Biology Osmosis and Active Transport M8 Y10
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the role of water
The transport of nutrients and dissolved substances, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose, etc.
Metabolic reactions such as respiration and photosynthesis.
Regulating temperature within organisms
Providing a living environment for organisms.
What is Osmosis
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential through a partially permeable membrane.
What is the movement of water molecules in osmosis?
Water molecules therefore move from an area with high concentration of water molecules to a low concentration of water molecules. In doing this, water moves down the concentration gradient.
How is diffusion and osmosis similar and different?
Osmosis is very similar to diffusion in terms of it being a random movement of particles and a passive process. The main difference is that osmosis is the movement of water molecules only, whereas diffusion is the movement of solutes, liquids and gases.
When referring to osmosis what is the concentration of a solution and the concentration of water?
A low concentration of dissolved solutes means there is a high concentration of water molecules.
A high concentration of dissolved solutes means there is a low concentration of water molecules.
Advice to help you when answering questions linked to osmosis.
Refer to the concentration of water molecules in the solution
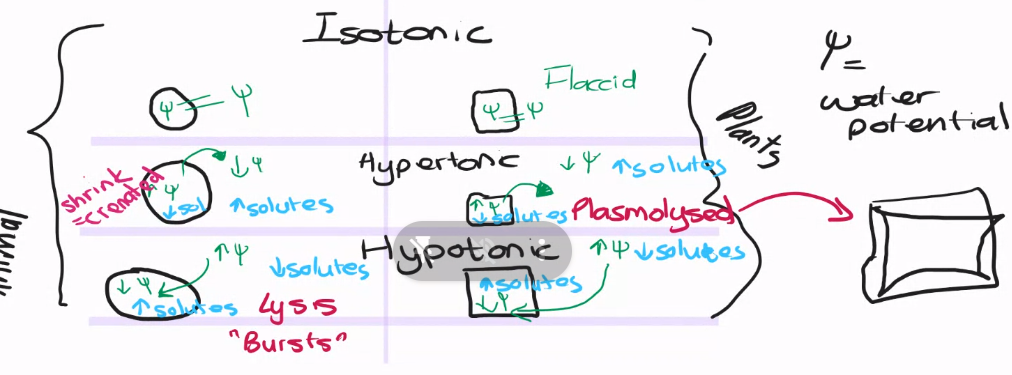
What is water potential?
Water potential is the cell's ability to draw water into itself.
Pure water has a water potential of zero and when solutes are added to it, the water potential falls and becomes more negative. Accordingly, salty water will have a lower water potential than pure water.
What is hypertonic?
A solution with a high solute concentration and a low water concentration.
What is isotonic?
A solution with a high solute concentration and a low water concentration.
What is hypotonic?
A solution with a low solute concentration and a high water concentration.
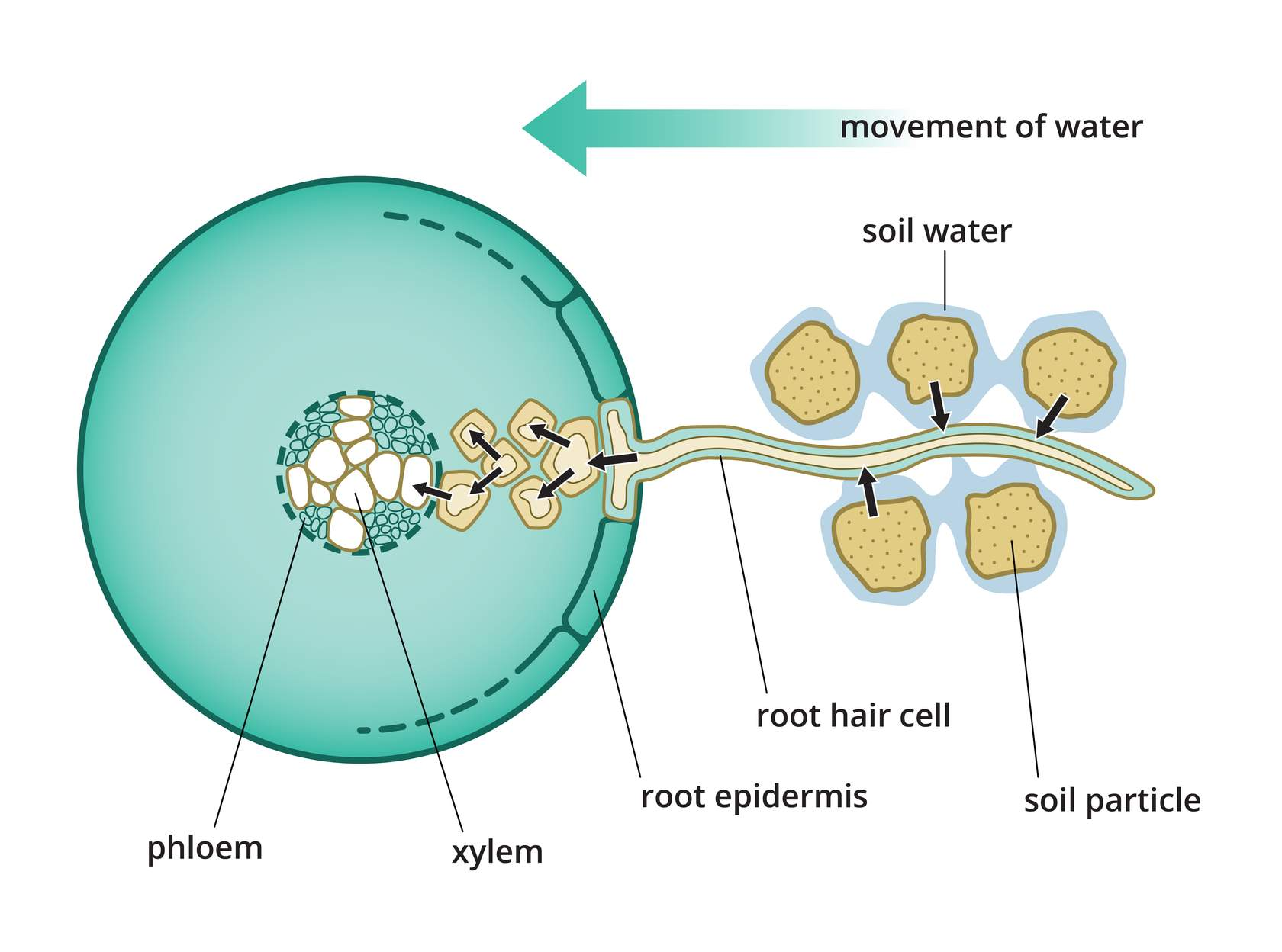
Osmosis and plant uptake of water
The roots of plants are surrounded by soil water and the cytoplasm inside the root hair cells has a lower concentration of water than the soil. Water molecules will therefore enter the root hair cells via osmosis.
The concentration of water within the root hair cell will increase and will become a higher concentration than in the surrounding cells of the root epidermis.
This will continue until the water molecules have reached the xylem vessels within the root. The water will then be transported along these vessels to other parts of the plan
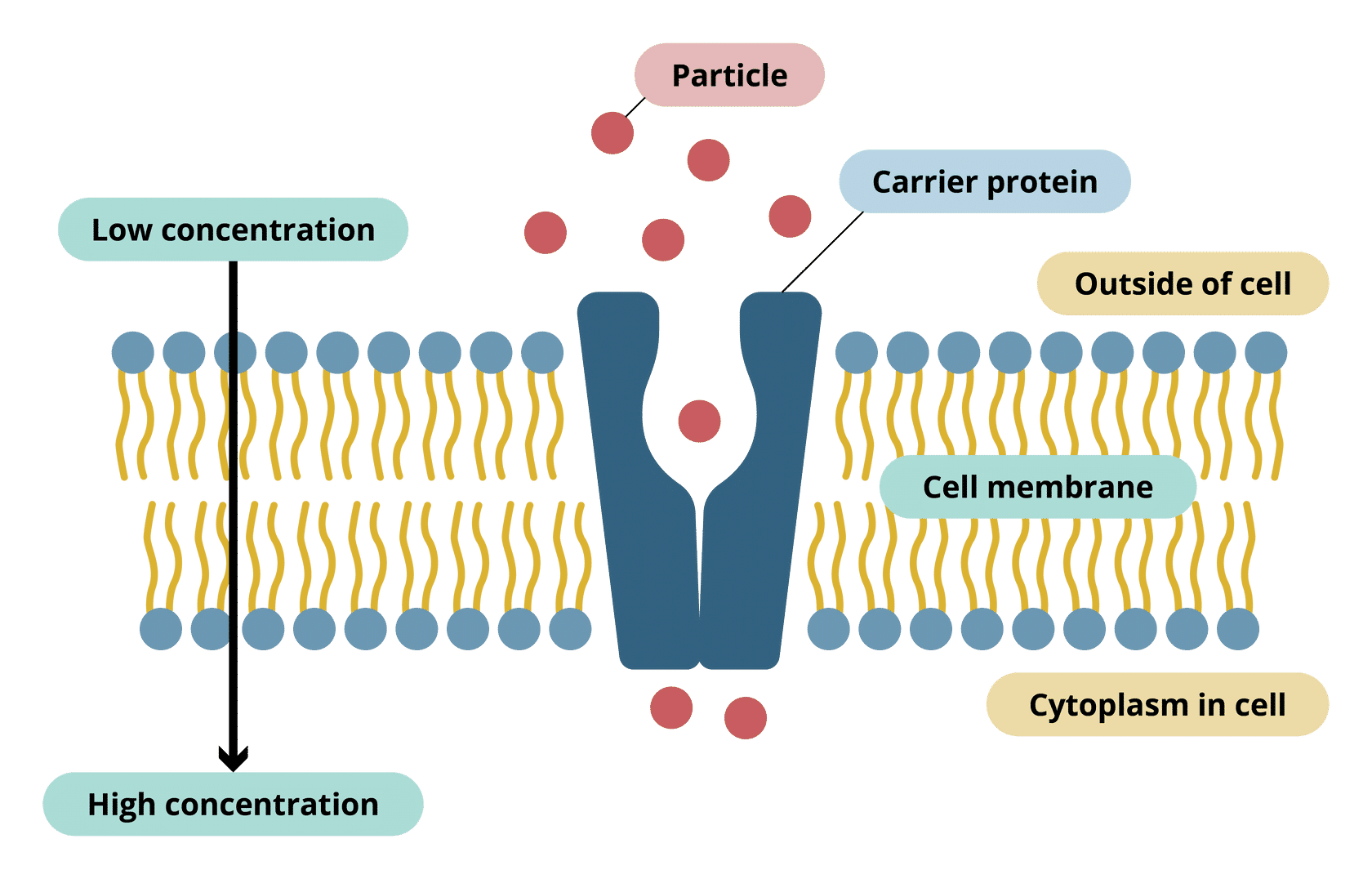
What is active transport?
Those particles then move against the concentration gradient: from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration through a partially permeable membrane.
Examples of active transport in animals
glucose is transported from the small intestine where it is digested into the bloodstream. This happens via active transport when an animal has not eaten and glucose concentrations in the intestine may be lower. This will therefore require energy. As the small intestine will have a lower concentration of glucose than the bloodstream, the glucose will move against the concentration gradient into the bloodstream where it is subsequently transported to the body's cells.
Examples if active transport in plant?
In plants, the root hair cells absorb nitrates and mineral ions from the soil. There is a higher concentration of nitrates and mineral ions within the root hair cells in comparison to the dilute solutions in the soil. By means of active transport, the nitrates and mineral ions will enter the partially permeable membrane of the root hair cells from the soil, moving against the concentration gradient.
What are the role of protein carriers
Active transport occurs when particles are transported across a partially permeable membrane of a cell. There are special carrier proteins in the cell membrane of cells that help to move the particles against the concentration gradient
What is an example of the role of protein carriers
The nitrate or mineral ion will enter the carrier protein on one side of the cell membrane. The carrier protein will then change shape; this change in shape will push the nitrate or mineral ion to the other side of the cell membrane. The carrier protein needs the energy to change shape and this energy is provided by the mitochondria of the cell.
Hypertonic and Hypotonic solutions in cells