Chem ch 8/9
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is the Core of an atom?
Set of é with the configuration of the nearest noble gas (eg Ar, Ne..) having an atomic # less than that of the atom being considered
What is an energy level
The specific amount of energy which an é in an atom can posses
What are isotopes
Atomic species having the same atomic # but different mass #
Democritus
Greek philosopher who believed that atoms are indivisible, first to come up with the idea of atoms
John Dalton
Developed atomic theory in 1800s
JJ Thomson
Discovered small é and developed crookes tube, cathode ray, and Plum pudding model
Sir Ernest Rutherford
Discovered the nucleus with his scattering experiment
Niels Bohr 1914
Came up with the idea of energy levels or shells. Helped explain Hydrogen Spectrum
Valence electrons
É that can take part in chem reaction
Mandeleev 1869
Published the first widely accepted Periodic table of Elements
Electronegtivity
The ability of an atom to attract é from another atom
Dipole
Partial separation of charge. Slighty postive/slightly negative charge. ɗ+/ɗ-.
Polarization
The process of repelling the é on a nearby atom which results in a temporary dipole
London forces
Weak attractive forces which is the result of temporarily dipolar attractions between neighboring atoms. Atoms may exist individually or as parts of molecules
Intramolecular
Strong forces between different molecules
Intermolecular
Weak forces known as Wan Der walls forces
Orbitals
Areas within atoms where there is a high probability (90%) of finding é
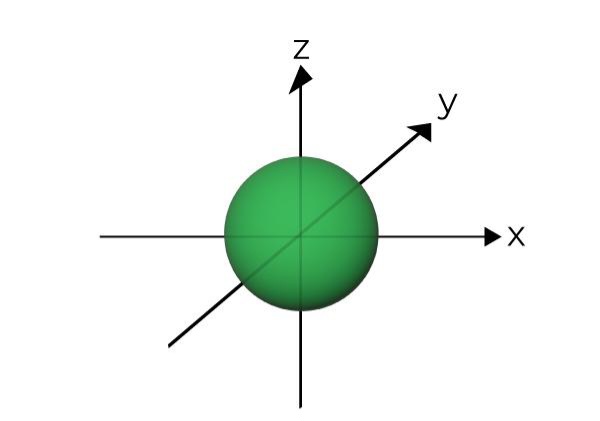
What orbital shape this is
S orbital
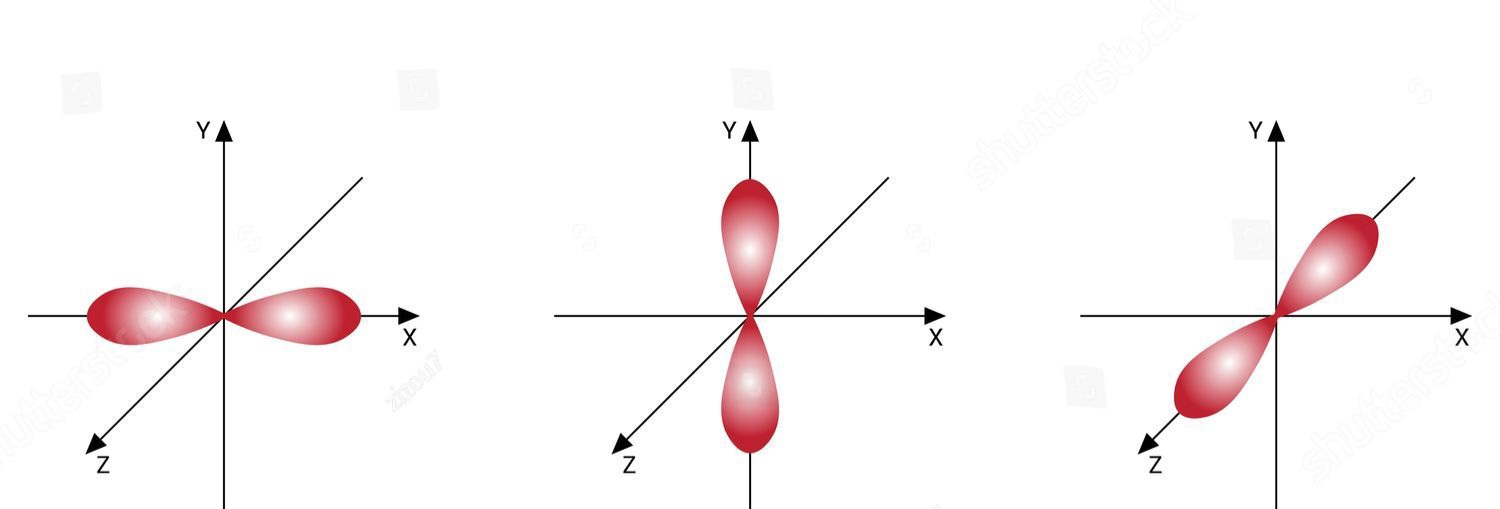
What orbital shape are these from left to right
Px, Py, Pz
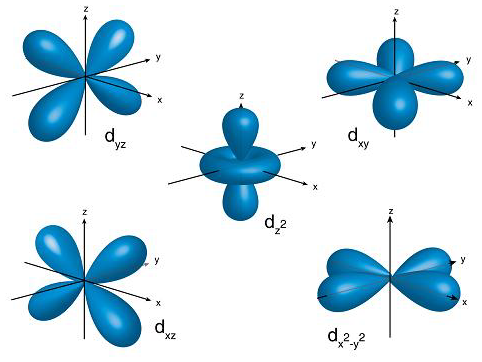
What orbital are these
D orbitals
Whats the maximum electron each orbital can hold?
2 electrons
What does isoelectron mean?
Same electron configuration but different atom (nuclei)
Electron configuration
A description of which orbitals in an atom contains electrons and how many electrons are in each orbital
Valence of an atom is the # unpaired é and sometimes called
Combining capacity
Dipole-Dipole
Bonding forces which exist as a result of an electro static attraction between molecules having permanent dipoles
What are the two main types of Van der waals forces
London forces and dipole-dipole
What is hydrogen bonding
A weak attraction (strong dipole-dipole attraction) where a Hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to one of N, O or F (each of which is highly electronegative)
Ions
Atoms with a charge - a full outer orbitals