types of reactions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
1
New cards
oxidation reaction
a loss of electrons, loss of hydrogens, or gain of oxygen
always occurs with a reduction reaction
always occurs with a reduction reaction
2
New cards
Oxidation of primary alcohols
loss of 2 hydrogen atoms to form an aldehyde
3
New cards
oxidation of secondary alcohols
loss of 2 hydrogen atoms to form a ketone
4
New cards
Combustion of alcohols
alcohols can undergo complete combustion in excess oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, heat and light.
5
New cards
substitution reactions
replacing one substituent on a saturated organic compound with another substituent
6
New cards
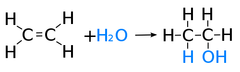
hydration
the addition of water across a double bond, converting alkenes to alkanes and adding alcohol. requires heat and a catalyst
7
New cards
halogenation
the addition of a halogen across a double or triple bond. (eg. adding Cl or Br) converting alkenes to alkanes
8
New cards
hydrohalogenation
the addition of a hydrohalide (HCl or HBr) across a double or triple bond.
9
New cards
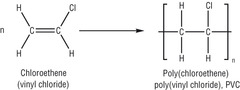
polymerisation
the addition of many monomers to form a polymer. needs a catalyst, heat and high pressure.
10
New cards
condensation reactions
when 2 molecules form to combine a larger molecule and a small by-product such as water. amides and esters are synthesized by condensation reactions
11
New cards
esterification
when esters are synthesised when a carboxylic acid and alcohol react. this reaction is reversible.
12
New cards
amide synthesized
synthesised from carboxylic acids and amines
13
New cards
Hydrogenation
is a reduction reaction. when hydrogen is added to a hydrocarbon chain and converts it from an alkene/ alkyne to an alkane.