Organic Chemistry Exam 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
SP3 hybridized
4 hybrid orbitals
4 sigma bonds
0 Pi bonds
~109.5 bond angle
tetrahedral
SP2 hybridized
3 hybrid orbitals
3 sigma bonds
1 Pi bonds
120 bond angle
trigonal planar
SP
2 hybrid orbitals
2 sigma bonds
2 Pi bonds
180 bond angle
linear
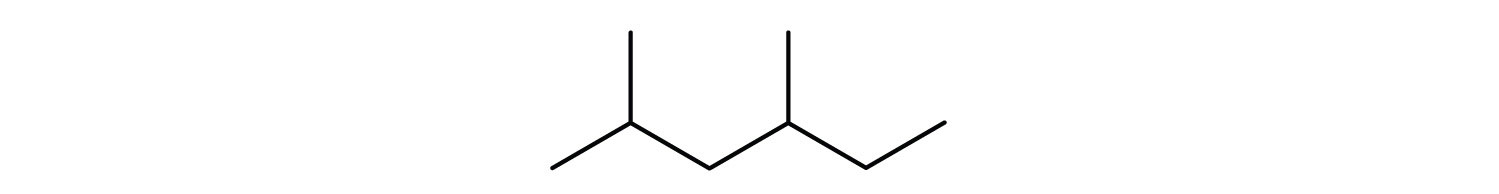
Alkane
Hydrocarbons that do not contain multiple bonds
(-ane)
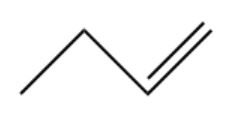
Alkene
Contain at least one C-C double bond
(-ene)
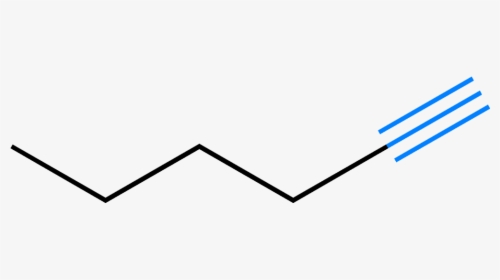
Alkyne
Contain at least one C-C tiple bond
(-yne)
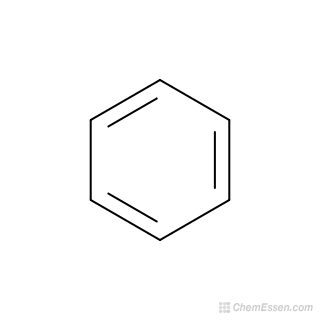
Aromatic
Contain a special type of ring
Ex: Benzene
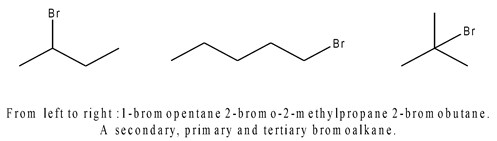
Haloalkane
R-X(Halogen, e.g. F, Cl, Br, I…)
Identify 1°, 2°, and 3° by identifying the number of carbons connected to the carbon connected to the halogen
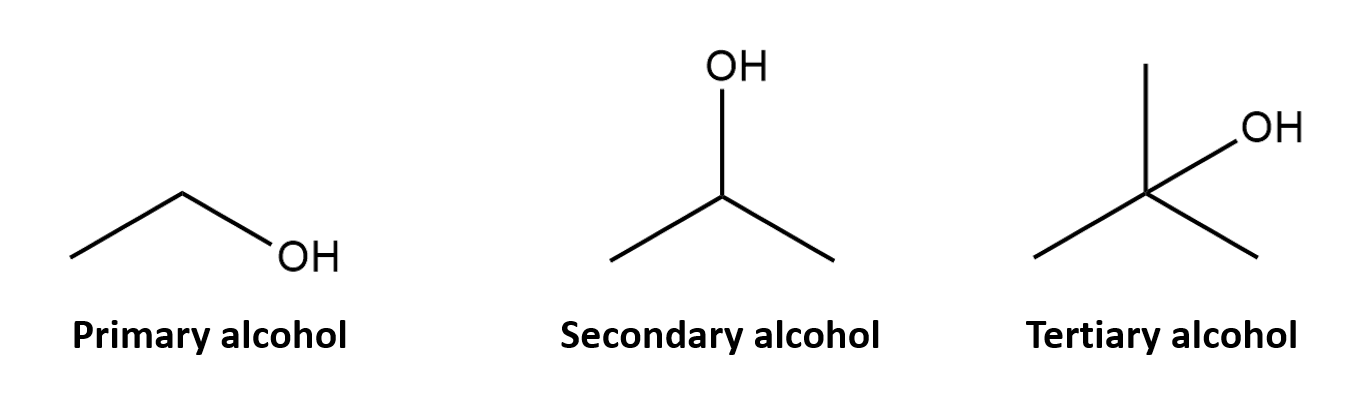
Alcohol
R-OH
(-ol)
H-bonding properties
Identify 1°, 2°, and 3° by identifying the number of carbons connected to the carbon connected to the OH group
Polar
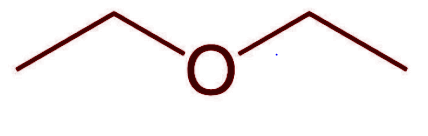
Ether
R-O-R’
“Carbon on ether side of oxygen”
H-bond ACCEPTOR, NOT DONOR
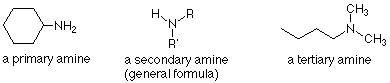
Amine
R-N
(-amine)
Identify 1°, 2°, and 3° by identifying the number of R groups connected to the carbon connected to the nitrogen
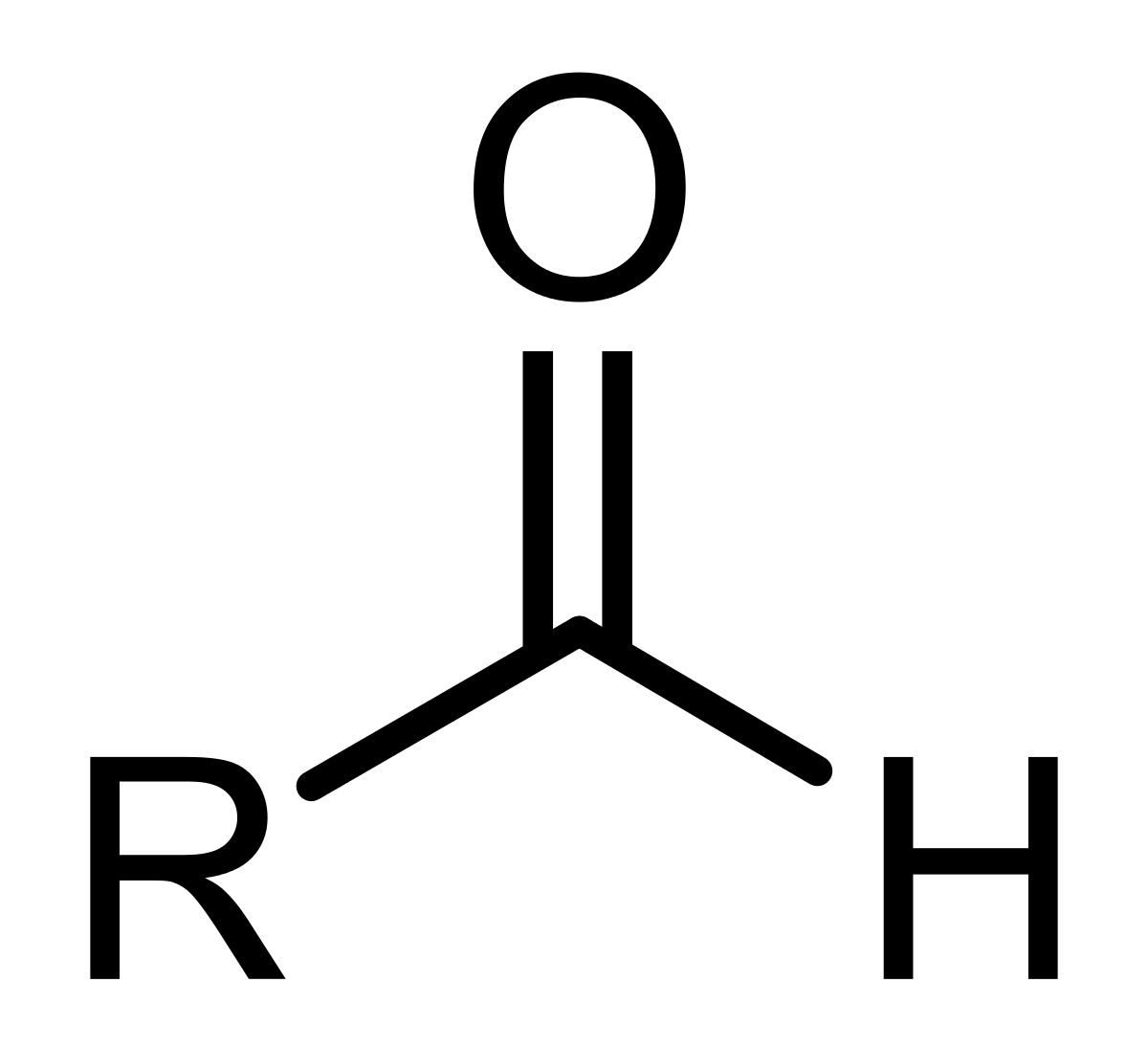
Aldehydes
O double bonded to a C with either an H on either side or 1 H and 1 C.
(-al)
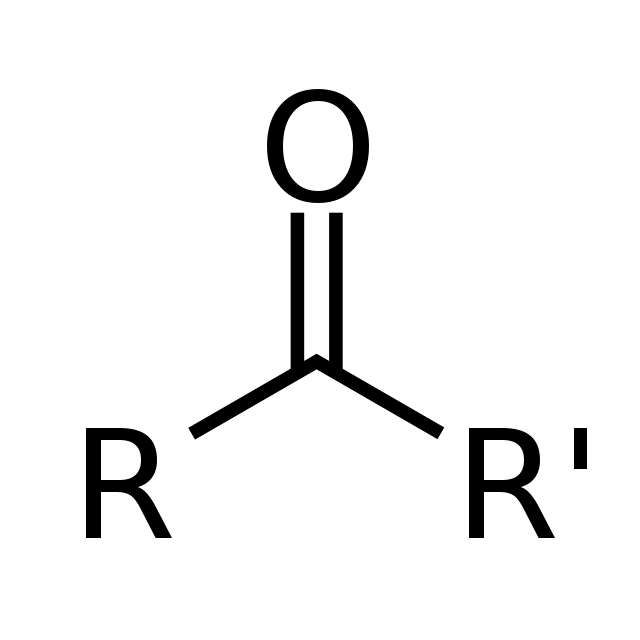
Ketone
O double bonded to a C with a C on either side.
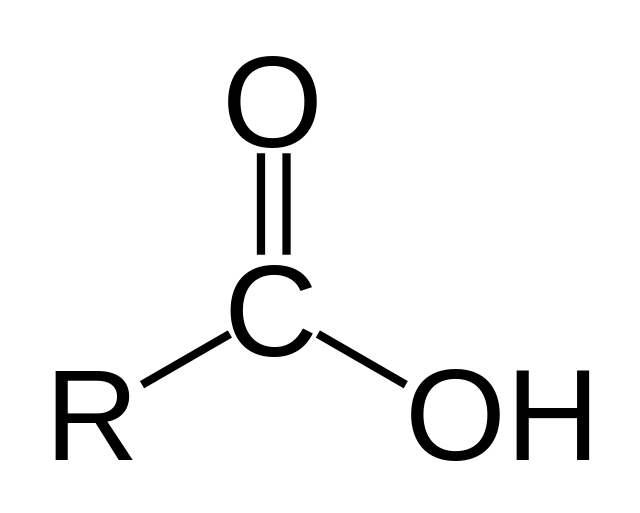
Carboxylic Acid
O double bonded to a C with either a C/H on one side, and an OH on the other
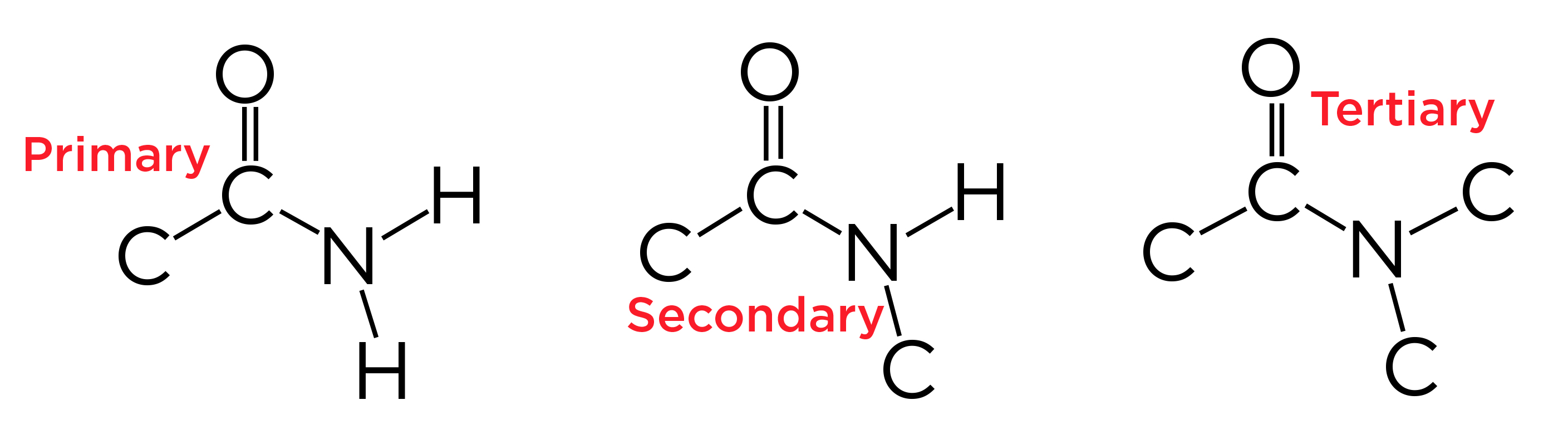
Amide
O double bonded to a C with a C/H on one side and an N group on the other
Identify 1°, 2°, and 3° by identifying the number of R groups connected to the N group
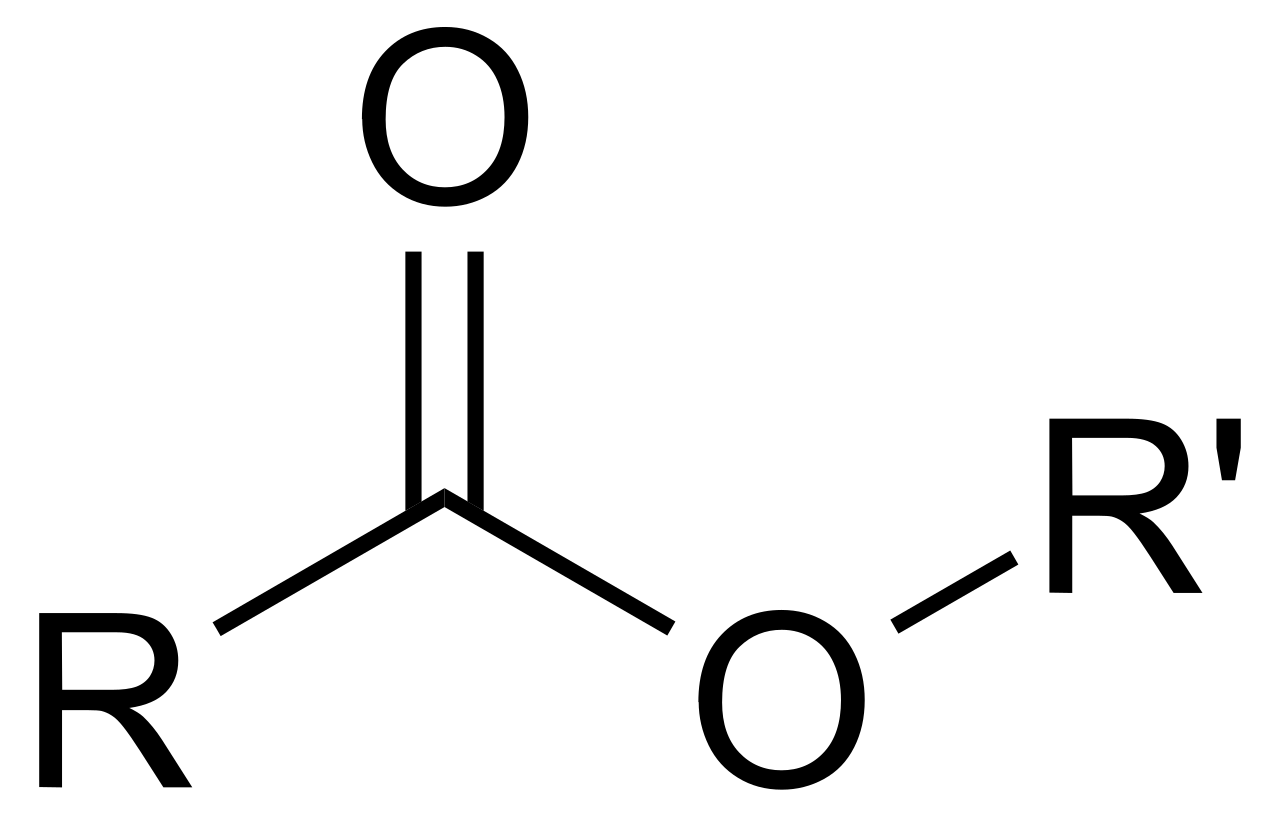
Ester
O double bonded to a C with a R/H on one side and an O-R group on the other
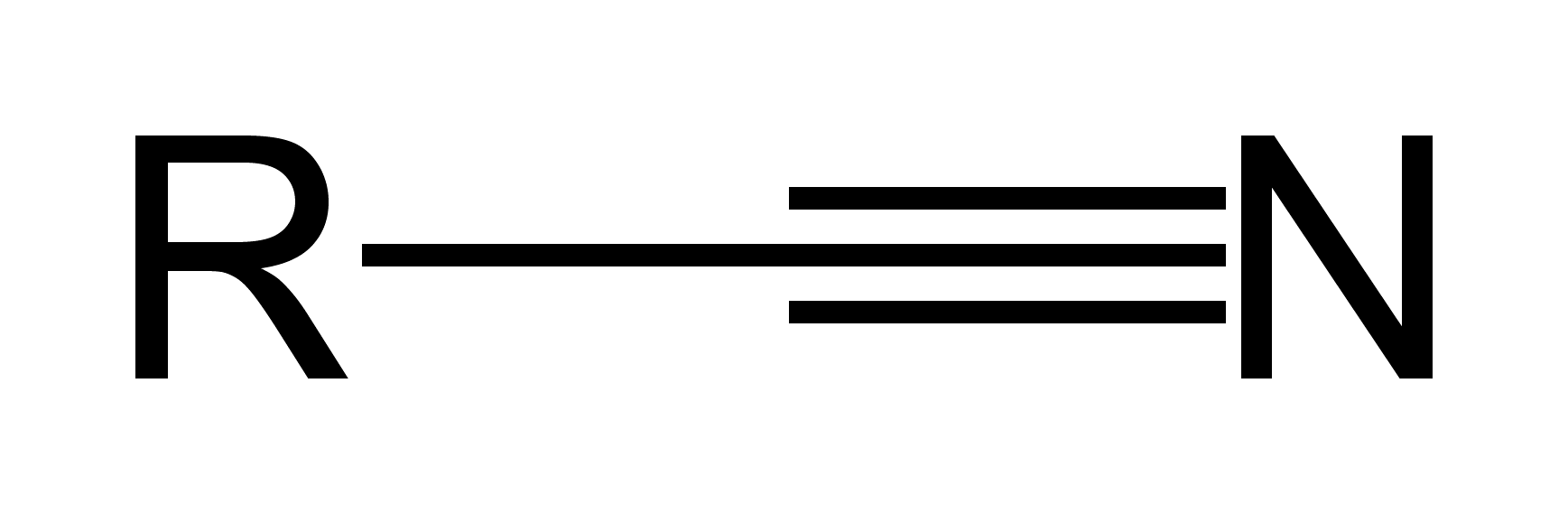
Nitriles
R-C(triple bond)N
(-nitrile)
Functional Groups
Alkene
Alkyne
Aromatic
Alkane
Haloalkane
Alcohols
Ethers
Amines
Aldehydes
Ketones
Carboxylic acids
Amides
Esters
Nitriles
Degree of Unsaturation steps
1) Calculate full saturation CnH(2n+2)
2)
If halogen in present +1H
If O is present do nothing
if N is present -1H
3) (Full saturation - actual formula)/2=u
Degree of unsaturation
Tells you how many Pi bonds you need or if you need a ring structure
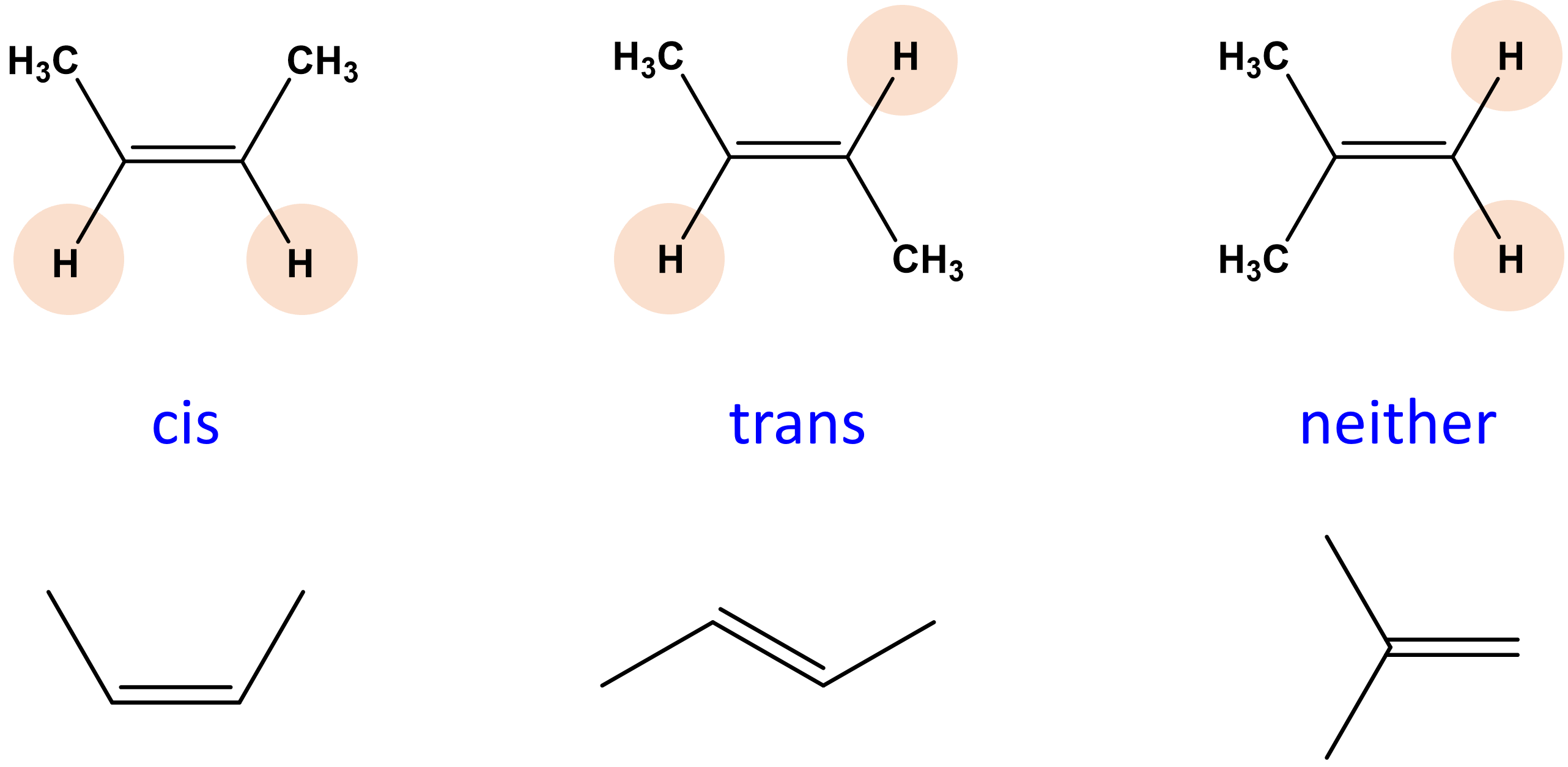
Geometric Isomer
Same connectivity, but different spatial arrangement/orientation
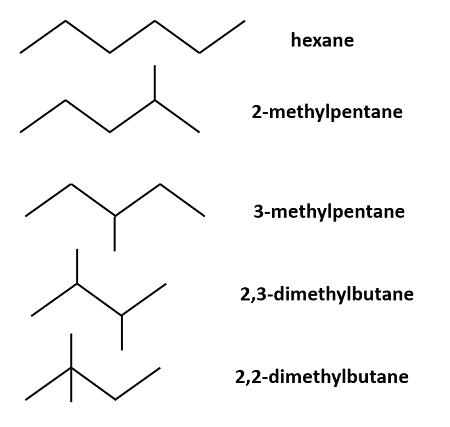
Constitutional isomer
Same formula, but different connectivity
Formal charge equation
= | formal charge | |
= | number of valence electrons | |
= | number of nonbonding valence electrons | |
= | total number of electrons shared in bonds |
IR O-H absorption
3600-3200 cm^-1
Strong and BROAD
IR N-H
3500-3200 cm^-1
medium
IR C-H Sp3
3000-2850 cm^-1
Strong absorption
IR C-H Sp2
3150-3000 cm ^-1
medium
IR C-H Sp
3300
medium
IR C≡C
2250 cm^-1
medium
IR C≡N
2250 cm^-1
medium
IR C=O
1800-1650 (OFTEN ~1700)
STRONG
IR C=C
1650 cm^-1
medium
IR Aromatic/Benzene ring
1600,1500 cm^-1
medium
1500-400 cm^-1 IR region
Fingerprint region on IR
IR methyls like isopropyl/geminal/tertbutyl
1375 cm^-1
“Snake tongue”
IR Long C-H chains
720 cm^-1
“rocking of the chain”
H+ absorption 12-9 ppm
Carboxylic acid (12-10) or Aldehyde(10-9)
H+ absorption 8-6.5 ppm
benzene ring(monosubstituted)/aromatic
H+ absorption 6-4.5 ppm
C=C
H+ absorption ~2.5 ppm
C≡C
H+ absorption 4-2.5 ppm
Methyl group with an N, O, or X on the end
H+ absorption 2.5-1.5 ppm
z=c-c-h z=C, O, N
H+ absorption ~1.7 ppm
Sp C-H bonds
H+ absorption ~1.3 ppm
Sp2 C-H bonds
H+ absorption ~0.9 ppm
Sp3 C-H
What base can fully deprotenate an alkyds/create one
2Na/NH2
2 HX (Hydrohalogenation)
Gives germinal dihalide alkane
2 X2 Halogenation
Tetrahalide. First trans as an intermediate with one equivalent.
H20/H2SO4(HgSO4) Hydration
Gives a ketone. Enol as an intermediate but through tautomerazation becomes ketone.
BH3/H2O2,OH- (Hydroboration Oxidation)
Gives ketone if internal, aldehyde if external. Also starts as enol but undergoes tautomerization.
Acetylide ions react in what kind of mechanism?
Sn2 (substitution unless the alkyl halide is 2° or 3°
2H2/Pd-C (reduction)
With an alkyne will give an alkane.
H2/Lindlar Catalyst
Reacts with alkyne to give a CIS alkene. Reacts with alkene to give SYN alkane.
Na/NH3
Reacts with alkyne to give trans alkene
LiAlH4/2H2O
Reacts with epoxies by opening the rings to make an alcohol