Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
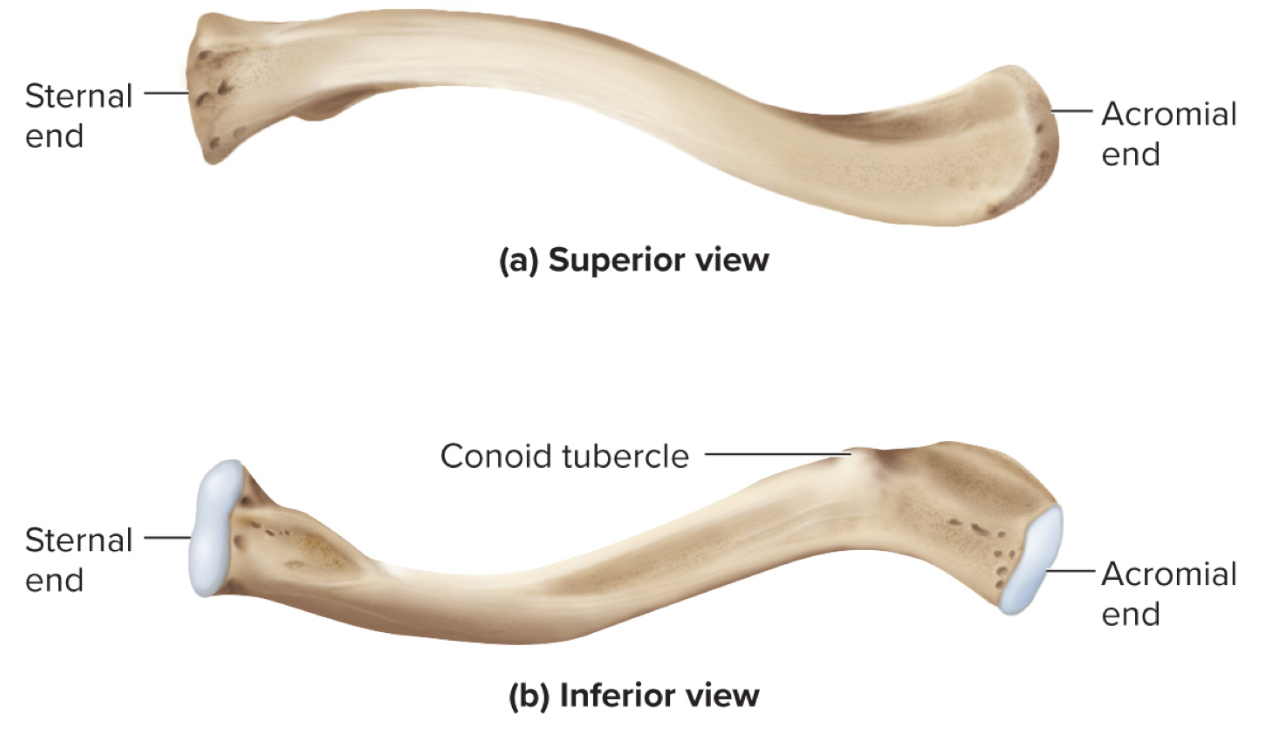
What are the parts of the clavicle?
sternal end
acromial end
conoid tubercle
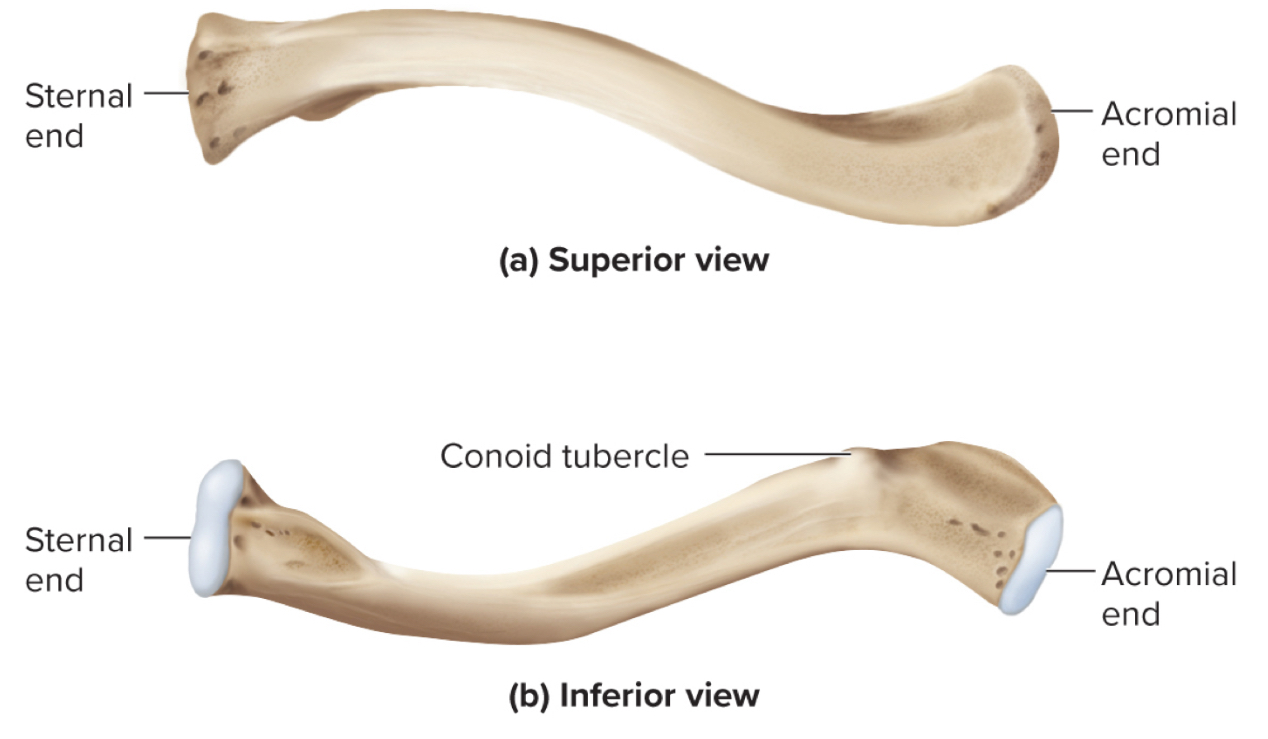
Sternal end of the clavicle:
site where the clavicle articulates with the sternum
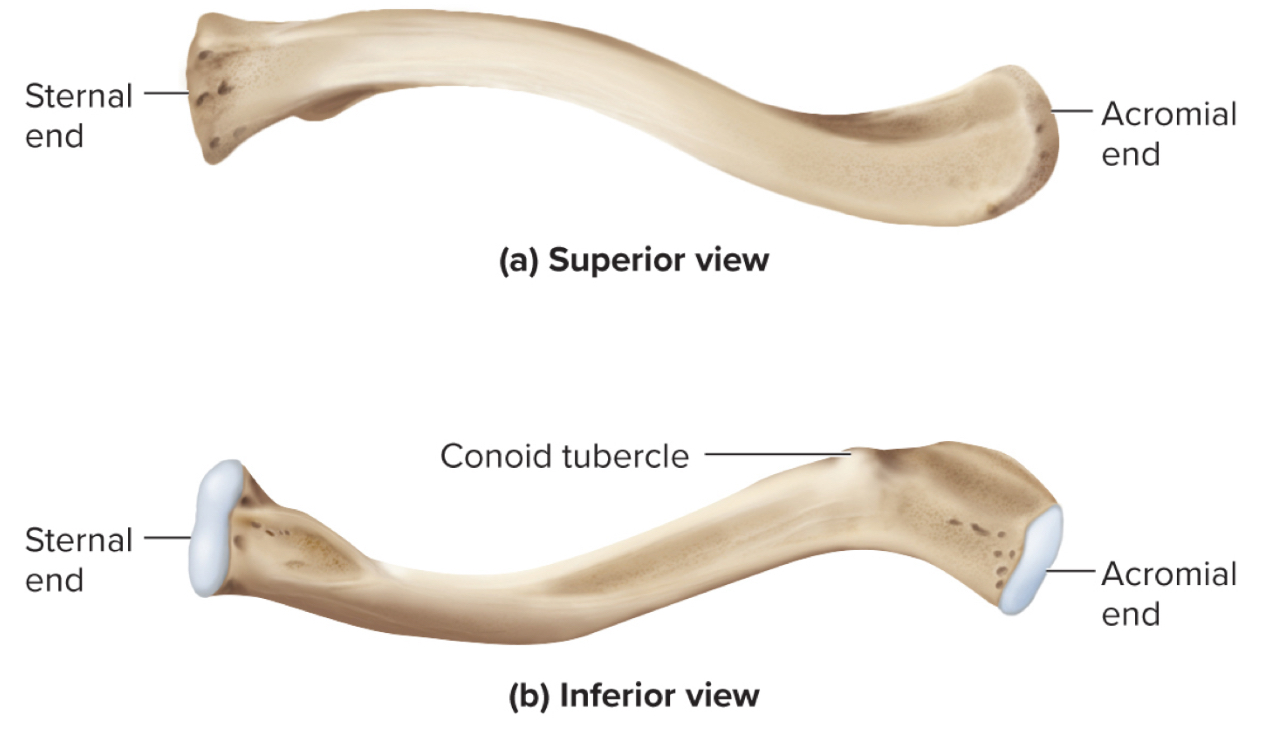
Acromial end of the clavicle:
site where the clavicle articuates with the acromion of the shoulder
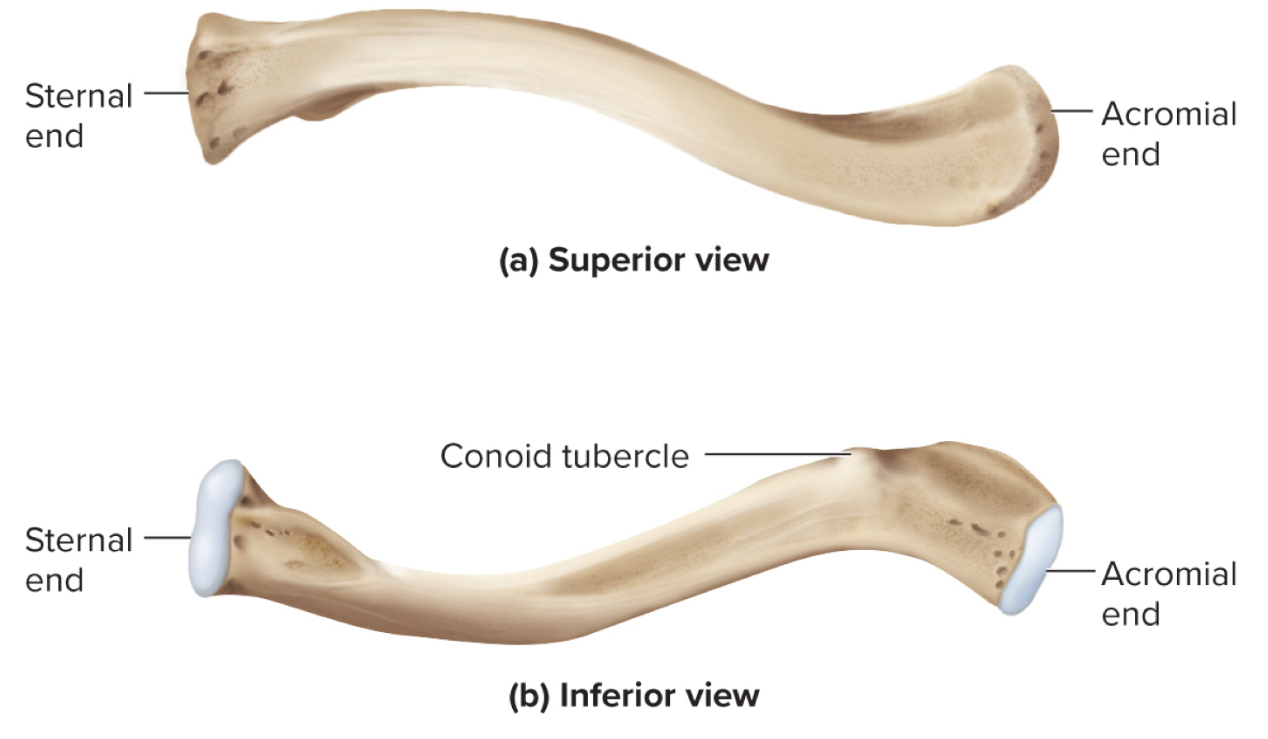
Conoid Tubercle of the clavicle:
site of muscle attachments
What is the most commonly broken bone in the body?
the clavicle
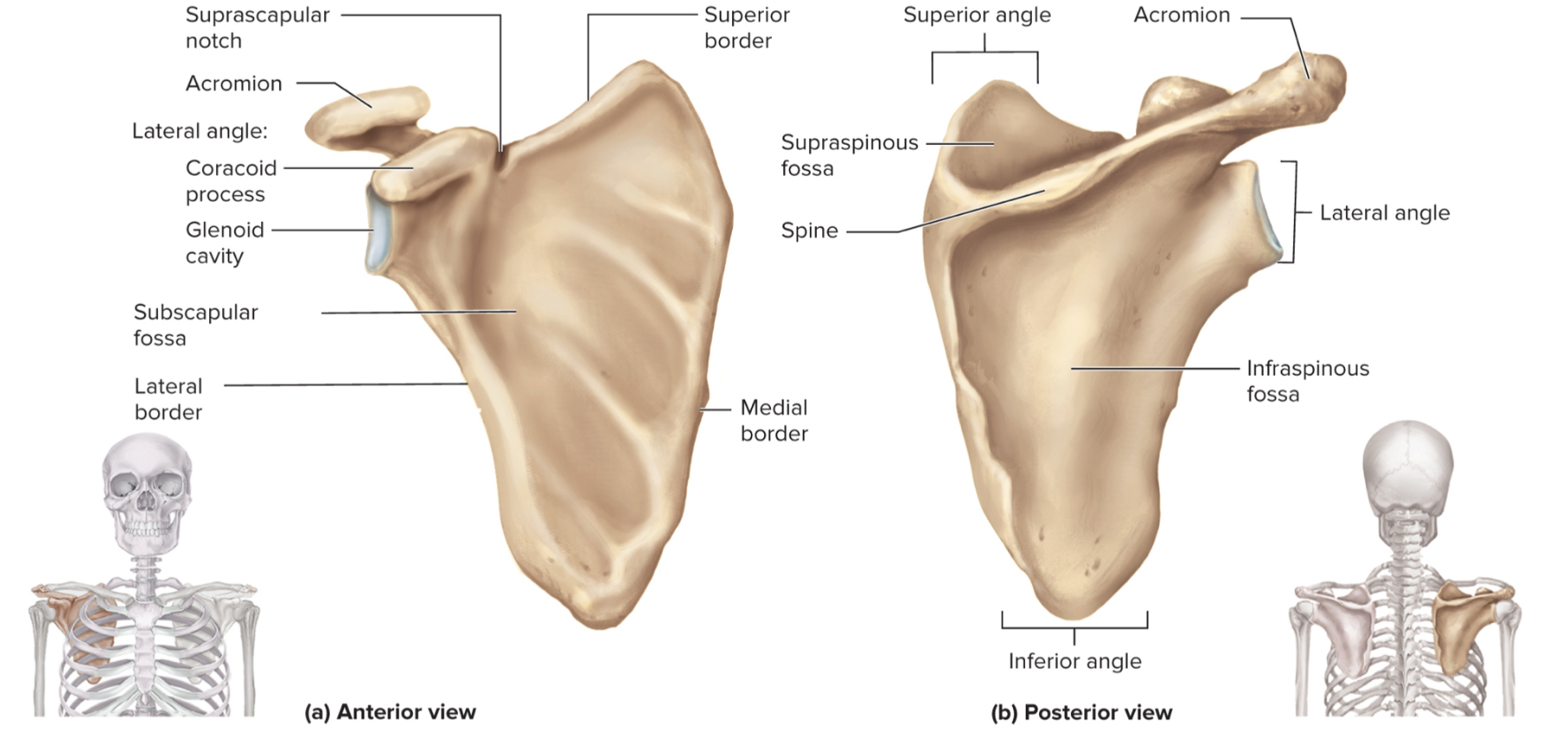
What are the parts of the scapula?
acromion
glenoid cavity
suprascapular notch
coracoid process
supraspinous fossa
infraspinous fossa
subscapular fossa
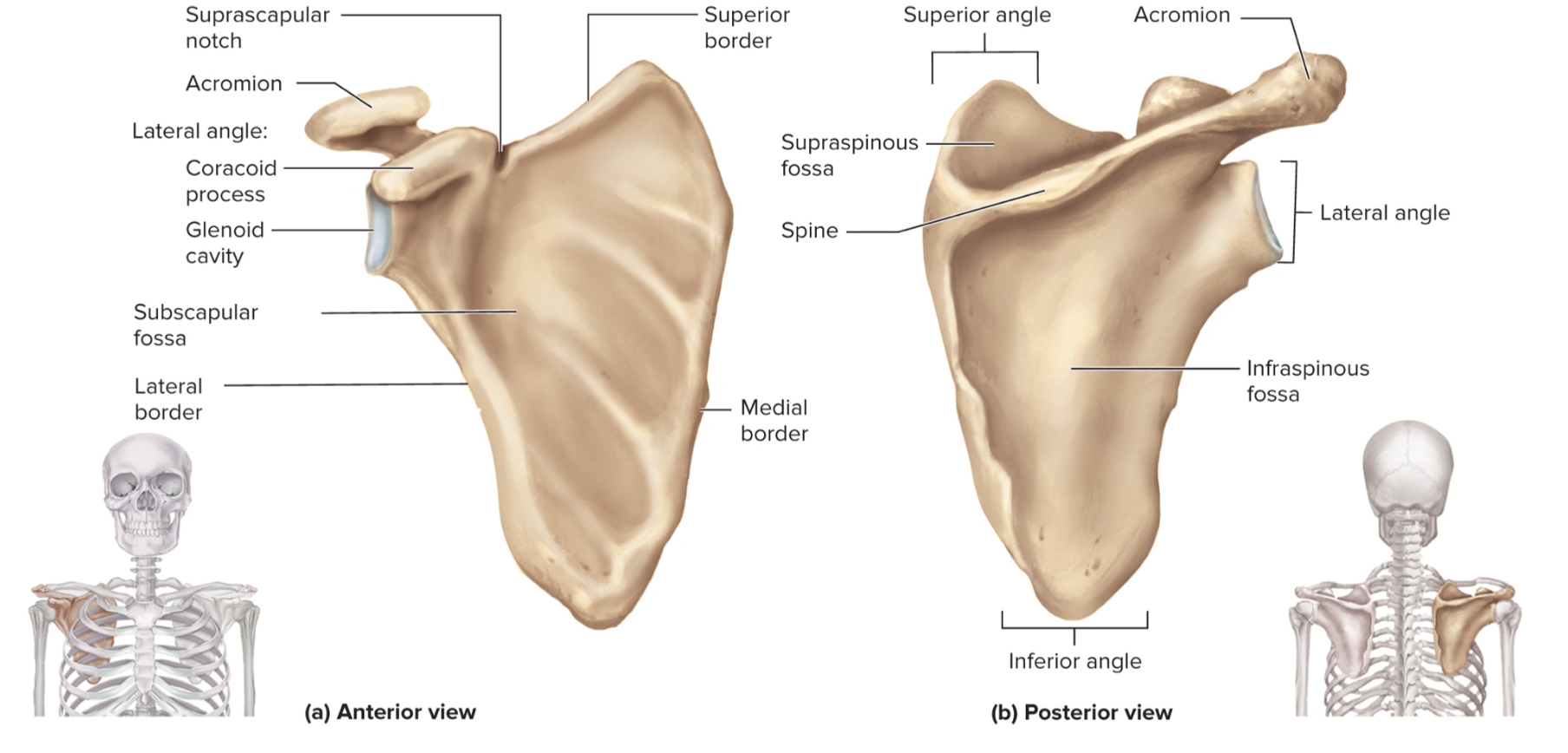
What is the acromion of the scapula?
upper portion of scapular that forms the acromioclavicular joint with the clavicle
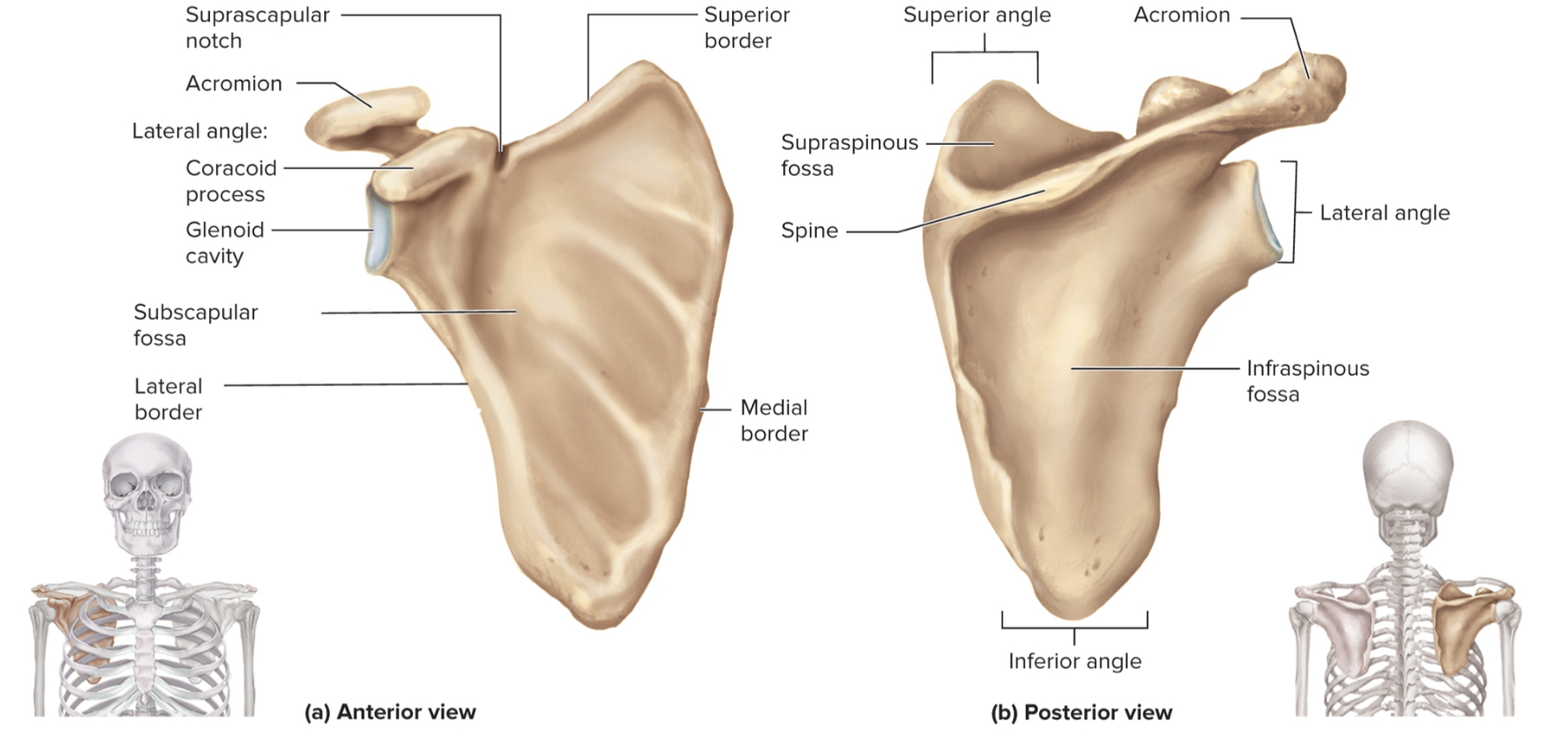
What is the glenoid cavity of the scapula?
fossa (shallow depression) where the humerus attaches to from shoulder joint
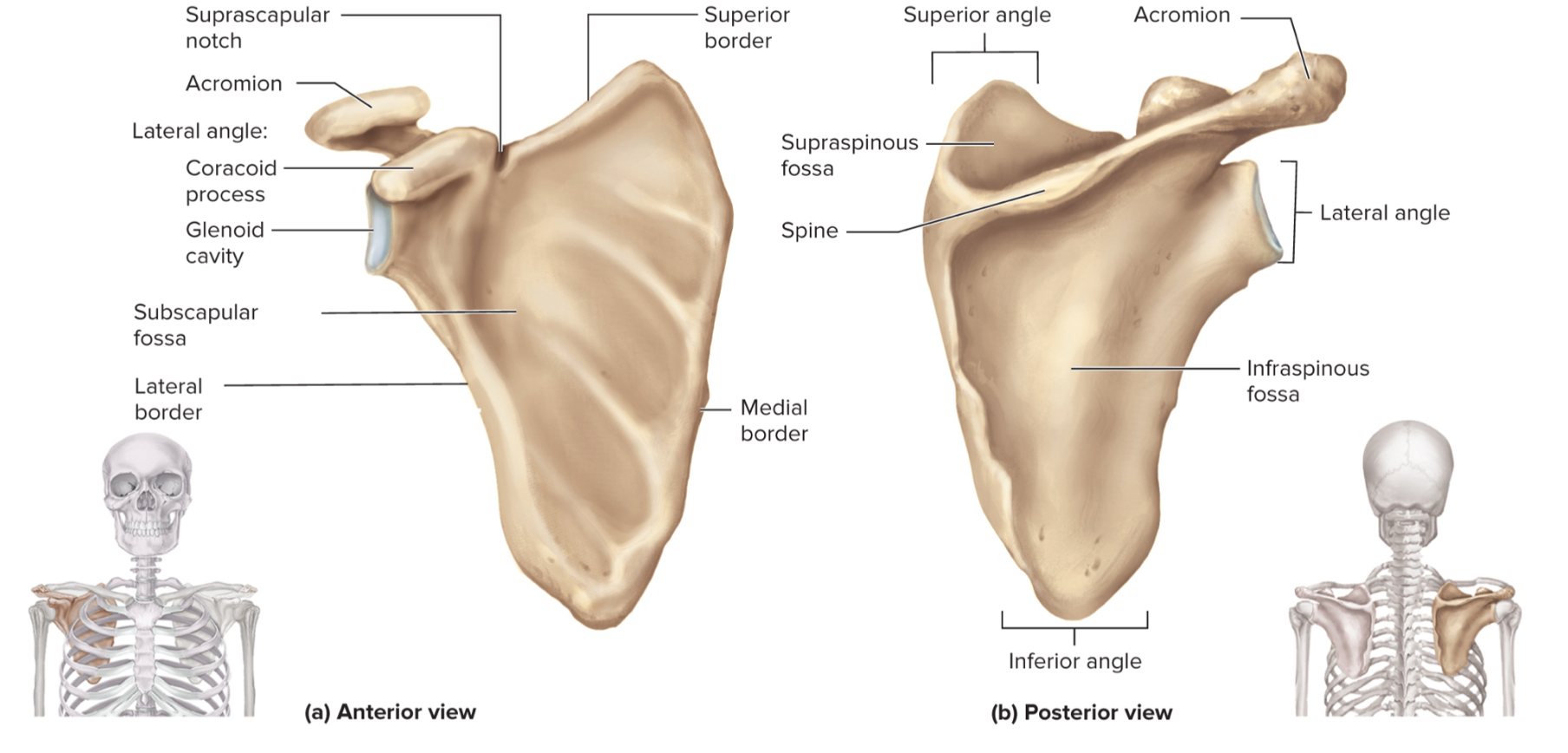
What is the suprascapular notch of the scapula?
a notch on the top edge of the scapula that allows the suprascapular nerve to pass through
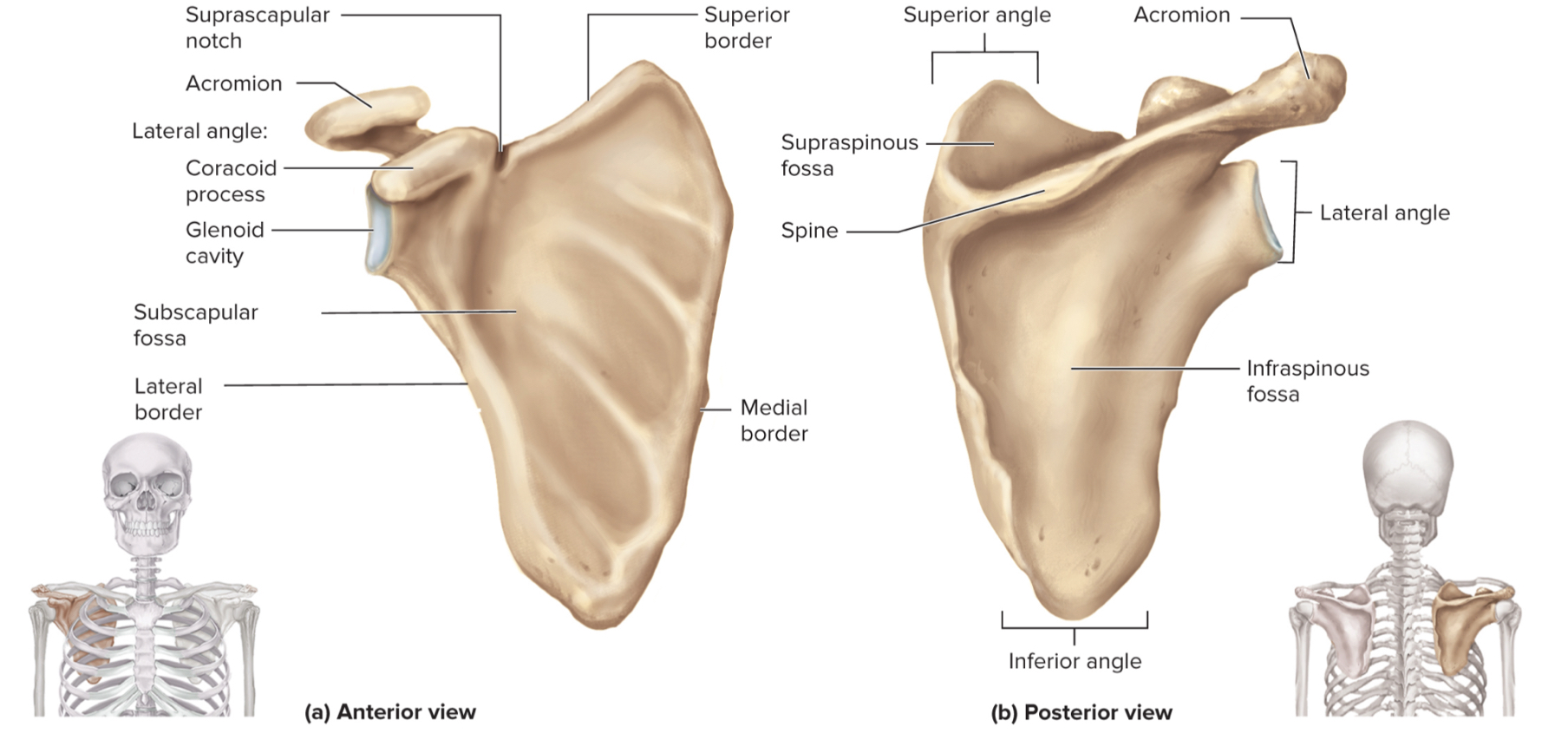
What is the coracoid process of the scapula?
a projection on the (anterior) front of the scapula that serves as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments of the shoulder
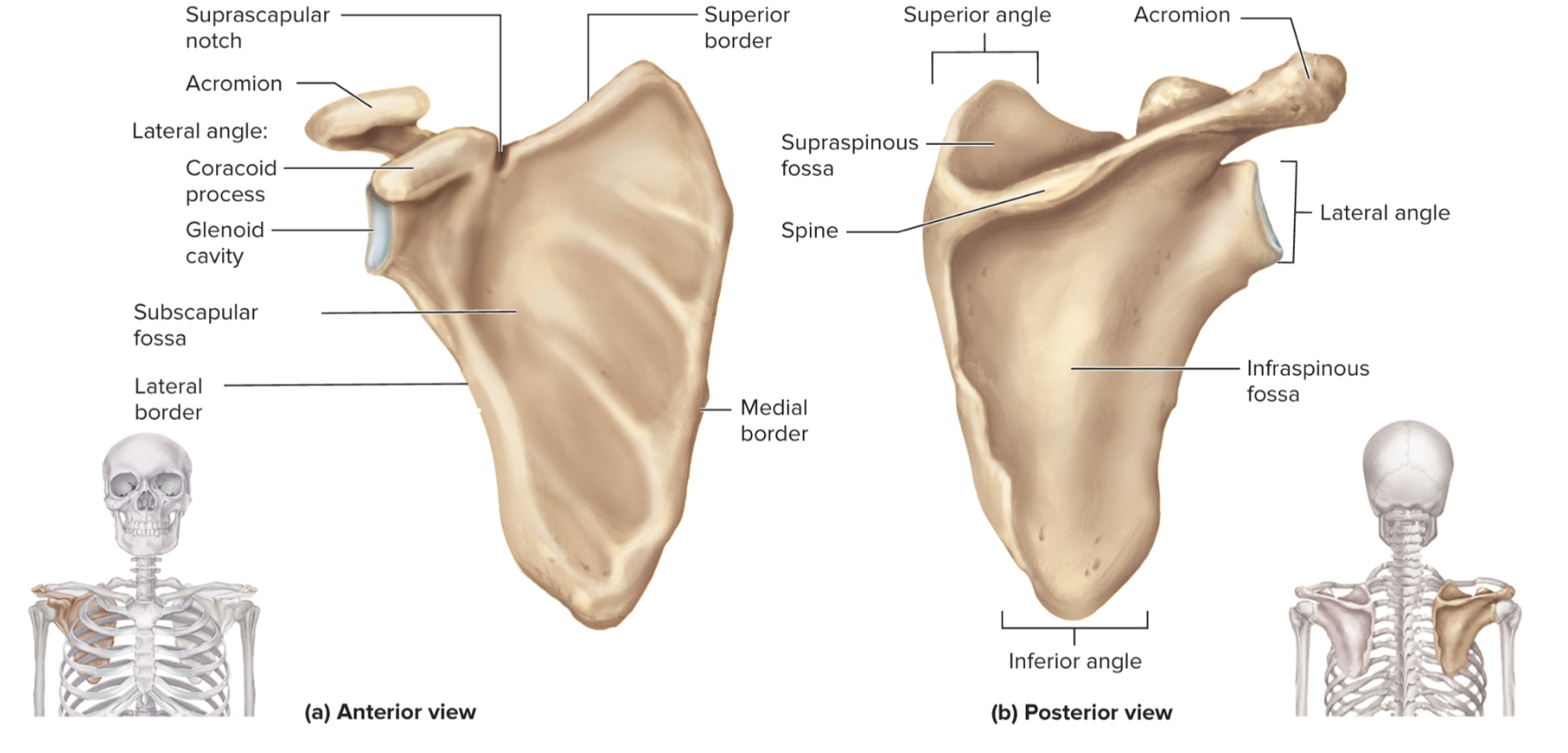
What is the supraspinous fossa of the scapula?
a depression on the posterior (back) side of the scapula where the supraspinatus muscle sits
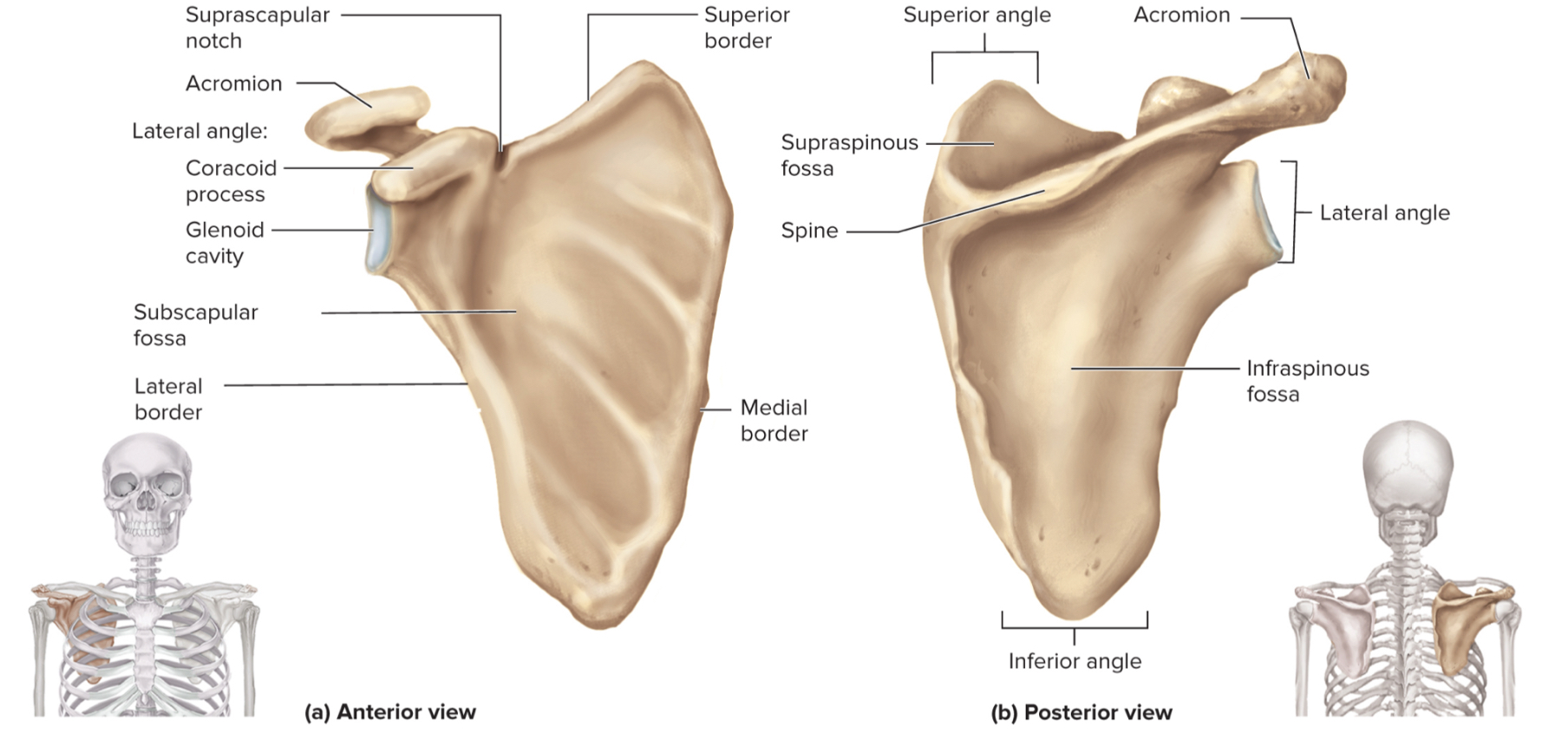
What is the infraspinous fossa of the scapula?
depression on the posterior side of the scapula where the infraspinatus muscle sits
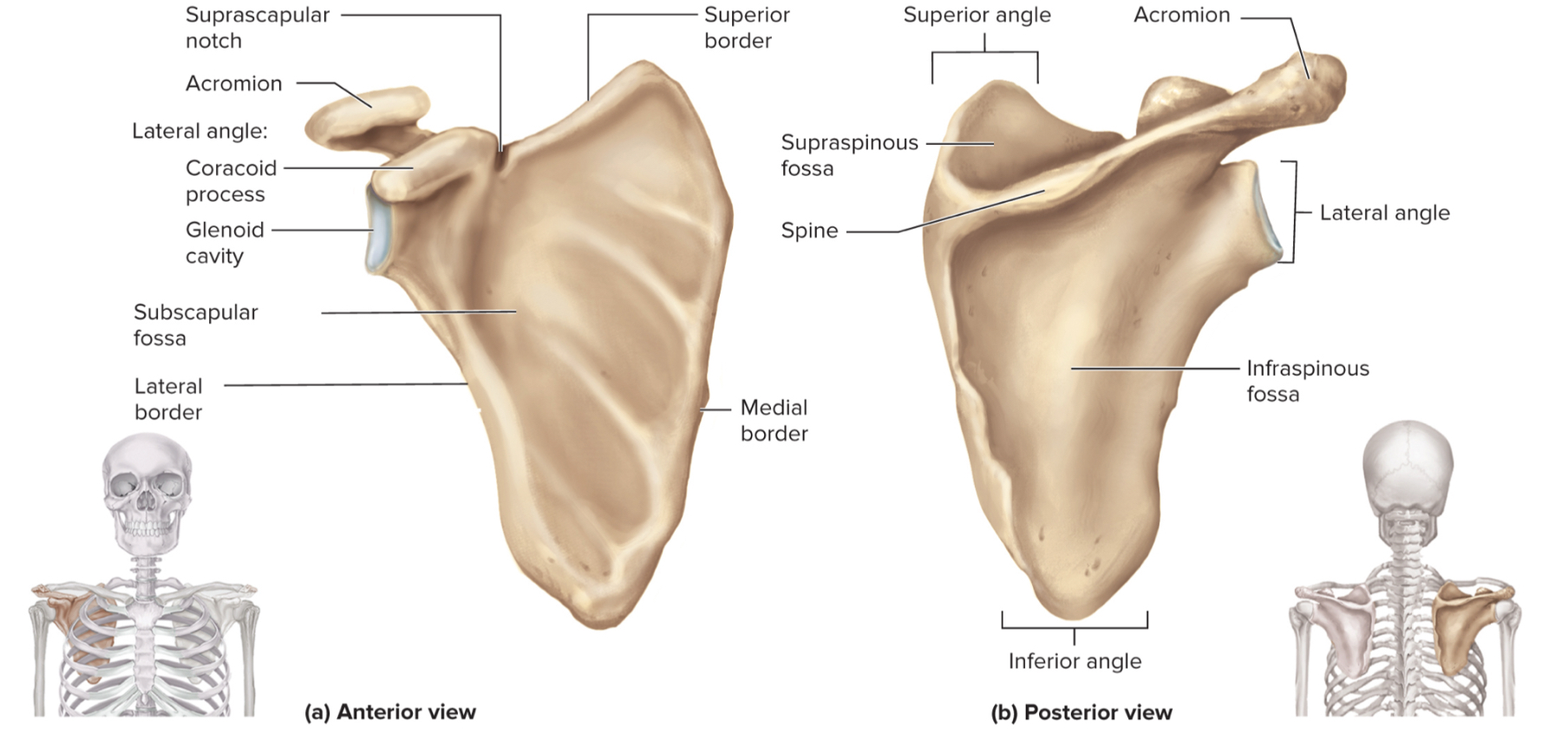
What is the subscapular fossa of the scapula?
a depression on the anterior side of the scapula where the subscapularis muscle sits
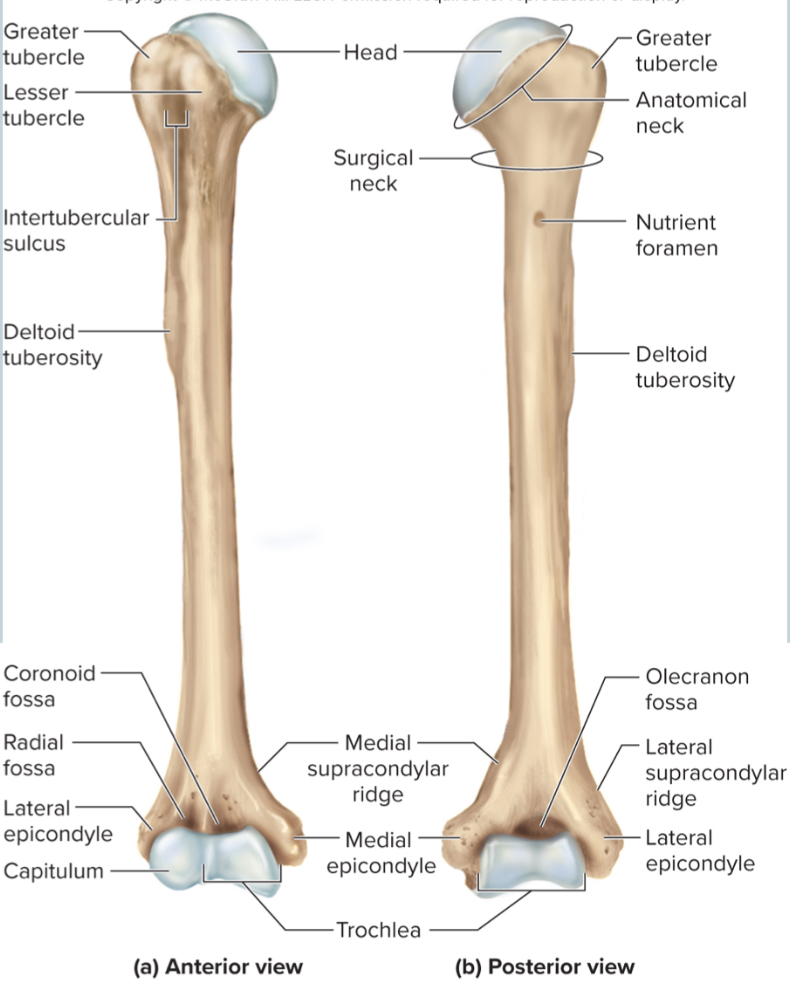
What are the parts of the humerus?
the head
the anatomical neck
the greater tubercle
the lesser tubercle
the surgical neck
the intertubercular sulcus
the deltoid tuberosity
the capitulum
the trochlea
the coronoid fossa
the olecranon fossa
the medial and lateral epicondyles
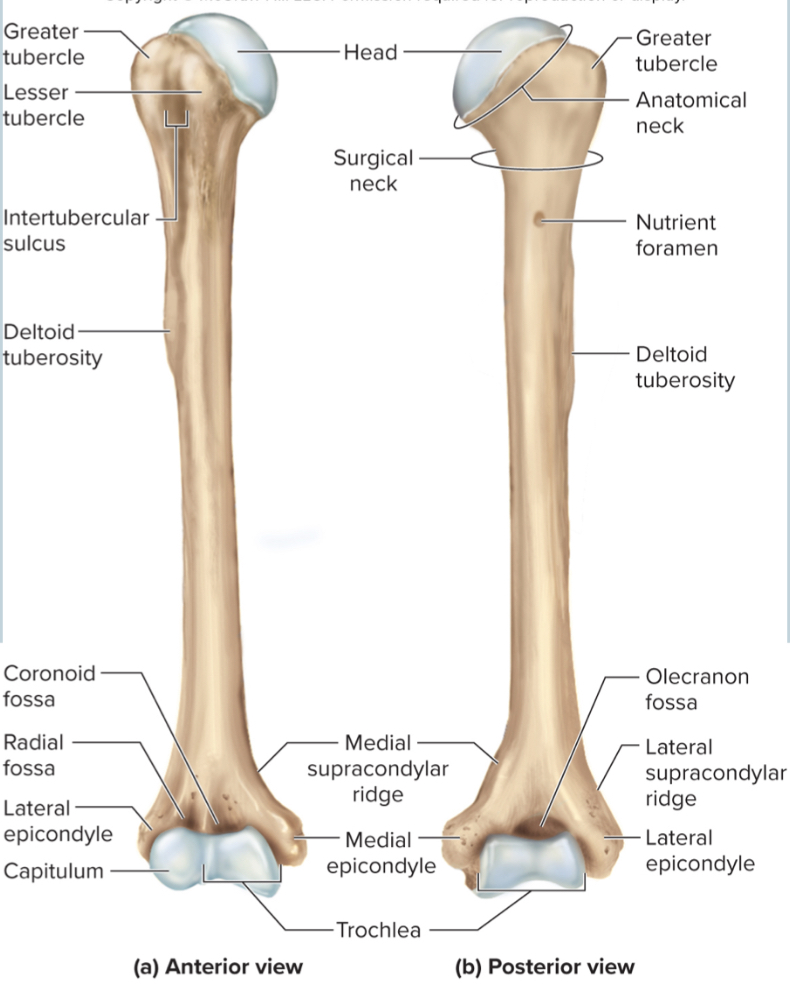
Head of humerus:
articulates with the glenoid cavity to form the shoulder joint
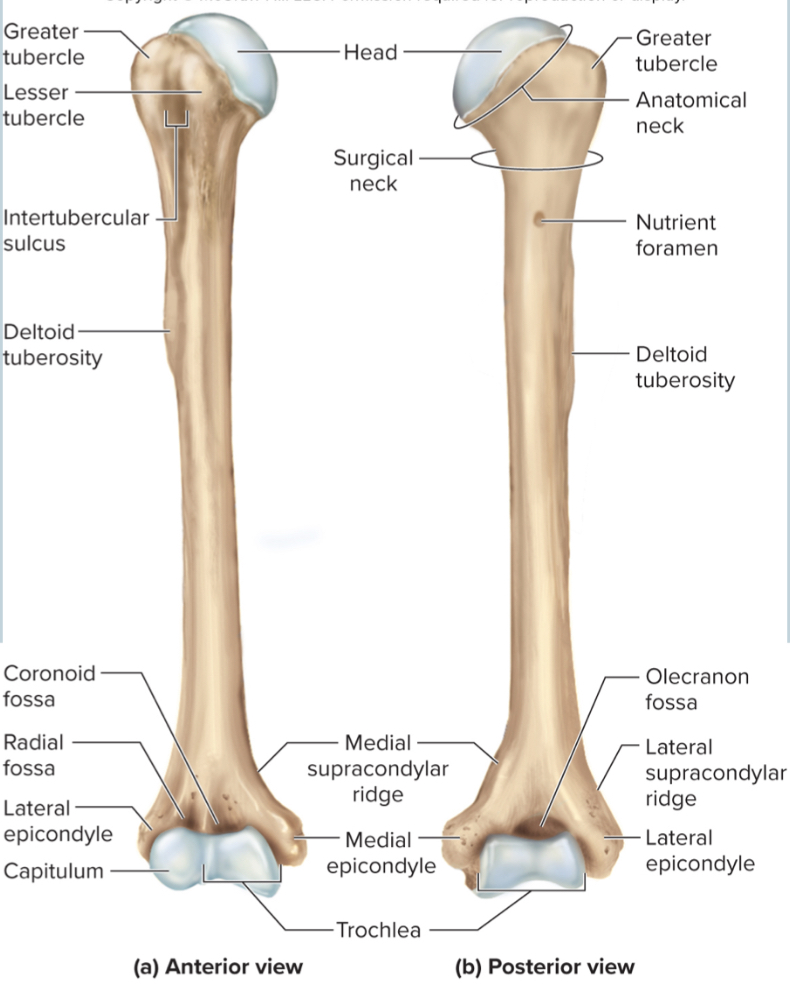
Anatomical neck of the humerus:
site of the epiphyseal plate
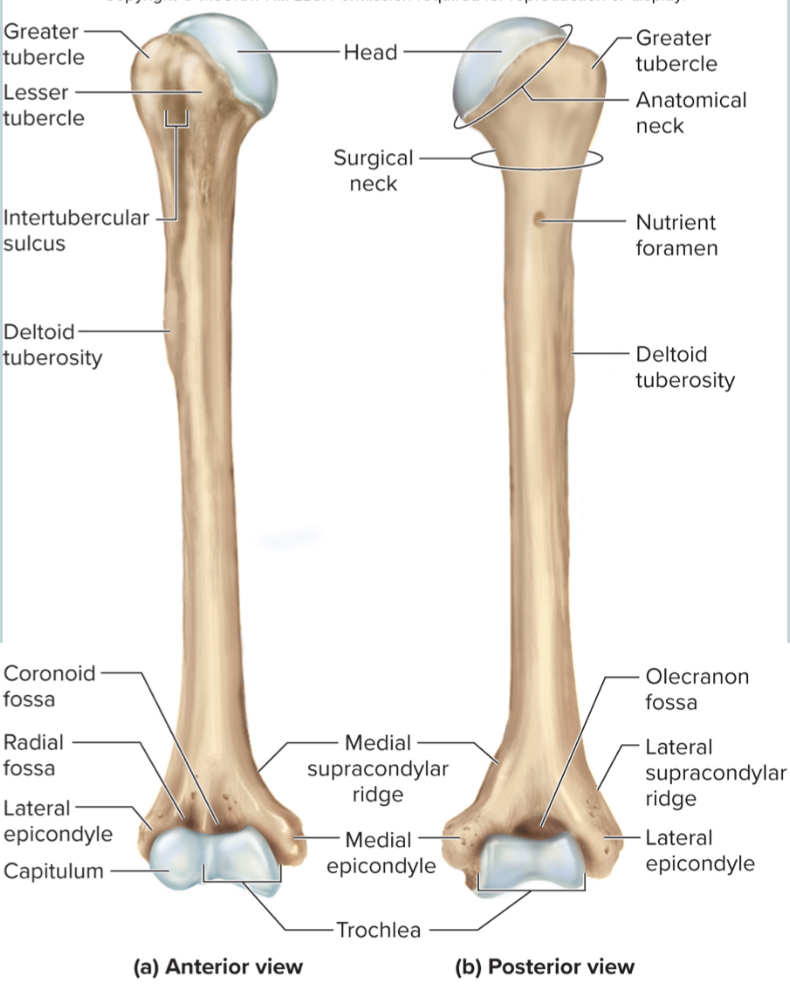
The greater tubercle of the humerus:
A large, lateral projection near the head of the humerus. It serves as an attachment site for rotator cuff muscles.
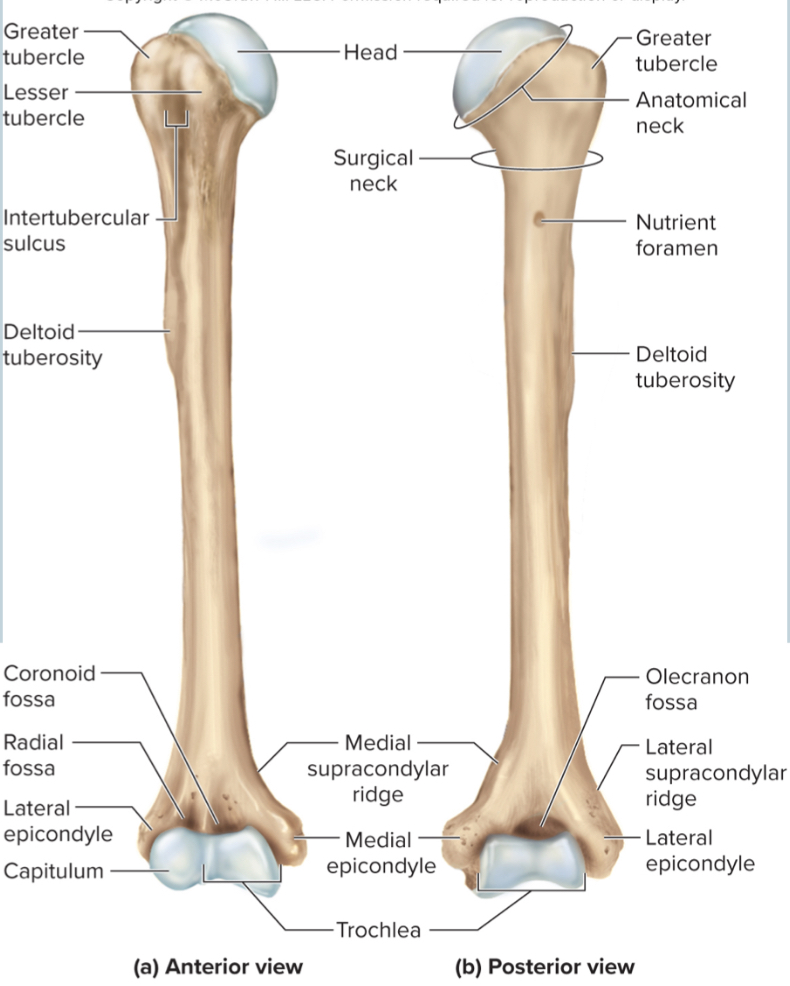
The lesser tubercle of the humerus:
A small, anterior projection near the head of the humerus. It serves as an attachment site for the subscapularis muscle.
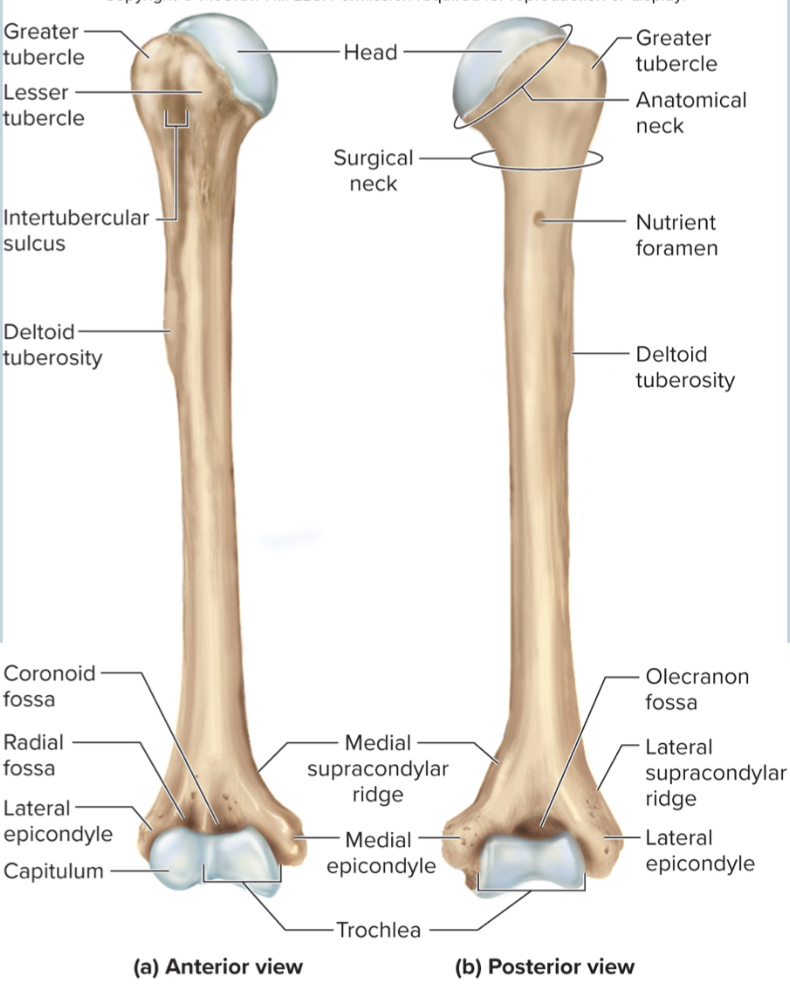
The surgical neck of the humerus:
a narrow region below the tubercles that is easily broken and requires surgery to repair
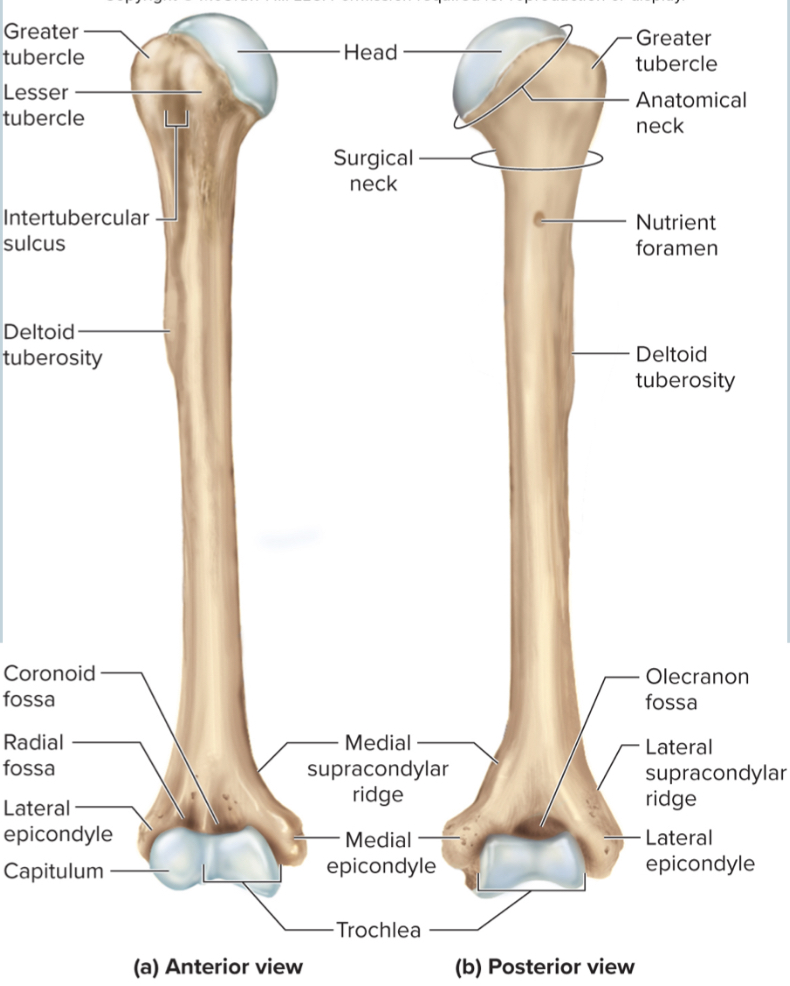
The intertubercular sulcus of the humerus:
a grove between the tubercles where nerves run through
hitting funny bone
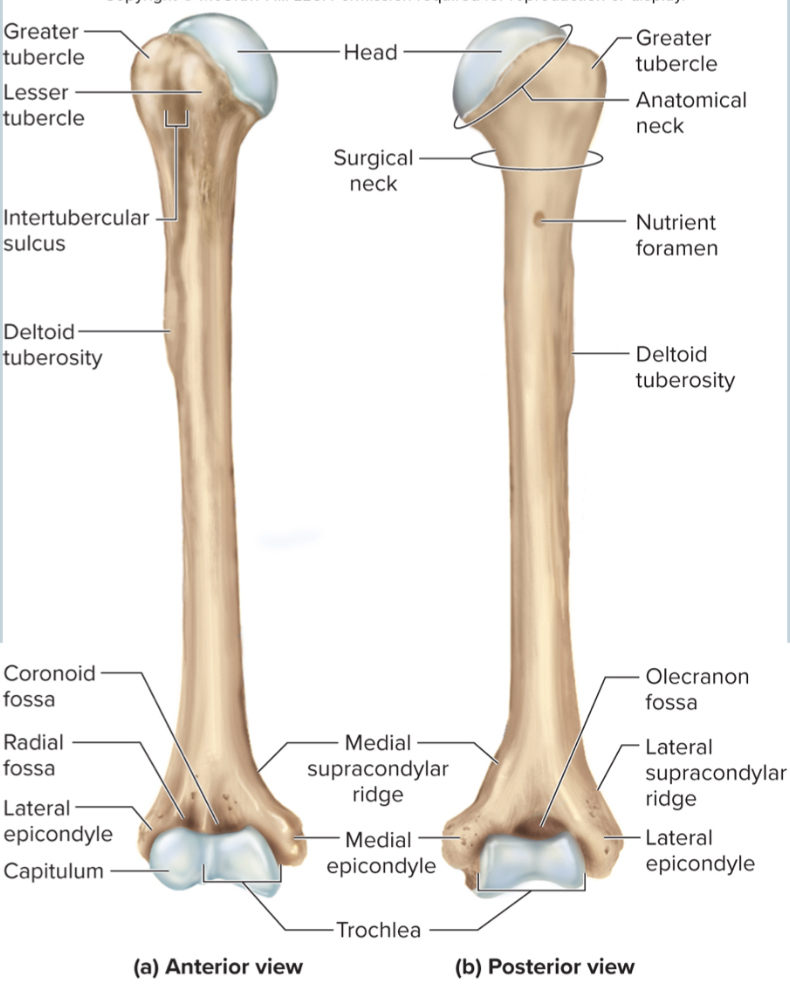
The deltoid tuberosity of the humerus:
site where the deltoid muscle attaches
this is where all injections are given because it is thick
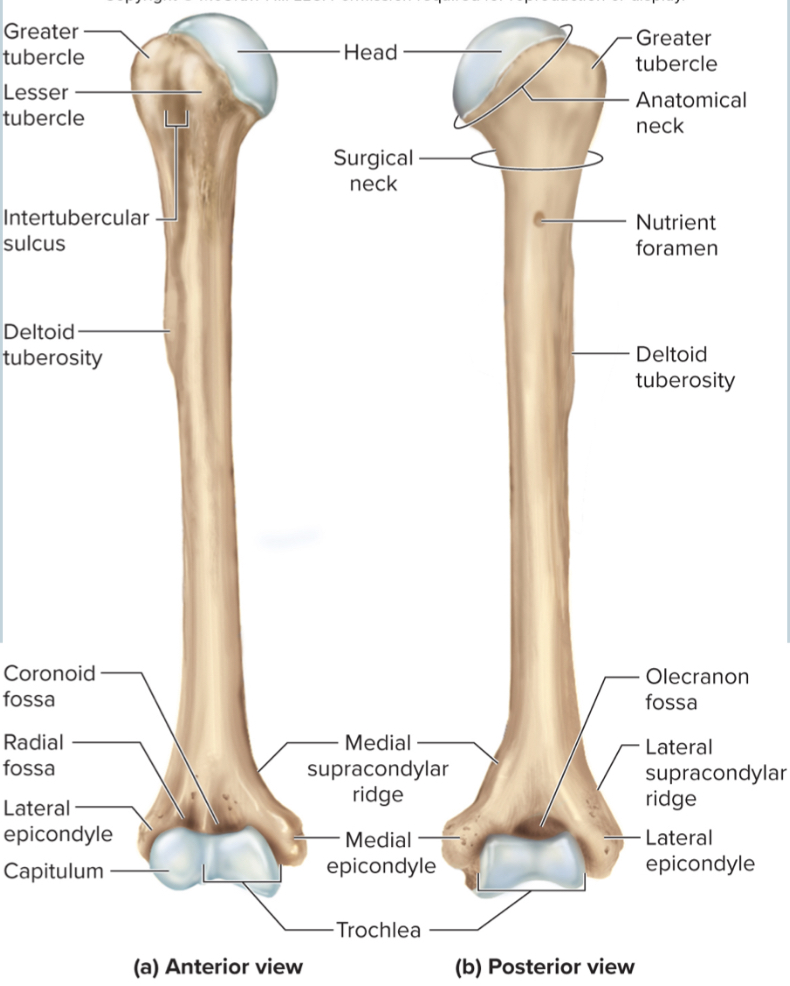
The capitulum of the humerus:
a rounded distal projection that allows the humerus to articulate with the radius
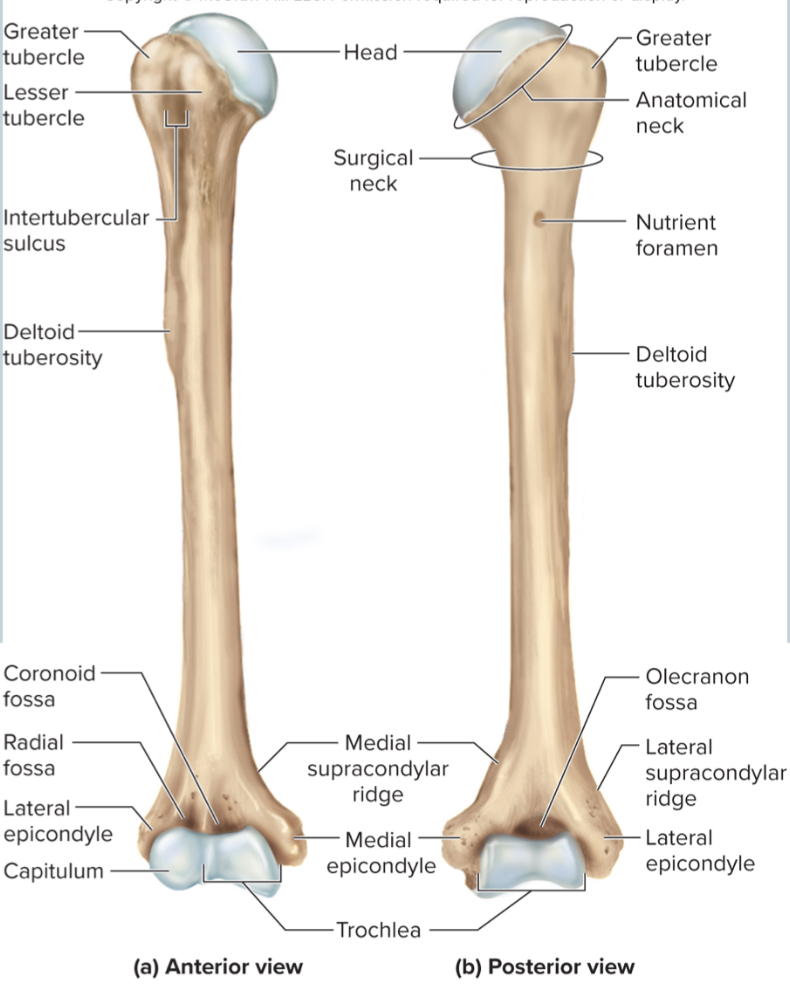
The trochlea of the humerus:
allows for articulation of the humerus with the ulna at the elbow joint
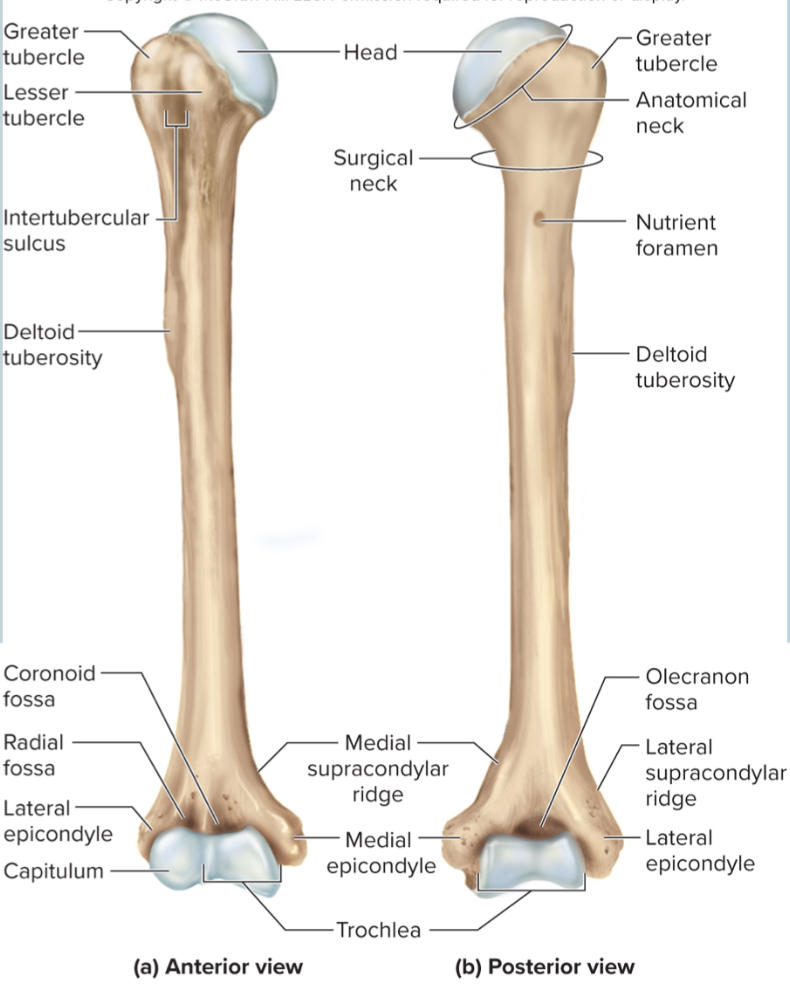
The coronoid fossa of the humerus:
depression in the humerus that receives the coronoid process of the ulna when the elbow is flexed
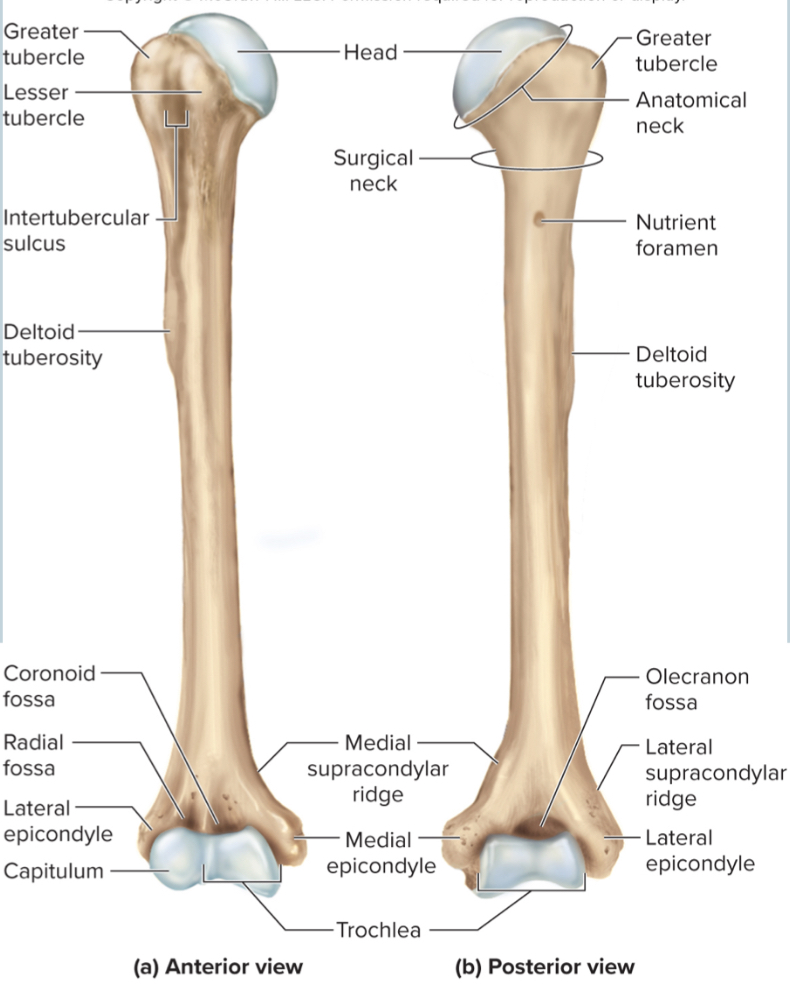
The medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus:
projections on the humerus that serve as muscle attachments
What nerve does the medial epicondyle protect?
the ulnar nerve that passes over the back of the elbow
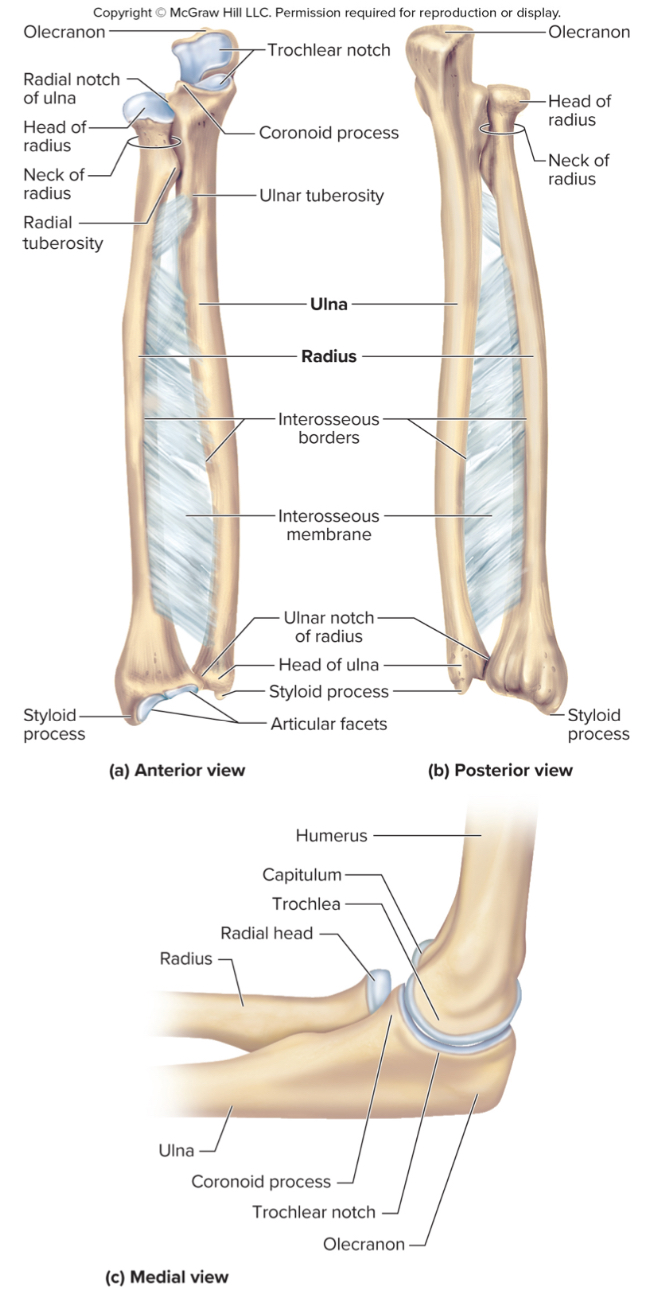
What are the parts of the ulna?
the olecranon process
the coronoid process
the radial notch
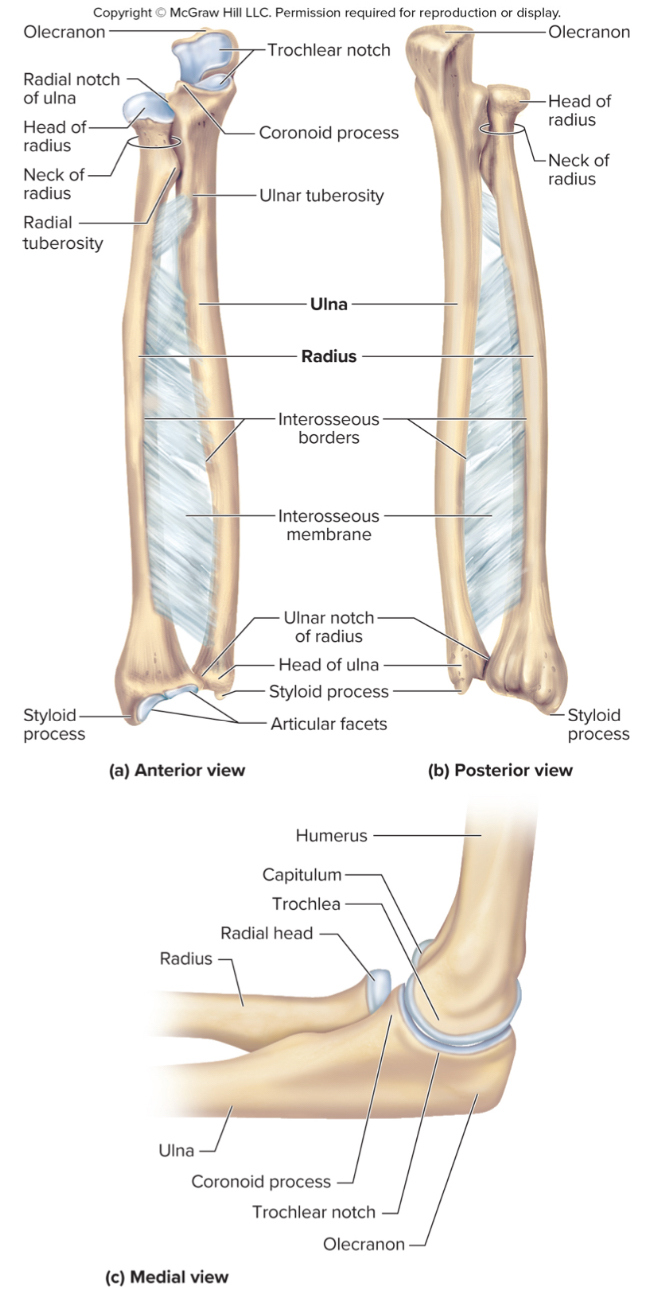
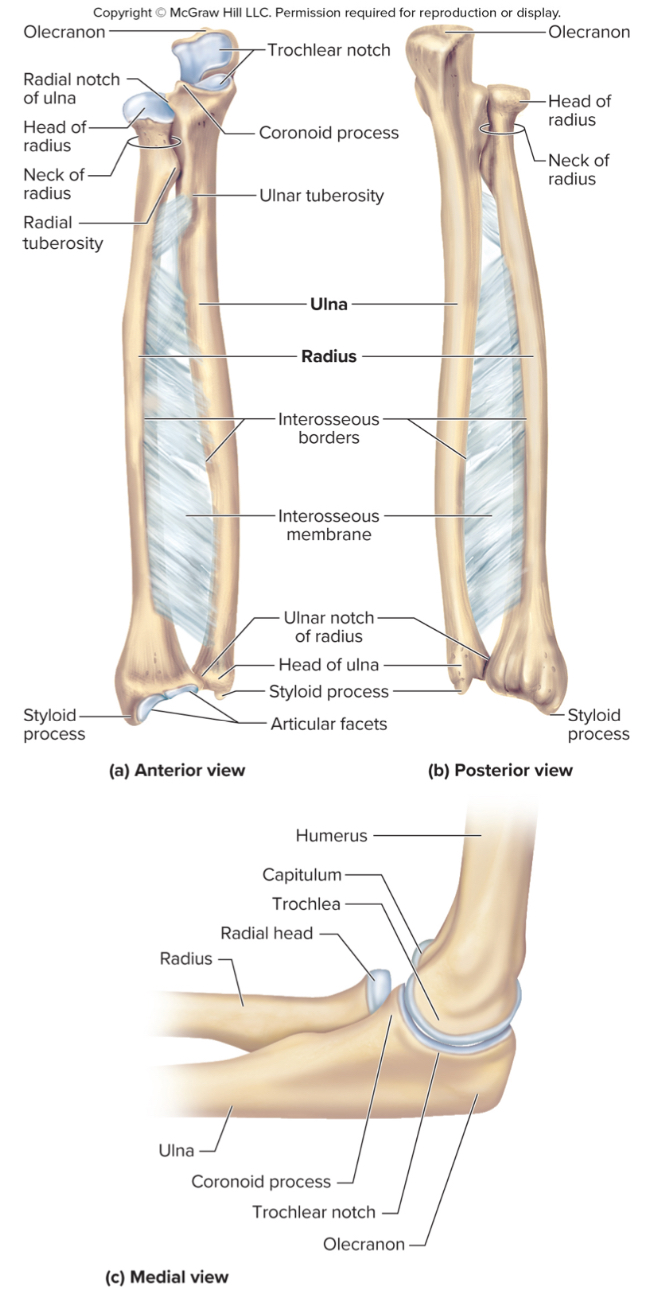
The olecranon process of the ulna:
A large projection on the ulna that forms the bony point of the elbow that fits into the olecranon fossa when the elbow is extended
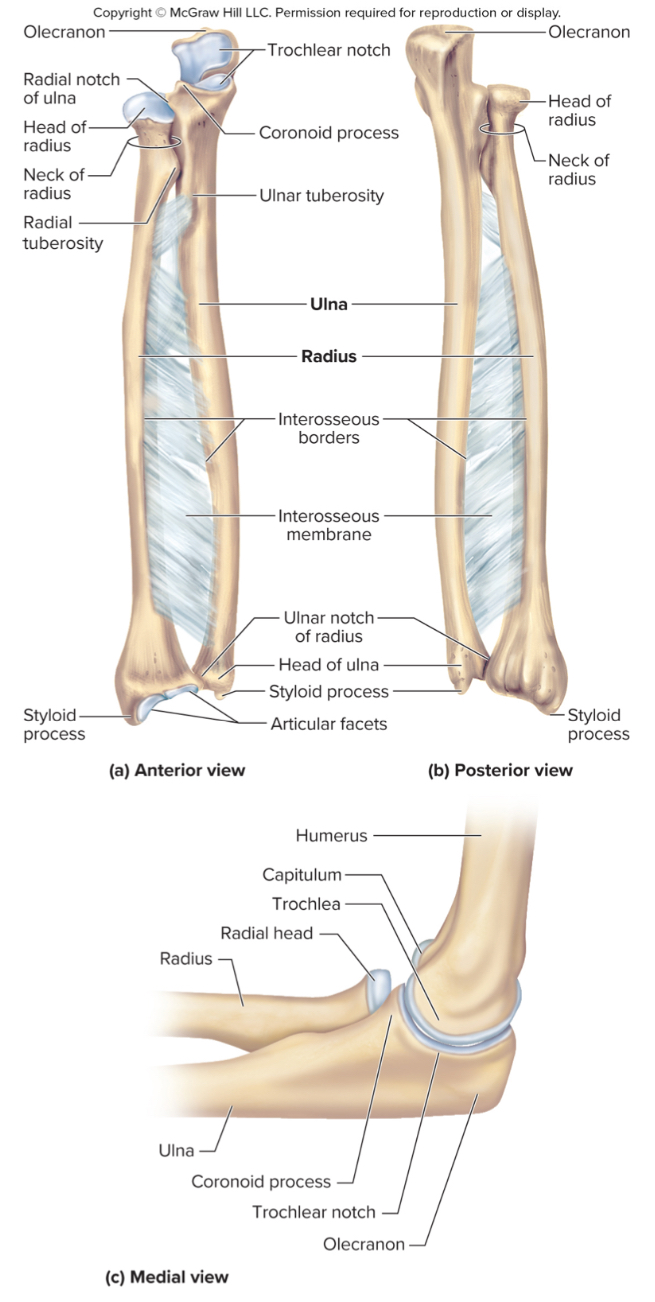
The coronoid process of the ulna:
a projection on the ulna that fits into the coronoid fossa when the elbow is flexed
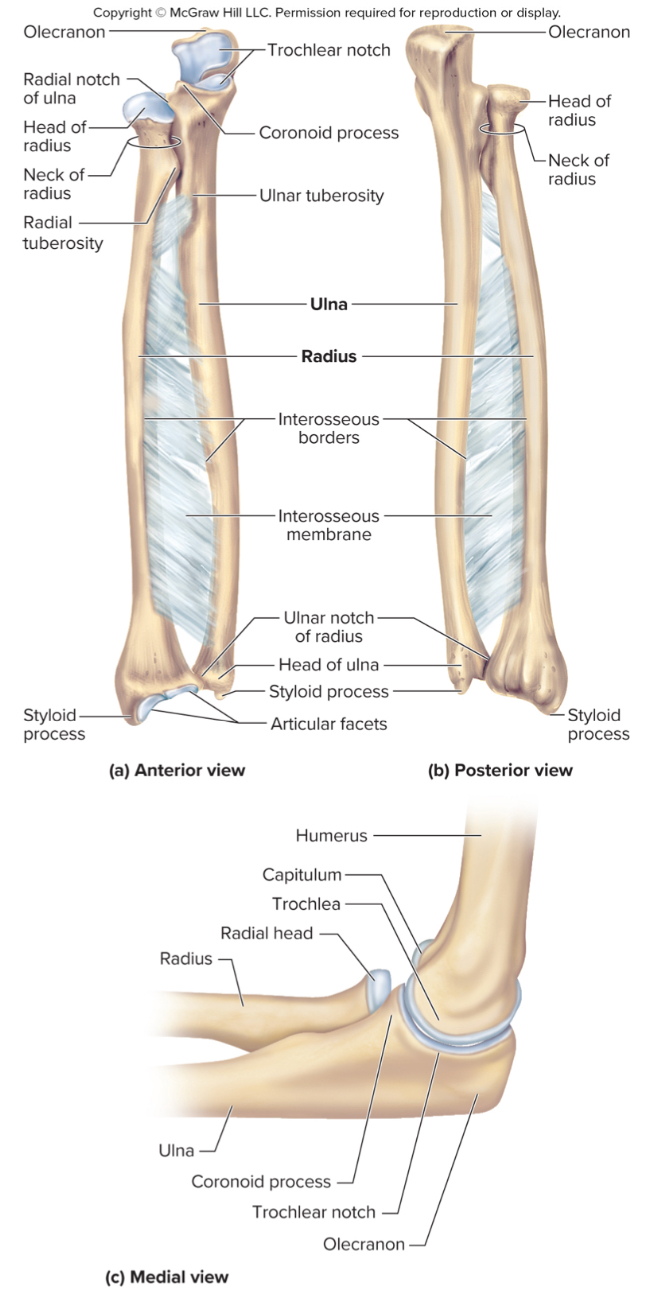
The radial notch of the ulna:
a small depression where the radius articulates with the ulna
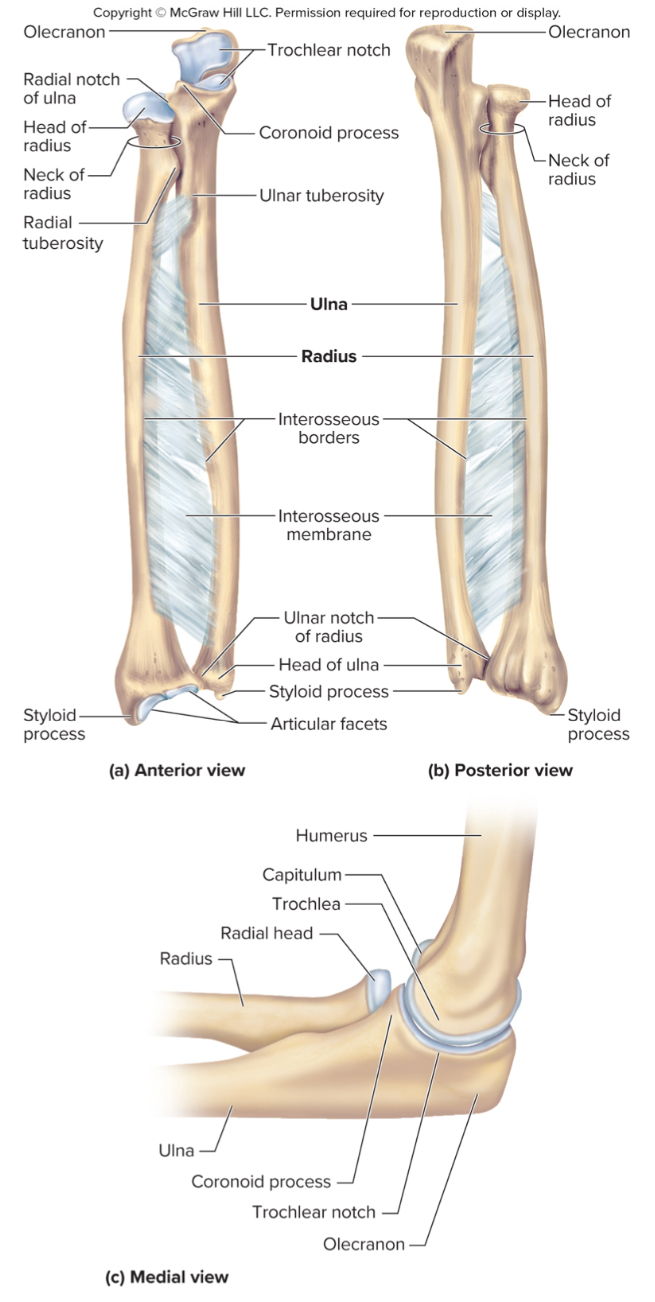
What are the parts of the radius?
the head
the radial tuberosity
ulnar notch
What purpose does the radius serve?
allows for us to rotate our forearm (turn our palm up and down)
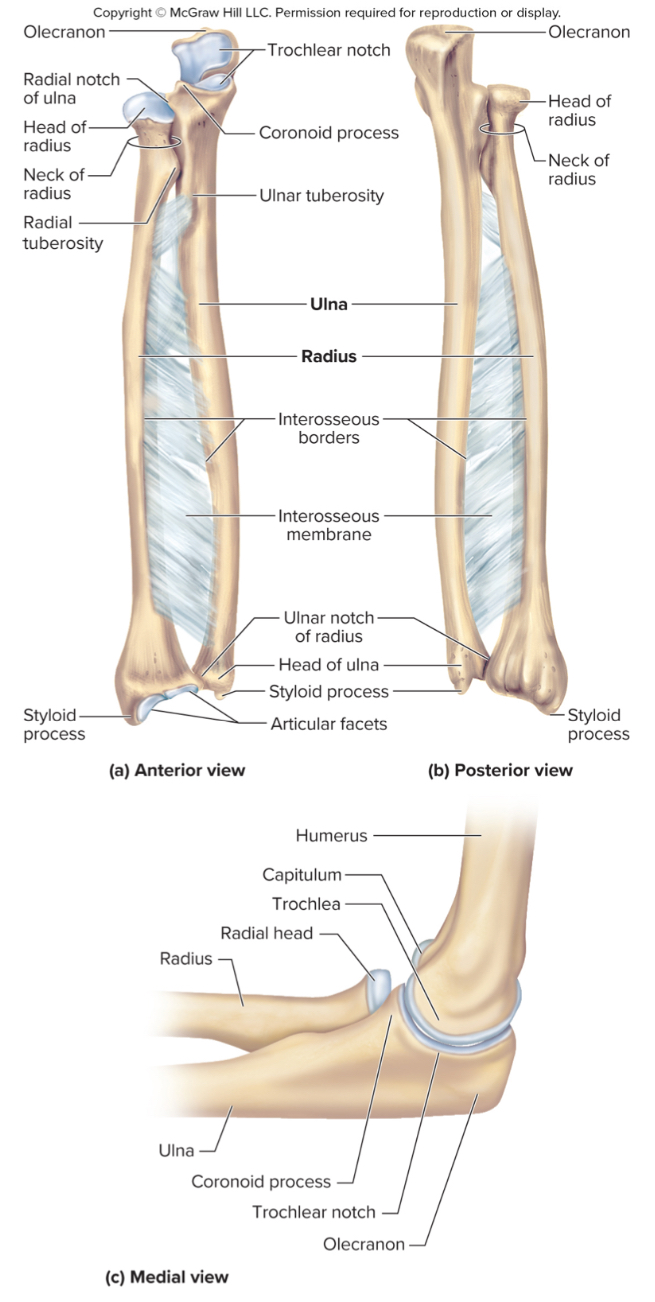
the head of the radius:
structure that articulates with the ulna
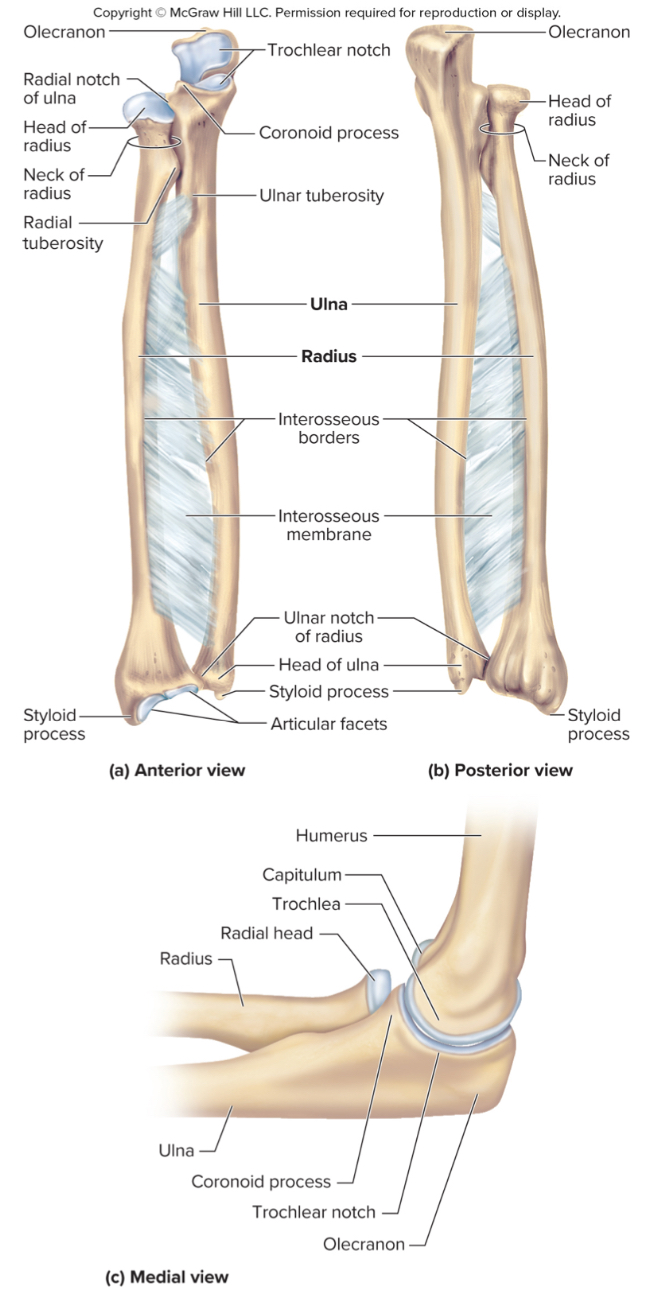
the radial tuberosity of the radius:
site of muscle attachment
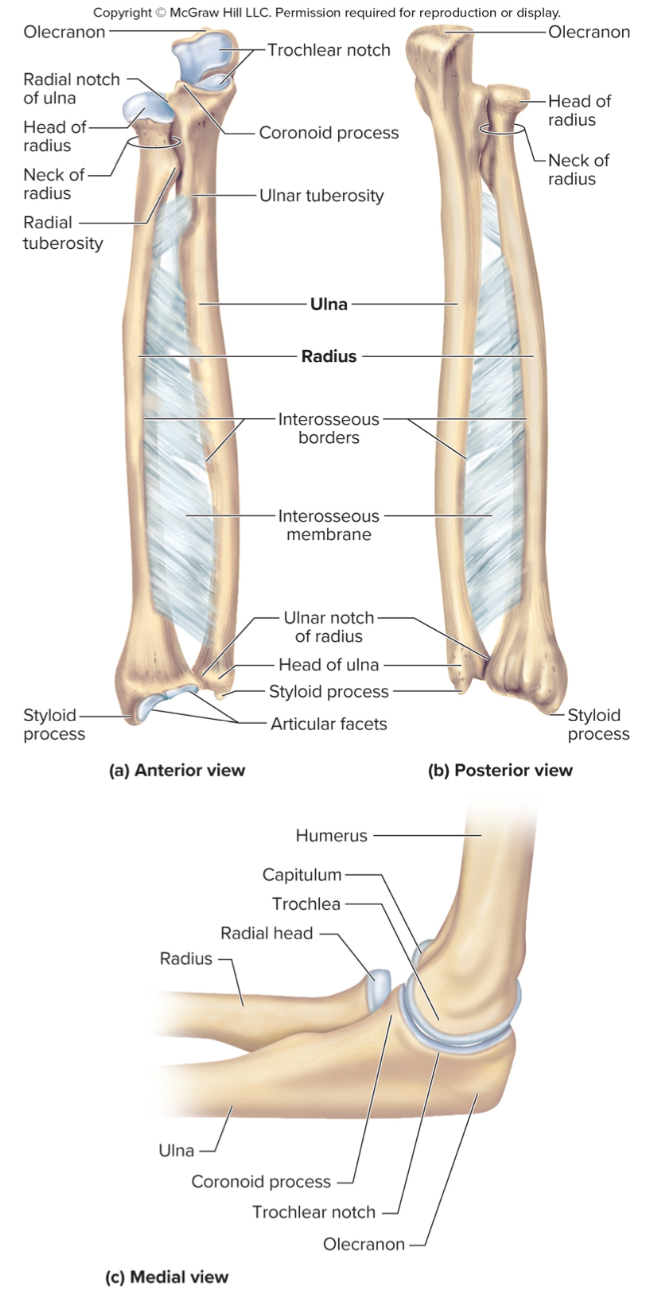
ulnar notch of the radius:
notch on the radius that articulates with the ulna down by the wrist
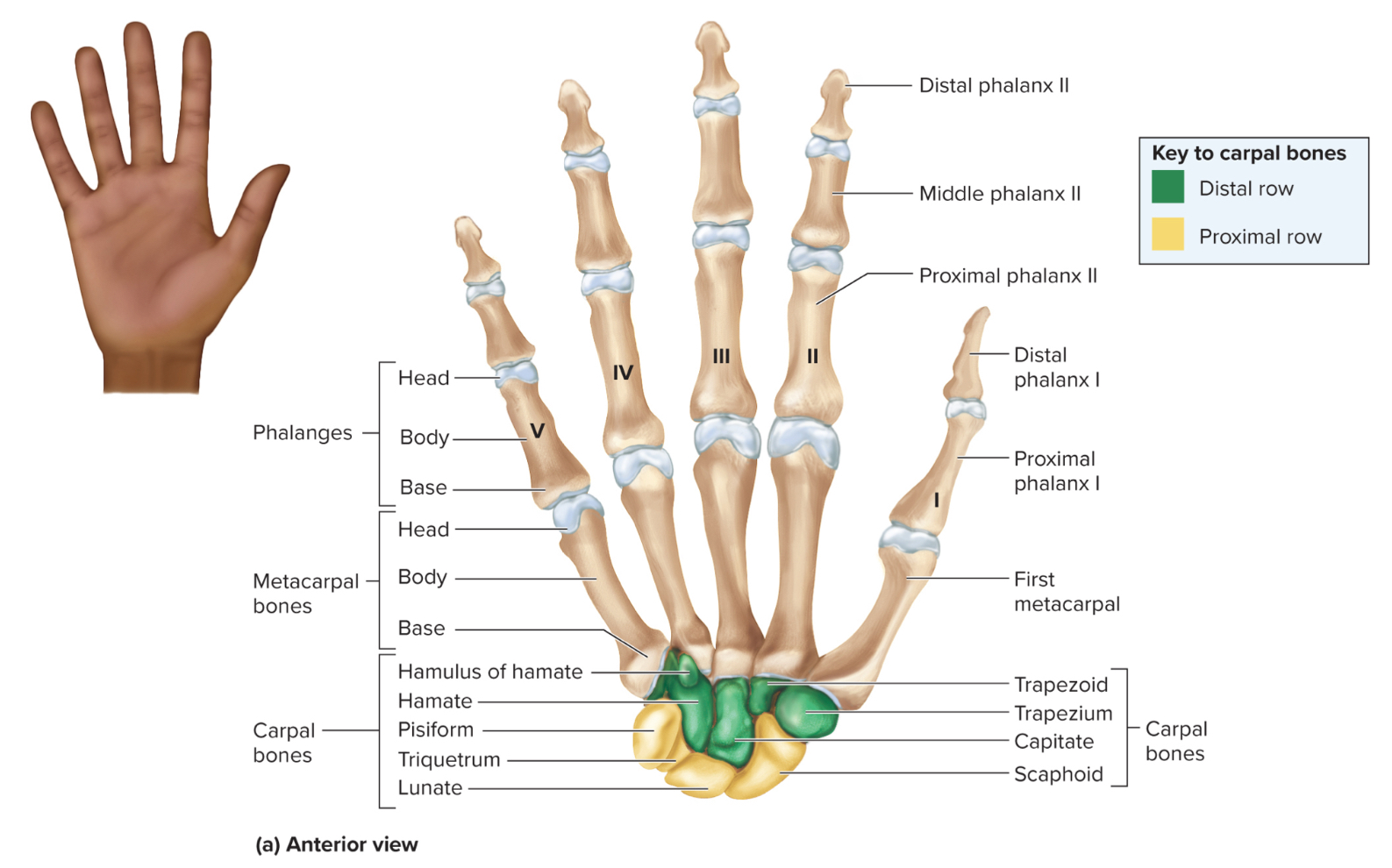
What are the parts of the hand?
carpals
metacarpals
phalanges
How many carpals are in each wrist?
8 carpals organized into 2 rows
What carpals make up the proximal row of the hand?
the pisiform, scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum
What carpals make up the distal row of the hand?
the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate
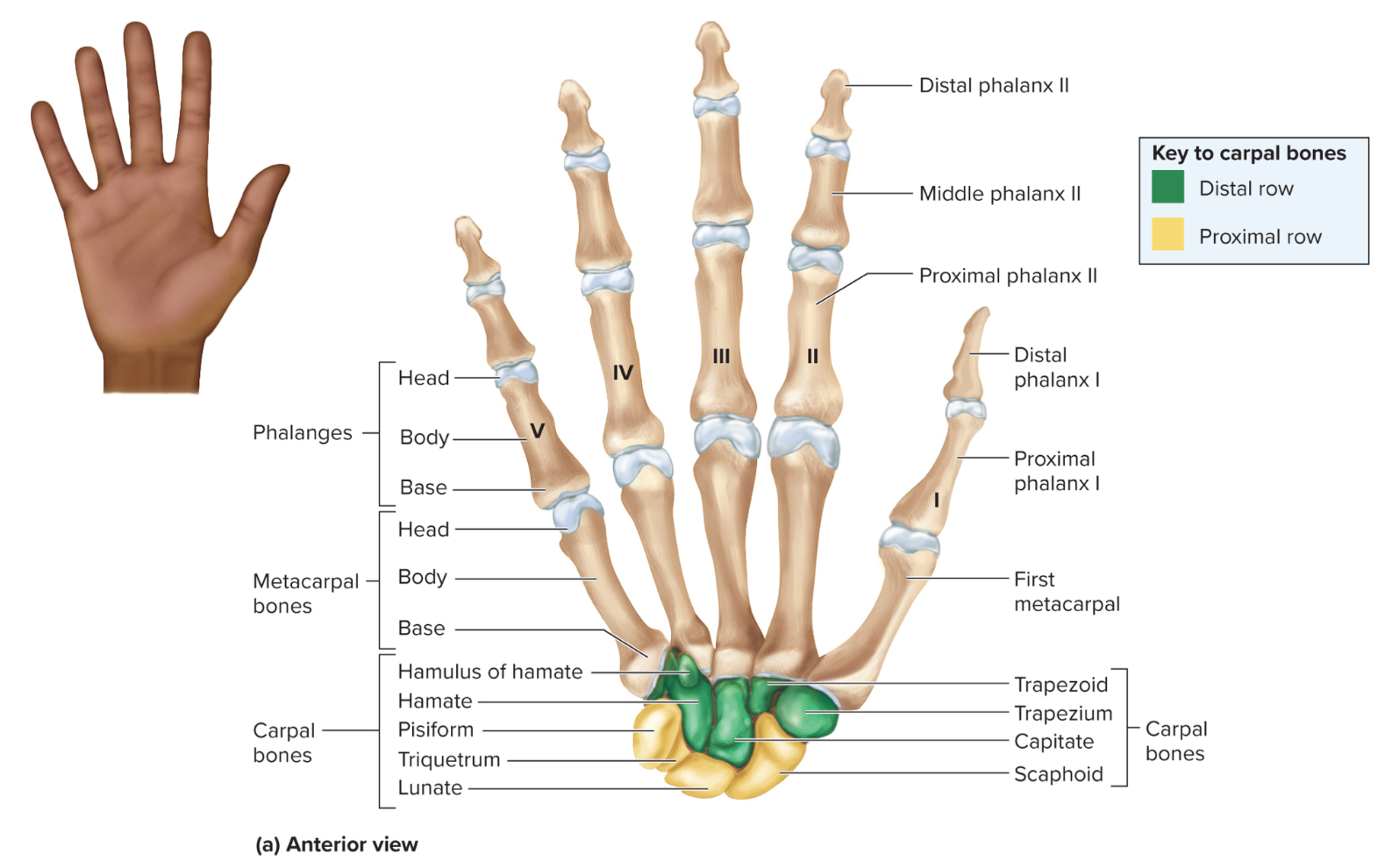
Metacarpals of the hand:
5 bones that form the palm of the hand
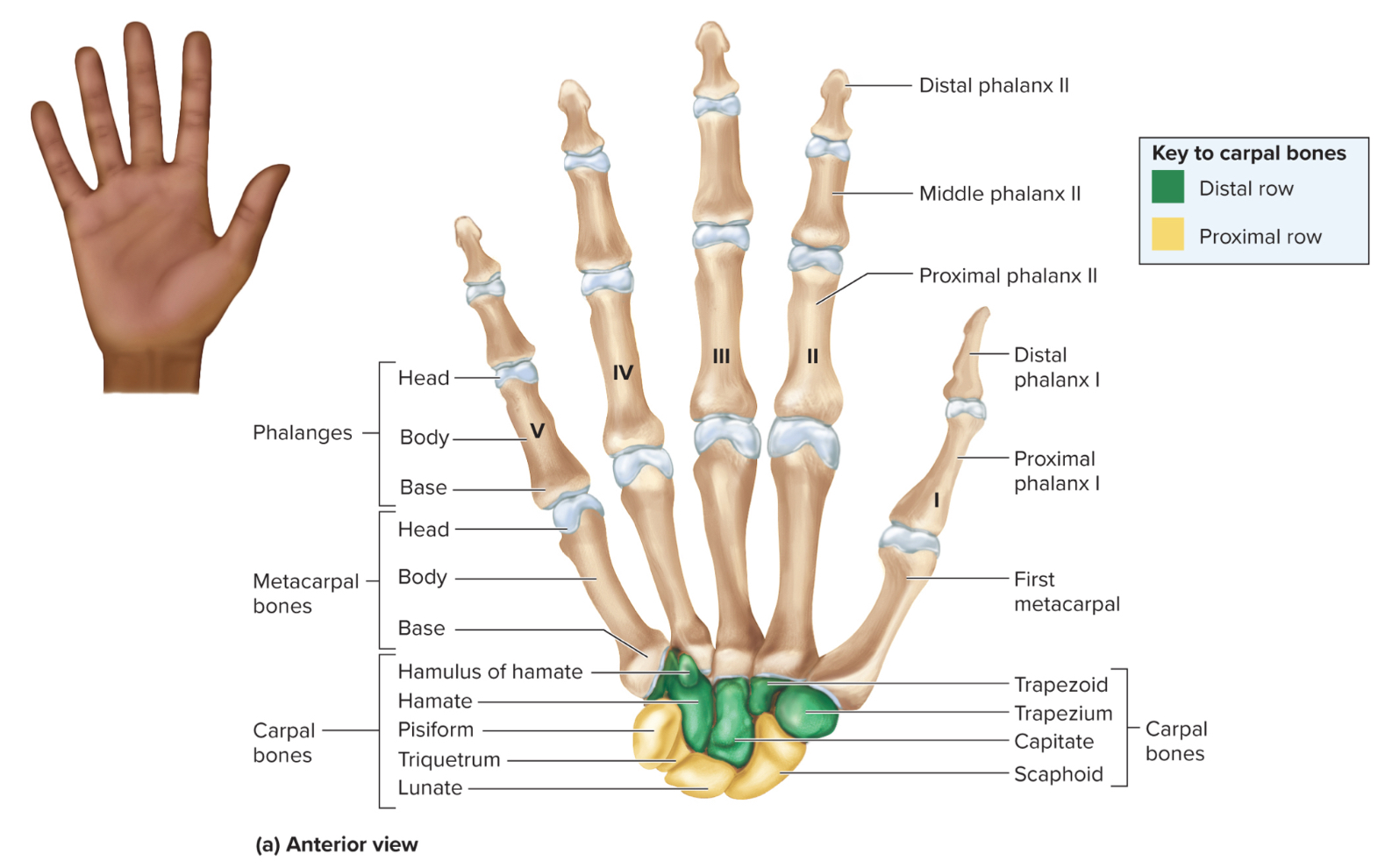
Phalanges of the hand:
14 bones in each hand that form the fingers
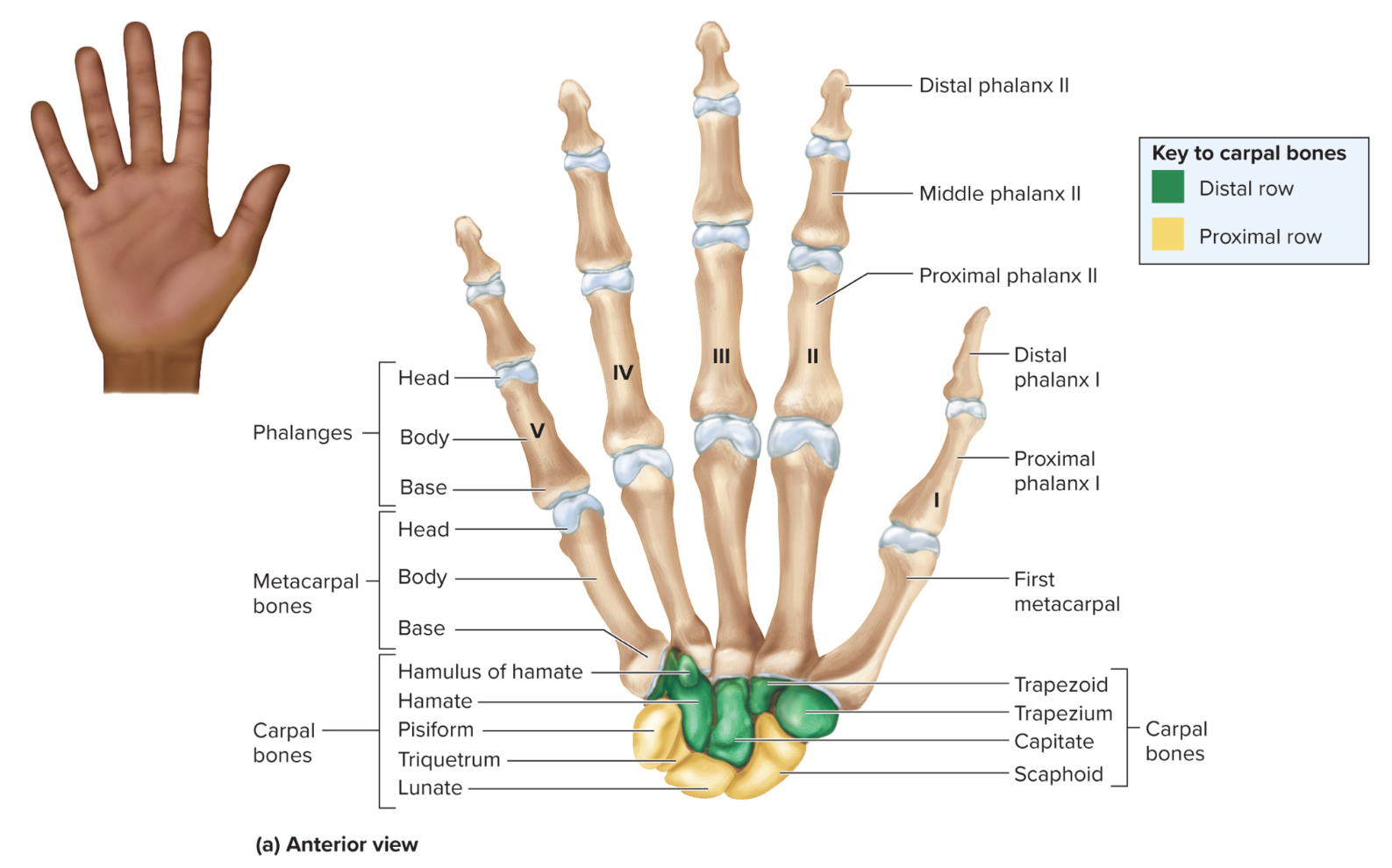
How are the phalanges of the hand organized?
each finger has three phalanges referred to as proximal, middle and distal phalanges
the thumb has two phalanges referred to as proximal or distal
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
condition in which nerves are impinged by displacement of the carpals. Causes nerves to be pinched and send impulses to the fingers. Symptoms include pain, numbness, and burning in the fingers
What is osteoarthritis?
degeneration of articular cartilage in the hand and wrist
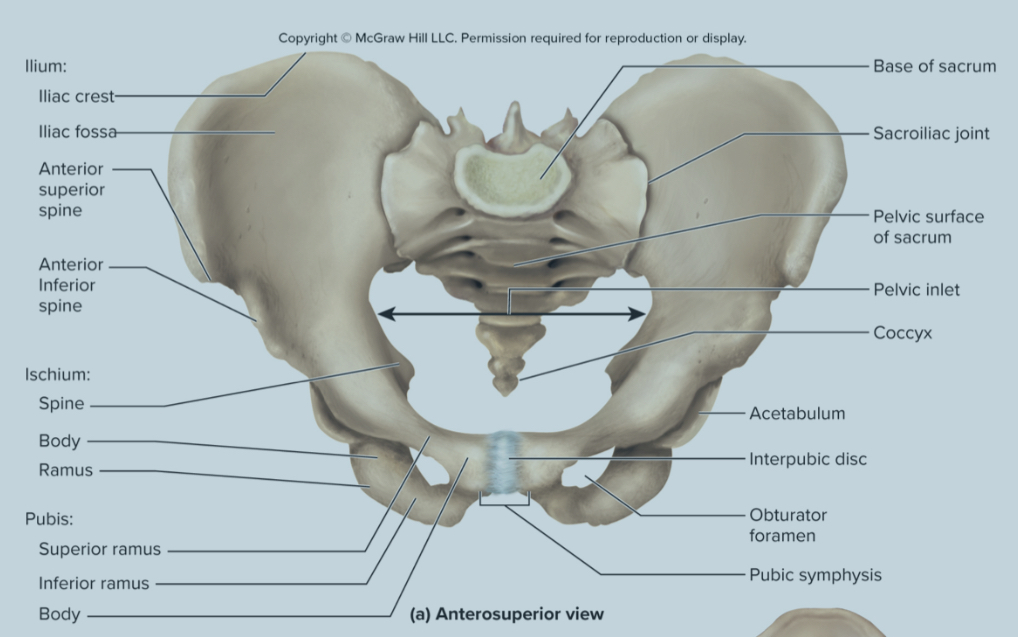
What are the bones of the pelvic griddle?
the ilium
the ischium
the pubis bone
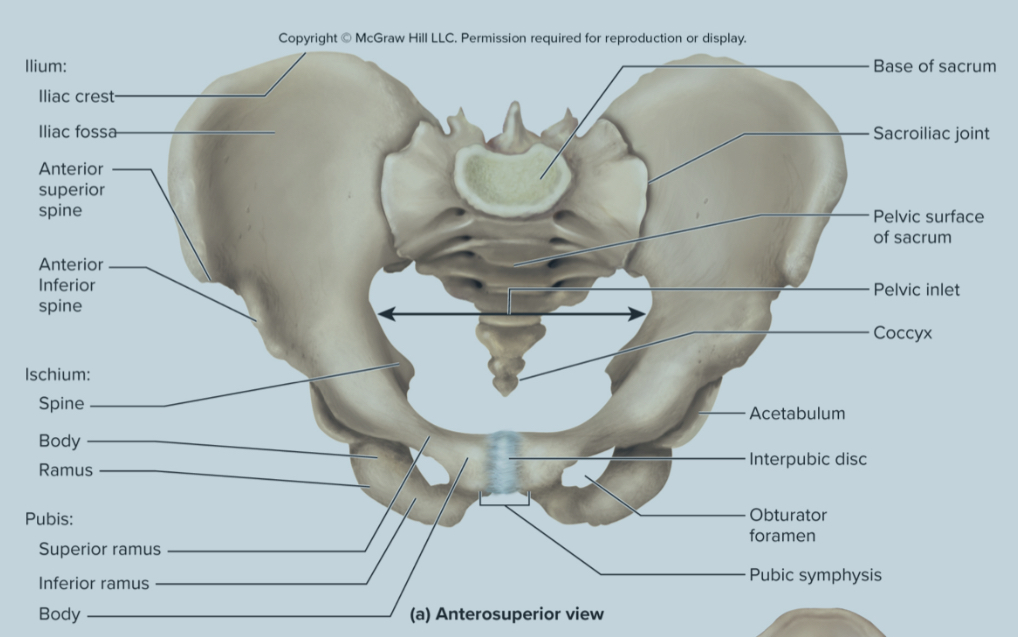
What are the parts of the ilium?
sacroliac joint
greater sciatic notch
the iliac fossa
the iliac crest
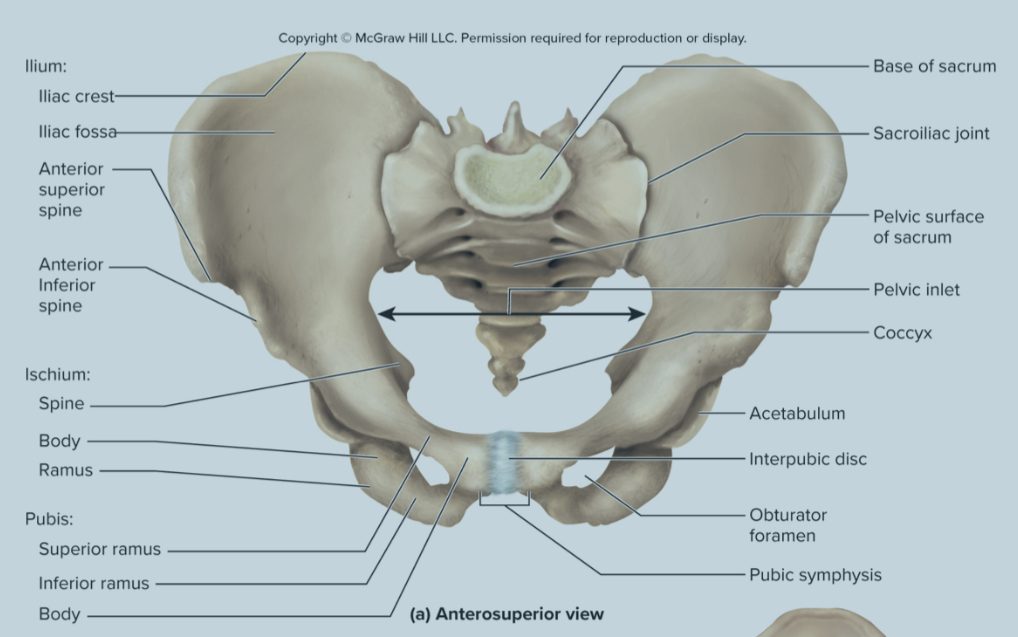
Sacroiliac joint of the ilium:
site where the sacrum and ilium attach
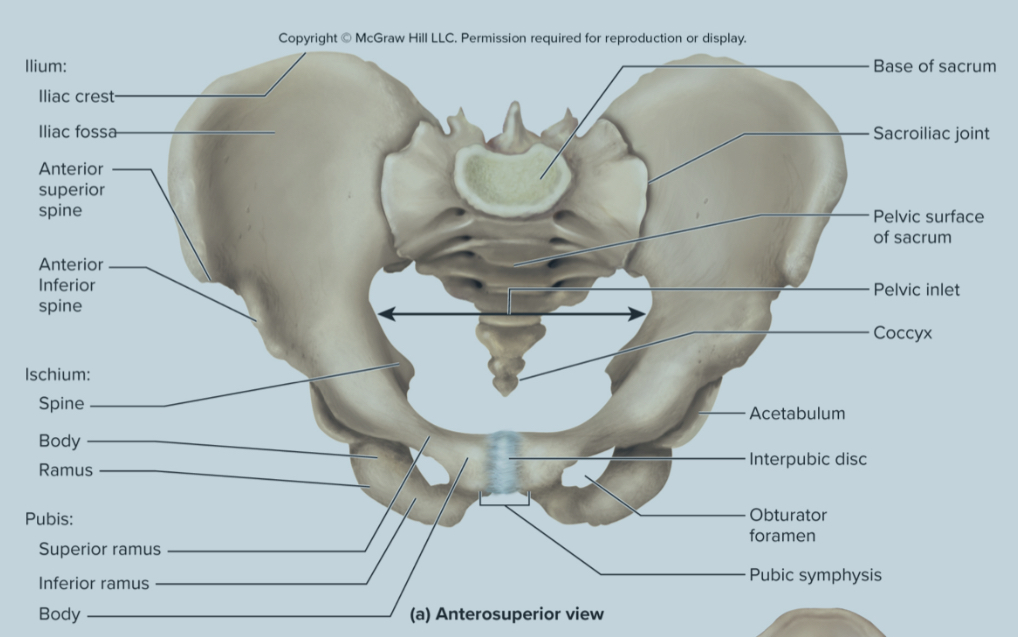
greater sciatic notch of the ilium:
the passageway for the sciatic nerve to the leg
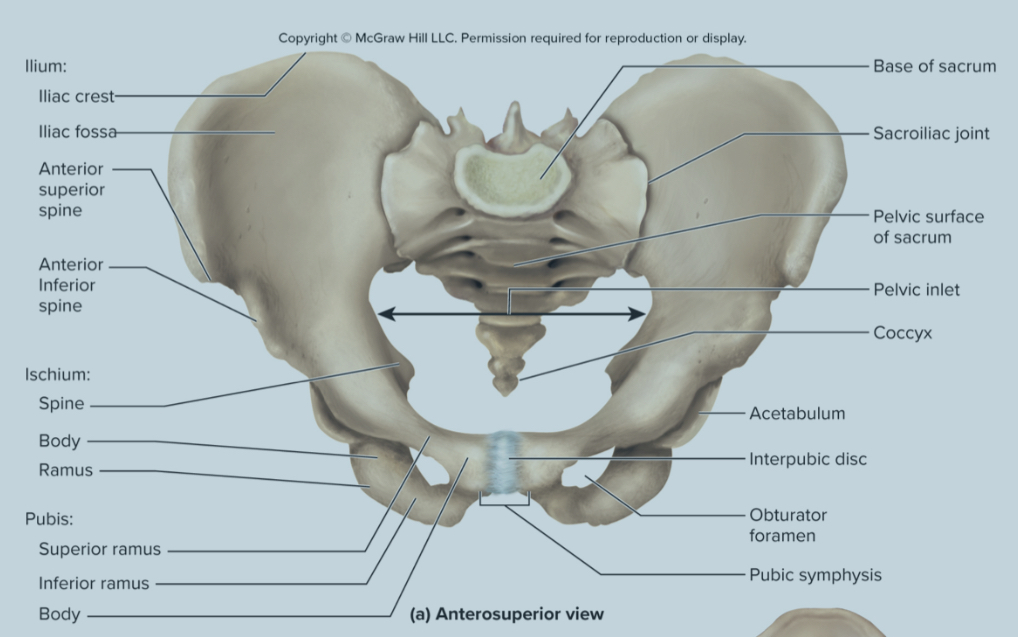
iliac fossa of the ilium:
the long ridge of the ilium where numerous muscles attach to
also a site where they can take red bone marrow from
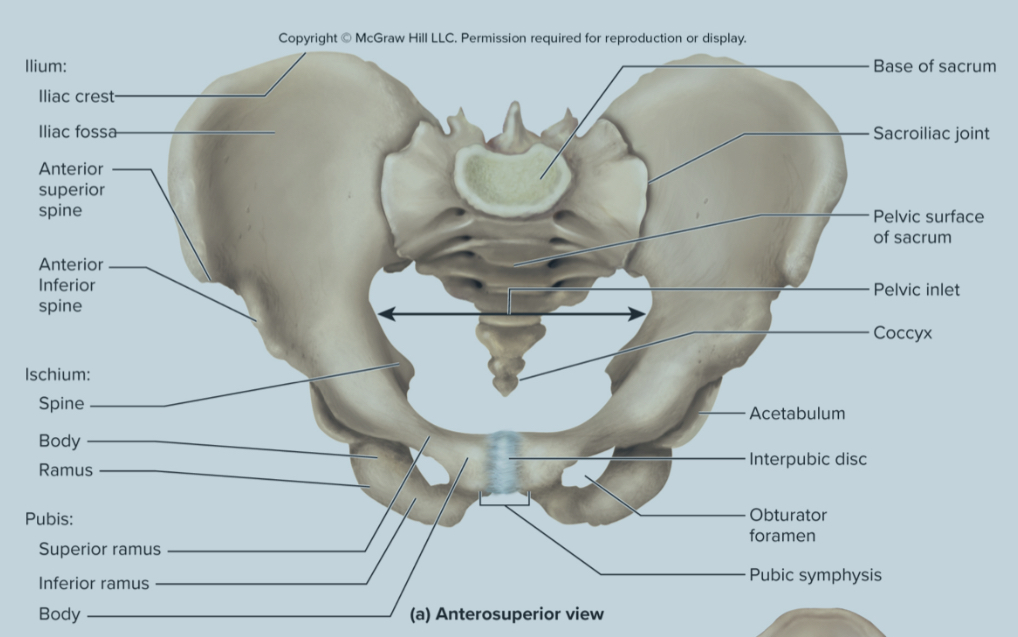
What are the parts of the ischium?
the obturator foramen
the ischial tuberosity
the acetabulum
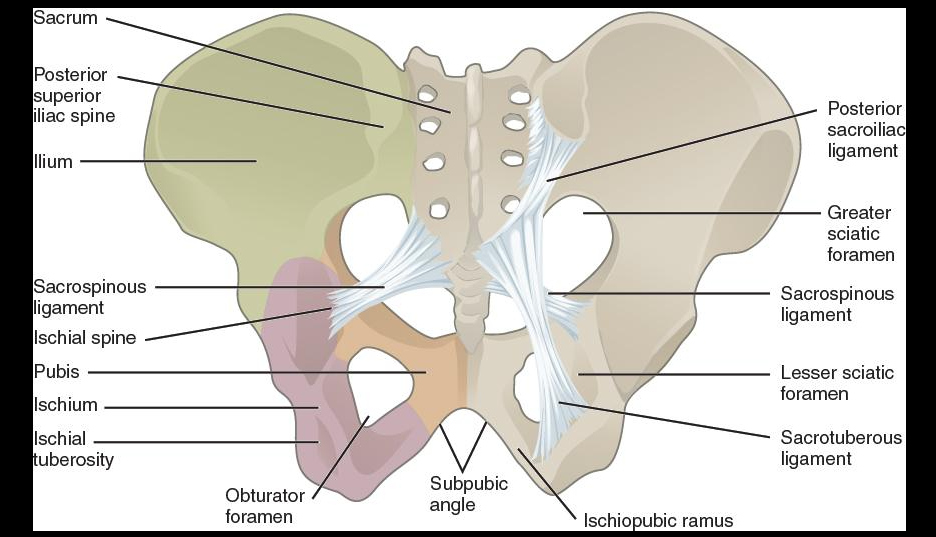
The obturator foramen of the ischium:
large hole where blood vessels and nerves pass through
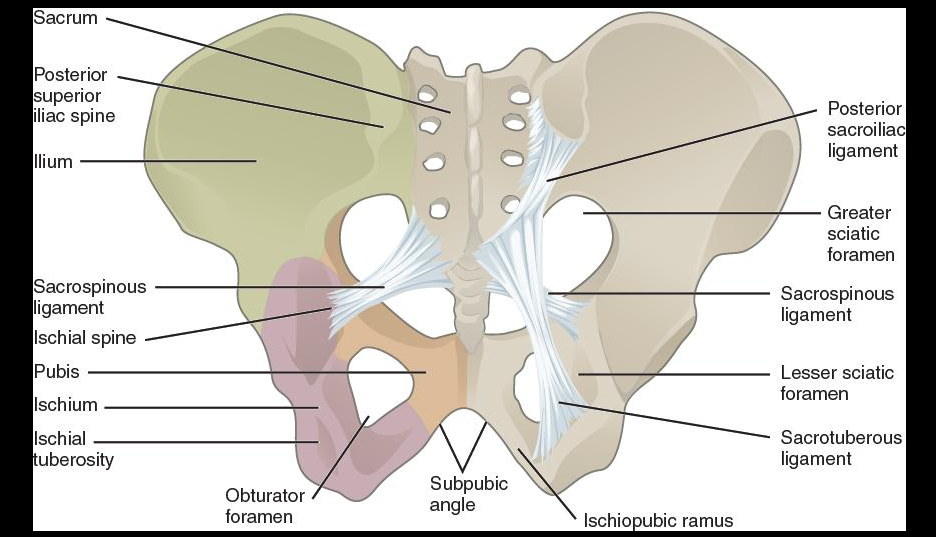
the ischial tuberosity of the ischium:
large projection on the posterior ischium that supports body weight when sitting and serves as an attachment site for hamstring muscles
the strongest part of the hip bone
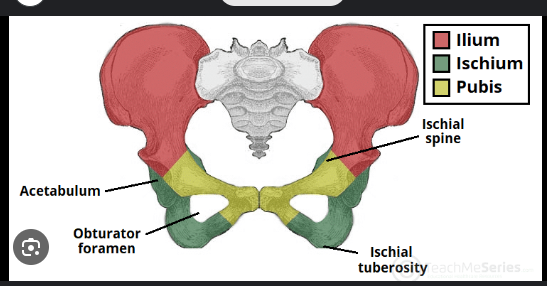
the acetabulum of the ischium:
deep socket that receives the head of the femur to form the hip joint
What is the pubis bone composed of?
the pubic symphysis
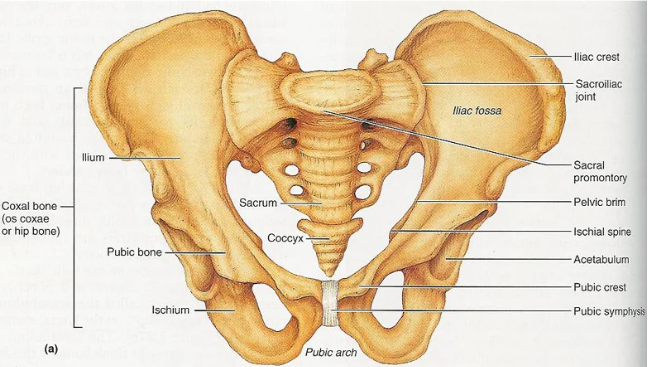
Pubic symphysis of the pubis bone:
formed by the extensions of the upbis that are connected by fibrocartilage and forms the pubic arch
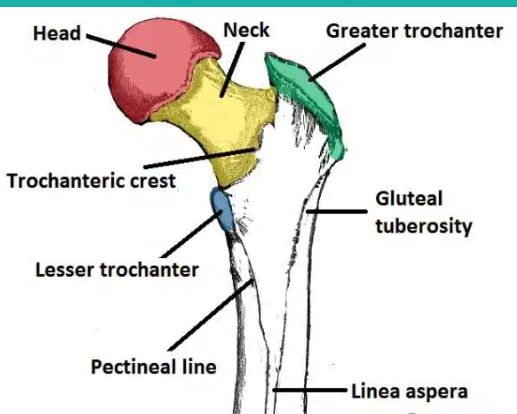
What are the parts of the femur?
the head
greater and lesser trochanters
the intertrochanteric line
the intertrochantric crest
the medial and lateral condyles
the gluteal tuberosity
the patellar surface
head of the femur:
inserts into the acetabulum of the ischium of the pelvic girdle to form the hip joint
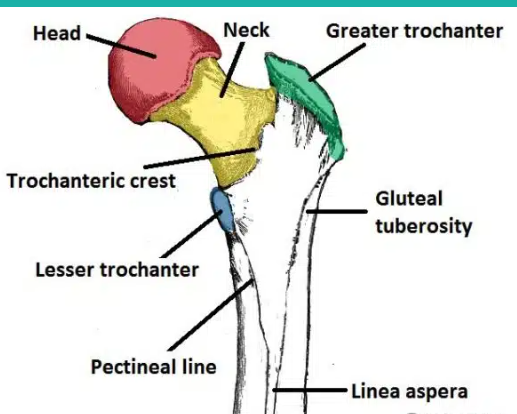
Greater and lesser trochanters of the humerus:
knobs for major muscle attachment, including the gluteal muscles
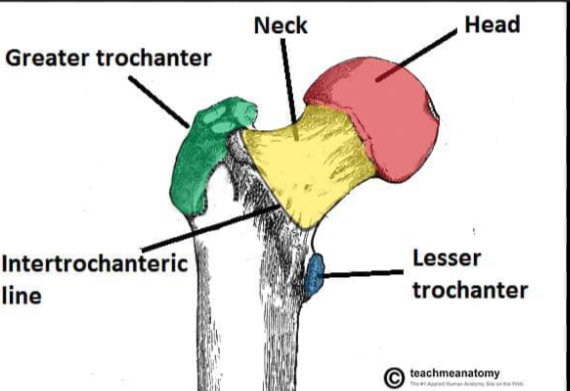
The intertrochanteric line of the femur:
A ridge on the anterior side of the femur between the greater and lesser trochanters. It serves as an attachment site for the iliofemoral ligament.
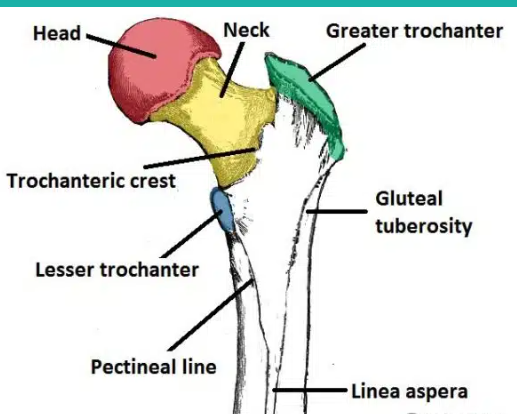
the intertrochanteric crest of the femur:
A ridge on the posterior side of the femur between the greater and lesser trochanters. It serves as an attachment site for the quadratus femoris muscle.
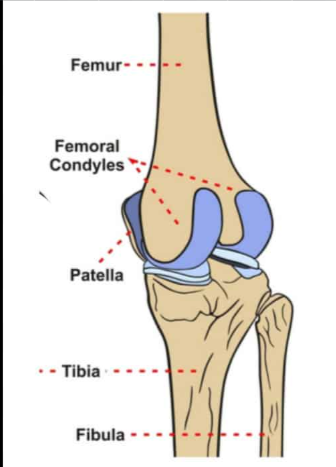
the medial and lateral condyles of the femur:
rounded projections on the distal end of the femur that articulate with the tibia to form the knee joint
the gluteal tuberosity of the femur:
A roughened ridge on the posterior side of the femur that serves as an attachment site for the gluteus maximus muscle
the patellar surface of the femur:
a smooth area on the anterior surface of the femur where the patella sits
Fun fact about the femur:
it is approximately one fourth of a person’s height
What is the patella?
a small, triangular sesamoid bone located in the front of the knee joint that is held in place by the patellar tendon
What is the largest bone in the body?
the femur
What is the second largest bone in the body?
the tibia
What are the parts of the tibia?
the medial and lateral condyles
the medial malleolus
the tibial tuberosity
the fibular notch
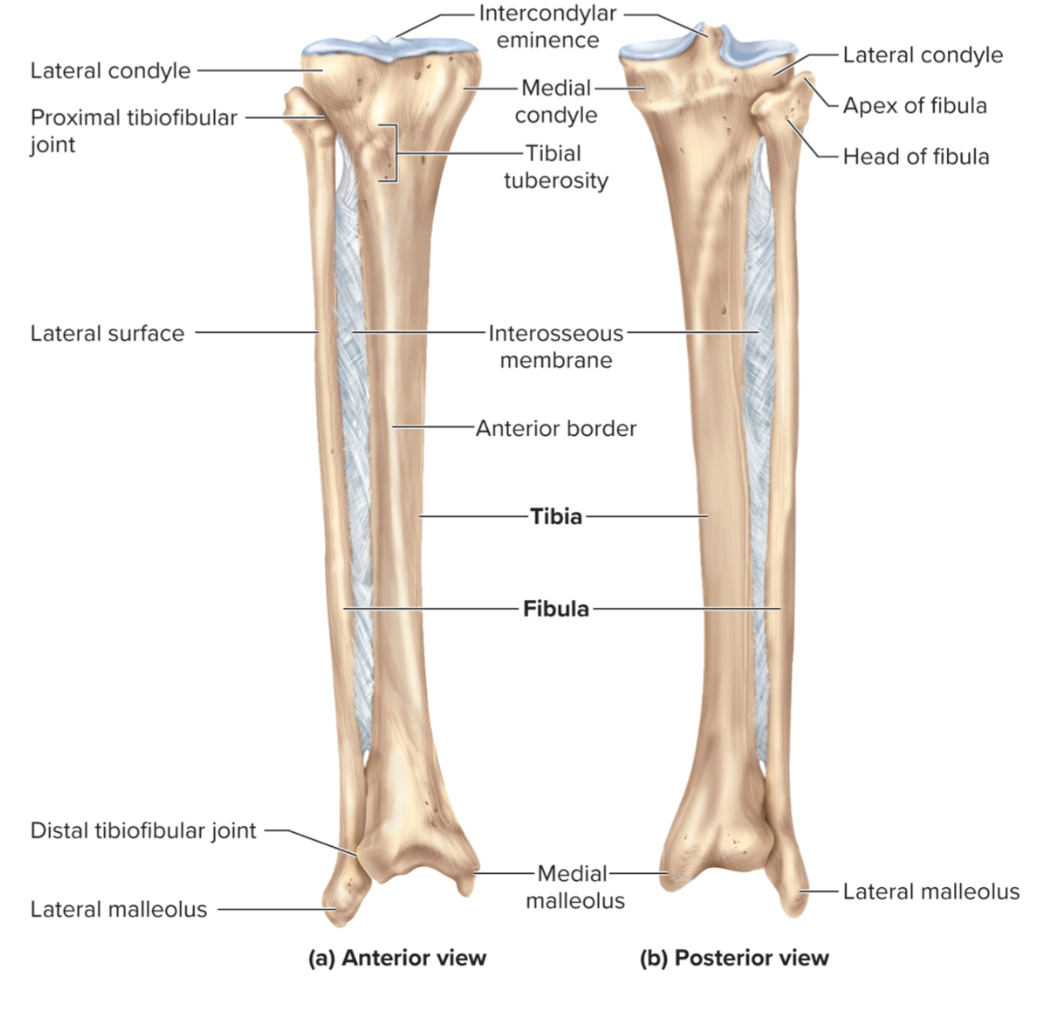
The medial and lateral condyles of the tibia:
regions on the tibia that articulate with the medial and lateral condyles of the femur to form the knee joint
the medial malleolus of the tibia:
a large, medial projection on the distal tibia that forms the inner ankle and provides ligament attachment for ankle stability.
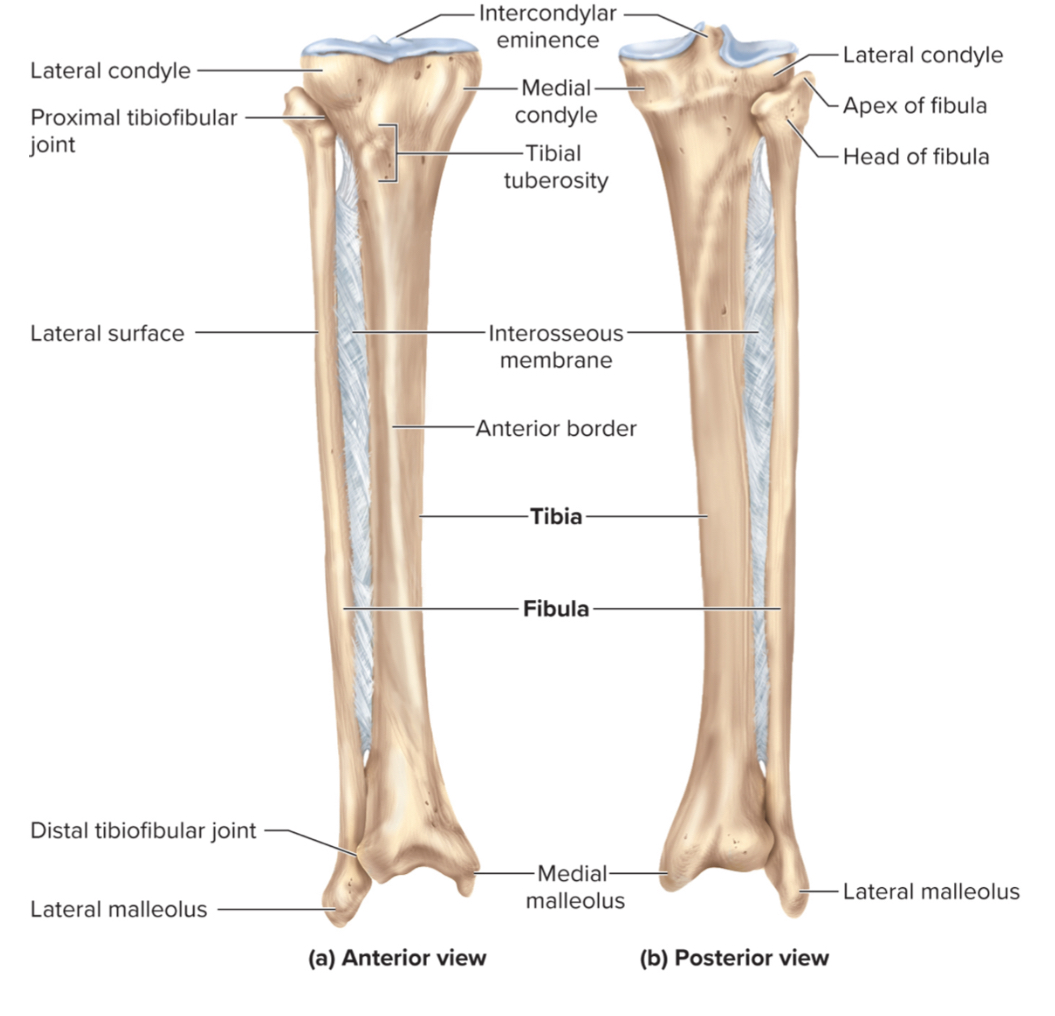
The tibial tuberosity of the tibia:
a large projection on the anterior, proximal tibia that serves as a site for the patellar ligament to attach
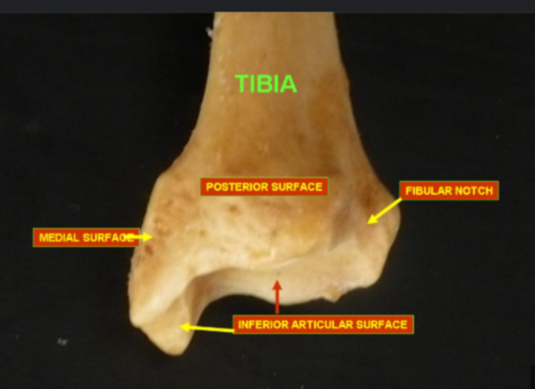
the fibular notch of the tibia:
a lateral depression on the distal tibia where the fibula and tibia articulate
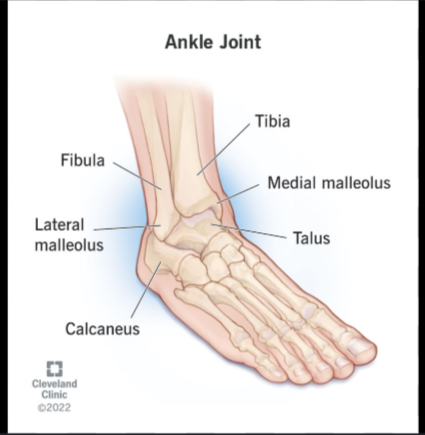
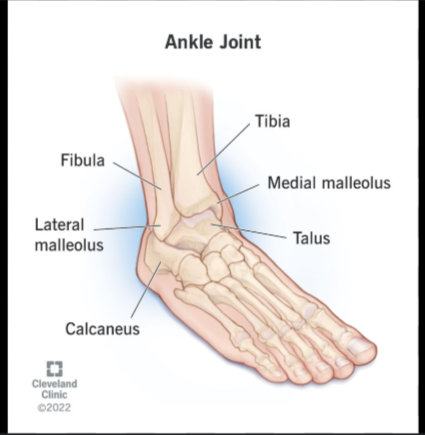
the lateral malleolus of the fibula:
A large, lateral projection on the distal fibula. It forms the outer ankle and provides ligament attachment for ankle stability.1
What three sets of bones make up the foot?
the tarsals
the metatarsals
the phalanges
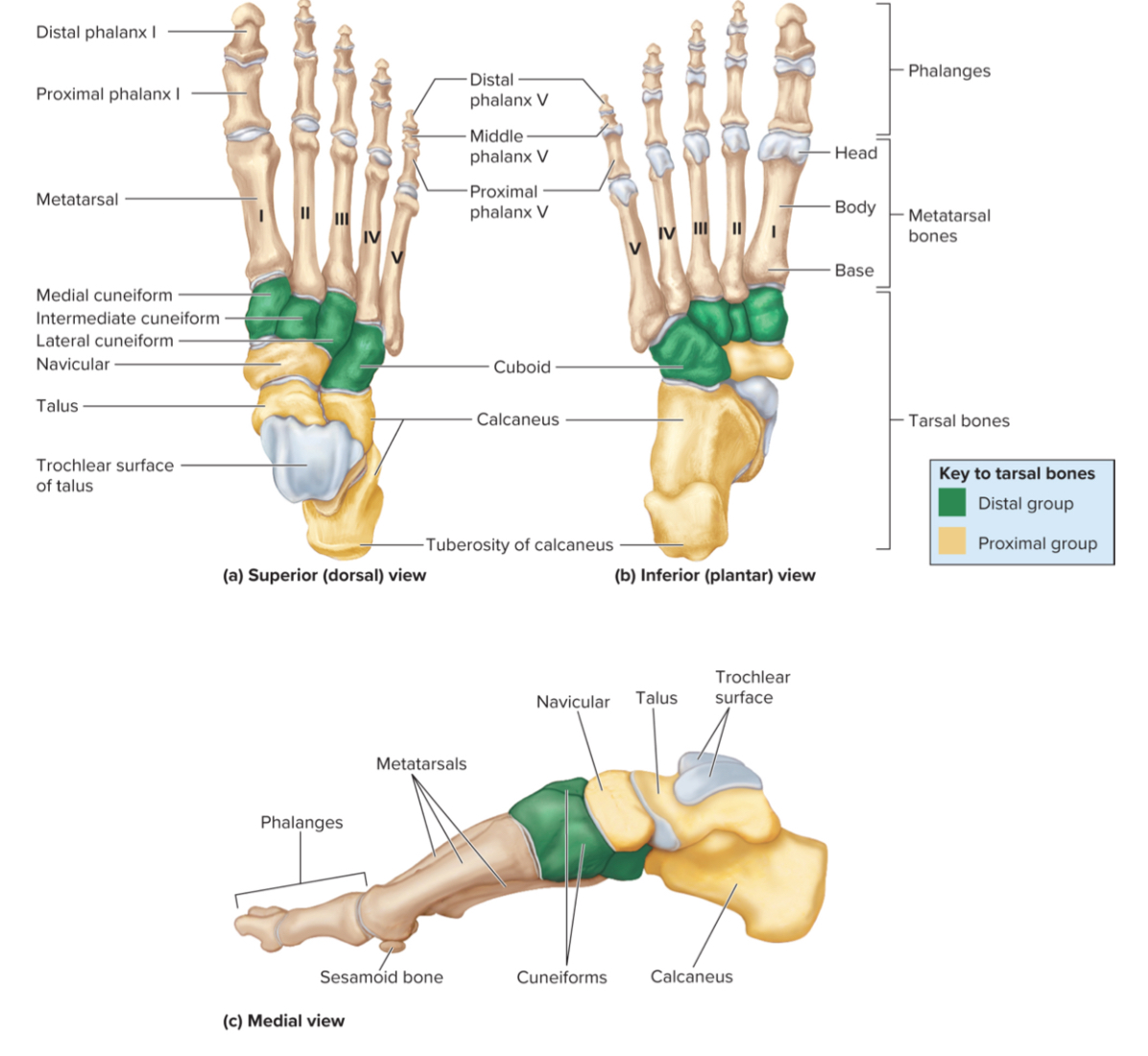
Tarsals of the foot:
Seven irregularly shaped bones in the ankle region that help form the ankle and support body weight
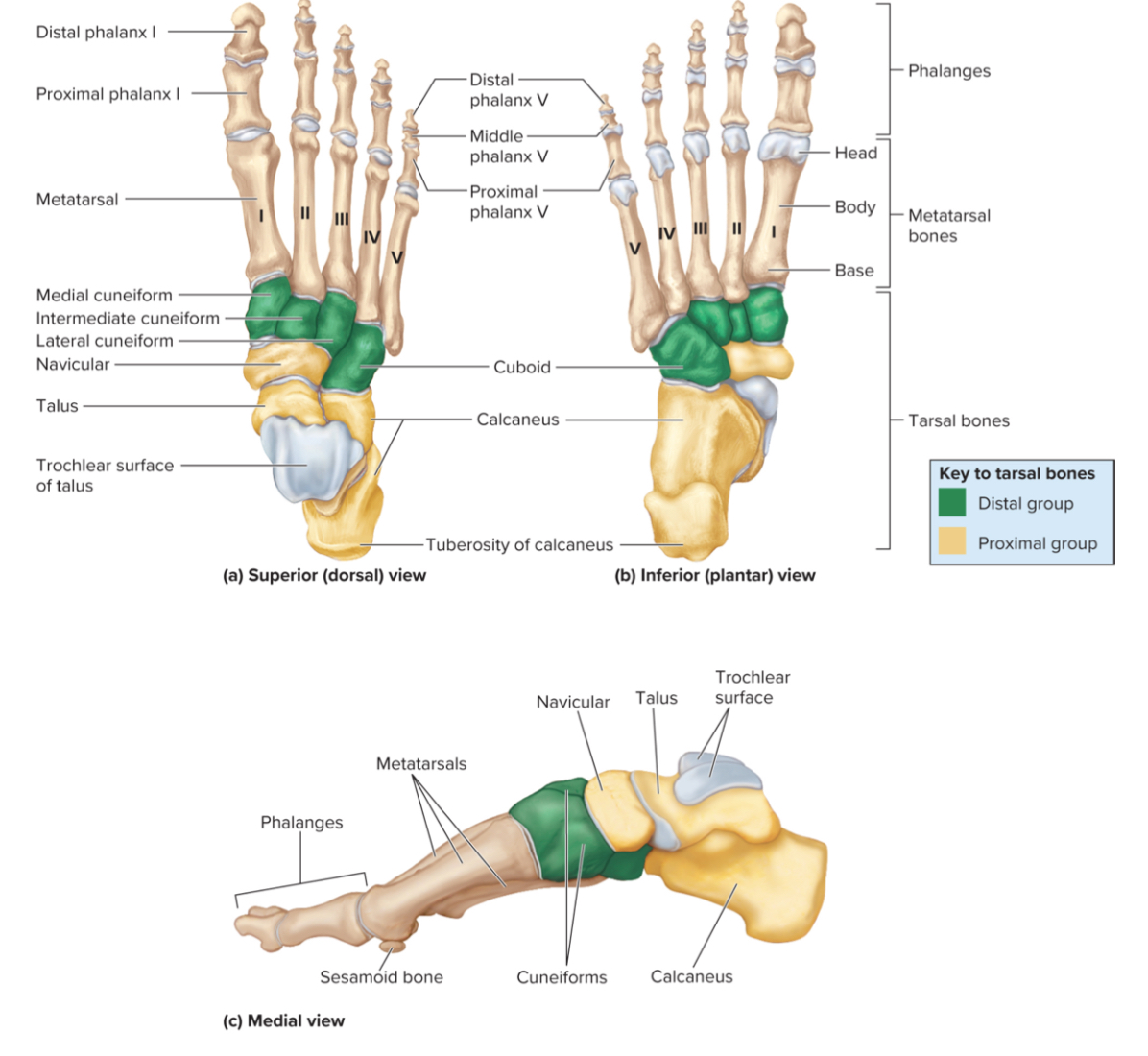
What are the 7 tarals of the foot?
the talus, calcaneus, navicular bone, cuboid, and three cuneiforms.
The calcaneus of the foot:
the largest tarsal bone that is the heel bone
it includes the calcaneal tuberosity is a projection of the calcaneus that touches the ground
What is planter fasciitis?
inflammation of the plantar fascia of the foot that causes pain on the underside of the calcaneus
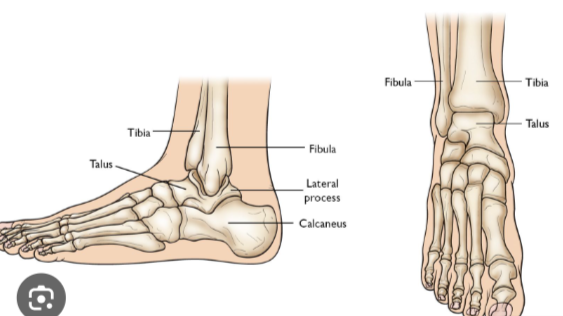
The talus of the foot:
A tarsal bone that sits on top of the calcaneus. It articulates with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint.
the metatarsals of the foot:
Five bones in the midfoot that connect the tarsals to the phalanges and help support body weight during walking and standing.
the phalanges of the foot:
the toes
What give the foot support and life to the foot and leg?
the three arches of the foot
What is pes planus?
aka flat feet which occurs when the arches fall or are absent all together
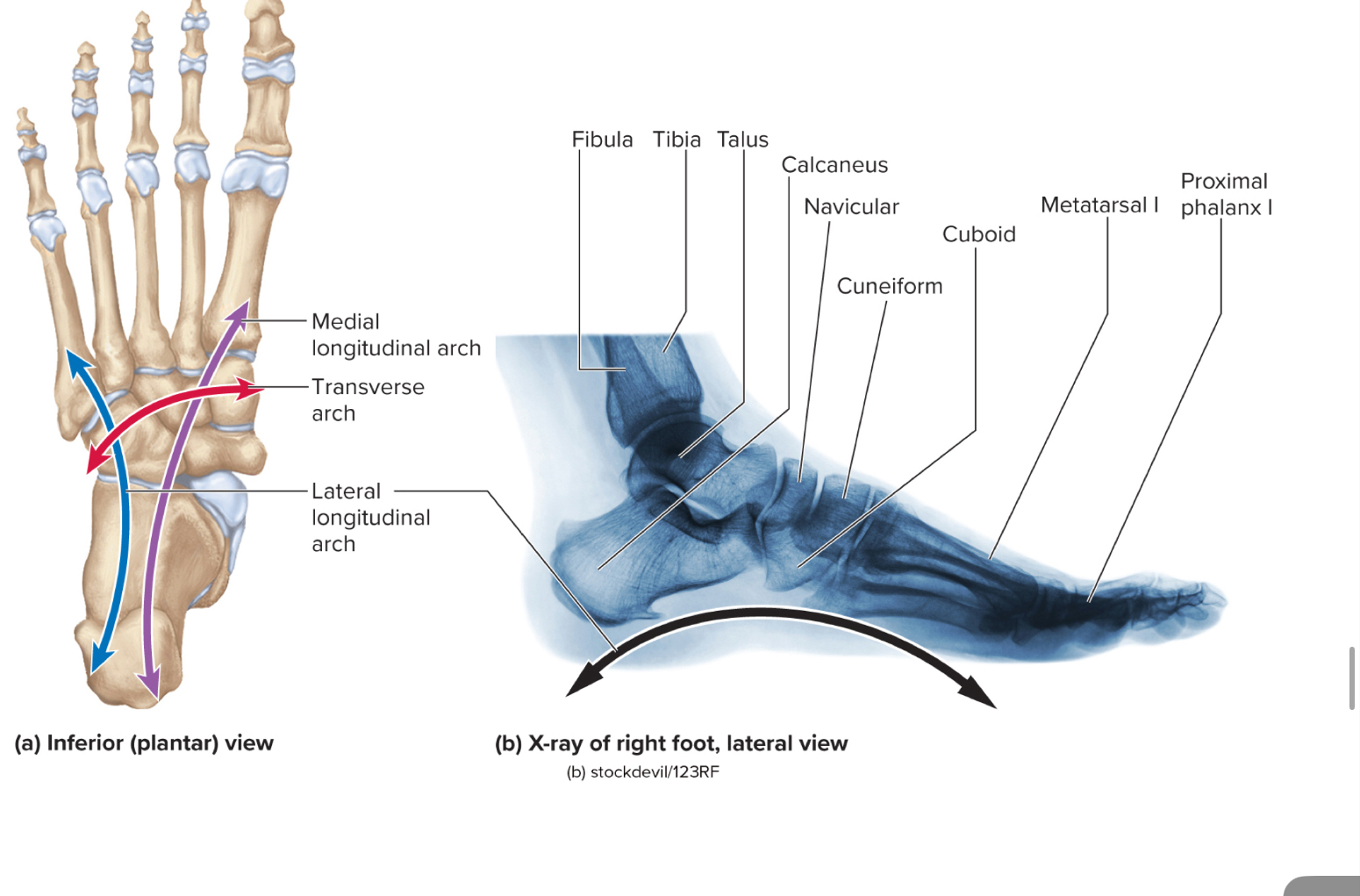
What are the three arches of the foot?
the medial longitudinal arch
the transverse arch
the lateral longitudinal arch