How does biofilm lead to development of periodontal diseases – introduction
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Periodontal Diseases
Bacterially-induced, immune-mediated inflammatory diseases of the tissues supporting the teeth.
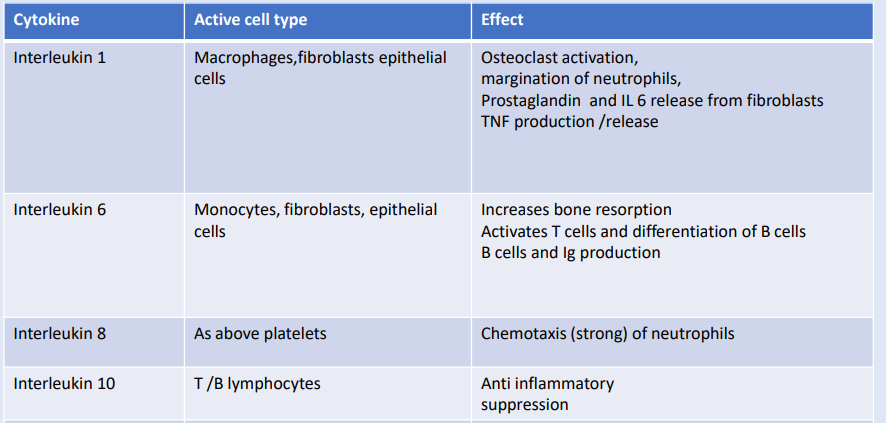
-Healthy sites: Well defined, precisely orchestrated, effective immune response.
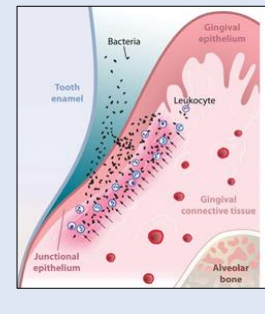
-Diseased sites: Exacerbated, uncontrolled, detrimental immune response
Periodontitis – Risk Factors (multi-factorial aetiology)
Dental plaque- primary aetiological factor
Local factors - promote accumulation of dental plaque (calculus, restorations with overhanging margins),
Systemic factors – modify the host-bacteria interaction (Diabetes mellitus, puberty, pregnancy, immunodeficiency
systemic factors can be further classified into…
modifiable and non modifiable
systemic - Non-modifiable (background) factors 4
Age
Race
Gene polymorphism
Hyper-responsive phenotype
systemic - modifiable - Environmental, acquired factors: 3
Smoking
Systemic diseases, medications
Psychosocial factors
Prerequisites for Periodontal Disease Initiation and Progression 3
Virulent periodontal pathobionts (adhesins, co-aggregation, invasion, factors that cause tissue damage),
Local environment,
Host susceptibility (gene polymorphism, PMN defects, smoking, diabetes, immunosuppression)
Periodontal Tissues Destruction -split
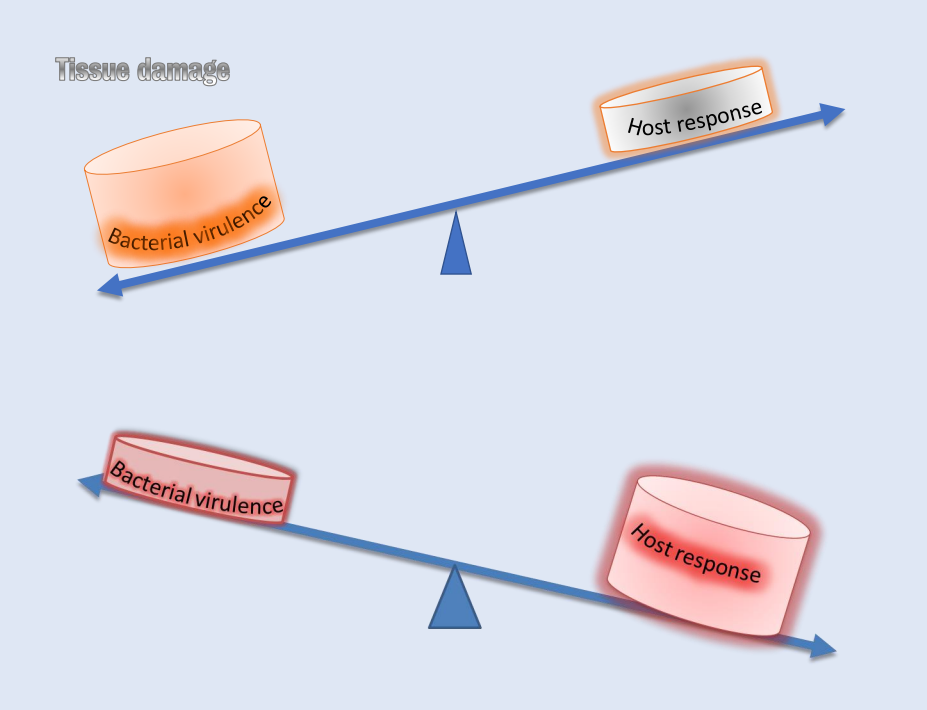
Direct action of the microorganisms (20%)
De-regulated inflammatory (immune) response to dental plaque m.o. (disruption of protective innate immunity or unresolved inflammation) 80%
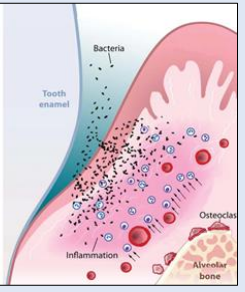
Bacterial Virulence Factors
Early colonisers are mainly using glycolysis, late colonisers use proteolysis - they use a different set of enzymes
They can produce collagenases - destroy periodontal tissues. Toxins to osteoblasts.
Direct tissue damage or poorly controlled immune response damage - which causes tissue damage
Specific pathobionts as late colonisers - antigens - triggers host inflammatory response - leads to tissue damage - clinical expression
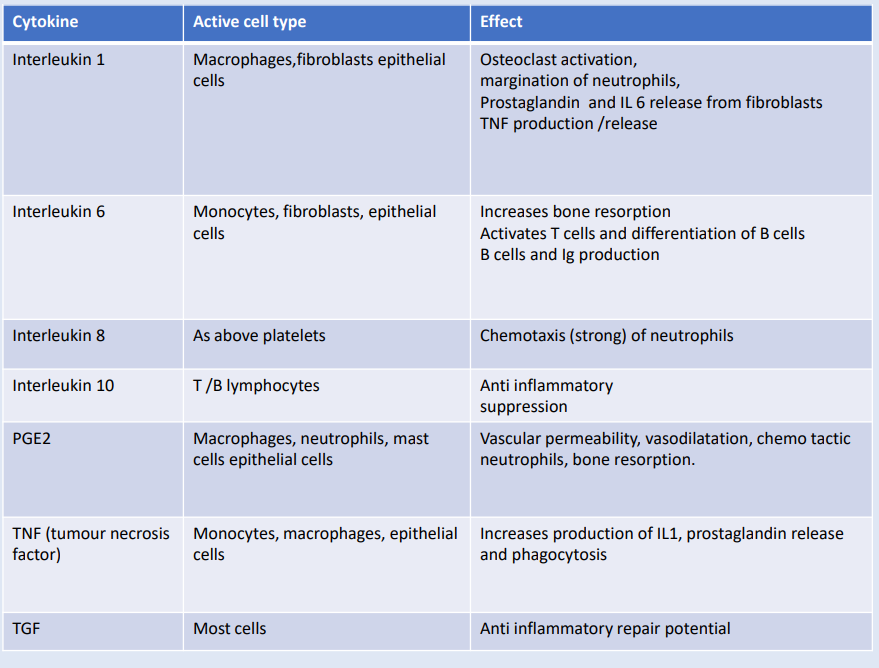
Many cells can sense antigens - can produce cytokines. The duration of the inflammation depends on the ratio of cytokines - prevalence of the pro-inflammatory cytokines - reach the peak of the inflammation
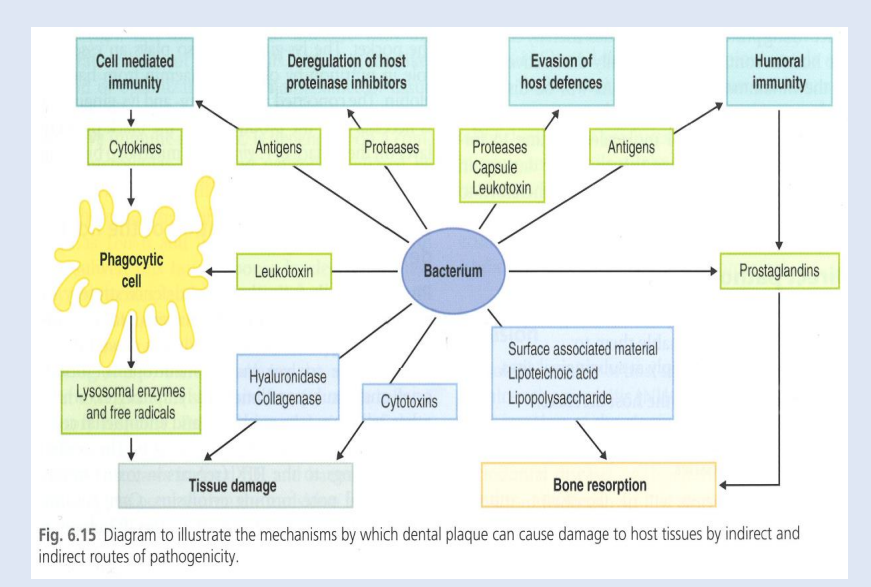
Direct and Indirect Tissue Damage
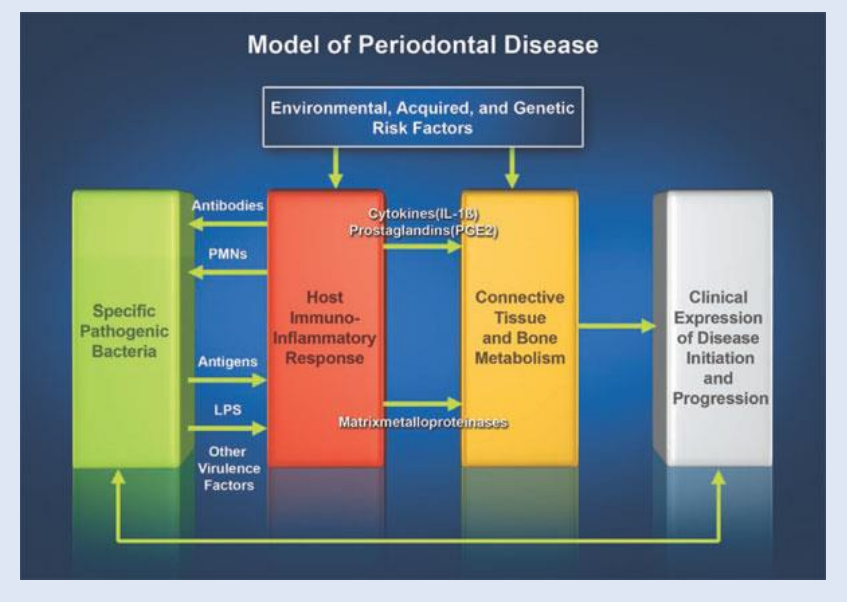
Tissue damage can occur for either combo
interleukin 1, 6 , 8 , 10