Metabolic pathways
1/39
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What controls each step of a metabolic reaction?
A particular enzyme
What codes for each enzyme in a metabolic reaction?
A particular gene
What do metabolic pathways consist of?
Several stages involving the conversion of one metabolite to another
What happens when the appropriate enzyme is present in a metabolic reaction?
The pathways proceeds
What happens when the appropriate enzyme is not present in a metabolic reaction?
The pathway stops
Metabolic pathways
Integrated and controlled pathways of enzyme-catalysed reactions within a cell
Metabolism
Biochemical reactions that take place in cells
What are the two types of metabolic pathways?
Anabolic reactions and catabolic reactions
Anabolic reactions
The build up of larger molecules from smaller molecules, this requires energy
Catabolic reactions
The break down of larger molecules into smaller molecules, this releases energy
Irreversible routes
The molecules are permanently changed
Reversible routes
The molecules can be converted back into its previous form
Example: reversible route
Anaerobic respiration (fermentation) in animal cells:
Alternative routes
A metabolic pathway that has more than one ‘route’ of getting the substrate to the product(s)
Where are metabolic enzymes found?
Embedded on the surface of membranes
What are the three proteins found embedded in the phospholipid membrane?
(Metabolic) enzymes
Protein pores
Pumps
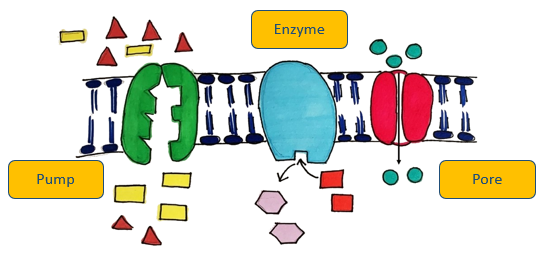
Diagram: phospholipid membrane
(Metabolic) enzymes
Enzymes that organise the sequence of reactions and control/speed them up without chemically changing the enzyme after the reaction
Protein pores
Holes in the membrane that are surrounded by proteins that allow small molecules through by diffusion
Pumps
Proteins in the membrane that allow small molecules through by active transport
What happens when a mutation is present in a metabolic reaction?
The enzyme coded for by the gene would be faulty and so the pathway would be blocked
The ‘lock and key’ mechanism
Enzymes have a specific shape and so their active site is shaped to complement that of their specific substrate(s)
The active site and its substrate(s)
The active site has a high affinity to these
The active site and its product(s)
The active site has a low affinity to these
How does the active site affect the activation energy of a reaction?
The active site helps to orientate the reactants, which lowers the activation energy of a reaction as the substrate(s) bind
Induced fit model
This is when the shape of the active site changes shape to better fit the substrate, after the substrate binds to ensure the active site comes into very close contact with the substrate
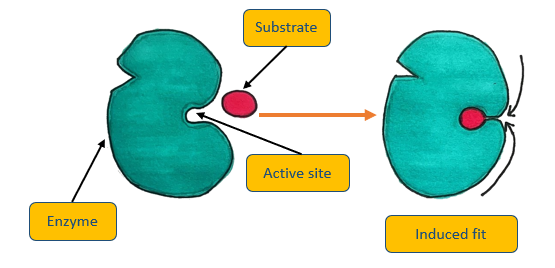
Diagram: induced fit
Activation energy
The energy required to initiate a reaction
What happens before a substrate becomes a product?
The substrate must overcome an energy barrier (the activation energy)
What do enzymes do in living cells besides organise the sequence of reactions and control/speed them up?
Reduce the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur
Inhibitors
Substances that prevent enzyme activity
What are the three types of metabolic inhibitors?
Feedback inhibitors
Competitive inhibitors
Non-competitive inhibitors
Feedback inhibitors
When the end-product reaches a critical concentration, the end-product can inhibit an earlier enzyme in the metabolic pathway (stops the enzyme from working)
How are feedback inhibitors beneficial?
They shut down the whole pathway, preventing the formation of additional end-products, which allows the process to control itself
Competitive inhibitors
These inhibitors compete with the substrate to fit into the active site of an enzyme, which they can do because they have a similar structure to that of a substrate
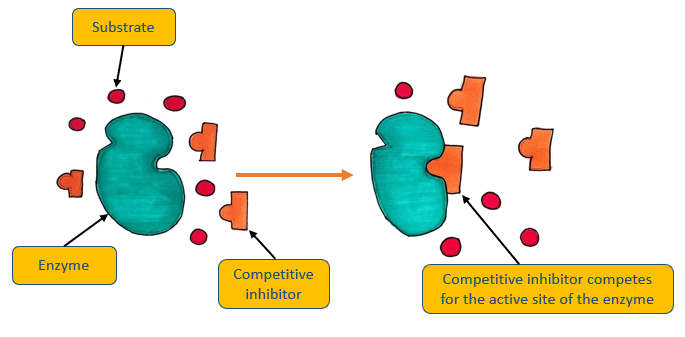
Diagram: competitive inhibitors
Why are competitive inhibitors affected by substrate concentration?
The substrate(s) will ‘win’ the competition to combine with the active site of the enzyme
Non-competitive inhibitors
These inhibitors bind elsewhere on the enzyme (the allosteric site), which causes the active site to change shape, preventing any substrates from binding
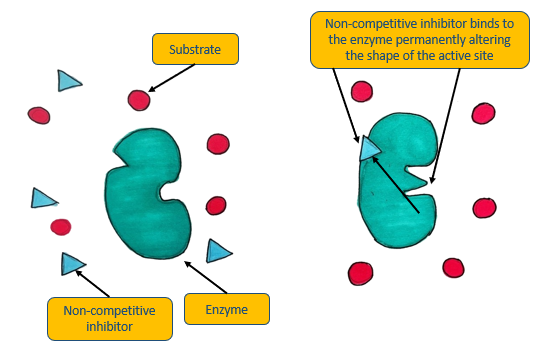
Diagram: non-competitive inhibitors
Why are non-competitive inhibitors unaffected by substrate concentration?
The inhibitor can bind elsewhere on the enzyme (the allosteric site)