Mitosis & life cycle
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What processes take place during interphase?
G1, S and G2
What occurs during G1? (3)
The first growth phase
Cellular components (excluding chromosomes) are duplicated
Cell increases in size
What occurs during S stage (2)
Synthesis phase
DNA is replicated in the nucleus (Each of the chromosomes are duplicated by the cell)
What occurs during G2? (5)
Second growth stage
Cell continues to increase in size
Proteins needed for cell division is made
Cell double checks duplicated chromosomes for errors
DNA mutations are checked for (if present apoptosis occurs)
What are checkpoints?
The control mechanisms of the cell cycle
Where is G1 checkpoint and what is checked? (4 checks)
End of G1 phase before entry to S
Cell size
Nutrients
Growth factors
DNA damage
If checks not met , enters G0
When is G2 checkpoint and what is checked? (3 checks)
End of G2 phase, before start of mitotic phase
Cell size
DNA replication
DNA damage
What is G0 and why would cells enter it? (3 reasons)
The phase when a cell permanently or temporarily leaves the cycle
Differentiation (a cell that becomes specialized to carry out a particular function can no longer divide)
DNA of a cell may be damaged
Lymphocytes in an immune response (can re-enter G1)
When is a cell viable to enter mitotic phase? (3)
When it is right size (end of G2)
Full set of DNA that is error free (end of S)
Chromosomes are found along the equator during mitosis
Chromosomes should be attached to spindles and have aligned (spindle assembly checkpoint (metaphase))
Stages of mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
What happens during prophase? (3)
Chromatin fibres condense and coil to form chromosomes that will take up stain to be visible
The nuclear envelopes begins to dissolve/break down
Centrioles start moving to opposite ends of cell, forming spindle fibres
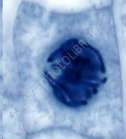
What happens during metaphase? (3)
Chromosomes (each with 2 chromatids) are moved by spindle fibres and align on the metaphase plate
Become attached to spindle by their centromere
At metaphase checkpoint, cell checks all chromosomes are attached to the spindle before mitosis can continue
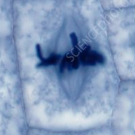
What happens during anaphase? (1)
Centromeres divide, separating each pair of chromatids and pulling them to opposite poles of the side by the shortening/contraction of spindle fibres
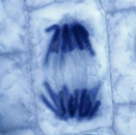
What happens during telophase?
Chromatids reach the poles are now called chromosomes
Two new sets of chromosomes assemble at each pole
Nuclear envelope reforms around them so are now 2 nuclei
Chromosomes uncoil and nucleolus is formed
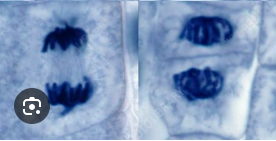
What happens during cytokinesis? (1)
The cell (cytoplasm) divides into 2 separate cells
There are now 2 genetically identical daughter cells
What takes place during the cell cycle? (3)
Interphase (G1, S and G2)
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
What does the cell cycle lead to?
2 genetically identical (daughter) cells
How does cytokinesis occur in animal cells? (2)
A cleavage furrow forms around the middle of the cell
Cytoskeleton pulls cell surface membrane inwards until it is close enough to fuse around the middle, forming 2 cells
How does cytokinesis occur in plant cells?
Forms a cell plate along centre of cell to make cell wall before it lyses
Vesicles from Golgi apparatus begin to assemble in the same place where the metaphase plate was formed
Vesicles fuse with each other and the cell surface membrane, dividing the cell into 2
New sections of the cell wall form along new sections of membrane
What is the significance of mitosis? (2)
Asexual reproduction in plants, animals and fungi
To make genetically identical daughter cells for growth, replacement and repair of tissues
What is mitosis?
Nuclear division that produces 2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells