Chapter 17: Classification
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

21 Terms
Classification
The grouping of organisms based on common traits.
Taxonomy
SCIENCE OF CLASSIFICATION; IN BIOLOGY, THE PROCESS OF CLASSIFYING ORGANISMS IN CATEGORIES
Taxa
Categories used to group organisms with shared characteristics.
Carolus Linnaeus
Father of Taxonomy

Binomial Nomenclature
"Two-name naming system" Linnaeus's Classification system in which each species is assigned a two-part scientific name....Genus and species
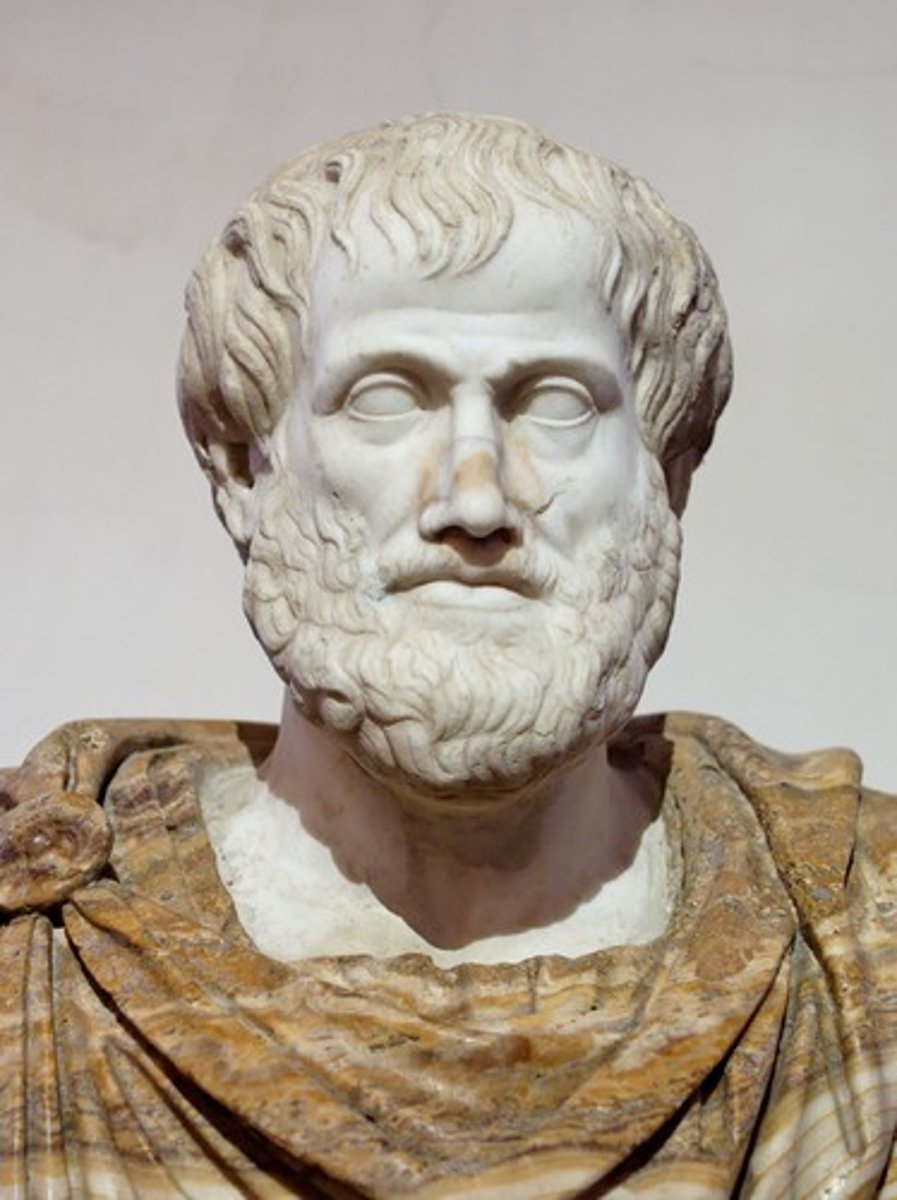
Aristotle
Designed the first classification system which divided living things into two categories: plants and animals.

Kingdom
Broken down into 6 - 4 have a nucleus and 2 do not. Plant, animal, protist, fungi, archaebacteria, eubacteria

Eubacteria
Kingdom of common unicellular prokaryotes. Cell walls contain peptidoglycan.
Archaebacteria
Kingdom of unicellular that live in extremely harsh environments

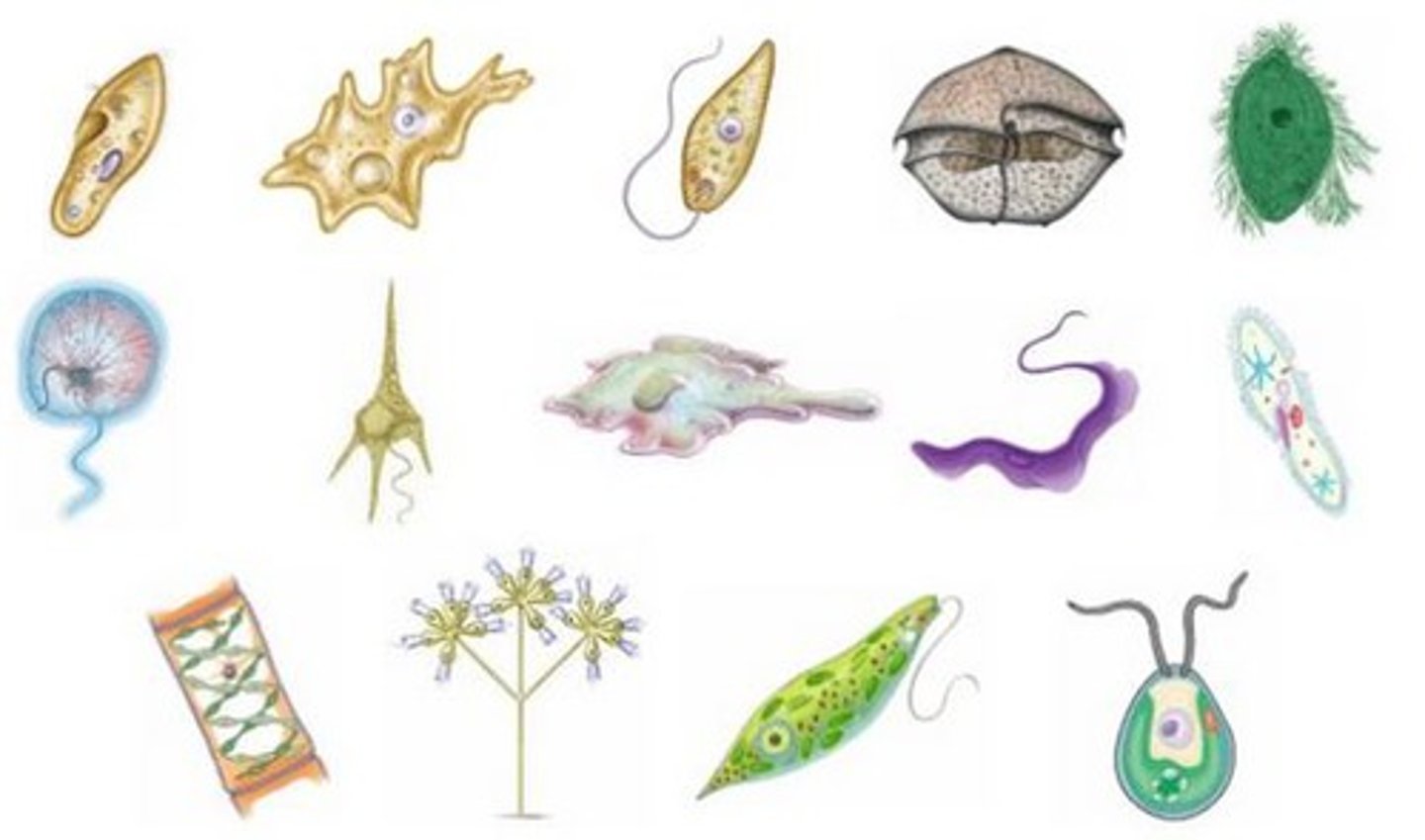
Protista
Kingdom composed of eukaryotes that are not classified as plants, animals, or fungi

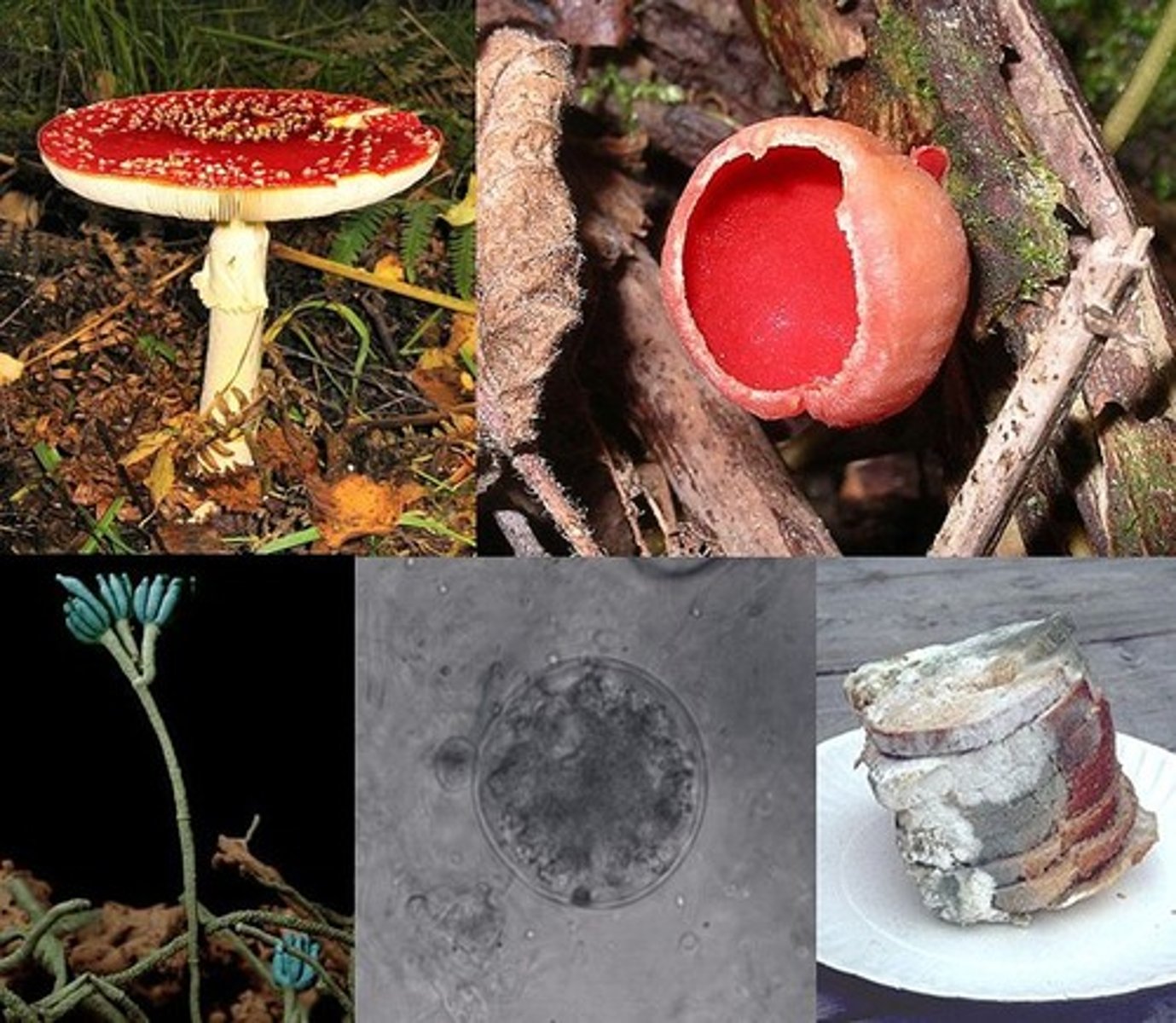
Fungi
A kingdom made up of eukaryotic organisms that cannot move, have cell walls made of chitin and get food by absorbing the nutrients

Plantae
Kingdom of multicellular photosynthetic autotrophs that have cell walls made of cellulose

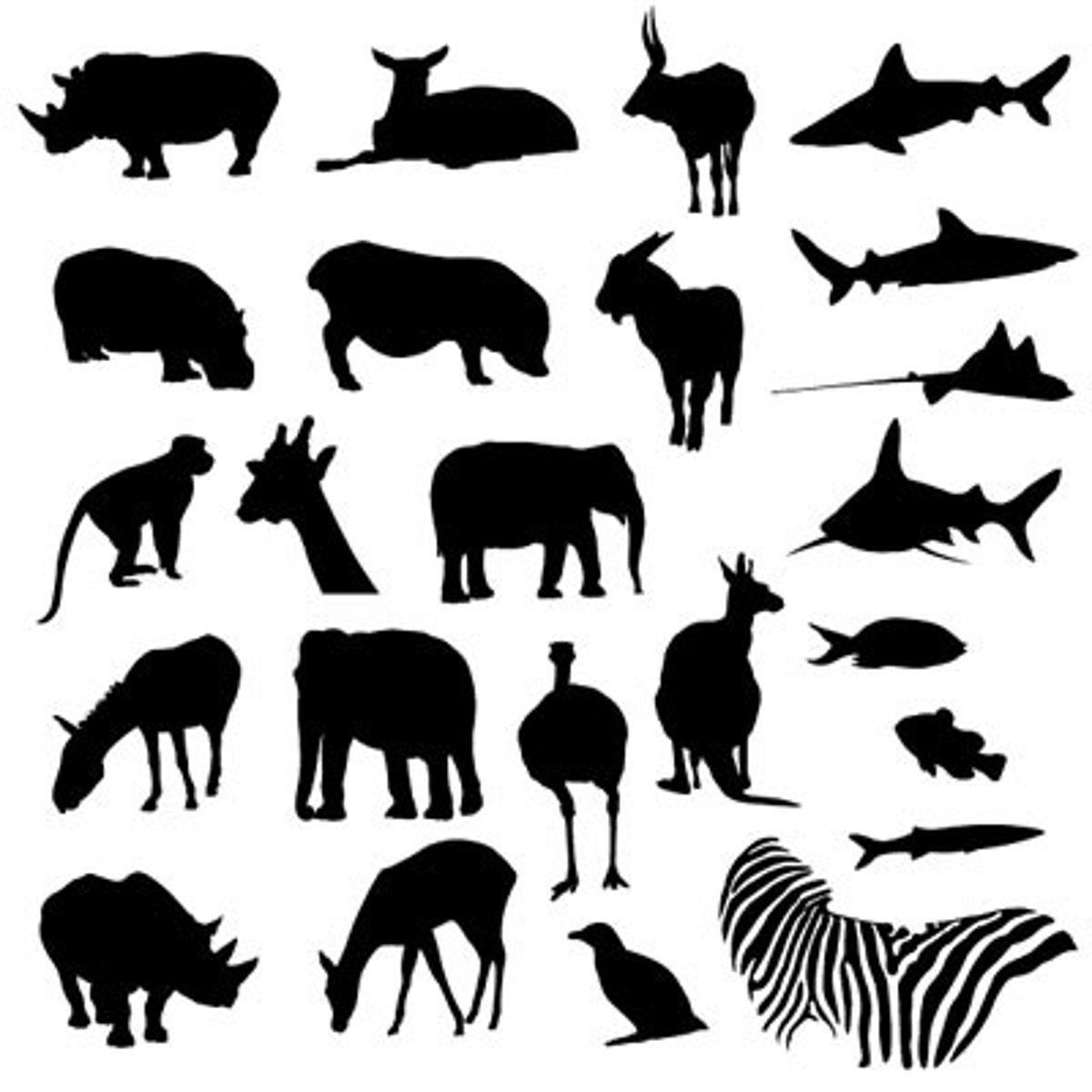
Animalia
A kingdom made up multicellular organisms with no cell walls, can usually move around, and quickly respond to their environment.

Chordata
phylum with a backbone

Species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.

Derived Trait
Newly evolved features that don't appear in fossils of common ancestors
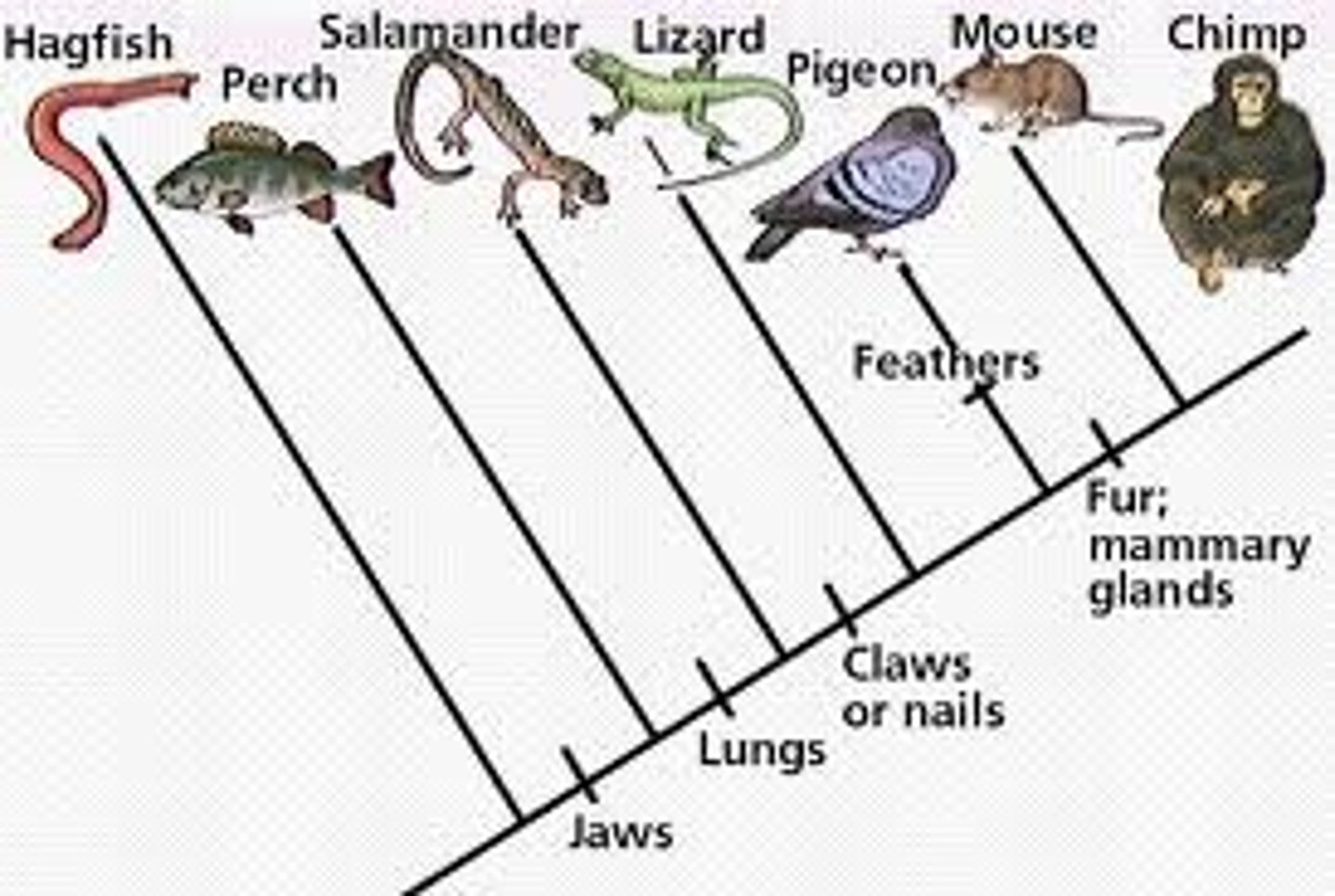
Ancestral Trait
A trait shared by all members of a group through a common ancestor.
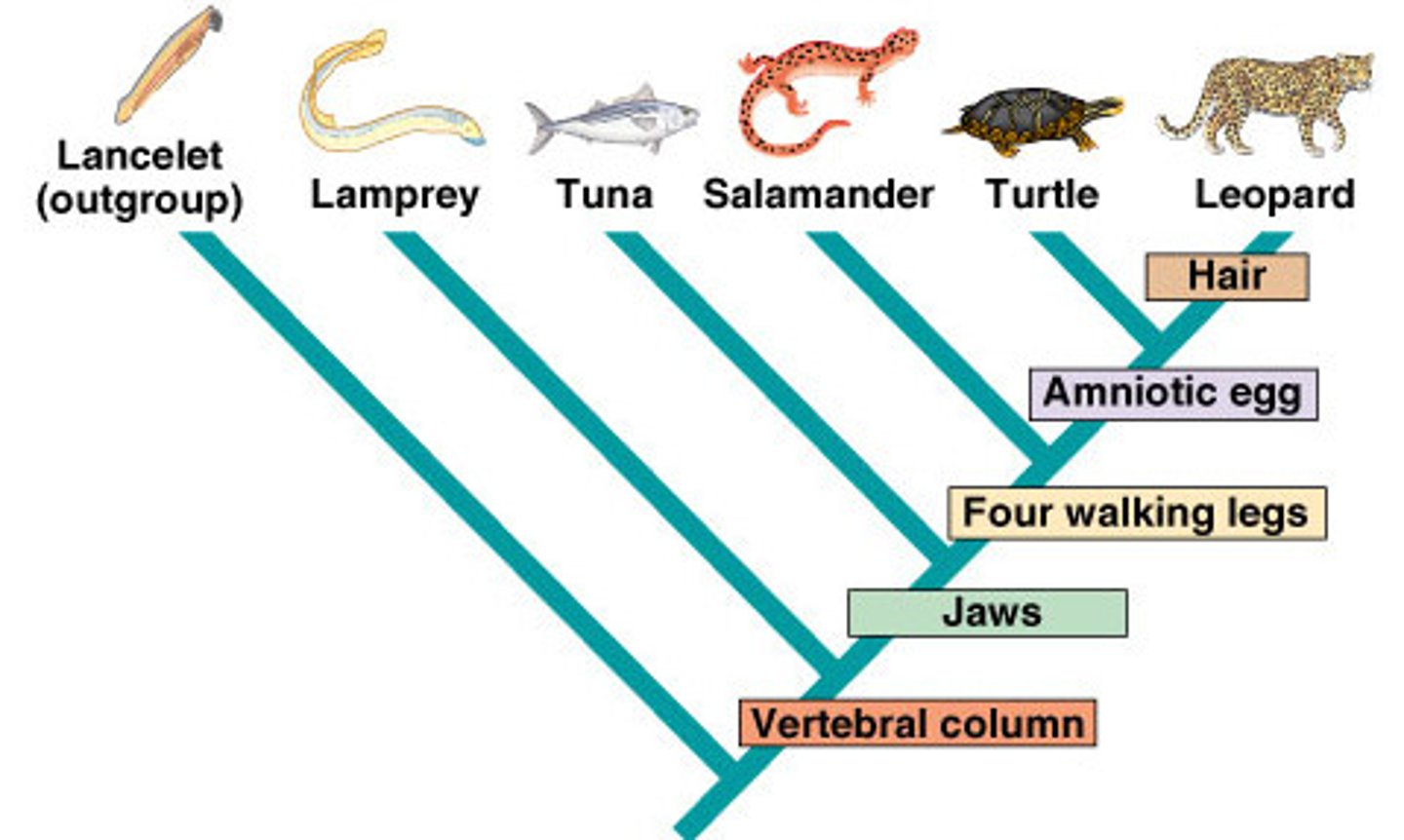
Cladogram
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms
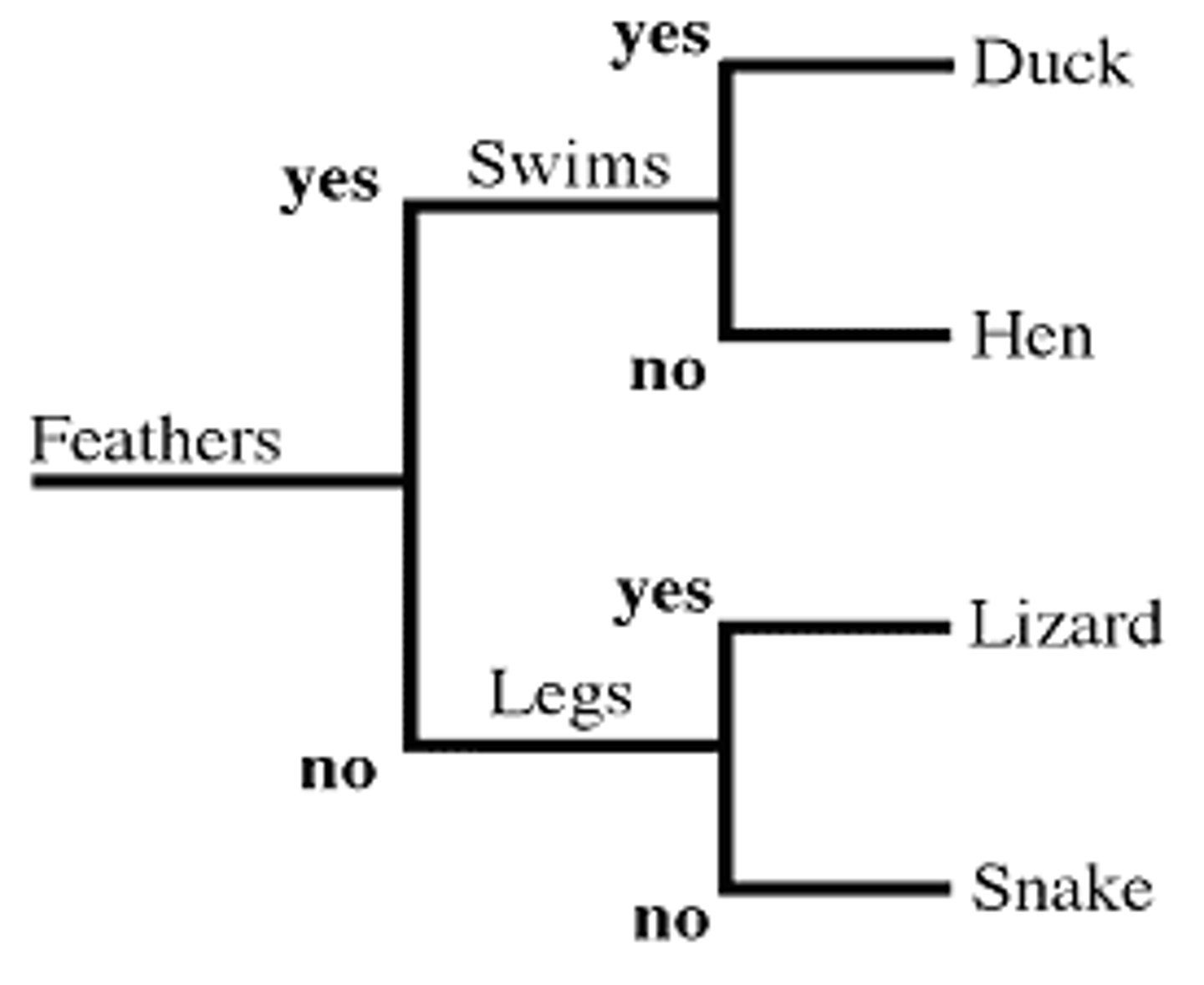
Dichotomous Key
A tool used to identify organisms based on a series of choices
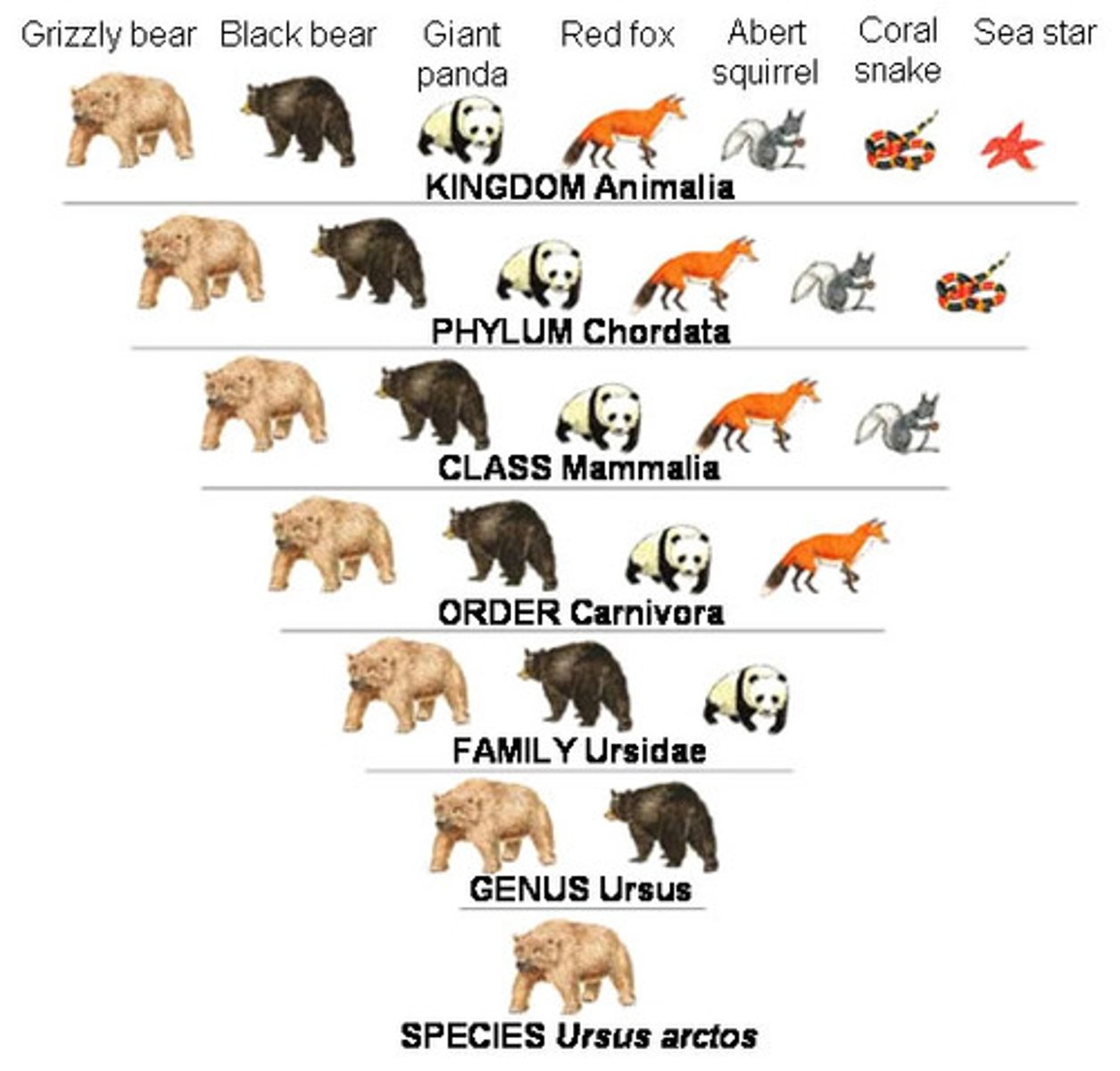
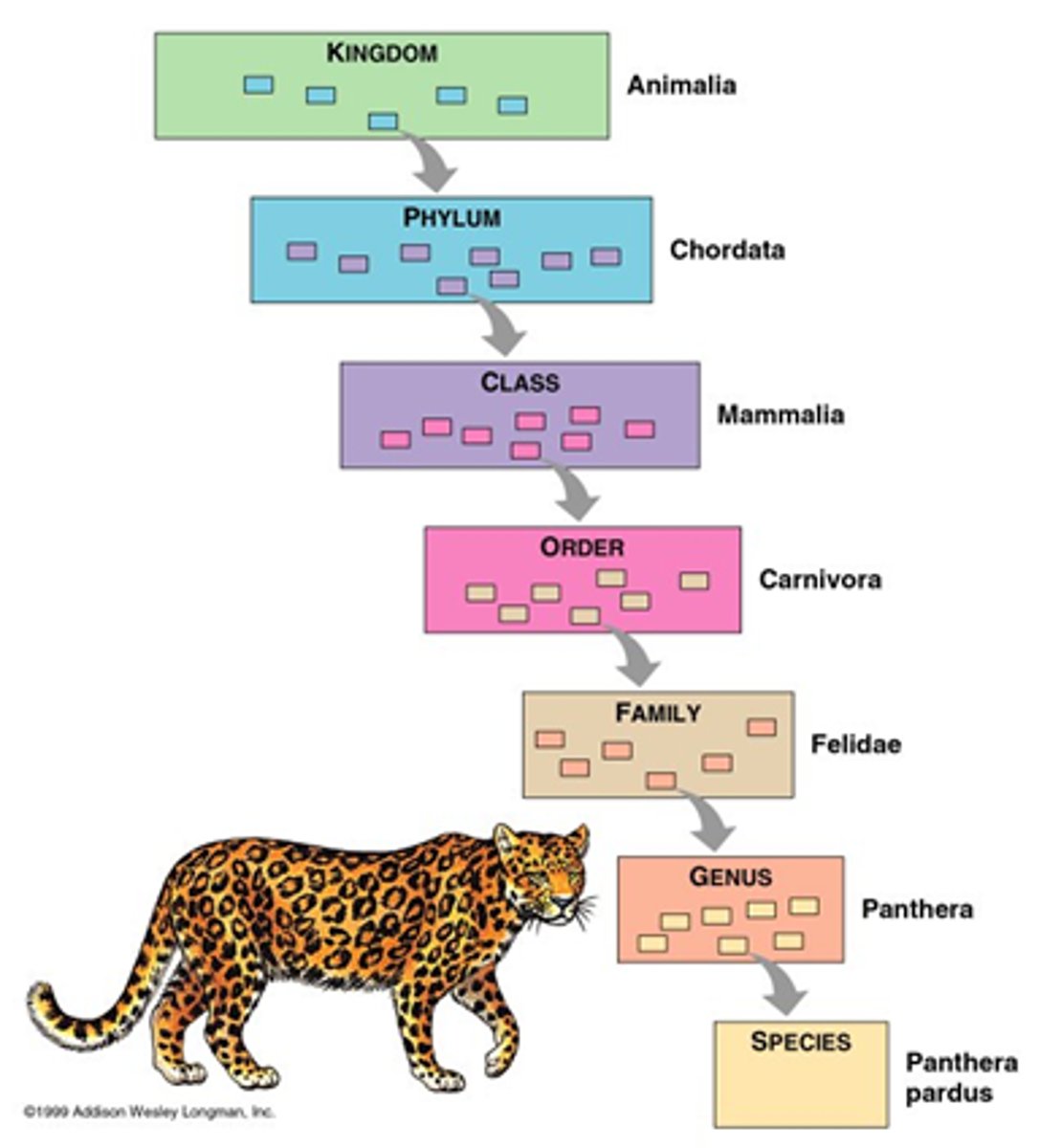
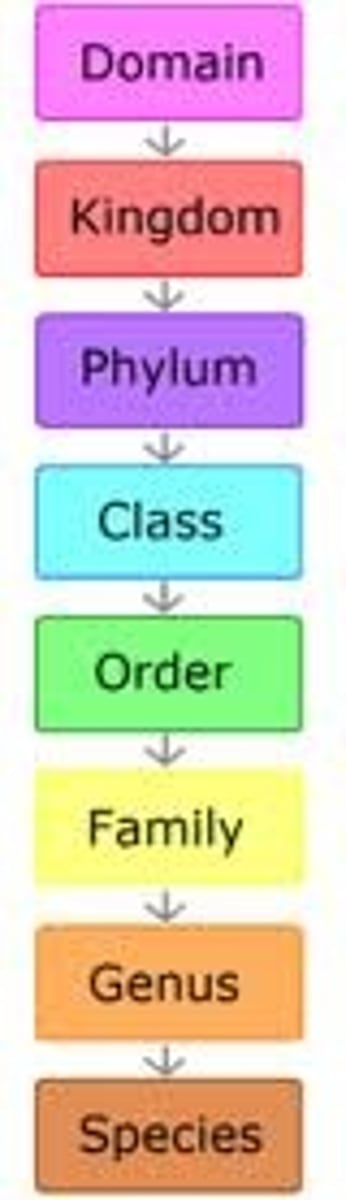
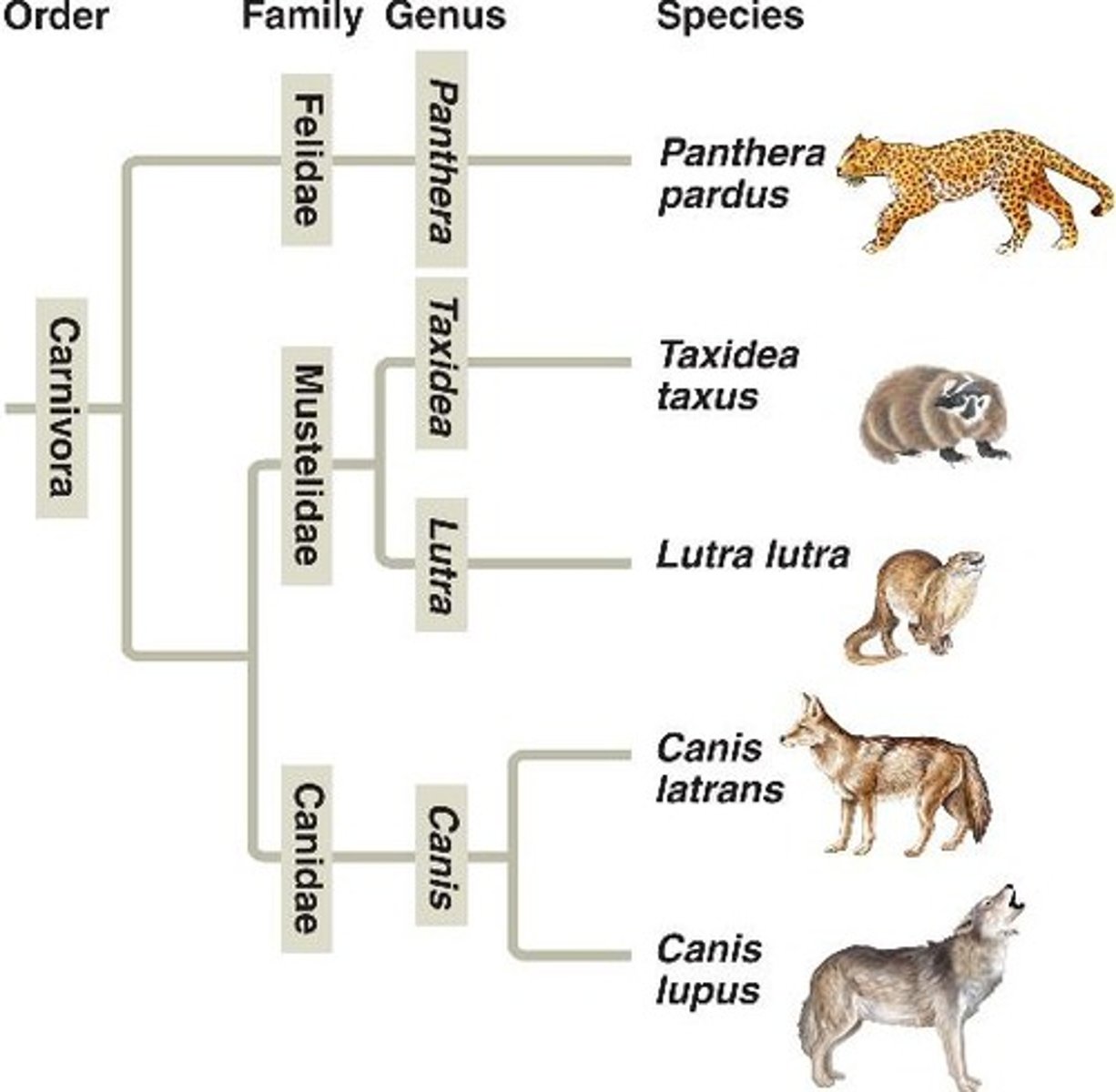
KPCOFGS
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Domain
A taxonomic category above the kingdom level. The three domains are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.