serotonin agents
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
serotonin general characteristics
first identified in the 40s, found to be associated with a variety of issues
includes anti-migraine agents, antiemetics,
migraines general characteristics
affects 12% of worldwide populations with a higher prevalence in women
intense pulsing and throbbing headache lasting 4hrs to 3 days
n/v, sensitivity to light, sound, movement
common migraine lacks aura while classical migraine has aura
triggers: fluctuations in estrogen, meds, foods, stress, etc.
triptans general characteristics
first introduced in the 90s
used for typical migraines only
5HT1B and D agonists (cranial blood vessels and trigeminal pain pathway)
MOA: causes vasoconstriction on the receptors of dilated cranial blood vessels and reduces transmission in trigeminal pain pathway
sumatriptan/imitrex ADME
can be used SC or nasal spray with a 10-15min onset
max dose: SC 12mg/24hrs, oral 200mg/24hrs, nasal 40mg/24hrs
lowest bioavailability of all the triptans - low lipophilicity
½ life 2.5hrs, metabolized by MAO-A
metabolite glucoronidated, undergoes renal excretion
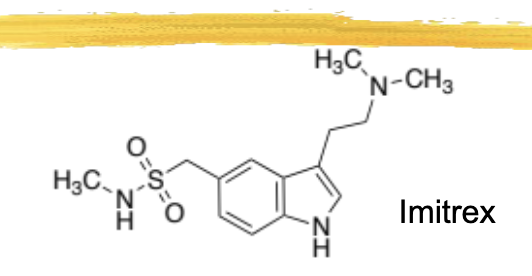
sumatriptan/imitrex general characteristics and structure
the first triptan
can’t be given iwht MAO-A inhibitors
available in several dosage forms - used for acute treatment
Onzetra/Xsail - nasal powder with 11mg dose, 3hr ½ life, low bioavailability
has the sulfur with 2 oxygens and the secondary amine hanging off the benzene ring
zolmitriptan/zomig ADME
rapidly absorbed orally and nasally
½ life 3-4hrs
bioavailability 40-50%
metabolized by 1A2 to a more potent metabolite that accounts for 2/3 of plasma concentration
metabolite degraded by MAO-A
renal excretion
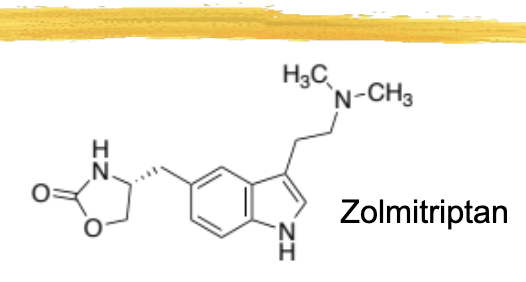
zolmitriptan/zomig general characteristics and structure
second triptan
available as tablet and ODT (2.5 and 5mg) or nasal spray (5mg)
has a 5 membered ring with an amide and an ester on it
naratriptan/amerge ADME
bioavailability 63-74%
high receptor affinity
half life 5-6hrs
metabolically stable - metabolized by multiple CYP450s to inactive metabolite
70% renally excreted unchanged
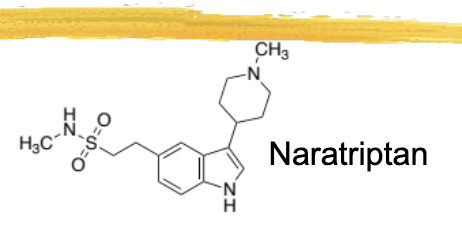
naratriptan/amerge general characteristics and structure
third triptan
highly lipophilic
looks similar to sumatriptan, but has a 6 membered nitrogen ring hanging off of the main 5 membered ring
rizatriptan/maxalt ADME
slightly faster onset than sumatriptan and available as ODT
½ life 2-3hrs
metabolized to active metabolite by MAO-A and 2D6
renal excretion
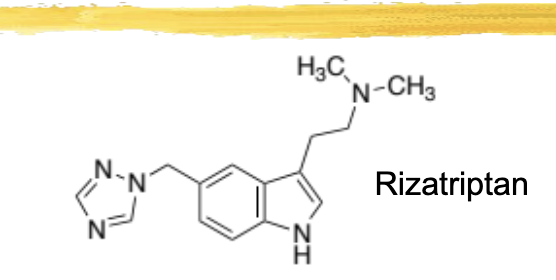
rizatriptan/maxalt general characteristics and structure
moderate lipophilicity
available in tablets and ODT (5 and 10mg)
dosing: 5-10mg, repeat after 2hr, max 30mg/24hrs
but if on propranolol max dose is 5mg or 15mg/24hrs
structure has a 5 membered ring with 3 nitrogens hanging off of the main benzene ring
almotriptan/axert ADME
metabolized by MAO-A and 3A4
½ life 3-4hrs
40% excreted renally unchanged
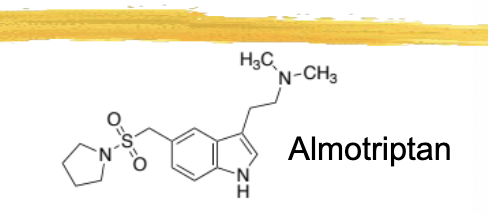
almotriptan/axert general characteristics and structure
highest oral bioavailability of all triptans - 70-80%
tablet doses 6.25 and 12.5mg
favorable ADR profile
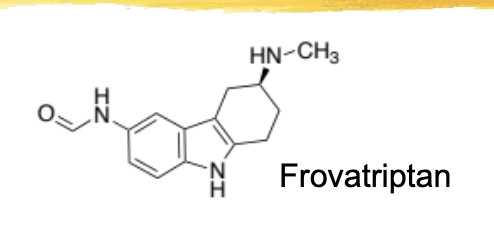
frovatriptan/frova general characteristics and structure
contains 3-alkylamino side chain
longest DOA (1/2 life 26hrs)
60% bioavailable
2.5mg tabs, repeat after 2hrs, max 7.5mg/24hrs
frovatriptan/frova ADME
onset of action 2-3hrs, higher water solublility than other triptans
highest affinity for 5HT1b receptors
metabolized to active metabolite by 1A2, where it is eliminated in feces
eletriptan/relpax ADME
50% bioavailability
½ life 3.6-5.5hrs
metabolized by 3A4 to active metabolite
also a substrate for P-gp efflux pumps
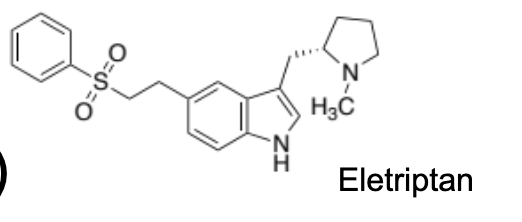
eletriptan/relpax general characteristics and structure
highest affinity for 5HT1B and D
well tolerated across 20-80mg dosing range, max 80/day
structure is the bulkiest one
general contraindications for anti-migraine agents
not given to pts with angina, PMH of MI, or silent ischemia due to vasoconstrictive properties
not used with other 5HT1 agonists
not used with MAOIs
not used in hemiplegic or basilar migraines
warnings: risk of cerebrovascular event and MIs
general anti-migraine ADRs
n/v, dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, pain or tightness in throat, chest, neck, abnormal sensations, muscle weakness
preventative medications to use with antimigraine agents
CV drugs: beta blockers, Ca channel blockers, antihypertensives
antidepressants: TCAs
AEDs: gabapentin, topiramate, valproate
cyproheptadine (antihistamine)
botox injections in forehead and neck
lasmiditan/reyvow general characteristics and structure
high affinity for 5HT1F (located on nerves, not blood vessels → no vasocons
ADR: dizziness, sleepiness, can cross BBB
CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) disruption in migraines
pro-inflammatory peptide that binds to CGRP receptor and causes vasodilation and inflammation
aimovig, ajovy, emgality, nurtec, and ubrelvy all act on this mechanism
ADRs: hypersensitivity, immunogenicity
aimovig/erenumab
binds CGRP receptor and blocks ligand binding
½ life of 28 days = once monthly injection
ajovy/fremanezumab
binds CGRP and prevents CGRP receptor activation
½ life 31 days = once monthly 225mg or quarterly 675mg injection
emgality/galcanezumab
binds CGRP and prevents CGRP receptor activation
also approved for cluster headaches
½ life 25-30 days = monthly injections
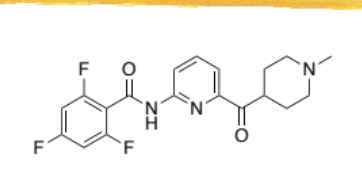
ubrely/ubrogepant
binds CGRP receptor and blocks ligand binding
small molecule, taken orally
½ life 5-7hrs
metabolized by 3A4
substrate of P-gp and BCRP efflux transporters
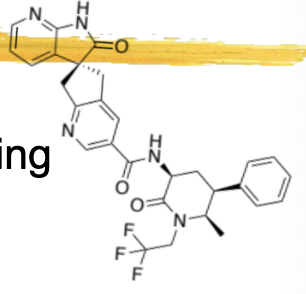
nurtec ODT/rimegepant
binds CGRP receptor and blocks ligand binding
small molecule, taken orally
½ life 8-12hrs
metabolized by 3A4 and partly by 2C9
substrate of P-gp and BCRP efflux transporters
3 phases of 5HT3 activation
nausea: sensation of wanting to vomit, cold sweat, pallor, salivation, reflux of intestinal contents into stomach
retching: coordinated contraction of abdominal muscles, diaphragm, intercostals
expulsion: strong pressure in stomach due to shifts in diaphragm and abdominal muscles, triggers upper esophageal sphincter to relax to allow for expulsion of gastric contents
mechanism of emesis
afferent inputs relay emetic signal to CNS
signal is received and processed, forming efferent signals from CNS
motor and chemical efferent pathways relay signals that cause physical action of emesis
medullary centers: CTZ and central emesis center
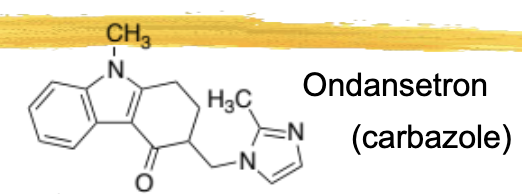
ondanestron/zofran ADME
½ life 3-4hrs
metabolized by 3A4 and 2D6
ondanestron/zofran general characteristics and structure
used mostly as an antiemetic following chemo
reduces activity of vagus nerve, deactivating vomiting center in medulla
blocks 5HT receptors in CTZ
ADRs: dizziness, headache, constipation
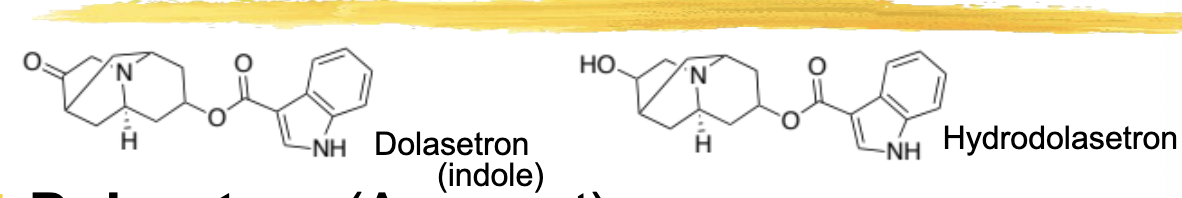
dolasteron/anzemet ADME
metabolite has 80% bioavailability and 4-9hr ½ life
60% of metabolite excreted unchanged
dolasteron/anzemet general characteristics and structure
used to treat emesis following chemo
ADRs: headache, dizziness, constipation
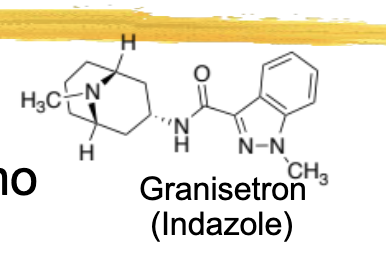
granisetron/kytril ADME
½ life 6hrs, but activity can last up to 24hrs
60% bioavailability, food increases absorption
metabolized by 3A4
excreted in urine and feces
granisetron/kytril general characteristics and structure
used to treat emesis after chemo
sustol: extended released injectible form that covers acute and delayed CINV for up to 5 days
ADR: headache, constipation
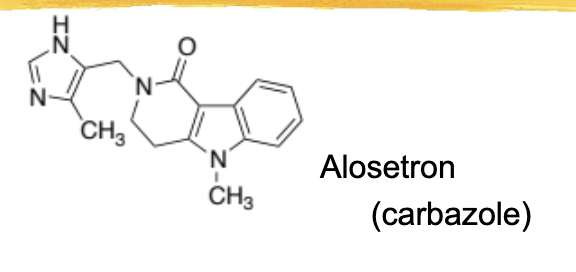
alosetron/lotronex general characteristics and structure
similar structure to zofran
5HT3 antagonist, but not used for nausea - used to treat IBS-D in women only
ADRs: ischemic colitis, constipation
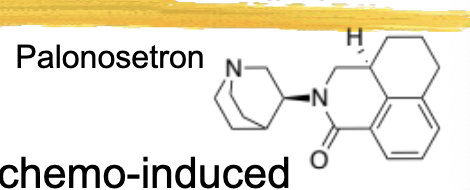
palonosteron/aloxi ADME
½ life 30-40hrs
metabolized by 2D6, 3A4, 1A2
palonosetron/aloxi general characteristics and structure
used for treatment of CINV in the first 24hrs after chemo - first in class for acute CINV
administered 30min before chemo via IV or 60min before via oral capsule
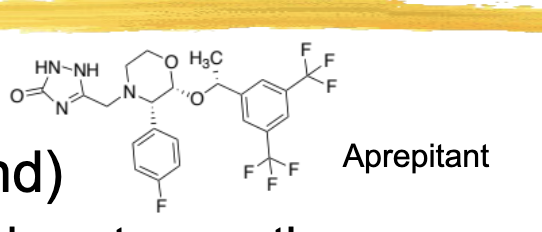
aprepitant/emend ADME
bioavailability 60-65%
metabolized by 3A4, 1A2, and 2C19
aprepitant/emend general characteristics and structure
used for CINV and post-op nausea
blocks the NK receptor in the CNS and PNS, with little-no affinity for other receptors
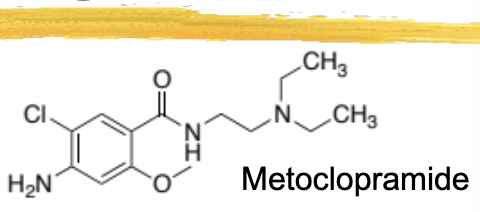
metoclopramide/reglan general characteristics and structure
D2 antagonist, 5HT3 antagonist, and 5HT4 agonist
enhances GI transit in stomach/small intestine
used to treat persistent heartburn and poor gastric emptying
ADR: restlessness, drowsiness, dizziness, changes in BP, extrapyramidal effects, most common cause of drug-induced movement disorders
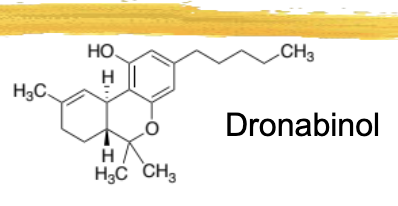
dronabinol/marinol ADME
onset after 1hr
peak effect after 2-4hrs
psychoactive effects last 4-6hrs
highly insoluble in water, 95% absorbed but 20% bioavailability
highly protein bound
metabolized by hydroxylation to 11-OH
excreted in urine and feces
dronabinol/marinol general characteristics and structure
pure isomer of delta 9 THC
used for anorexia in AIDS pts and CINV, may also be useful for pts with Tourette’s
ADR: seizures, paranoia, fast heart rate, light-headedness, cannabinoid effect
syndros: dronabinol oral solution that was FDA approved in 2016
nabilone/cesamet ADME
well absorbed and distributed
extensively metabolized with some active and some inactive metabolites
moderate inhibitor of 2C8 and 2C9
weak inhibitor of 2E1 and 3A4
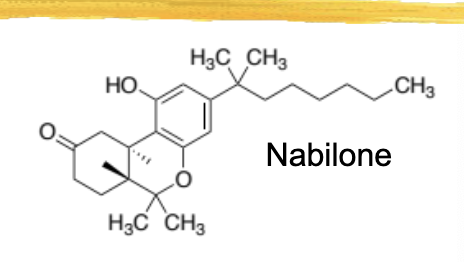
nabilone/cesamet general characteristics and structure
synthetic analog of delta 9 THC
used as an antiemetic for CINV and analgesic
used for those who don’t respond to conventional therapy
racemic mix of isomers
ADR: hallucinations, paranoia, elevated heart rate, lightheadedness, dizziness, vertigo, dry mouth, euphoria, ataxia headache, poor concentration