Human Wellbeing
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What is human wellbeing?
Human wellbeing is an overall measure of the health and quality of life of a group of people.
Wellbeing can look different depending on location and economic status, e.g. in poor areas wellbeing is having the basics, whereas in richer areas it is measured by health, wealth, education, and happiness.
For high standards of wellbeing, people must access both primary needs (e.g. clean water) which are essential for survival, and secondary needs (e.g. access to education) which helps people live better lives.
Indicators to measure health, wealth, and education
Differences in health, wealth and education are causes of variations in human wellbeing
We can measure differences in these factors through key indicators
Measure Health
Health is the state of physical, mental, and social wellbeing
Indicators to measure health include;
Life expectancy
Infant Mortality Rate
Percentage of underweight children under 5
Access to healthcare (e.g number of doctors per 1000 people)
Access to safe drinking water
Reliable access to nutritious food (food security)
Access to healthcare varies widely in different regions
Indicators like life expectancy correlate with improved wellbeing factors (e.g. medical care)
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to the provision of facilities and services for the safe management and movement of human excreta from a toilet to a storage.
Approximately 30% of Central and South Asia do not have access to any form of sanitation
Lack of sanitation can lead to the spread of infectious diseases (e.g. diarrhoea)
Education
Education provides opportunities to read, write and count
It is a key sector which must be addressed to lift nations out of struggle or poverty
Education allows for people to become;
More engaged w/ society
Have a range of skills and tools to better themselves
Become part of the workforce
Be healthy + combat poverty
Reduce wellbeing inequalities
There are many barriers to a successful education;
System barriers (e.g. lack of teachers)
Attendance barriers (e.g. poor transport facilities)
Social barriers (e.g. language barriers, world conflict)
GNH (Global National Happiness Index)
A qualitative measure to measure happiness
Assumption that happiness correlates w/ other wellbeing indicators
GNH uses social indicators, (e.g. life expectancy, freedom, GDP) to rank countries overall happiness
Bhutan, invented the GNH, and prioritizes it over other measures such as GDP
This is done by;
Environmental conversation
Sustainable development
Preservation of culture
HDI (Human Development Index)
A measure of wellbeing that combines many individual indicators (e.g. health, education, and income)
HDI is a value between 0-1
Infant mortality rate (IMR)
measure of the number of children who die under one year of age for every 1000 children born
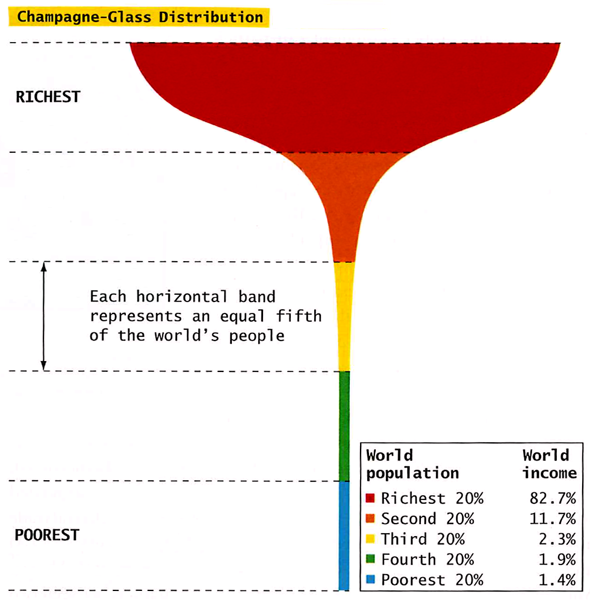
Champagne glass distribution
Is a model that illustrates the extreme inequality in global wealth distribution. The top is wealthy that controls a vast majority of the wealth, and the majority of the population at the bottom having very little control. This gives a large number of poor people with limited resources and opportunities