conjunctiva
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what are the fxns of the conjunctiva
lubricates the surface of the eye
physical and chemical antimicrobial barrier
participates in diffuse lymphoid tissue system
provides stem cells for corneal epithelial renewal
conjunctiva characteristics
mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eye
thin
vascularized
transparent
continuous with the skin at the margin of the eyelids —> mucocutaneous jxn
continuous with the corneal epithelium in the limbal region
what are the 3 regions of the conjunctiva
palpebral (eyelids)
fornices (folds on itself)
Bulbar (eye)
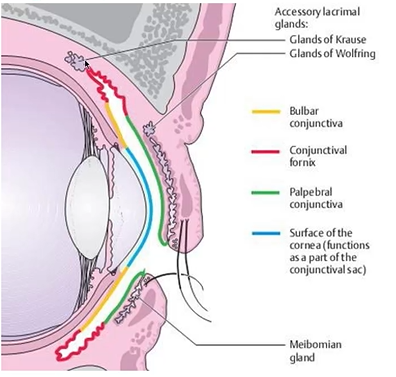
describe the palpebral conjunctiva
tightly bound to the tarsal plate
continuous with the lacrimal drainage system
describe the palpebral conjunctiva zones
marginal zone
transition between skin of eyelid and conjunctiva
tarsal zone
over tarsal glands (meibomian)
thin
immobile - tightly bound down to back of eye
very vascular
orbital zone
thin, losose, horizontal folds
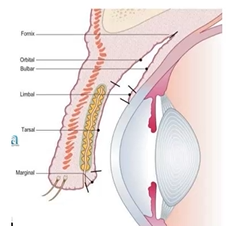
describe the fornices conjunctiva
in contact w fascial sheaths of the levator palebrae superioris and recti msucles - MOBILITY OF EYE
look up and eyelid goes up
bulbar conjunctiva
fewer goblet cells
lies loosely and mobile over underlying tissue
FLUID CAN ACCUMULATE
covers anterior 1/3 of sclera
caruncle
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
modified skin that has:
fine, colorless hairs
sweat and sebaceous galnd
accessory lacrimal glands
well vascularized and innervated
11 in pic
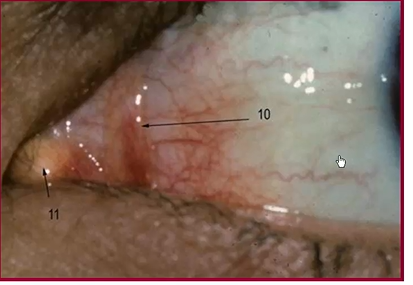
plica semilunaris
fold of conjunctiva lateral to caruncle
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
contains goblet cells
highly vascularized
conjunctiva epithelium
non keratinized stratified
squamous - limbus, palpebral close to lid margin
cuboidal - bulbar
columnar - palpebral and fornices
specializations of conjunctiva epithelium
microvilli w glycocalyx
like cornea - helps to hold mucus layer of tears to surface of eye
surface cells joined by junctional complex
like cornea
what connects the conjunctiva epithelium to a basement membrane
hemidesmosomes
like we saw in cornea
where is the limbal conjunctiva
right next to edge of cornea
what is unique about the limbal conjunctiva
Contains epithelial stem cells that replenish the corneal epithelium
few or no goblet cells
what is the Palisades of Vogt and where is it
in limbal conjunctiva
radially oriented channels (papillae) within stroma of limbal conjunctiva
separated from each other by ridges of epithelium (rete pegs)
irregular connection between epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue
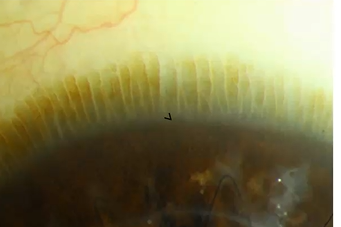
what are palisades
papillae - connective tissue
rete pegs - epithelium
irregular connection between epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue
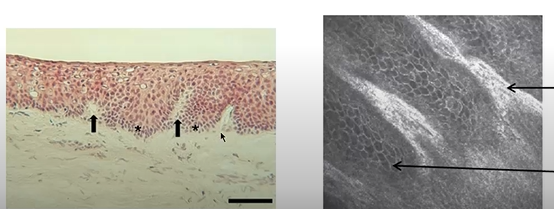
epithelium in fornices
basal epithelium more columnar
numerous goblet cells forming pseudo glands of Henle
goblet cells fxn in conjunctiva
secrete mucin to lubricate the surface of the eye
not evenly distributed on all parts of conjunctiva
more at fornice
substantia propria in conjunctiva layers
two layers
superficial lymphoid
mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils
deep fibrous
glands of Krause
what gives the conjunctiva its anti-infectious capability
the make up of the two layers in the substantia propria
we have mast cells (histamine), lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils in those two layers
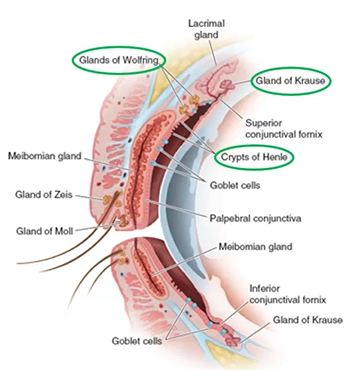
what are glands of the conjunctiva
Glands of Wolfring - accessory lacrimal gland
Gland of Krause - accessory lacrimal gland
Crypts of Henle - have a lot of goblet cells
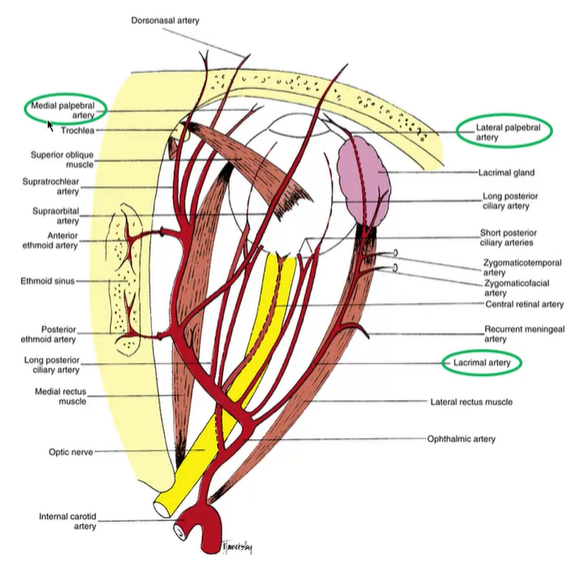
what is the difference between the lateral and medial palpebral artery
ophthalmic artery - lacrimal artery - enters upper and lower eye lid to form lateral palpebral artery
directly off ophthalmic artery - medial palpebral artery
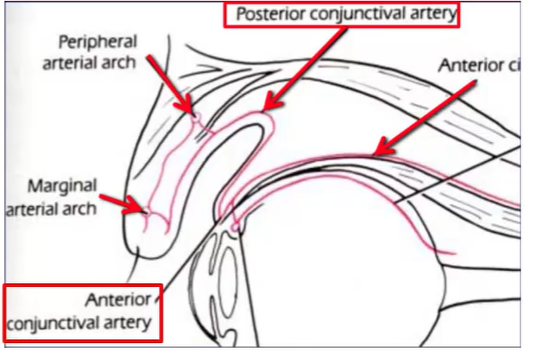
describe the blood supply in the palpebral and fornix conjunctiva
two papebral arterial arcades in both upper and lower eyelid
peripheral arcade - medial and lateral palpebral arteries merge
branch forms posterior conjunctival artery to supply bulbar conjunctiva and fornices
marginal arcade - medial and lateral palpebral arteries merge
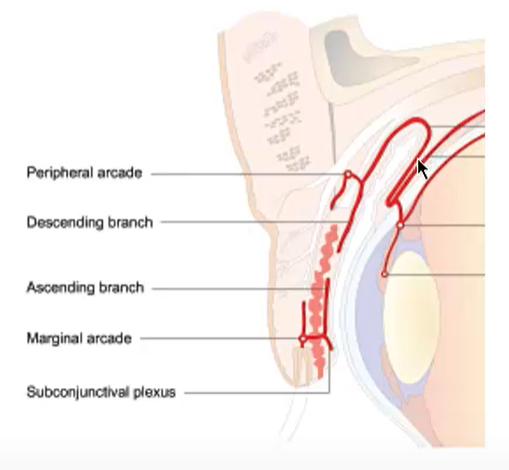
bulbar conjunctiva
posterior conjunctival artery
proceeds toward limbus
at limbus it anastomose with the Anterior conjunctival artery
anterior conjunctival artery
branch of anterior ciliary artery
Together they form the superficial marginal or pericorneal plexus
describe the lymphatic drainage of the eyelids
drains into ½ lymph node regions
lateral - preauricular (superficial parotid) noes
in front of the ear
lateral 2/3 of upper lid
lateral 1/3 of lower lid
medial - submandibular nodes
under jaw
medial 1/3 of upper lid
medial 2/3 of lower lid

describe the innervation of the conjunctiva
superior palpebral and fornix
frontal and lacrimal branches of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve V1
inferior palpebral and fornix
lateral: lacrimal branch of V1
Medial infraorbital nerve of maxillary division of trigeminal nerve V2
what is the sensory innervation for the bulbar conjunctiva
long posterior ciliary nerves - Nasociliary N-V1