Posterior Dental Anatomy
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
University of Honolulu
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
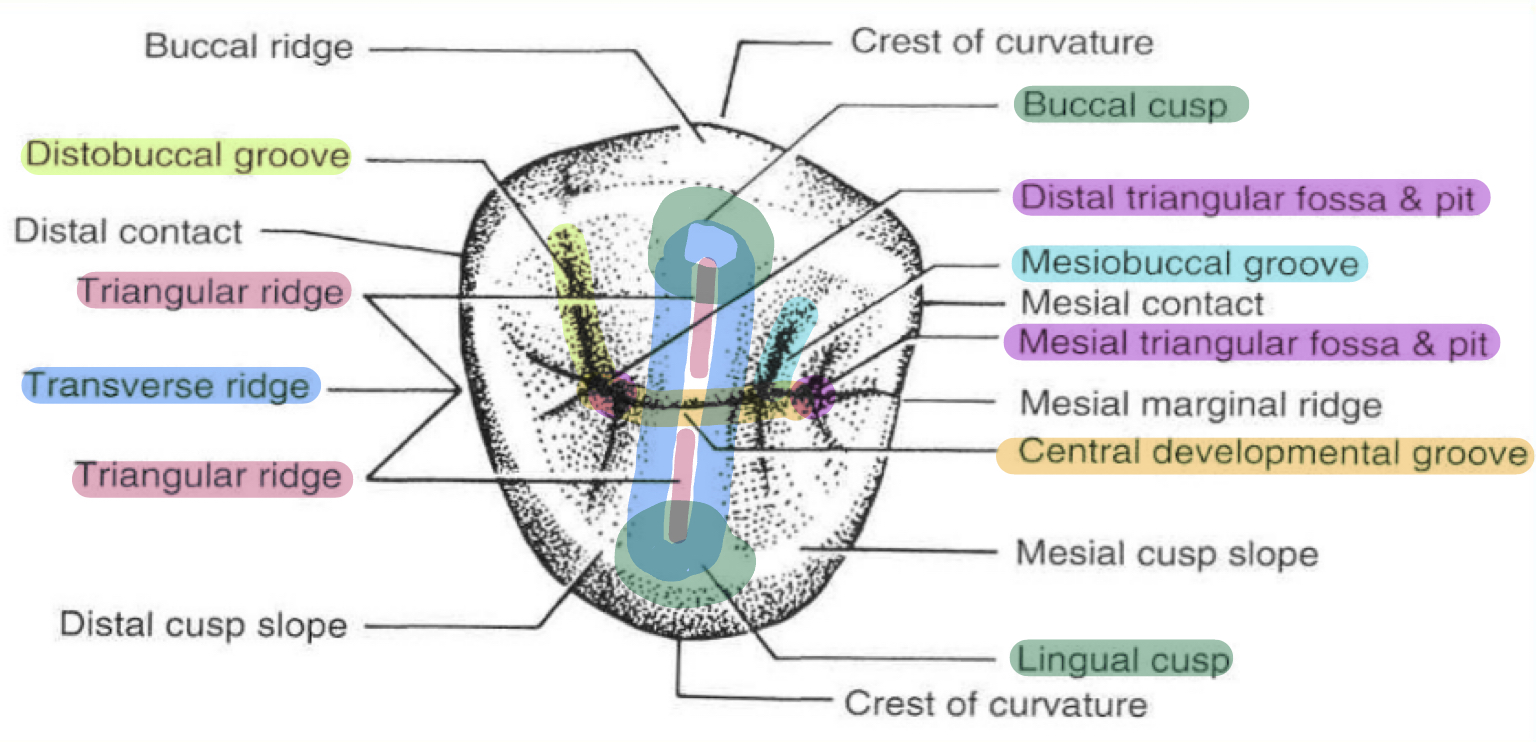
Heights of contour
Premolars: Facially on cervical 3rd, Lingually on middle 3rd
Molars: Facially on gingival 3rd, Lingually on middle 3rd
Name all posterior contacts from facial
Mesial: Middle 3rd, close to junction of occlusal and middle (more occlusal)
except mandibular 1st premolar, has distal contact more occlusal
Distal: Middle 3rd
Are premolars succedaneous or nonsuccedaneous? why?
Yes, they replace the primary molar’s position (primary dentition has no premolar)
Premolar facial cusp tip vs Cusp ridge
All cusp tips mesial to mid-root axis except maxillary 1st premolar which is distal
All cusp ridges are distally longer, except maxillary 1st molar which has mesial side longer
Ridges correspond to the opposite of tips, if tip is mesial, then the distal is inevitably going to be longer
Posterior Teeth Marginal Mesial vs Distal Ridge more occlusal (occlusal height)
All mesial ridges are more occlusal except the mandibular 1st premolar which has a more occlusal distal marginal ridge
MD vs. FL width
All teeth in dentition are FL wider than ML, except:
Mandibular molars
Maxillary central and lateral incisors
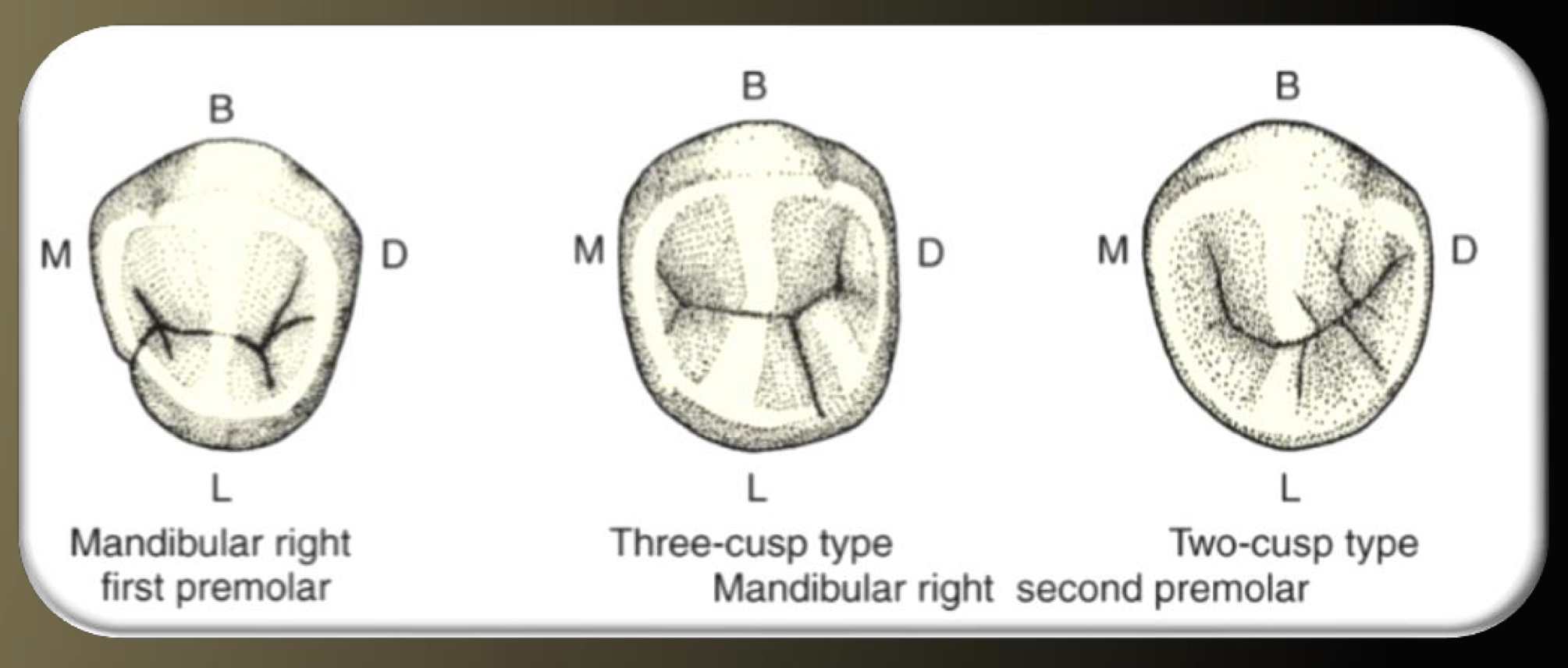
How many cusps in pre-molars? Any exceptions?
Most have 2 cusps except mandibular 2nd premolar can have 3
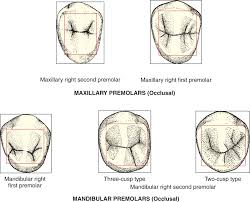
Crown shapes of maxillary pre-molars
Facially a pentagon like the canines
1st are longer, sharper cusps than second and more prominent buccal ridge
Maxillary Proximally a trapezoid
Premolar Occlusal shape
Maxillary 1st: oblong, asymmetrical, bent mesially on lingual
Maxillary 2nd: oblong, more symmetrical, oval
Mandibular 1st: square/diamond
Mandibular 2nd: round oblong oval (2cusp) or square (3cusp)
Note: most lingual cusps converge towards mesial
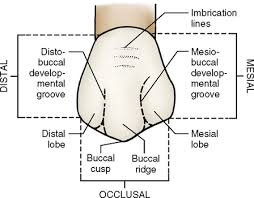
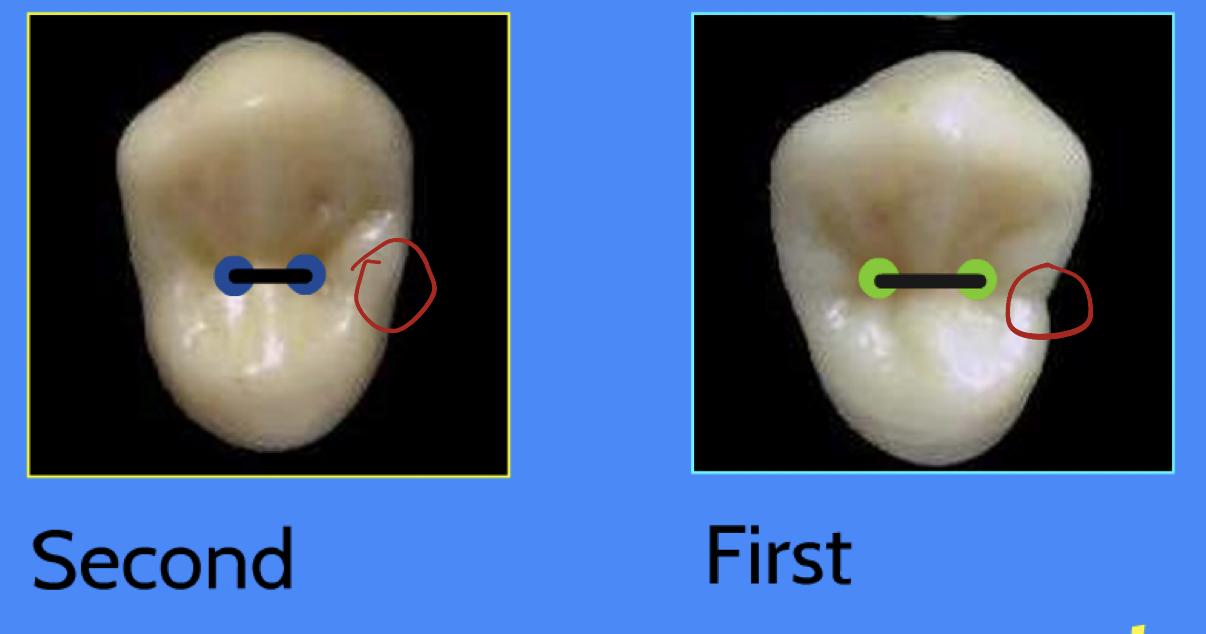
M and D contact areas from occlusal view (Maxillary Premolars)
Maxillary 1st: distal more B than mesial
Maxillary 2nd: mesial more B than distal
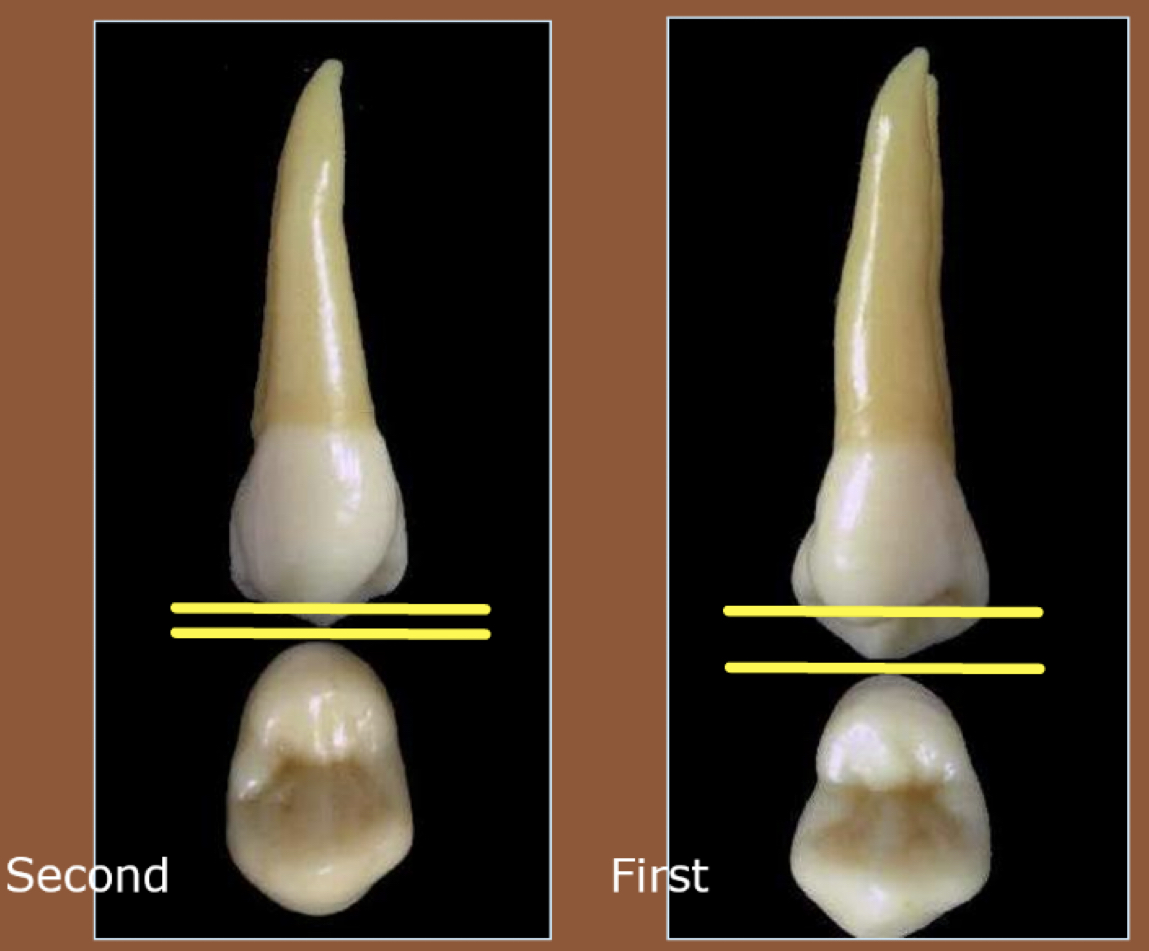
Crown tilt of posterior teeth (L inclination)
Maxillary: crown aligned with root
Mandibular premolars: Both tilted but 1st is noticeably more tilted towards lingual
need to tilt drill to not perforate side
Mandibular molars: tilted towards lingual
Developmental Lobes in Premolars, exceptions?
Similar to anterior teeth
3 buccal and 1 lingual/palatal lobe = 4 lobes
except mandibular 2nd: usually (54%) has 2 lingual = 5 lobes
2 buccal depressions
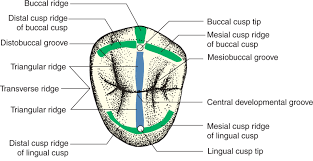
Premolar Ridges
2 triangular ridges join to form a transverse ridge in all premolars except the mandibular 2nd premolar, which can have 3 ridges and no transverse ridges
Maxillary 1st premolar Root form
2 roots (67%)
root bifurcation (separation) happens at apical third
palatal root shorter than buccal
usually cannot see palatal root from facial
root relatively straight and taper towards palatal
mesial depression is deeper and goes from bifurcation to MMR Groove
CEJ more curved on Mesial
Maxillary 2nd premolar Root form
1 root
distal depression deeper
depression does not reach crown
root longer than maxillary 1st premolar
CEJ more curved on mesial
Maxillary 1st Premolar KEY FEATURES
usually 2 roots
Only tooth with mesial marginal ridge (MMR) Groove
only tooth that has root depression deeper on mesial
mesial crown concavity
mesial root depression resulting from bifurcation can be the cause of periodontal disease
Only premolar with cusp tip towards distal and mesial cusp ridge longer
Maxillary 2nd Premolar KEY FEATURES
longer root than 1st maxillary premolar
looks like a skinnier/symmetrical version of the 1st but no MMR groove
Eruption order
max 1st premolar: 10-11yoa
max 2nd premolar and man 1st: 10-12yoa
mand 2nd premolar: 11-12
max 1st > max2nd = mand1st > mand2nd
Maxillary pre-molars: Occlusal anatomy
Both have mesiobuccal/palatal and distobuccal/palatal grooves, a central groove and two triangular fossa&pit
maxillary first has a longer central groove and thus a greater space between the fossas&pits
maxillary central has grooves on mesial meet the marginal ridge
Lingual vs Buccal Cusp Height in Premolars
Lingual always shorter
Crown shapes of Mandibular Premolars
Facially a pentagon like the canines
1st are longer, sharper cusps than second. Overall both less prominent than maxillary buccal ridges
2nd has wider crown (proximal view)
may have developmental notches (Bumps from cusp to cusp)
2nd may have two cusps on lingual, and thus a lingual ridge to separate the two cusps
2nd has less lingual convergence than 1st
Proximally a rhomboid
Mandibular 1st Pre-molar Root Form
straight or curves distal (58%)
single root maybe be divided in apical third
depression on distal side deeper than mesial
Mandibular 2nd Pre-molar Root Form
root wider than 1st
no mesial depression, distal depression
Maxillary Premolar Lingual Cusps bend towards?
mesial
Mandibular 1st Pre-molar KEY FEATURES
mesiolingual groove (69%)
distal marginal ridge more occlusal (mesial more cervical)
most pronounced transversal ridge
Tilts more towards lingual
root may divide in apical third
lingual cusp smaller not functional
Mandibular 2nd pre-molar KEY FEATURES
-2 or 3 cusps
-lingual groove in 3 cusp
Only tooth with No depression on distal
Mandibular pre-molars: Occlusal anatomy
1st pre-molar: “little y” shape
diamond outline
mesiolingual groove
2nd premolar (2 cusp type): “U” shape
curved central groove
triangular ridge on lingual is smaller
distal triangular fossa larger (has more supplemental grooves)
round outline
2nd premolar (3-cusp-type): “big Y” shape
3rd cusp is distolingual
has a central fossa
buccal cusp larger, lingual cusps much smaller than on first
3 triangular ridges no transverse ridge (none are across from each other)
lingual groove off the bottom of the Y
more squared outline, wider on lingual
3rd cusp may be non-functional
What is the largest tooth type in each arch
what is the largest tooth overall in permanent dentition?
Molars
Maxillary 1st molar
Are molars succedaneous?
No, they occupy a space that is empty in primary dentition
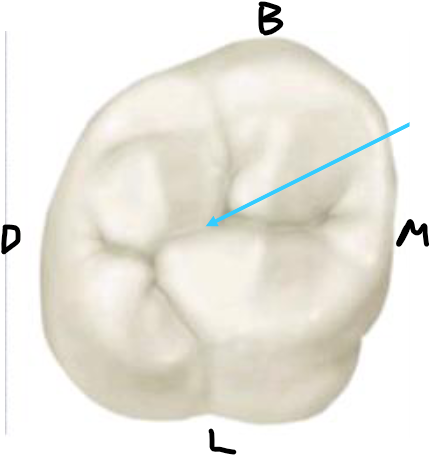
What tooth type has the broadest Occlusal surface
The molars do, which makes sense as they do most mastication and grinding
Which tooth type has the shortest crowns CO (Cervical-Occlusal)
Molars have the shortest CO
M vs D crown height on all molars
distal height is always lower
Crown shapes of Maxillary molars
Maxillary 1st:
occlusal: parallelogram/rhomboid with more acute angles being MB and DL (pointing towards mesial)
facial: trapezoid with buccal ridge separating MB and DB cusps up to middle 3rd.
MB cusp longer and lingual cusps show slightly
lingual: trapezoid, lingual ridge reaches middle 3rd,
ML taller than DL
proximal: 2 cusps visible mesial (+carabelli if present), 4 cusps visible on distal (+ carabelli if present)
MMR longer and more occclusal than D, therefore you can see MMR from distal but not DMR from mesial
Maxillary 2nd:
occlusal:
4 cusp: twisted parallelogram, less squared, same but more acute angles than 1st, tapers from B-L more than 1st
3 cusp: heart shaped, tapers BL
facial: trapezoid
buccal groove is shorter than 1st (doesn’t reach middle 3rd)
MB is considerably taller than DB (almost the same on 1st)
lingual: trapezoid
2 visible cusps on 4 cusp type, lingual groove does not reach middle 3rd
1 visible cusp on 3-cusp type, so no lingual groove
proximal: trapezoid shape, same as 1st but
no carabelli cusp, DL cusp may be missing if it is a 3 cusp type
M view has little occlusal visible, distal view has more visible
Crown shapes of Mandibular molars
Mandibular 1st:
occlusal: pentagonal (MD widest), tapers towards lingual
facial: trapezoidal crown
MB cusp longer than DB
DB sharper
ML tallest cusp and DL can be seen from this view
M outline straight, D convex
lingual:
Lingual cusp tips sharper than buccal tips
L cusps are nearly equal in size and hide B cusps
proximal: rhomboid
tilted towards lingual
cannot see much occlusal surface from mesial, can see more from distal
Mandibular 2nd:
occlusal: oblong rectangle, tapers less to B-L than 1st
M outline straight, D convex
facial: more pronounced buccal cervical ridge
tapers less toward cervical than 1st because of absence of D cusp
MB taller and wider than DB
ML and DL cusps can be seen
1B groove that may end in a pit
lingual:
can’t see B cusps
CEJ straight
proximal:
less wide FL than 1st
lingual tilt
cant see much occlusal surface from mesial
can see some occlusal surface from distal
Root shapes of Maxillary Molars
Maxillary 1st:
FACIAL AND LINGUAL VIEWS
CEJ less curved on distal
3 roots: palatal, MB, DB ( tallest to shortest, same order as cusp height)
roots are twice as long as crown
MB and DB roots have plier form and shape is as wide as crown
palatal root has longitudinal depression
4 canals (2MB, 1DB, 1 palatal)
PROXIMAL VIEW
MB root wider than DB and extends beyond crown
has longitudinal depression
Palatal root looks like banana also extends beyond crown
root trunk (trifurcation) at cervical and middle junction
DB root thinner than MB and does not extend past crown
no depression, has concavity close to CEJ on distal
Maxillary 2nd: similar to 1st with some differences
FACIAL AND LINGUAL VIEWS
3 roots and 4 canals, but lower incidence of 2nd MB canal
MB and DB roots more parallel and less separated
Roots rarely extend beyond crown
root trunk longer than 1st maxillary molar
more distal bend
PROXIMAL VIEW
root trunk longer than 1st maxillary molar
Root shapes of Mandibular Molars
1st:
FACIAL AND LINGUAL VIEWS
2 roots (D shorter, 3 canals (2M,1D)
roots twice as long as crown, highest root/crown ratio
roots narrower on lingual
root bifurcation closer to CEJ than in maxillary
root trunk is longer on lingual
longitudinal depression between root bifurcation reaches crown
Both roots are usually distally inclined
M root curves towards mesial for first half and then deflects distally for second half
D root straighter
CEJ straight or irregular and more occlusal on lingual
PROXIMAL VIEW
M longer and wider than D root
deep depression on M root
2nd:
FACIAL AND LINGUAL VIEWS
2 roots, 3 canals ( M taller and wider)
root trunk very close to CEJ but longer than in 1st
M and D roots more parallel and close together than 1st
roots sharper than on 1st
CEJ nearly straight
longitudinal depression from furcation to crown
PROXIMAL VIEW
less broad M root than 1st
M root depression
M root visible from distal
Maxillary Molars Occlusal Anatomy
1st:
4 cusps: ML, MB, DB, DL (largest/tallest to smallest/shortest)
Primary cusp triangle are the biggest 3 cusps (ML,MB,DB)
May have nonfunctioning Cusp/depression of Carabelli between ML and DL
Transverse ridge (ML and MB) and Oblique ridge (DB and MB), Lone Triangular ridge (DL)
4 fossa: Central, DL, M, D (deepest to shallowest)
5 developmental grooves (make a Gemini looking sideways I) : Transverse groove central groove, buccal groove, distal oblique groove, lingual (D) groove
Stuart Groove ay be present as continuation of buccal ridge into MB cusp
5th cusp Carabelli groove: may be present
2nd: 4-cusps type (2/3) follows the same morphology as 1st with some differences:
More variation in DL cusp size
smaller oblique ridge
no 5th cusp of carbelli
many more supplemental grooves and pits, especially in oblique ridge
2nd: 3-cusp type (1/3): similar morphology as 1st but missing features
DL cusp missing = 3 cusps total
3 grooves ( horizontal Y with arms towards mesial): central groove, buccal groove and transverse groove
no oblique ridge
Mandibular Molars Occlusal Anatomy
1st:
5 well-developed cusps: ML, DL, MB, DB, D (longest to shortest)
MB is still the largest/bulkiest overall
2 Transverse ridges: MB&ML and DB&DL
D cusp is a lone triangular ridge
3 fossae: Central fossa, mesial fossa, distal fossa (largest to smallest)
4 developmental grooves (slingshot shape): central groove, Lingual groove, MB groove, DB groove
2nd: very similar to 1st but D cusp missing
4 cusps: ML, DL, MB, ML (longest to shortest)
no D triangular ridge
2 transverse ridges: MB&DB and DB&DL
3 fossa: central, M, D
3 developmental grooves (cross shape): Central, Buccal and Lingual
Occlusal view of contacts for molars
Mesial contact on 1st are more buccal than distal contact
mesial contact for 2nd molar match the 1st molar’s distal, but the distal contact for the 2nd molar cannot be predicted due to the morphology of the 3rd molar being so varied
3 longest max roots in order
maxillary canine
maxillary 2nd premolar
maxillary 1st molar
Maxillary 3rd Molars vs Mandibular 1st molars
Both
greatest morphologic variance
bulbous crowns, short roots
Max
20% of population never develop 1 or more
shortest of all permanent teeth
long root trunks
may resemble 1st or 2nd maxillary molars
smaller than 1st and 2nd maxillary molars
lots of supplemental grooves
small occlusal surface
1-8 cusps
Mand
shortest of all mandibular teeth
root fused
may resemble 1st or 2nd mandibular molars
Mandibular 1st molar KEY FEATURES
largest MD dimension of any tooth
largest root/crown ratio of any tooth
Curve of Wilson
even though ML and DL cusps are taller on mandibular molars, the teeth are positioned on the arch in a way that they tilt towards lingual, therefore the MB cusp looks taller when the tooth is in the mouth
Mesial FL ridge vs Distal FL ridge length
mesial is always longer than distal, therefore it makes less sharp V
except mandibular 2nd premolar that has shorter mesial FL ridge
Maxillary 1st Molar KEY FEATURES
root concavity on distal