p13 and p14 em waves
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
what are all em waves
transverse waves which transfer energy from a source to an absorber
what do all EM waves travel at through space or a vacuum
the same speed
what is this speed
3 × 10^8 m/s
what do em waves form
a spectrum over a range of frequencies
what are the types of em waves (7)
radio
microwaves
infrared
visible light
ultraviolet
x-rays
gamma
why do em waves occur over such a range of frequencies
they are generated by a variety of changes in atoms and nuclei
what are em waves made up of
oscillating electric and magnetic fields
how are these oscillating electric and magnetic fields formed
oscillating charges make up alternating currents. as the charges oscillate, they produce these fields
what is the frequency of the waves equal to
the frequency of the alternating current
how can you produce radiowaves
using an alternating current in electrical circuits
what is a transmitter used for in this
the object in which charges (electrons) oscillate to create the radio waves
when transmitted radio waves reach a receiver, what happens
the radio waves are absorbed
how is energy from the waves transferred to the receiver
energy is transferred to electrons in the material of the receiver
what does this energy then cause
electrons to oscillate, producing an alternating current
when will alternating currents not be produced
if the electrical circuit is not complete
what is the wavelength range of radio waves
longer than about 10cm
why can long wave radio signals be received half way around the world
they diffract around the earth’s curved surface
diffract
bend
what can long range radio signals do
be received even if the receiver isnt in line with the transmitter
how can short wave radio signals transmit data over long distances
they are reflected from the ionosphere
what is the ionosphere
an electrically charged layer in the earth’s upper atmosphere
what is an example of this
bluetooth uses short wave radio waves to send data over short distances wirelessly
how do medium wave signals behave
they also reflect from the ionosphere (depending on the time of day and atmospheric conditions)
what is the requirement for receiving TV and Fm radio transmissions (which are very short)
you must be in direct sight of the transmitter
what are microwaves used for
communication to and from satellites (including satellite Tv signals + satellite phones)
why are microwaves used
they pass easily through the earths atmosphere
what happens to the signal in satellite communication
transmitted to satellite receiver dish, then received by satellite dish in a different position on earth
what is a negative of satellite communication
there is a slight time delay because of the long distance the signal must travel
how do microwave ovens heat food (3)
water molecules in the food absorb microwaves
microwaves penetrate up to a few cm into food before absorbing and transferring energy to water molecules
this heats the food
what gives out infrared radiation
all objects
what does infrared radiation indicate about an objects temperature
hotter objects emit more infrared radiation
what can infrared cameras be used to detect
infrared radiation
how do infrared cameras work
they detect IR radiation and turn it into an electrical signal, which is displayed as an image
how do hotter objects appear
as brighter images
what does absorbing IR cause
an object to get hotter
how can food be cooked with IR radiation
the temperature increases as it absorbs Ir radiation
how do electric heaters use IR radiation
they contain a long wire which heats up when a current flows through it - this emits radiation which will be absorbed by objects and the air
what are optical fibres
thin glass or plastic fibres which carry data over long distances as pulses of visible light
how do optical fibres work
light rays reflect, bouncing back and forth, till they reach the end of the fibre
is light easily absorbed or scattered as it travels through the fibre
no
what is fluorescence
a property of certain chemicals - uv is absorbed and visible light is emitted
what do fluorescent lights generate
UV radiation which is absorbed and remitted as visible light
what absorbs and remits this radiation
a compound called phosphor in the bulb
when is this useful
its energy-efficient, so for lights which are on for long periods of time
uses of UV light (3)
security pens
sun tanning
tanning beds
what do radiographers use x-rays for
taking x-rays or ‘photographs’ of people to see if they have broken bones
how do x-rays work
they pass easily through flesh but are absorbed by denser materials like bones or metal
what does this leave
bright areas where x-rays are absorbed, and dark areas where x-rays pass directly through
what do radiographers use x-rays and gamma rays for
treating cancer, or radiotherapy
how does this work
high doses of these rays kill all living cells → they are carefully directed at cancer cells to avoid killing healthy cells
how is gamma radiation used as a medical tracer
a gamma emitting source is injected into a patient, and its progress is tracked around the body
why is gamma radiation a good option for this
it will pass out through the body quickly, not causing too much harm
how do radiographers minimise health damage when doing these tasks
wear lead aprons and stand behind lead screens, or leave the room
what is the effect of low frequency waves on people (e.g. radiowaves)
they dont transfer much energy and so mostly pass through soft tissue without being absorbed
what is the effect of high frequency waves on people (e.g. UV, x-rays, gamma)
transfer lots of energy and can cause lots of damage
how is UV dangerous
it damages surface cells → leads to sunburn, premature ageing, blindness and skin cancer
what are x-rays and gamma rays
ionising radiation which means they carry enough energy to knock electrons off atoms
what does ionising radiation cause
gene mutation, cell destruction and cancer
what is a big debate
whether the benefits outweigh the risks
how is radiation dose measured
in sieverts, or millisieverts
what is radiation dose
a measure of the risk of harm from the body being exposed to radiation
what does the risk depend on
the total amount of radiation absorbed and the type of radiation absorbed
how to convert from sv to mSv
1000 mSv = 1 Sv
how can risk vary within a person
e.g. chest is much more susceptible to damage then the head
how do lenses form images
by refracting light and changing its direction
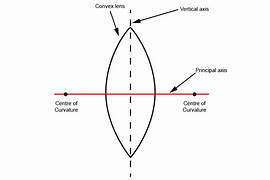
what are two types of lens
convex and concave
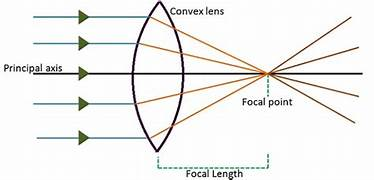
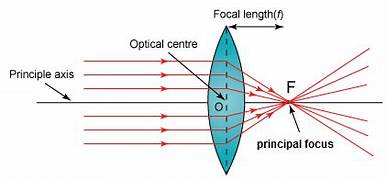
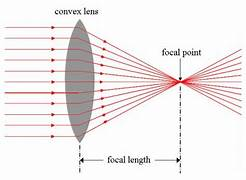
what do convex lenses look like and how does this affect their function
causes rays of light parallel to the axis to converge at the principal focus
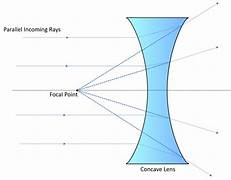
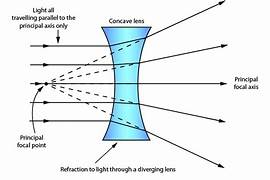
what do concave lenses look like
causes rays of light parallel to the axis to diverge
converge
come together
diverge
spread out
what is the axis of a lens
a line passing through the middle of the lens
what is the principal focus of a convex lens
where rays hitting the lens parallel to the axis all meet
what is the principal focus of a concave lens
the point where rays hitting the lens parallel to the axis appear to all come from
what is on each side of the lens
principle focus
what is the focal length
the distance from the centre of the lens to the principal focus
what is a real image
when the light from an object comes together to form an image on a screen
what is a virtual image
when rays are diverging so light from the objects appears to be coming from a completely different place
what do you get when looking through a magnifying glass
a virtual image → looks bigger then it actually is
to describe an image properly (for 3 marks)
how big it is compared to the object
whether its upright or inverted (upside down) compared to the object
whether its real or virtual
how to draw a ray diagram for convex (4)
draw ray from top of object to the arrow/lens
draw its refracted ray passing through F
draw another ray from top of object right through the middle of the lens, continuing until it meets the refracted line
draw a third ray (to check) through F until it hits the lens. then, connect it to the other two connecting lines
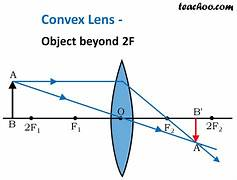
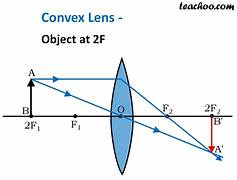
an object at 2F will form (4)
a real image
an inverted image
the same size
at 2F
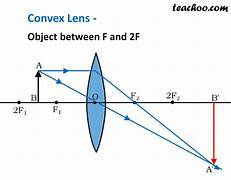
an object between F and 2F will form (4)
a real image
an inverted image
bigger then object
beyond 2F
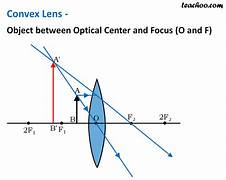
an object nearer then f will form (4)
virtual image
upright
bigger then object
on the same side as the lens
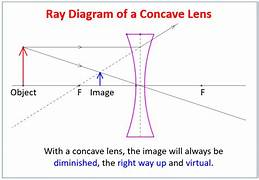
how to draw ray diagram for concave (3)
draw line from top of object parallel to axis line. this is refracted as if its coming out of F. draw dotted line from F and then continue refracted line as normal
draw another ray from top of object right through lens. this doesnt refract
mark where the refracted rays meet - this is the top of the image
how do you know whether its concave or convex
look at the arrows
the further an image is from the concave lens…
the smaller the image produced
unlike convex lenses, what will the concave lens ALWAYS produce (4)
virtual
upright
smaller then the object
on the same side of the lens as the object
how do magnifying glasses work
the object magnified must be closer to the lens then the focal length
how do you calculate magnification
magnification = image height / object height
what is the only part of the em spectrum visible by the naked eye
visible light
what is visible light
a range of wavelengths which we perceive as different colours
what does each colour have
its own narrow range of wavelengths and frequencies
what is the range of these
violents down at 400nm, to reds at 700nm
what can different mixtures produce
more shades e.g. red and blue make purple
what happens when all the colours are put together
white light is produced
what are opaque objects
non see through. they do not transmit light.
what do opaque objects do when visible light hits them
they absorb some wavelengths of light and reflect others
what does the colour of an opaque object depend on
which wavelengths are most strongly reflected
example with a red apple (3)
white light (combination of colours) hits the apple
red light is reflected
all other colours are absorbed
how does this work with opaque objects which arent primary colours
they may be reflecting corresponding colours, or the wavelengths which mix to make that colour