Lecture 12 Midlatitude and Tropical Weather and Climate
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Anticyclones (10)
a large high pressure region
anticyclonic rotation
wide isobars = low winds and persistence
has air spiralling away from it at the surface, creates descent
descending air gets warmer
assuming the total water content is conserved, this means the air will get less saturated, so any clouds (liquid water) will evaporate (to water vapour)
so anticyclones tend to be cloud-free and sunny
generate hot weather in the summer
also slow moving, so can persist for several days leading to heatwaves
well spaced isobars, weak pressure gradients, low winds can accumulate air pollution
Typical Anticyclone Characteristics (5)
motion: ~0-few 100 km/day
size: ~4000 km
lifetime: up to weeks
pressure gradient: ~<10hPa/1000km
central pressure: >1020 hPa
Anticyclone Formation (3)
converging air aloft, descent and surface divergence
if upper-level convergence is stronger than surface divergence -> surface pressure rises -> surface high deepens
vertical motion: descends by ~1cm/sec (1km/day)
July 2022 Heatwave (12)
16-19th July 2022 ‘unprecedented’
UK record temperature of 40.3C set in Lincolnshire
Scotland record temperature of 34.8C
temperatures above 39C recorded as far north as Yorkshire
daily minimum temperatures set new record of 25.8C in London
associated with a longer heatwave in Western Europe and large high pressure systems
Office of National Statistics attributed 3,271 excess deaths from this heatwave
led to southerly airflow
short-lived in the UK due to cold front from low pressure system
46 stations exceeded previous UK temperature record
record high temperatures in last 30 years, especially last 5 years stand out
exceptional outlier in a 250-year series of central England
ITCZ (4)
InterTropical Convergence Zone
easterly trade winds converge near the equator along the ITCZ
warm moist air rises all the way to the tropopause -> thunderstorms form
this air then drives the Hadley Cell Circulation with descending air at about 30°
ITCZ Migration (5)
ITCZ follows the migration of the sun’s overhead position with a delay of 1-2 months
ocean heats up slower than land
moves further north and south over land areas than over water
in July and August, the ITCZ lies north of the equator over Africa, Asia, and Central America
in January and February lies further south in South America, central Africa and Australia
responsible for wet (short and long rains) and dry seasons in the tropics
Monsoons (6)
important seasonal feature linked to ITCZ
a regional large-scale sea breeze circulation
in summer, solar heating over continent leads to low pressure as warm air rises
brings moist oceanic air and heavy rainfall
in winter, land cools faster than water
high pressure over ocean
wind moves offshore
wind reversal
sea-to-land in summer
land-to-sea in winter
occurs in India, West Africa, East Asia, Northern Australia, Central America
Monsoons: India
in summer, the ITCZ is known as the monsoon tough
causes low pressure over North and North West India
PGF air moves in from sea
trade winds over India and Indian Ocean blow from southwest
lots of rain, moist air
in winter, ITCZ moves south and the winds reverse (trade winds from northeast)
dry, continental air
rainfall amount and intensity follows ITCZ
East Asia
in winter, the East Asian monsoon carries cold dry air from the Siberian High Pressure Region offshore
in summer, the East Asian monsoon carries moist air from the Indian and Pacific oceans to the east Asian continent
Tropical Cyclone Characteristics (3)
typically ~100-500km, smaller than mid-latitude cyclones
typical central pressures of 950hPa, but record low of 870hPa, lower than mid-latitude cyclones
lots of rain
Hurricane Irma more than 274 mm per hour
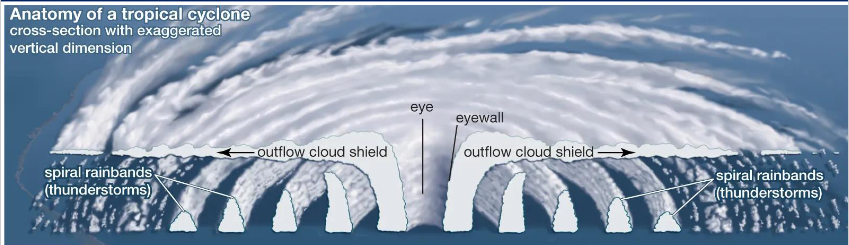
Tropical Cyclone Structure
eye in centre
eyewall with outflow cloud shield
spiralling winds between spiral rainbands
dry air sinks in centre, winds flow inward and spiral upward
Conditions for Tropical Cyclone Formation (3)
only form over oceanic regions where SSTs are greater than 26.5C
do not form within 5° of the equator due to negligible Coriolis force
form in regions where the vertical wind shear between the surface and upper troposphere is low (less than 23 mph or 10 m/s), no jet stream
Sources of Tropical Cyclones
form from tropical disturbances
a localised area where air is converging
two mains mechanisms in the tropics for convergence
Easterly waves
originate over continents as air moves across mountains/deserts e.g. off west coast of Africa
ITCZ
easterly trade winds converge
Saffir Simpson Scale
measures tropical storms
Tropical Depression (TD), Tropical Storm (TS), Hurricane 1, Hurricane 2, Hurricane 3, Hurricane 4, Hurricane 5
2024 Hurricane Season
June 19 2024 - November 18 2024
Milton strongest storm
18 depressions, 18 storms, 11 hurricanes, 5 major hurricanes
401 total fatalities
$129.5 billion in damage
Hurricane Milton Impacts
explosive intensification due to warm SSTs in Gulf of Mexico
category 5 with winds of 180mph, 897hPa
landfall as category 3 in Florida with 120mph winds
Mexico
evacuations
flooding
3 deaths
12,000 people without power
Florida
6 million evacuations
32 deaths
46 tornadoes
3 million homes without power
misinformation rife