Periodic table origin and development
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Johann Wolfgang Dobreiner
Discovered the Law of triads

Law of triads
Grouping of elements in three. The atomic mass of the middle element is the average of the other two.
23
Lithium has the atomic mass of 7, sodium has 23, and potassium has 39. If you add the 1st and 3rd one and divide it by 2, what is the mean of 1 and 3?
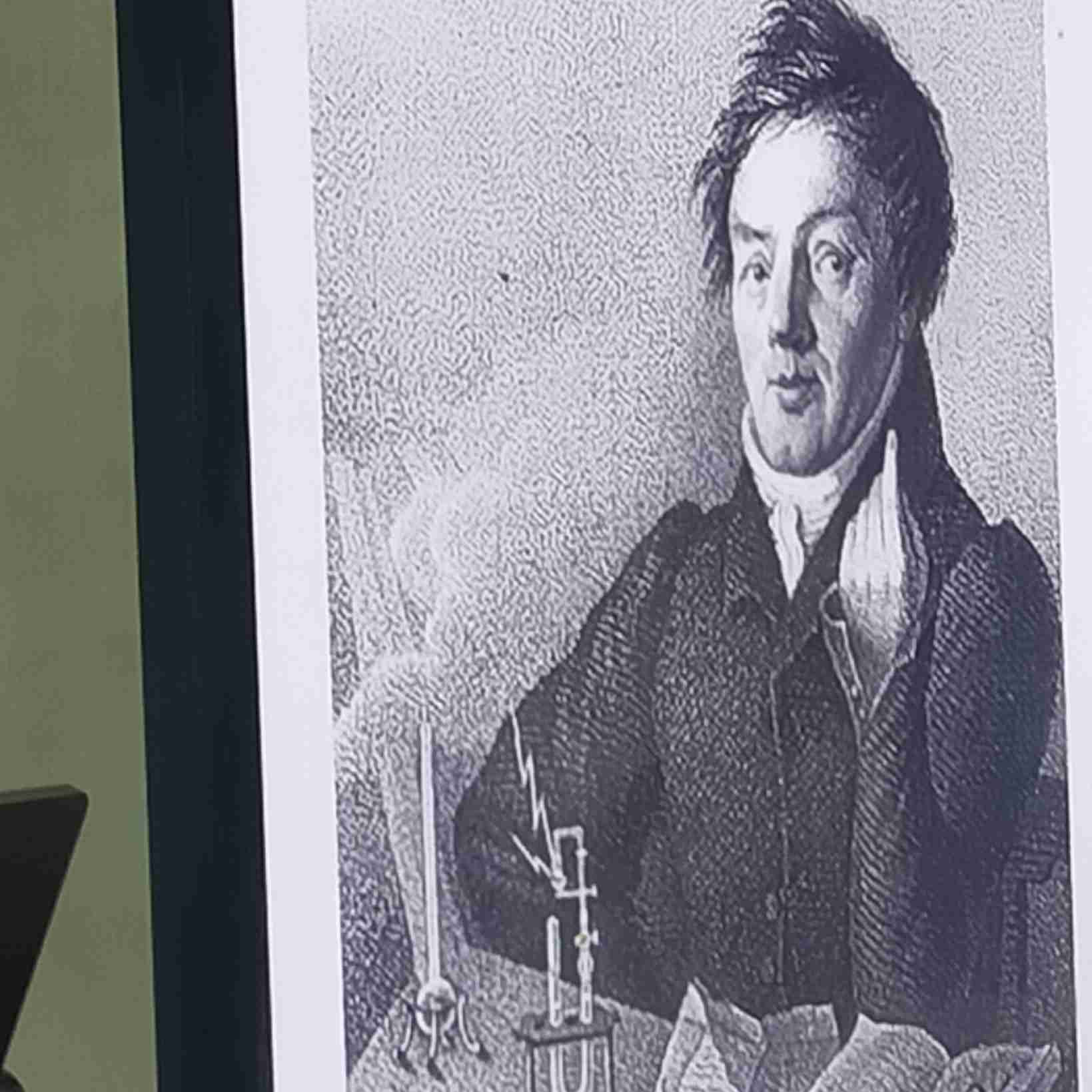
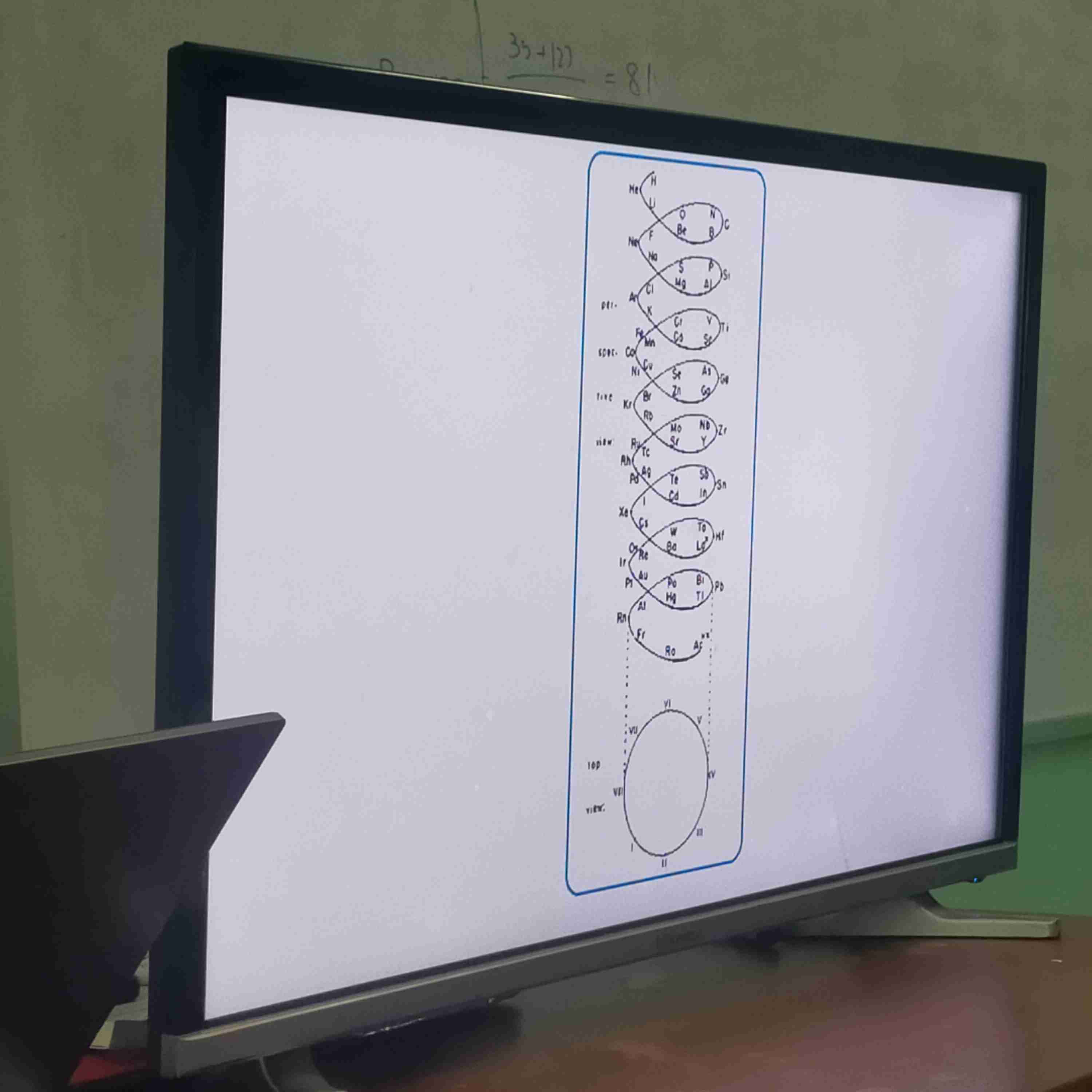
Alexander Beguyer De Chancourtois
The first person to organise elements by atomic weights.

The organizing of elements by atomic weights
Plotting a helical graph of the elements around a cylinder with a circumference of 16 units corresponding to the weight of oxygen.
John Newlands
devised the first periodic table and arranged the elements according to increasing weights
Explain the given law:Law of octaves by John Newlands
John Newlands arranged the elements according to increasing weights and observed that the properties of the elements are repeated after an interval of eight elements.
Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer
__ created the first periodic table and was shortly followed by ?
Meyer and Mendelev arranged the elements by their mass. They proposed that __?
They proposed that certain properties periodically reoccur
Atomic Volume and(or) Molar Volume
Meyer formed his periodic law based on ____ or ____, which is the atomic mass divided by the density in solid form.
Henry Moseley
Rearranged the elements in the periodic table according to increasing atomic number.
How did Moseley rearranged the periodic table?
According to the increasing atomic number. This is the basis of the modern periodic table
Glenn Seaborg
discovered the transuranium element?
What is the transuranium element?
It has the atomic number of 92-102.
What else did Seaborg add?
The lanthanide and actinide
Periodic law
This law states that when elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic number, elements with similar properties appear at periodic intervals.
The horizontal or row is called ___
Period or series of the elements in the periodic table
Group of family
Vertical column is the ____ of elements
Period Number
The ____ indicates the occupied highest main energy level of the elements.
Because of period number,
the elements belong to the same period or series
what are the lanthanide and actinide by glenn seaborg?
The Lanthanide and actinide series projected perpendicular to the plane of the periodic table
Elements with similar chemical properties have the same number of valence electrons. Because of this, the element belong to the same group family.
Chemical Families
Where are electrons found?
These are found in the outermost or highest main energy level.
Two ways of numbering the groups or families
1-18 groups and IA-VIIIA groups
1-18 groups
International union of pure & applied chemistry (IUPAC)
IA-VIIIA groups
older notation - US usage
Family 1- Alkali Metals
Single electron in their outermost energy level
soft, silver-white, shiny metals
it can be cut with a knife
good conductors of heat and electricity
can bond readily with other substances
they are very reactive
react violently with water
can easily burn and may explode
Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, Francium
Family 1-Alkali Metals
Family 2- Alkali EARTH Metals
Never found in nature as uncombined elements
Have no valence electrons
Not as reactive as the other
Some are used and industries as alloys and some are important elements found in the human body
Family 3 up to 12 - Transition Metals
Have properties similar to one another and to other metals ut they are different from the properties of any other family
Also good conduct of heat and electricity
Brightly Colored and often used as color paint
Some are used for jewelry making, and component of some measurements tools
Can form many different compounds when losing one or more
Family 13 - Boron Family
Has 3 Valence electrons
Hard and brittle and never uncombined in nature
Visually combined with Oxygen
Often used for glass wares and cleaning compounds such as borox
Other metal elements are often used as components in the production of cars, trains, and planes
Boron
A metalloid (but in the boron family, the other is metal)
Carbon
A non mental and the element that is the basic of your life
Family 14- Carbon family
Two elements, silicon and germanium are metalloids, while ___ is non-metal
Almost all compounds that are important for our body have this
Metals under the carbon family are used for:
Metals are used for making cans that are tin and in production of paint and component in gasoline but removed because of its harmful effects.
Nitrogen
This makes up 75% of the atmosphere and is used for the production of pesticides, explosives, medicines, and dyes
Phosphorus
Belongs in family 15- Nitrogen family
an active non-metal used in making tips of matches and flares
Arsenic
Belongs in family 15- Nitrogen family
an ingredient in many insecticides
Antimony and Bismuth
Belongs in family 15- Nitrogen family
used in making alloys
Family 15- Nitrogen family
Has five valence electrons. The elements in this family: makes up 75% of the atmosphere, used for:
Pesticides
Explosives
Medicines
dyes
making tip of matches and flames
ingredient for insecticides
making alloys
Oxygen
The most abundant element in the Earth’s crust
Family 16- Oxygen family
Very important in all forms of life
Can form compounds with other elements or form a molecule by bonding itself such as ozone
Sulfur, selenium, and tellurium are brittle solids used in the manufacture of medicines, gunpowder, color grass red, and enamels, and alloys. What chemical family does this belong to?
Family 16- Oxygen family
Polonium
Part of family 16 - Oxygen Family which is an extremely rare element
Family 17
Have 7 valence electrons
Most active non metals
Never found in nature
Can share or gain 1 electron with other atoms to form compounds
Bond with other atoms to form salts, an important component in making toothpaste, used to melt snow and ice on streets, and used in photographic film
Bromine is one of the few liquid element while iodine and the other metalloid astatine are solids
Family 18 - Noble Gases
Normally unreactive
Do not readily form compounds with other elements
Also called as inert gases
Among noble gases, helium has 2 valence electrons while some have 8 electrons
Some of the noble gases are used as theatrical effects and colored signs, and neon lights
Radon is used to treat certain cancers
Argon and xenon are used in light bulbs and lamps
Lanthanoid Series
This is made up of soft, malleable metals that have high luster and conductivity. They are used in making various alloys and high-quality glass in industry.
Actinoid Series
Composed of elements which are radioactive. Uranium is used as fuel in nuclea powered electric generators
Basic Properties and trends on the periodic table
Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, Electron affinity, Electronegativty
Atomic Size
Defined by the atom’s atomic radius (One half the distance from the two nuclei of two adjacent atoms).
Ionization energy
Energy that is needed to remove the valence electron
Electron Affinity
Energy released or required when electrons are added to an atom in the gaseous phase
Electronegativity
The tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards itself in the chemical bond
Linus Pauling
Developed the electronegativity values presented in the periodic table
Metalic Property
elements can be metal, non-metal, and metalloids
Octet Rule
It states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until they are surrounded by eight valence electrons.
An atom either loses or gains electrons to achieve the electron configuration of the noble gases.
Octet Rule
Noble gases
These are stable and have high ionization energy. The s and p orbitals are completely filled.
Gilbert Lewis
Proposed the Lewis Electron Dot Structure
the Lewis Electron Dot Structure
It indicates the number of valence electrons in an atom represented by dots scattered on four sides of the atomic symbol