AP Cellular Respiration
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
quizlet: https://quizlet.com/965594126/ap-cellular-respiration-flash-cards/?i=3xfdzz&x=1jqt
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
start of cell res
glucose (C6H12O6)
4 steps of cell res
1. Glycolysis
2. Pyruvate oxidation
3. CAC
4. Oxidative Phosphorylation
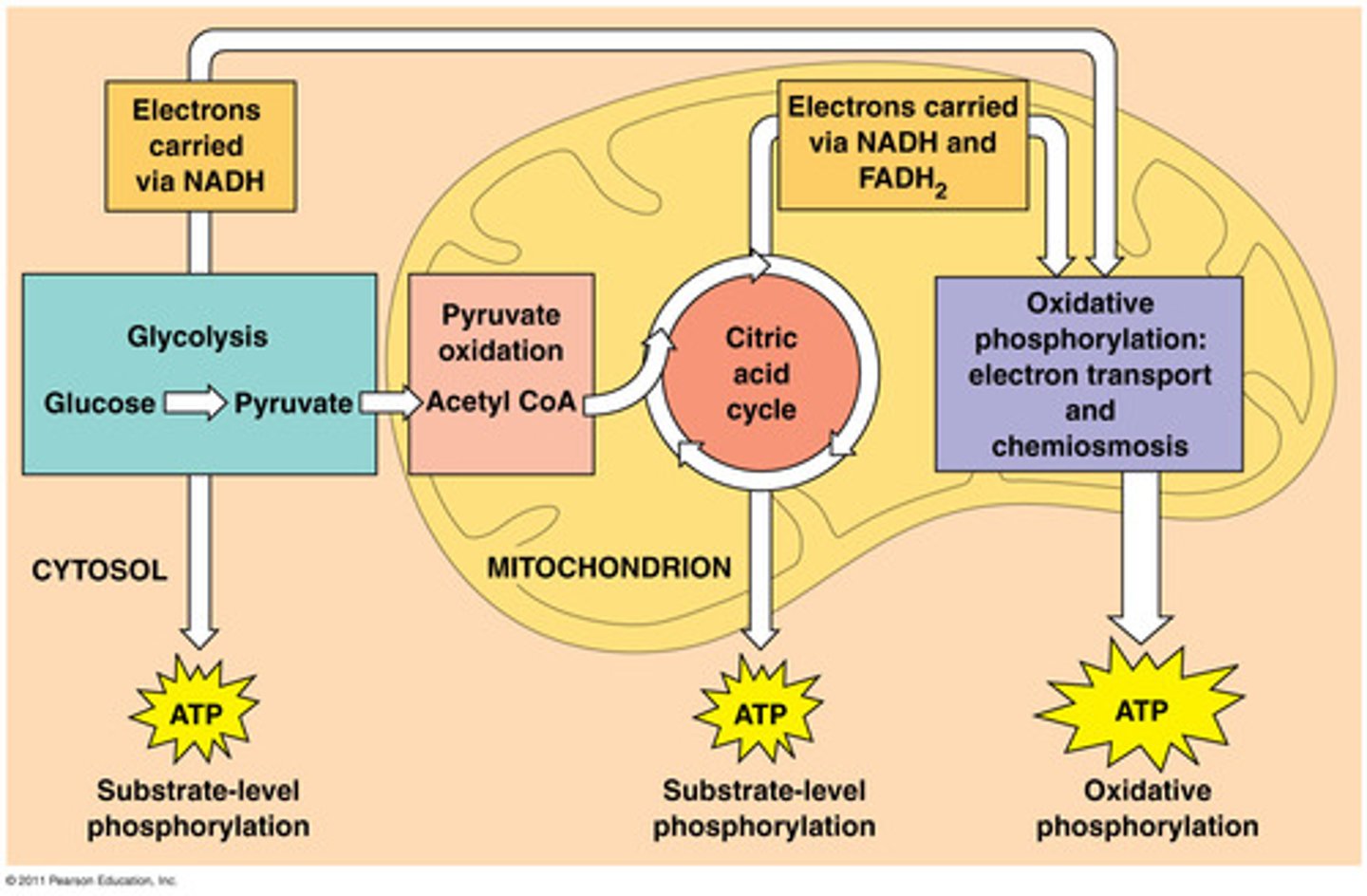
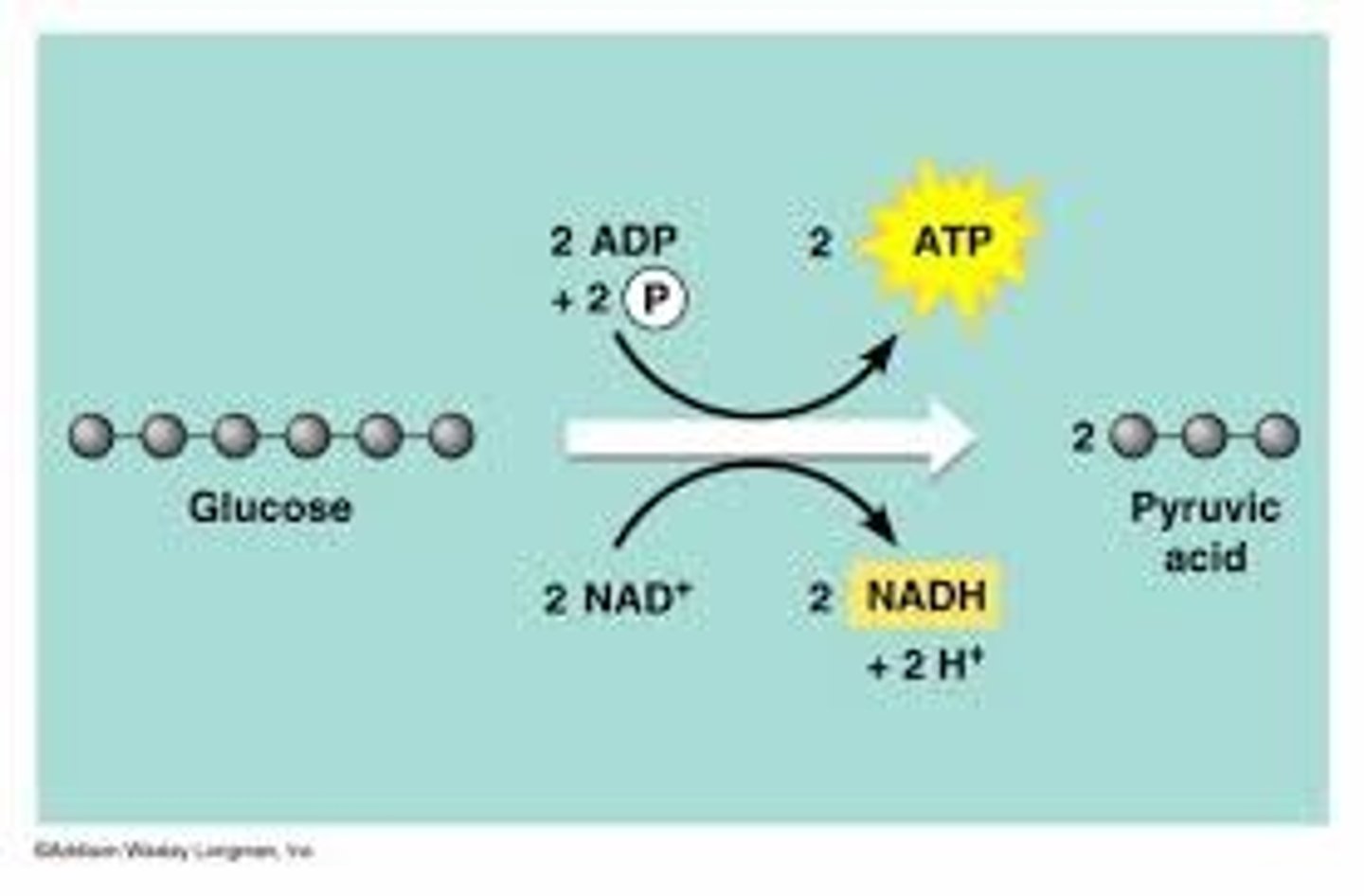
What happens to glucose during glycolysis?
C6H12O6 -> Pyruvate in the cytoplasm
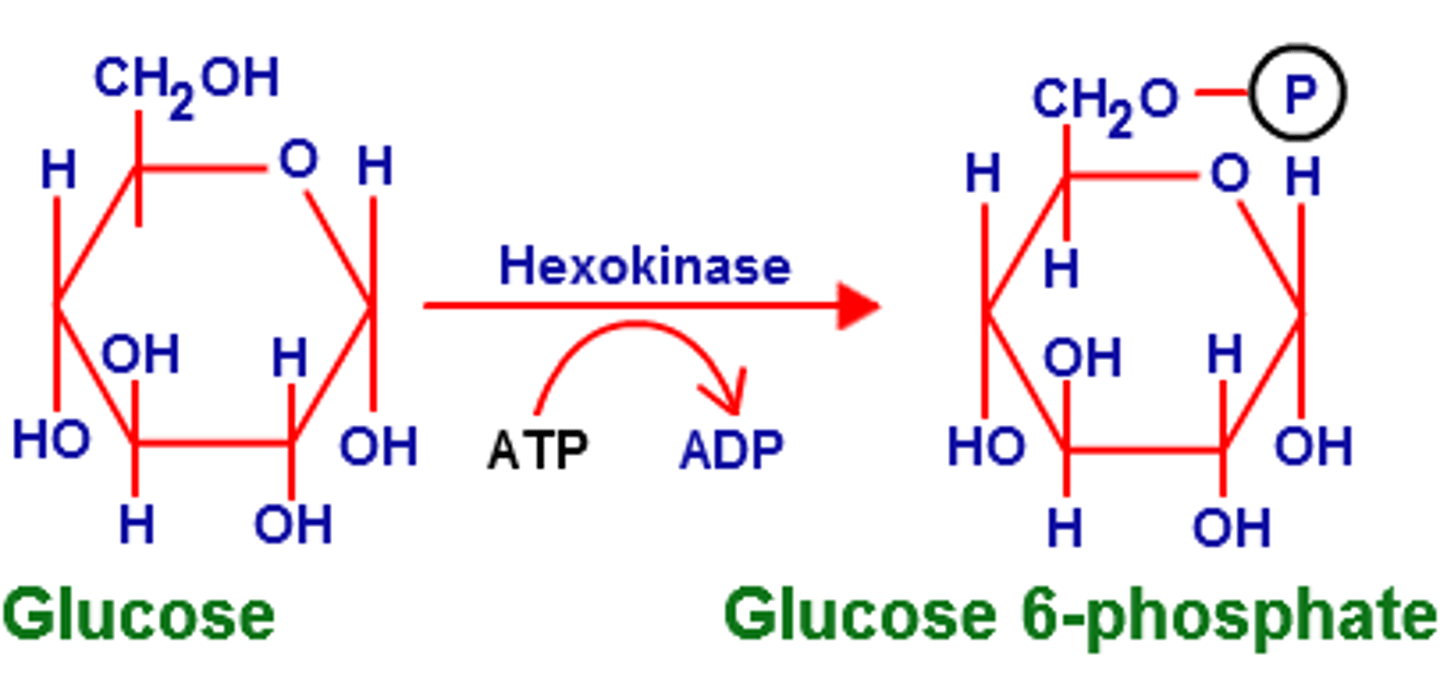
Hexokinase
turns glucose into glucose-6-phosphate by phosphorylating it
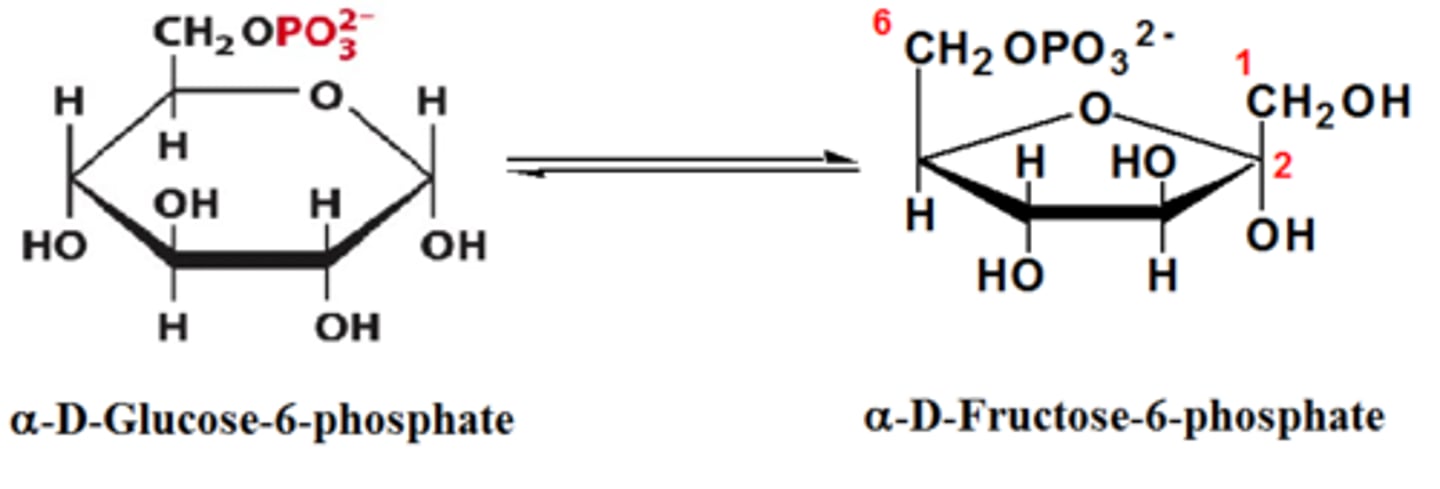
Phosphoglucoisomerase
turns glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate
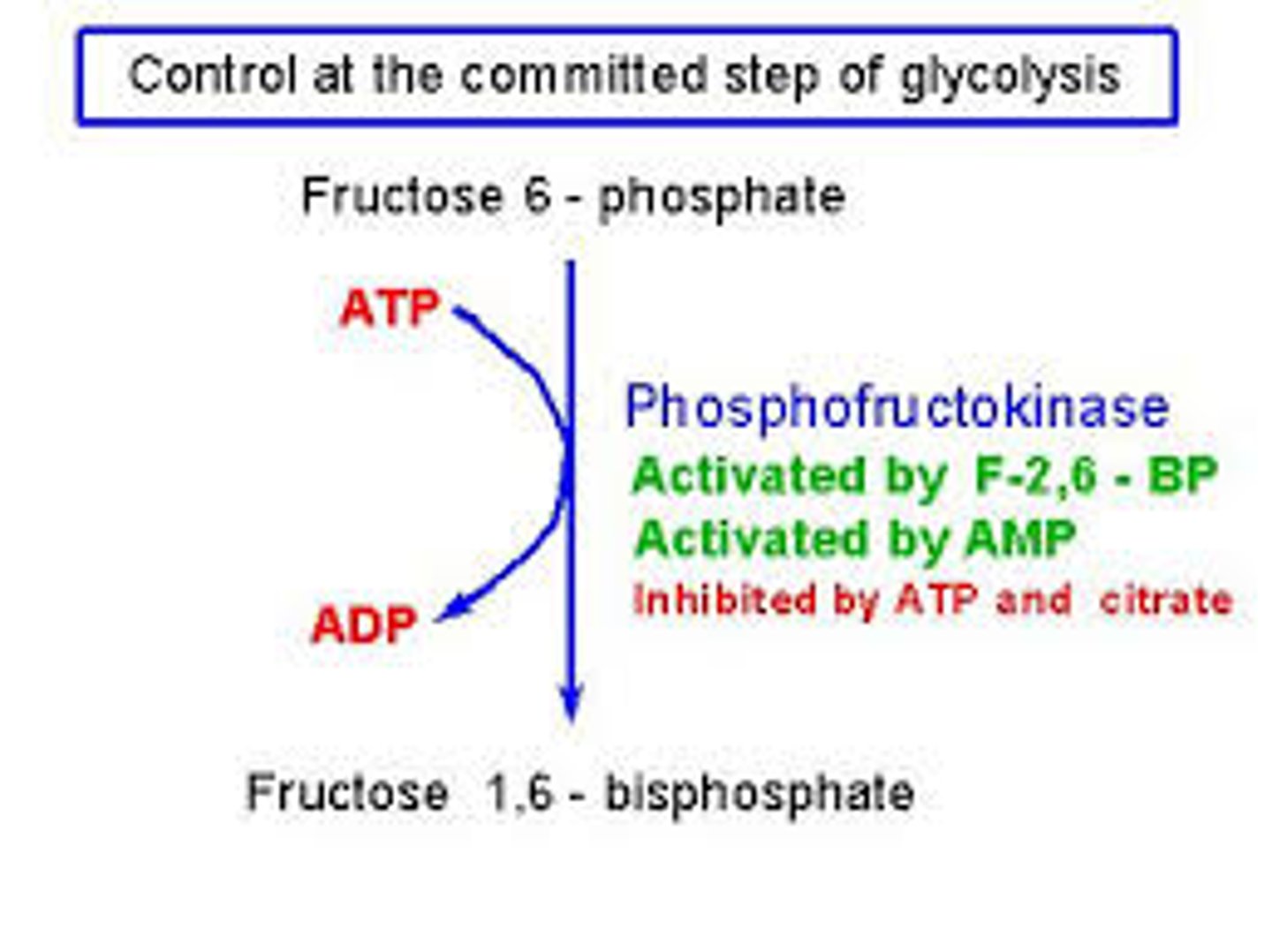
Phosphofructokinase
turns fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by phosphorylating it
Aldolase
splits fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into 2 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
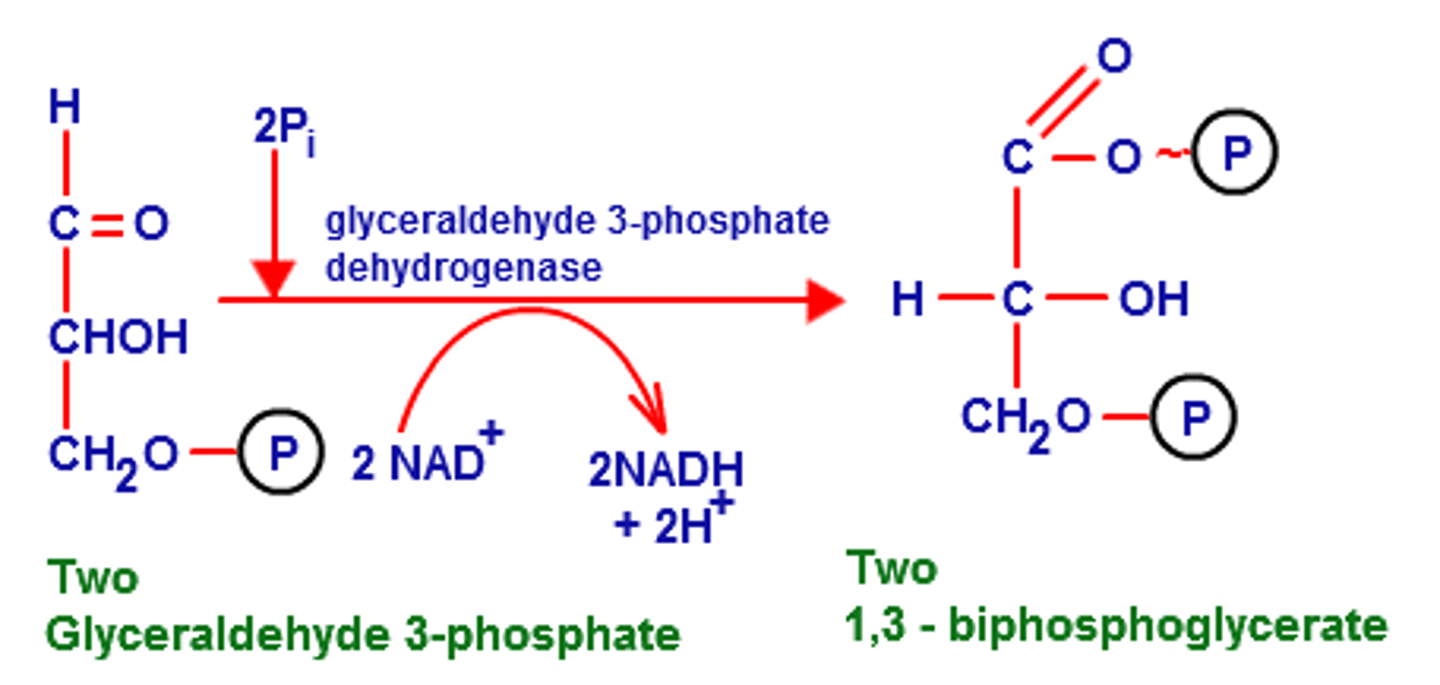
Triose Phosphate Dehydrogenase
oxidizes G3P, turning it to 1,3-bisphotoglycerate and allowing NAD+ to join with a p+ by reducing it w/ 2 e- (happens 2x)
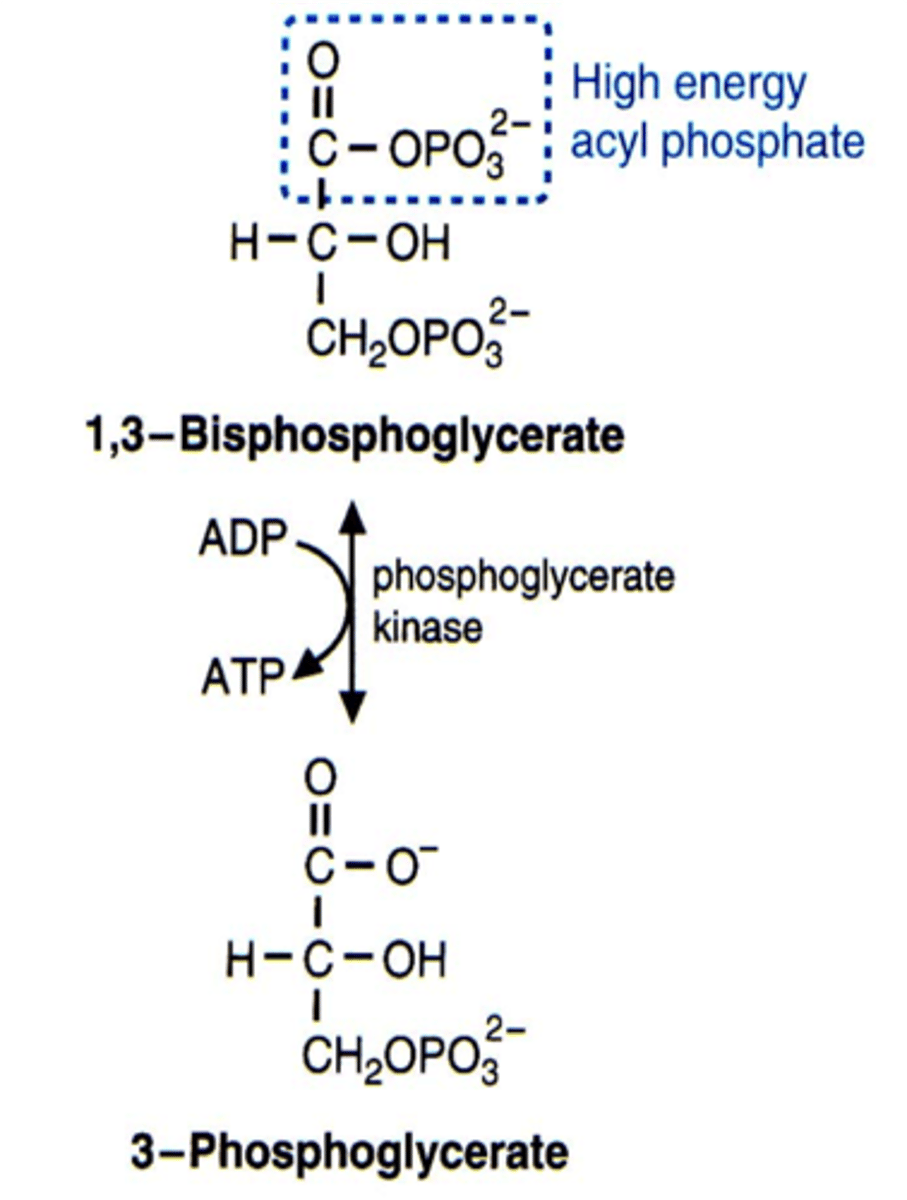
phosphoglycerakinase
turns 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate, generating the first ATP through substrate-lvl dephosphorylation (happens 2x)
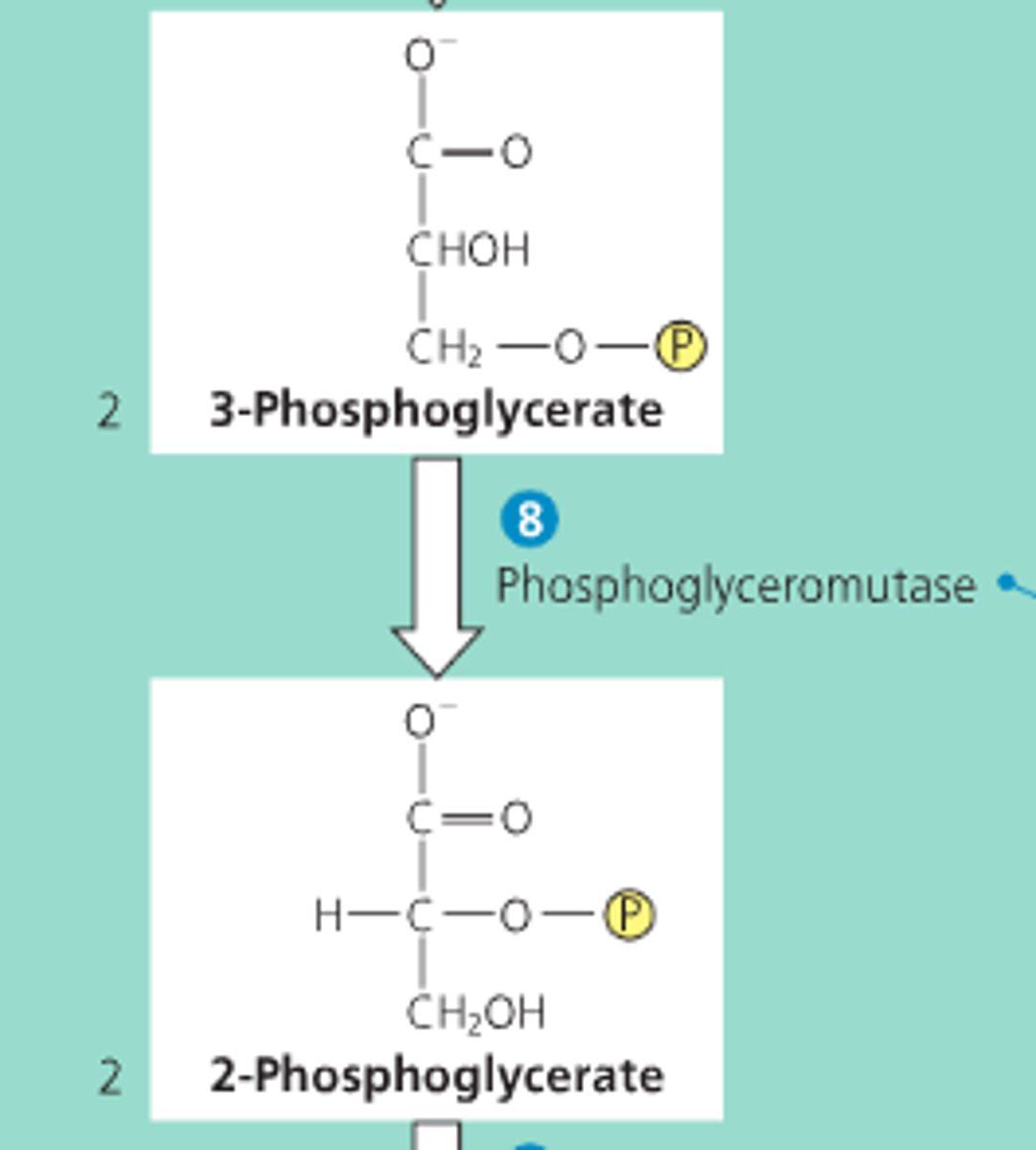
Phosphoglyceromutase
turns 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate (happens 2x)
Enolase
turns 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) (happens 2x)
Pyruvate Kinase
turns PEP to pyruvate (happens 2x)
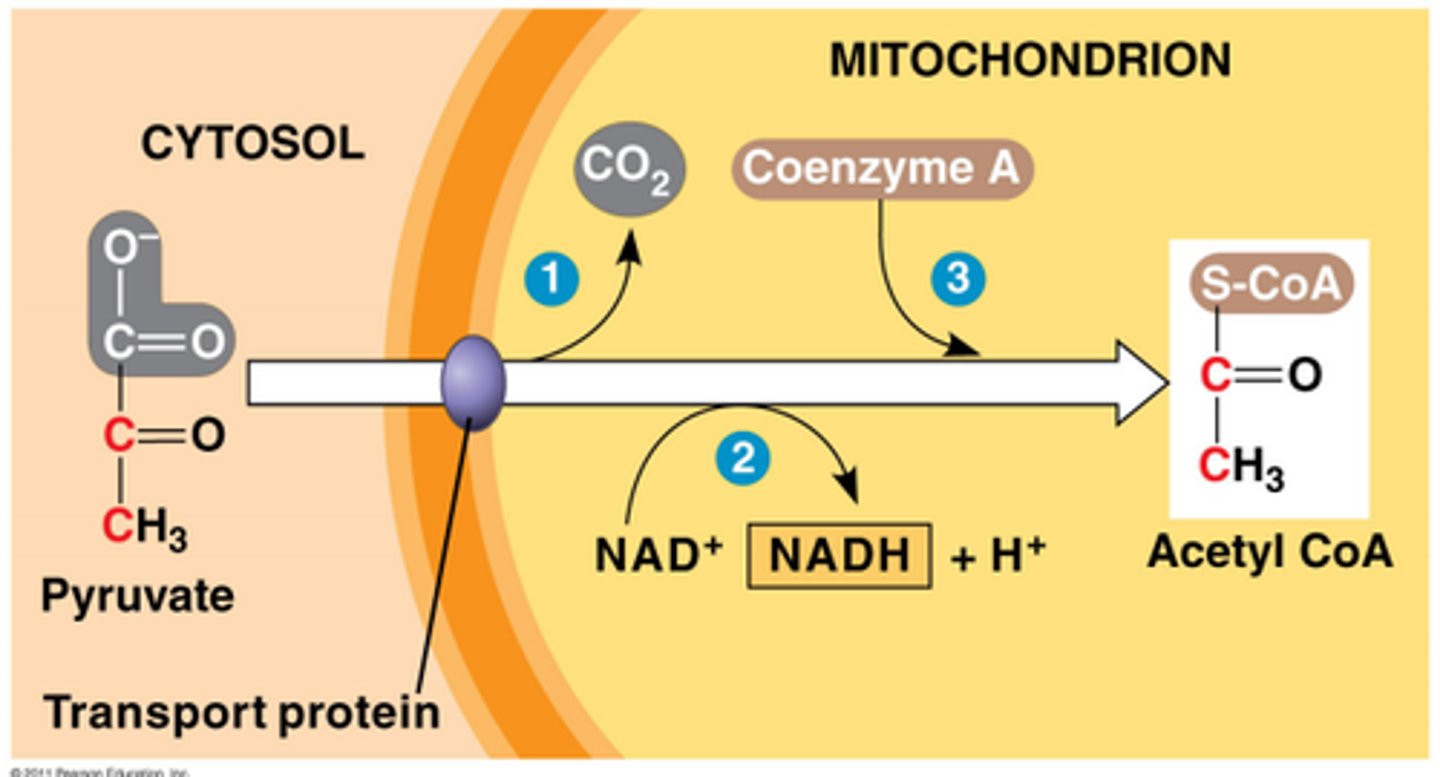
What happens during pyruvate oxidation?
Pyruvate -> Acetyl CoA (cytoplasm -> matrix)
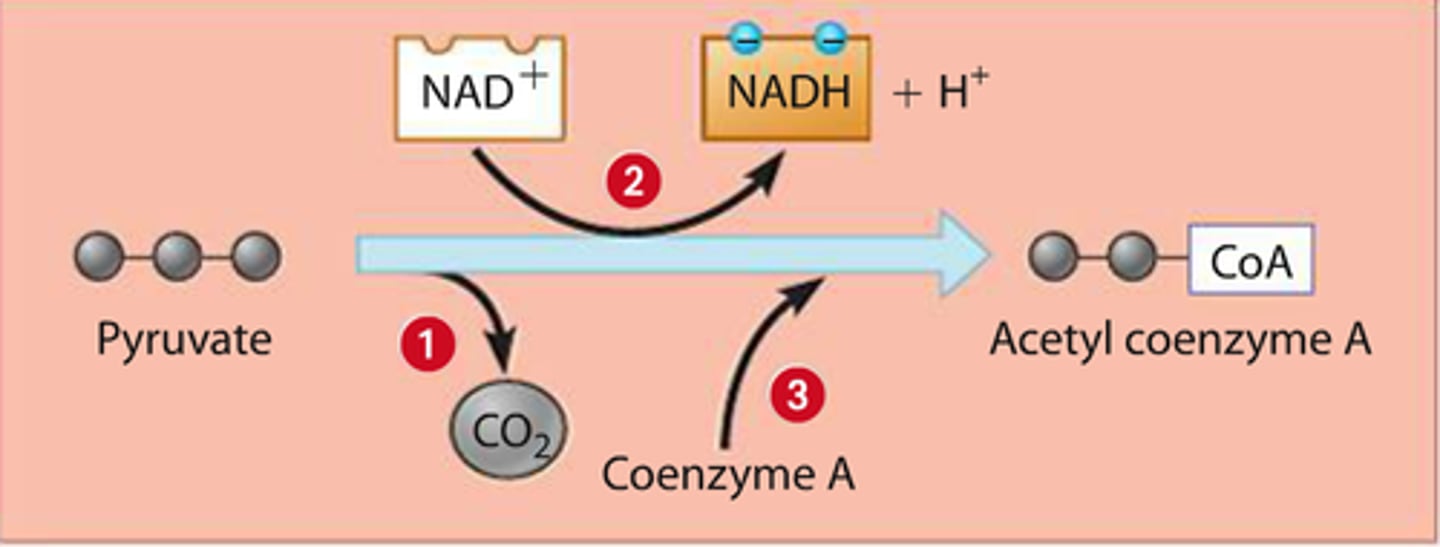
Coenzyme A
oxidizes pyruvate and removes CO2, turning it into acetyl CoA and allowing NAD+ to join with a p+ by reducing it w/ 2 e (happens 2x)
the first 2 of the 6 of glucose molecules leave the cell at this point (humans and other animals exhale CO2)
What happens in the CAC?
the remaining carbons in pyruvate are released as CO2 (matrix)
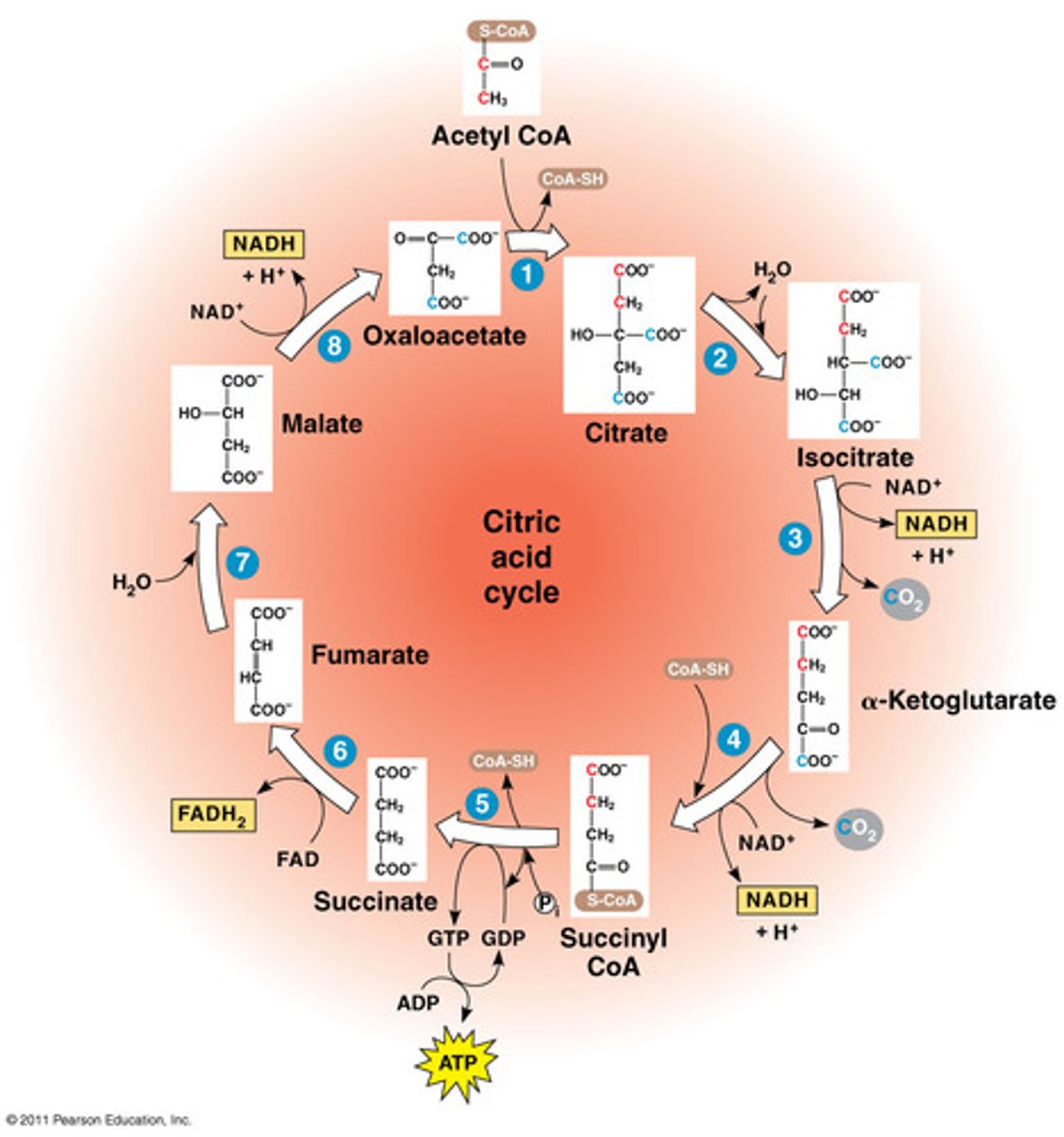
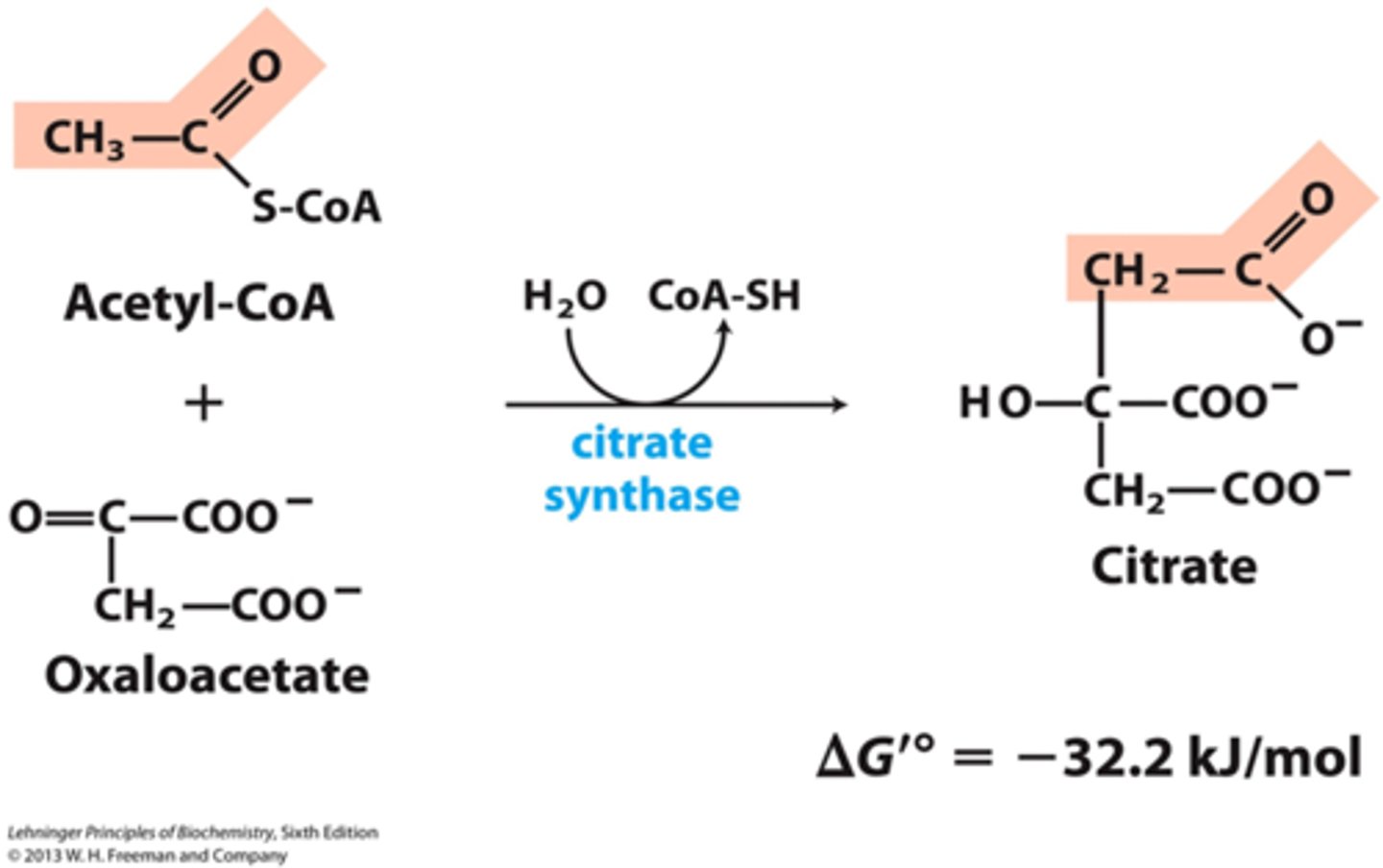
CAC Step 1: Acetyl CoA -> ?
An enzyme removes CoA from Acetyl CoA and the remaining
2 C + Oxaloacetate (4 C) -> Citrate (6 C) (happens 2x)
CAC Step 2: Citrate -> ?
Another enzyme comes and oxidizes the citrate, turning it into α-ketoglutarate (5 C)
2 e- are released, so (NAD+) + 2(e-) + (H+) = NADH
CO2 also exits the cycle
(all happens 2x)
at this point, 4 of the og 6 carbons are gone
CAC Step 3: α-ketoglutarate -> ?
α-ketoglutarate turns into succinate (4 C) after:
- it's dephosphorylated
- CO2 is removed
- it's oxidized, giving 2 e- to NAD+ to make NADH
(happens 2x)
now all of the original glucose carbons have been released into the wild, unfortunately kind of (barely, ik, don't yell at me) contributing to the number of greenhouse gases in the air which is making Halloween 80 degrees instead of the normal 40-50, October have no rainfall in NJ, and November have 70 degree weather days and all people can think about is politics and G3P. help. its 930 and my brain checked out on sep 5
CAC Step 4: Succinate -> ?
succinate turns into malate (4 C) after being dephosphorylated again, this time turning FAD+ to FADH by donating 2 e- (happens 2x)
CAC Step 5: Malate -> ?
malate turns into oxaloacetate again (this is why it's called a cycle) after it is oxidized one more time (reduce NAD+ -> NADH)
What happens during oxidative phosphorylation?
make ATP (ETC & ATP synthase) on the cristae
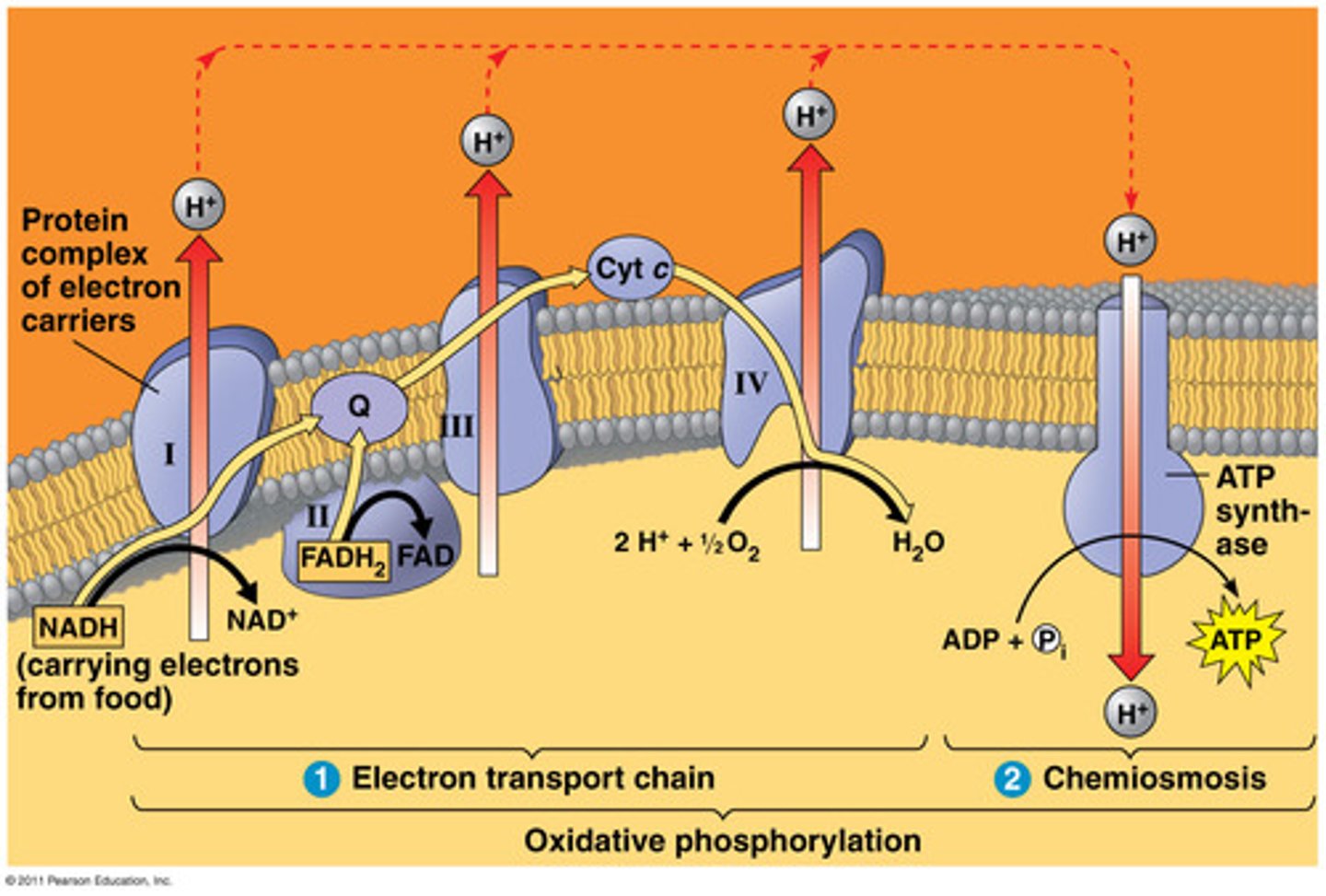
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
10 NADH & 2 FADH drop off their e- (2x10+2x2=24totalithink-usepemdas) to the ETC. As the e- pass thru, they attract H+, which go toward the e-. The e- pass thru the ETC and merge w/ molecular oxygen, which splits in half and takes up H+ to form H2O (which can go thru the lipid bilayer). The attracted H+ go thru the proteins that make up the ETC from the inner membrane space to the intermembrane space.
Chemiosmosis
The increased concentration gradient of H+ in the intermembrane space forces them to find a transport protein that will fit them because ions can't pass through the plasma membrane. ATP synthase allows the H+ to pass thru, which make the protein spin, creating rotational energy that is used to put ADP & P together to make ATP.
How much ATP is produced total?
answer is disputed, but generally 32-38
(net) 2 from glycolysis
2 from CAC
the rest from oxidative phosphorylation