Chemistry Exam 1; Hydrocarbons-Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Aromatics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Alkene's have ______ bonds.
double
Alkene's end in ______.
-ene
Alkenes are a _______ hydrocarbon.
unsaturated
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Chains of hydrogen and carbon without all single bonds.
Alkene formula
CnH(2n-2)
Physical Properties of Alkenes
1. Insoluble in water
2. Soluble in nonpolar solvents
3. Lower density than water
4. Lower melting point than Alkanes
The two common alkenes;
Propylene(propene) and Ethylene(ethene)
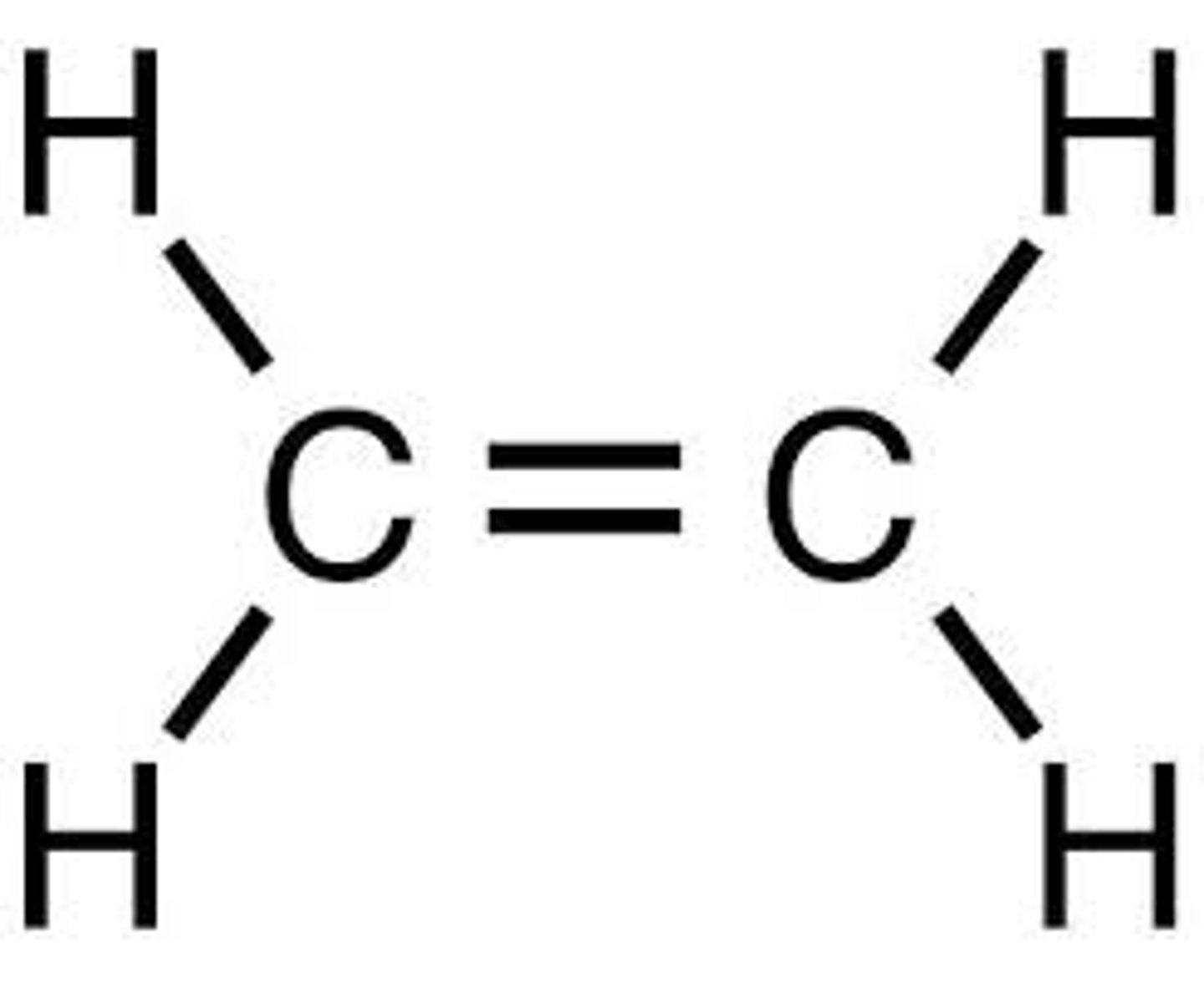
Ethylene (ethene)
C2H4, Ch2=Ch2.
Ripens fruit faster.
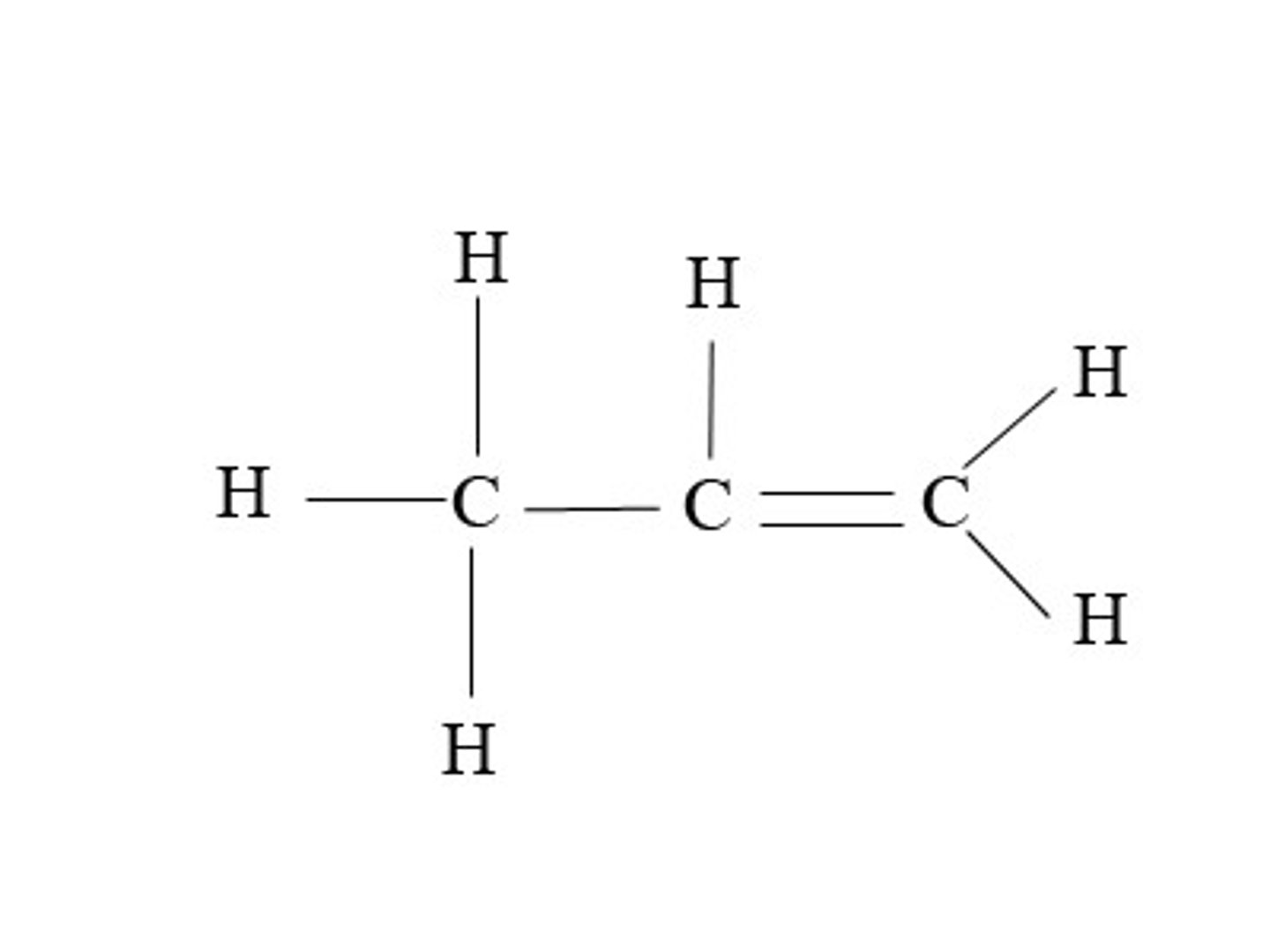
Propylene(propene)
C3H6, CH2=CH-CH3.
Two naturally occurring alkenes;
Pheromones, and Terpenes
Purpose of Pheromones
Gives off signals by insects/animals during mating season.
Terpenes
A hydrocarbon chain with two or more 5-carbon isoprene units.
Example of Terpenes
Betacarotene; found in carrots.
Tertbutyl
l
CH3--C--CH3
l
CH3
Isopropyl
l
CH--CH3
l
CH3
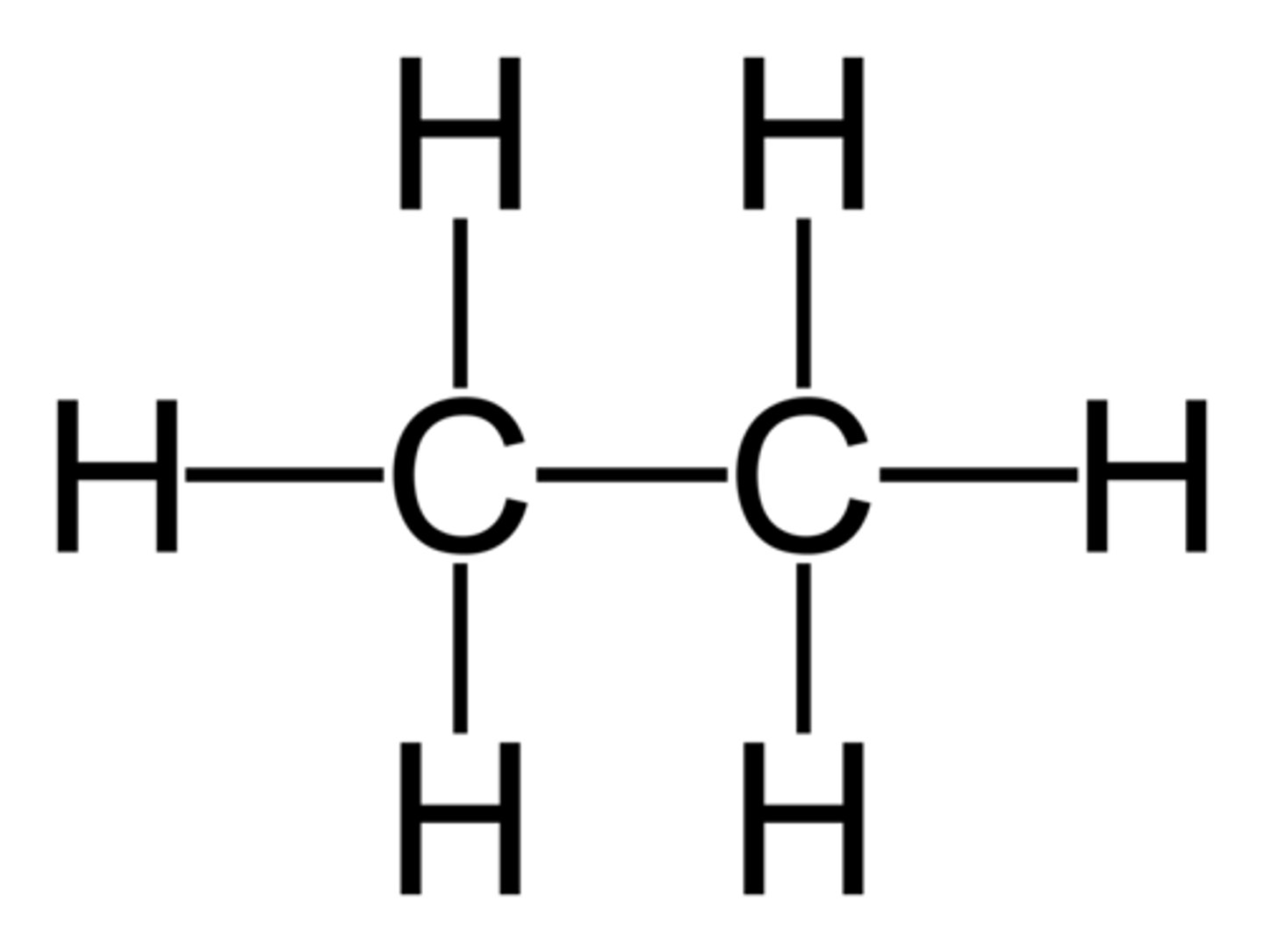
Saturated hydrocarbons
All single bonds
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
1 or more multiple bonds
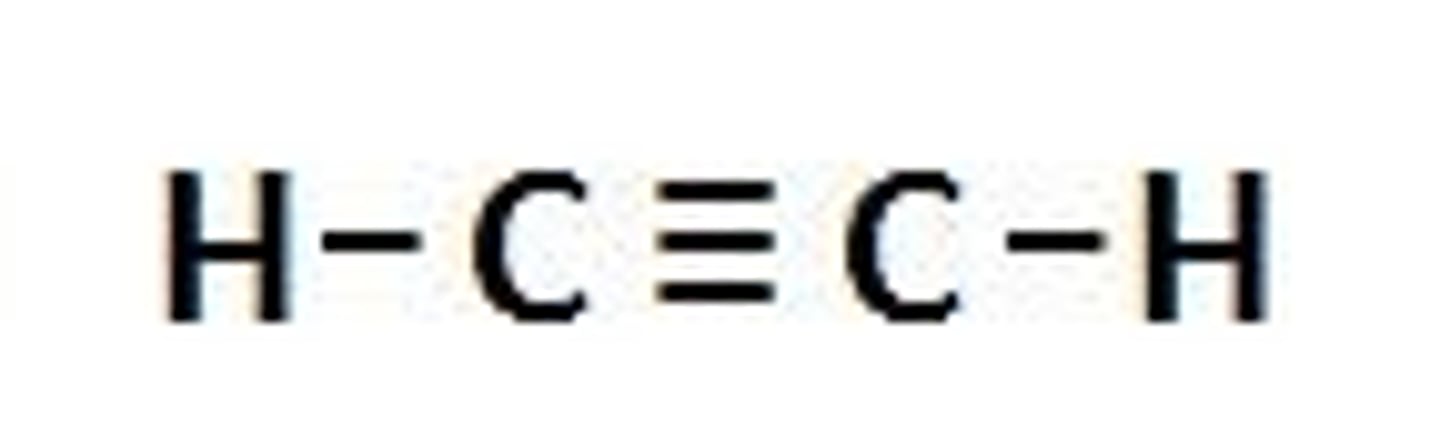
Physical Properties of Hydrocarbons
1. Not soluble in water
2. Less dense than water
3. The larger the structure the higher the boiling point, because there are more bonds to break.
Combustion
The products of this reaction are always CO2 and H2O.
Two types of reactions for alkanes
1. Combustion
2. Halogenation
Halogenation is an example of a ___________ reaction. This is the only type of _________ reaction that alkanes can do.
Substitution
The diatomics of a halogenation reaction will be;
F2, Br2, Cl2, I2.
In a _______ reaction I'm always adding a _________ to form a halogenated (cyclo)alkane. To name them I'm using the element as a prefix- for example 'Chloro.'
halogenation; halogen
Methane is the simplest __________.
alkane
Alkanes end in _____.
-ane
Steps of naming alkanes
Find the longest carbon chain
# the carbon chain
name alkyl groups
What? Where? How many?
Alphabetize
#,# #-word
Alkene + _________ = ___________
This is a __________ reaction.
hydrogen; alkane
hydrogenation
What is the smallest cycloalkane?
Cyclopropane
Positional Isomers
Same carbon arrangement but hydrogens are arranged differently because of the placement of the double bond.
Skeletal Isomers
Cis and trans isomer
Cis isomer
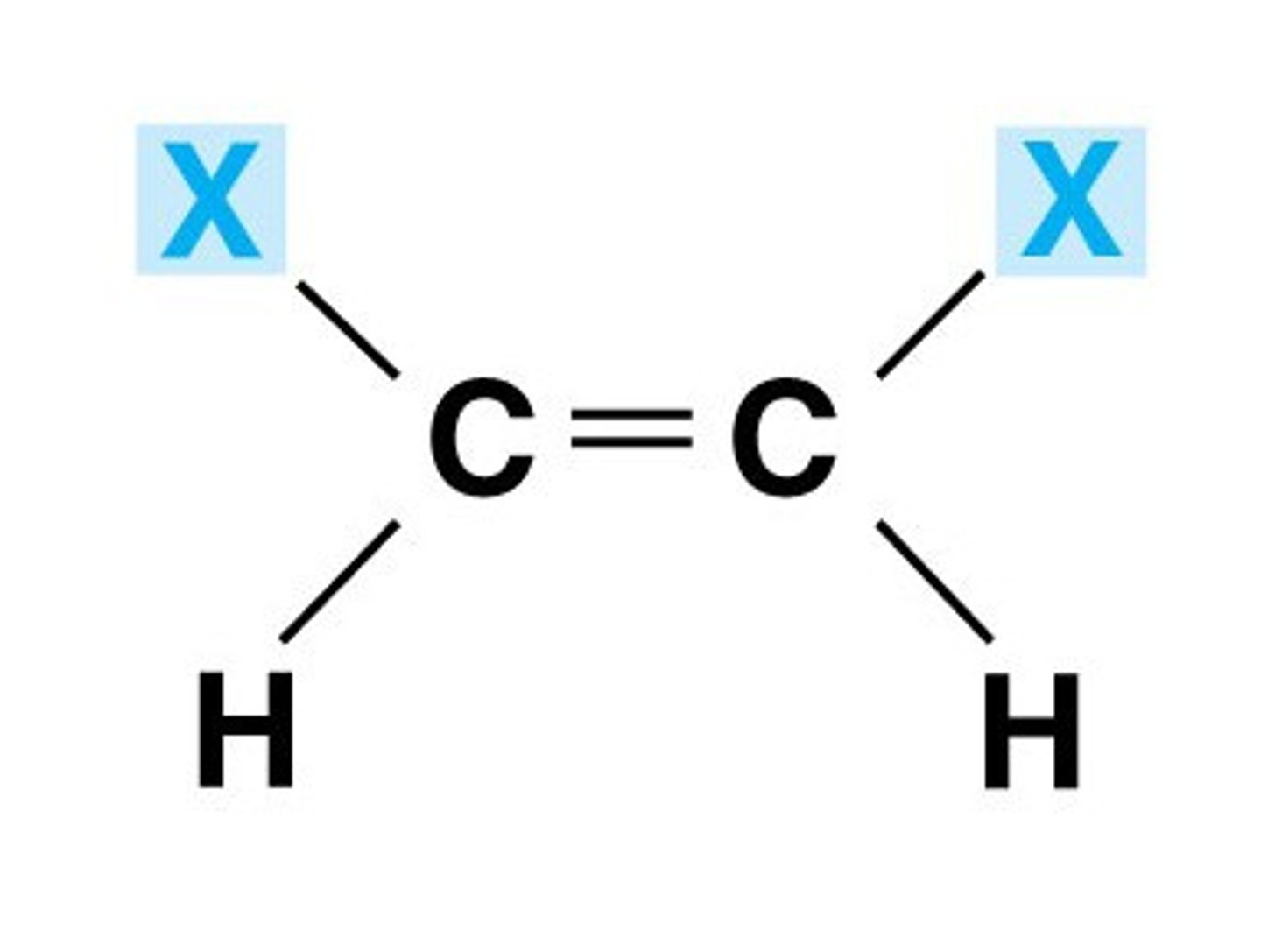
Trans isomer
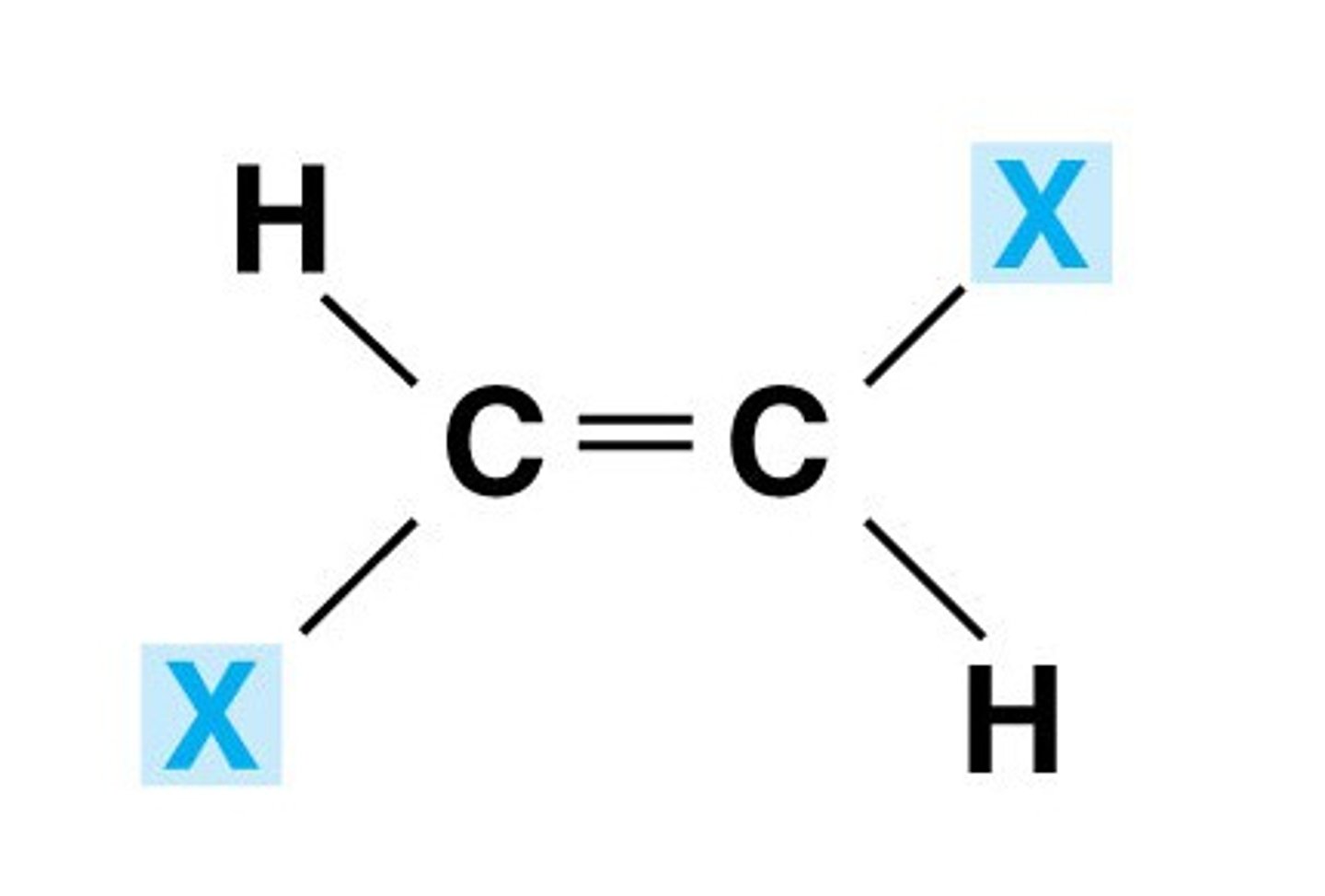
Symmetrical Addition
Hydrogenation and Halogenation
Unsymmetrical Addition
Hydrohalogenation and Hydration
Rules of naming Alkenes
End in -ene
Largest chain with double bond
# closest to the double bond
Give position of the double bond
If multiple double bonds; -diene, -triene, -tetrene
Cyclo- == bond is always between C1 and C2, but is not written.
Cyclo- multiple double bonds; lowest number possible
Functional Group
Part of the molecule where the reactivity occurs
Benzene
The simplest aromatic hydrocarbon.
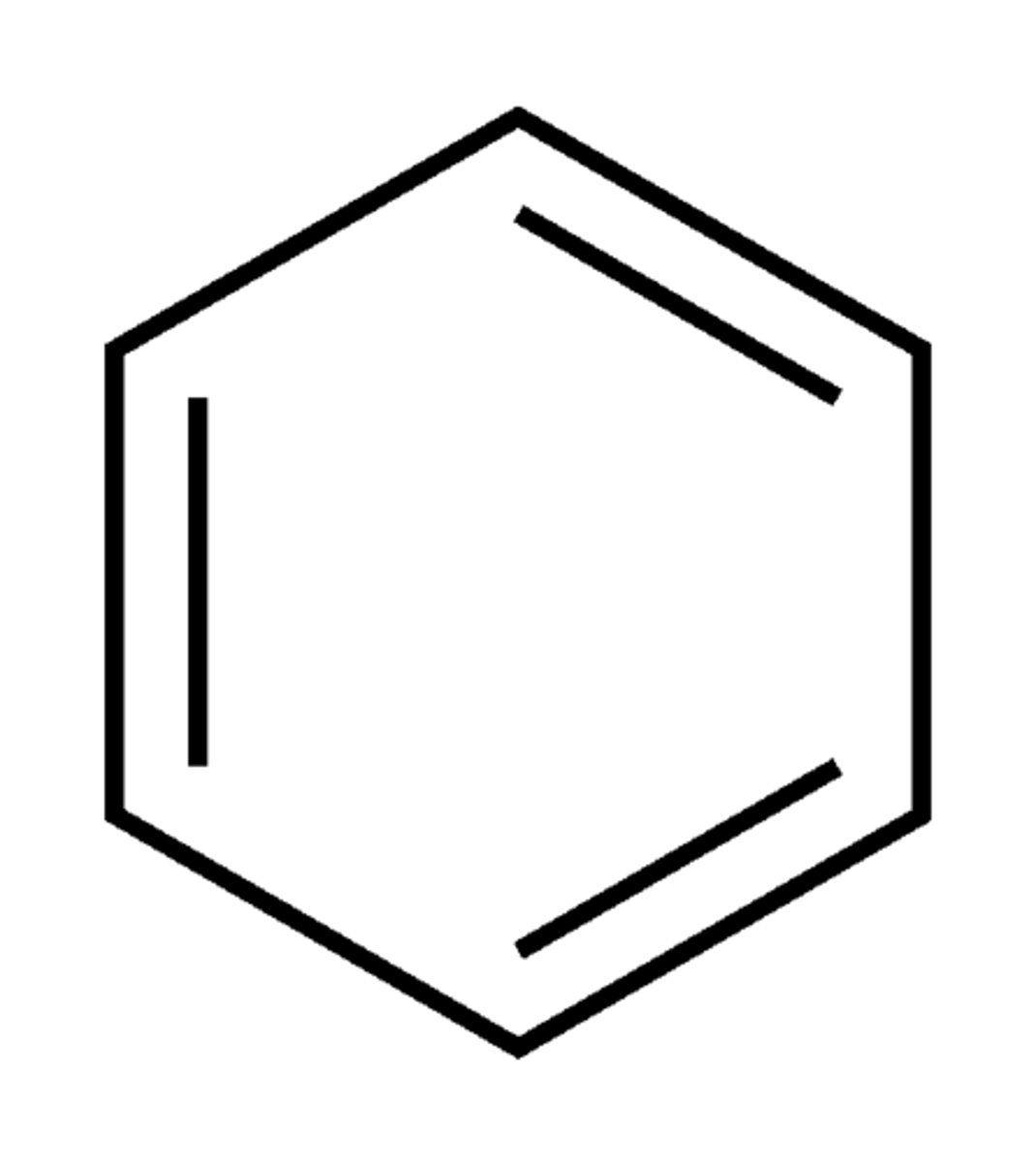
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon which does not readily undergo addition reactions.
Benzene has______ bonds. Which are...?
Delocalized bonds; Covalent bond in which electrons are shared among more than 2 atoms.
Toluene and it's IUPAC
methylbenzene
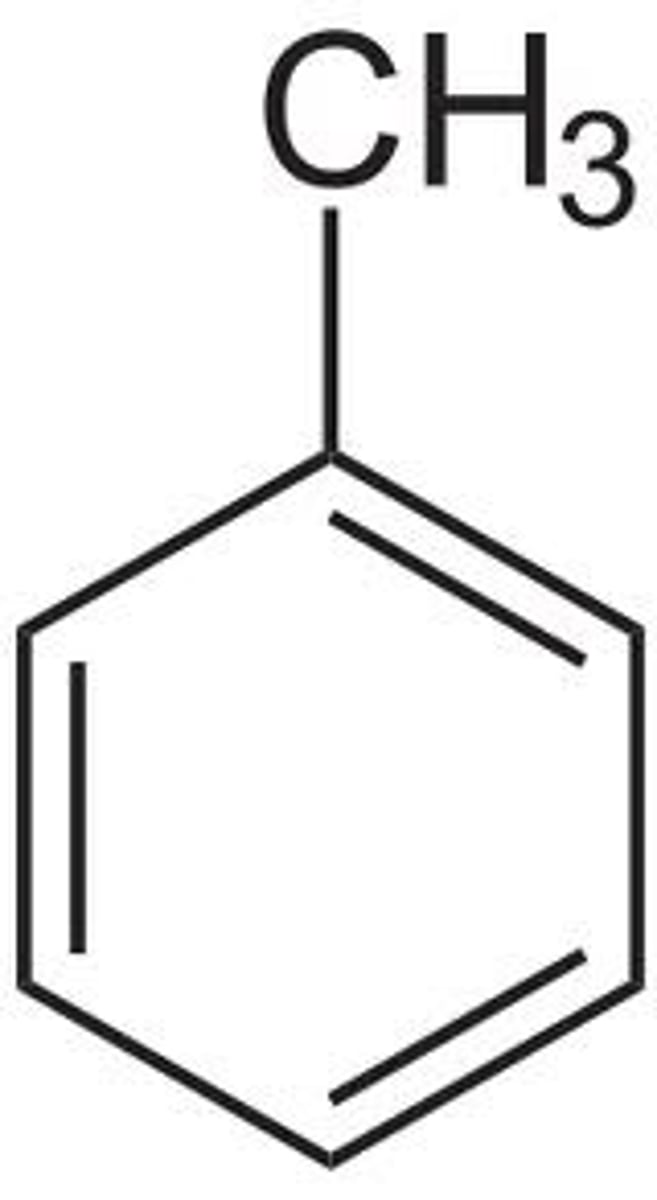
Xylene
Common name for isomers of dimethylbenzene.
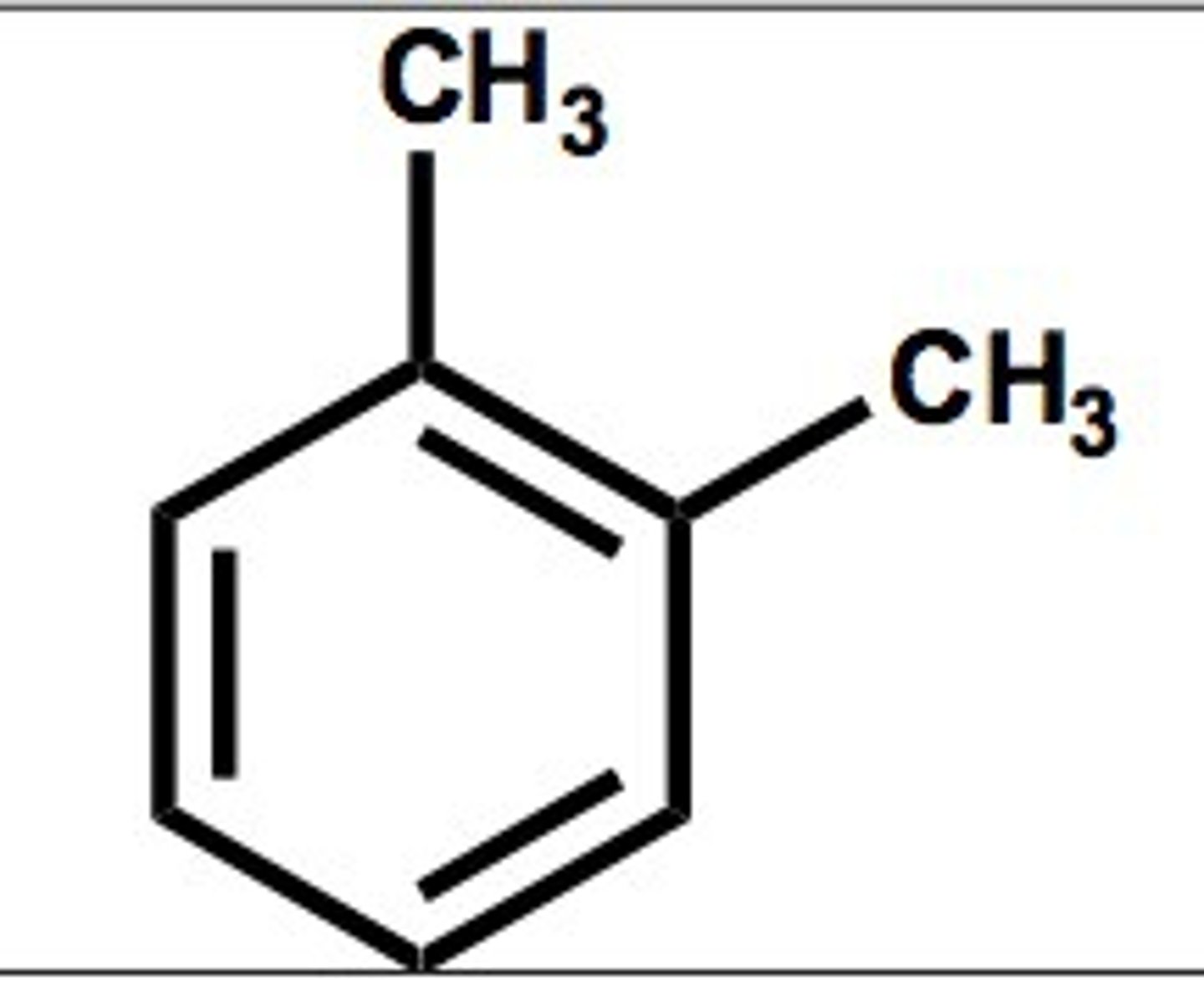
Ortho-xylene
On carbons 1 and 2
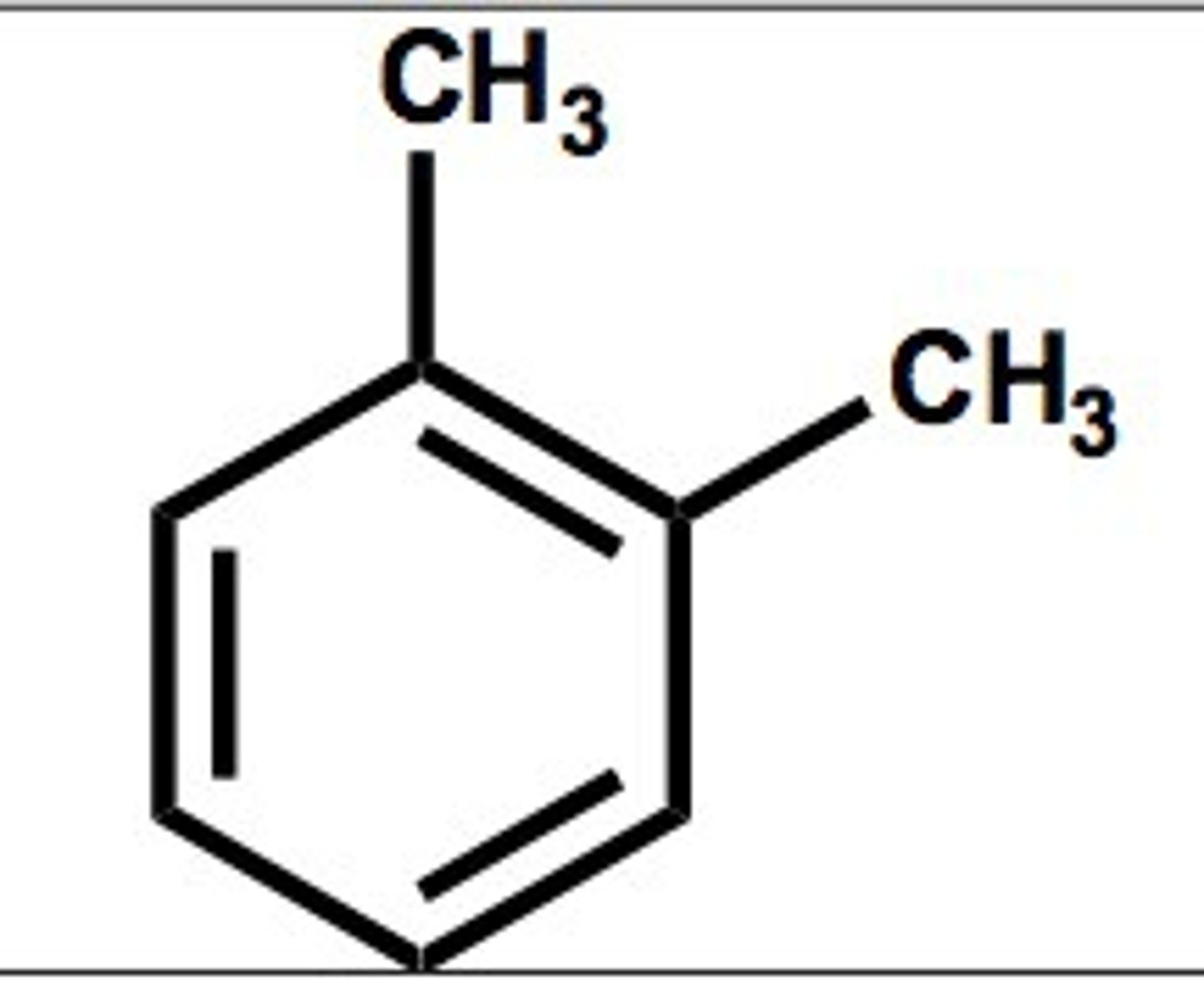
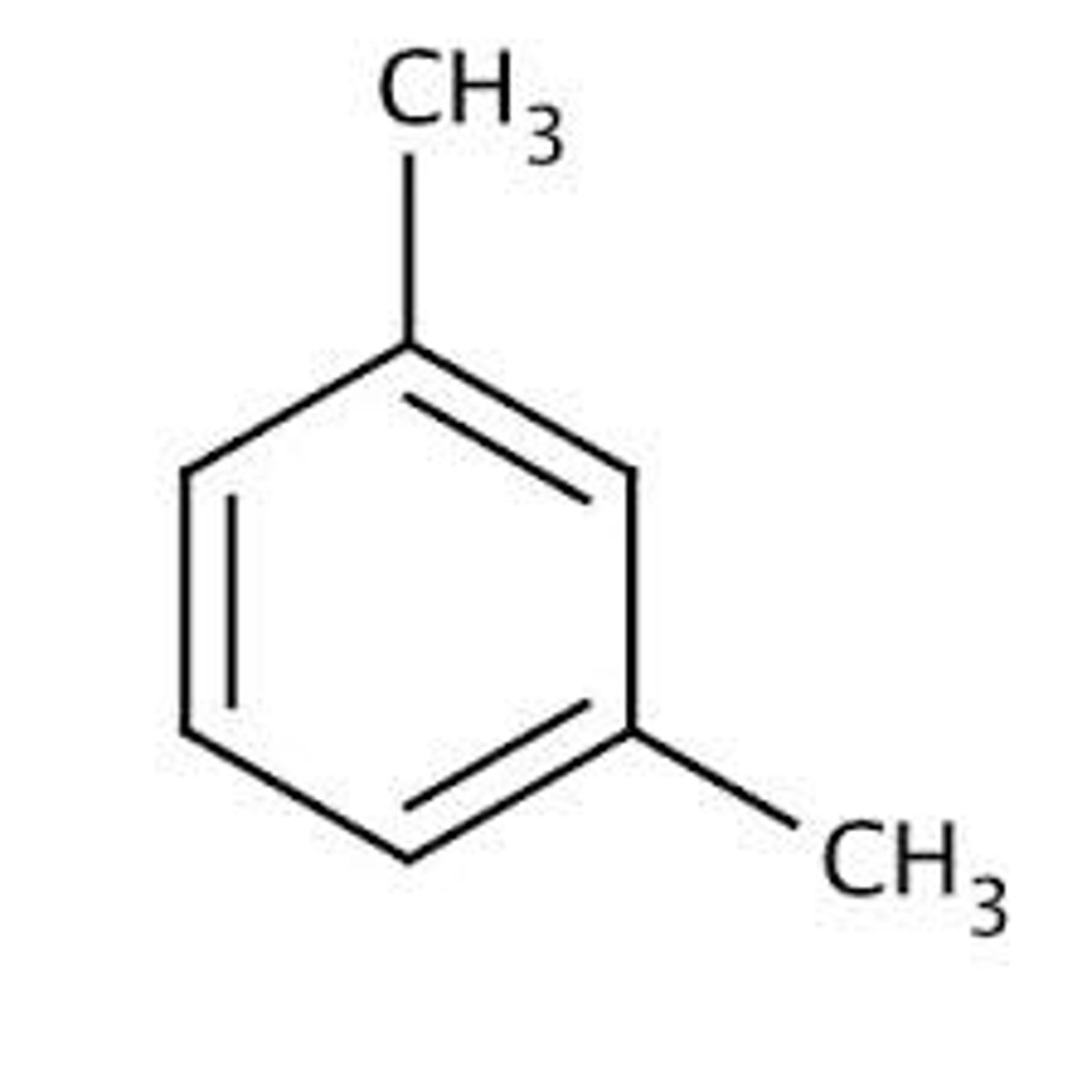
Meta-xylene
On carbons 1 and 3
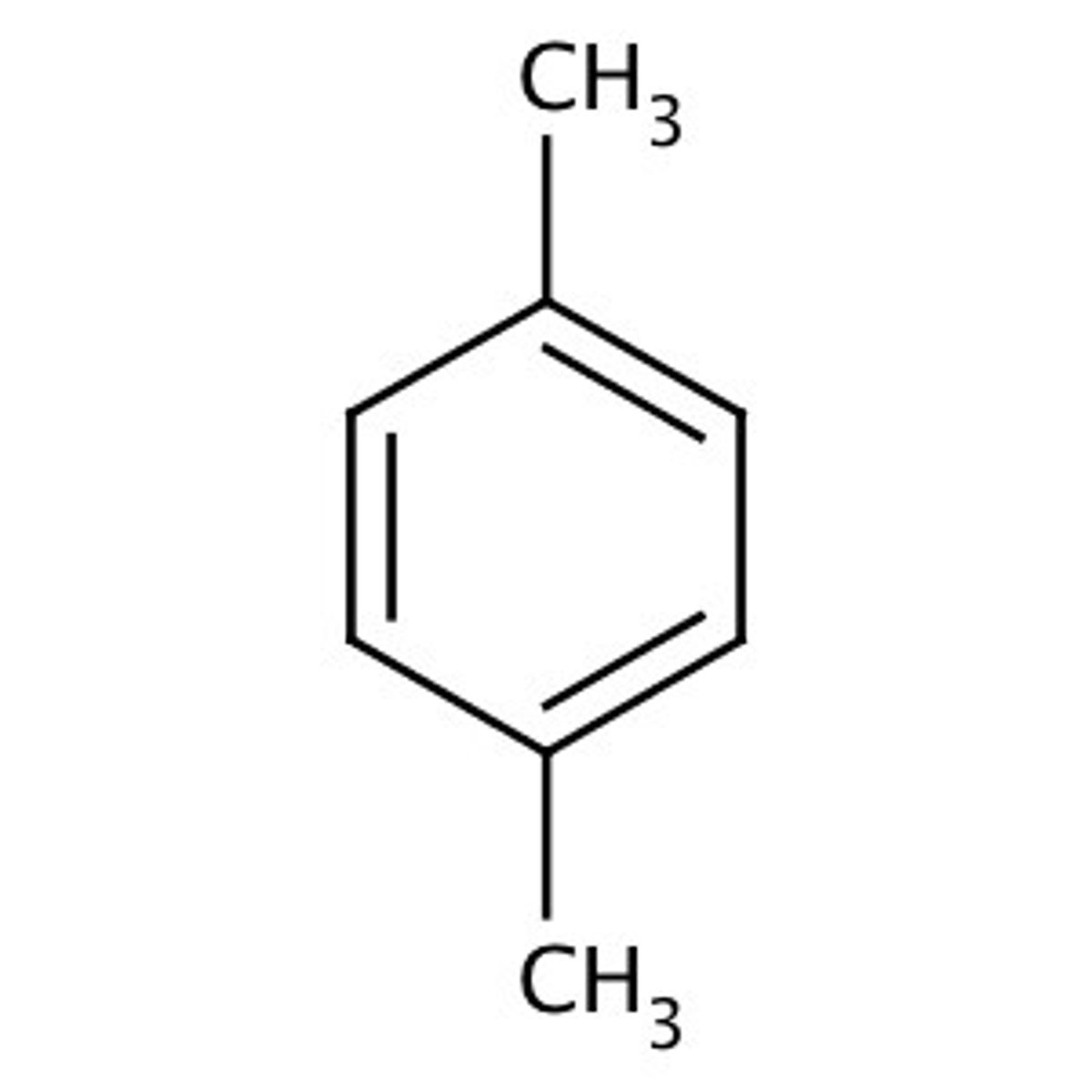
Para-xylene
On carbons 1 and 4
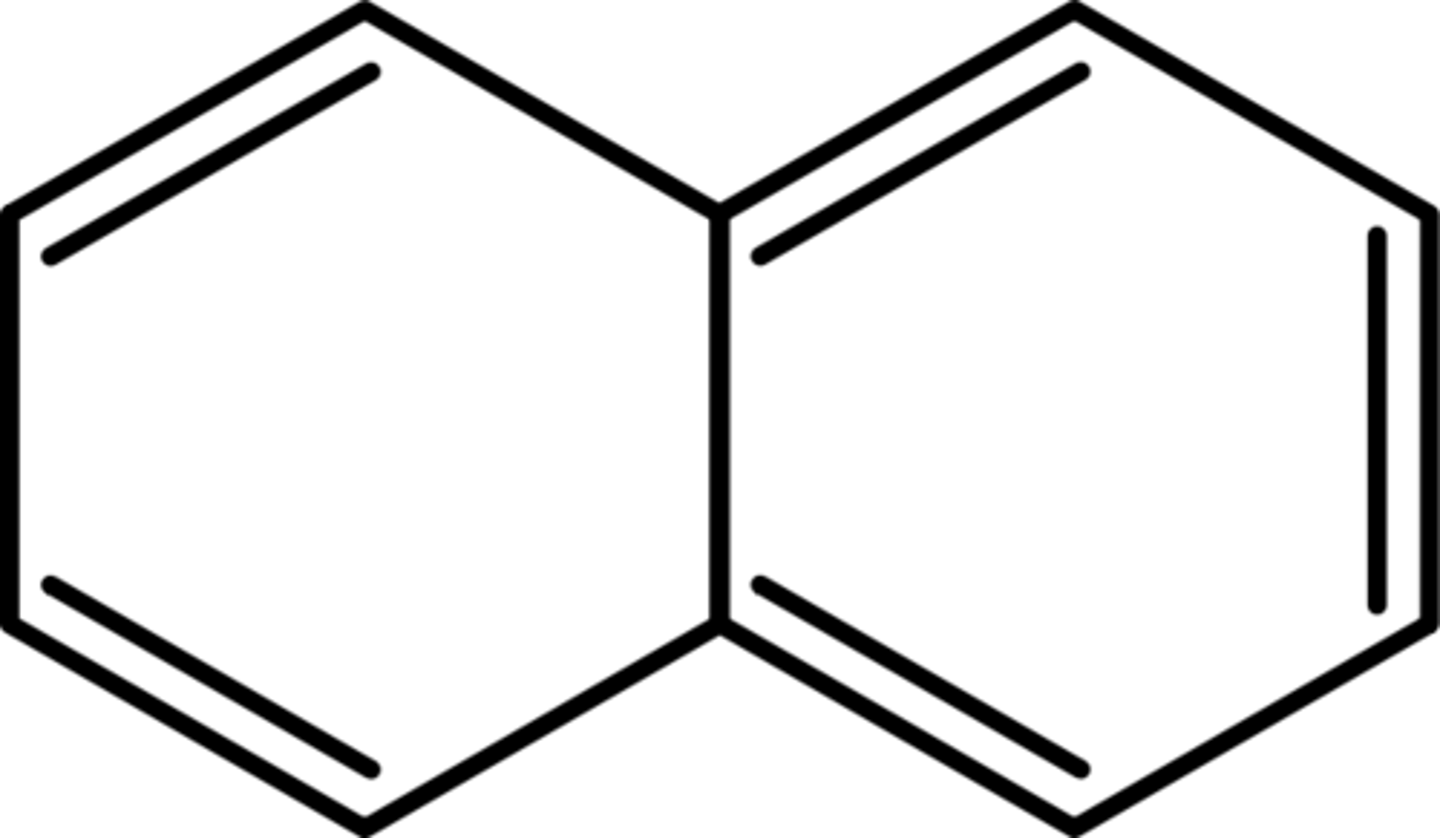
Napthalene
Bad smelling mothball
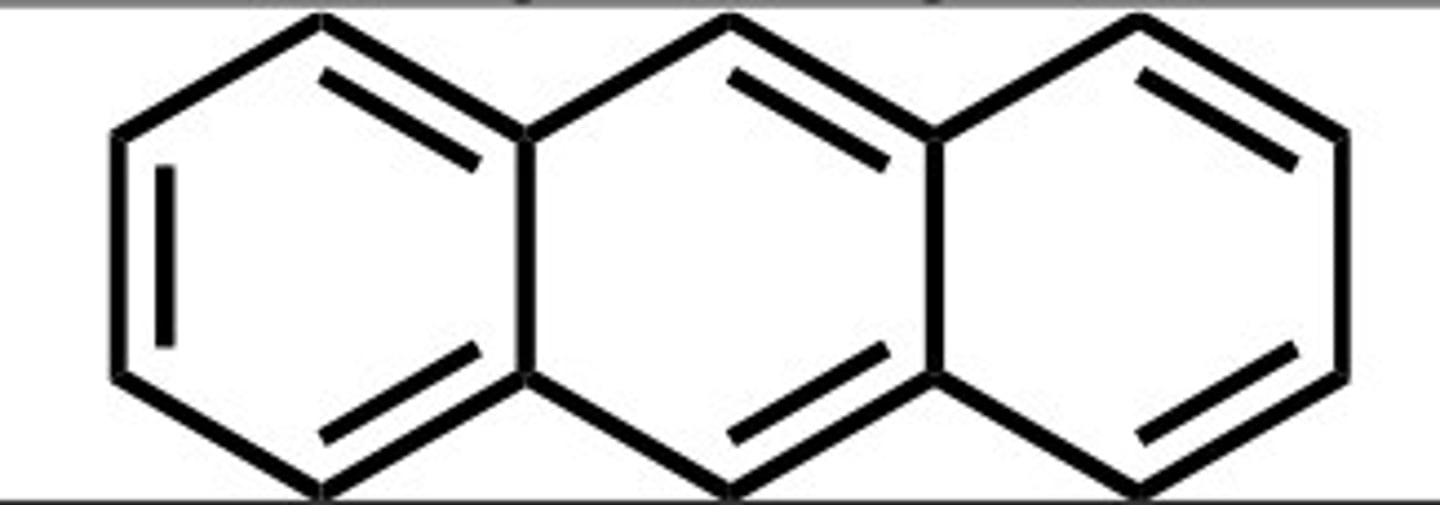
Anthracene
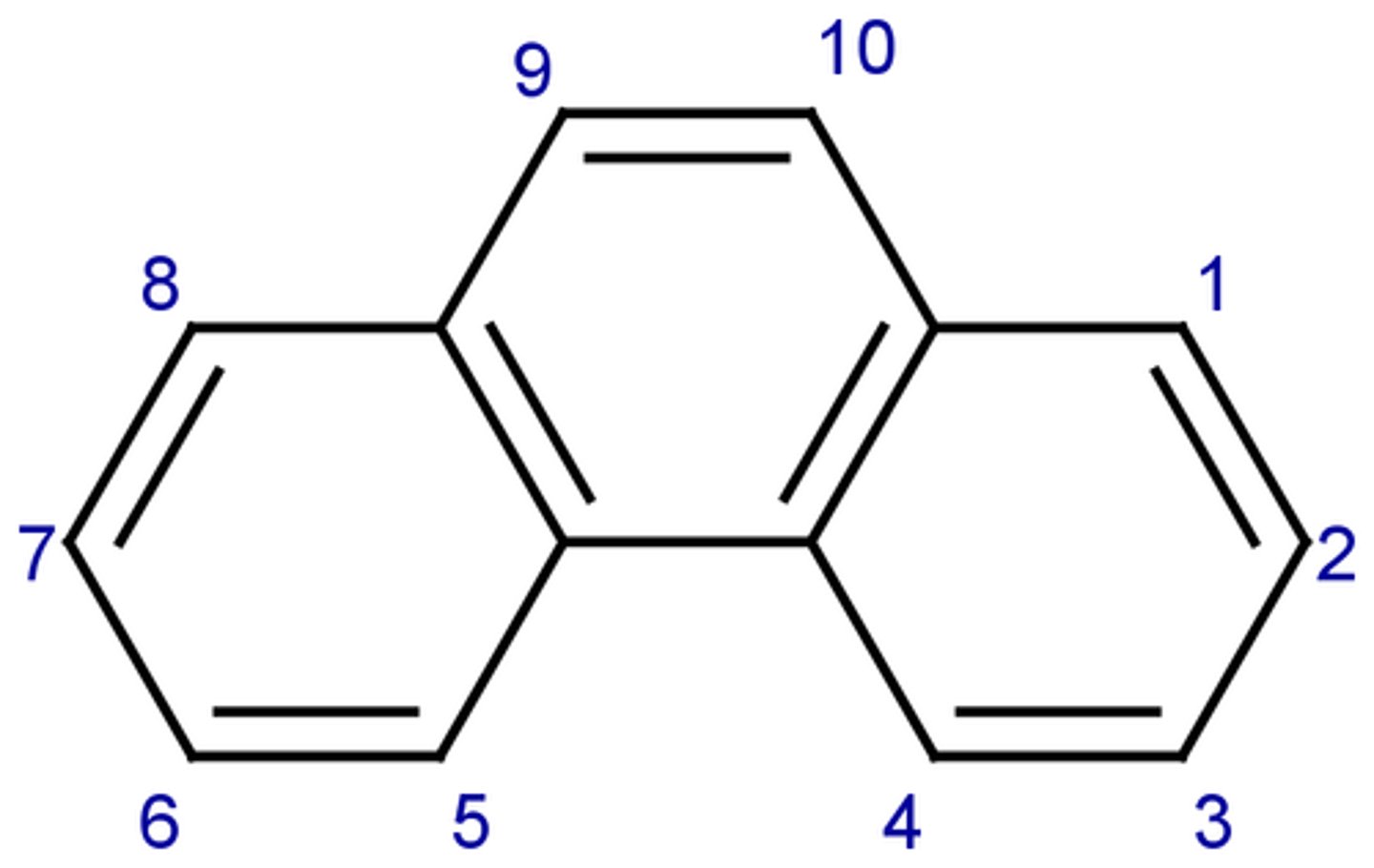
Phenanthrene
________ __________ are the only hydrocarbons that can undergo alkylation.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
AlCl3 is a catalyst of this type of reaction.
Alkylation