Pediatric Musculoskeletal Disorders: Classification, Treatment, and Nursing Care
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What are red-flag musculoskeletal emergencies?
Fractures, traction, compartment syndrome
What are key pediatric deformities?
Clubfoot, Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH), scoliosis
What is osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)?
A congenital genetic disorder characterized by fragile bones that break easily
What is the treatment for juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)?
Medication and home care instructions
What are the major physiologic effects of immobility?
Decreased muscle strength/mass, bone demineralization, cardiovascular issues, respiratory complications, and increased risk for pressure injuries
What does the acronym RICE stand for in soft-tissue injury management?
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
What is a common cause of shoulder dislocation?
Falling on an outstretched arm or excessive overhead activity
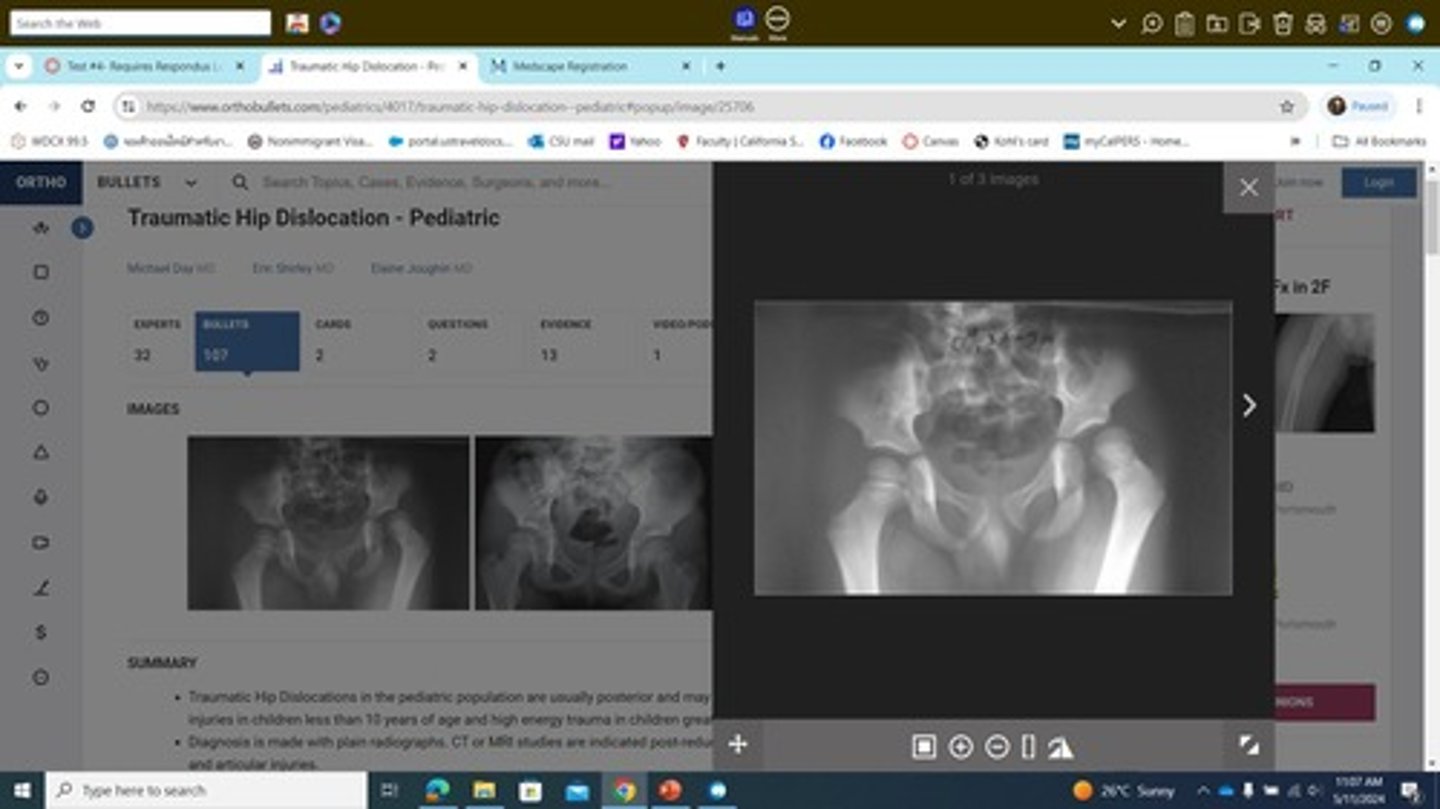
What is the treatment for a hip dislocation?
Closed reduction under general anesthesia and sedation within 60 minutes of injury
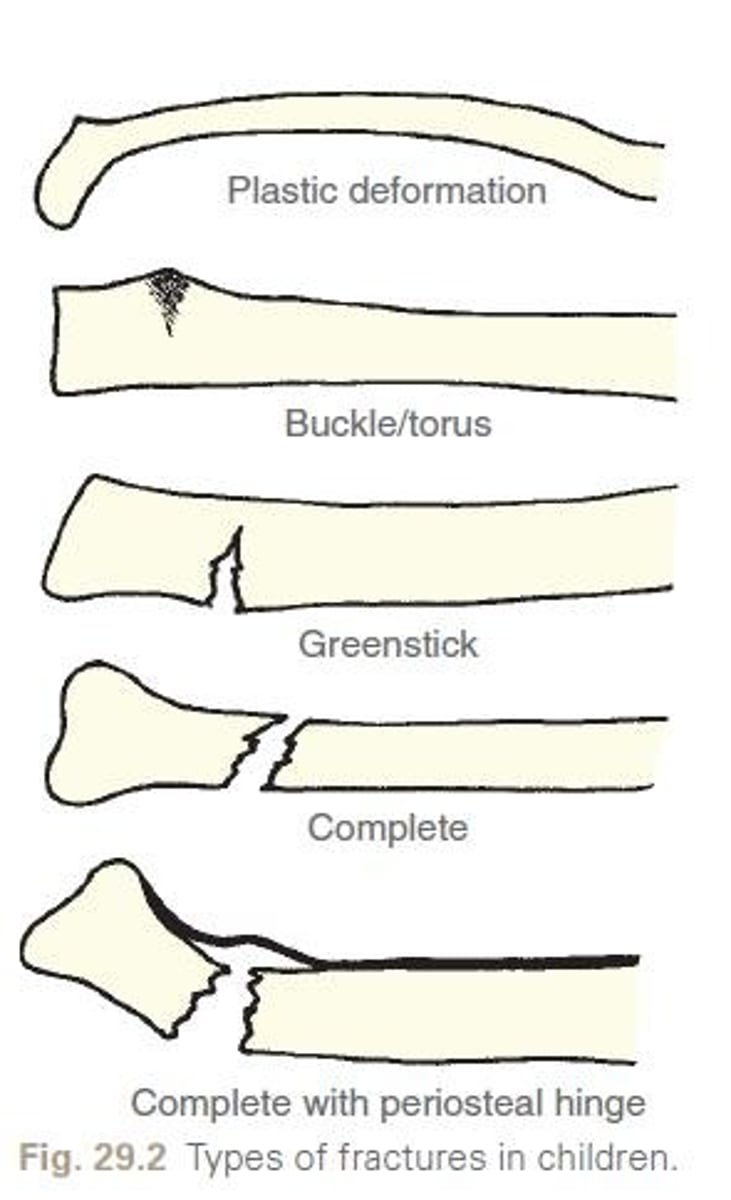
What are the characteristics of pediatric fractures?
Bones are more porous and flexible, growth plates are vulnerable, and they have a thick periosteum for rapid healing
What is a greenstick fracture?
A fracture where one side of the bone breaks and the other side bends
What are the signs of a sprain?
Rapid swelling, joint instability, and a 'pop' sound may be heard
What is Nursemaid's Elbow?
Radial head subluxation caused by sudden traction on an extended, pronated arm
What are the signs of a dislocation?
Severe pain, swelling, joint deformity, and inability to move the joint
What is the management for soft-tissue injuries?
RICE principles: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
What is the sequence of treatment for clubfoot?
Initial manipulation and casting, followed by possible surgical intervention if necessary
What is the impact of immobility on psychosocial development in children?
Can lead to boredom, sensory deprivation, regression, anger, withdrawal, and depression
What are the signs of compartment syndrome?
Severe pain, swelling, and decreased sensation or movement in the affected limb
What is the purpose of a hip spica cast?
To immobilize the hip joint in children under 10 years after dislocation
What are the common causes of fractures in pediatric patients?
Falls, sports injuries, and accidents
What is the treatment for osteomyelitis?
Antibiotic therapy and possibly surgical intervention
What is the role of physical therapy in shoulder dislocation recovery?
To strengthen shoulder muscles and improve joint stability
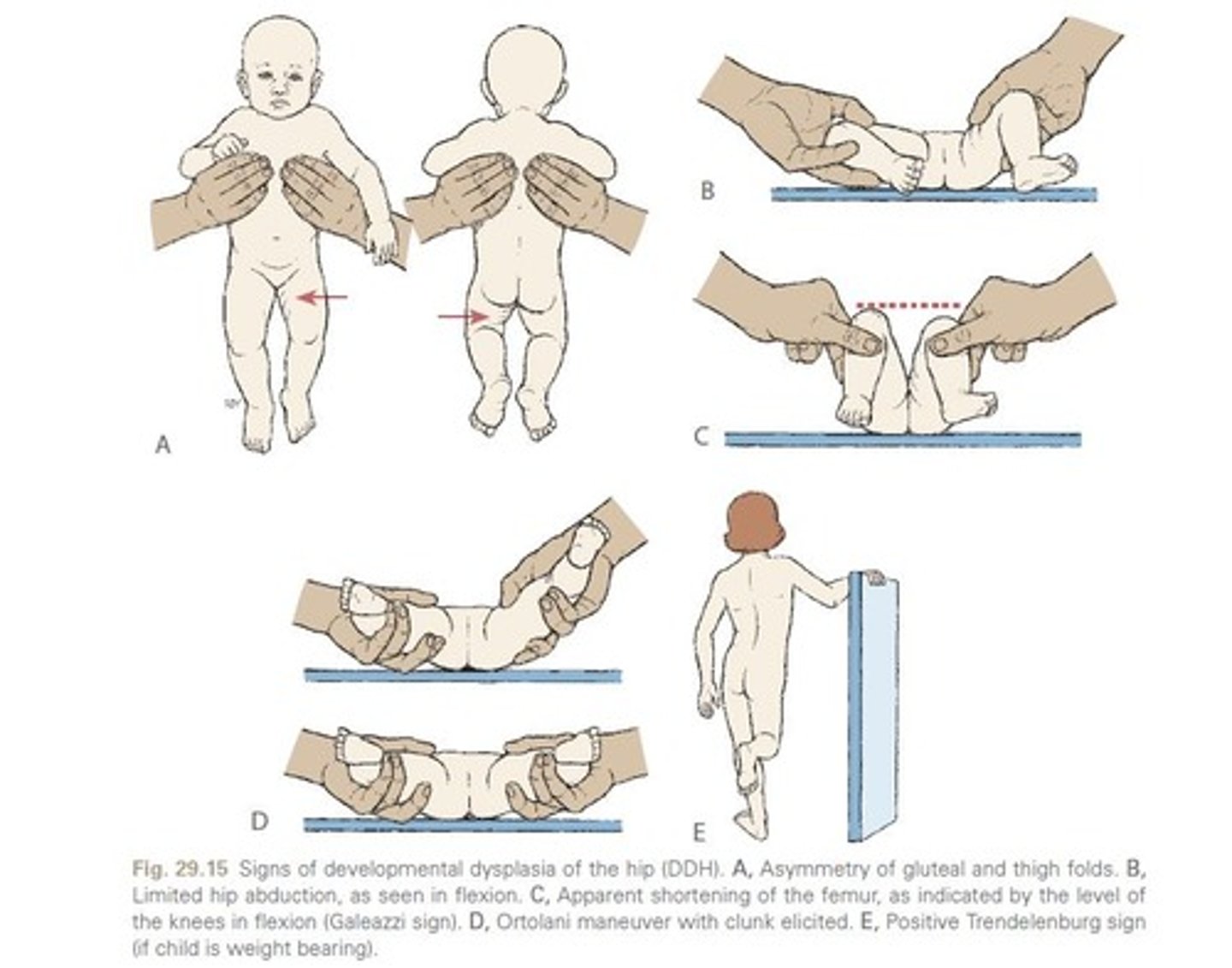
What are the signs of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)?
Asymmetry of the gluteal folds, limited hip abduction, and a positive Ortolani or Barlow test
What is the significance of a spiral fracture in a non-mobile child?
It is a red flag for potential abuse
What is the primary goal of nursing care for an immobilized child?
To prevent complications and promote comfort and mobility as much as possible
What is the healing time for neonates?
2-3 weeks
What is the healing time for early childhood?
4 weeks
What is the healing time for later childhood?
6-8 weeks
What is the healing time for adolescence?
8-12 weeks
What factors influence healing time?
Location, blood supply, and alignment
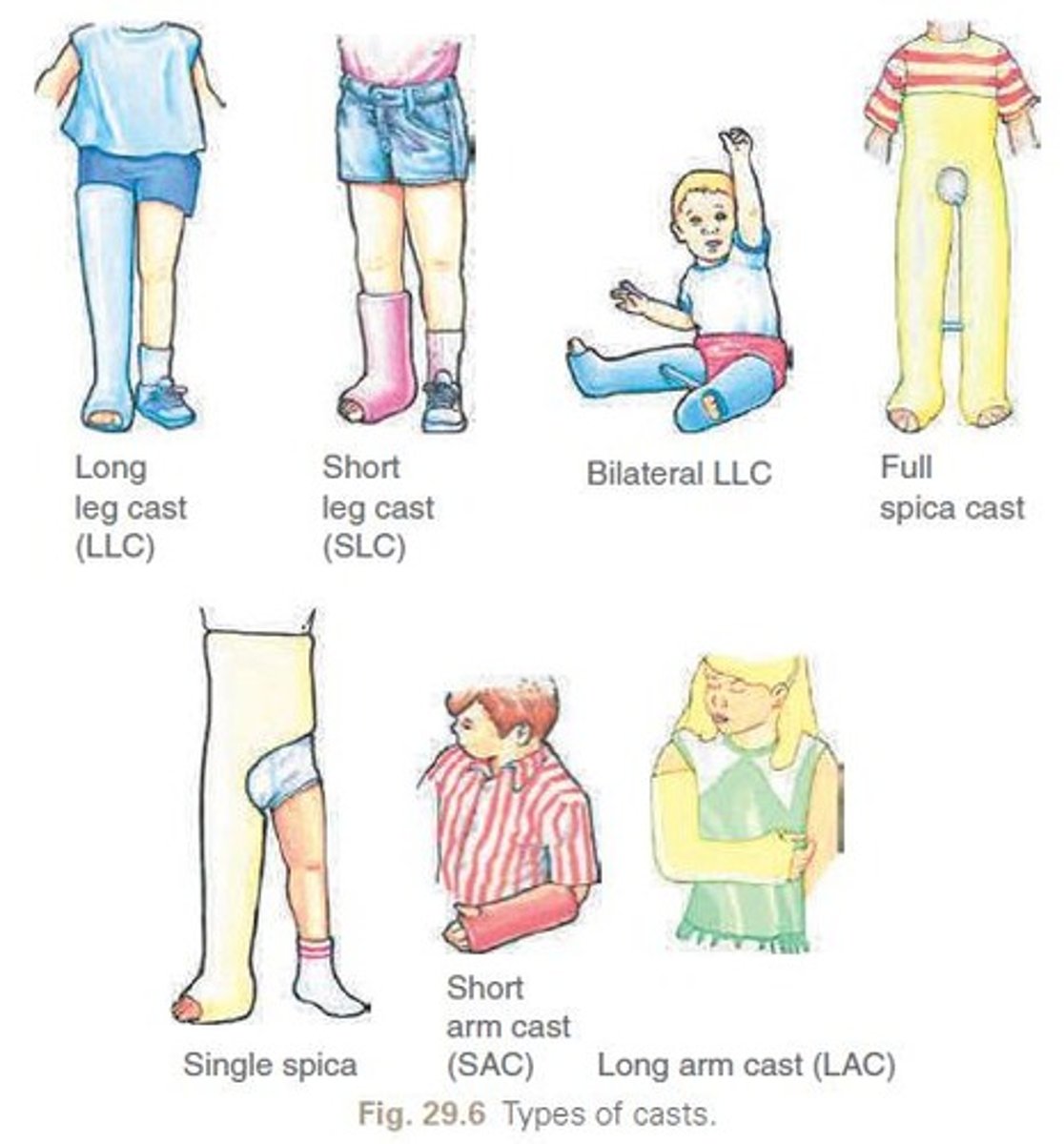
What is the purpose of a pediatric cast?
To immobilize joints above and below an injury
What are the types of pediatric casts?
Short/long arm, short/long leg, spica, body cast, cervical cast
What materials are commonly used for pediatric casts?
Plaster and fiberglass
What should be checked before applying a cast?
Skin integrity
What are the 6 P's in cast nursing care?
Pain, pulselessness, pallor, paresthesia, paralysis, poikilothermia
What is a sign of compartment syndrome?
Pain unrelieved by medications
What should be done if a child in a cast shows signs of infection?
Check for hot spots or foul odor
What is the first action if weights in traction are touching the floor?
Lift the weights to ensure they hang freely
What is the purpose of traction in pediatric care?
To align and immobilize fractures, reduce muscle spasms, and prevent contractures
What is the difference between skin traction and skeletal traction?
Skin traction uses skin and straps, while skeletal traction uses pins/wires through bone
What is the nursing responsibility for pin site care in traction?
Monitor for redness, drainage, and loosening
What is the purpose of the Ilizarov technique?
Used for limb lengthening, angular correction, or stability
What are common causes of amputation?
Congenital issues, trauma, malignancy
What is a common postoperative care practice for amputation?
Residual limb shaping with a figure-eight bandage
What is a common symptom of stress fractures?
Localized pain that worsens with activity
What does RICE stand for in injury management?
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
What is Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)?
A condition with shallow acetabulum, subluxation, or dislocation of the hip
What is the Galeazzi sign in infants?
Shortened limb on the affected side
What is the treatment for DDH in infants 0-6 months?
Pavlik harness worn 23-24 hours a day
What should parents be taught about the Pavlik harness?
Do not adjust the harness straps; the provider makes all adjustments
What is a common complication of casts?
Compartment syndrome
What should be done to prevent contractures after amputation?
Avoid prolonged stump elevation for more than 24 hours
What is phantom limb pain?
A normal sensation experienced after amputation
What should be monitored to prevent skin irritation in infants with harnesses?
Check skin 2-3 times a day for redness in skin folds; avoid lotions/powders.
What is the primary congenital foot deformity characterized by forefoot adduction?
Clubfoot or talipes equinovarus (TEV).
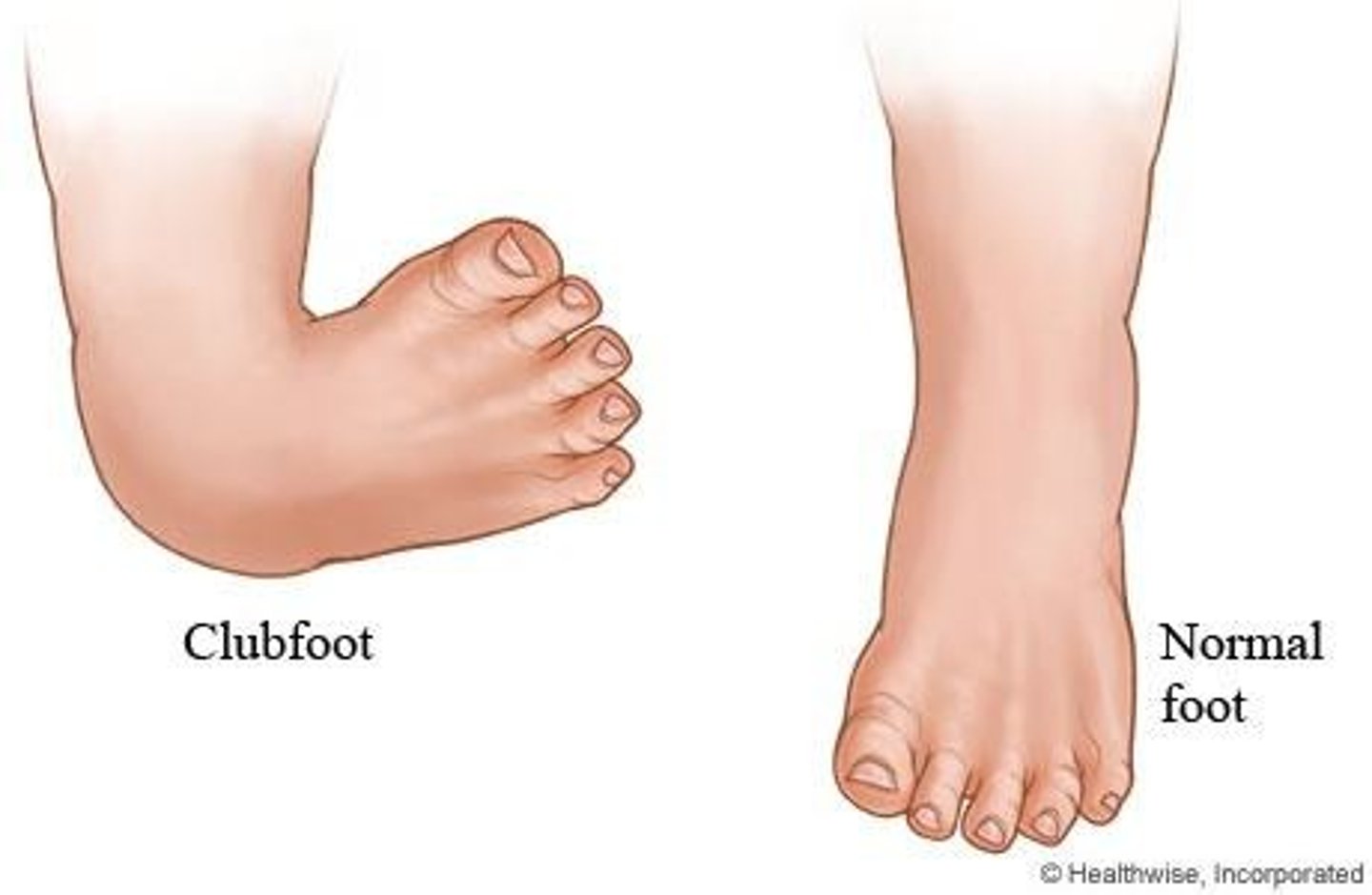
What are the four components of clubfoot?
Forefoot adduction, midfoot supination, hindfoot varus, ankle equinus.
What are the three types of clubfoot?
Positional, idiopathic (congenital), and syndromic (teratologic).
What is the Ponseti method for treating clubfoot?
Weekly serial casting for 6-8 weeks followed by a percutaneous Achilles tenotomy.
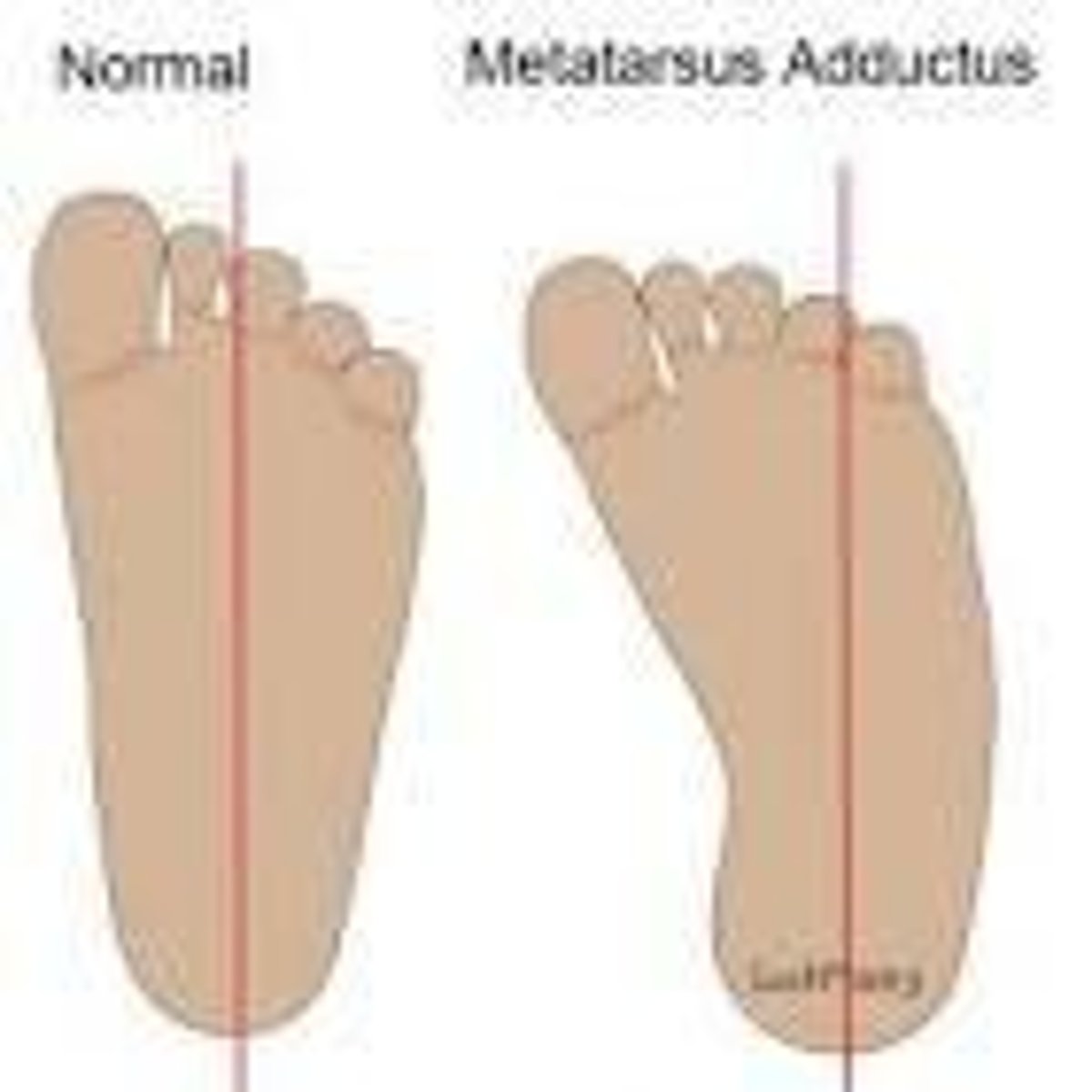
What is the most common infant foot deformity?
Metatarsus Adductus.
What characterizes metatarsus adductus?
Medial deviation of the forefoot while the hindfoot remains neutral.
What is the treatment for flexible metatarsus adductus?
Stretches and observation.
What are the physical signs of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)?
Limited abduction, skin folds asymmetry, positive Ortolani/Barlow tests.
What is the frequency of skeletal limb deficiencies in births?
Occurs in 1 in 2000 births.
What are the types of transverse limb deficiencies?
Transverse terminal and transverse intercalary.
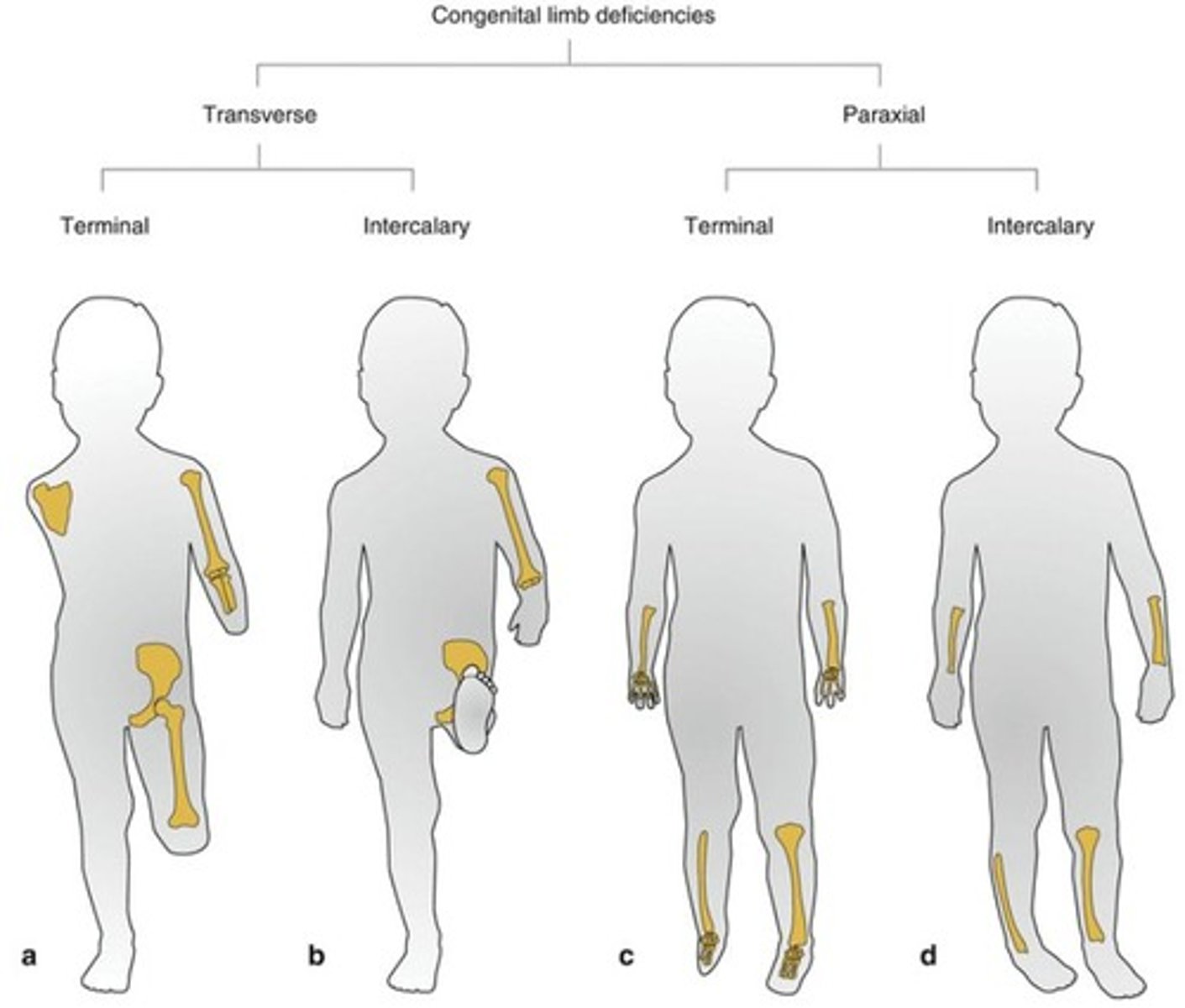
What is the management for skeletal limb deficiency?
Early prosthetic fitting, ongoing PT/OT, and support for parents.
What should parents be taught regarding handling a child with OI?
Handle gently, avoid twisting or pulling, and support the body evenly.
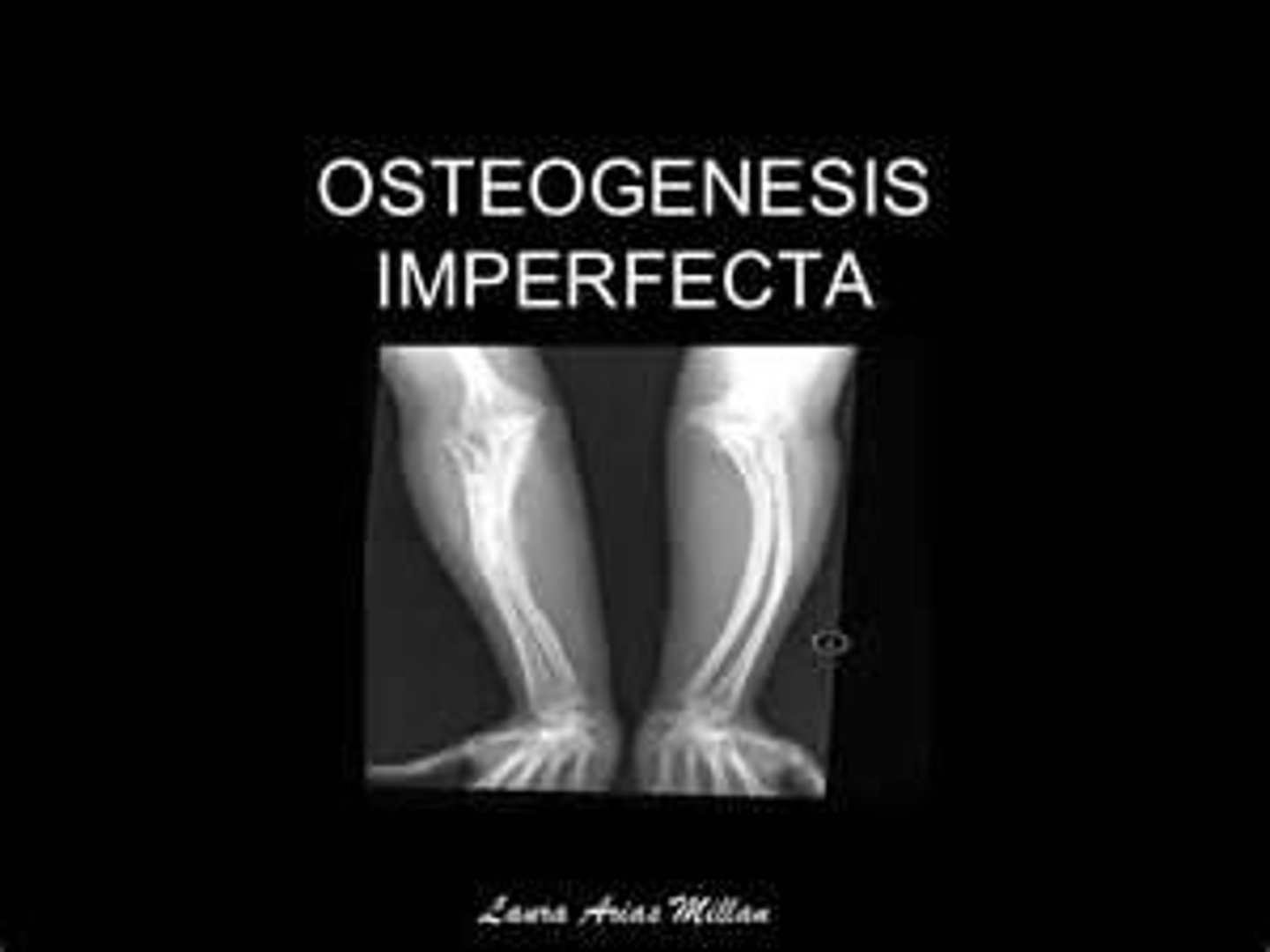
What is the prognosis for children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Varies by type; mild forms allow active lives, while severe forms may involve frequent fractures.
What is Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease (LCPD)?
A self-limiting disorder caused by avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
What are the clinical manifestations of LCPD?
Intermittent painless limp, hip/thigh/knee pain, limited ROM, and leg-length discrepancy.
What is the goal of treatment for LCPD?
To keep the femoral head contained in the acetabulum to prevent deformity.
What should families be taught about activity restrictions in LCPD?
Limit activity/weight-bearing as prescribed and support participation in ROM exercises.
What is the recommended follow-up for children with skeletal limb deficiencies?
Regular follow-up for prosthetic adjustments and monitoring of development.
What is the significance of the Ponseti method in clubfoot treatment?
It involves a systematic approach to correct the deformity through casting and bracing.
How does metatarsus adductus differ from clubfoot?
Metatarsus adductus is flexible and corrects past midline, while clubfoot is rigid.
What is the role of physical therapy in managing limb deficiencies?
To facilitate mobility training and support developmental milestones.
What is the importance of monitoring skin and circulation under casts?
To prevent complications such as skin irritation or circulation issues.
What should be avoided when caring for a child with OI?
Avoid twisting, pulling, or lifting by ankles or arms.
What is the typical age range for children affected by LCPD?
Most commonly occurs in boys ages 4-8.
What is Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)?
Displacement of the proximal femoral epiphysis, usually occurring during an adolescent growth spurt.
What are common signs of SCFE?
Limp, external rotation of the leg, knee or groin pain.
What is the immediate treatment for SCFE?
Immediate non-weight-bearing and surgical pinning in situ to stabilize the epiphysis.
What is the long-term outlook for SCFE with early treatment?
Best prognosis; delays increase risk for permanent hip damage and later arthritis.
What is kyphosis?
Exaggerated posterior curvature of the thoracic spine, often referred to as 'humpback'.
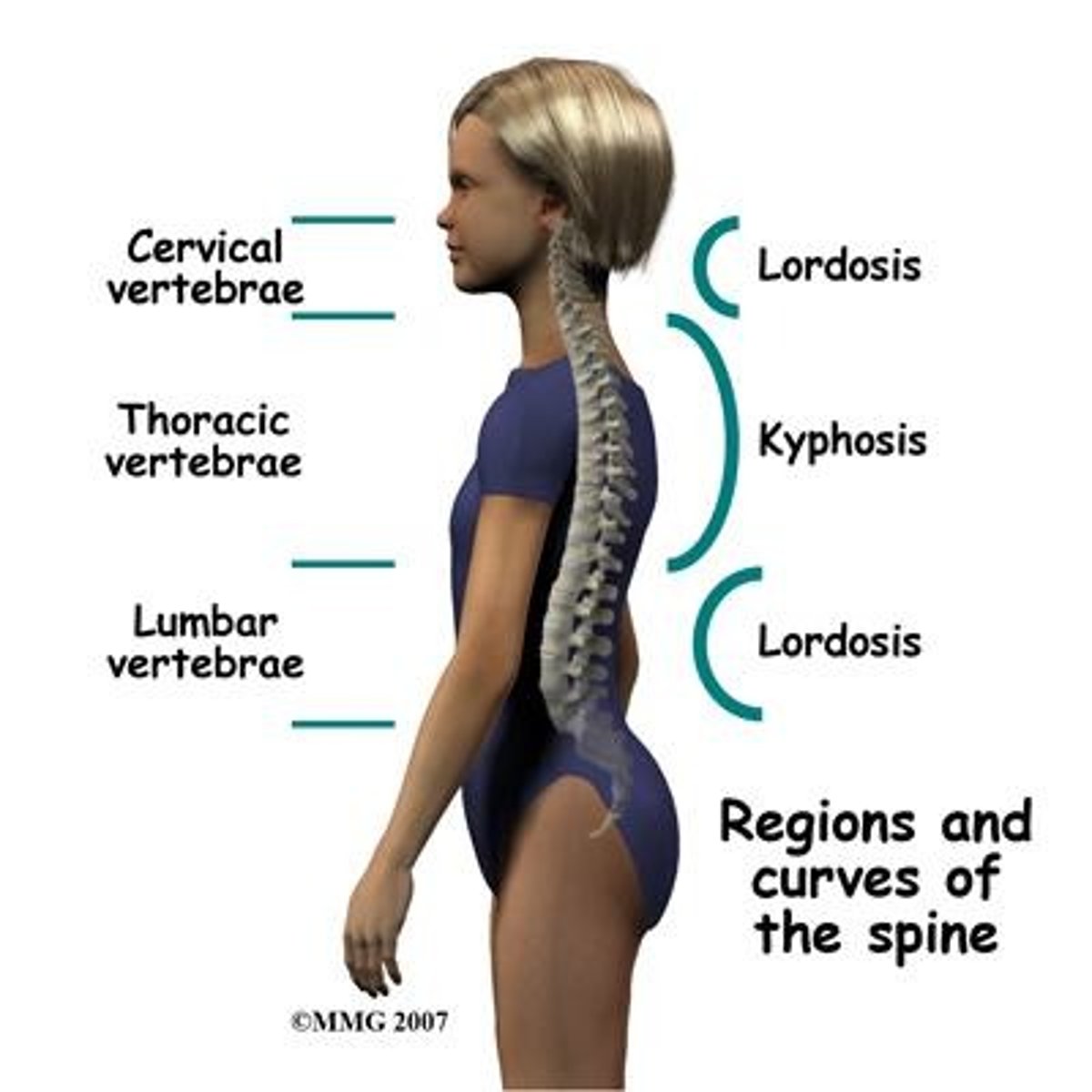
What are common causes of kyphosis?
Poor posture, Scheuermann disease, or vertebral anomalies.
What is lordosis?
Exaggerated inward curve of the lumbar spine, often referred to as 'swayback'.
What are common assessments for lordosis?
Prominent buttocks, anterior pelvic tilt, and lumbar pain.
What is scoliosis?
Lateral spinal curvature greater than 10° with vertebral rotation, leading to rib and trunk asymmetry.
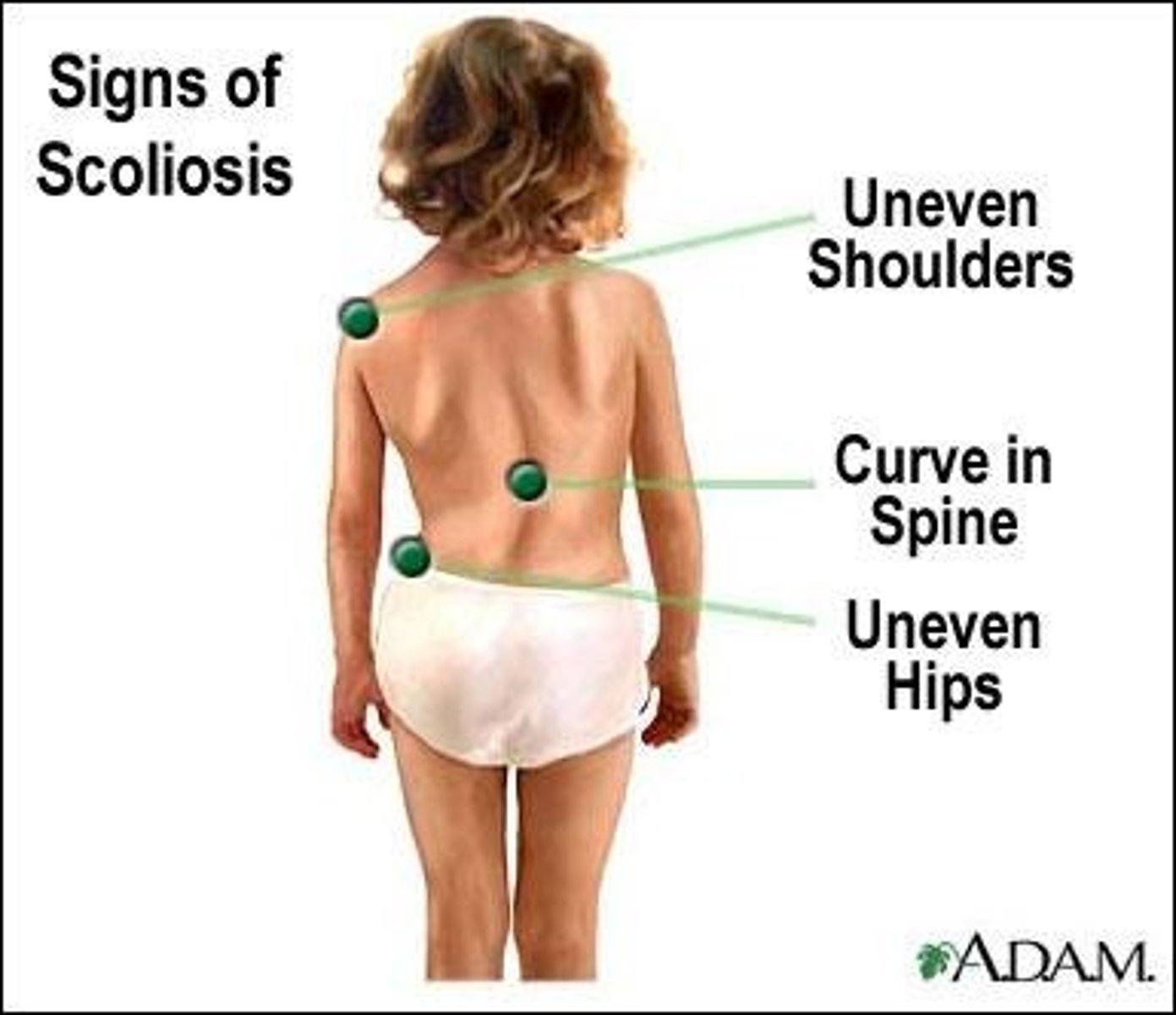
What is the most common type of scoliosis?
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, typically identified during the preadolescent growth spurt.
What is the management for mild scoliosis (10-25°)?
Observation and prescribed exercises to strengthen the spine and abdominal muscles.
What is the management for moderate scoliosis (25-45°)?
Bracing for 16-23 hours a day to prevent progression.
What is the management for severe scoliosis (>45°)?
Surgery with spinal fusion/rods, with a good prognosis if performed during ages 3-11.
What is osteomyelitis?
Infection of bone, usually from hematogenous spread or injury.
What are common symptoms of osteomyelitis?
Fever, irritability, tachycardia, localized pain, swelling, warmth, and decreased range of motion.
What is the most common organism causing osteomyelitis in children?
Staphylococcus aureus, including MRSA.
What are the diagnostic methods for osteomyelitis?
Cultures, lab tests (increased WBC, ESR, CRP), and imaging (X-rays, MRI, CT).
What is the initial therapeutic management for osteomyelitis?
Obtain cultures and start empiric IV antibiotics covering S. aureus/MRSA.
What is septic arthritis?
Bacterial infection of a joint, most commonly affecting the knee, hip, ankle, or elbow.
What are common clinical manifestations of septic arthritis?
Severe joint pain, swelling, warmth, decreased range of motion, and systemic symptoms like fever.
What is the management for septic arthritis?
Joint aspiration, IV antibiotics, possible surgical drainage, and pain control.
What is skeletal tuberculosis?
Spread to bone/joint via lymphohematogenous route from primary TB infection, often affecting the spine.
What are the nursing care considerations for skeletal tuberculosis?
Monitor pain, mobility, joint function, and ensure adherence to long-term TB medications.