantine
Herd immunity
Based on notion that if a population or group is mostly protected from a disease by immunisations (> 85%), then chance of a major epidemic occurring is limited.
Herd immunity provides barrier to direct transmission of infections through population.
Lack of susceptible persons stops spread of a disease through throughout group.