Econ 1B - Midterm 1 (popojj)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is thinking on the margin?
a. Making decisions that are of noneconomic importance.
b. Making choices that are based on historical precedents.
c. Making choices that ignore the marginal benefits, but not the marginal costs, of some activity.
d. Making choices by comparing the additional benefits and additional costs from doing a little bit more of some activity.
d. Making choices by comparing the additional benefits and additional costs from doing a little bit more of some activity
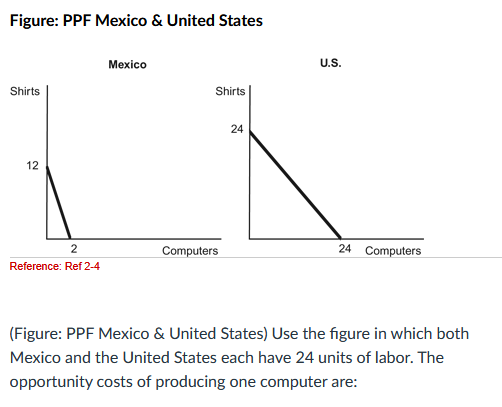
a. six shirts for Mexico and one shirt for the United States.
b. 1/6 of a shirt for both Mexico and the United States.
c. one shirt for Mexico and 1/6 of a shirt for the United States.
d. six shirts for both Mexico and the United States.
a. six shirts for Mexico and one shirt for the United States.
When the price of inputs increase:
a. the supply curve shifts down and to the right.
b. the supply curve shifts up and to the left.
c. there is an upward movement along the supply curve.
d. there is a downward movement along the supply curve.
b. the supply curve shifts up and to the left.
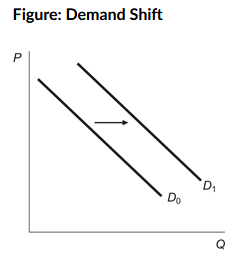
a. Consumer income increases in the market for a normal good.
b. Consumer income falls in the market for a normal good.
c. Consumer income rises in the market for an inferior good.
d. Consumer income remains the same and the price of the good falls.
a. Consumer income increases in the market for a normal good.
The quantity supplied:
a. shows how much buyers are willing and able to buy at different prices.
b. is the amount that buyers are willing and able to buy at a particular price.
c. shows how much sellers are willing and able to sell at different prices.
d. is the amount that sellers are willing and able to sell at a particular price.
d. is the amount that sellers are willing and able to sell at a particular price.
For an inferior good, higher income results in:
a. an increase in demand.
b. a decrease in demand.
c. a movement up along the demand curve.
d. a movement down along the demand curve.
b. a decrease in demand.
If market demand decreases:
a. equilibrium price and quantity will both increase.
b. equilibrium price and quantity will both decrease.
c. equilibrium price will increase but equilibrium quantity will decrease.
d. equilibrium price will decrease but equilibrium quantity will increase.
b. equilibrium price and quantity will both decrease.
If market supply increases:
a. equilibrium price and quantity will both increase.
b. equilibrium price and quantity will both decrease.
c. equilibrium price will increase but equilibrium quantity will decrease.
d. equilibrium price will decrease but equilibrium quantity will increase.
d. equilibrium price will decrease but equilibrium quantity will increase.
How did the spread of the Internet affect the market for newspapers?
a. Demand increased, causing the price to rise.
b. Demand decreased, causing the price to fall.
c. Supply decreased, causing the price to rise.
d. Supply increased, causing the price to fall.
b. Demand decreased, causing the price to fall.
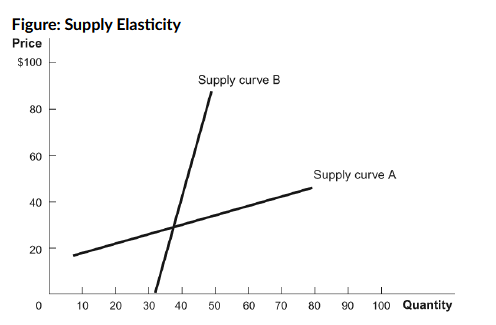
Refer to the figure. It shows two different supply curves. Based on the graph, which statement is TRUE?
a. The same price increase would cause a bigger increase in the quantity supplied along curve A.
b. The same price increase would cause a bigger increase in the quantity supplied along curve B.
c. Curve A reflects a less responsive supply.
d. If comparing responsiveness from a common point, like the intersection, we can conclude that supply curve B is more elastic.
a. The same price increase would cause a bigger increase in the quantity supplied along curve A.
The supply of ancient Egyptian papyrus manuscripts is probably:
a. elastic.
b. inelastic.
c. unit elastic.
d. hyperelastic.
b. inelastic.
The demand curve is inelastic if the absolute value of the elasticity is:
a. greater than 1.
b. greater than 0.
c. less than 1.
d. equal to 1.
c. less than 1.
The elasticity of demand:
a. equals the inverse of price to quantity demanded.
b. measures how far the demand curve shifts from a change in price.
c. tells us how responsive consumer purchases are to price changes.
d. estimates the relationship between quantity demanded and production costs.
c. tells us how responsive consumer purchases are to price changes.
Which of the following statements is TRUE? The buyer will pay more of the tax burden if:
I. the good is a luxury good.
II. the good is a necessity.
III. the good has no substitutes.
a. I only
b. II only
c. II and III only
d. I and III only
c. II and III only
Government subsidies to California cotton farmers:
a. create deadweight losses because the billions of dollars of resources used to grow cotton in deserts could be put to higher-valued uses.
b. correct a market failure because cotton prices are too low to support cotton farmers.
c. raise prices to consumers and lower prices received by cotton farmers.
d. benefit California cotton buyers because they pay only a small fraction of the world price.
a. create deadweight losses because the billions of dollars of resources used to grow cotton in deserts could be put to higher-valued uses.
If consumers pay 100 percent of a commodity tax, what could one conclude?
a. Suppliers have more effective lobbying in Washington than consumers.
b. The commodity in question has a perfectly elastic supply curve.
c. The commodity in question has a perfectly elastic demand curve.
d. Neither side has a perfectly elastic curve but the supply side is more elastic than the demand side.
b. The commodity in question has a perfectly elastic supply curve.
If a tax is imposed on sellers of a product, the demand curve will:
a. shift upward.
b. shift downward.
c. not shift.
d. shift upward or downward depending on elasticity of demand.
c. not shift.