T1 PP PMT
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASK: 6,9, 11, 70// [1-17MT] CVD[18-33] heart disease[34-44] ECFpre2017[45-53] POST2017[45-64] datacollpre2017[65-73] cardiovascsystem:pre2017[74-76] post2017: [77-87] DCApost2017:[88-94]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms

(7) + (3)
(3)
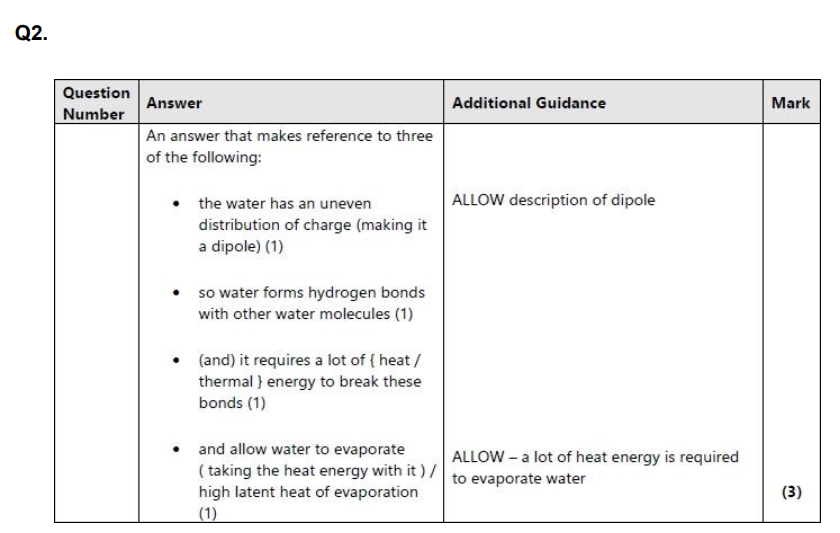
water has uneven distribution of charge and therefore a dipole
*so it forms hydrogen bonds with other molecules*
therefore lots of thermal energy is required to break these bonds
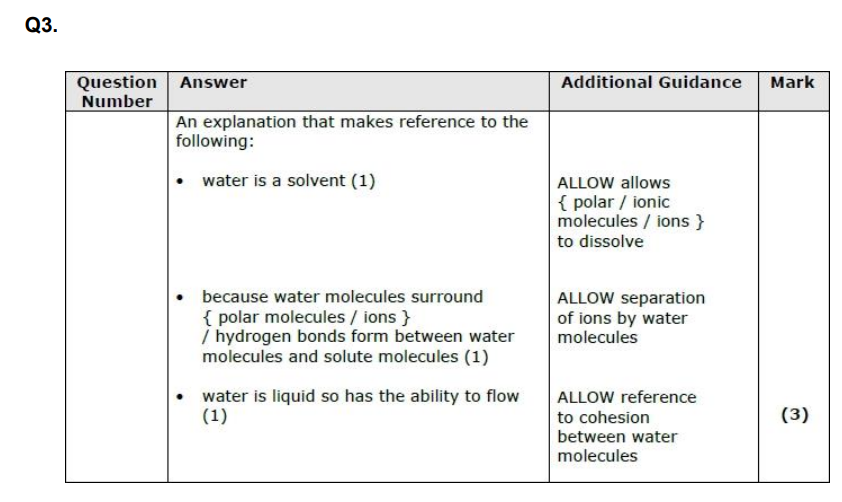
water is a solvent = water molecules surround the ions/polar molecules and hydrogen bonds are formed between the dolute molecules and h20 molecules
Cohesion:
Biological Importance:
Transpiration stream in plants: Cohesion allows water molecules to stick together and move as a continuous column through the xylem, from roots to leaves.
Helps maintain a constant flow of water, enabling transport of nutrients.
Adhesion:
Definition: The attraction between water molecules and other polar surfaces (like xylem walls).
Biological Importance:
Aids capillary action, helping water rise up narrow tubes like xylem vessels.
Helps counteract the force of gravity in tall plants.
High Latent Heat of Vaporisation
Definition: The amount of energy needed to convert 1 gram of water from liquid to gas without a temperature change.
Biological Importance:
Thermoregulation in organisms:
In humans, sweating is an effective cooling mechanism. As sweat evaporates, it absorbs a lot of heat energy from the body, cooling it down.
In plants, water evaporation from leaves (transpiration) cools the plant, preventing overheating.
Allows organisms to maintain a stable internal temperature — essential for enzyme function and metabolic processes.

(8) + (2)
(1)
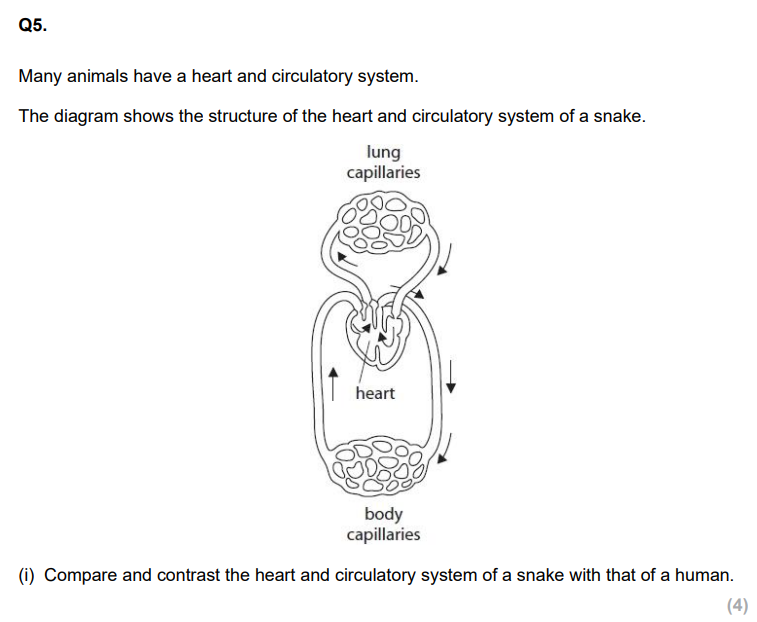
suitable substance eg. oxygen/glucose to body cells but also removal of CO2/waste from body
SA:vol ratio to small = so distance for diffusion is larger
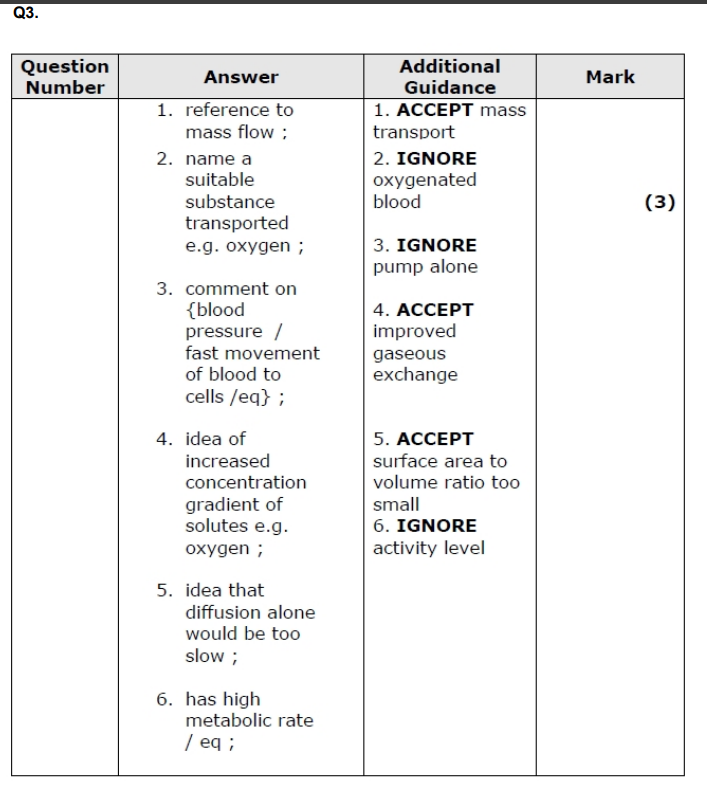
How does the heart affect the concentration gradient of solutes? (3)
The heart pumps blood around the body, maintaining a constant flow.
This delivers solutes like oxygen and glucose to tissues and removes waste products.
Continuous circulation prevents equilibrium and maintains steep concentration gradients for efficient diffusion between blood and cells.


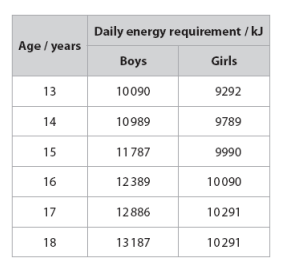
Many foods are labelled in kilocalories (kcal). One calorie is equal to 4.18 joules. Which of the following is the average energy requirements for girls aged 13 in kilocalories (kcal)?
2223 kcal
what will happen to the additional energy if an individual takes in more energy than is required? (1)


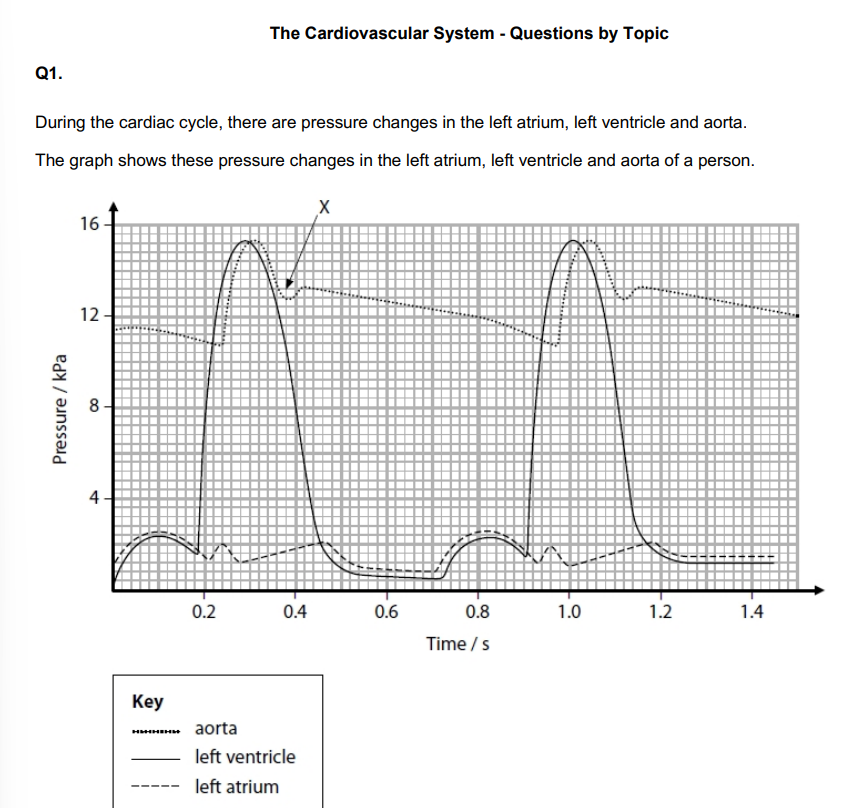
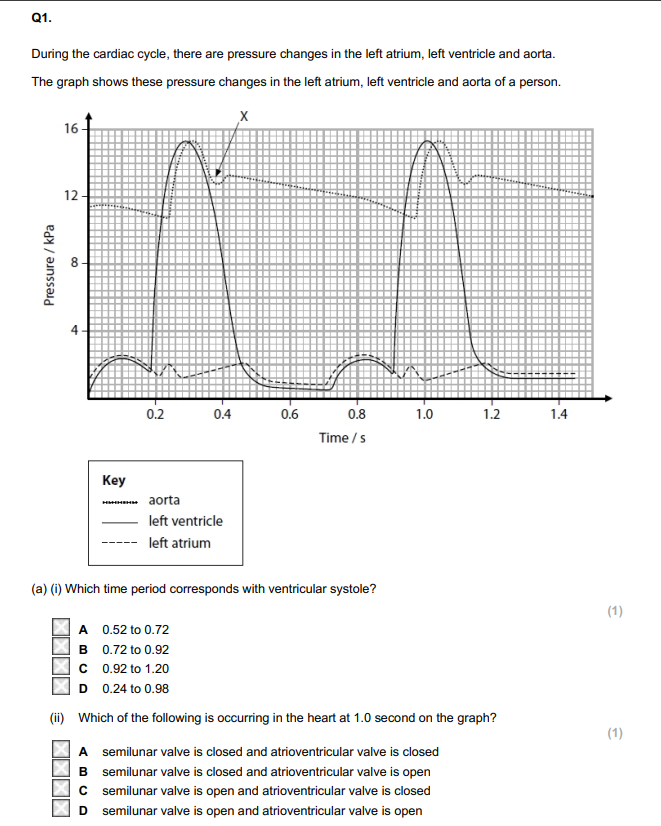
State a time from the graph when the sound of an atrioventricular valve closing would be detected.
0.19s/0.91
Explain why the atrioventricular valves need to close. (2)

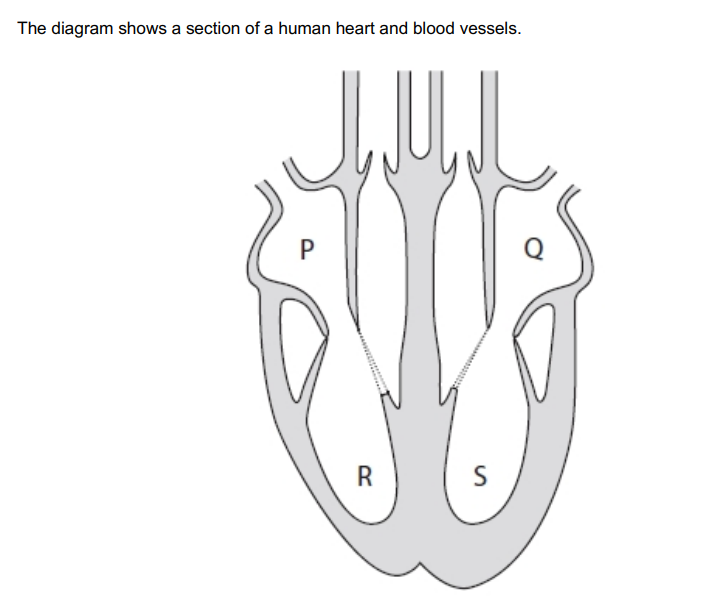
Which structures will fill with blood as a result of atrial systole? (1)
R & S



Explain why high blood pressure can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD). (3)
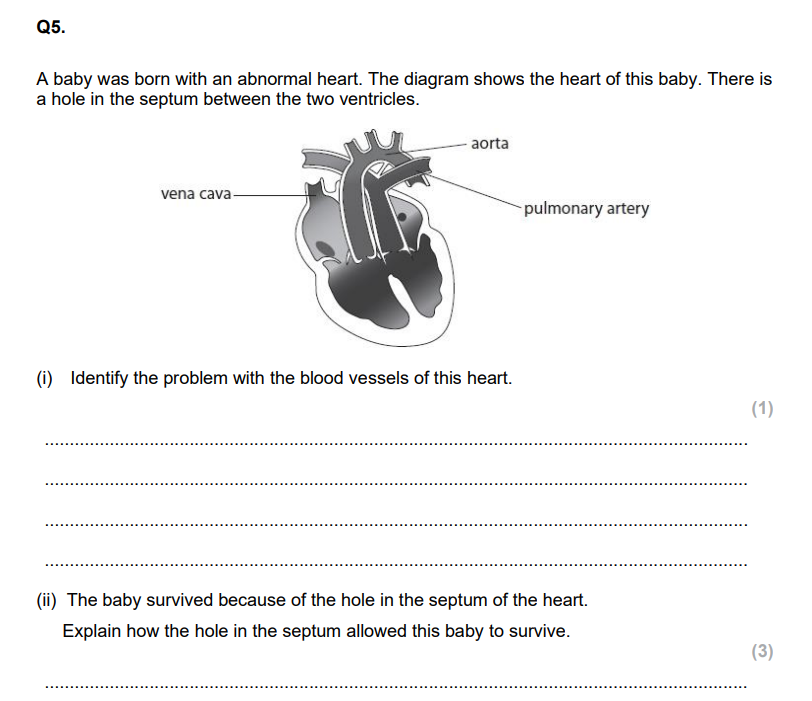
Q2. During the development of the mammalian heart, there is a hole between the left ventricle and the right ventricle. This hole usually becomes sealed before the mammal is born. If it is not sealed, the mammal will become easily tired due to a lack of energy. Explain why a mammal born with a hole between the two ventricles will have these symptoms. (3)
Q3. Diet is one factor that affects the development of CVD. Explain how the diet of a person could affect the development of CVD. (4)

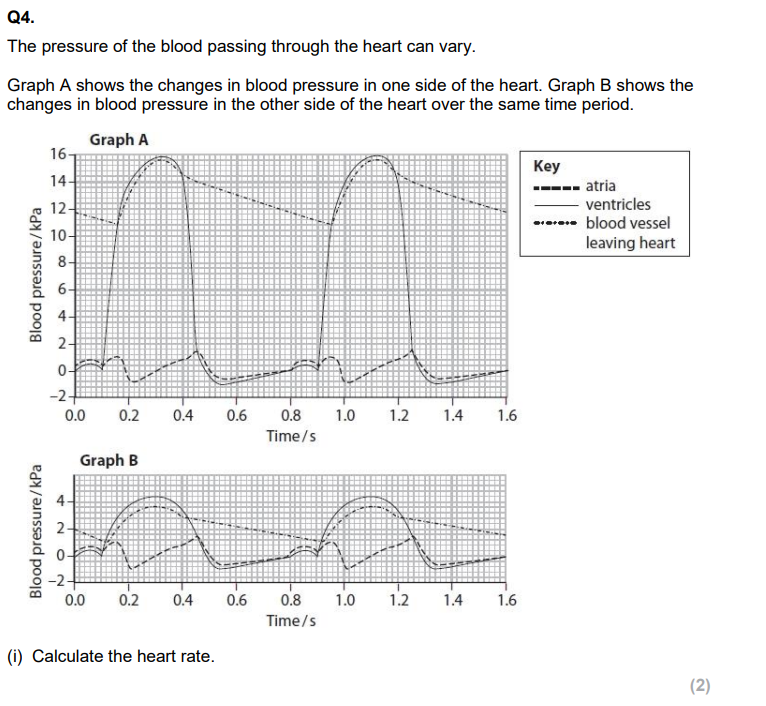
70bpm

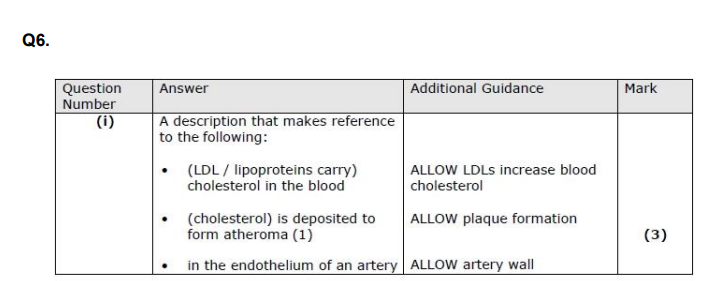
Explain how atherosclerosis can result in damage to heart muscle. (3)
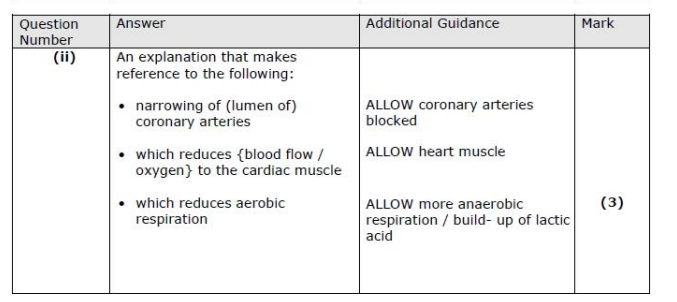
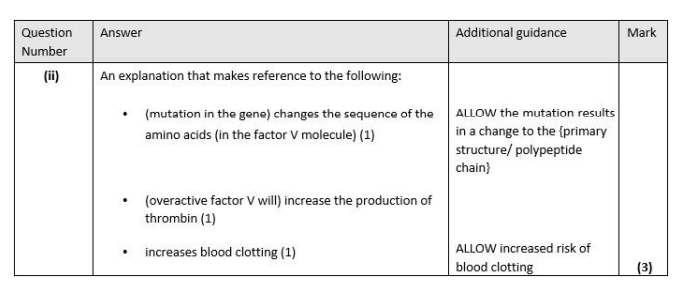
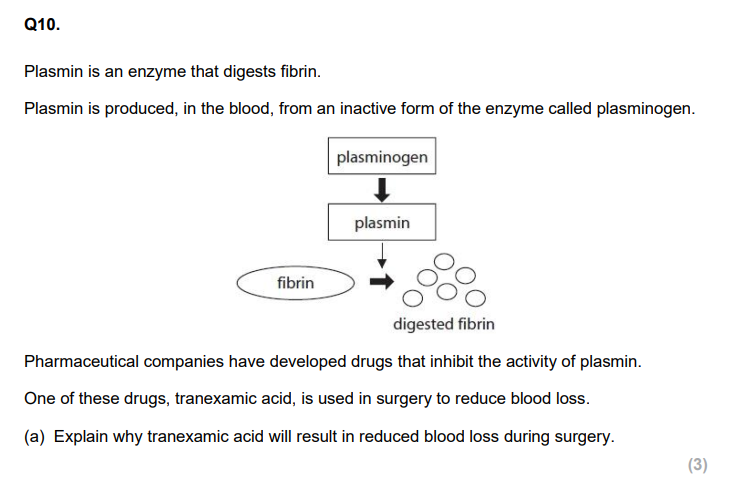
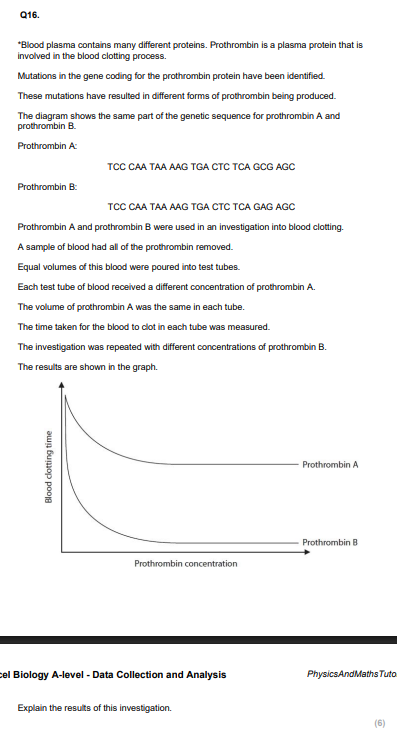
(i) Describe the role of thrombin in blood clotting. (3)

Factor V is involved in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
(ii) Explain why a mutation in the gene coding for the protein factor V may increase the risk of VTE. (3)
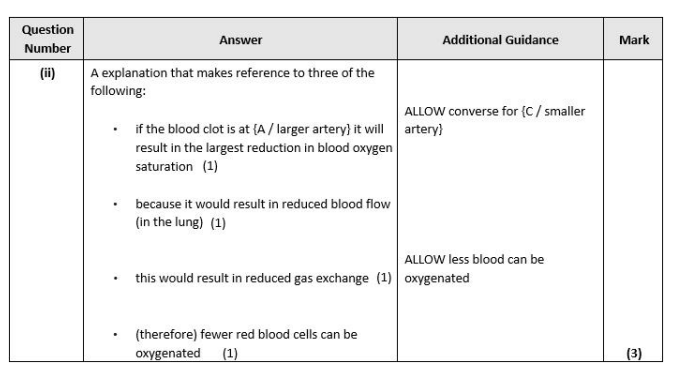
Explain why the location of the blood clot would affect the oxygen saturation of the blood leaving the right lung. (3)
Q9. An ischaemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked by a blood clot. Explain how a blood clot could form in a blood vessel. (4)
Q11. Atherosclerosis is more likely to occur in arteries due to the higher blood pressure in these blood vessels. A person with very high blood pressure has an increased risk of developing atherosclerosis. (i) Describe how very high blood pressure could result in atherosclerosis. (4)


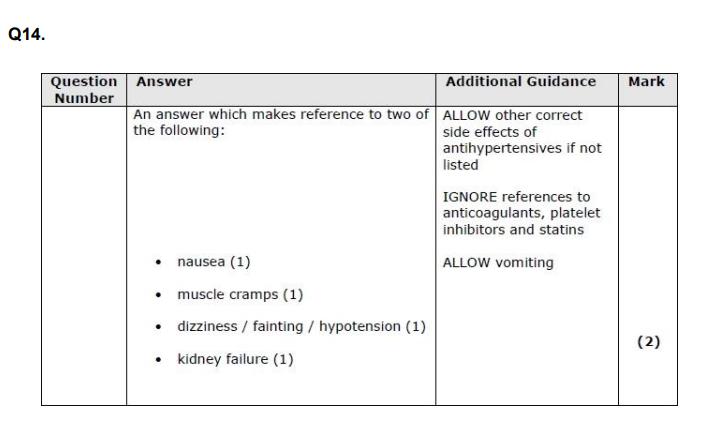
State two possible side effects of taking drugs to reduce blood pressure. (2)
u on ur period minus the kidney failure xx
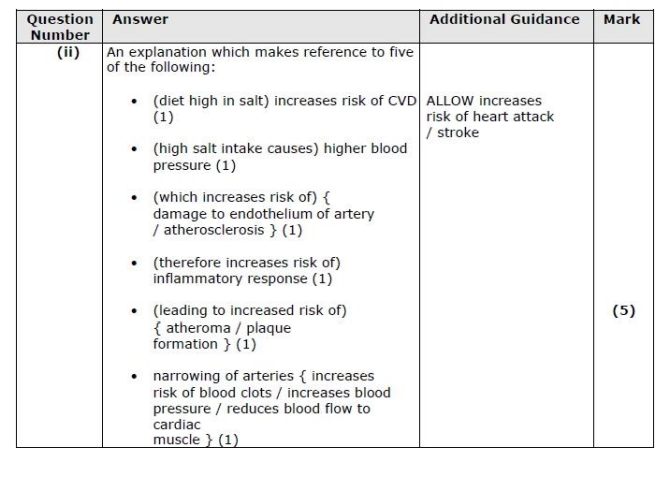
(ii) Explain the effect that a diet high in salt could have on a person's risk of developing cardiovascular disease. (5)
forgot:
leads to inflammatory response
leads to more inc blood pressure + clots
narrowing of artery
Explain how the structure of the aorta relates to its function. (3) ((12))

Describe two differences between the structure of a capillary and the structure of a vein. (2)
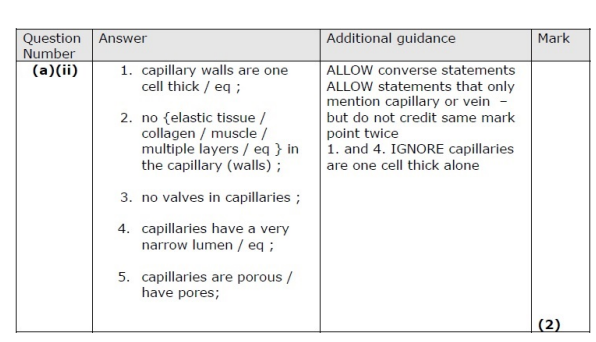

C is a cell fragment that releases thromboplastin
Fibrinogen is…
a soluble plasma protein
Explain why a blood clot in an artery leading to the brain could cause a stroke. (3) ((7))
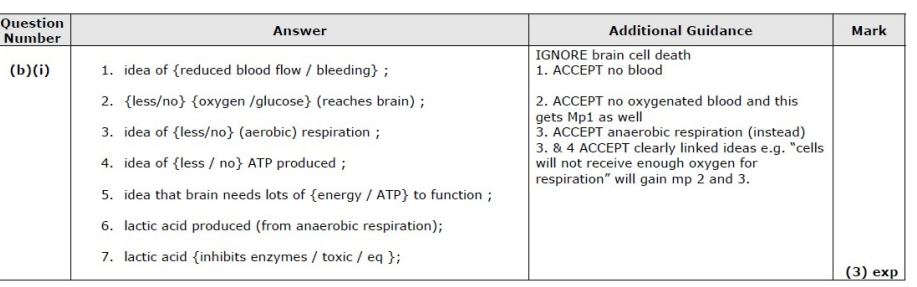
Some foods and drinks contain plant statins. Explain the benefits of plant statins to human health. (2)
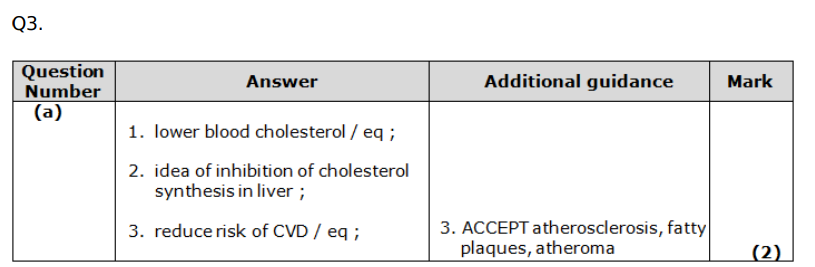
Suggest why there was an increase in the percentage of patients taking statins over years (2)
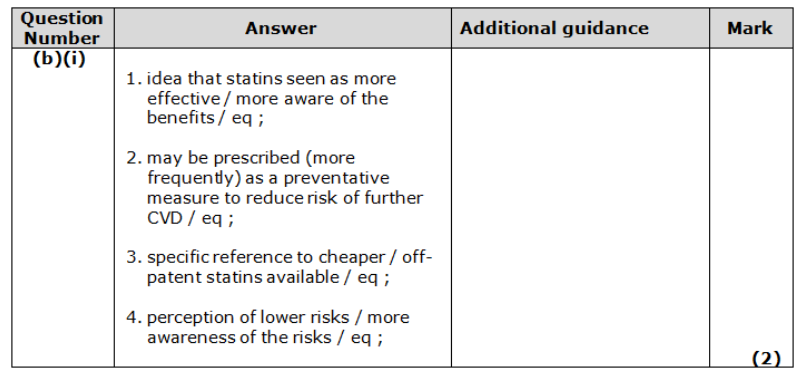

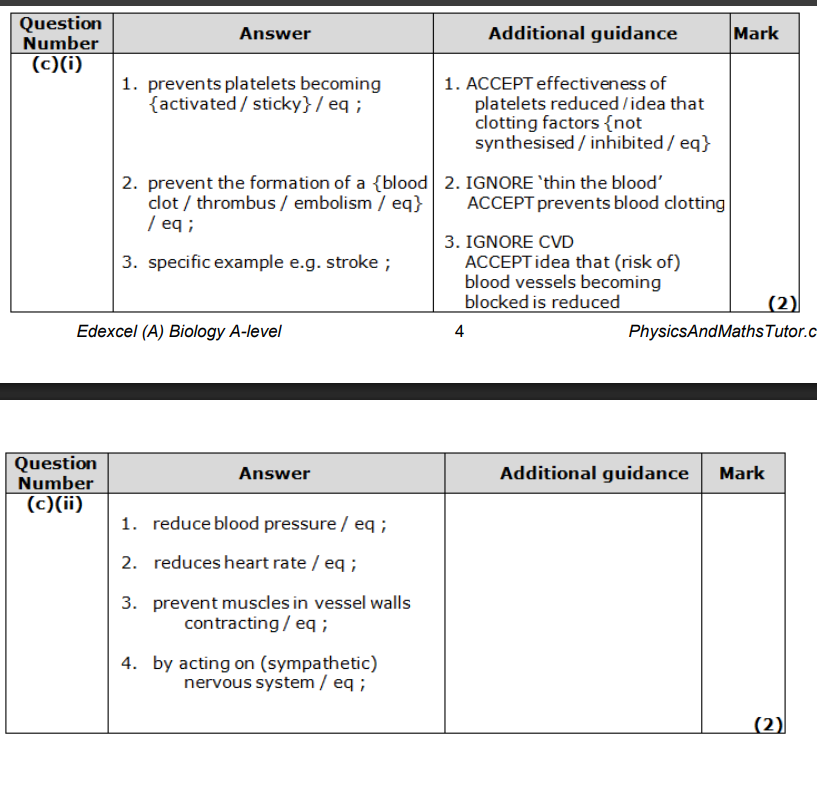
Give six differences between the structure of an artery and a capillary. (2)
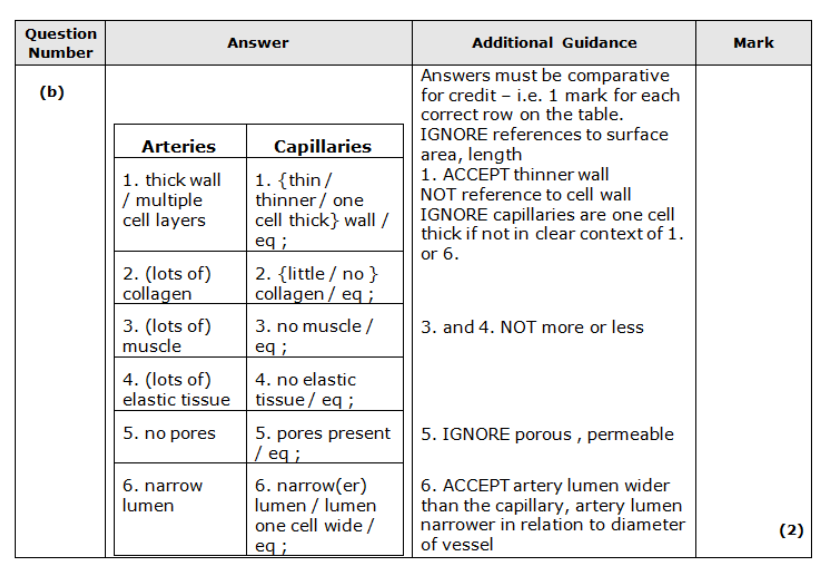
Explain how anticoagulants can help reduce the effects of CVD. (2)
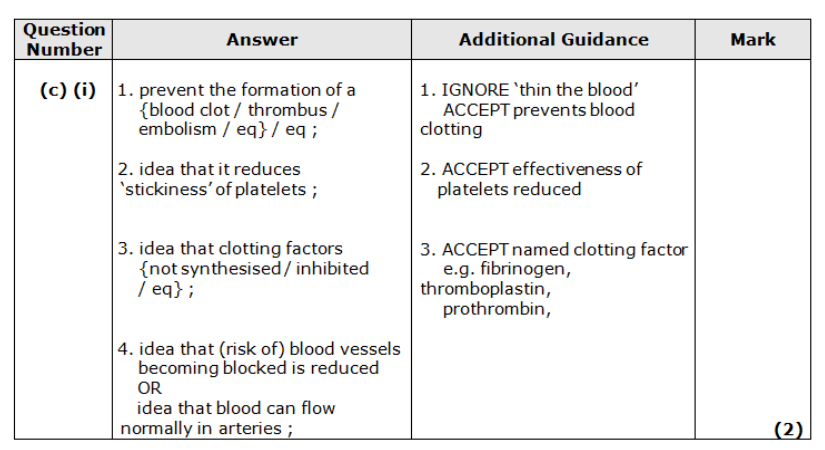
State one risk associated with the use of anticoagulants. (7)
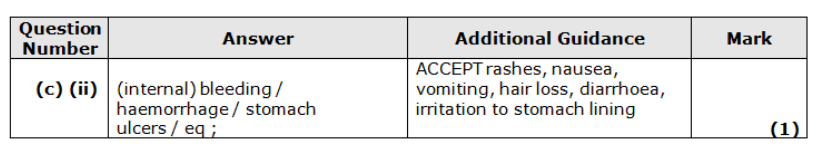
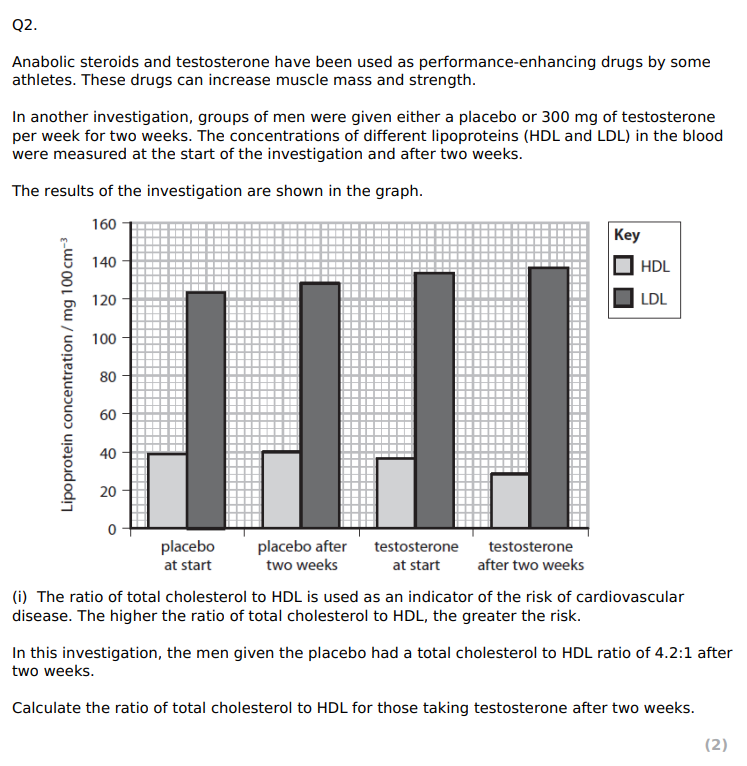
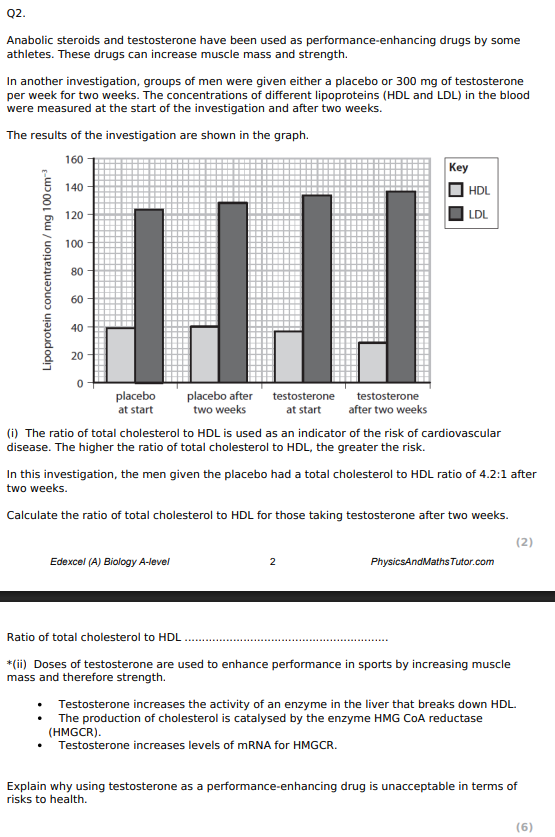
5.86 : 1
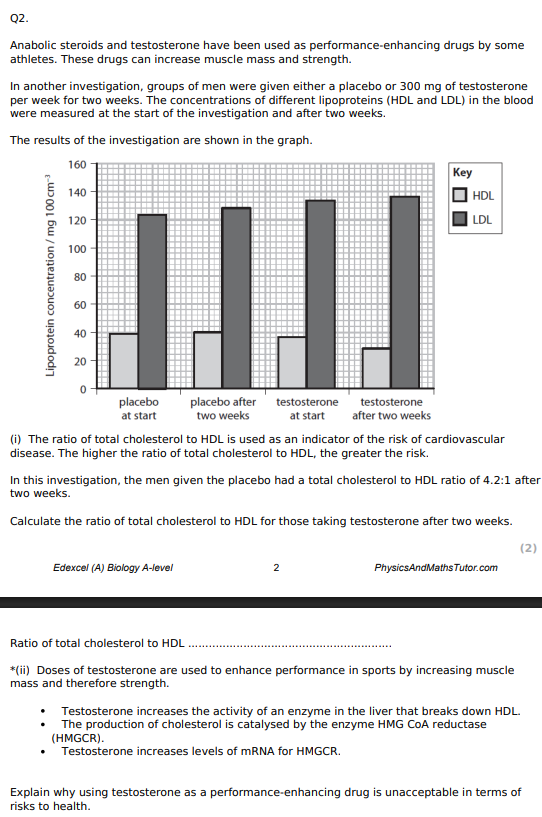
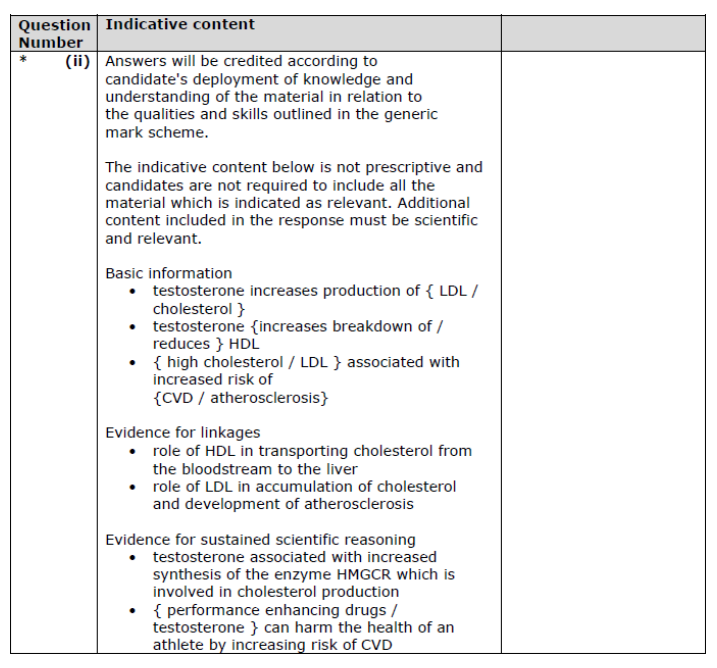
Explain the meaning of the term causal relationship. (1)
change in 1 VARIABLE leads to direct RESULT of change in another VARIABLE
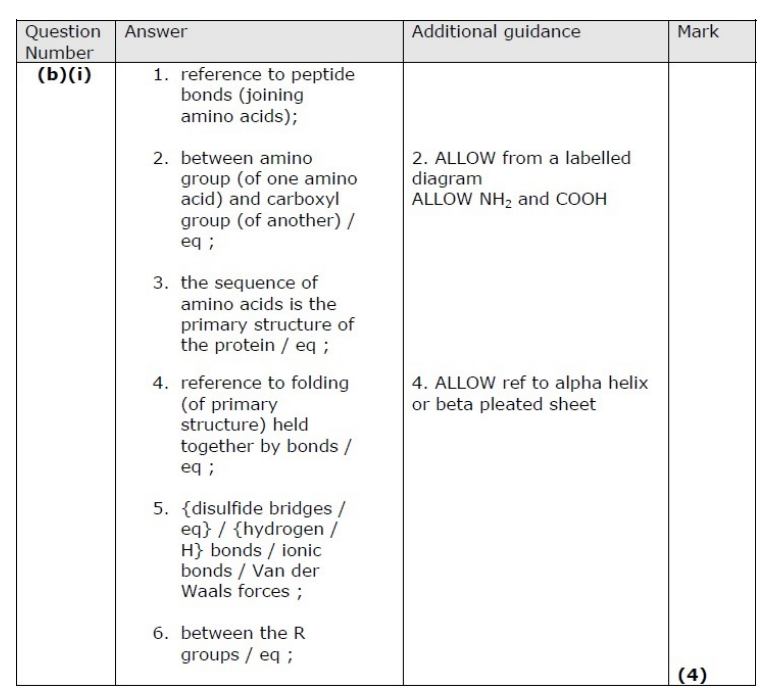
Lipoproteins are composed of phospholipids, cholesterol and proteins. (i) Proteins are made up of amino acids. Describe how amino acids join together to form the three-dimensional structure of a protein. (4)
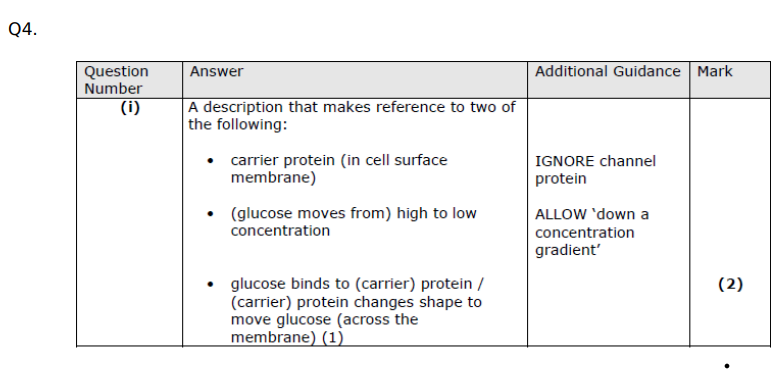
Describe how glucose moves into cells by facilitated diffusion. (2)
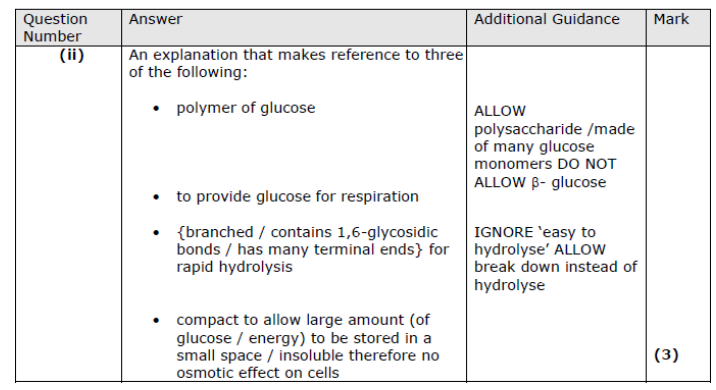
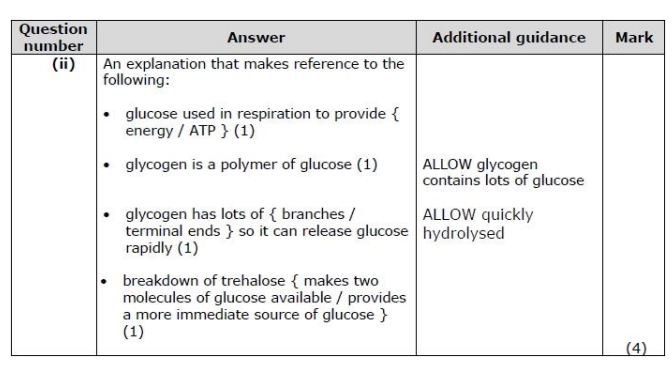
Explain how the structure of glycogen allows it to be an energy store. (3) ((4))
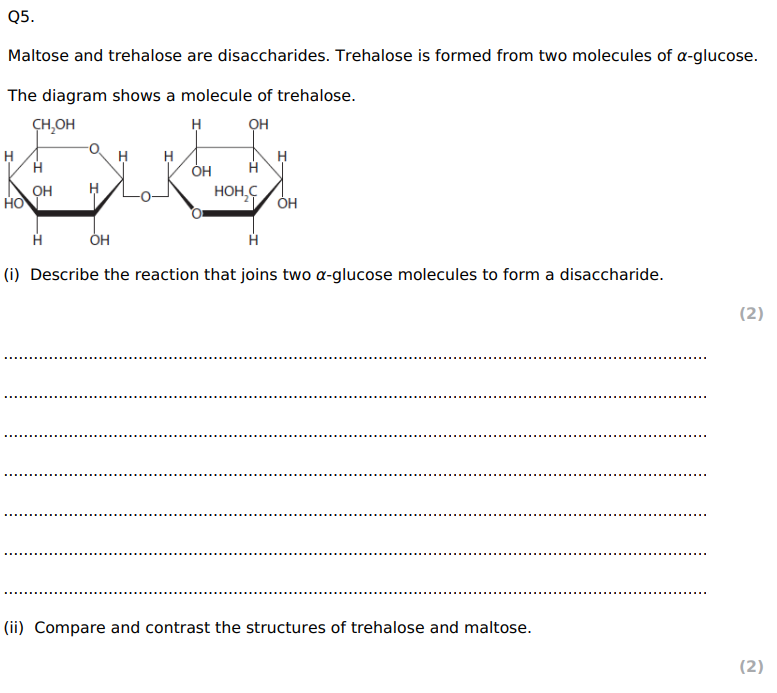
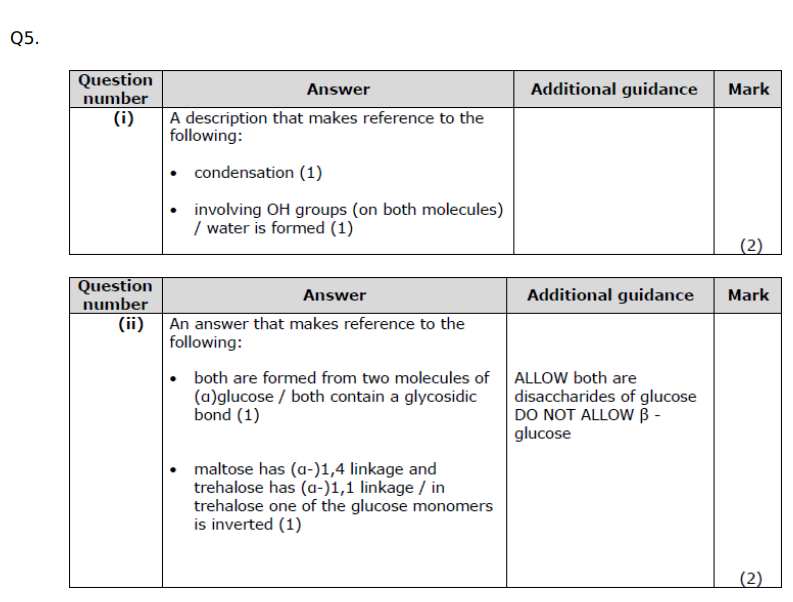
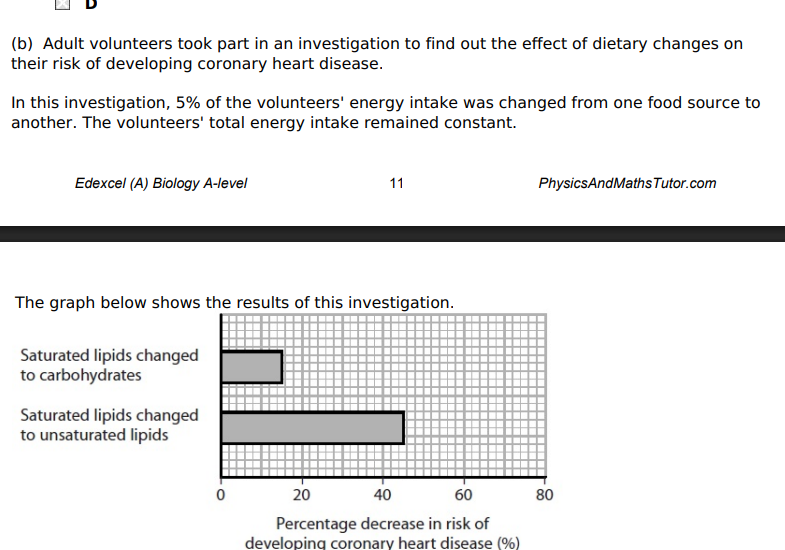
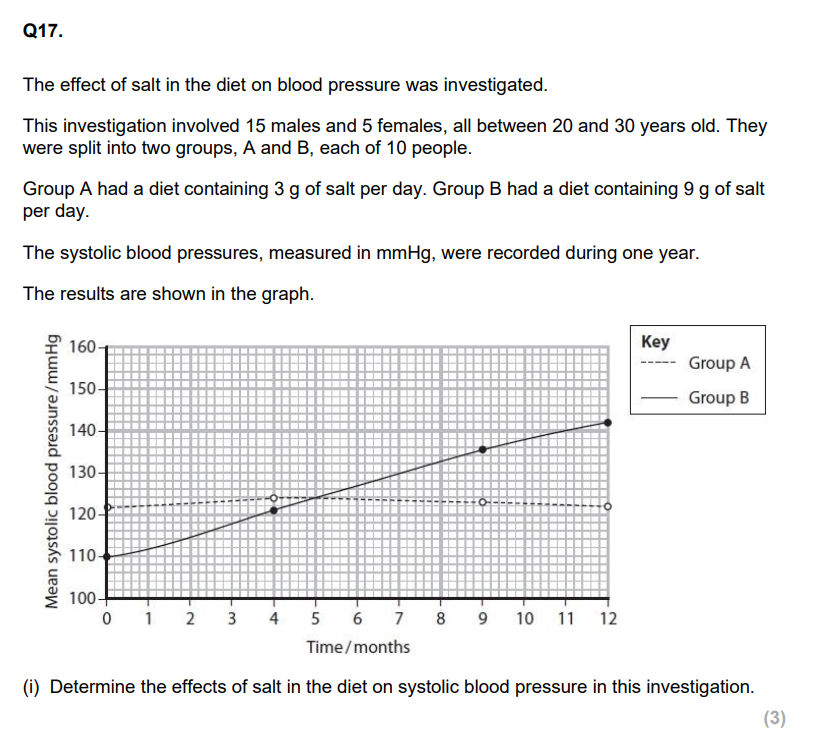
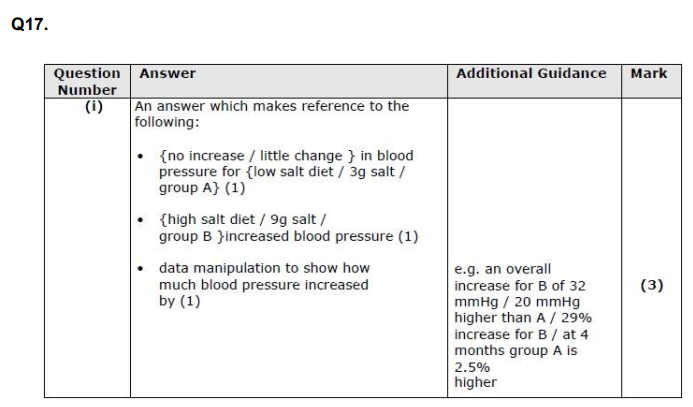
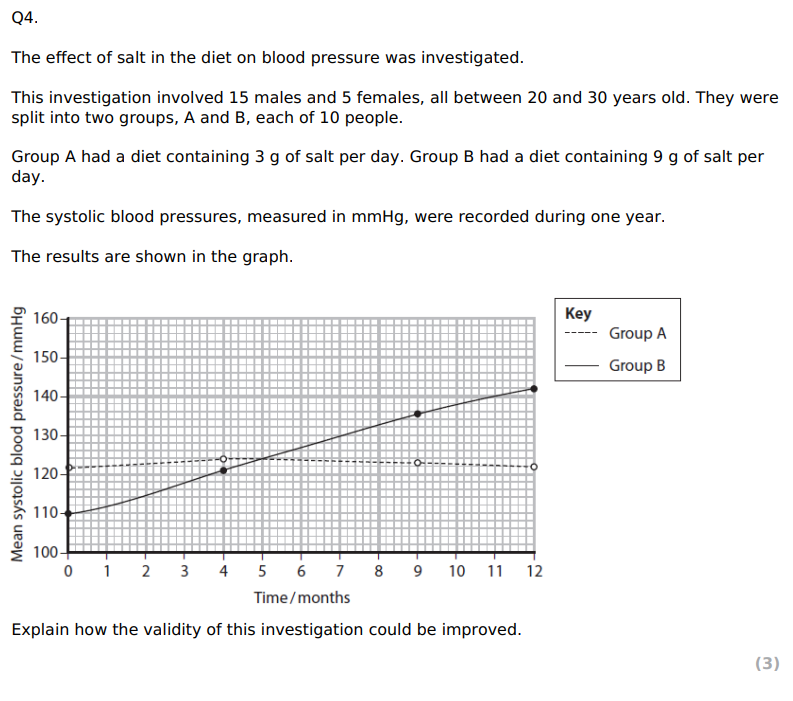
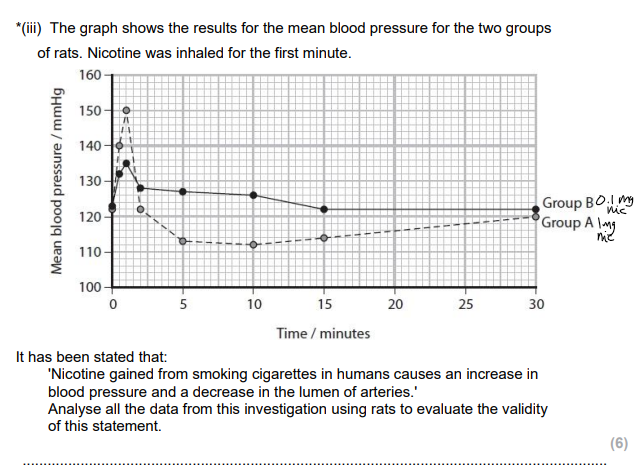
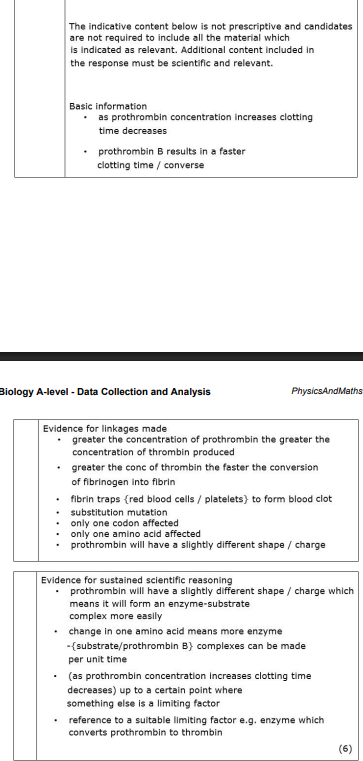
Using the information in the graph and your own knowledge, suggest an explanation for the results of this investigation.



C
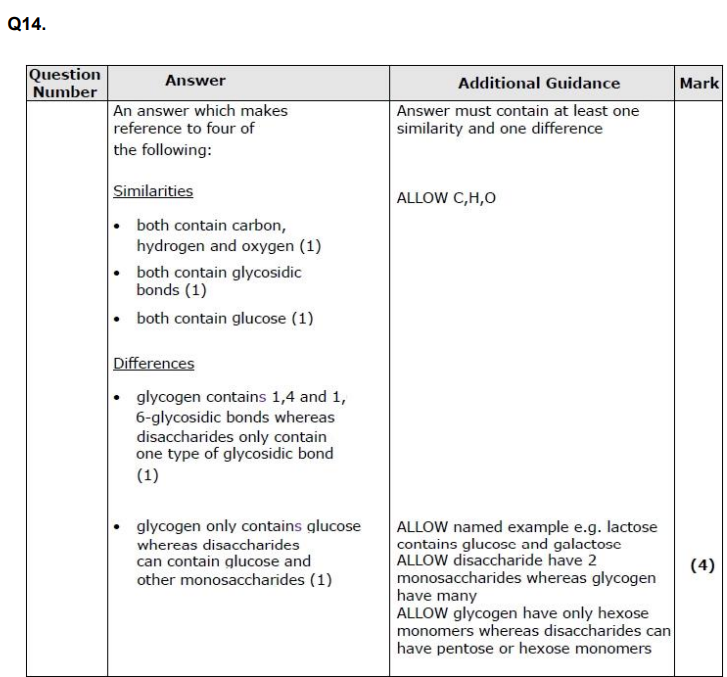
Q7. Explain how the structures of amylopectin and glycogen make them suitable for storing energy
Insect flight uses a lot of energy. Explain the advantage of insects storing both trehalose and glycogen. (4)
The R group differs between the amino acids. The R group may contain elements that are not found in a carbohydrate. Name one of these elements. (1)
N / S
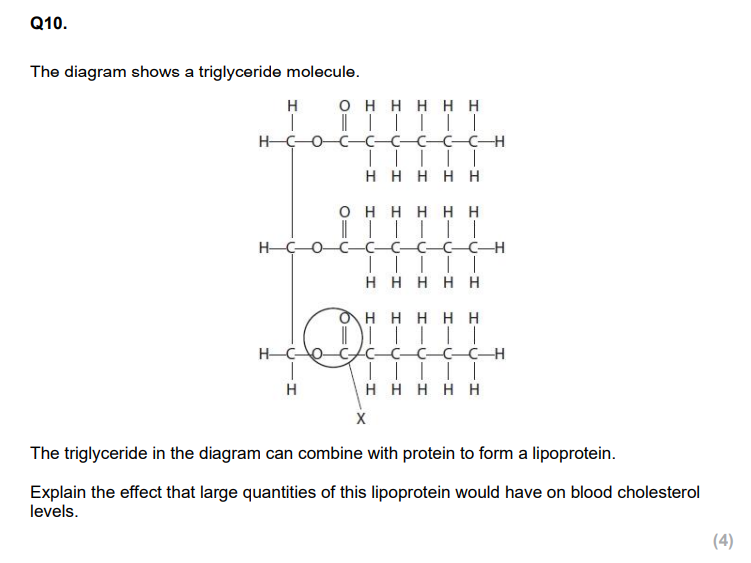
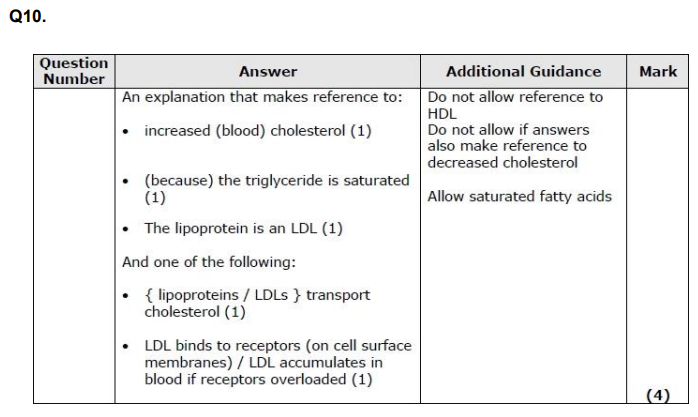
Compare and contrast the structure of a disaccharide with glycogen. (4)

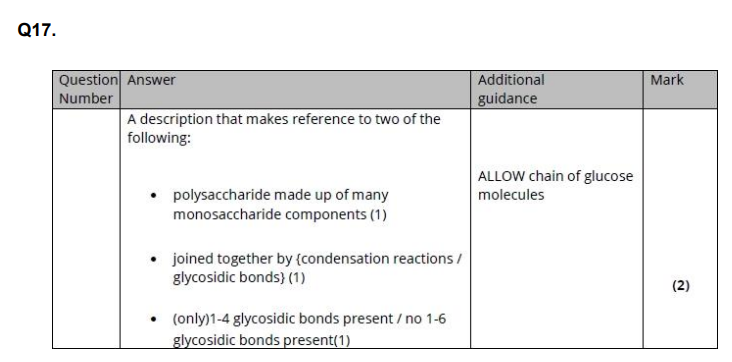
Describe the formation of glycogen from glucose. (2)
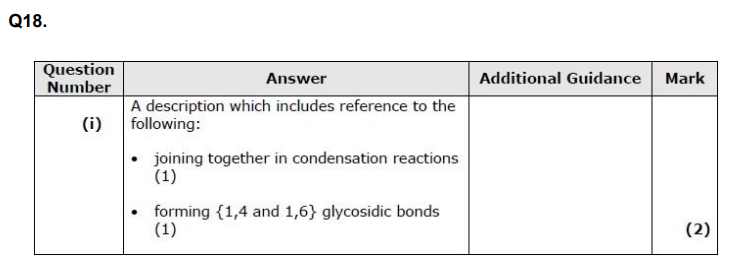
Which of these molecules is transported by tRNA? (1)
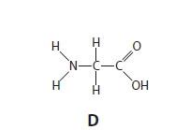
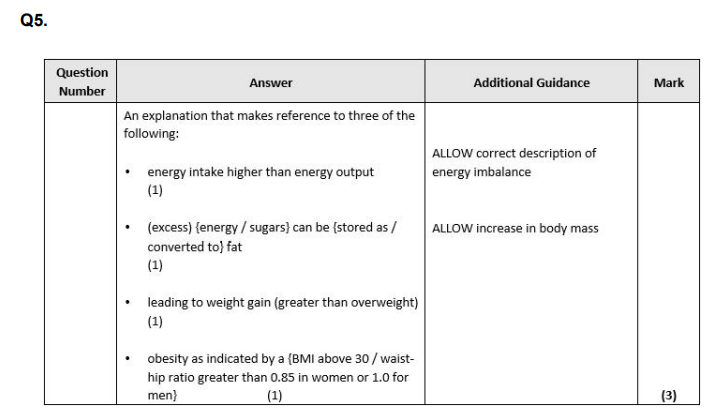
Explain why high levels of sugars in a person's diet could lead to obesity. (3)
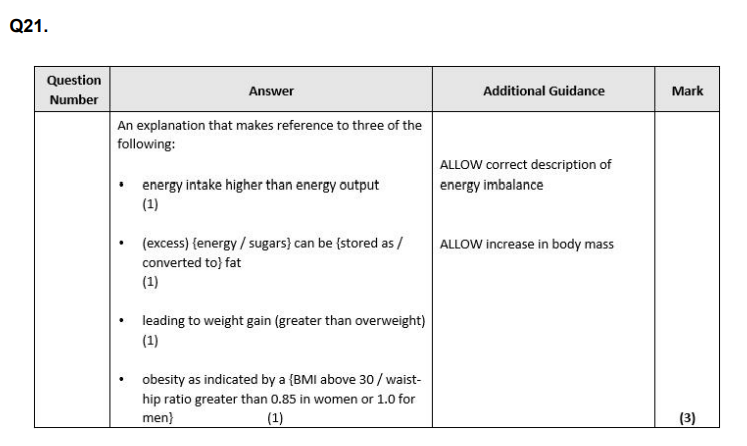
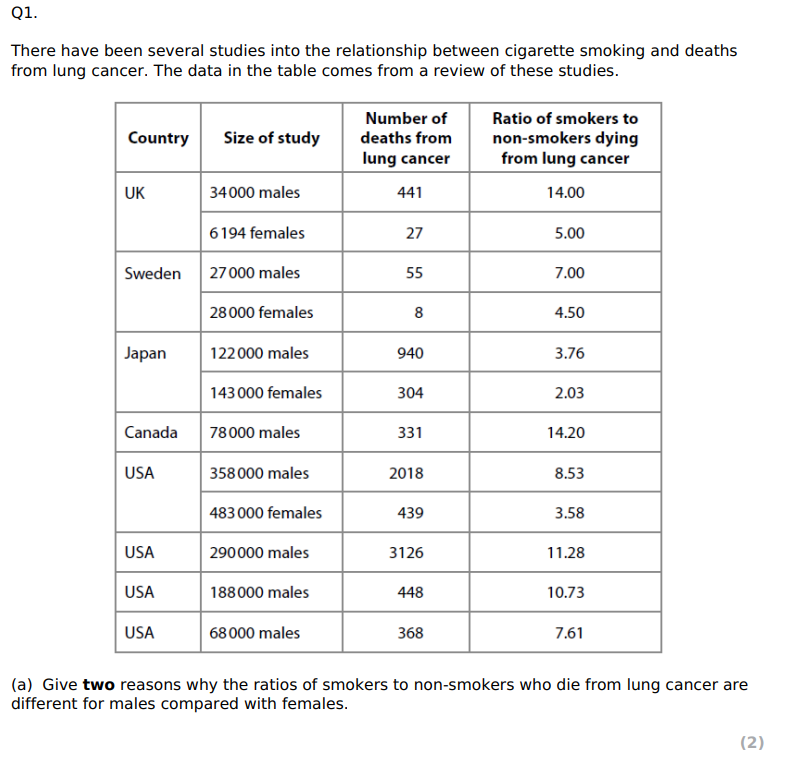
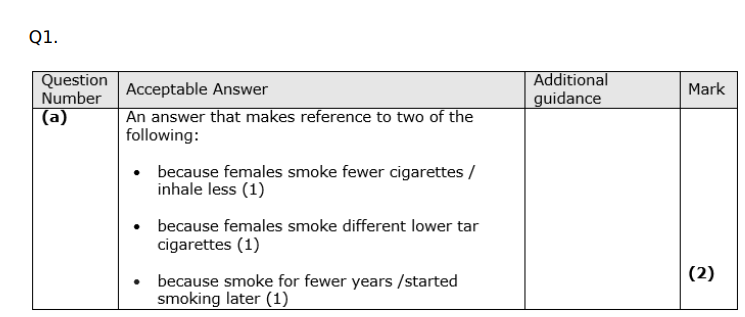
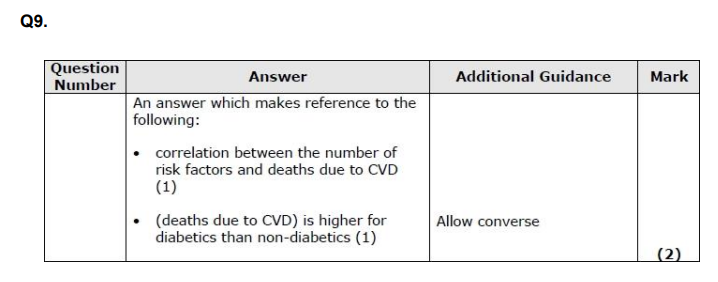
State what is meant by correlation. (1)

Explain how smoking increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis. (3)

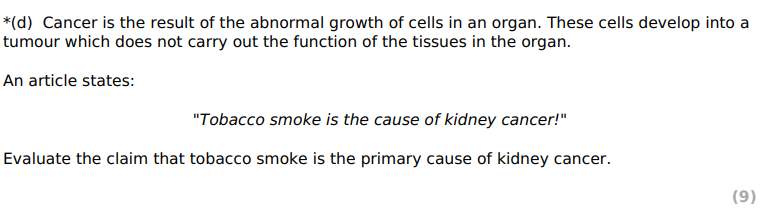
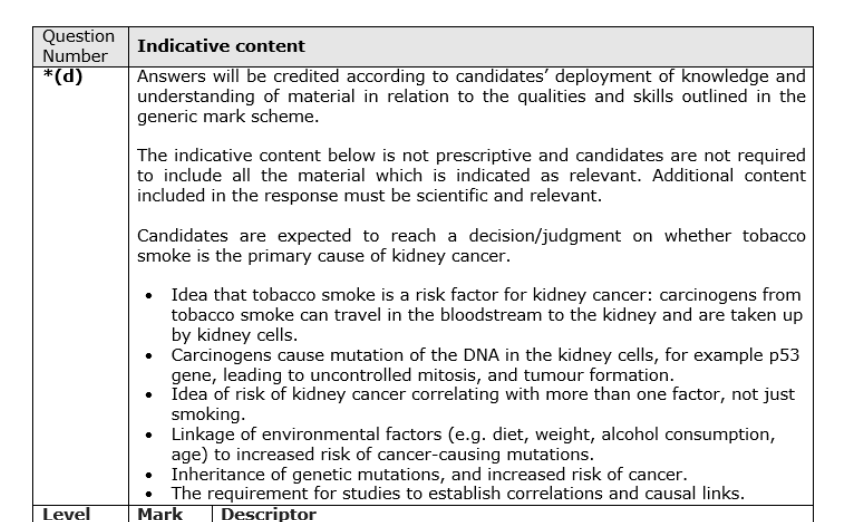
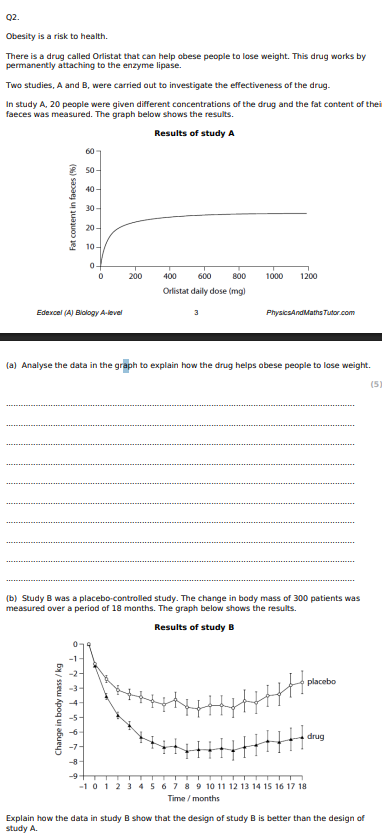
RESULTS MORE RELIABLE: ERROR BARS
It is possible that the men and women in these studies underestimated their alco consumption. Suggest one reason for this.
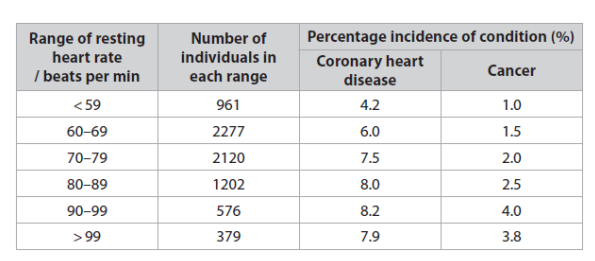
Give two reasons why the number of people in each resting heart rate group did not a the validity of this investigation. (2)
calc heart rate
C, C
one cycle=0.72, 83.3bpm
right atrium has less what to the ventricles
less muscle




Prepare equal concentrations of decaffeinated and regular coffee solutions (e.g. 1%) using distilled water. Ensure both are at the same temperature and pH.
Place a Daphnia of similar size and age into a cavity slide with a few drops of the coffee solution. Allow it to acclimatise for 2 minutes to reduce stress effects.
Use a microscope to observe the Daphnia’s heart. Count the heartbeats for 30 seconds with a stopwatch and double the value to get beats per minute.
Repeat with at least 5 Daphnia per solution. Control variables include: water temperature, light intensity, volume of solution used, and time of exposure before counting. Use a fresh solution and clean slide each time.
If you're comparing two means (e.g. heart rate with and without caffeine), the t-test is used.
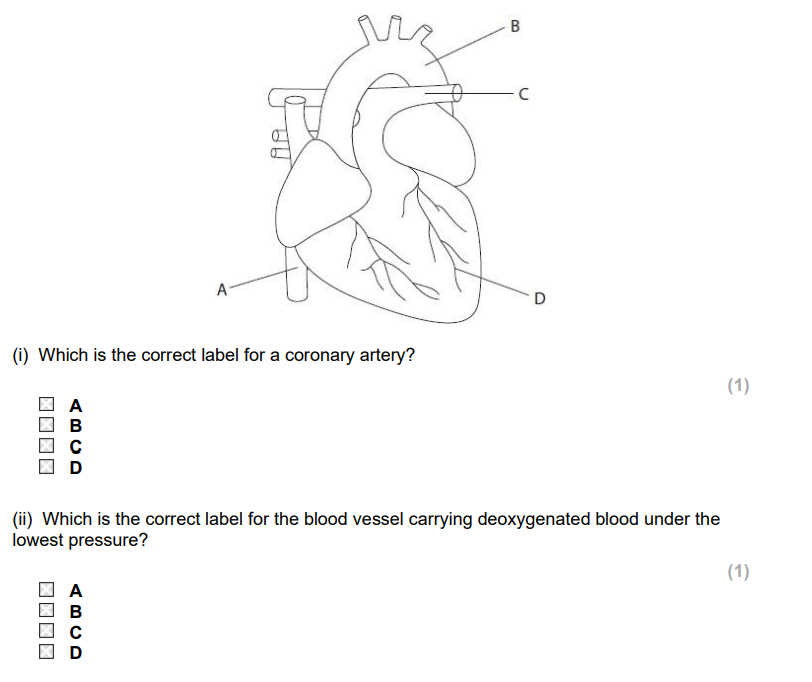
D, A
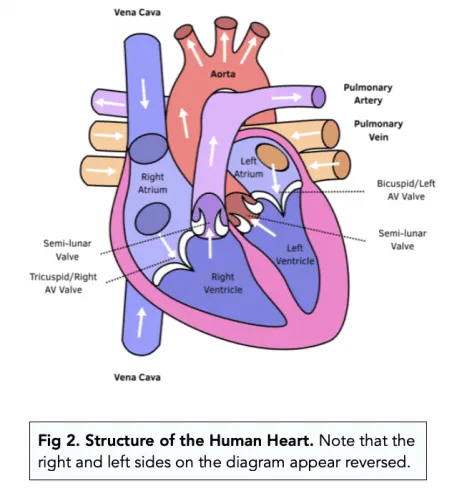
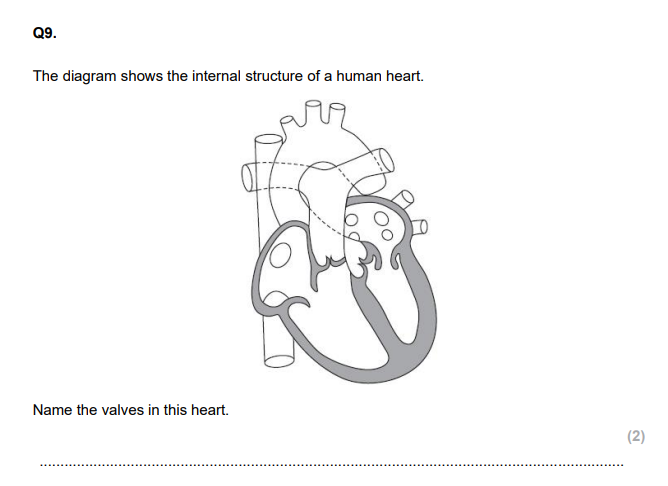
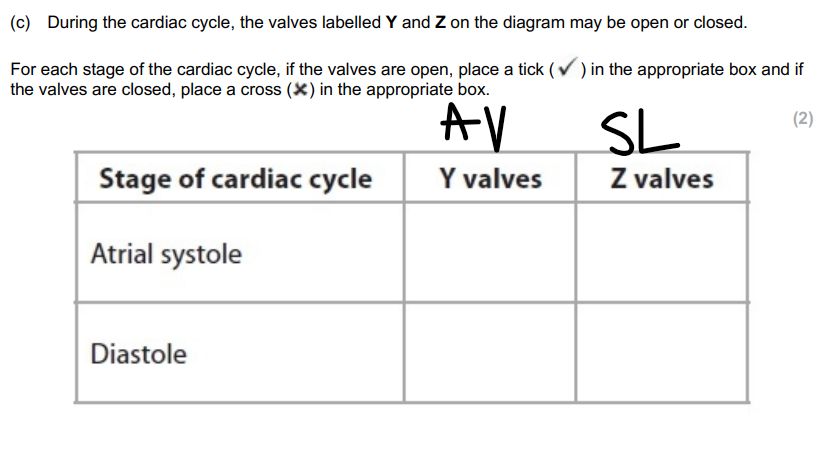
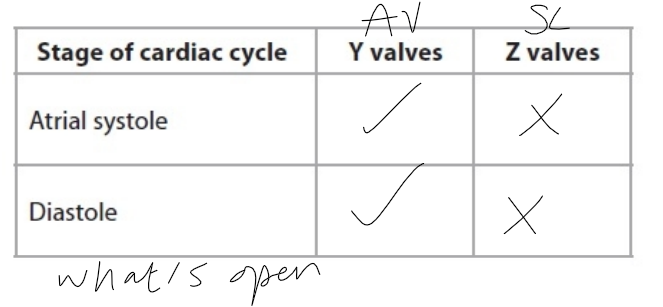
AV / SL
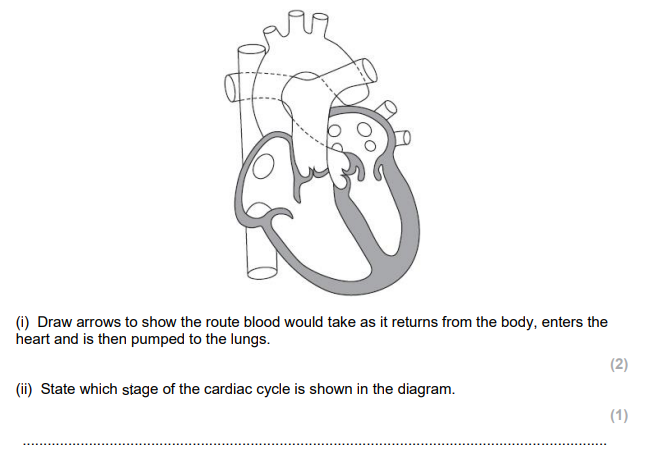
atrial systole
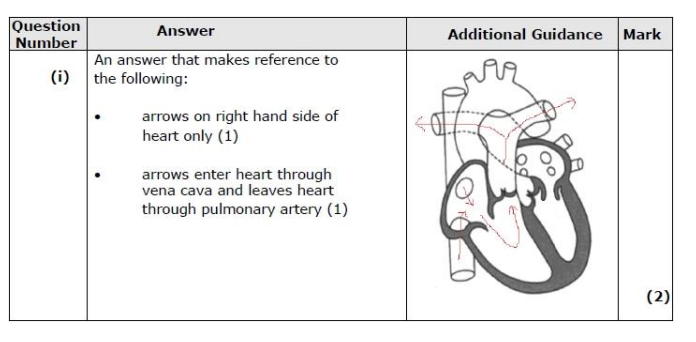
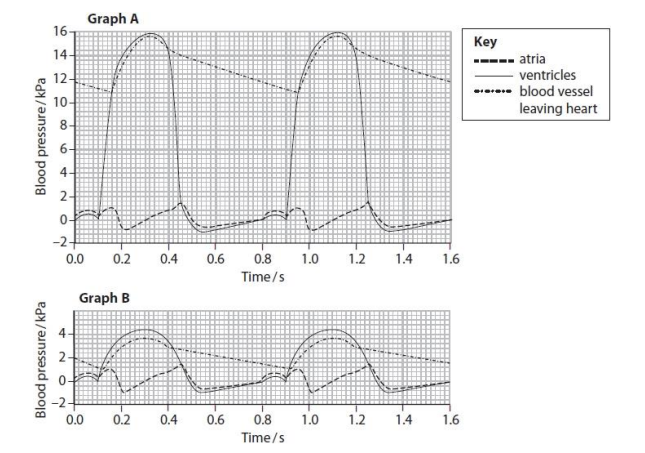
In graph A, the blood pressure inside the ventricle changes between 0.0 and 0.45 seconds. Explain how these changes in blood pressure occur in this part of the cardiac cycle. (4)
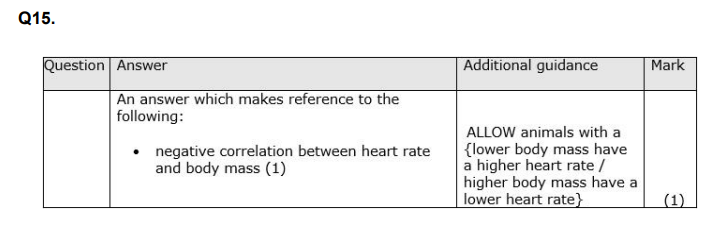
Men who smoke have an increased risk of having an ischaemic stroke. Analyse the data to discuss what advice could be given to a smoker, who has had one ischaemic stroke, to reduce his risk of having another stroke. (6)
INCLUDE ALL RISK FACTORS WITH THESE QS eg. reduce blood cholestrol, reduce saturated fat in diet, take statin, anticoagulants, reduce BMI, increase excercise
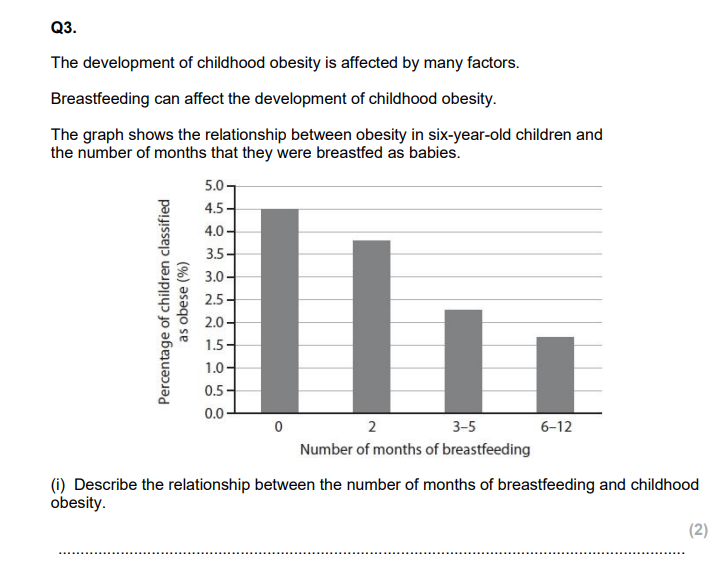
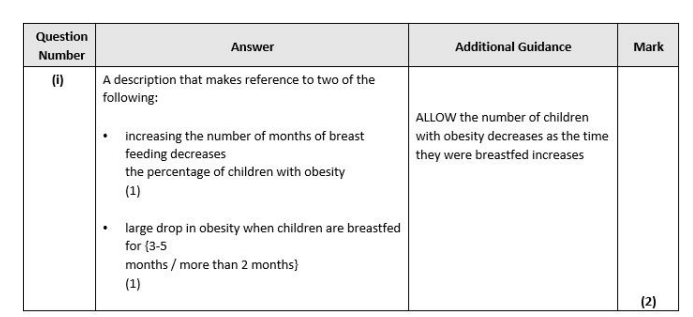
always state: is there a change, wheres a big/small change, error bar overlap?, give values.
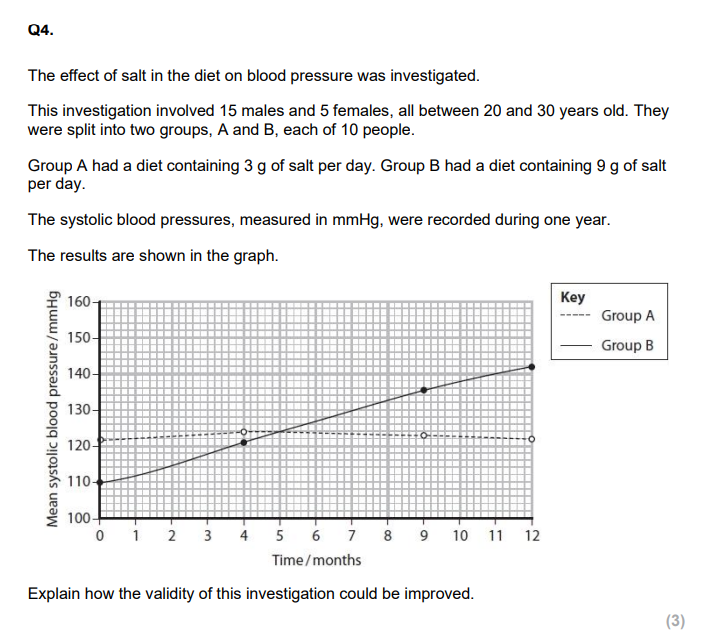
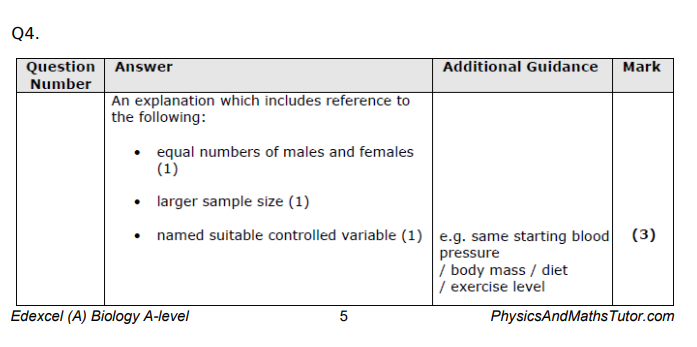
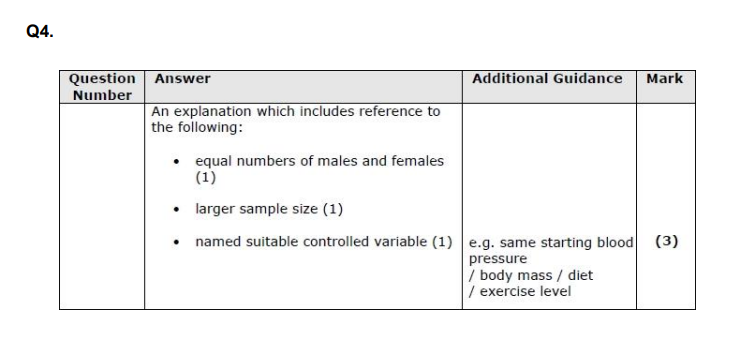
control variable, larger sample, equal no. groups( of each gener eg.)

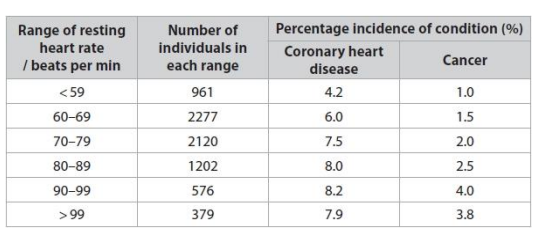
Give two reasons why the number of people in each resting heart rate group did not affect the validity of this investigation. (2)

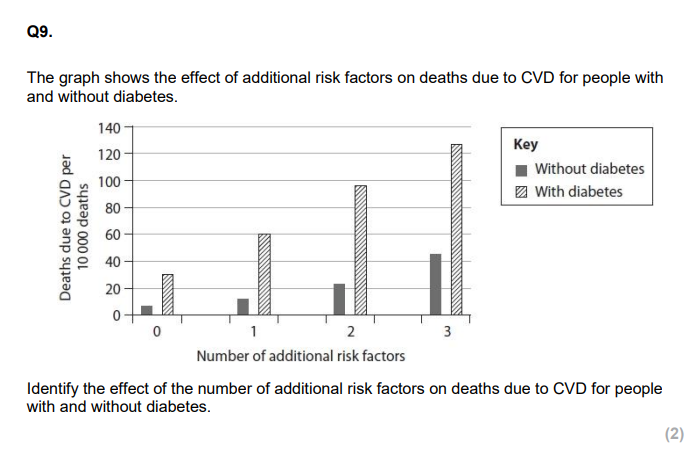
CORRELATION!!
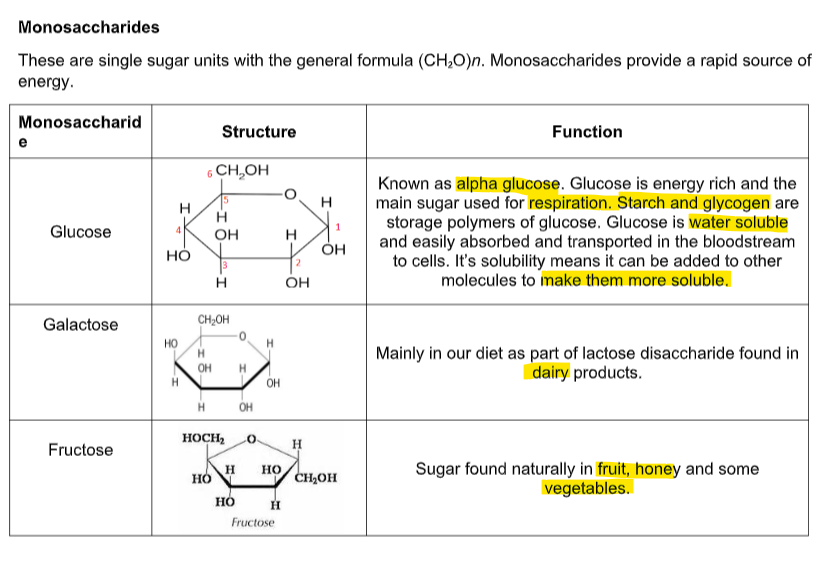
what are the 3 monosaccharides and what do they do (8)
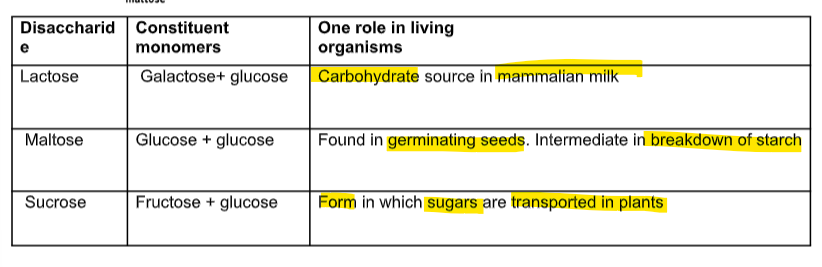
3 disaccharides and function
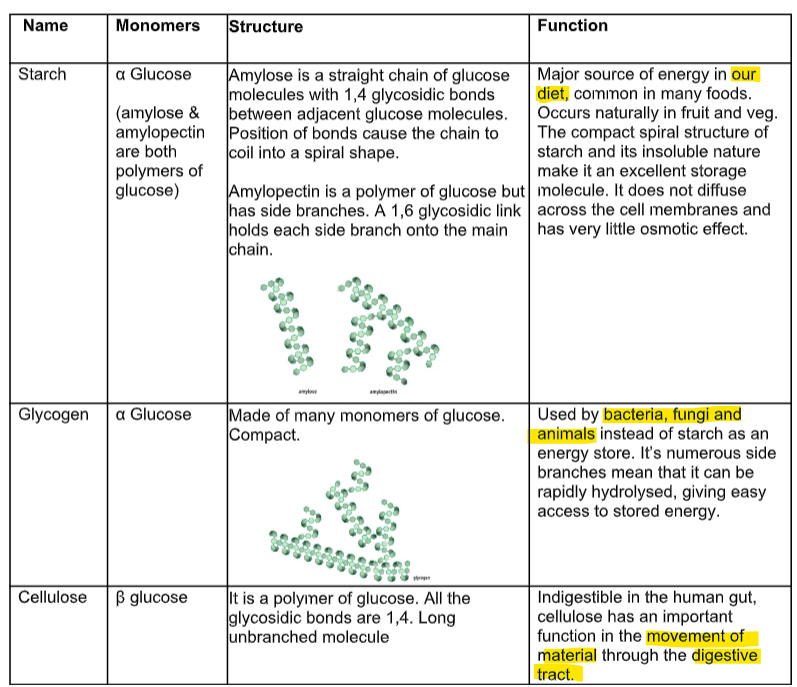
3 polysaccharides and function
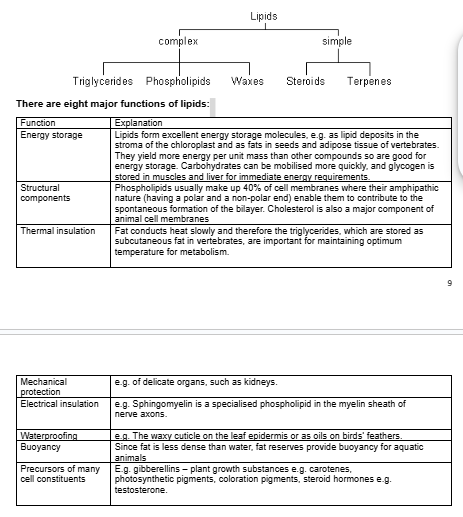
lipid function (8)/ simple complex lipids
how do animals obtain lipids?
Since all cells contain lipids, any animal that eats a plant or animal cell will take in some lipid.
Triglycerides and phospholipids are hydrolysed by lipase into glycerol and fatty acids.
Since lipids do not dissolve in water, they are not easy to digest and their digestion is accelerated in vertebrates by the secretion of bile salts, which emulsify them into smaller particles, greatly increasing the surface area on which lipase can act.
saturated/unsaturated fats
sat
high mp
animal fats from meat/dairy
unsat
lower mp
kink in fatty acid chain
olive oil/vegetable oil/nuts/fish