CC2 - Prostaglandins
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Eicosanoid
eicosa — Greek for "twenty"
signaling molecules
the networks of controls that depend upon eicosanoids are among the most complex in the human body
Eicosapentaenoic acid
Arachidonic acid
Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid
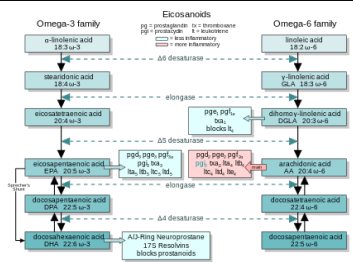
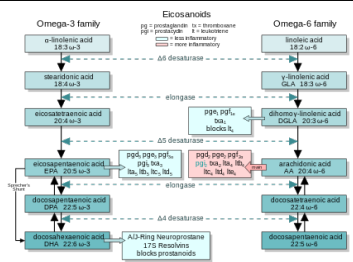
The collective term for oxygenated derivatives of three different 20-carbon fatty acids
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA
an ω-3 fatty acid with 5 double bonds
Arachidonic acid (AA)
an ω-6 fatty acid, with 4 double bonds
Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA)
an ω-6 fatty acid, with 3 double bonds.
20-carbon fatty acids
eicosanoids are made by oxidation of ____________________
Omega 3 (ω-3) or omega-6 (ω-6)
Eicosanoids are derived from this types of fatty acids
ω-6 eicosanoids
pro-inflammatory eicosanoids
ω-3 eicosanoids
less pro-inflammatory
Effects of imbalance in eicosanoid-controlled functions
Cardiovascular disease
Triglycerides
Blood pressure
Arthritis
Aspirin (other NSAIDs)
anti-inflammatory drugs that down regulate eicosanoid synthesis
Sub-families of Eicosanoids (Prostaglandin)
Types of prostaglandin:
Prostacyclins
Thromboxanes
Lipoxins
Leukotrienes
Eicosanoids Sub-Families (Notes)
For each, there are two or three separate series, derived from either an ω-3 or an ω-6 EFA
In these series different activities largely explain the health effects of ω-3 and ω-6 fat
Classic Eicosanoids
Leukotrienes and Prostanoids
Three types of Prostanoids
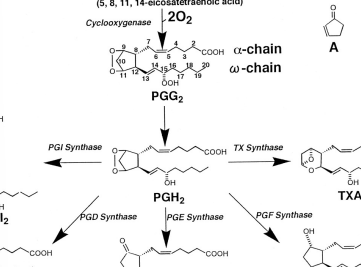
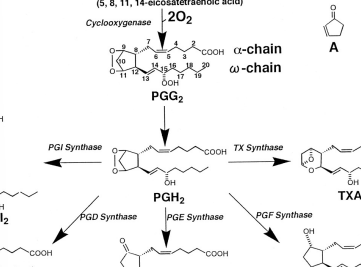
Prostaglandins (PG)
Prostacyclins (PGI)
Thromboxanes (TX)
Several other classes are also technically termed eicosanoid they includ
Hepoxilins
Resolvins
Isofurans
Isoprostanes
Lipoxins
Epi-lipoxins
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and Endocannabinoids.
A particular eicosanoid is denoted by a four-character abbreviation, composed of:
Its two-letter abbreviation (above)
One A-B-C sequence-letter and
A subscript, indicating the number of double bonds.
3 double bonds
The EPA-derived prostanoids have ________________ (e.g., PGG3, PGH3, PGI3, TXA3)
5 double bonds
EPA-derived leukotrienes have _____________ (LTB5).
2 double bonds
AA-derived prostanoids have ___________ (e.g. PGG2, PGH2, PGI2, TXA2)
4 double bonds
AA-derived Leukotrienes have _________ (LTB4)
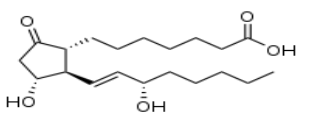
Prostaglandin E1 — The 5-member ring is characteristic of the class.
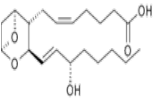
Thromoxane A2 — Oxygens moved into the ring
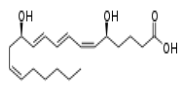
Leukotriene B4. — Note the 3 conjugated double bonds
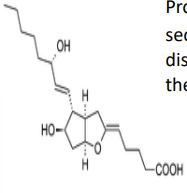
Prostacyclin I2 — The second ring distinguishes it from the prostaglandins.
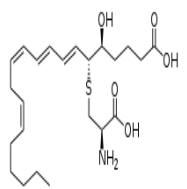
Leukotriene E4 — Example of a cysteine leukotriene
PGD2
promotion of sleep
PGE2
smooth muscle contraction; including pain, heat, fever; bronchoconstriction
PGE2α
Uterine contraction
PGI2
inhibition of platelet aggregation; vasodilation; embryo implantation
TXA2
stimulation of platelet aggregation; vasoconstriction
15d-PGj2
Adipocyte differentiation
LTB4
leukocyte chemotaxis
Cysteinyl-LTs
Anaphylaxis; bronchial smooth muscle contraction
Inflammation; immunity
Eicosanoids are mainly in ___________ or ____________
Central Nervous System
As messengers in the ___________________. They are found in most living things
hormones
In humans, eicosanoids are local ____________ that are released by most cells, act on that same cell or nearby cells (i.e., they are autocrine and paracrine mediators), and then are rapidly inactivated
short half-life
Eicosanoids have a __________, ranging from seconds to minutes
Dietary antioxidants
Inhibit the generation of some inflammatory eicosanoids, e.g. trans-resveratrol against thromboxane and some leukotrienes.
G protein-coupled receptor
Most eicosanoid receptors are members of the __________________ superfamily
Specific receptors of Leukotriene:
CysLT1 (Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor type 1)
CysLT2 (Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor type 2)
BLT1 (Leukotriene B4 receptor)
Specific receptors of Prostanoids:
PGD2: DP-(PGD2)
PGE2:
EP1-(PGE2)
EP2-(PGE2)
EP3-(PGE2)
EP4-(PGE2)
PGF2α: FP-(PGF2α)
PGI2 (prostacyclin): IP-(PGI2)
TXA2 (thromboxane): TP-(TXA2)
COX and LOX
Two families of enzymes catalyse fatty acid oxygenation to produce the eicosanoids
Cyclooxygenase (COX)
generates the prostanoids
Lipoxygenase (LOX)
in several forms
5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)
generates the leukotrienes and via trans cellular biosynthesis is also involved in lipoxin generation.
synthesized
Eicosanoids are NOT stored within cells, but are ______________ as required.
cell membrane; nuclear membrane
Eicosanoids are derived from the fatty acids that make up the _____________ and ______________
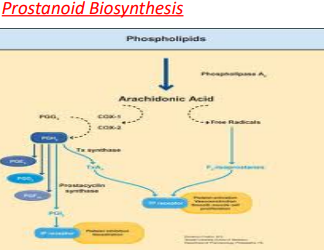
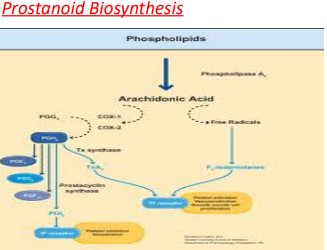
Eicosanoid biosynthesis
Begins when a cell is activated by mechanical trauma, cytokines, growth factors or other stimuli. (The stimulus may even be an eicosanoid from a neighboring cell; the pathways are complex.)
Phospholipase
Eicosanoid biosynthesis triggers the release of a _______________ at the cell membrane
travels to the nuclear membrane
Phospholipase A2
The phospholipase catalyses ester hydrolysis of phospholipid
Phospholipase C
The phospholipase catalyses ester hydrolysis of diacylglycerol
rate-determining step
Phospholipase frees a 20-carbon fatty acid. This hydrolysis appears to be the ______________________ for eicosanoid formation.
Phospholipase A2 ( cPLA2)
The fatty acids may be released by any of several phospholipases.
Of these, type IV cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) is the key actor
As cells lacking cPLA2 are, in general, devoid of eicosanoid synthesis.
SN2
phospholipase cPLA2 is specific for phospholipids that contain AA, EPA or GPLA at the ______ position
Platelet-activating factor
cPLA2 may also release the lysophospholipid that becomes ____________________
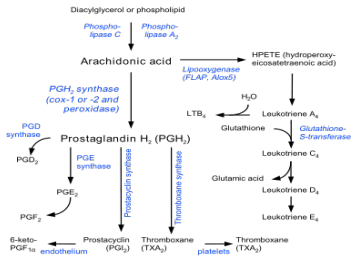
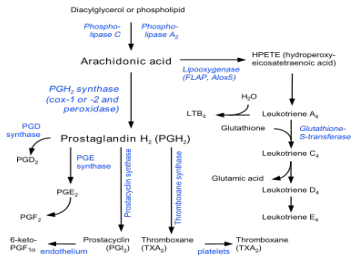
Peroxidation and reactive oxygen species
The free fatty acid is oxygenated along any of several pathways
The eicosanoid pathways (via lipoxygenase or COX) add molecular oxygen (O2)
chiral
Although the fatty acid is symmetric, the resulting eicosanoids are _______
Stereoselectivity
The oxidations proceed with high _____________ (enzymatic oxidations are considered practically stereospecific)
hazardous
The oxidation of lipids is _______________ to cells, particularly when close to the nucleus.
Reactive O2 notes
There are elaborate mechanisms to prevent unwanted oxidation.
COX, the lipoxygenases and the phospholipases are tightly controlled
Isoforms
There are at least eight proteins activated to coordinate generation of Leukotrienes. Several of these exist in multiple __________
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Oxidation by either COX or lipoxygenase releases _______________________ and the initial products in eicosanoid generation are themselves highly reactive peroxides
adducts
LTA4 can form _________ with tissue DNA.
Cellular damage
Other reactions of lipoxygenases generate ____________
atherosclerosis
Rat(murine) model studies have shown to implicate 15-lipoxygenase in the pathogenesis of
compartmentalized
The oxidation in eicosanoid generation is ___________; this limits the peroxides' damage.
DNA; protein
In biology, an adduct is a complex that forms when a chemical binds to a biological molecule, such as ________ or ________
exposure to carcinogens
DNA adducts are altered forms of DNA that occur as the result of ____________________ (in the case of smokers these would be the carcinogens present in cigarette smoke)
DNA adduct
once formed, can be repaired, resulting in a return to the original DNA structure or be mis-repaired, resulting in a mutation.
Protein adduct
DO NOT have adverse biological effects but can be used as a measure of exposure to a foreign substance
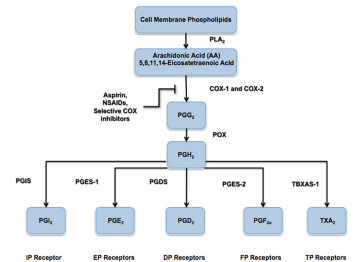
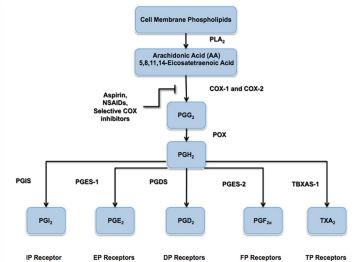
detoxification of ROS
The enzymes that are biosynthetic for eicosanoids -- e.g., glutathione-S-transferases, epoxide hydrolases, and carrier proteins belong to families whose functions are involved largely with cellular detoxification.
This suggests that eicosanoid signalling might have evolved from the ________________