Human Body Systems HBS PLTW WCHS Mr. Alasti 1.1 Review
1/222
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
223 Terms
Radiology
A branch of medicine that uses imaging technology to diagnose and treat disease
What are the day to day activities of an X-ray technician?
Producing timely, accurate, and safe radiation images for a patient, assisting in surgeries, starting IVs that are needed for injecting contrast
How are bones able to endure stretching and squeezing?
Thanks to the hard mineral salts and flexible collagen fibers in bones
Fracture
A crack or break in a bone
How does a fracture happen?
When they are under abnormal forces such as twisting, bending, or impact
Compression force
The force that occurs when a physical force presses inward on an object, causing it to become compacted
Closed fracture
A break in a bone that does not penetrate the skin
Open fracture
A broken bone that breaks through the skin, creating an open wound
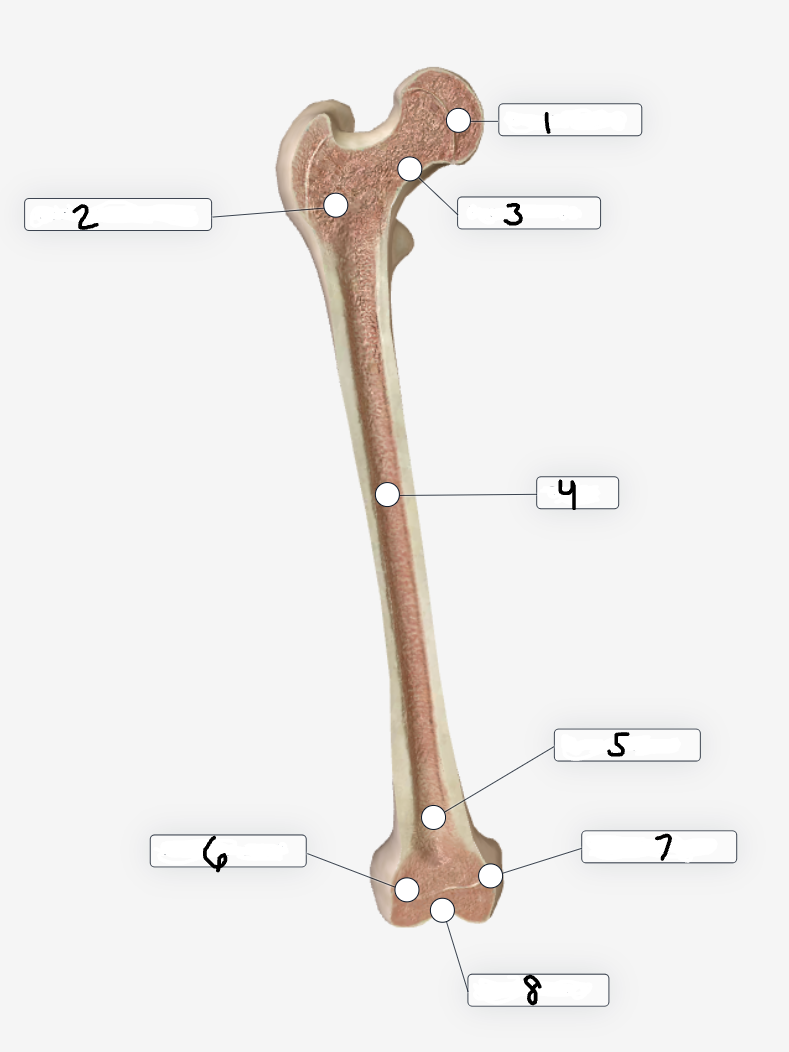
Label region 1
Femoral head
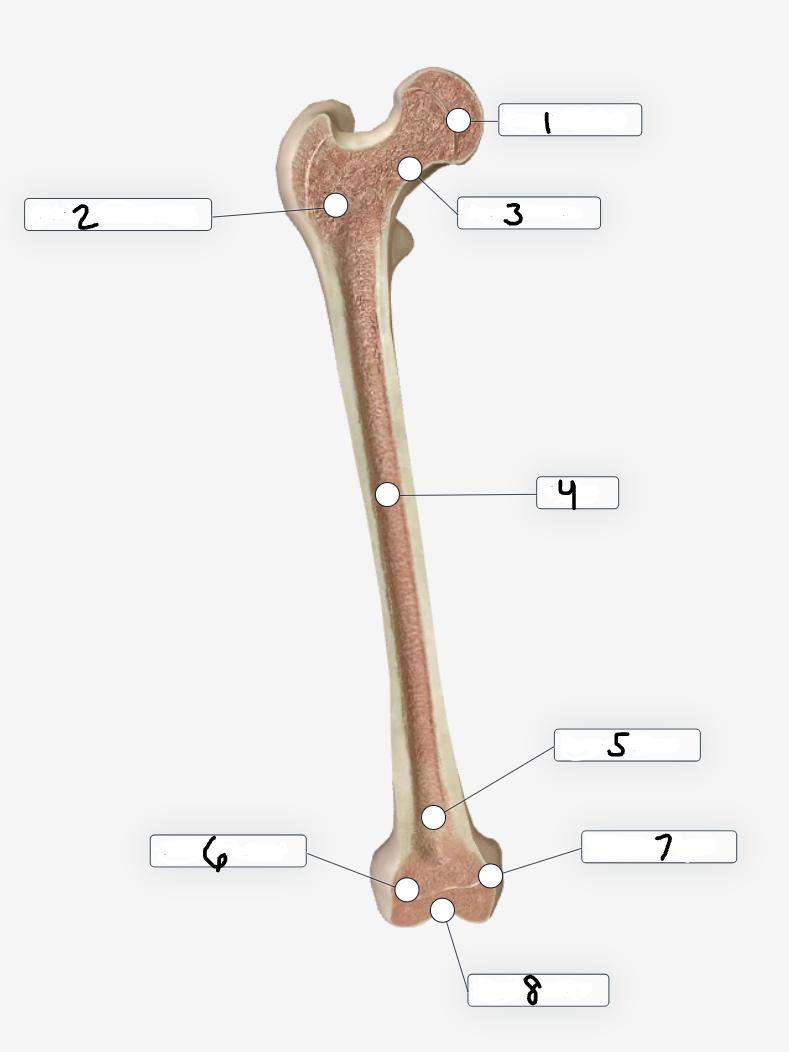
Label region 2
Trochanteric region
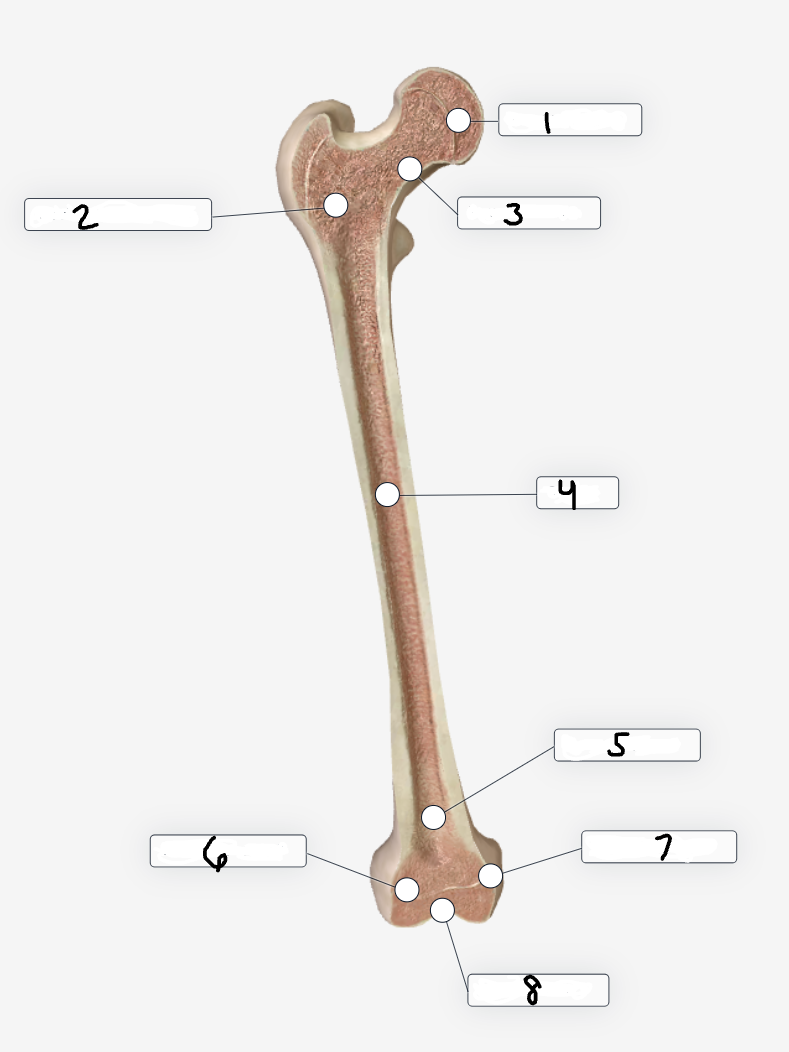
Label region 3
Femoral neck
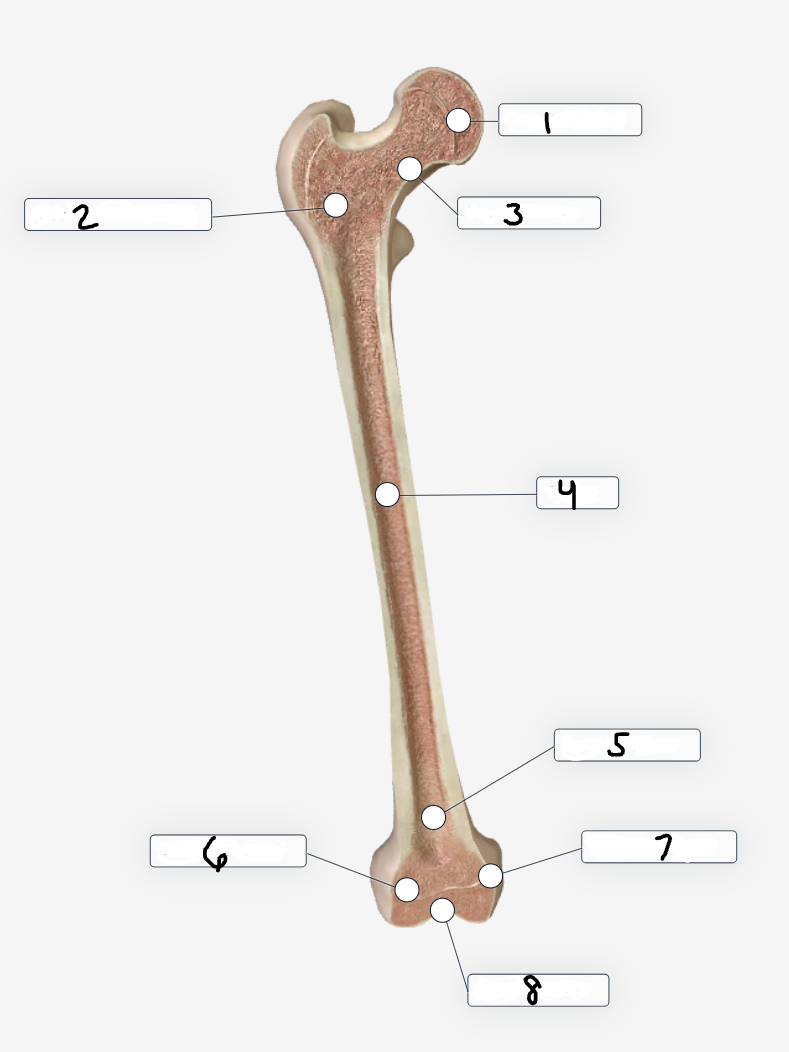
Label region 4
shaft
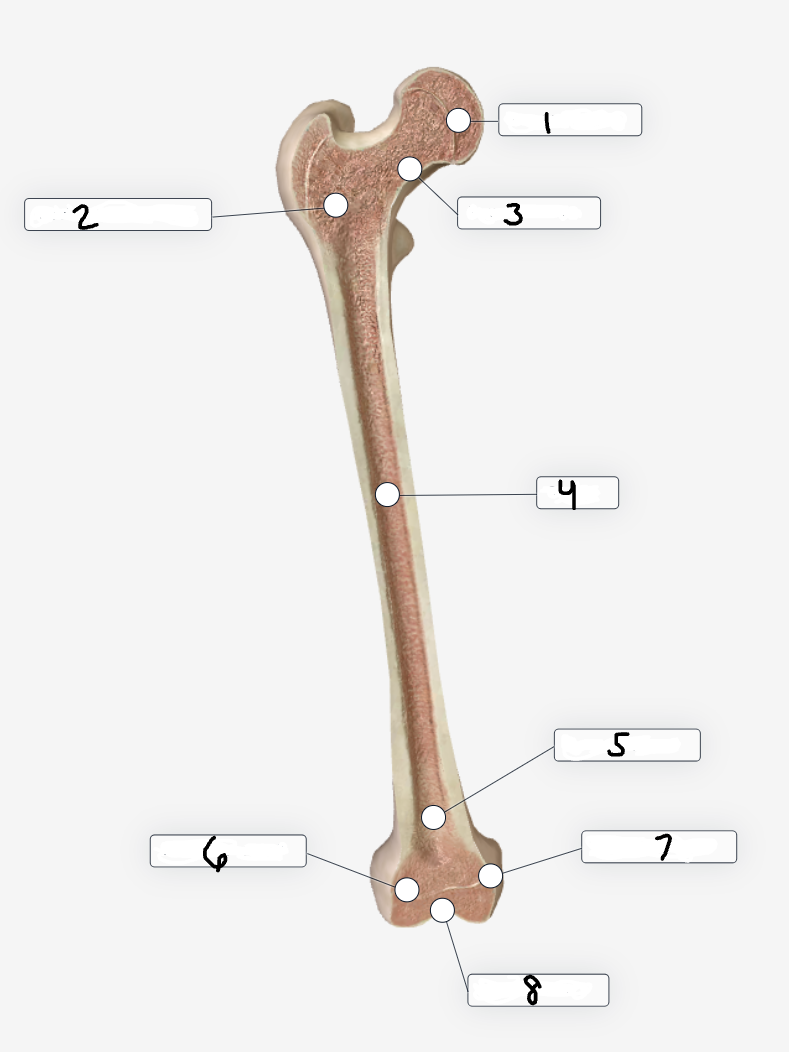
Label region 5
Extra-articular
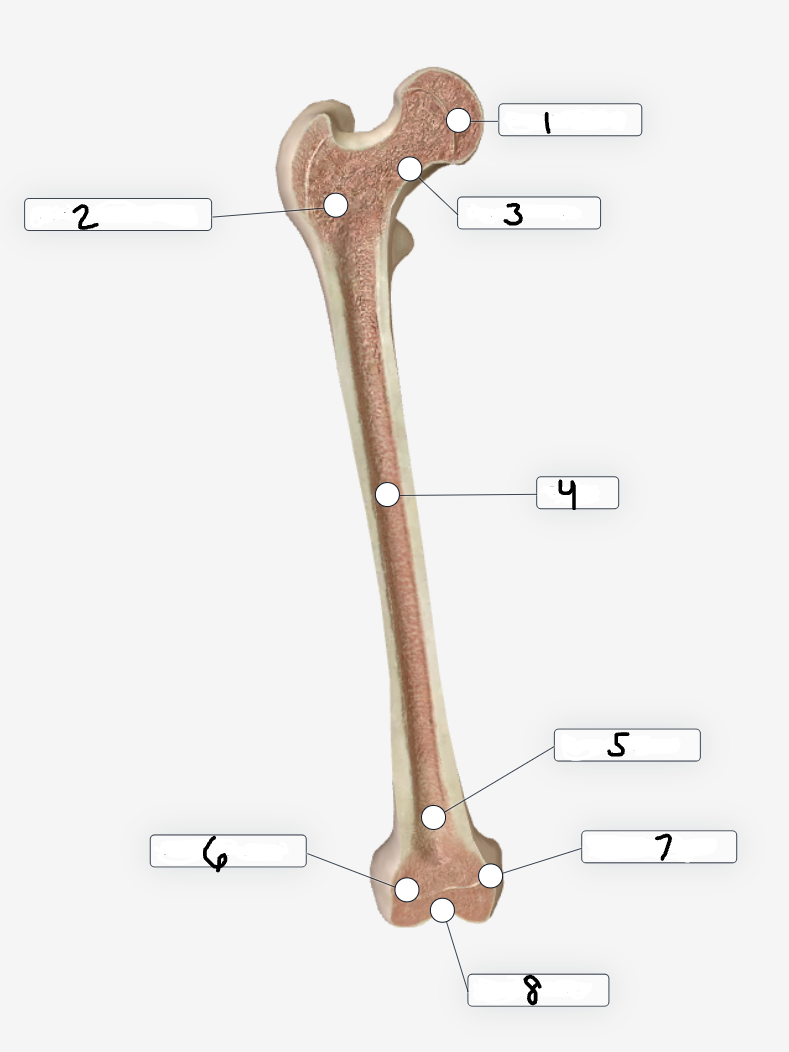
Label region 6
Lateral condyle
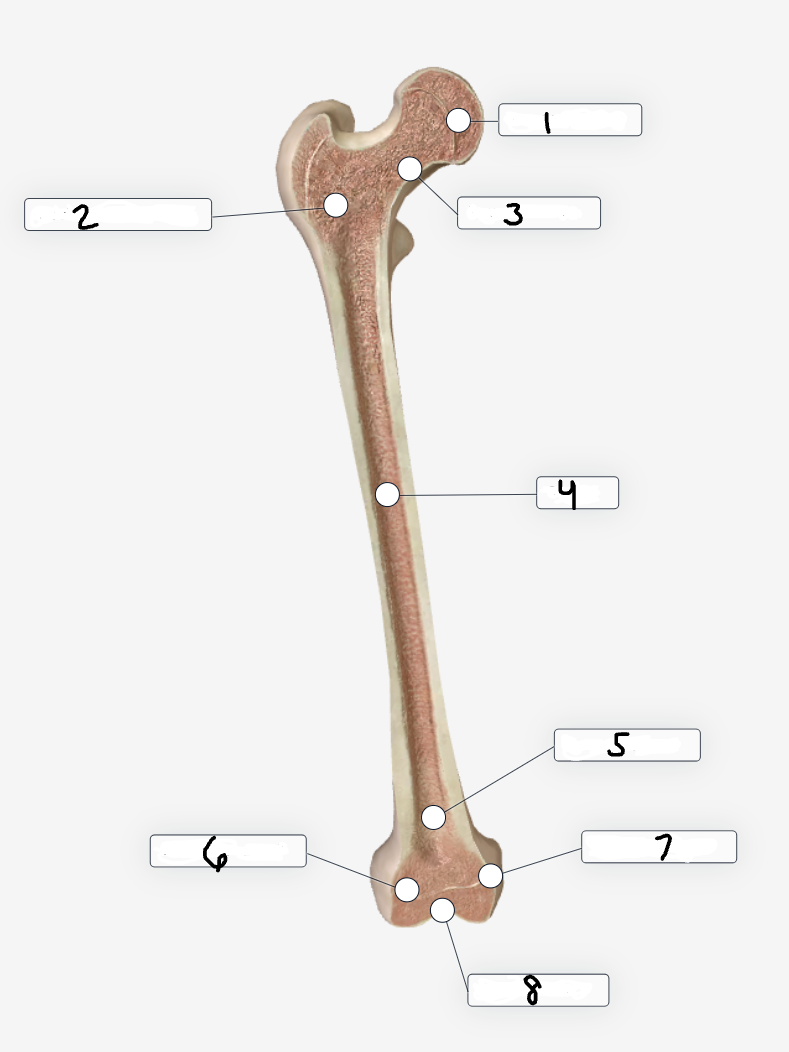
Label region 7
Medial condyle
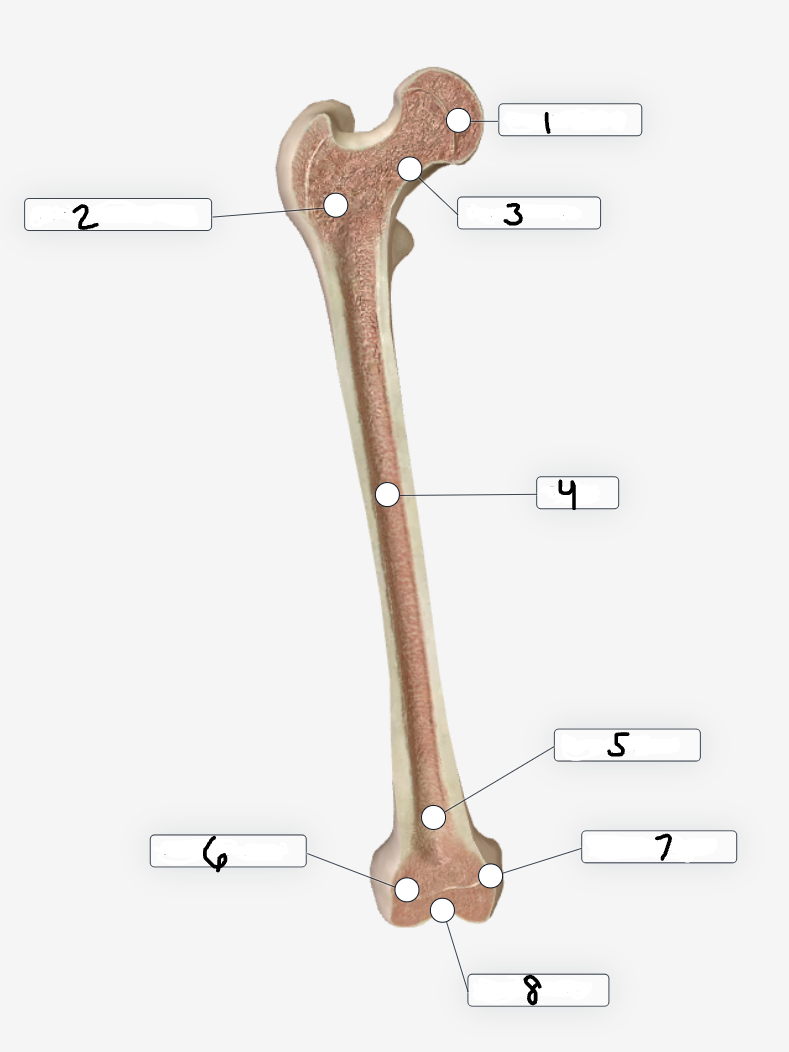
Label region 8
Intra-articular
What are x-rays?
A painless imaging technique that allows doctors to view internal injury and diagnose a variety of illnesses
How are x-rays administered?
A high-energy form of radiation is passed through the body and projected onto a film. Hard tissues such as bone absorb the X-rays and appear white. Softer tissues, such a muscle, appear black and gray
X-ray discoveries in 1895
Willhelm Conrad Rontgen received the Nobel Prize for Physics for his discovery of X-rays which revolutionized diagnostic medicine
X-ray discoveries in 1898
Marie Curie worked on the X-ray machine discovered by Willhem Roentgen, used her newly discovered element (radium) for x-rays, made the x-rays stronger and more accurate, and made small, portable x-ray machines
X-ray discoveries in 1939-1945
Industrial radiography began to develop during WWII to detect flaws in pressure vessels, pipes, and other equipment
X-ray discoveries in 1942
The Met Lab was established at the University of Chicago to carry out research for the atomic bomb project. Ernest O. Wollan’s job was assembling and heading up a group of radiation protection specialists
True or false: Bone is living tissue
True
Osteoblasts
A bone-forming cell
Osteoclasts
Any of the large multinucleate cells closely associated with areas of bone resportion (such as in a fracture that is
What do osteoblasts and osteoclasts do together?
Help maintain a balance of building new bone and breaking down old or damaged tissue
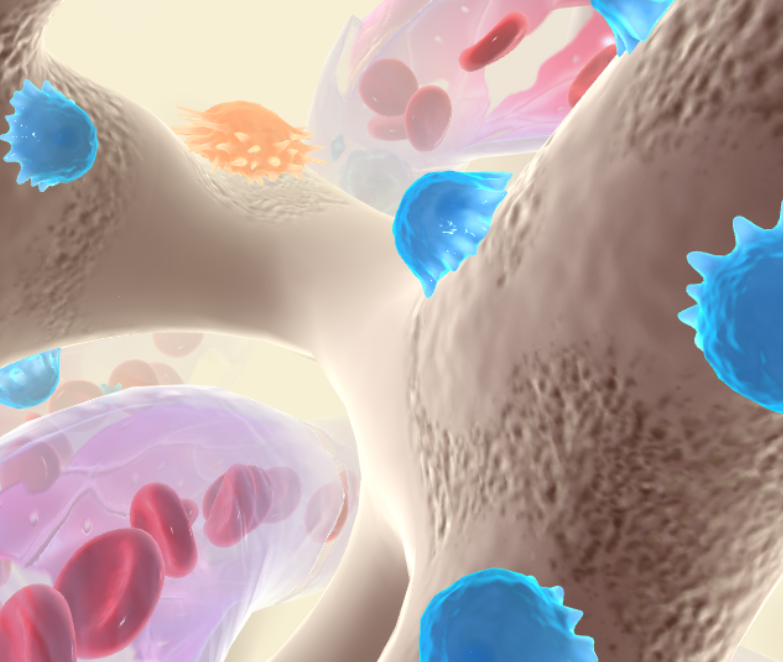
What are the blue figures?
Osteoblasts
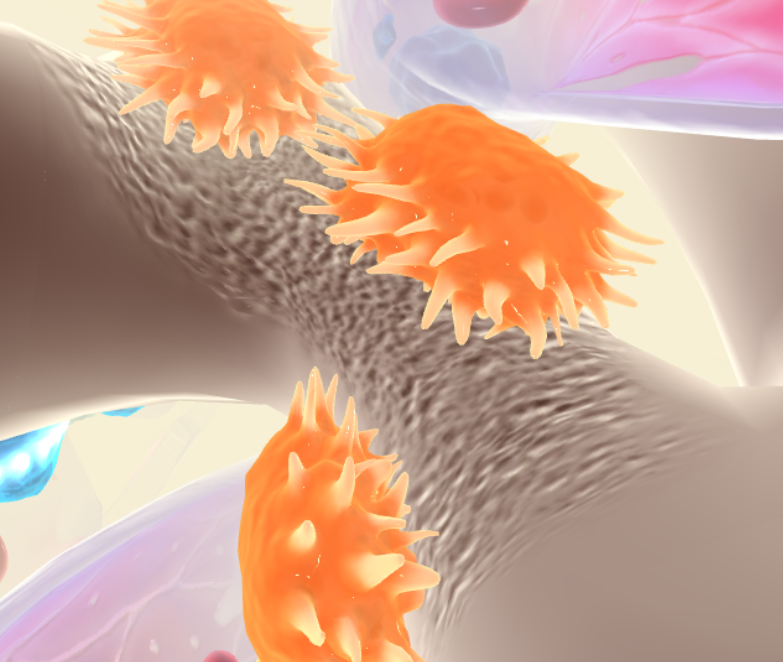
What are the orange figures?
Osteoclasts
List the stages of fracture healing
Hematoma Formation
Fibrocartilage Callus Formation
Bony Callus Formation
Bone Remodeling
What takes place during the hematoma formation stage?
Blood vessels that are ruptured during the break swell to form a mass called a hematoma between the broken bones. This clotting reduces the blood supply to many of the cells in the region, resulting in the dying of those cells
What takes place during the fibrocartilage callus formation stage?
New capillaries begin to form into the clotted blood and connective tissues cells form a mass of repair tissue called a fibrocartilage callus. This callus contains some cartilage, some bone, and some collagen fibers. This closes the gap between the broken bones
Callus
Fibrous tissues and cartilage that replace the blood clot at the fracture site
What takes place during the bony callus formation stage?
The fibrocartilage callus is gradually replaced by one made of spongy bone, referred to as the bony callus. Osteoclasts and osteoblasts move to the area and multiply
What takes place during the bone remodeling stage?
Over the weeks and months to come, the callus is remodeled with the help of osteoclasts and osteoblasts. The shape of the bone will gradually return to normal and there will be little evidence of the fracture
What are the main ways of repairing a bone fracture?
Casting
External fixation
Internal fixation (plating & nailing)
Pros and cons of casting when repairing a fracture
Pros:
Non-invasive
Reduces risk of infection since there is no surgical aspect
Cons:
Bulky
Works best on children and may not be efficient on adults
Hard to deal with hygiene
Pros and cons of external fixation when repairing a fracture
Pros:
Minimally invasive
Quick solution
Cons:
Involves some surgery
Temporary, so another route must be taken eventually
Pins increase the chance of infection
Pros and cons of internal fixation, specifically plating, when repairing a fracture
Pros:
Most stable option
Preferred on most adult patients
It can be customizable for everyone
Cons:
A large incision is needed
Surgery increases the risk of infection
Pros and cons of internal fixation, specifically nailing, when repairing a fracture
Pros:
Smaller incision which is aesthetically pleasing and lowers risk of infection
Shorter recovery time
Cons:
Preferred on specifically long bones
Cast technician
Help doctors and surgeons in clinical settings with tasks such as setting bones, applying and removing casts, orthopedic bracing, the removal of sutures and staples, and teaching patients to use walking aids
X-rays
A type of radiation that uses electromagnetic waves. X-ray imaging created pictures of the inside of your body. The images show the parts of your body in different shades of black and white
Ultrasounds
Imaging that uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of your body
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
A medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to take pictures of the soft tissues of the body
Functions of the skeletal system
Leverage
Storage of minerals (calcium phosphate)
Storage of lipids (yellow marrow)
Blood cell production (red marrow)
Protection
Support
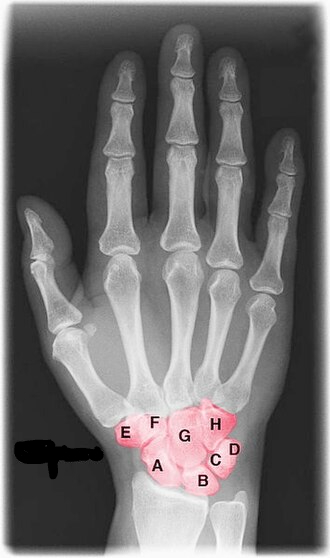
What is this region?
Carpal
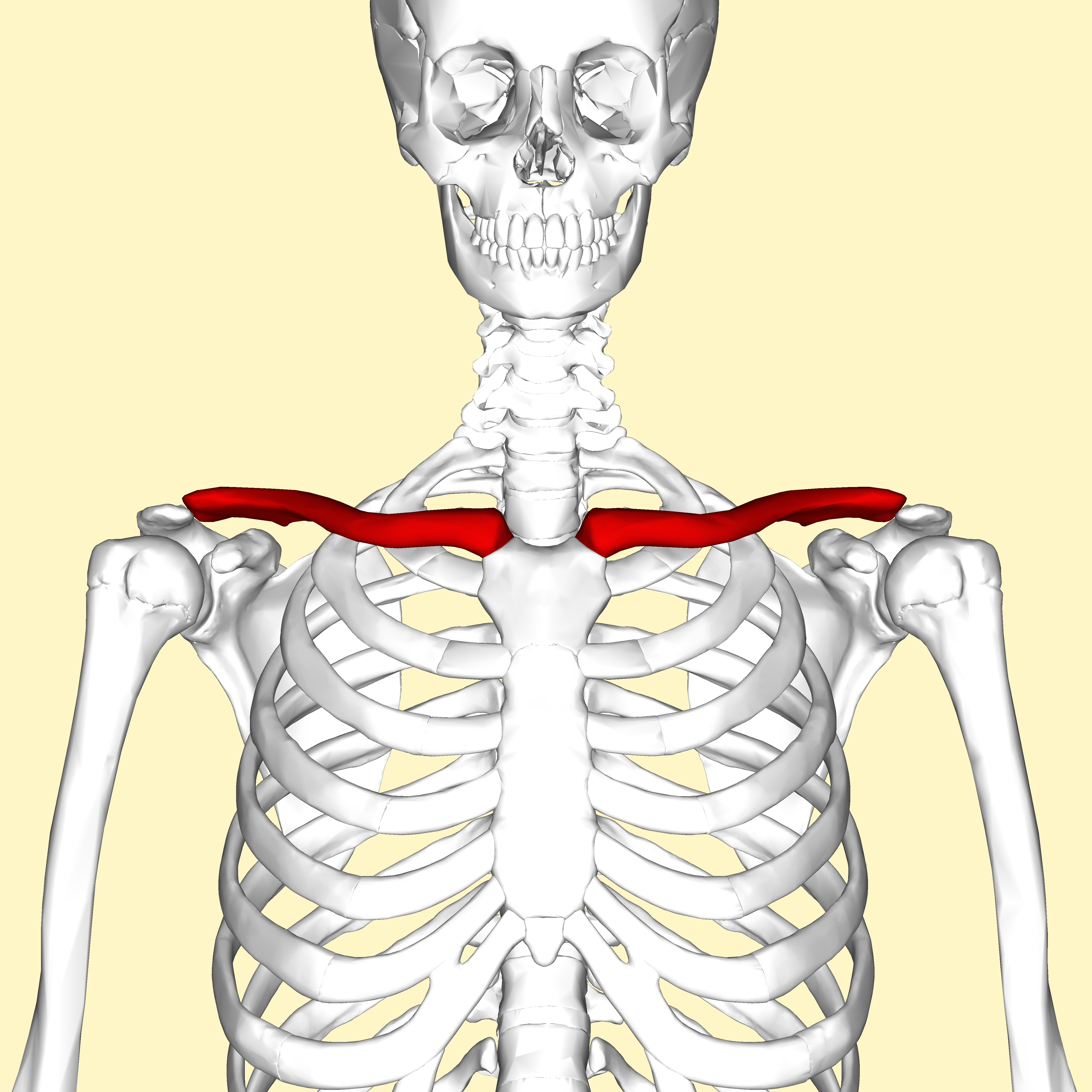
What is this region?
Clavicle
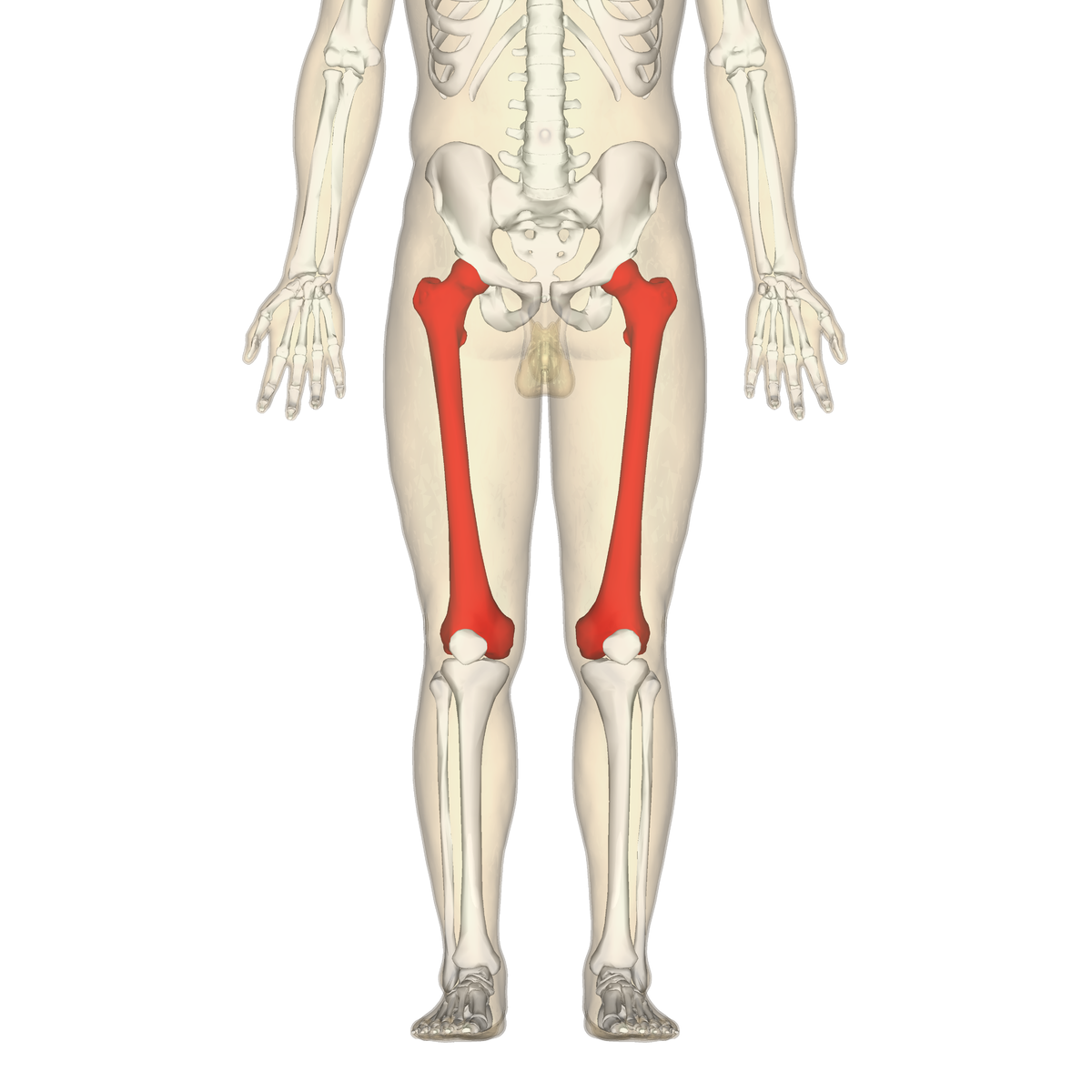
What is this region?
Femur
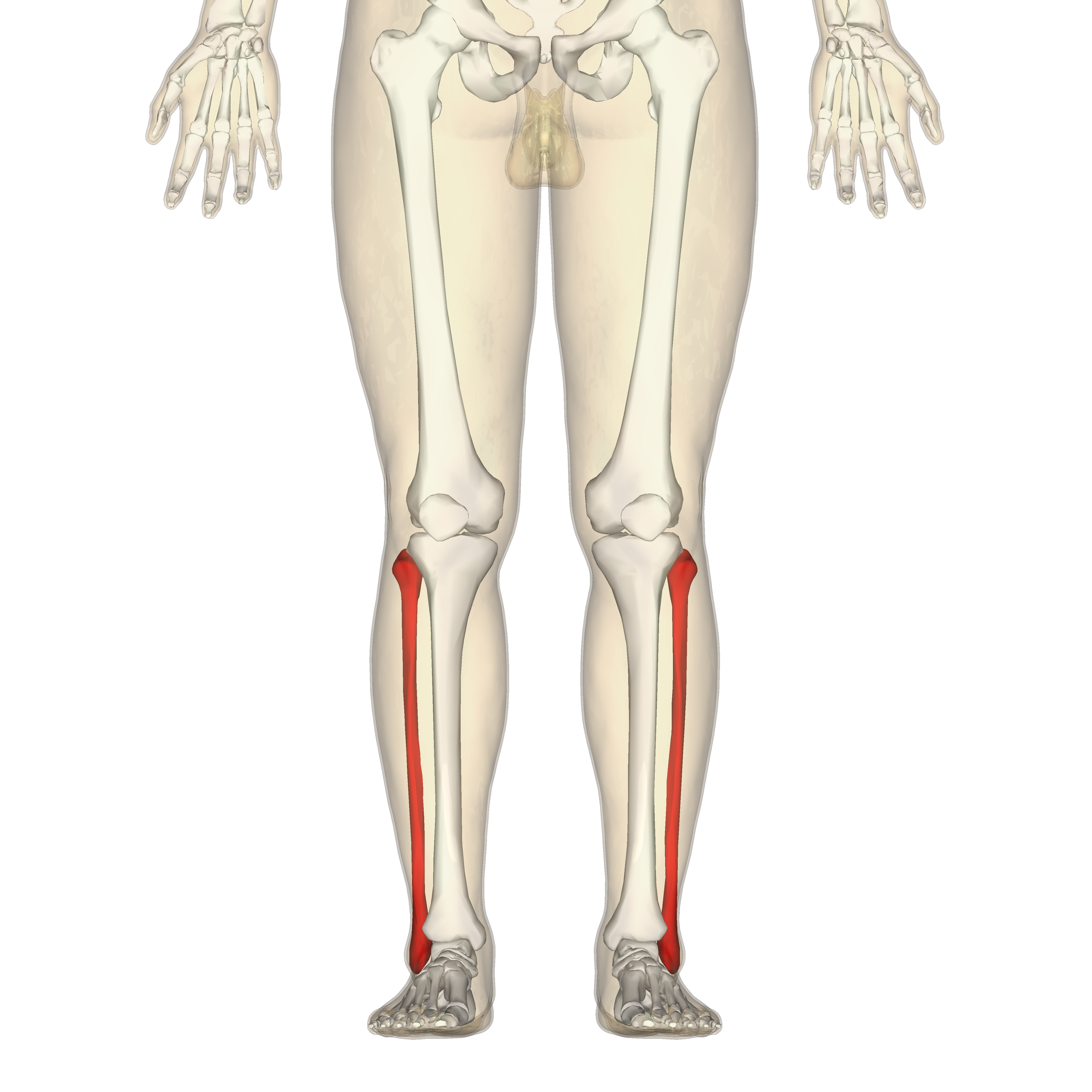
What is this region?
Fibula
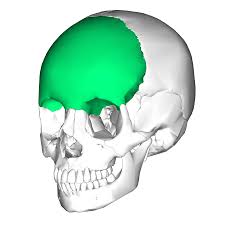
What is this region?
Frontal Bone
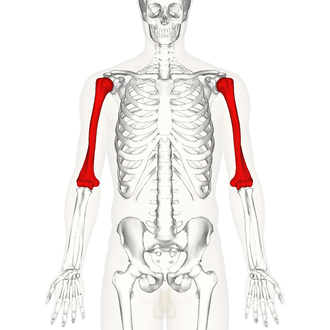
What is this region?
Humerus
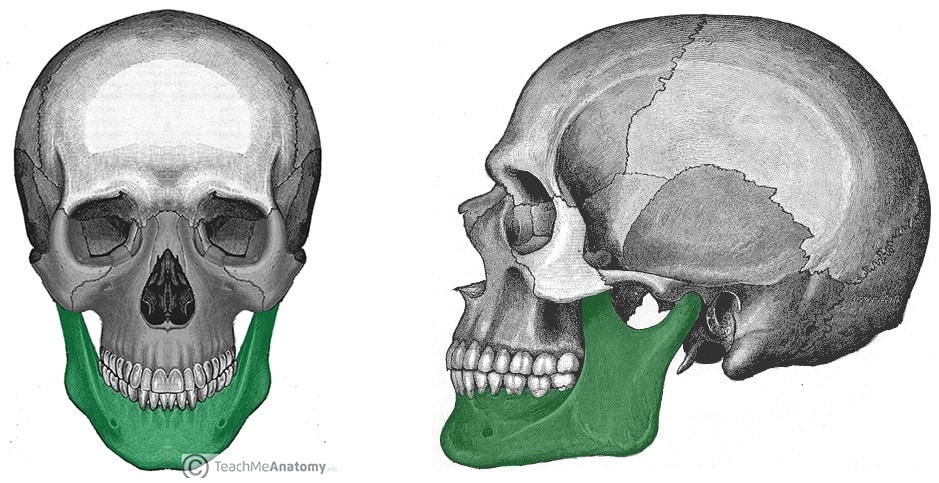
What is this region?
Mandible
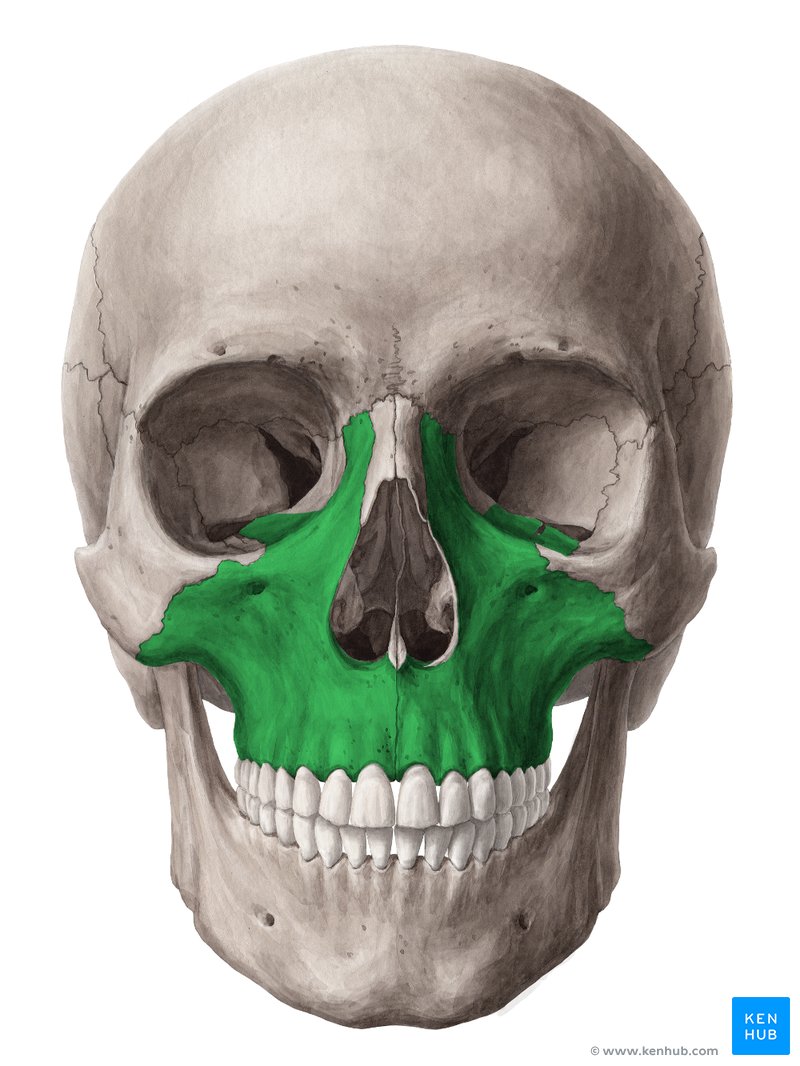
What is this region?
Maxilla
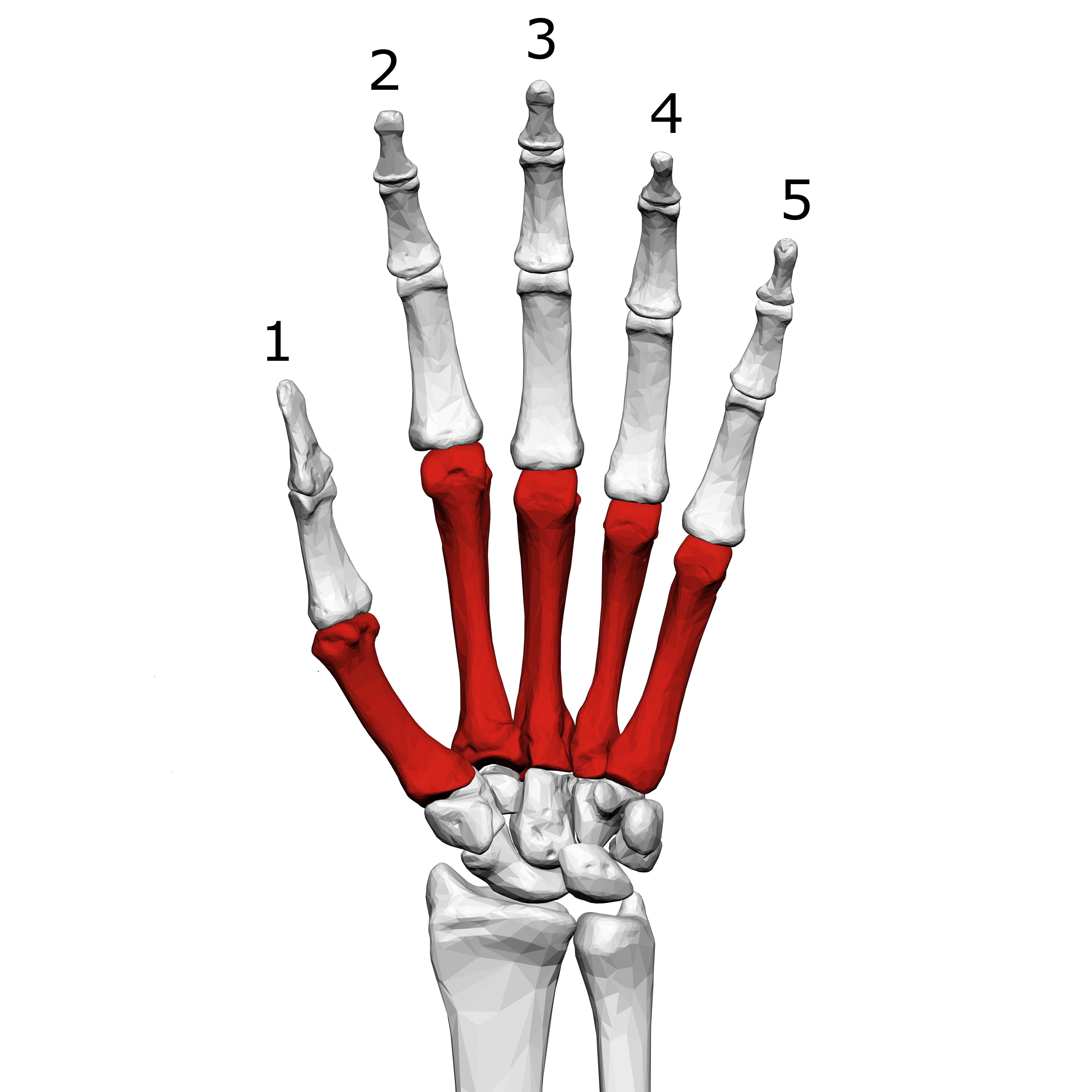
What is this region?
Metacarpals
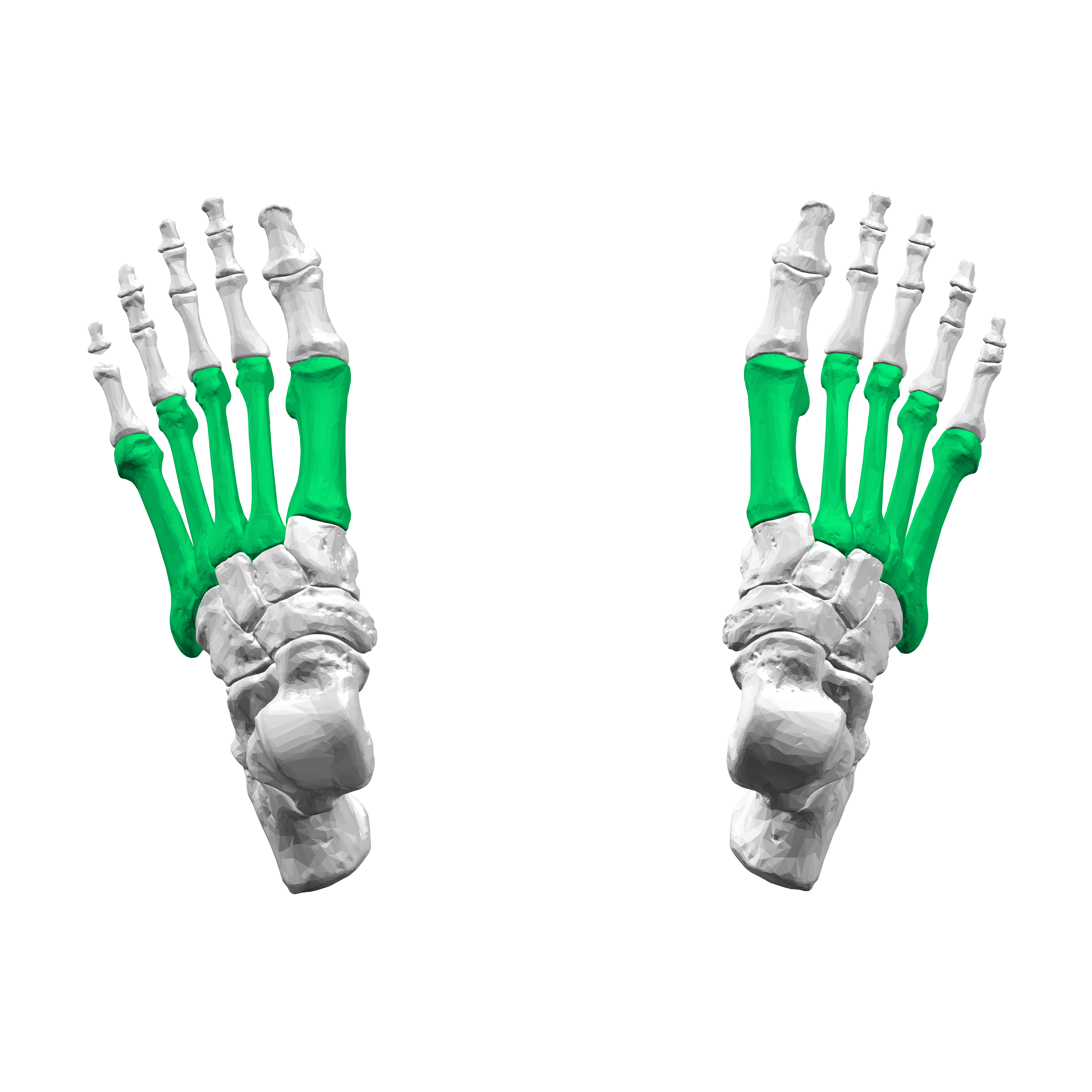
What is this region?
Metatarsals
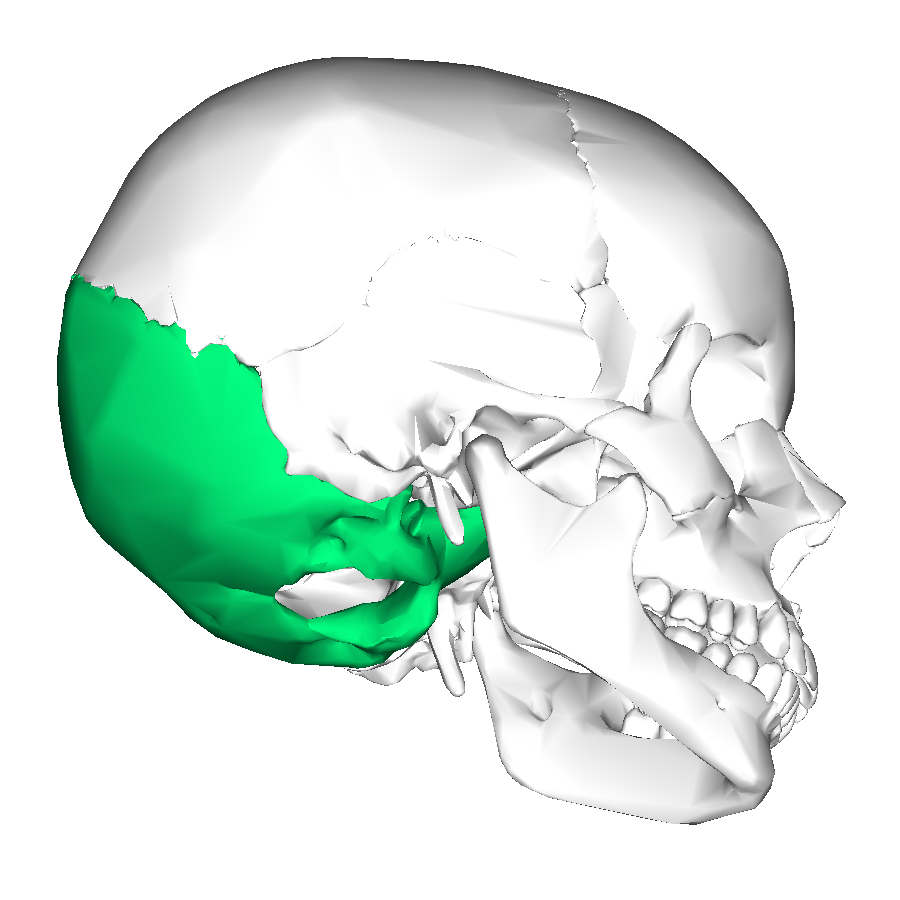
What is this region?
Occipital Bone
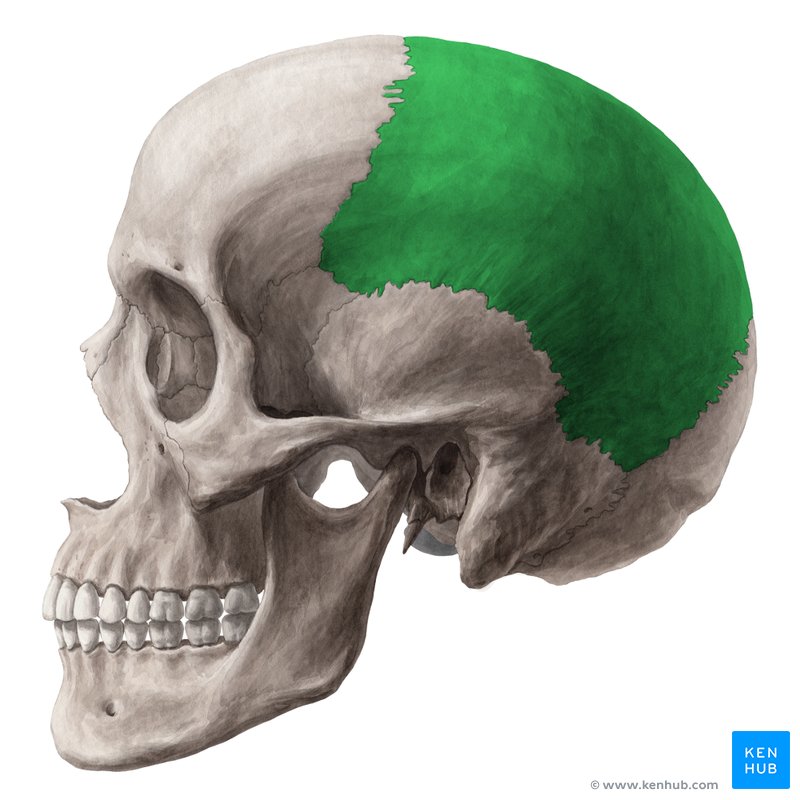
What is this region?
Parietal Bone
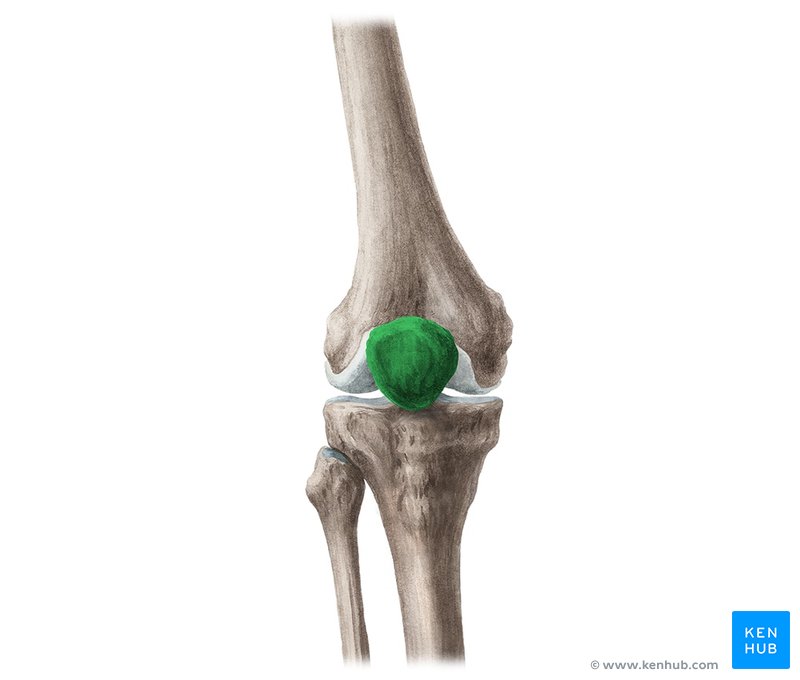
What is this region?
Patella
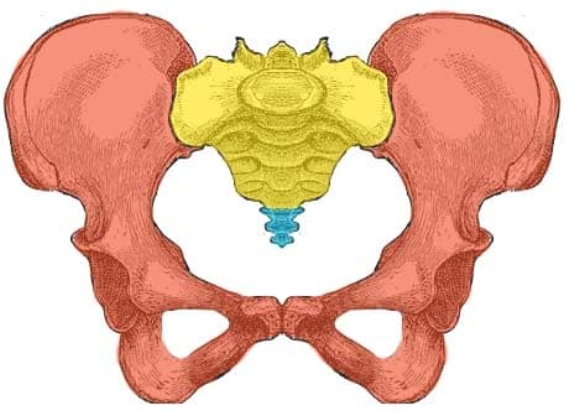
What is this region as a whole?
Pelvic Girdle
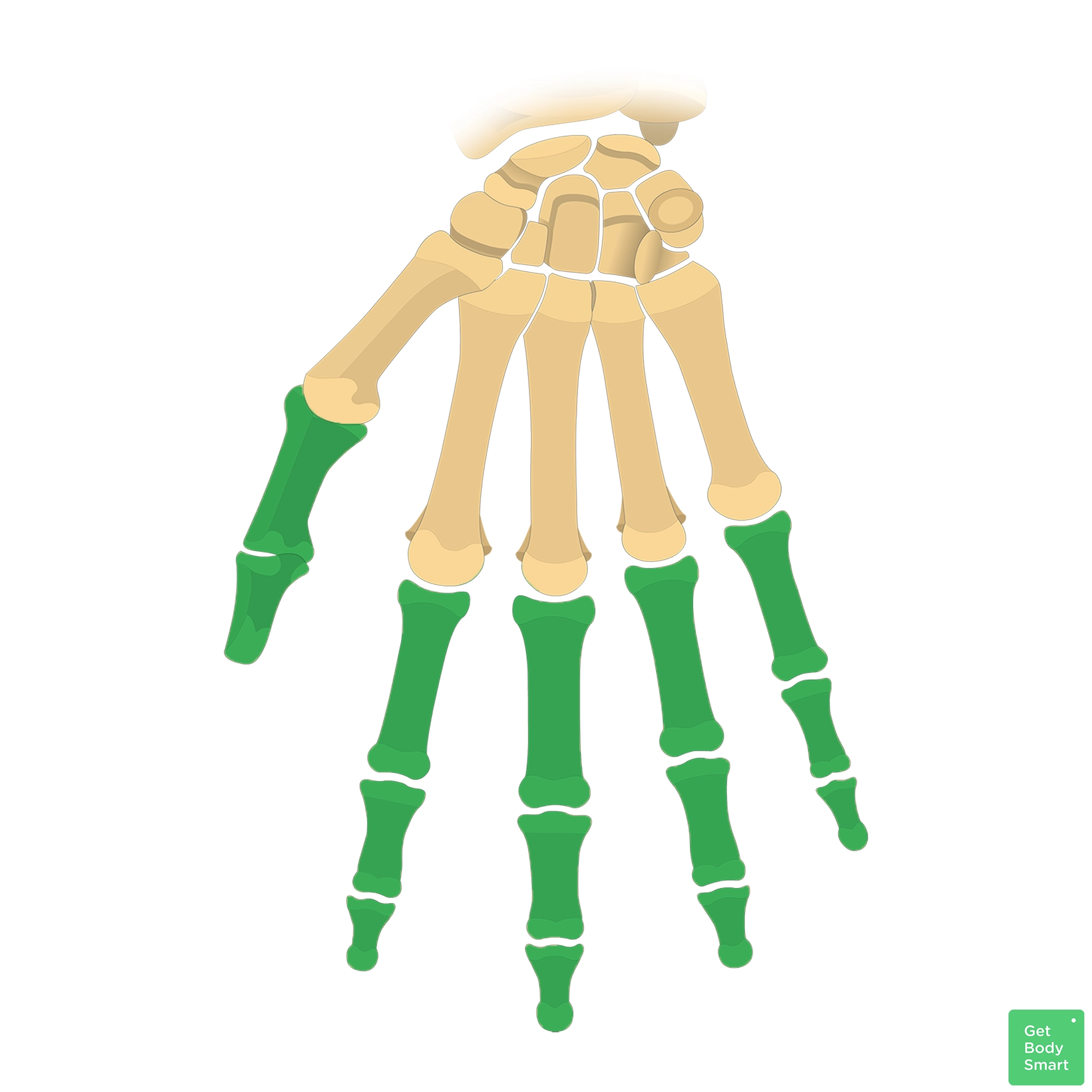
What is this region?
Phalanges
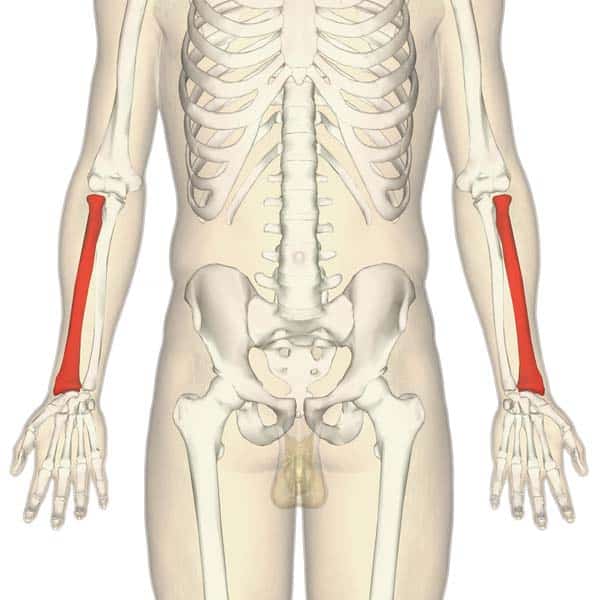
What is this region?
Radius
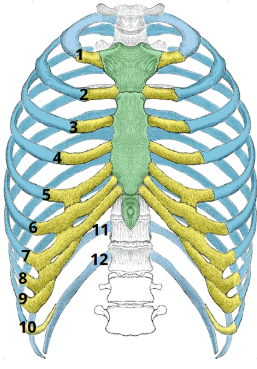
What is this region?
Rib Cage
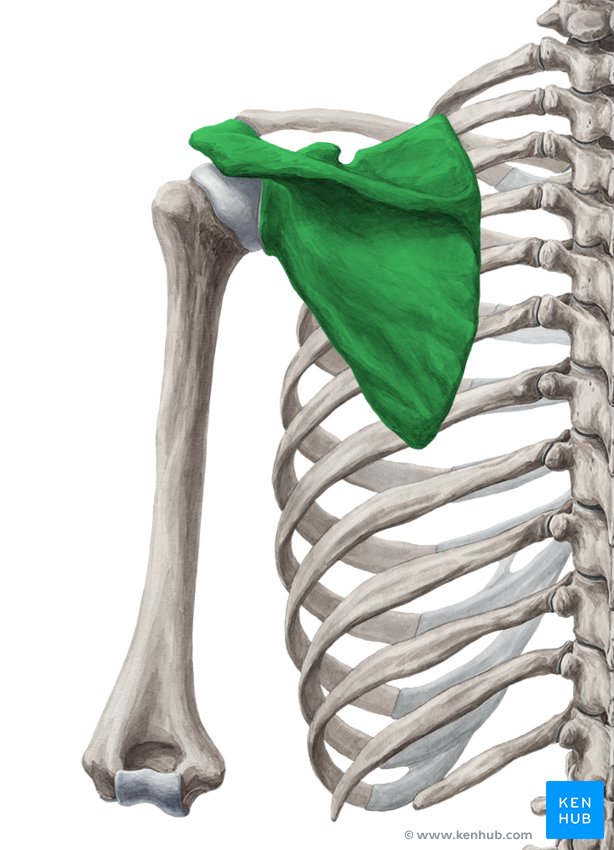
What is this region?
Scapula
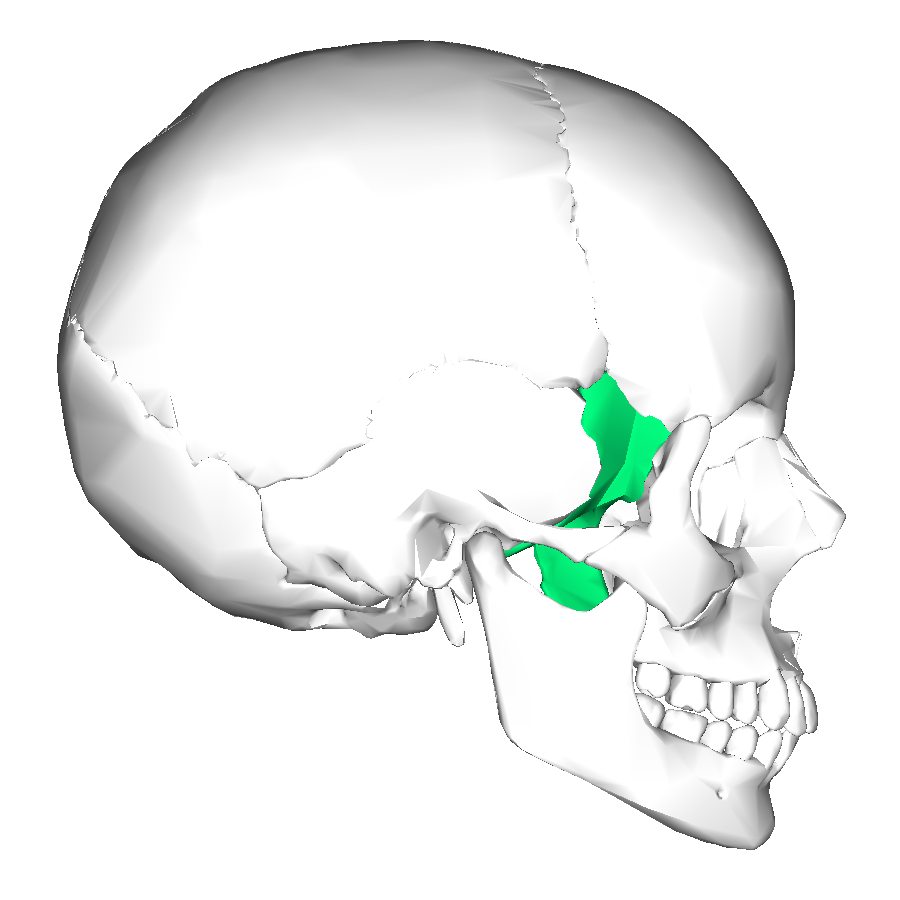
What is this region?
Sphenoid Bone
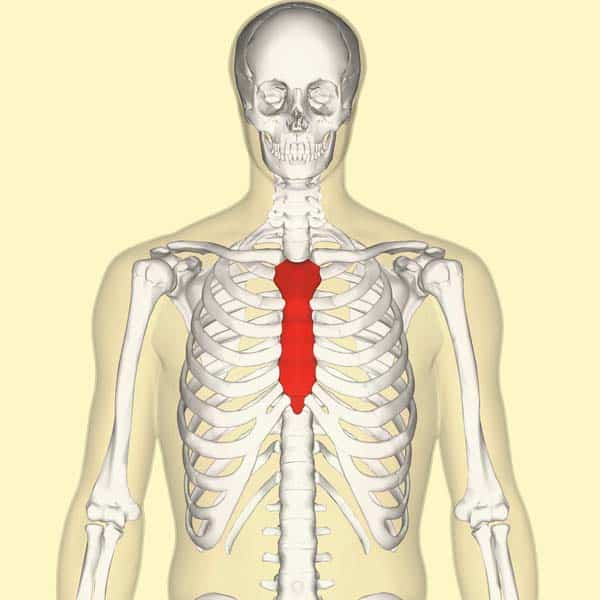
What is this region?
Sternum
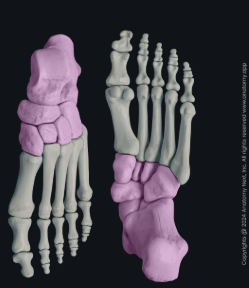
What is this region?
Tarsals
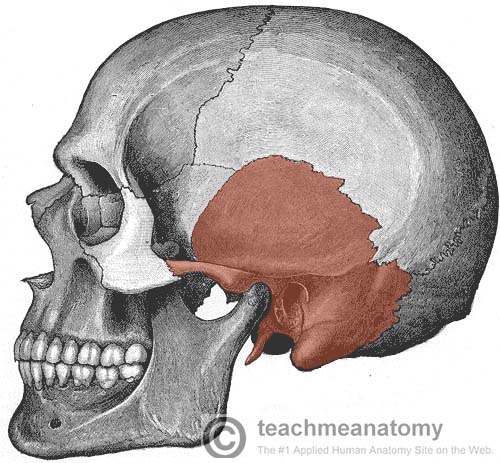
What is this region?
Temporal Bone
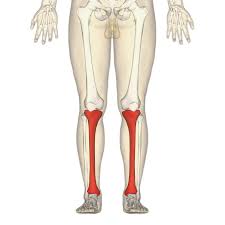
What is this region?
Tibia
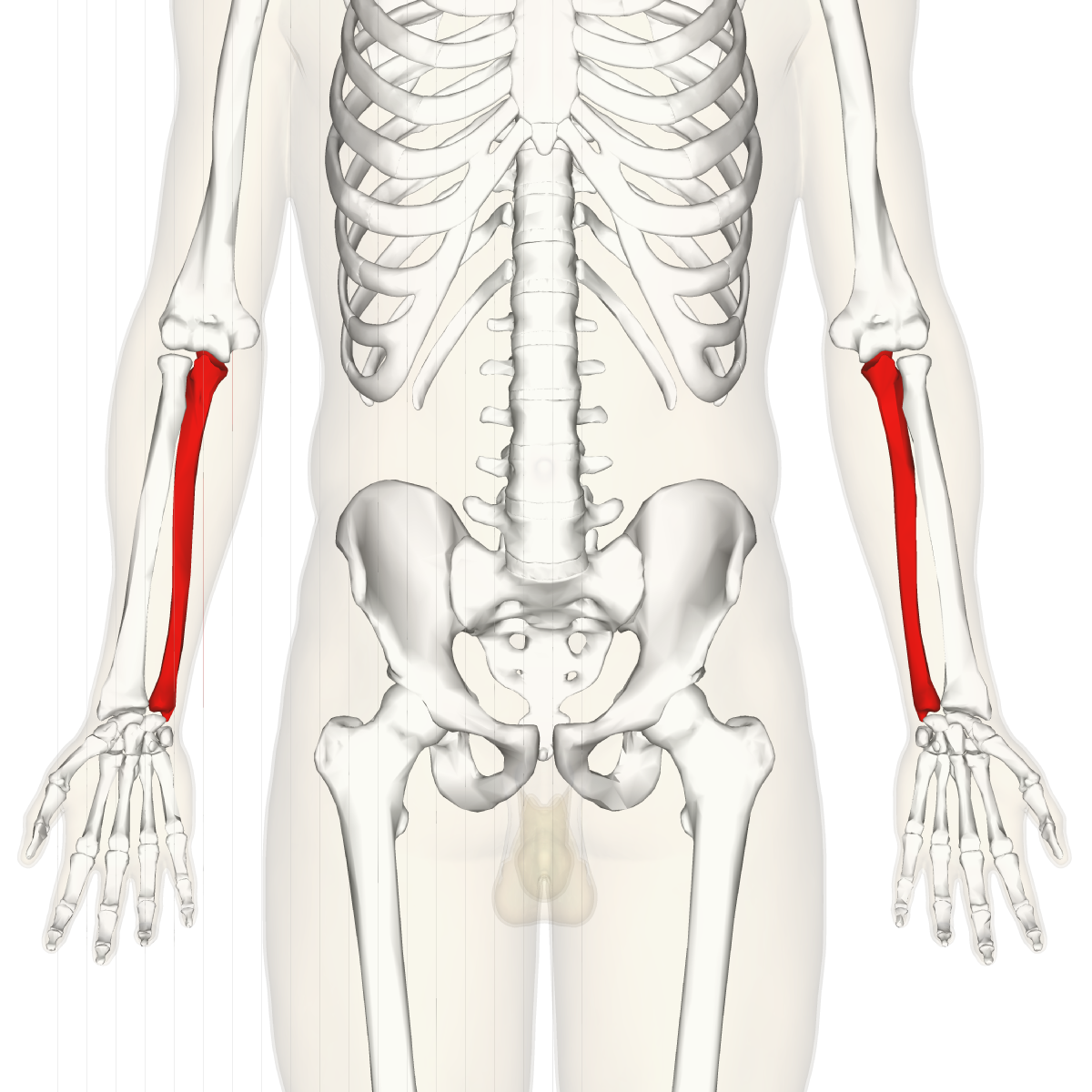
What is this region?
Ulna
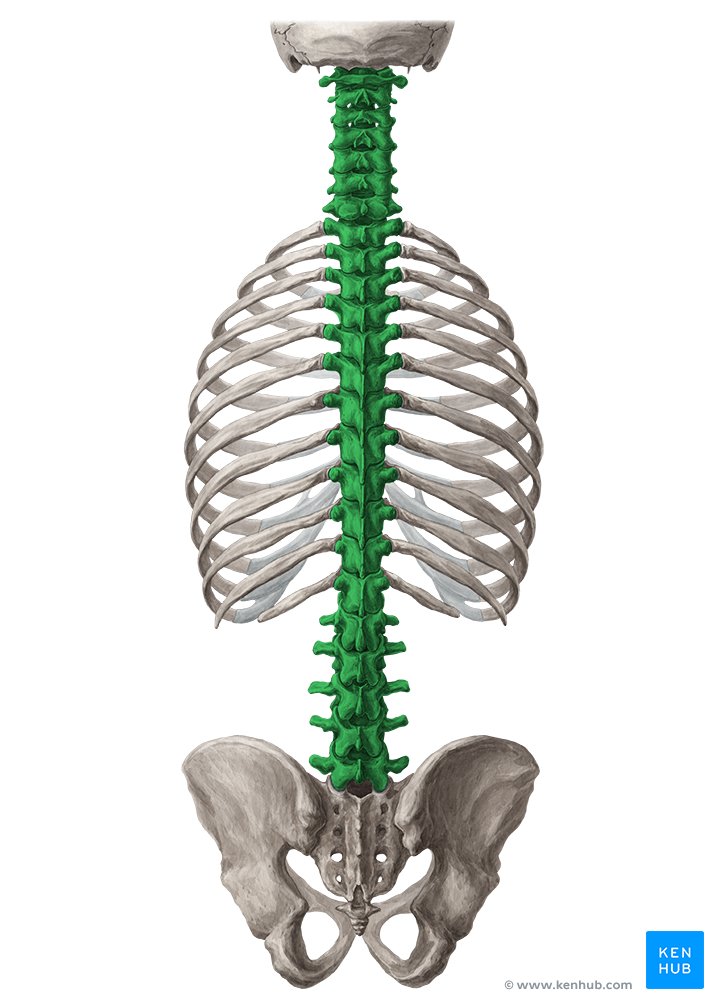
What is this region?
Vertebral column
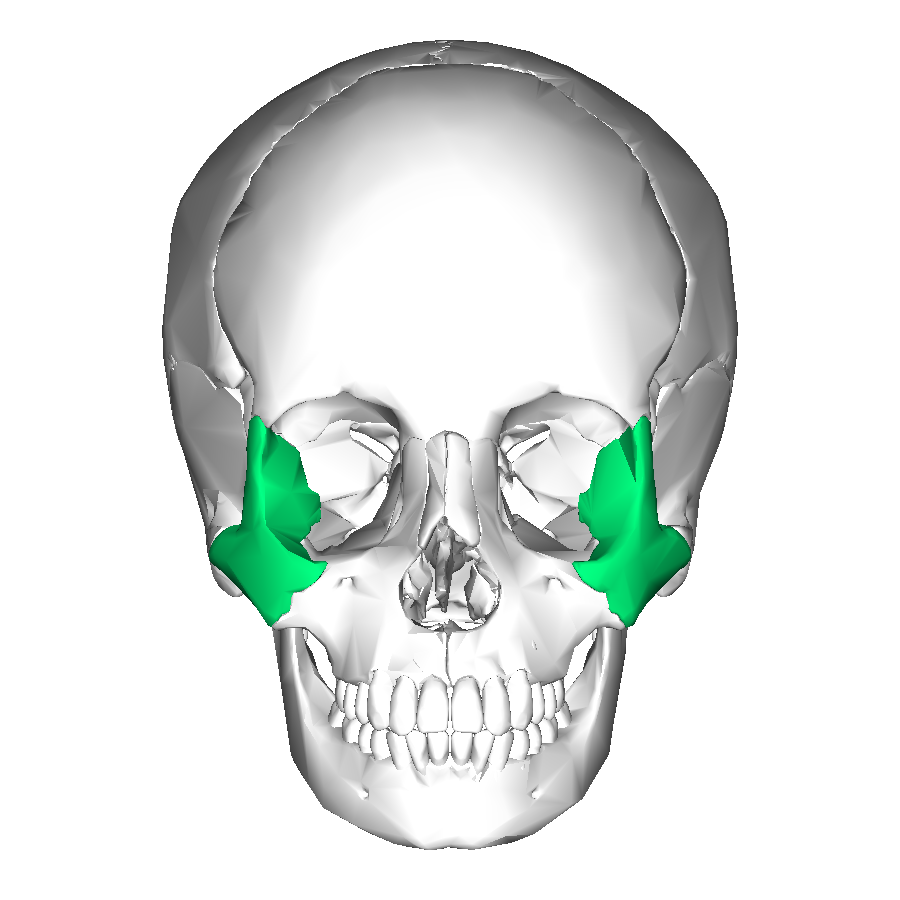
What is this region?
Zygomatic Bone
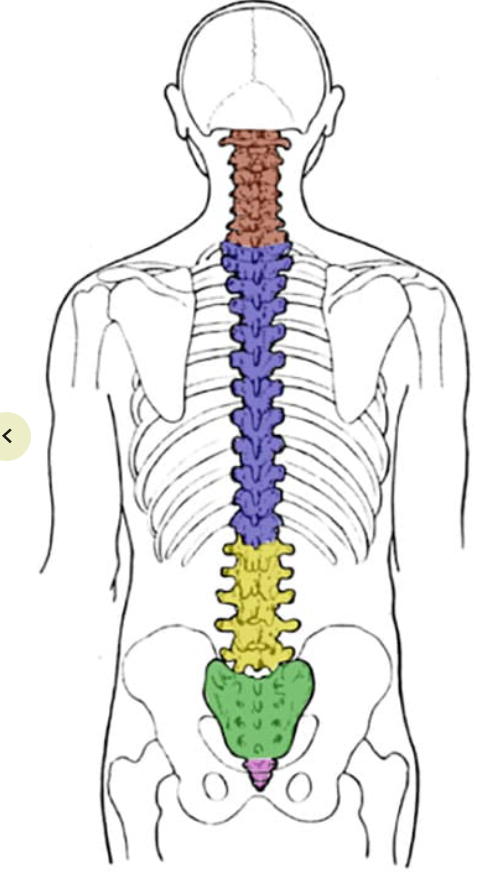
What is the red section? How many vertebrae are in that section?
Cervical; 7
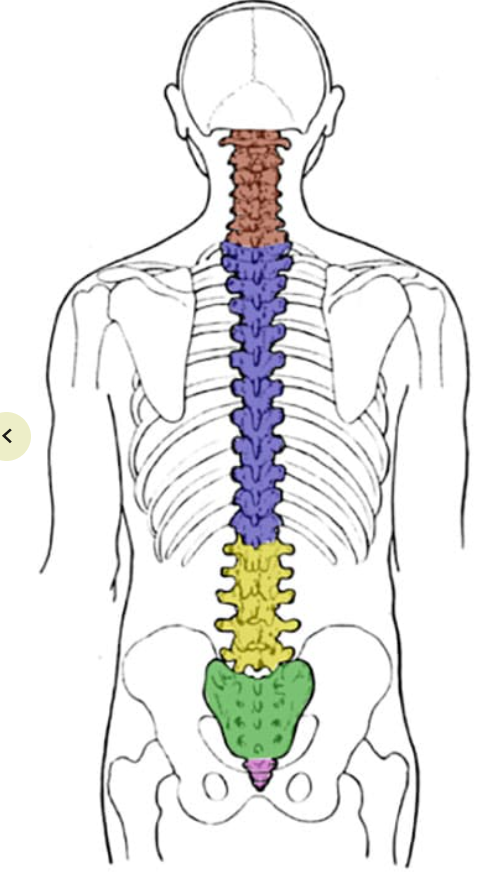
What is the blue section? How many vertebrae are in that section?
Thoracic; 12
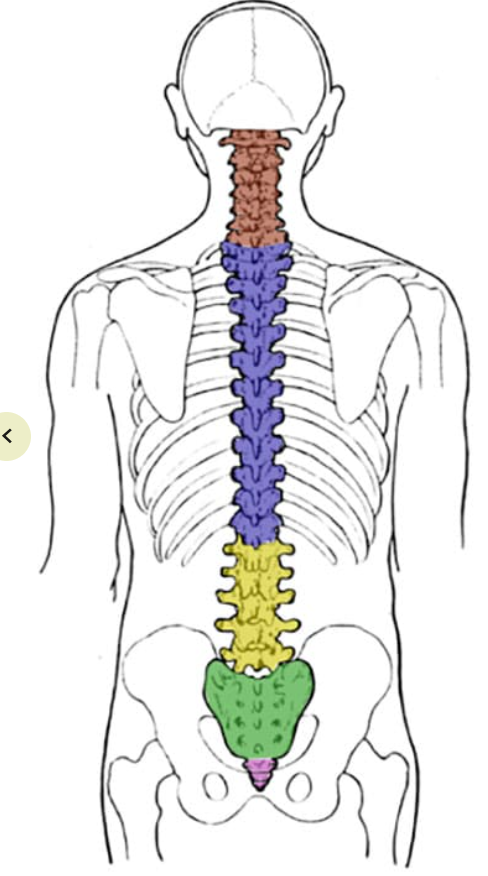
What is the yellow section? How many vertebrae are in that section?
Lumbar; 5
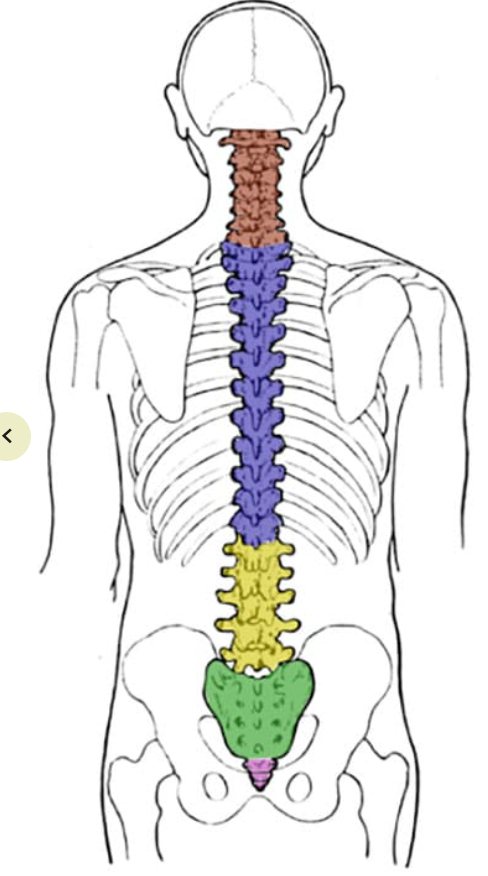
What is the green section? How many vertebrae are in that section?
Sacrum; 4-5 fused
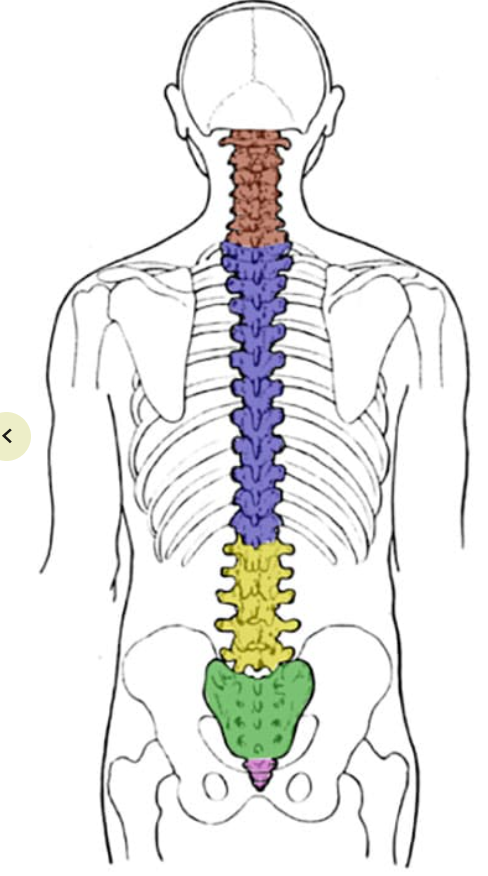
What is the pink/purple section? How many vertebrae are in that section?
Coccyx; 3-5 fused
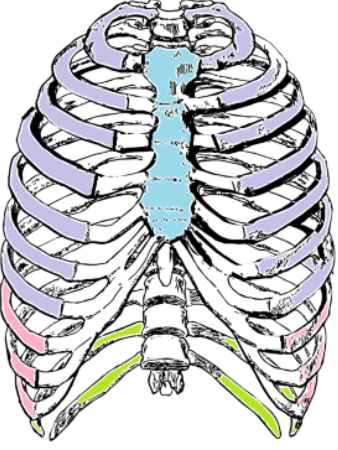
What kind of ribs are the ones labeled in purple? What numbers are they?
True Ribs (1-7)
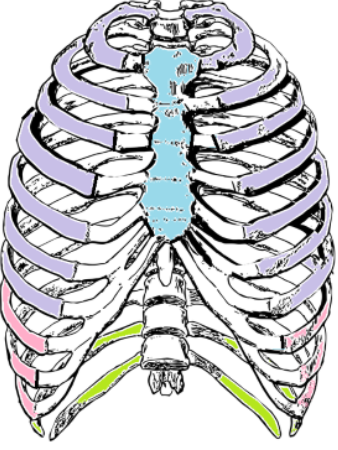
What kind of ribs are the ones labeled in pink? What numbers are they?
False Ribs (8-12)
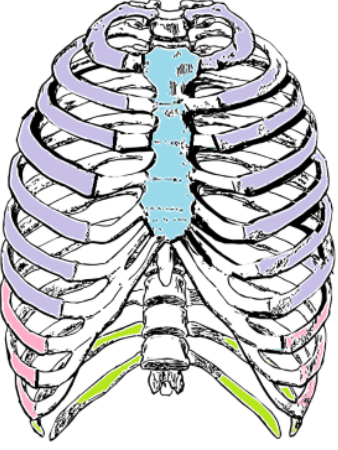
What kind of ribs are the ones labeled in green? What numbers are they?
Floating Ribs (11 & 12)
What are the differences between the male and female pelvis?
The male pelvis is longer and narrower, while the female pelvis is shorter and wider
What is the function of the vertebral cartilage?
Provides support and cushion for your vertebrates, it also allows the spine to stay flexible during movement, ultimately preventing damage
What is the largest bone in your body?
Femur
What is the smallest bone in your body?
Stapes (in the ear)
What are skull sutures?
Interlocking immovable joints of the skull
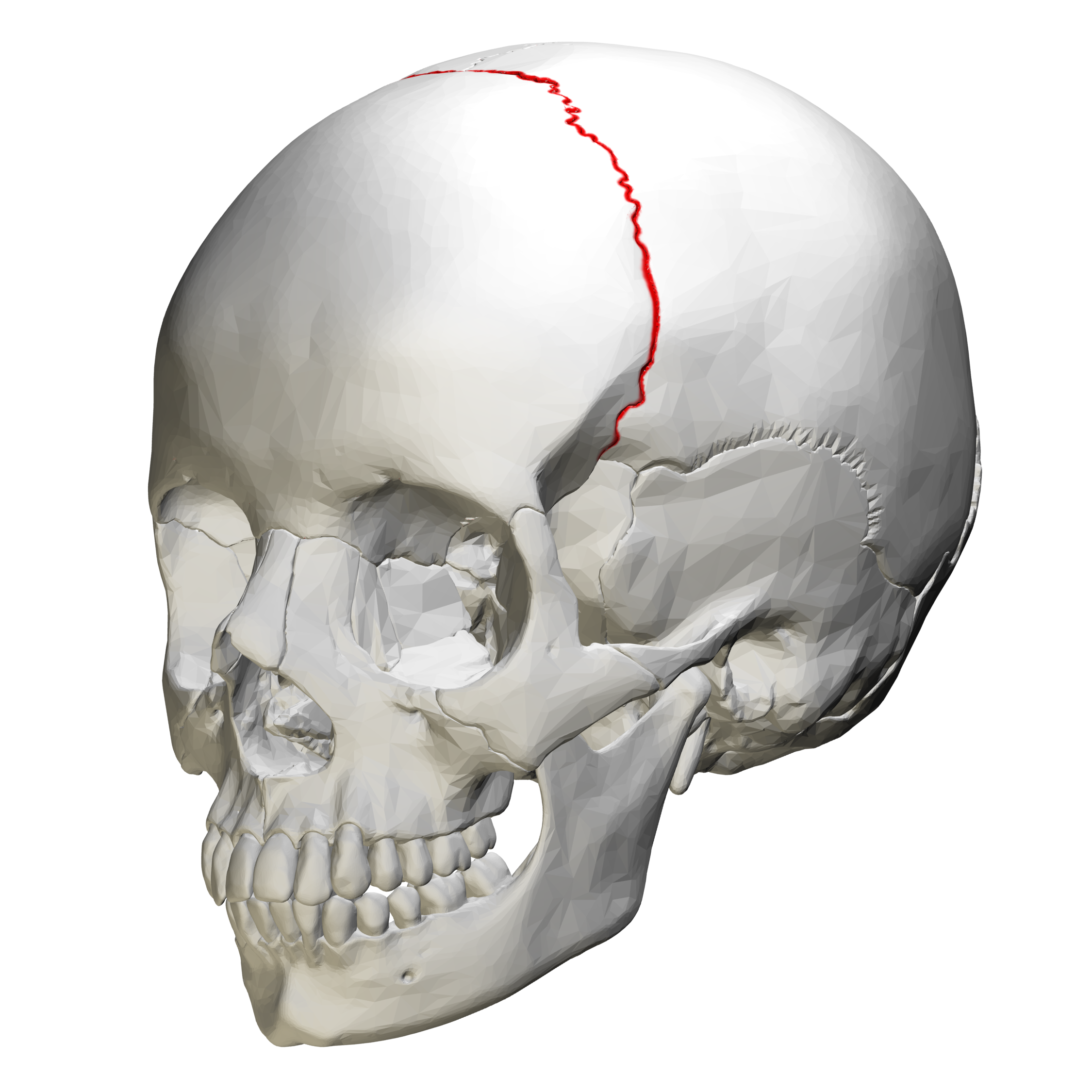
What suture is this?
Coronal Suture
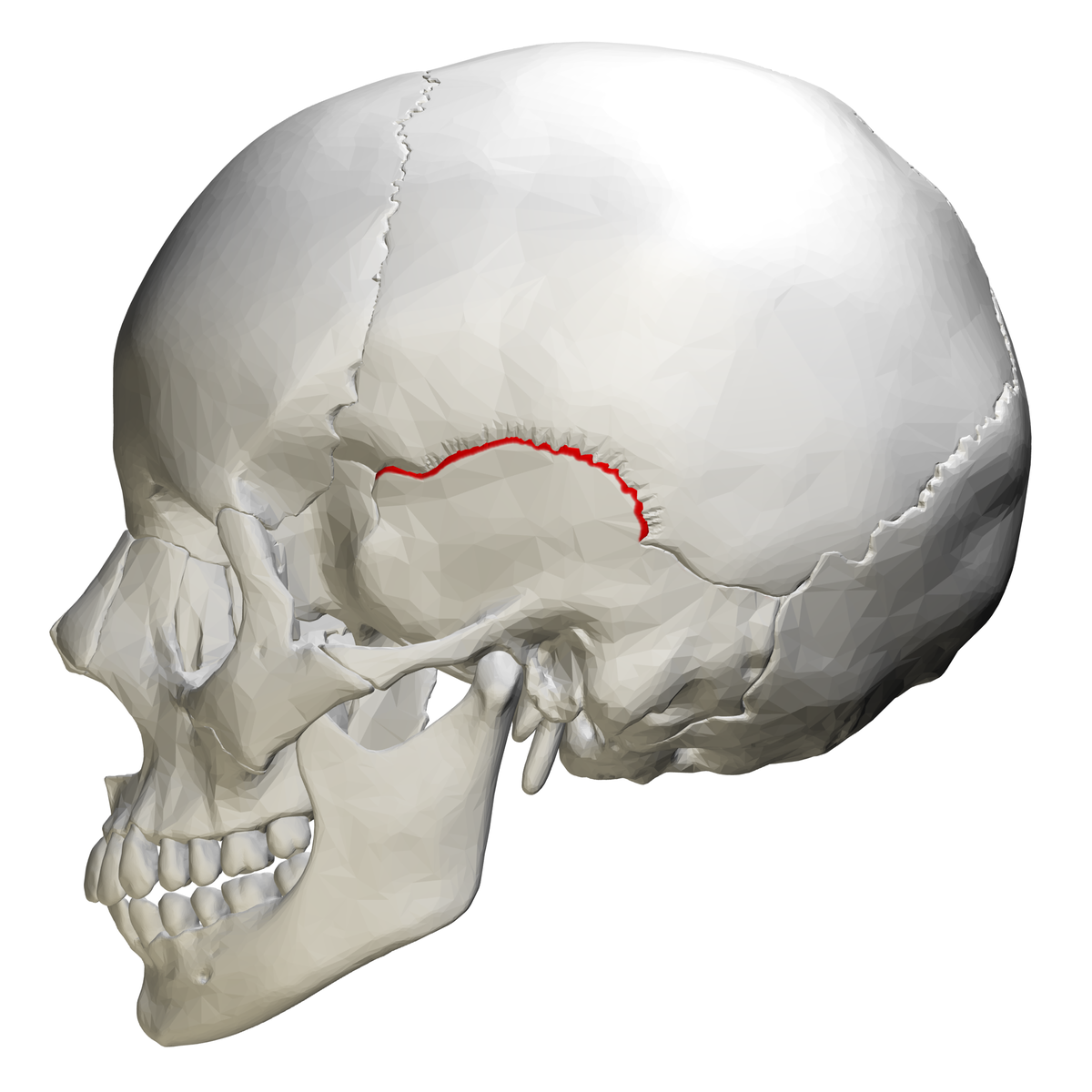
What suture is this?
Squamous Suture
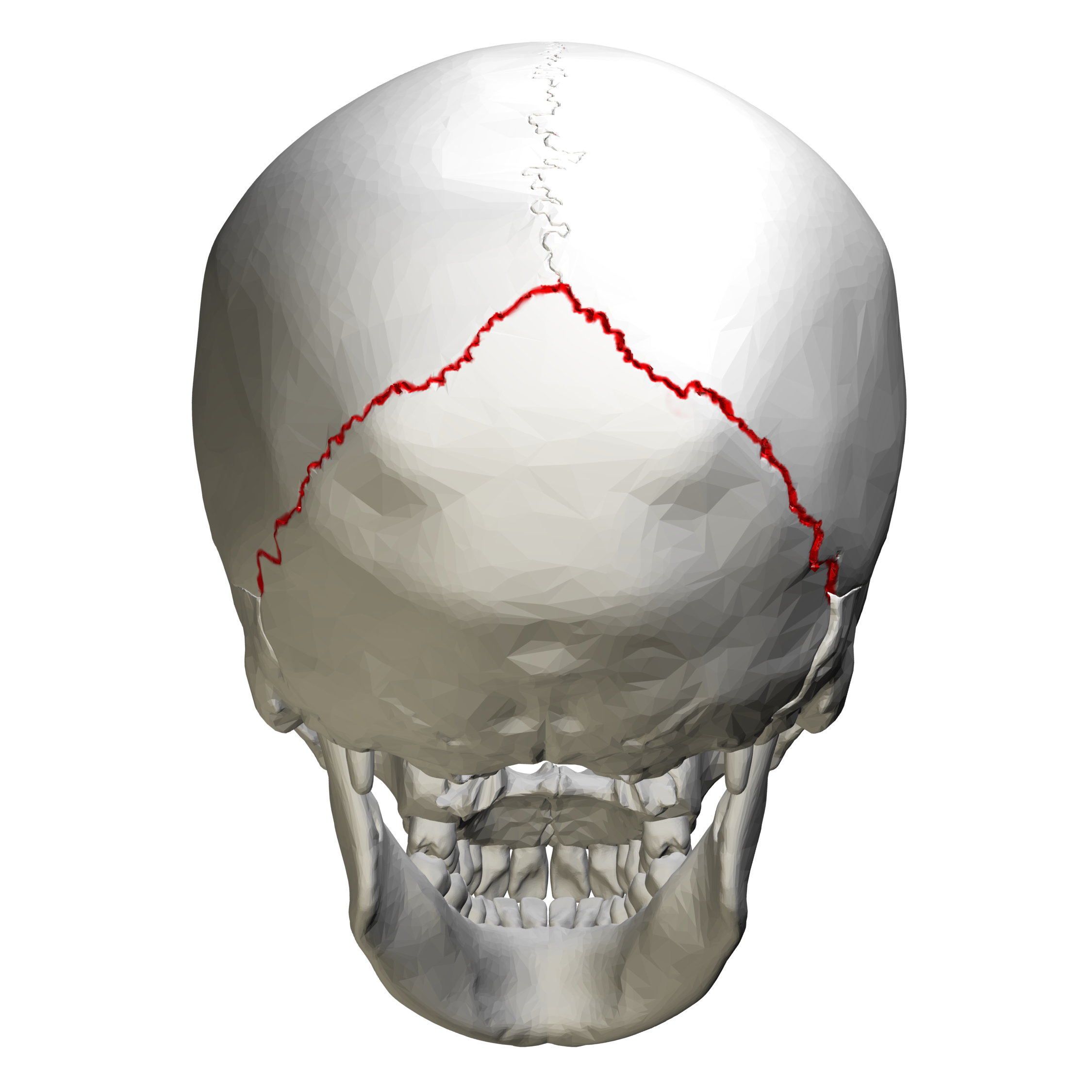
What suture is this?
Lambdoidal Suture
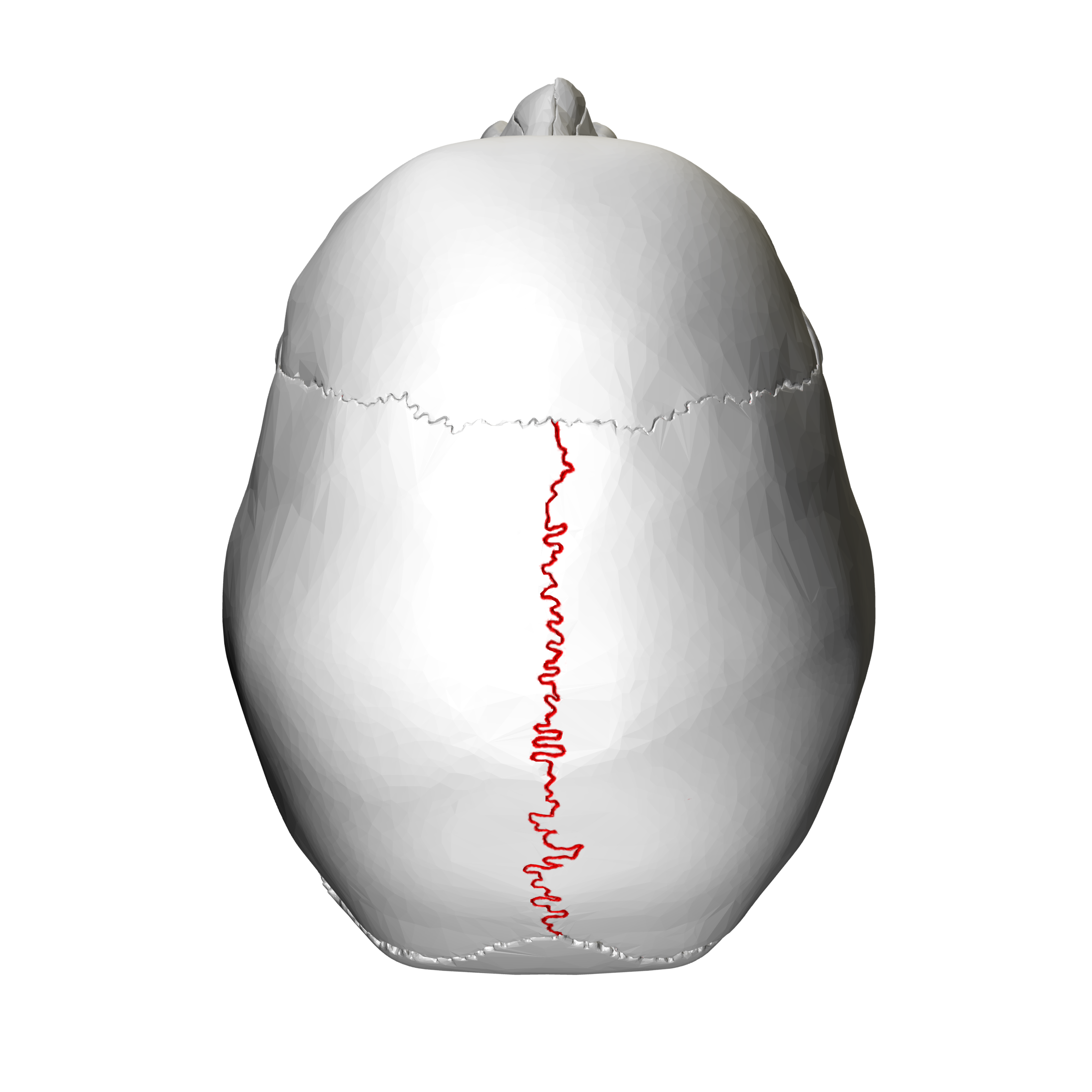
What suture is this?
Sagittal Suture
What do sutures tell you about the skull?
It shows that the skull is made up of more than one bone
How many bones are you born with? How many bones does an adult have?
You are born with 270-300 bones, and an adult has 206 bones since over time, some bones fuse together
How many bones does one hand and wrist have? Why is that necessary?
One hand and wrist has 27 bones, which is essential for a wide range of motion and the ability to perform fine motor skills
What is the only bone not attached to another bone?
The hyoid bone
What is limb length discrepancy?
A difference in length of arms or legs
How drastic of limb-length discrepancy can result in gait asymmetry?
A leg length discrepancy of over 2 centimeters can lead to gait asymmetry, causing pain in the lower back, hips, knees, and ankles
How does leg length discrepancy happen?
Due to something happening to the growth plates, such as poorly healed bone fractures, bone tumors, and infections such as polio or a staph infection
What is the axial skeleton made up of?
Skull, spinal column, ribs, sternum, hyoid bone, and ear bones
What is the appendicular skeleton made up of?
Everything except the skull, spinal column, ribs, sternum, hyoid bone, and ear bones
What does bone provide for the body?
A tough, flexible frame for the body while still being living tissue
What is the skeletal system made up of?
Bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
How are bones classified?
By their shape, internal tissues, and bone markings
What are the 5 bone shapes
Long bones
Flat bones
Irregular bones
Short bones
Sesamoid bones