BIOL 4103 - Exam 3 Seibenhener Auburn University
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
NPF
Nucleation Promoting Factor
WH2 domain
Domain on NPF proteins in the WAVE family that
interact with profilin-bound ATP-actin
C and A
Domains on NPF proteins in the WAVE family that interact with ARP 2/3

WAVE
family of proteins that bind ARP 2/3 and Profilin-bound GTP-actin

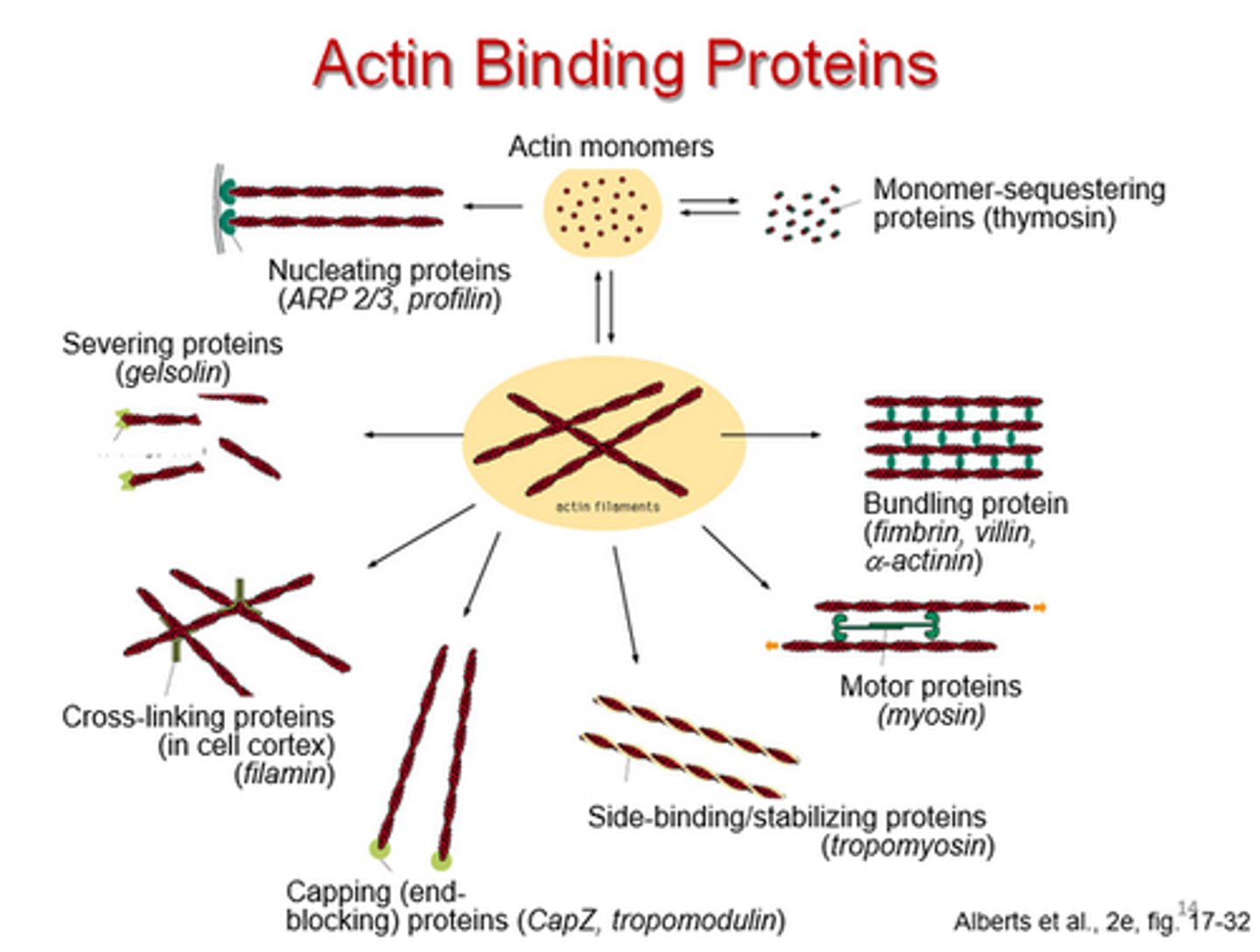
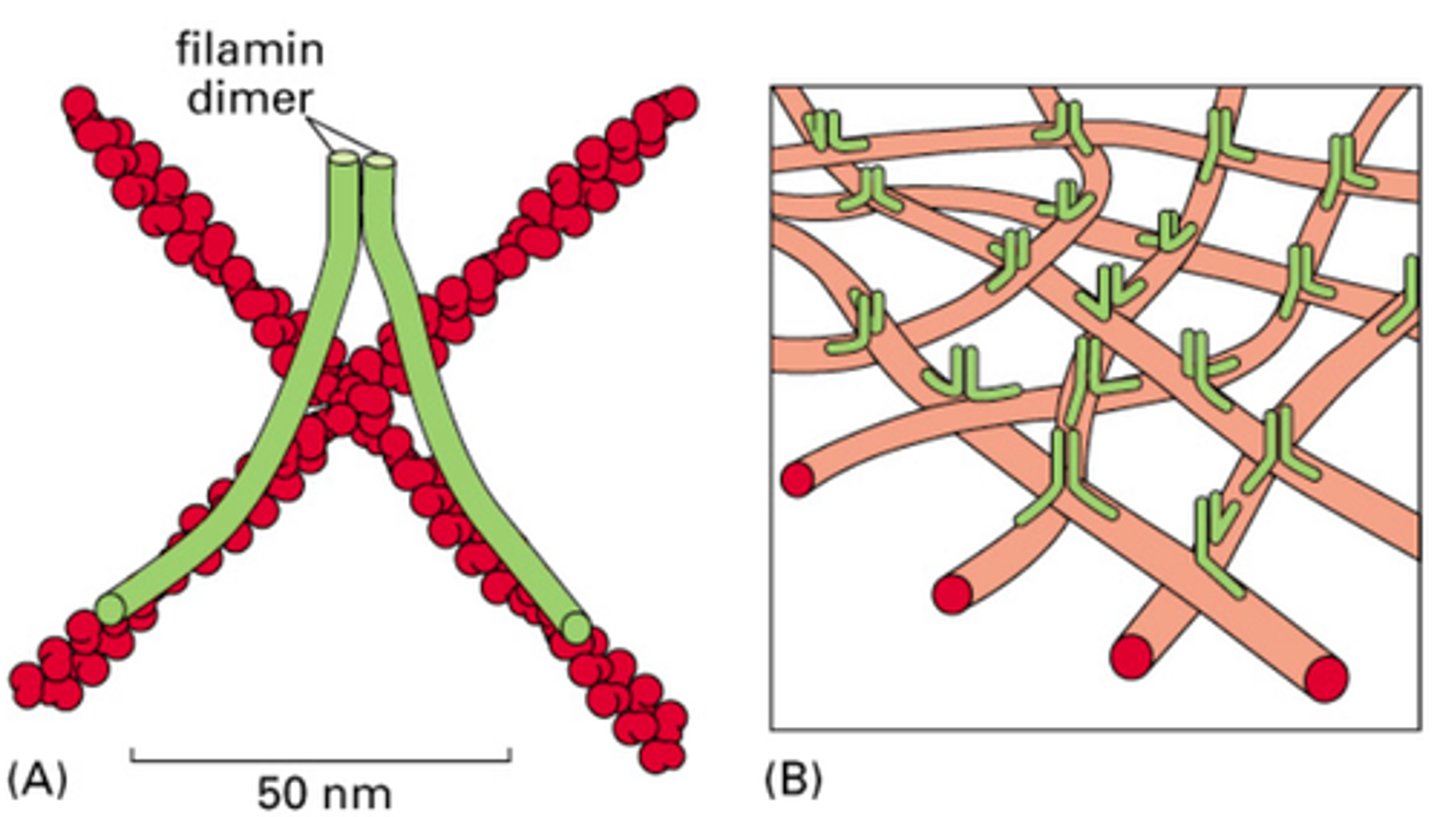
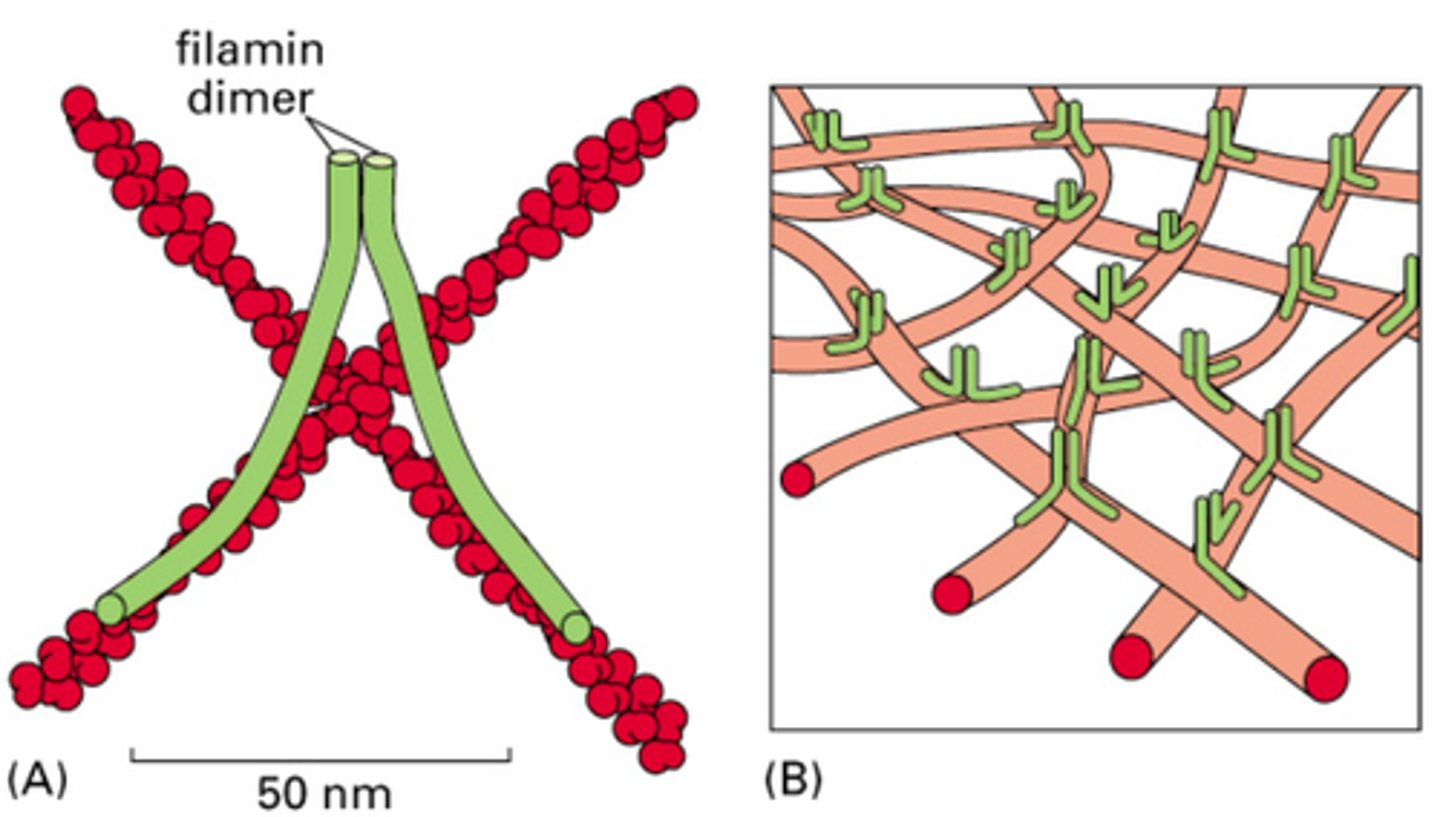
Filamin
An actin-binding protein that cross-links actin filaments into networks.
Dimer of two subunits 280-kD each (560-kD total)
V-shaped molecule
Actin Binding Domain (ABD) is at the amino terminus and the Dimerization domain is at the carboxyl terminus.
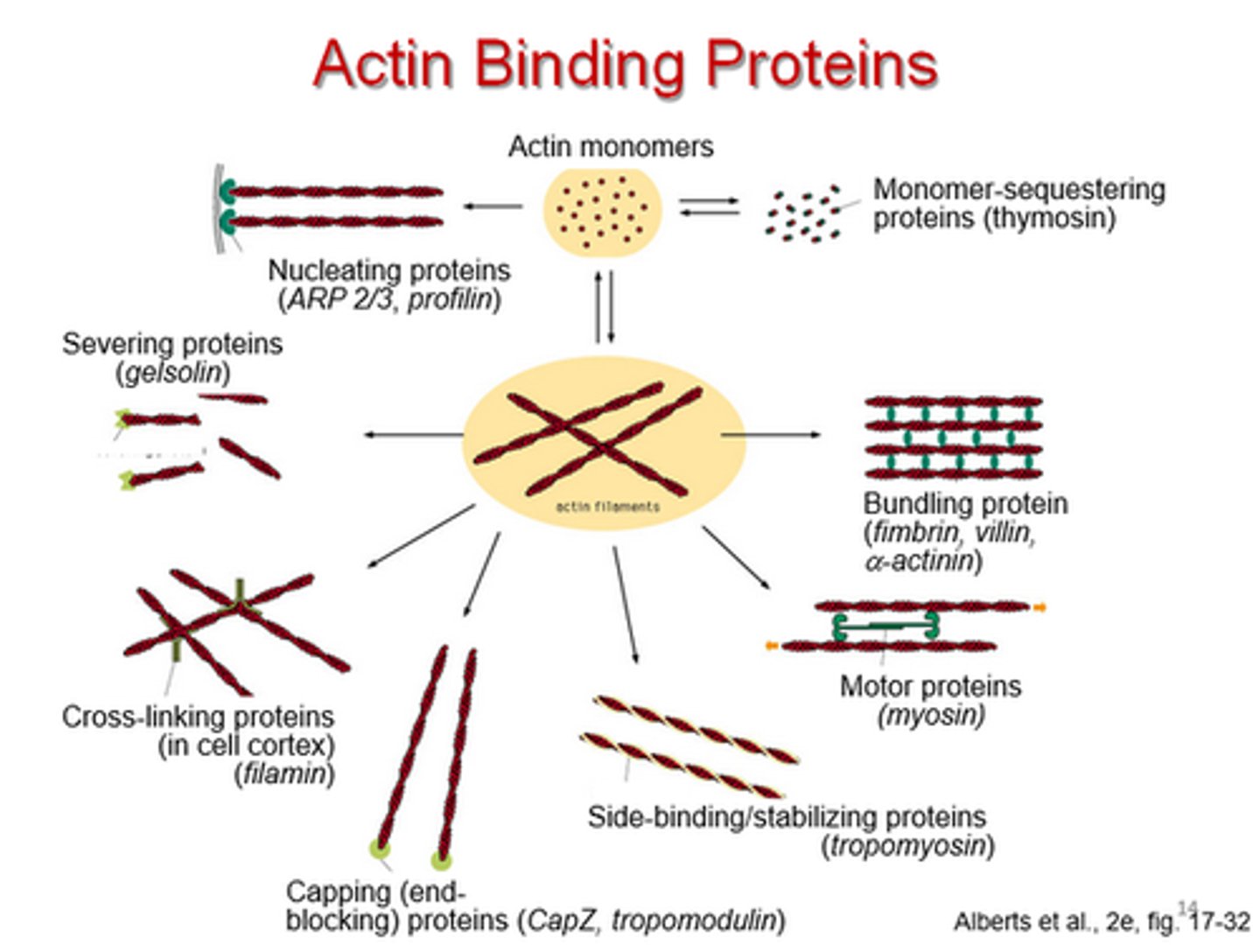
Fimbrin
Bundles actin filaments with little space in between because this monomeric 68-kD protein is very small (14 nm)
Has 2 Actin Binding Domains (ABD)
Has 2 CA^2+ domains
ABD
Actin Binding Domain abbreviation
Filamin
Does Filamin or Fimbrin allow greater angles between actin filaments
Profilin
binds actin subunits and speeds elongation

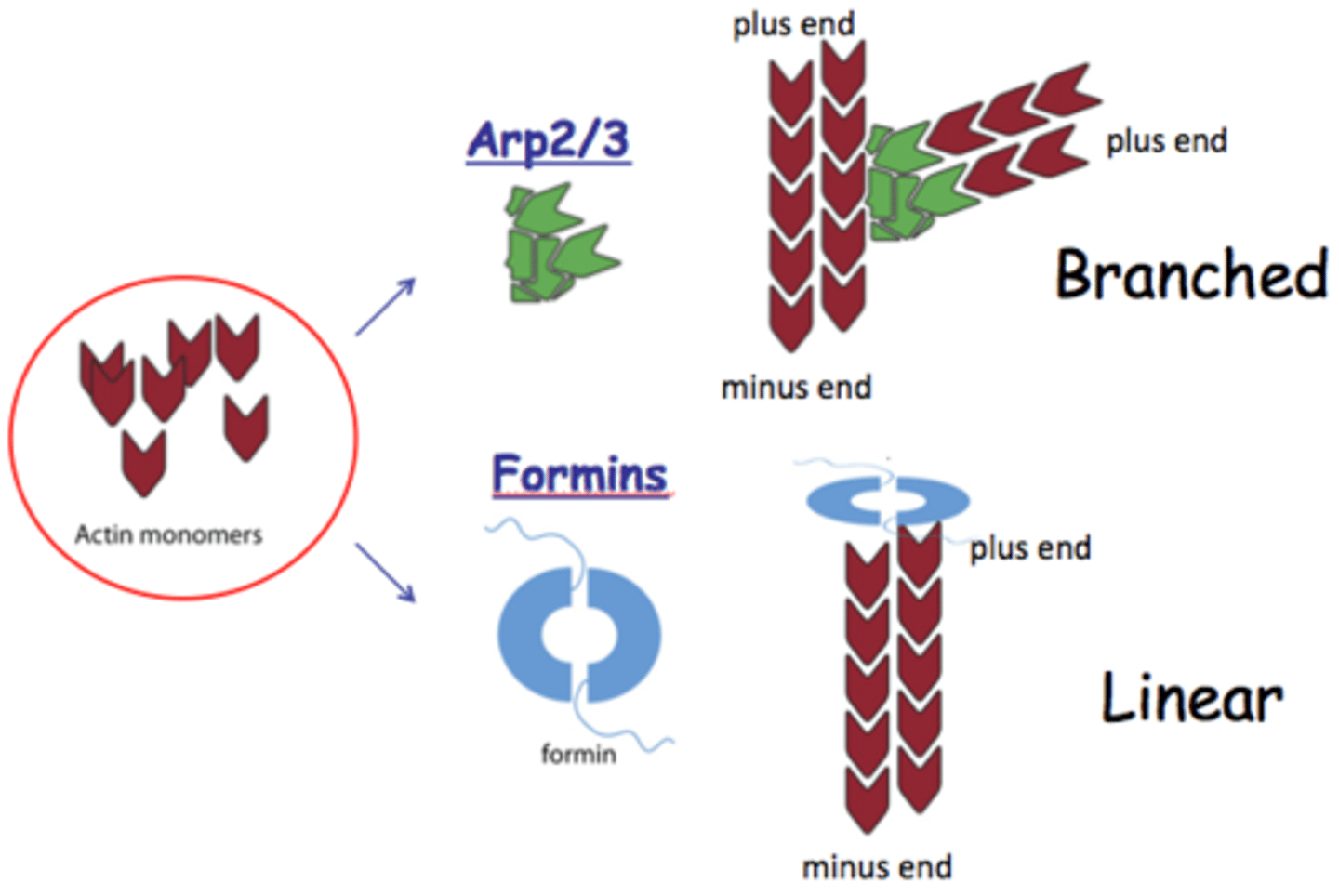
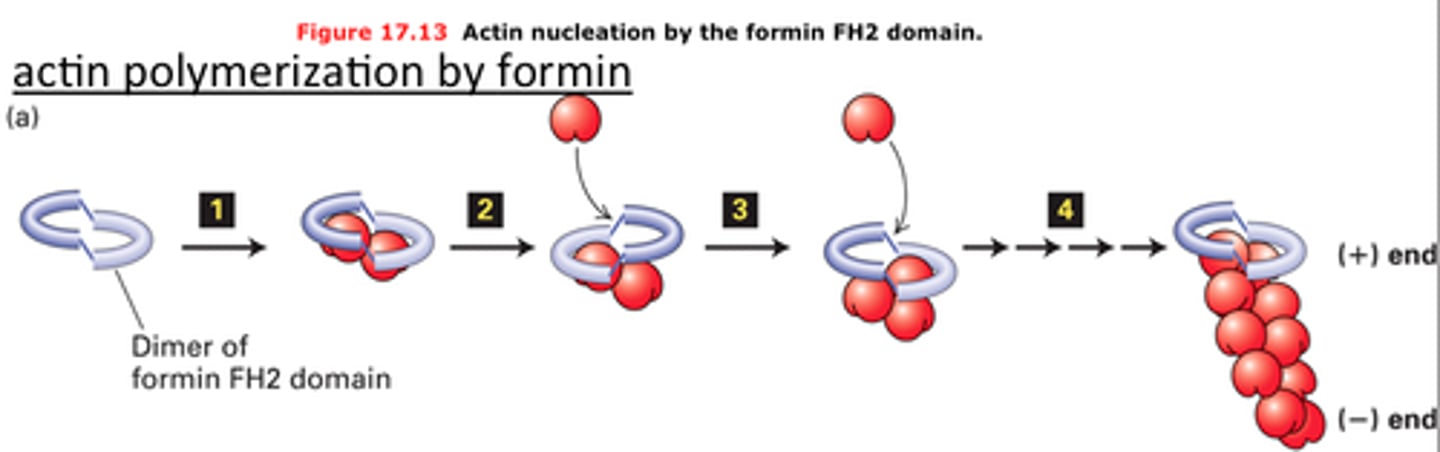
Formin
nucleates assembly and remains associated with the growing plus end
Cofilin (aka ADF)
Breaks F-actin into smaller segments by destabilizing the filament, allowing for small amount of force to break the filament.
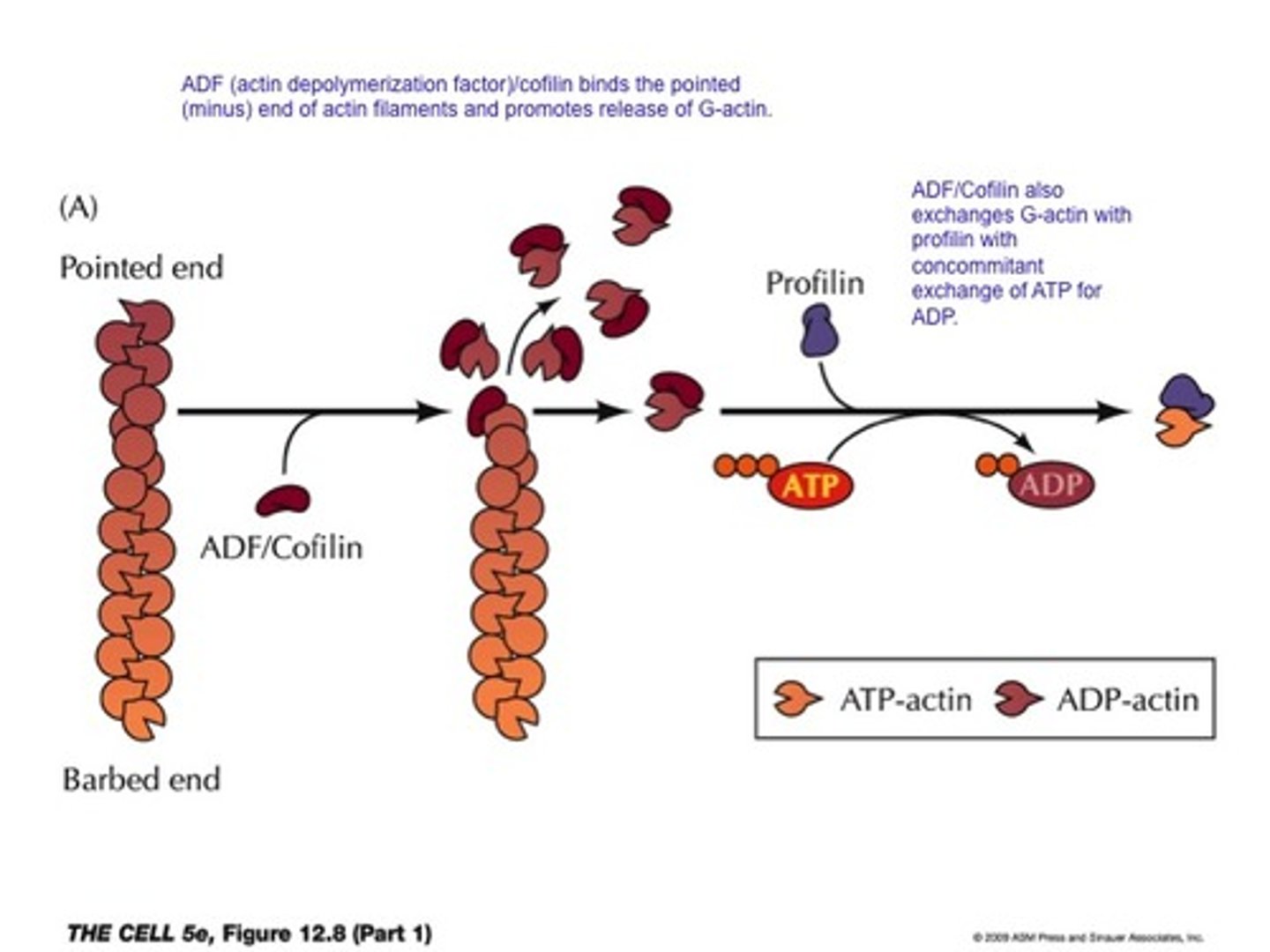
ADF
Actin Depolymerizing Factor abbreviation
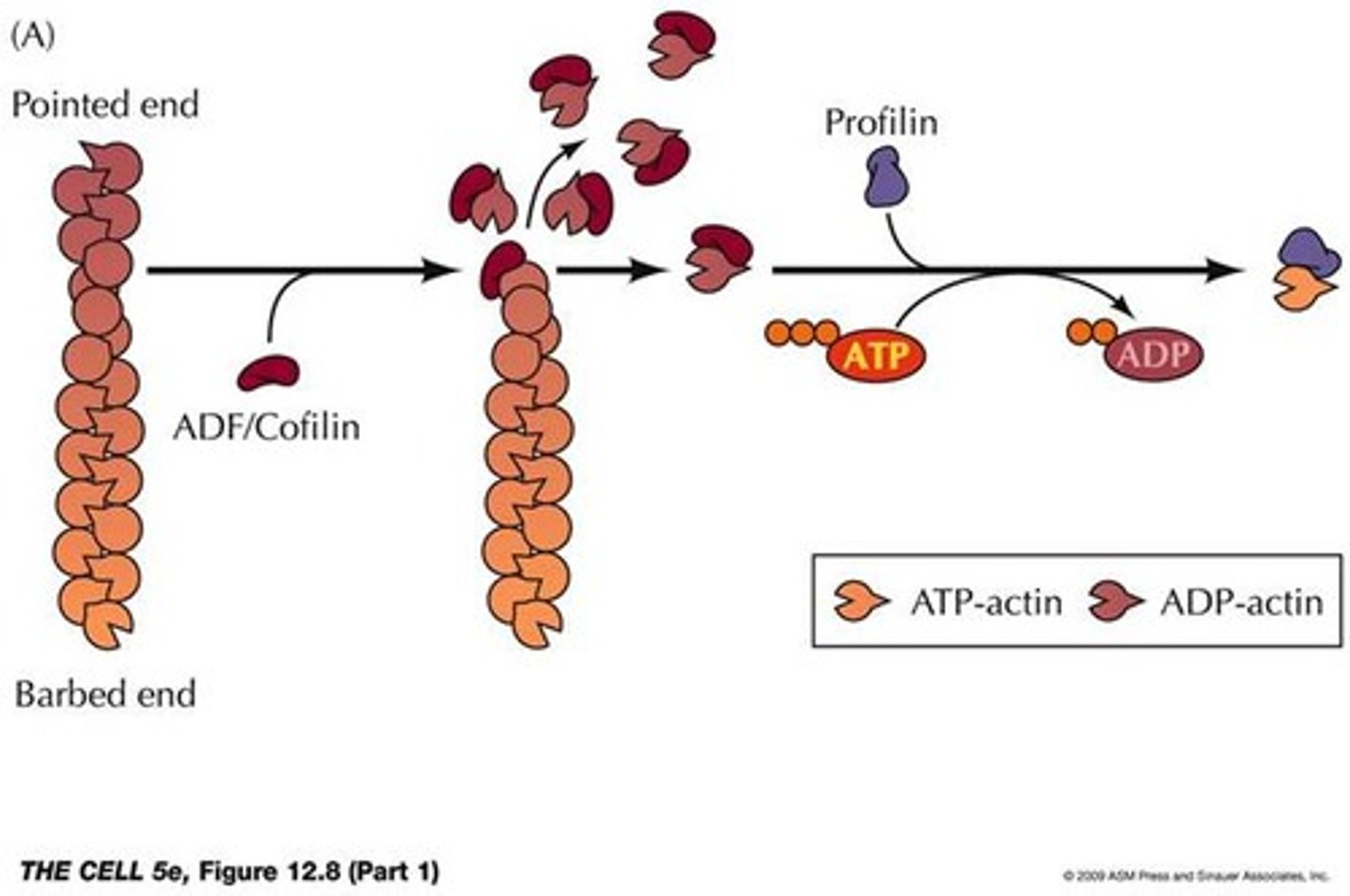
Arp 2/3 (ARP complex)
Actin related protein complex which binds to the sides of existing filaments and nucleates the formation of branched actin networks
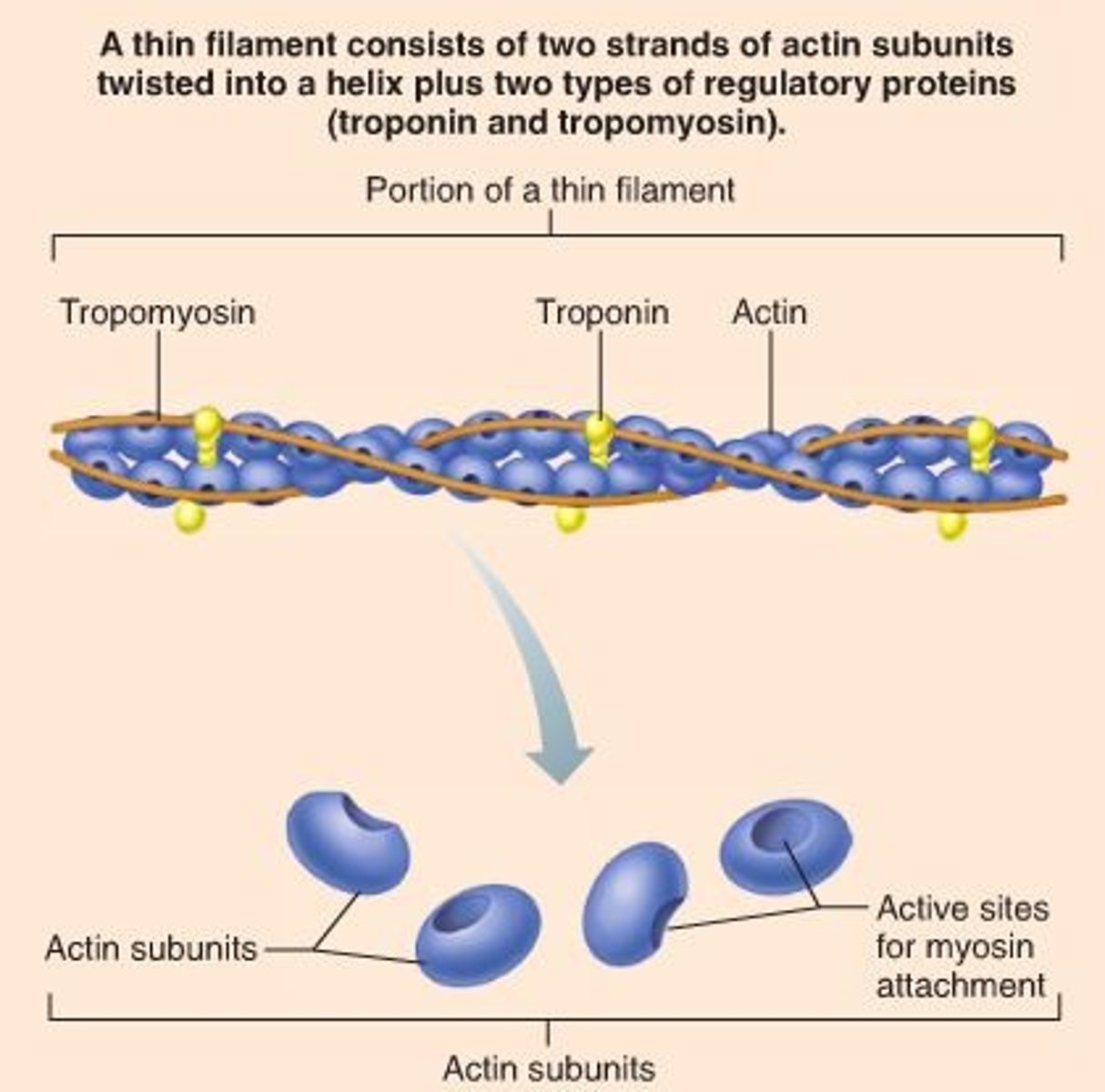
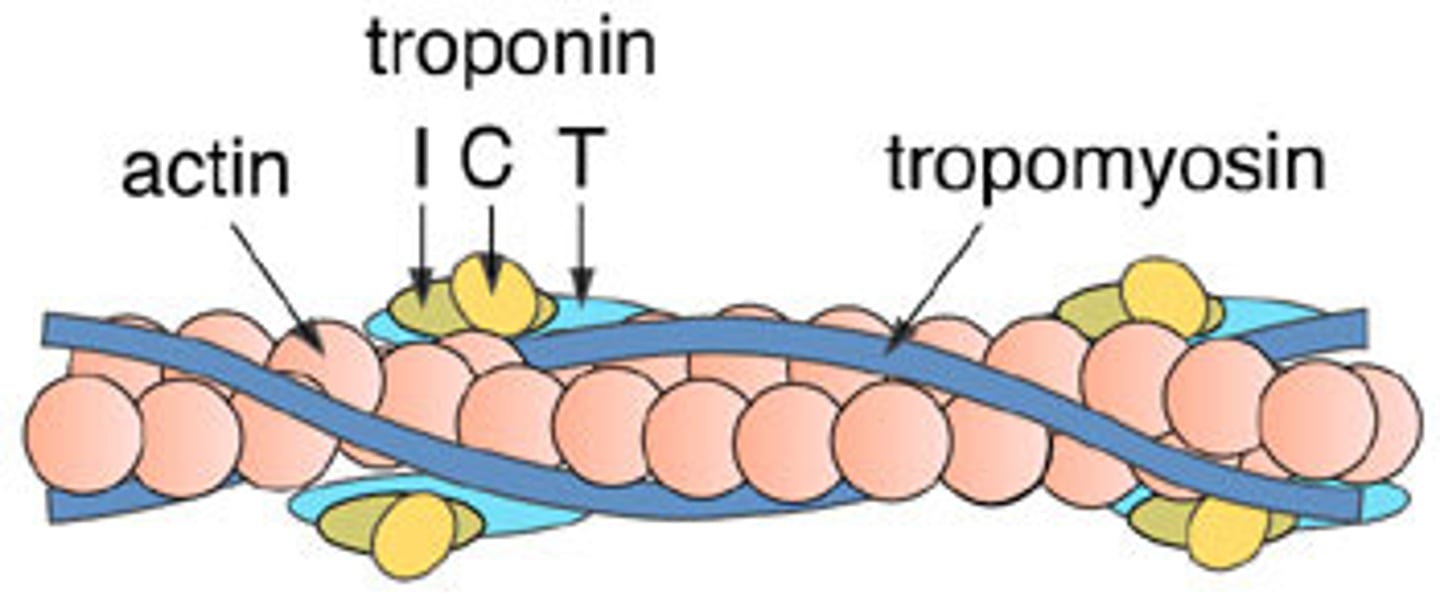
Tropomyosin
Protein that covers myosin binding sites on the actin molecules
crosslinked polymer
A polymer in which adjacent linear molecular chains are joined at various positions by covalent bonds.
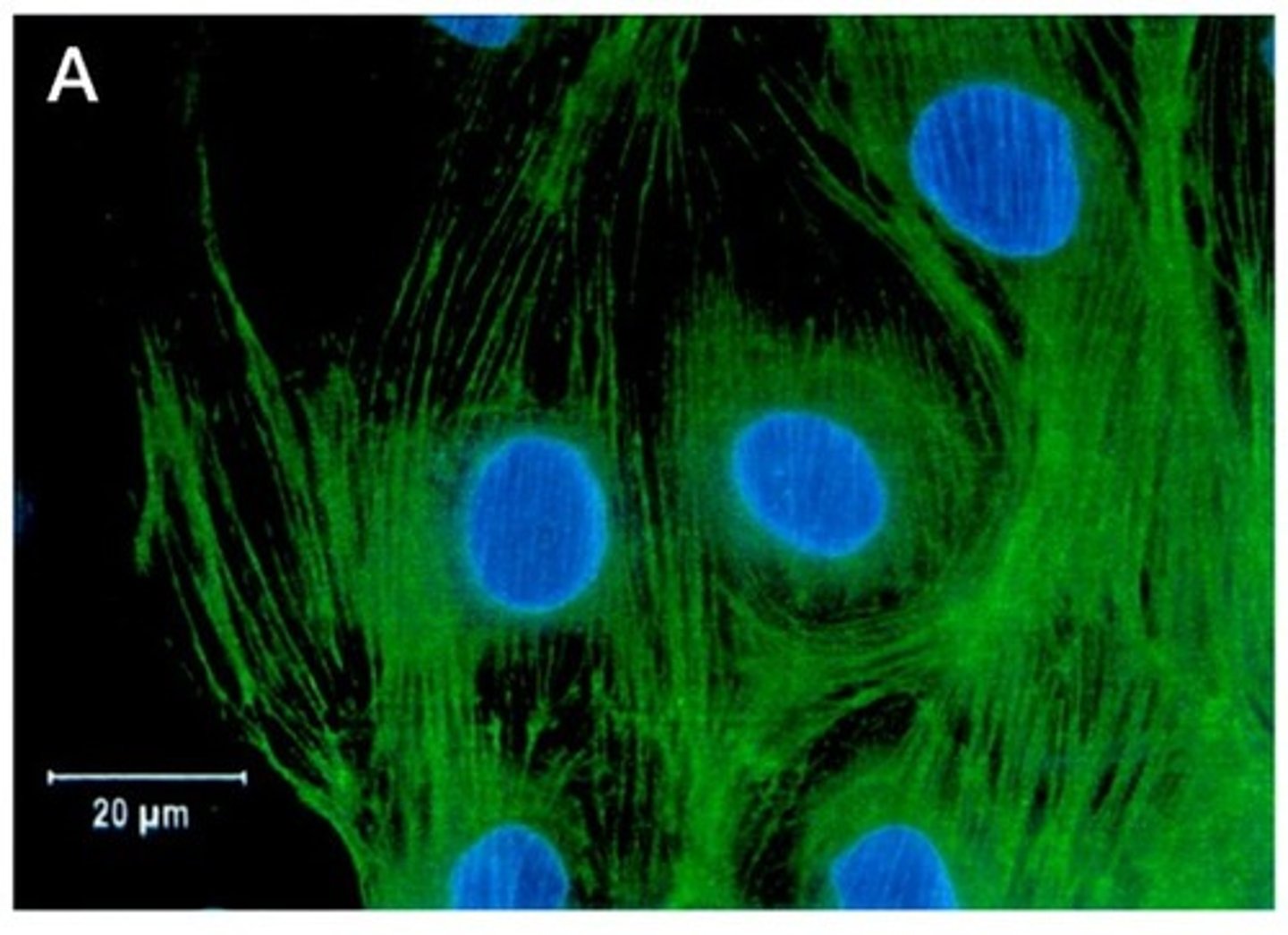
Phalloidin
Drug that binds and stabilizes actin filaments.
Used with a fluorescent dye to visualize actin filaments in a cell
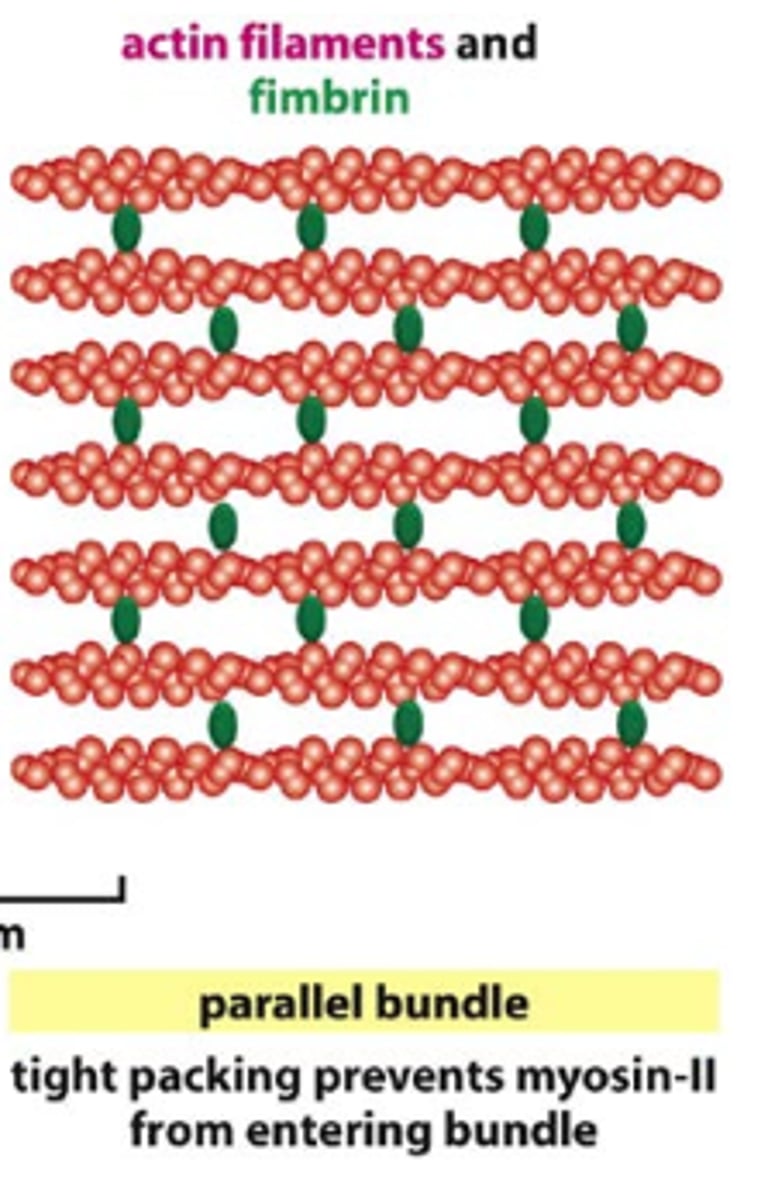
Fascin
Actin bundling protein that performs the same function that α actinin and fimbrin do

2 types of Actin bundles
parallel bundles and contractile bundles
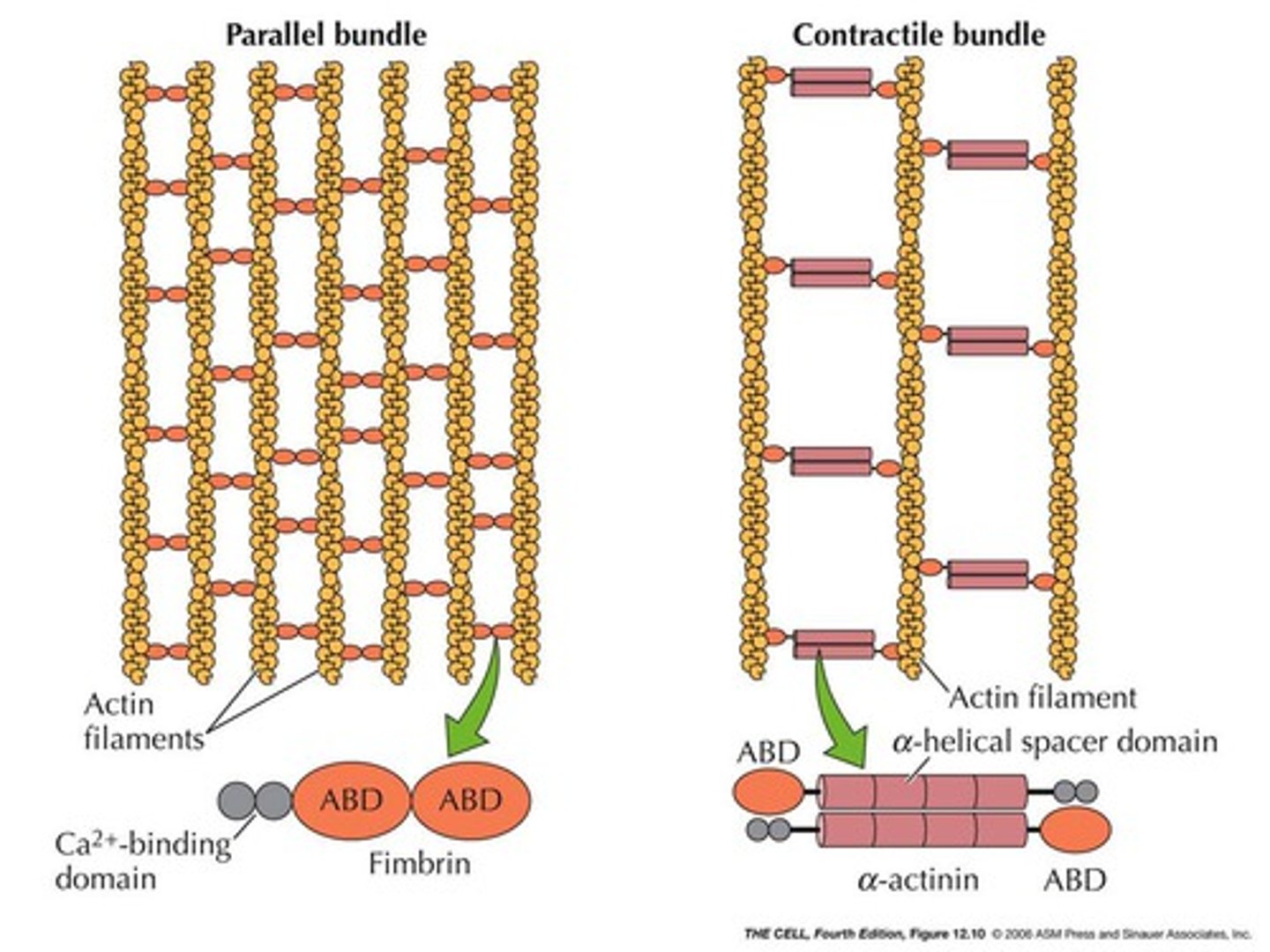
parallel bundles
structure that contains closely spaced F actin aligned in parallel
functions to support outward projections from within the plasma membrane
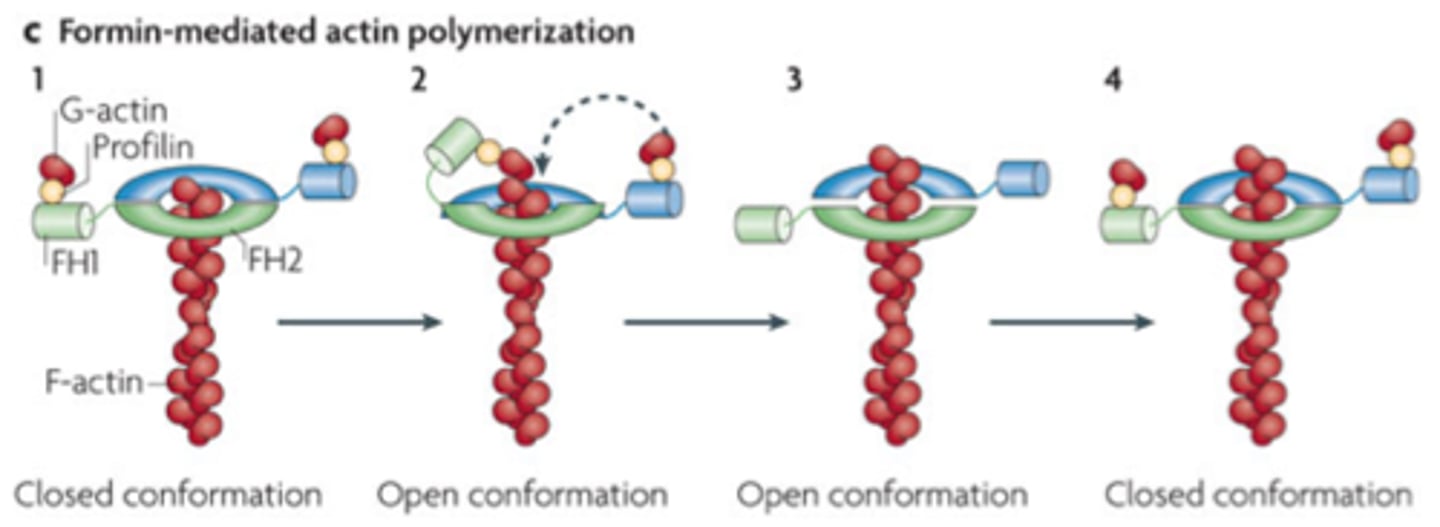
FH2
Abbreviation for Formin Homology (domain) 2
Domain on each peptide in the Formin dimer that is wrapped around the barbed (+) end of the actin filament and adds ATP-Actin bound to profilin to the growing end of the F actin
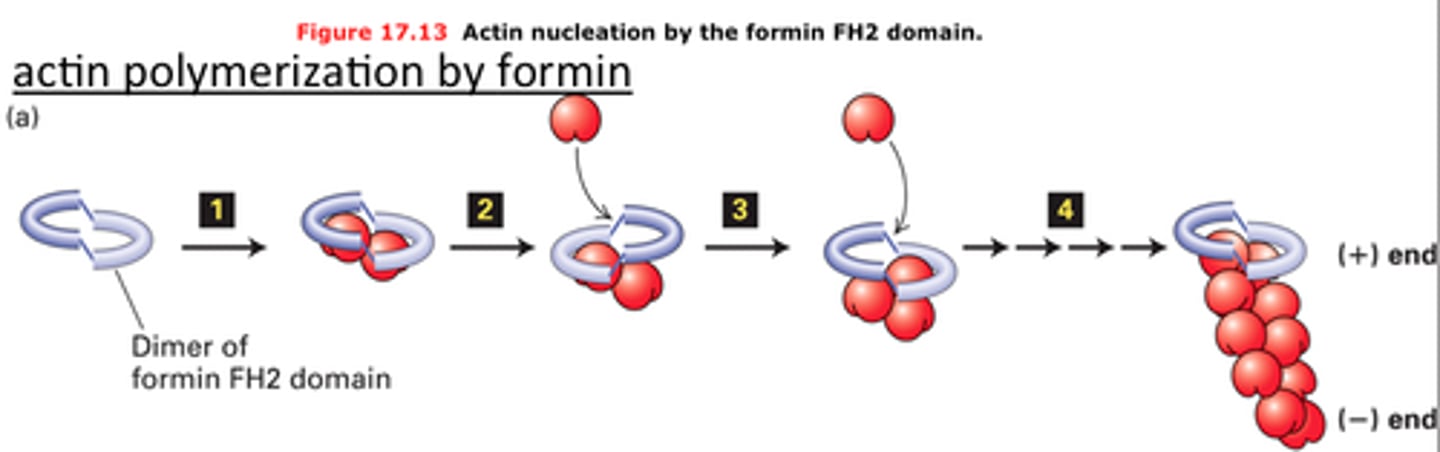
FH1
Abbreviation for Formin Homology (domain) 1
Acts as a lasso to bring in Profilin-bound ATP-Actin for polymerization
Ena/VASP
protein that promotes actin's barbed-end polymerizing and inhibits capping protein binding

Persistant severing
severing of one actin filament into two by ADF/Cofilin. Event happens at low concentrations of ADF/Cofilin. The new filaments can either begin to grow again or degrade to G-ADP-actin to be recycled into G-ATP-actin by profilin for reuse
High cofilin concentration
possible outcomes resulting from cofilin binding:
breakage
bundling and rod formation
growth from barbed ends
Low cofilin concentration
possible outcomes resulting from cofilin binding:
persistant severing
degradation of new filaments
growth from barbed ends of new filaments
Myosin induced disassembly
results when myosin stays contracted very tightly over an extended period of time
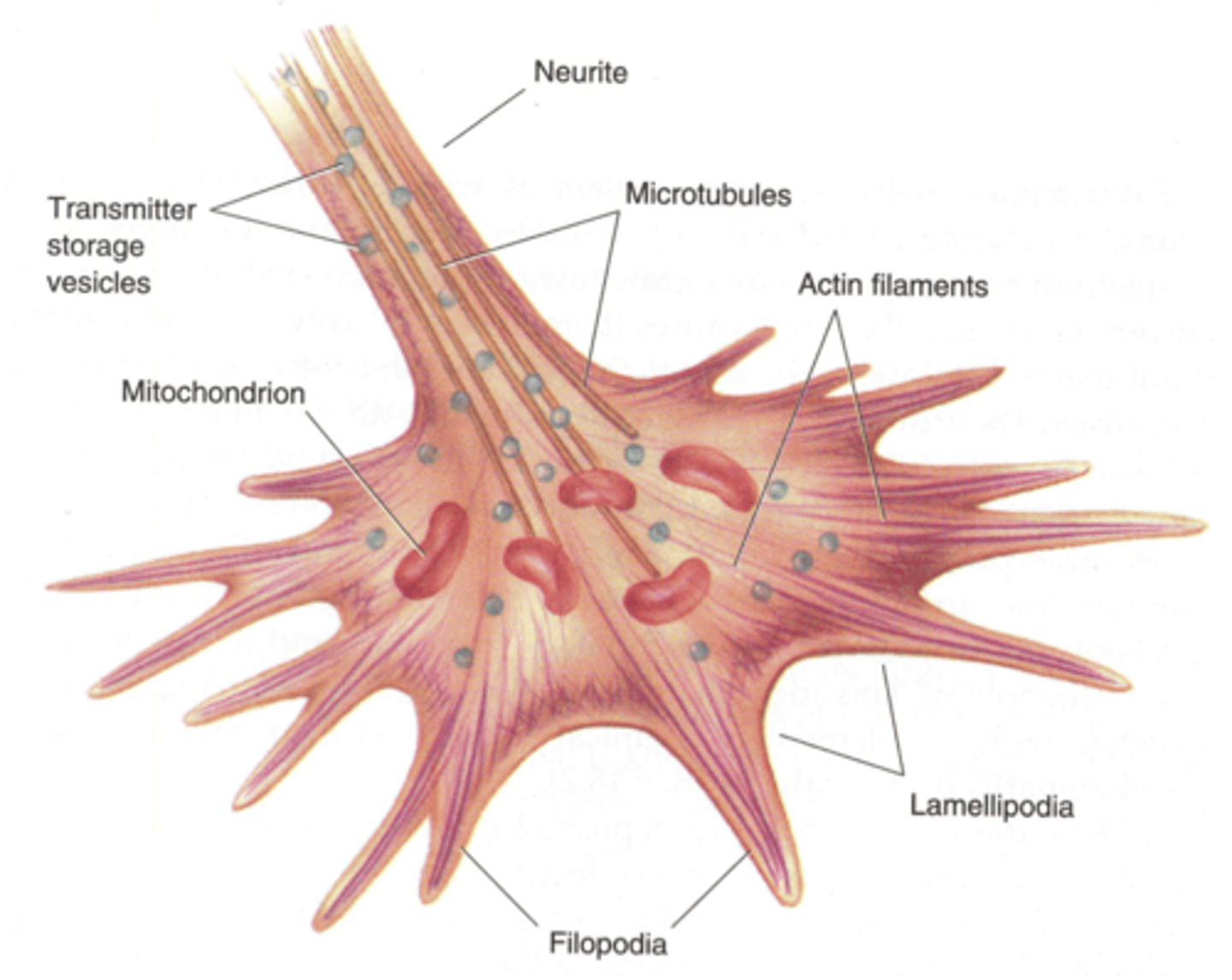
Lamellipodia
Projection on the leading edge of the cell that propels the cell across the substratum
Branched actin filaments, so nucleation is reliant on Arp 2/3 complexes mostly
Crosslinking of these filaments is done by alpha-actinin and filamin
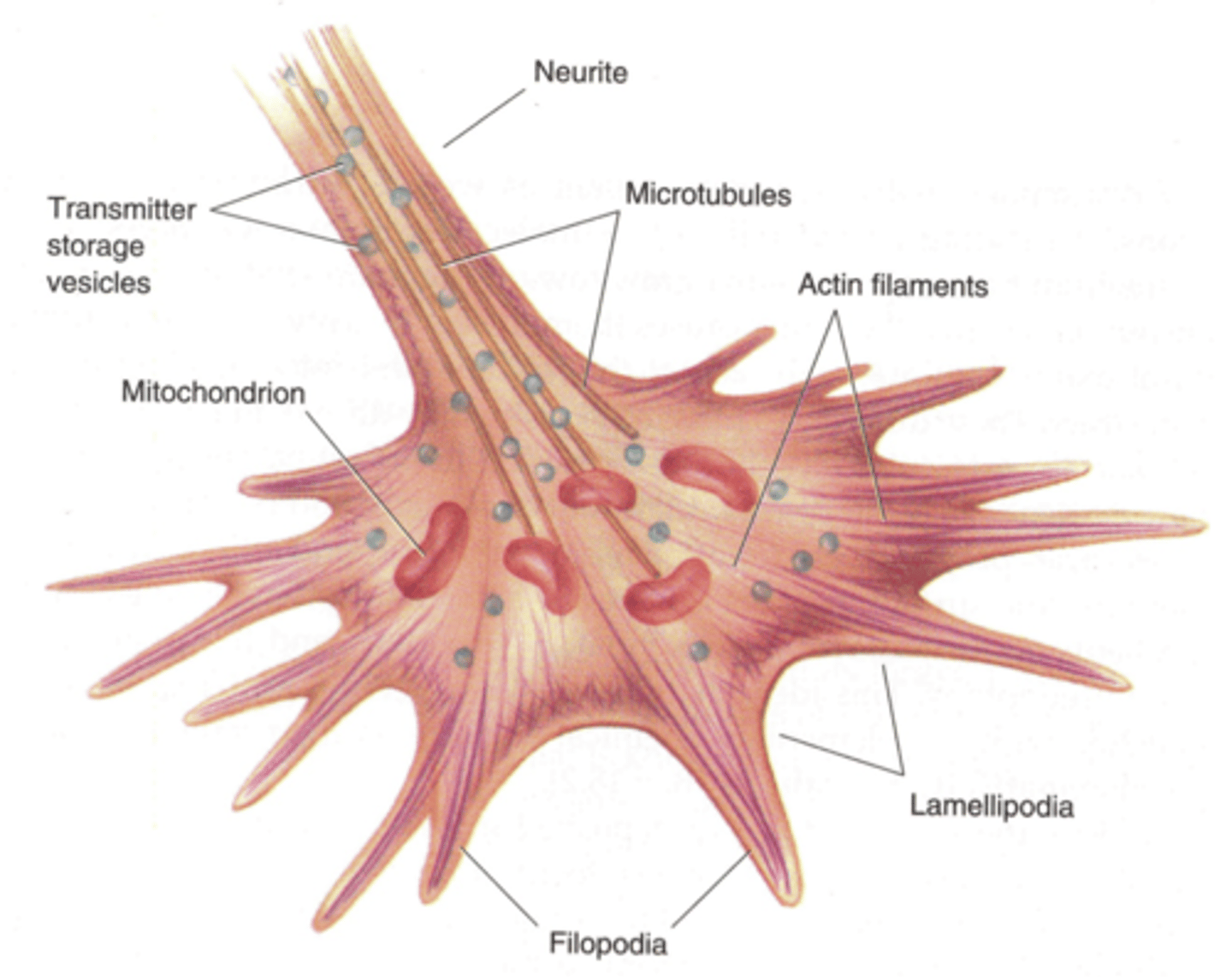
Filopodia
Projections extending beyond the leading edge of the cell thought to be involved in changes to cell direction
Unbranched actin filaments nucleating from formin mostly
Ena/Vasp proteins keep the actin bundles from being capped so they can grow indefinitely
Stress fibers and transverse arcs
Two types of contractile fibers
parallel to lamellipodia
Orientation of transverse arcs
perpendicular to lamellipodia
Orientation of stress fibers
stress fibers
Actin filaments concentrated into parallel bundles that function to pull the rear of the cell along during movement
Cell cortex
Reinforcing mesh of cytoskeletal elements under a plasma membrane
Contains both branched and unbranched actin filaments
Connected to the plasma membrane through ERM proteins
Invadopodia
Associated with metastatic tumor cells
Projection from the plasma membrane that allow the tumor cell to poke a hole and invade another cell
These are a way how cancer cells can metastasize into a host cell
Microtubules
Right handed helix made of tubulin protofilaments
Involved in organelle transport within a cell and cell division
Requirements for microfilament assembly
Calcium ion chelators
GTP
Tubulin
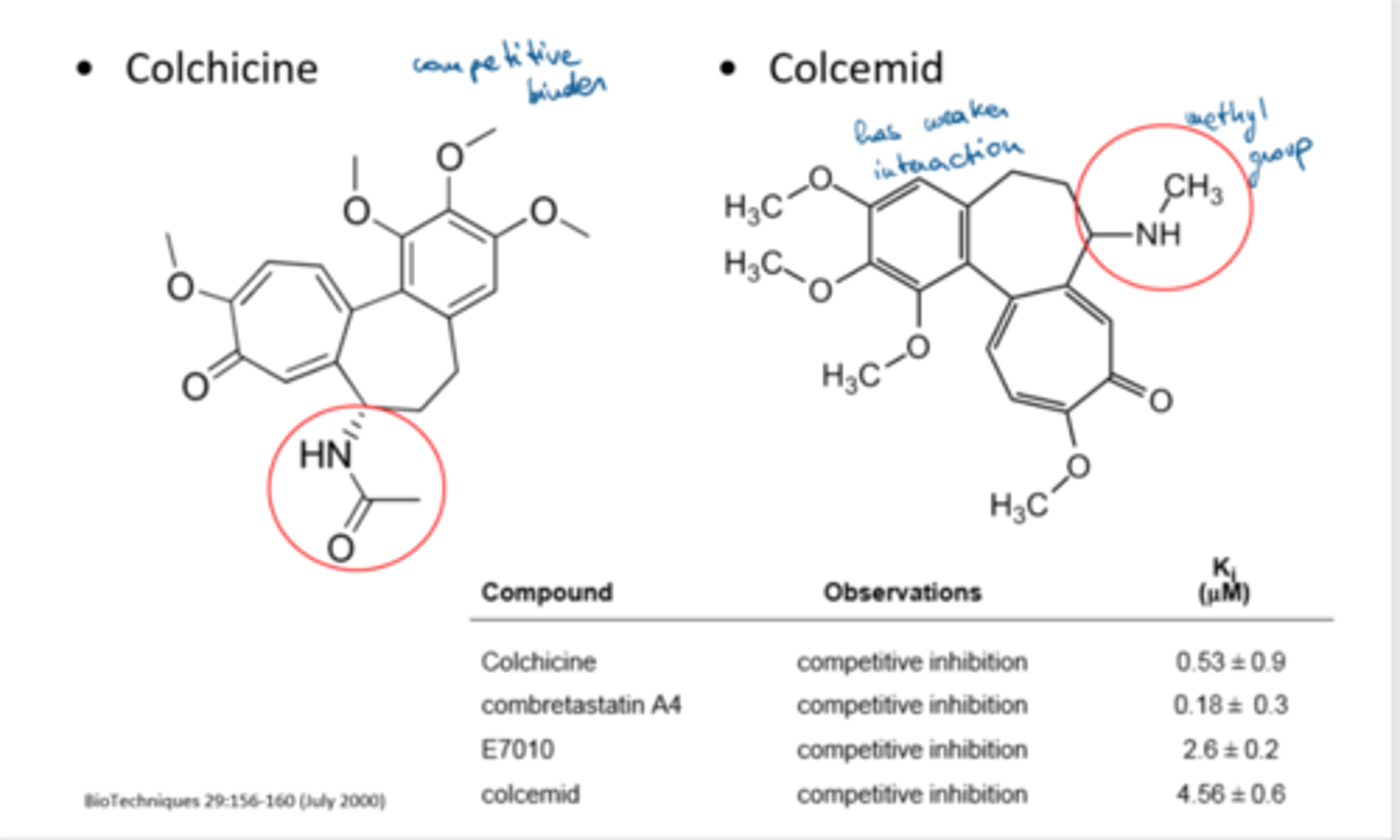
Colchicine
Depolymerizes tubulin microtubules by binding tubulin, inhibiting microtubule polymerization.

Colcemid
Depolymerizes tubulin microtubules by binding tubulin, inhibiting microtubule polymerization.
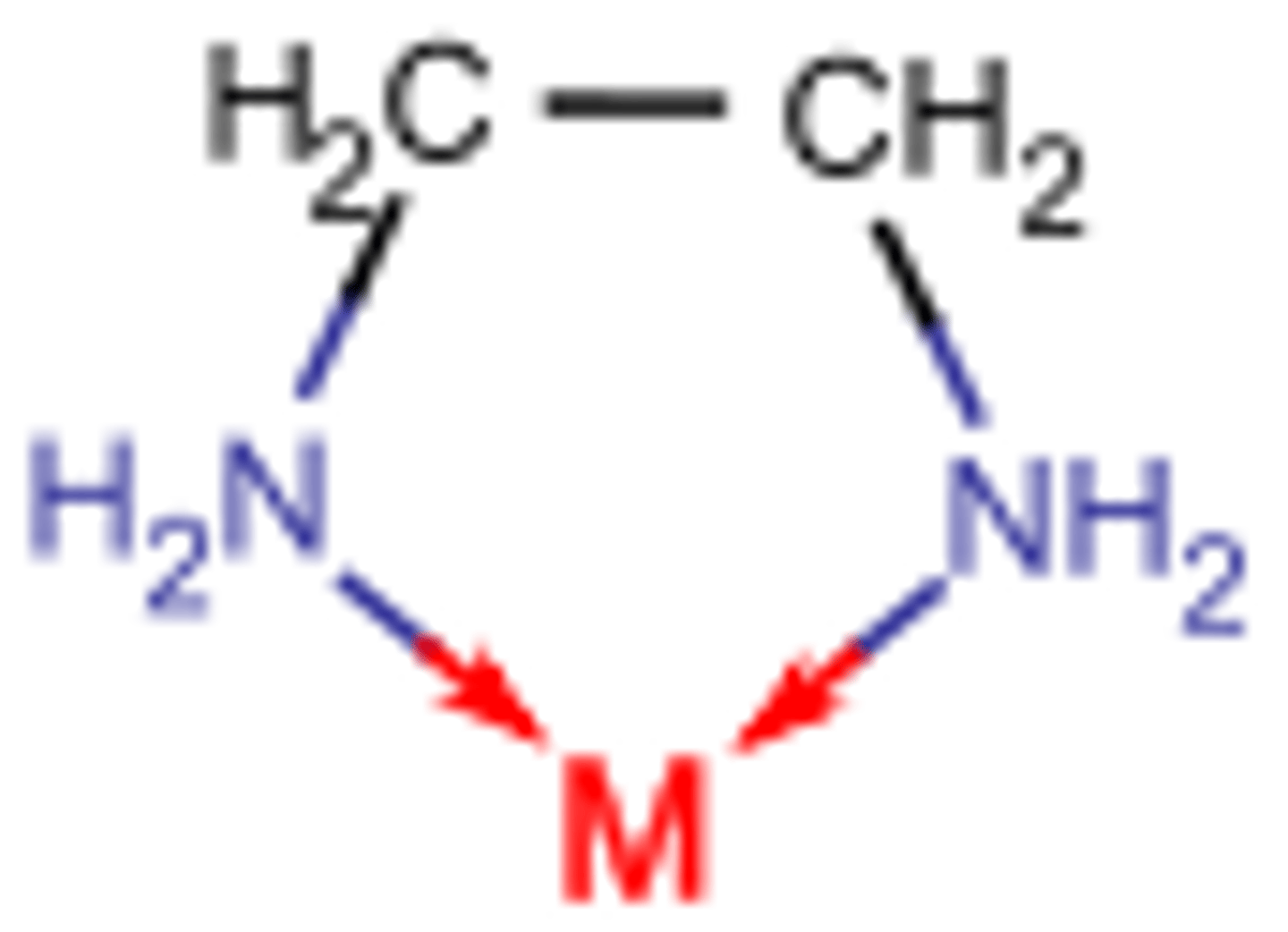
Chelator
Molecule that binds to a metal ion
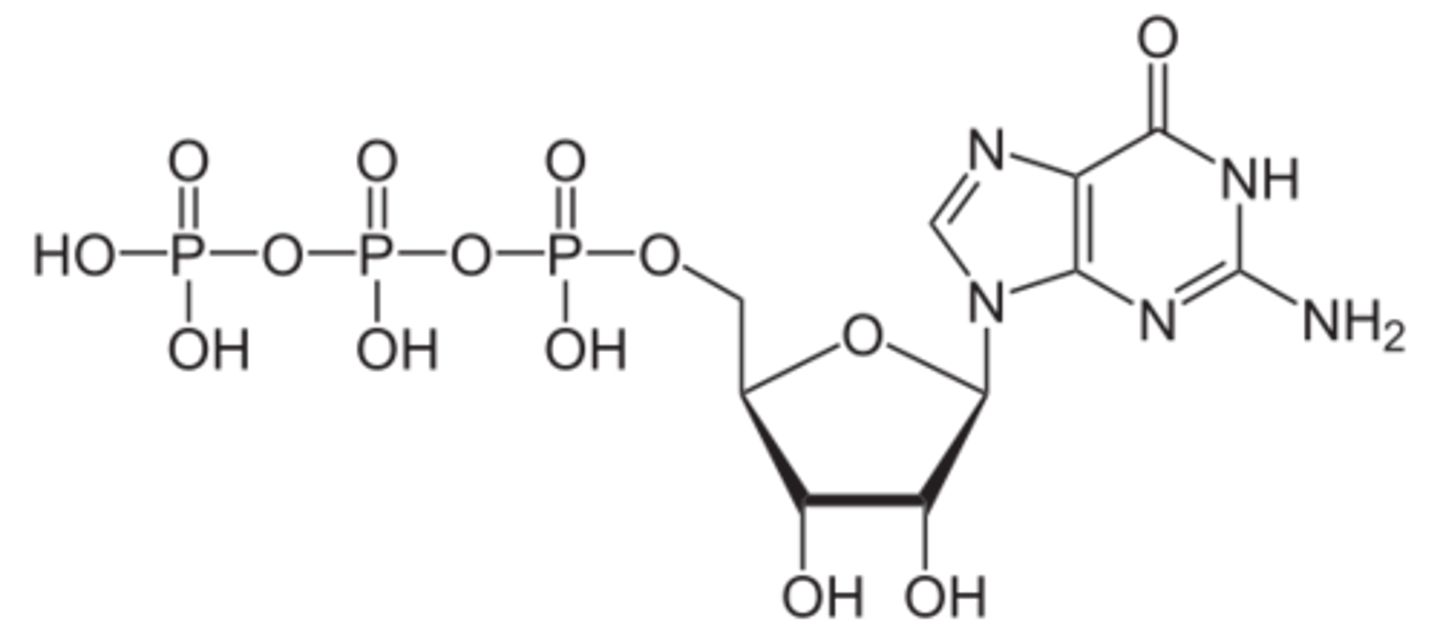
GTP
Energy source required for microtubule assembly
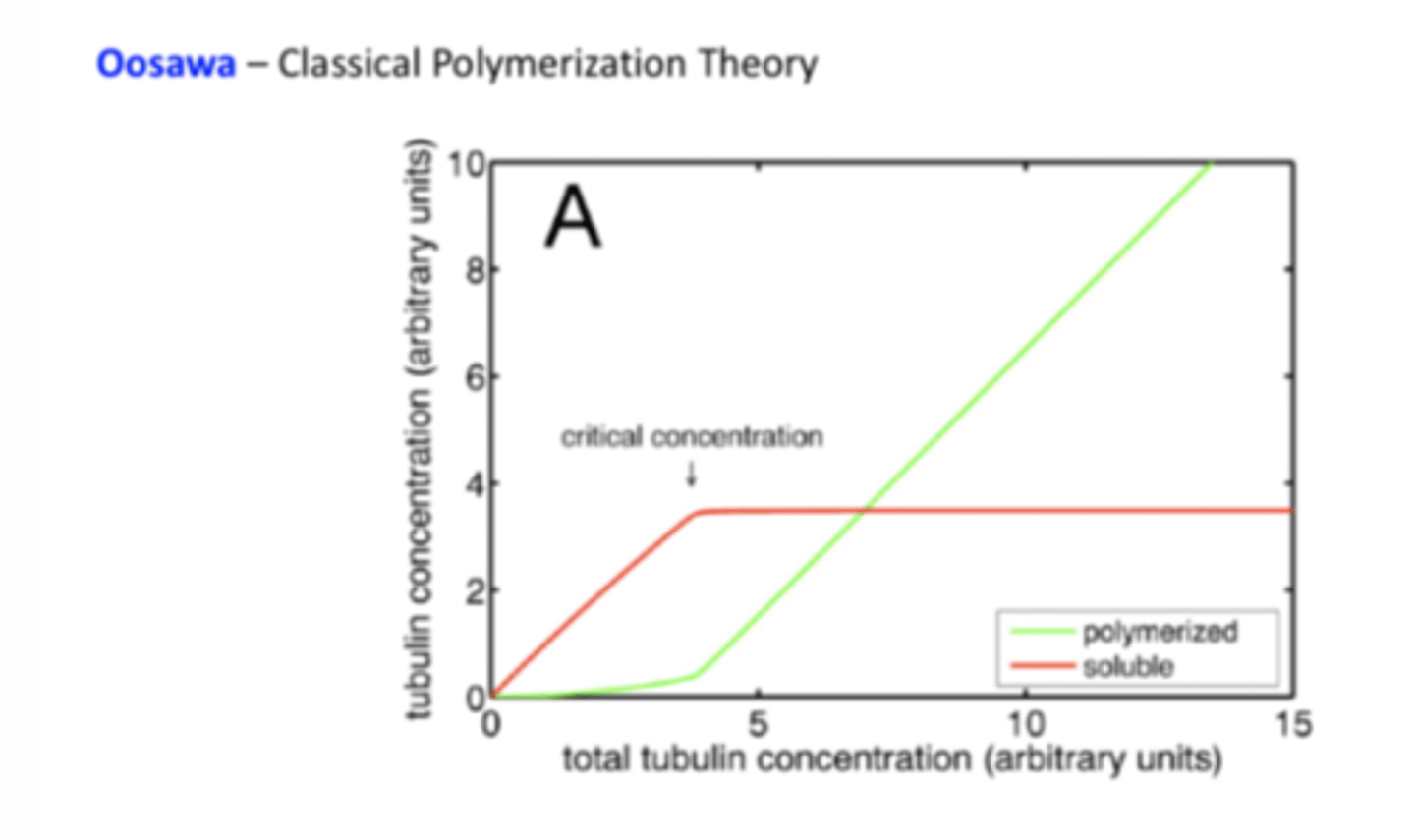
Classical polymerization theory
Proposes that soluble tubulin begins to polymerize when it reaches a critical concentration in the cell, with the concentration of soluble tubulin staying constant when this occurs
Yes
Does treadmilling occur in microtubules?
Dynamic
Microtubulues are _______, always growing or shrinking at one end
Alpha tubulin
Tubulin subunit that binds GTP and has its GTP-binding site covered up by the binding of the other tubulin subunit
GTP is never hydrolyzed and provides structural support to the molecule
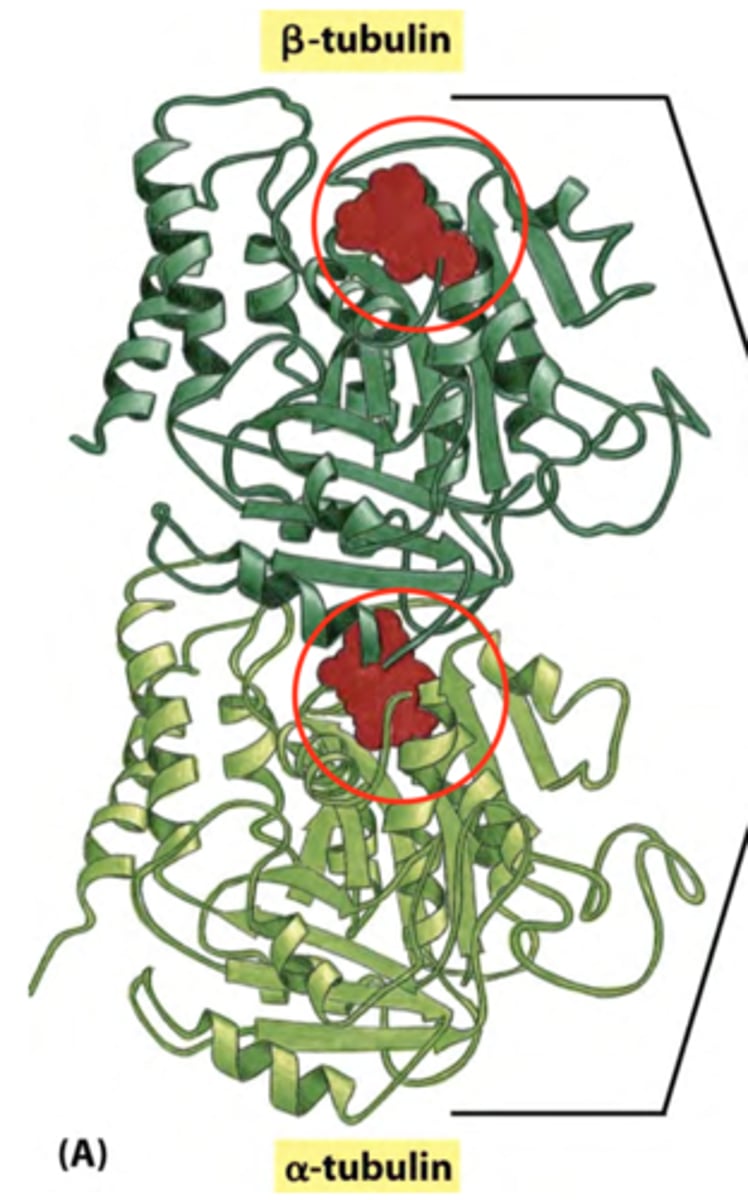
Beta tubulin
Tubulin subunit that binds GTP and has its GTP-binding site exposed to the surrounding environment
GTP can be hydrolyzed to GDP in this subunit
This subunit's bound guanine phosphate must be in the GTP state for tubulin polymerization to occur.
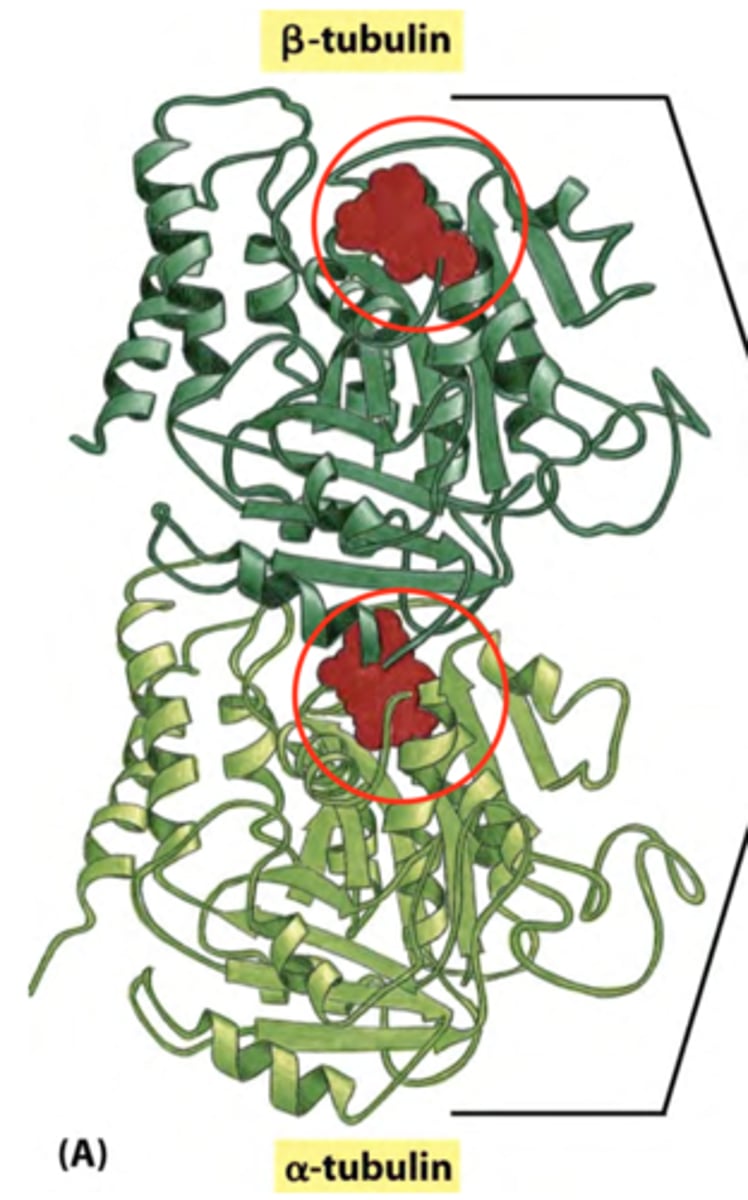
Dimerization of tubulin
First step of microfilament assembly
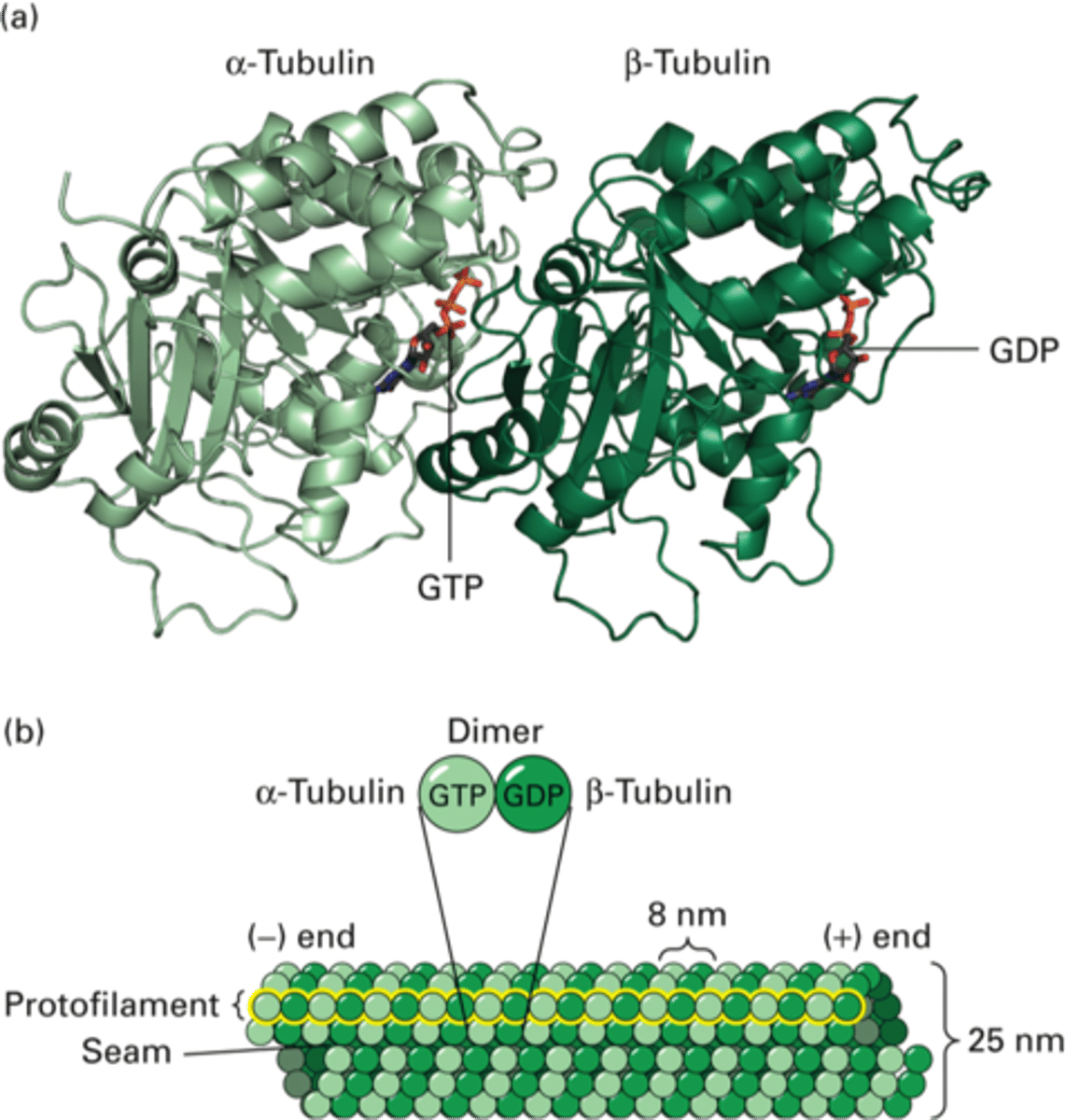
Oligomer
Short chain of monomers that is not long enough to be considered a polymer.
Heterodimer
The alpha and beta tubulin subunits dimerize to form tubulin that is a ___________
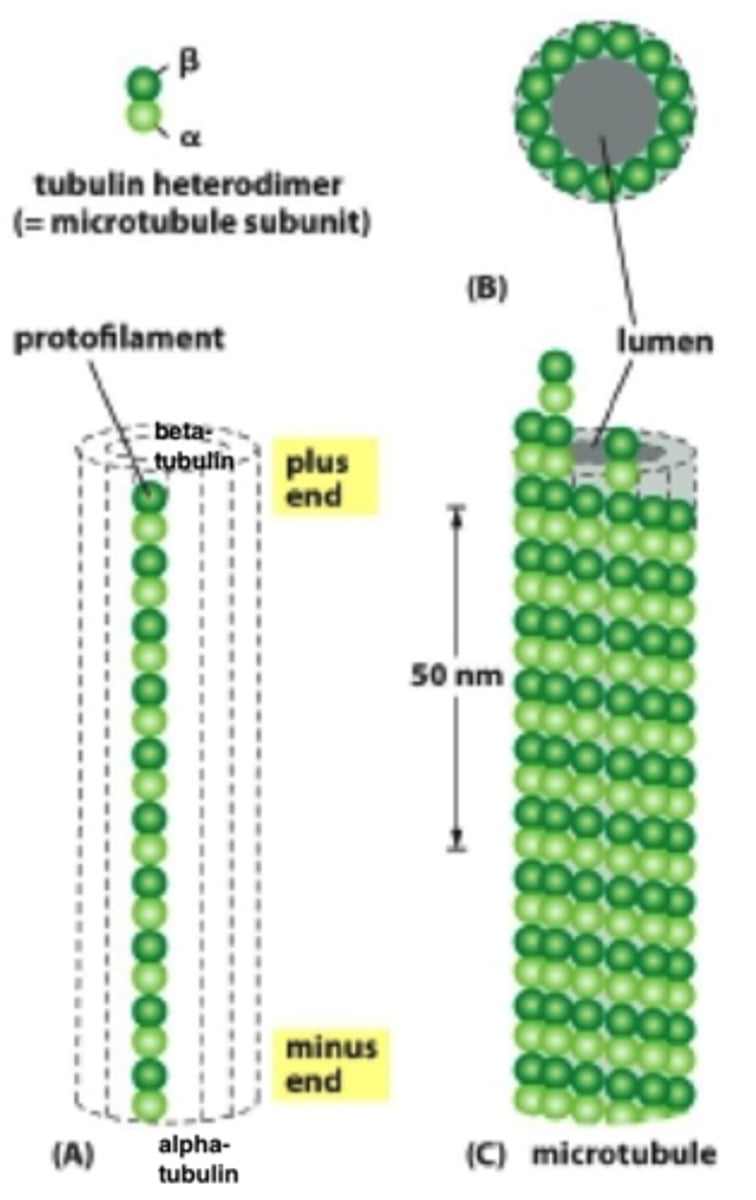
Protofilament
linear chain of tubulin subunits about 15-16 units long
GTP
What is the beta tubulin subunit bound to at the plus (+) end of the protofilament/microtubule?
GDP
What is the beta tubulin subunit bound to at the minus (-) end of the protofilament/microtubule?
13
How many protofilaments assemble laterally to form a microtubule?
Left handed
Handedness of the microfilament helix
Inter-PF contacts
Lateral contact sites between protofilaments in a microtubulule. Almost all of these contacts are homologous (beta-beta or alpha-alpha) except at the seam, where the contacts are heterogenous (alpha-beta)
Intra-PF contacts
Contact sites between tubulin subunits of a protofilament
PF
Abbreviation for protofilament
Seam
Only place where heterogenous inter-protofilament contact sites are
How colchicine and colcemid are used to treat cancer
Colchicine and colcemid bind tubulin, inhibiting microtubule polymerization, which in turn blocks mitosis
Disassembly
Which is faster, assembly or disassembly?
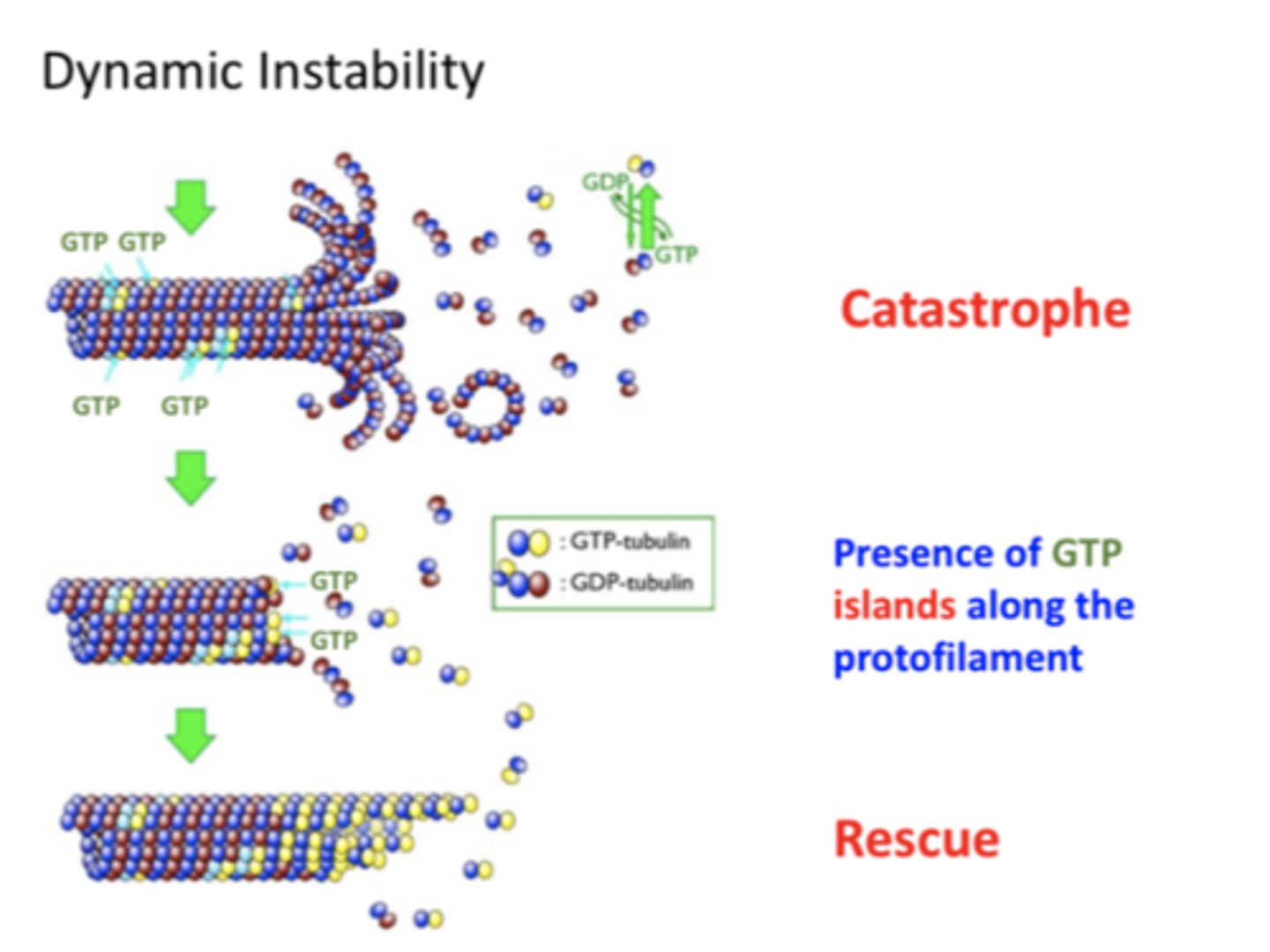
Dynamic instability
Co-existence of growing and shrinking microtubules in the same conditions
GTP hydrolysis on beta tubulin
A curved microtubule is a sign of a weak microtubule and is caused by what?
GTP cap
Band of GTP bound to beta tubulin at the plus end of a microtubule

Rescue
The transition from microtubule shrinkage to growth

CLASP
Proteins that mediate rescue

Catastrophe
Transition from growth to shrinkage
Occurs when rate of GTP hydrolysis is faster than the rate of GTP-tubulin assembly

GTP islands
Regions of GTP-bound beta tubulin on a protofilament that can spontaneously initiate rescue
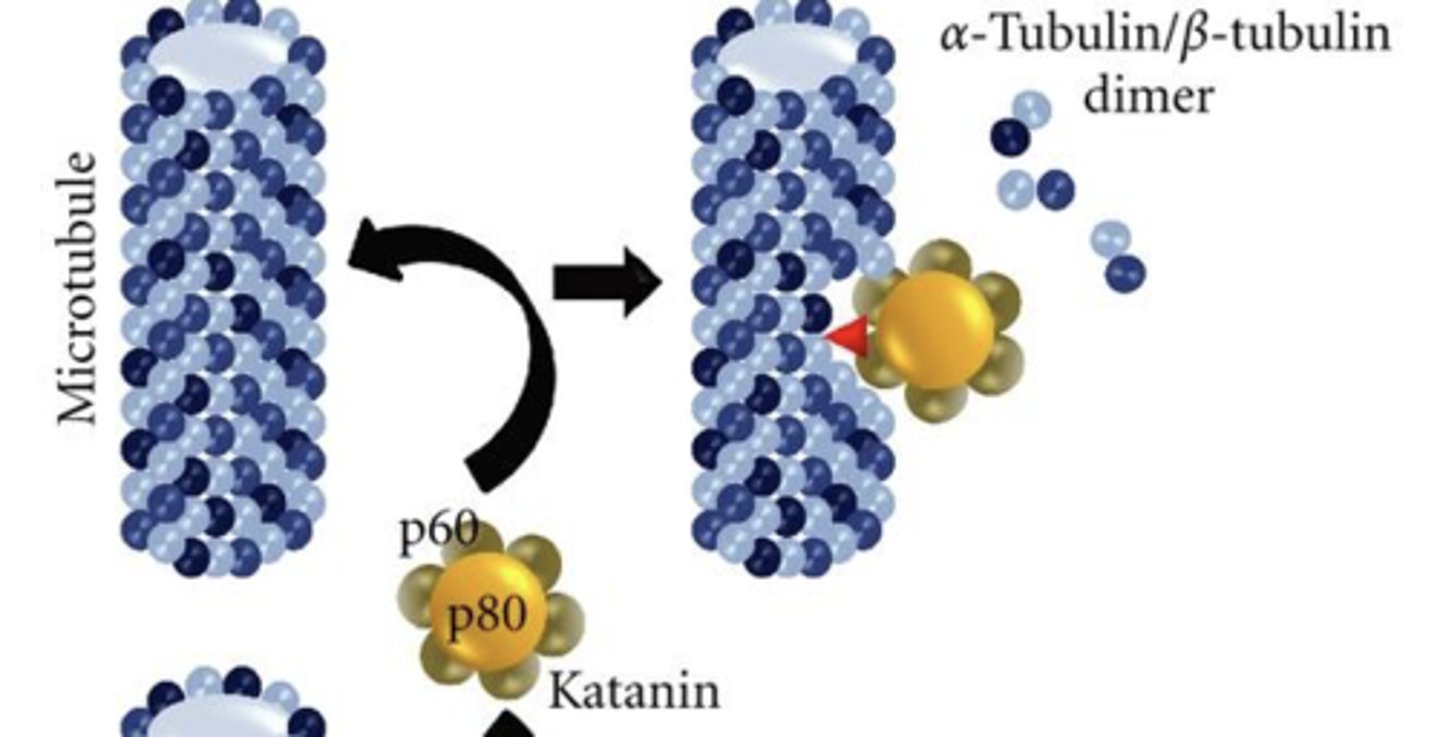
Spastin and fidgetin
Enzymes other than katanin that function to break the microtubule
Katanin
Severs microtubules like a katana severing a paper towel roll
suuh veeeer innnnggg
How to pronounce the word "servering" according to our prof

MTOC
Abbreviation for Microtubule Organizing Center

MTOC
Structure from which microtubules grow
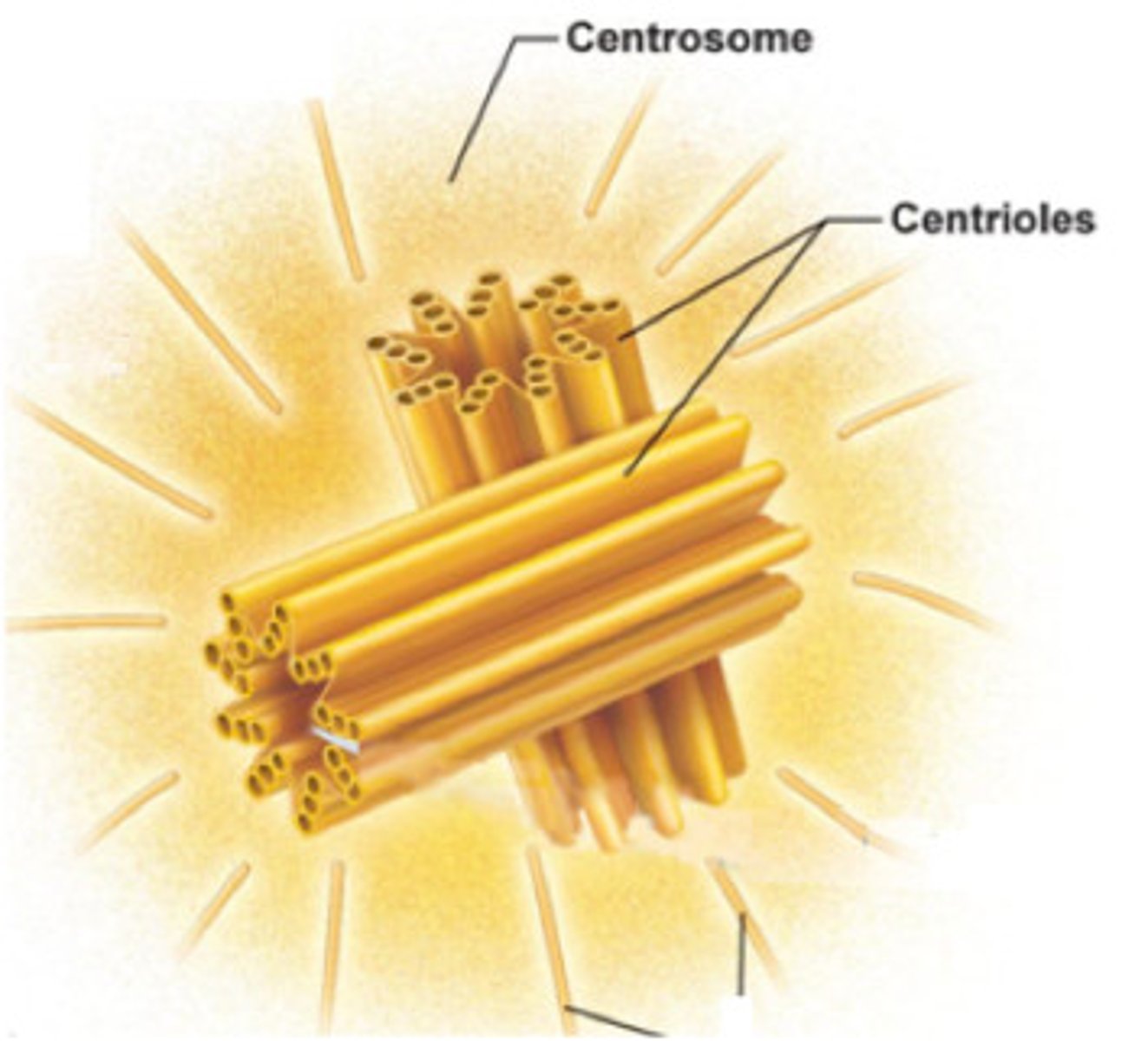
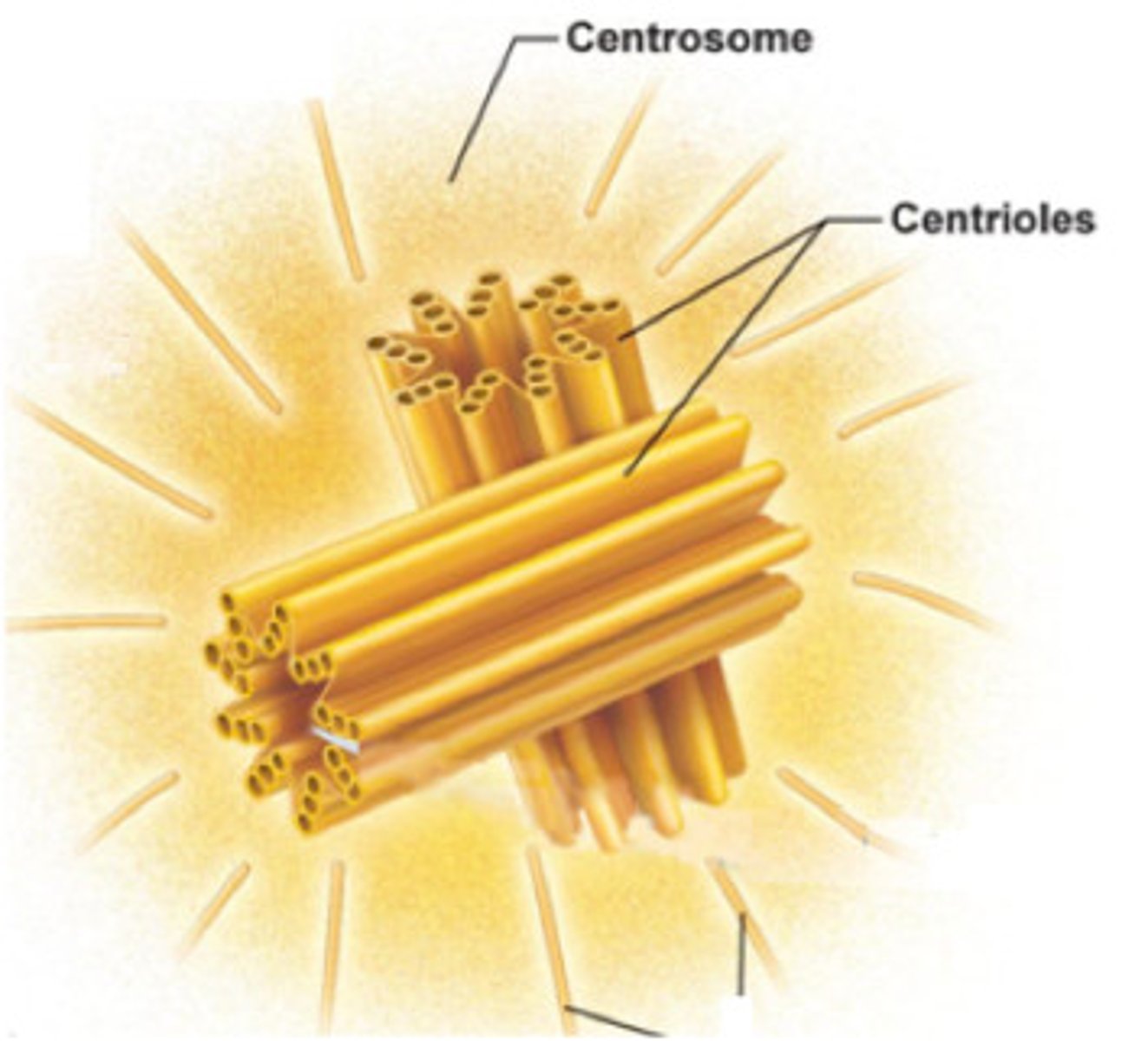
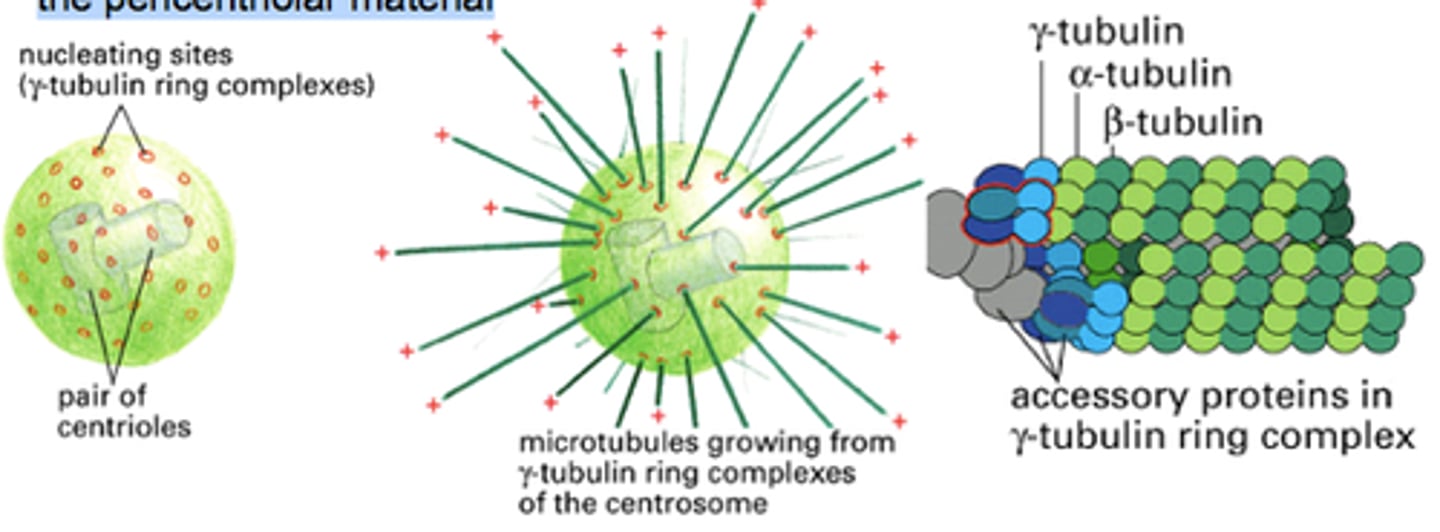
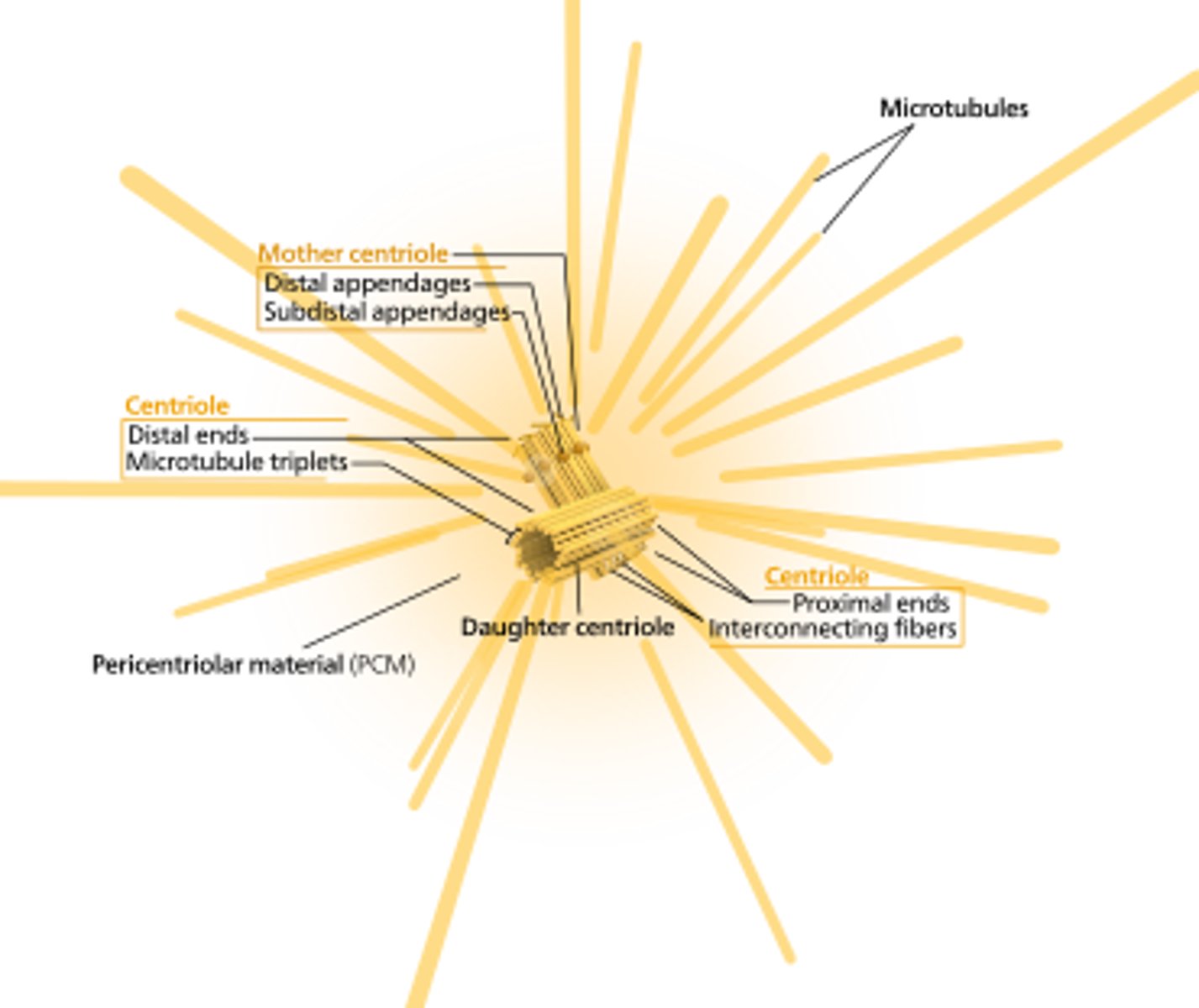
Centrosome
Made of two perpendicular centrioles and the pericentriolar material
Gamma tubulin
Type of tubulin that, along with associated proteins, forms a ring complex from which microtubules are nucleated within cells
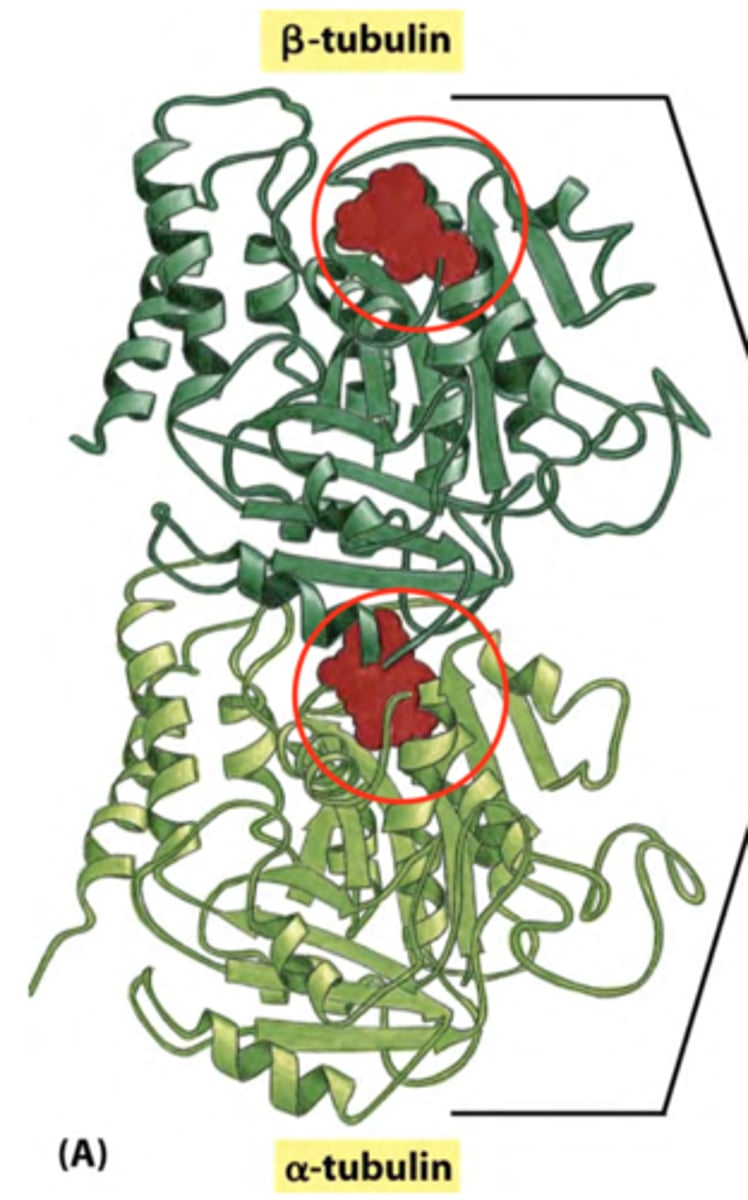
Alpha tubulin
Which subunit of the tubulin heterodimer attaches to gamma tubulin?
Juxtanuclear
means "next to the nucleus"

pericentriolar material
Surrounds the centrioles and contains hundreds of ring-shaped complexes composed of the protein gamma tubulin
The complexes involving gamma tubulin are the organizing centers for the growth of the mitotic spindle.
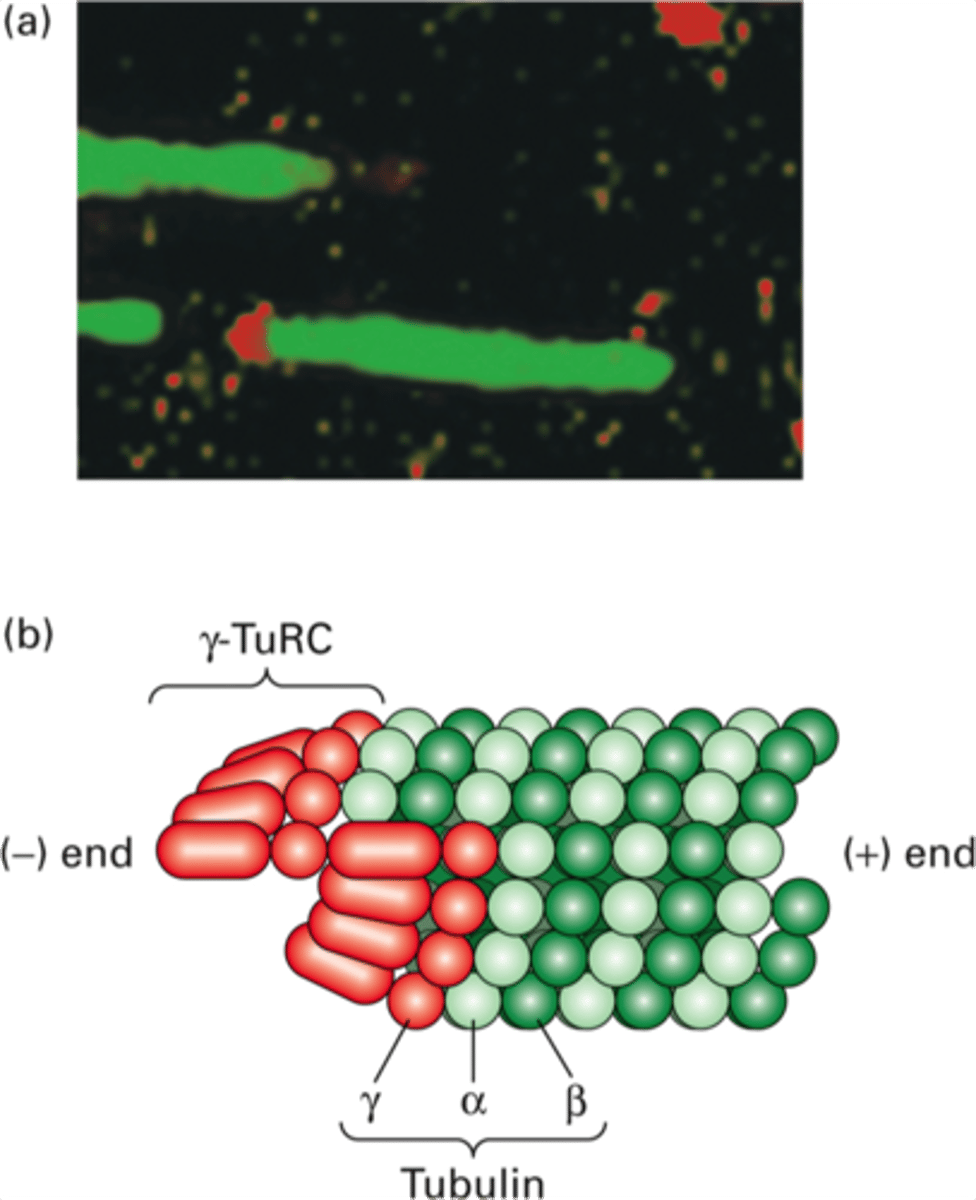
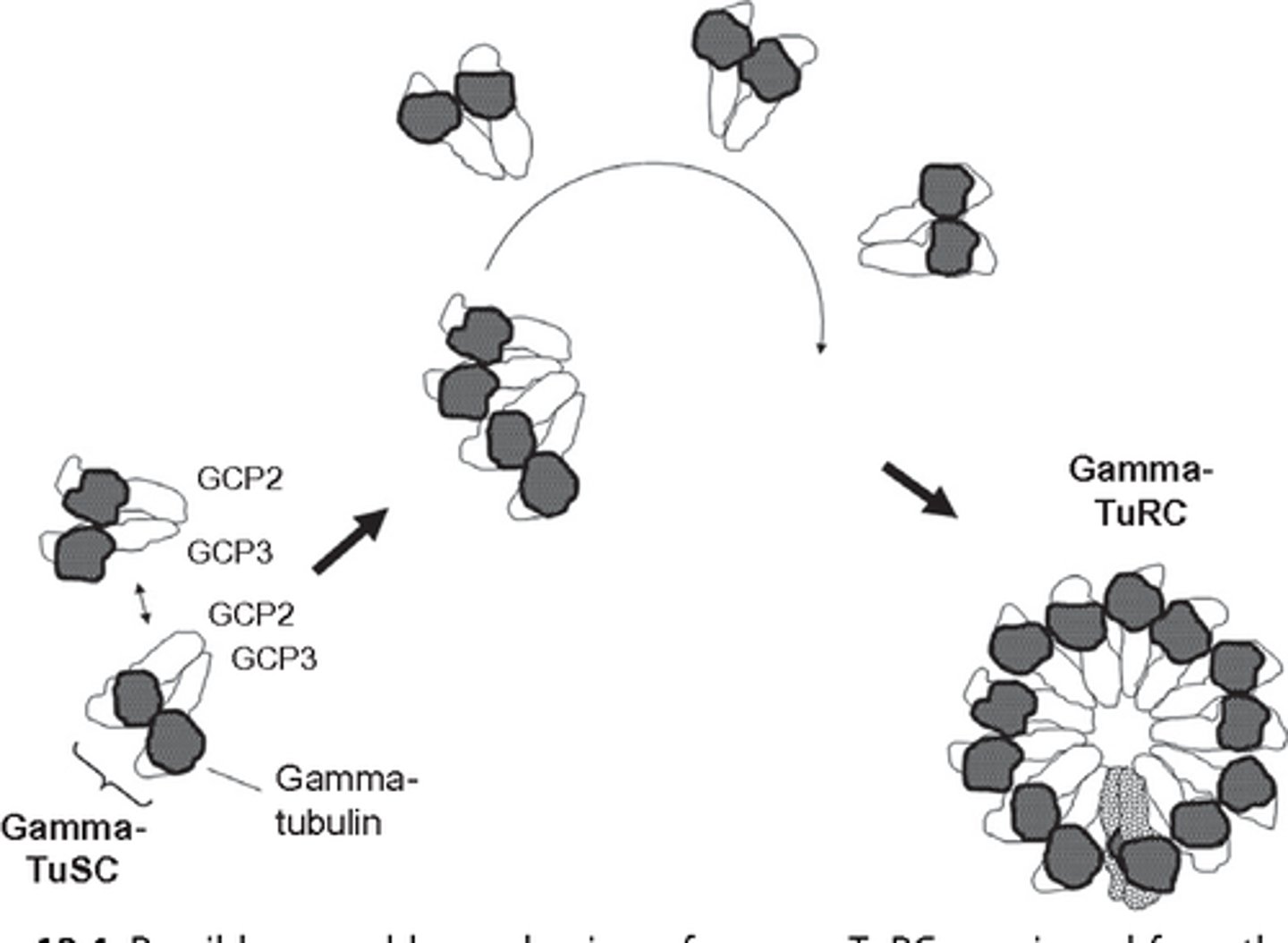
GCP2 and 3
Tubulin gamma complex proteins
Connect gamma tubulin and SPC110
Spc110
Spindle pole complex protein 110
subunit of the gamma tubulin small complex
gamma-TuSC
Gamma Tubulin Small Complex
gamma-TuRC
Gamma Tubulin Ring Complex
gamma-TuRC
Ring complex of gamma-TuSC proteins
Where microtubule nucleation begins
Located in the MTOC
gamma-TuSC
Protein complex where nucleation of a protofilament occurs
Located in the MTOC
Augmin
Complex that allows microtubules to branch at 40 degrees from existing microtubules
Is responsible for non-MTOC gamma-TuRC localization (so that nucleation can occur)
MAP
Abbreviation for Microtubule Associating Proteins
MAPs
Proteins that interact with the microtubules of the cellular cytoskeleton
Class 1 MAPs
MAPs that promote the assembly of microtubules, or prevent the dissociation of microtubules
e.g. Tau, MAP1, MAP2, MAP4
Class 2 MAPs
MAPs that destabilize microtubules
e.g. MCAK, EB1, Kinesin 8/13
Type 1 and type 2
two types of class 1 MAPs
Type 1 MAP
Prevent microtubule dissociation by binding class 2 MAPS like EB1/3 and thus reduce the effective concentration of EB1/3 available to bind to microtubules enhancing microtubule polymerization
Do not actually bind to the microtubule itself
e.g. MAP1a and MAP1b
Type 2 MAP
MAPs that bind to the microtubule itself, providing stability, promoting rescue, or preventing depolymerization
e.g. MAP2 and MAP4
Tau protein
MAP that normally functions to hold protofilaments together when it is dephosphorylated
Hyperphosphorylation
Reaction that leads to dissociation of tau from the microtubule and development of paired-helical filaments
Tau hypothesis
Hypothesis that states that excessive or abnormal phosphorylation of tau results in the transformation of normal adult tau into PHF-tau and NFTs
PHF-tau
Abbreviation for Paired Helical Filaments of Tau
NFT
Abbreviation for Neurofibrillary Tangles
+TIPS
Abbreviation for + end Tracking Proteins
+TIPS
Proteins that follow the + end of a microtubule wherever it goes, proteins of all function do this
Hitchhiking
Attaching to a motor protein to get to the + end of a microtubule
cross-linking proteins
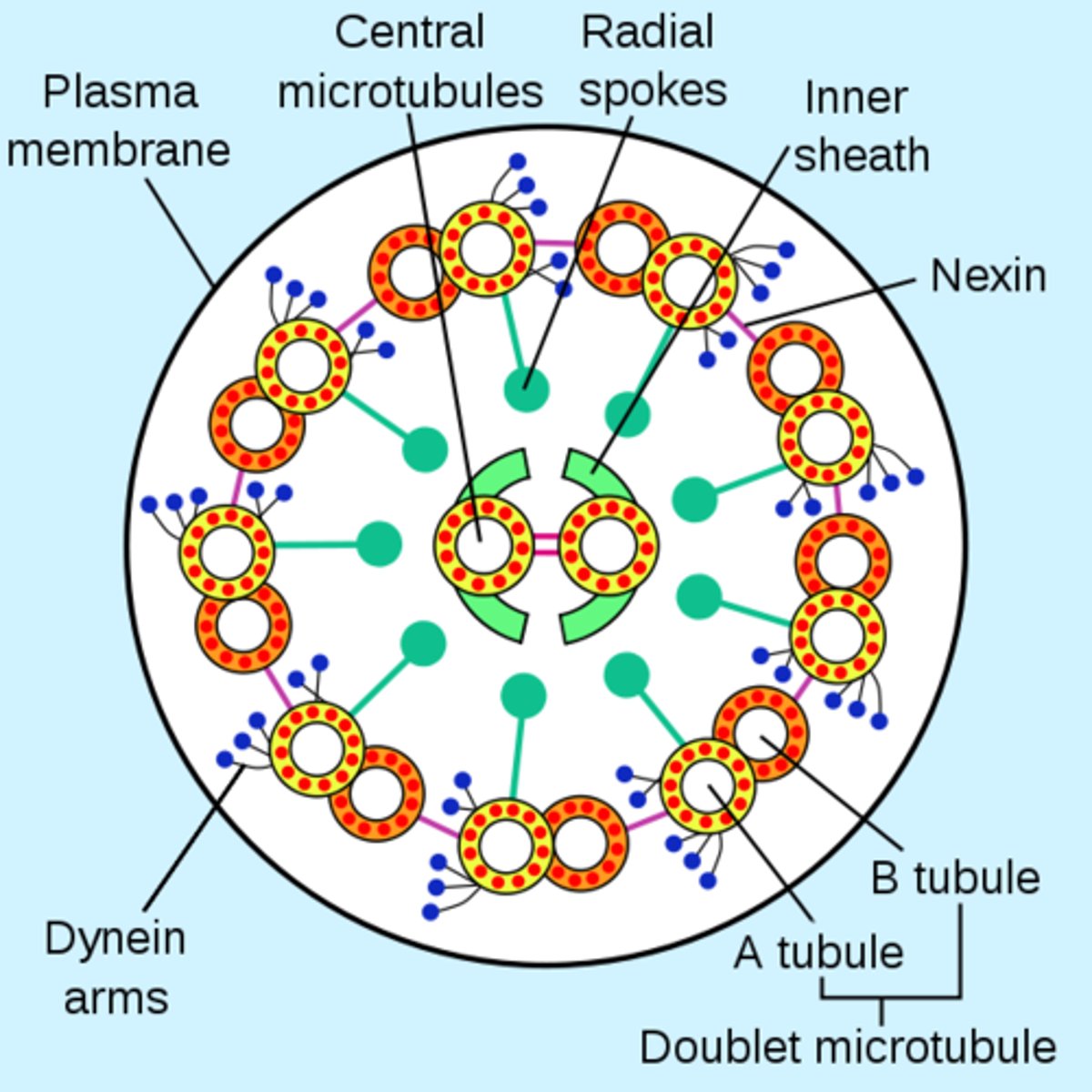
What in a cilium/flagellum causes the microtubules to bend, not just slide?
Axoneme
core of cilia that is the structural basis for ciliary movement