Ch-4 Pulmonology
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Pulmonology
The medical specialty that studies the respiratory system.
nas/o
nose
-al
pertaining to
Pharynx
The pharynx is a common passage for inhaled air, exhaled air, and food. Three parts: Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx
Larynx
Voice box- During swallowing, the
larynx pulls up to the
epiglottis, forcing food into
the esophagus
Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) (disease)
Upper respiratory infection, A bacterial or viral infection of the upper
respiratory tract; a head cold. treated with antibiotics.
Trachea
The trachea (windpipe) is a passageway for inhaled and exhaled air. Has a column of C-Shaped Cartilage.
Bronchi
The trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi (the plural of bronchus).
• The primary bronchi enter into the lungs and divide into smaller bronchioles
• Bronchi are supported by rings of cartilage,
similar to the trachea.
Bronchioles
The bronchioles are the smallest bronchi with a
diameter of 1 millimeter or less.
The smooth muscle can contract or relax, to narrow or widen
the bronchial lumen.
Asthma
Hyperreactivity of the bronchi or
bronchioles to an allergen or inhaled
substances
Bronchitis
Acute or chronic infection or inflammation
of the bronchi.
• Acute bronchitis is due to infection.
• Chronic infection is due to smoking or
pollution.
Bronchiectasis
Permanent enlargement and loss of elasticity in the bronchioles; allows secretions to accumulate.
• bronchi/o- = bronchus
• -iectasis = condition of dilation
Bronchi/o- bronchus
Reactive Airway Disease
Blanket term for conditions with reversible
airway narrowing and wheezing.
Trachea, Bronchi, and Bronchiole Diseases
Lungs
The lungs are spongy, air-filled structures
RIGHT Lung
The right lung contains three lobes (divisions) and the
left lung contains two lobes.
• right upper lobe (RUL)
• right middle lobe (RML)
• right lower lobe (RLL)
• left upper lobe (LUL)
• left lower lobe (LLL)
The top of the lung is the apex.
• The base rests on the diaphragm
Abnormal Breathing Sounds (BS) (Disease)
Abnormal Breathing Sounds- Lung sounds that are different from normal and may indicate a lung disease or condition. (LUNG)
Atel/o
Incomplete
Atelectasis
Collapse of all or part of the lung.
• atel/o- = incomplete
• -ectasis = condition of dilation
-ectasis
Condition of dilation
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)(Disease)
Any type of chronic obstructive lung
disease, including chronic bronchitis
and emphysema. (LUNG)
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) (Disease)
Inherited condition caused by a recessive gene;
causes problems with respiratory, digestive, and
sweat secretions. (LUNG)
Cyst/o
Bladder
Fibr/o
Fiber
-osis
Abnormal Condition
Empyeme
Localized pockets of pus that have collected
inside a body cavity of the lung due to a bacterial
infection. (LUNG)
Em-
In
py/o
pus
-ema
Condition
Influenza
Respiratory infection caused by a virus.
• Mild forms cause fever, muscle ache, and
cough for several days.
• Severe forms can be life threatening.
Legionnaire’s disease
Severe, sometimes fatal bacterial infection;
starts with flulike symptoms and progresses to
severe pneumonia and liver and kidney
degradation.
Occupational Lung Disease
Group of disease caused by constant workplace
exposure to inhaled particles.
• Asbestosis
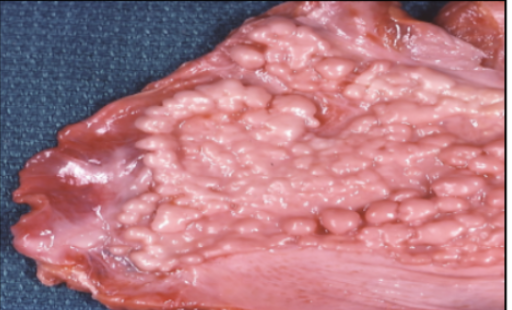
Lung Cancer
Most common among smokers when tar
deposits in the lungs become cancerous and
spread.
Pneumonia
Infection of lobes of the lungs; fluid, white
blood cells, and microorganisms fill passages.
• Bacterial
• Viral
• Double (both lungs)
• Aspiration - inhaled material (food, vomit,
saliva)
Aspir/o
to breath in
Pulmonary Edema
Build up of fluid in the alveoli caused by
left-sided heart failure, chest wall trauma,
or pneumonia.
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) (Disease)
Severe, communicable viral illness that can
be fatal; associated with close contact and
enclosed spaces.
Pulmonary Embolism
Traveling clot or fat globule that lodges in the
lung, blocking blood flow and causing
shortness of breath (SOB); often occurs in
patients on bedrest. Easily trapped in smaller blood vessels, causing possible strokes
Tuberculosis (TB) (Disease)
Communicable disease that is caused by
Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• Causes nodules (= tubercules) in the lungs.
• Waxy coating makes bacterium resistant.
• Requires treated with a 9-month course of
drugs.
Thorax
The thorax is the bony cage between the neck and the diaphragm.The sternum, ribs, and spine
protect the lungs and thoracic
cavity.
–The lungs fill most of the
thoracic cavity
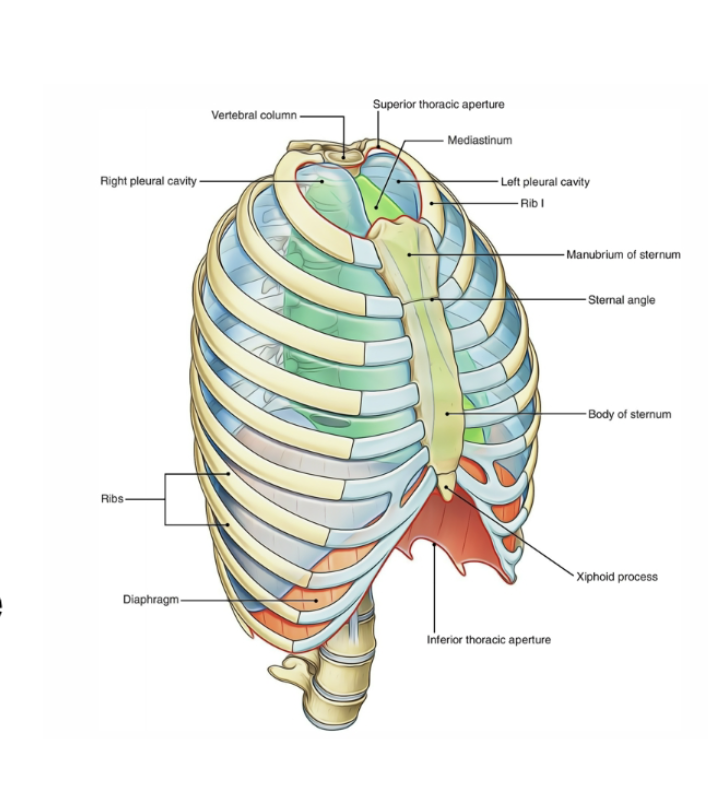
Mediastinum
lies between the lungs
Diaphragm
makes up the
inferior border of the thoracic
cavity.
Hemothorax (Disease)
Blood in the thoracic cavity, usually due to
trauma.
• hem/o- = blood
• -thorax = chest, thorax
(THORAX)
Hem/o
Blood
-thorax
Thorax/Chest
Pleural Effusion (Disease)
Accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural
space due to inflammation or infection.
• effus/o- = flowing out
(THORAX)
effus/o
Flowing out
Pleurisy/Pleuritis (Disease)
Inflammation or infection of the pleura that
causes the two pleural layers to rub against one
another and create a pleural friction rub.
• pleur/o- = lung membrane
• -isy = condition of infection /inflammation.
(THORAX)
pleur/o
lung membrane
-isy
Condition of infection/inflammation
Pneumothorax
Air in the pleural space that causes the lung to
collapse; usually the result of penetrating
trauma (e.g., car accident, fractured rib).
• pneum/o- = air, lung
• -thorax = chest