General Lab Practice SOLO 3
1/75
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
total quality management
the management philosophy and approach that focuses on processes and their improvements as the means to satisfy customer needs and requirements
Five Q framework
defines how quality is managed objectively with the scientific method or PDSA cycle
PDSA stands for..
plan systems improvement, the 5 phrases
do a test pilot of the change
study the results
act or implement the change
Quality Laboratory processes (QLP)
include analytical processes and the general policies, practices, and procedures that define how all aspects of the work are done
establishes standard processes for the way things are done
new process implemented through this
Quality control (QC)
emphasizes statistical control procedures
includes non-statistical check procedures
linearity checks
reagent and standard checks
temperature monitoring
new process measured and monitored through this
Quality assessment (QA)
provides broader measures of laboratory performance
turnaround time
specimen identification
patient identification
test utility
new process measured and monitored through this
Quality improvement (QI)
provides a structured problem solving process to help identify the root cause of a problem and a remedy for that problem
the new process is improved through this
Quality planning (QP)
standardizes the remedy
establish measures for performance monitoring
ensure that the performance achieved satisfies quality requirements
document the new QLP
provides the planning to eliminate performance problems
the new process is re-planned through this
total quality control measures
a surveillance process which monitors the performance of
personnel
instrumentation
methods
materials
Quality control program
monitor consistency of performance
detection of nonconformity to standards
documentation is the backbone
Why have a QC program?
necessity
communication
application
Labs should perform an analysis of it’s testing process to…
identify areas of potential error
Inventory of control materials inncludes…
adequate supply
proper ID (lot, dates, initials)
proper storage
parallel or comparison testing
standard materials
determine the concentration of an unknown quantity
assess patient values by means of reference range
verify measurement assignment of values
instrument calibration
control materials
verify the precision or reproducibility of lab procedures
evaluate methodology and instrumentation
closely resembles unknown test specimens
Stable, same matrix, normal and abnormal
Lyophlized controls
reconstituted by the addition of water or a specific diluent solution
assayed controls
come with expected values of concentration, means, and standard deviation from the manufacturer
may be expensive
preferable for a reference method used to measure a particular analyte
unassayed controls
do not have assigned analyte values provided by the manufacturer and are not linked to specific assay systems by labeling or other means
frequency of internal quality control
regulatory requirements
manufacturer instructions
analytical stability
risk of harm
event based (recalibration or maintenance)
dispersion
increased frequency of both high and low outliers
trend
a series of values that continue to increase or decrease above or below the mean over a period of several concecutive days
shift
sudden upward or downward change in values
Which Westgard rules result in a warning?
1-2s
Which westgard rules result in a rejections?
1-3s
2-2
4-1s
10x
R-4s
clinical laboratory improvement act of 1967
federal goverment account for variation in pahses of testing as part of overall quality assessment and assurance requirements
clinical laboratory improvement act of 1988
mandats proficiency testing as a major part of accreditation process
six sigma process
business management strategy that seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and removing the causes of defects and variation
approach to TQM and the performance goal that siz standard deviation should fit with the tolerance limits for the process
lean production
a process management philosophy derived from the toyota production system
focused on creating more value by eliminating wasteful activities
Joint Committee for Traceability in Lab Medicine (JCTLM)
created to meet the requirement for a worldwide platform to promote and give guidance on internationally recognized equivalence of measurements in lab medicine and traceability to appropriate measurement standards
ISO 9000
set of four standards enacted to ensure quality management and assessment in manufacturing and service industries
type 1 reagent water
most pure
reagent grade water
of highest quality and is used in test methodologies where minimum interference and maximum precision and accuracy are needed
pre-filters, activated carbon, submicron filter, UV oxidation, reverse osmosis and ion exchange all used
special reagent water
may require different preparation that reagent grade water according to intended us, such as sterility specification for tissue of organ culture, nucleic acid content for DNA testing, metal content for trace metal analysis
type II reagent water
used in most areas of the lab
water for lab dishwashers and autoclaves; purified to contain only low levels of organics, inorganics, and aprticulate matter so it does not leave residue on glassware or contaminate material in autoclave
type III reagent water
used to make type I and II water
might be used in qualitative areas such as urinalysis
standard of purity
many grades of chemicals are available, it is essential to understand which grade or type should be used for a specific chemical method
analytical reagent grade chemicals
contains a high degree of purity in accordance to the American Chemical Society specifications
used often in the preparation of solutions in the clinical laboratory
recommended for quantitative or qualitative analysis
ultra pure reagents
may be used in some clinical laboratories
additional processing makes them suitable for special procedures
labeled according to used: spectrograde, nanograde, or HPLC pure
Do not use chemicals labeled what?
purified, practical, technical, or commercial
primary standards
highly purified chemicals that are weighed or measured to produce a solution with an exact concentration
used for calibration of definitive methods
secondary standards
solutions whose concentration cannot be prepared by weighing the solute and dissolving a known amount into a volume of solution
its values are determines by repeated analyses, using a reference method calibrated by primary standard
National Institute of Standards and Technology
produces and provides standard reference materals for purchase
Standard reference materials and certified reference materials
have values determined by high-quality analysis and the chemical composition is certified
used for calibration of an instrument, verification of a measurement mehtod or assignment of values to materials
To contain pipette
calibrated for the total volume
must be washed out comepltely with the diluting fluid to obtain the desired amount
holds exactly the volume indicated on its side
to deliver pipette
calibrated from the volume delivered
can measure and deliver the indicated volume into another container
blow-out pipette
last drop should be dispensed
continuous etched ring or two small rings near bulb
self-draining pipette
allow the contents to drain freely
tip should make contact with side of the container
transfer pipette
designed to transfer a known volume of liquid
volumetric pipette
calibrated to deliver accurately a fixed volume of a dillute aqueous solution
TD
drain by gravity
bubble-like enlargement of stem
ostwald-folin pipette
specific type of transfer pipette
blow-out
buld closer to delivery tip
TD
viscous fluids
measuring/graduated pipette
designed to deliver various volumes by means of multiple graduations uniformly along its length
Mohr pipette
calibrated between two marks on the stem
straight with multiple graduations
capable of dispensing various volumes
TD
drain by gravity
serologic pipette
graduated marks down to the tip
TD
etched rings: blow out
micropipettes
used for measurements of microliter volumes
TC
proper use requires rinsing with final solution
gravimetric pipette calibration
a specific amount of water is pipetted, the weight of the water is determined and proportional to the volume
volumetric pipette calibration
a specific amount of dye is pipetted into a specific volume of water
the absorbance of the solution will determine the solume of the pipette
desiccants
drying agents that absorb water from air or other material
used to provide dry environment for chemical materials
absorption of water changes color indicator from blue to pink
CLSI standard of centrifugation of blood
RCF of 1000-2000 x g for 5-15 minutes
relative centrifugal force
the amount of force required to separate two phases of a solution
Relative centrifugal force calculation
1.118 × 10-5 x r x rpm²
types of centrifuges
horzontal-head or swinging bucket
fixed-angle or angle-head
ultracentrifuges or high-speed
centrifuge maintenance
time check
temeprature check
tachometer or stroboscopic light
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
used in calculating the acid or base to salt ratio required to establich a desired pH in a buffer solution
pH=pK+log([A-}(salt)/[HA](acid))
constant systematic error
error that is always in one direction and has the same magnitude regardless of the snample concentration
interference experiment
random error
due to chance
1 in every 20 tests falls out of ±2SD
replication experiment
proportional systematic error
has the same percentage of the concentration being measured so the absolute mangitude increases as the concentration increases
recovery experiment
ethical issues in the lab
confidentiality
allocation of resources
code of conduct
conflict of interest
publishing
specificity
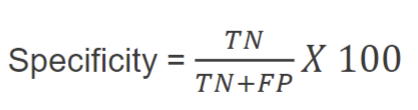
sensitivity
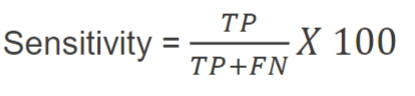
positive predictive prevalence

negative predictive prevalence
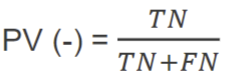
standard deviation
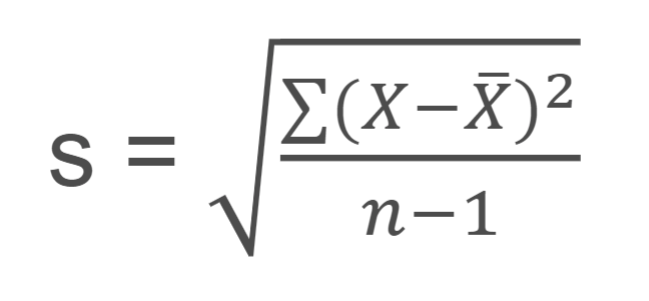
coefficient of variation
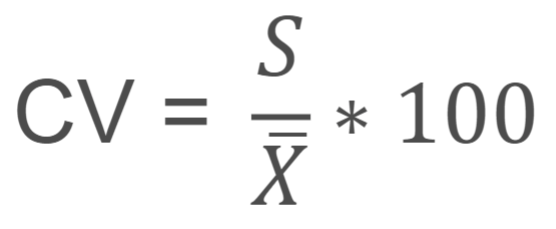
molarity
number of mols/numbers of liters
mols
mass/GMW
normality
Molarity x Valence
Equivalence
GMW/valence