L13 Cardiovascular System and Cardiac Cycle Vocabulary
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary related to the cardiovascular system, blood circulation, and the cardiac cycle.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Blood
Think of blood as a river that flows through your body. It's a fluid that carries everything your cells need, like food (nutrients) and air (specifically, oxygen), and it also picks up waste like carbon dioxide to take it away.
Heart
The heart is like the engine of a car. It's a muscular pump that pushes the blood (the river we talked about) through your body, making sure everything gets what it needs.
Blood Vessels (Vasculature)
These are the roads (or pipes) that the blood travels through. They include veins, arteries, and capillaries. Each has a specific job to do in transporting blood.
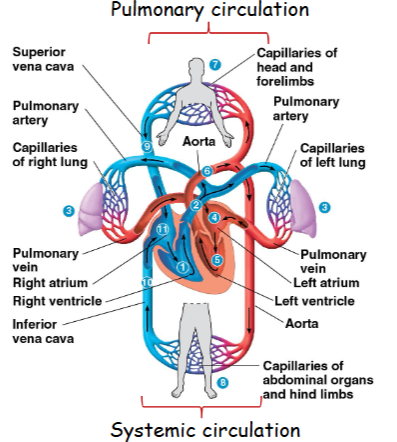
Double Circulation
Imagine the circulatory system as two loops working together. One loop sends blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen, and the other sends the now oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. This 'double loop' system is called double circulation.
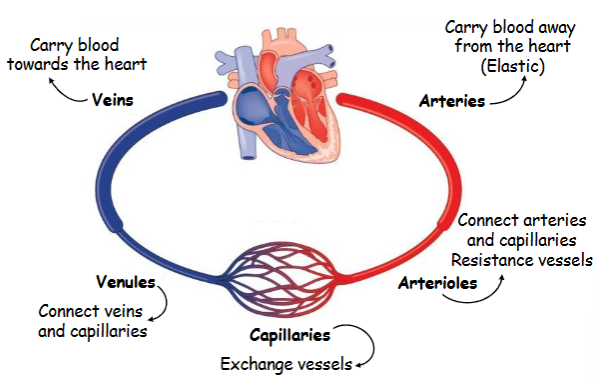
Veins
Veins are like one-way streets that carry blood towards the heart. They bring blood back from different parts of your body.
Arteries
Arteries are like highways that carry blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. They transport oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery).
Capillaries
Capillaries are tiny, tiny roads that connect the arteries and veins. They're so small that oxygen and nutrients can easily pass from the blood into the body's cells, and waste can pass from the cells into the blood.
Systemic Circulation
This is the part of the double circulation that sends blood from the heart to all the organs and tissues in the body (except the lungs) and then back to the heart. It also acts like a container that withstands the changing pressure.
Venous Circulation
This part of the circulation is like a reservoir that holds a large amount of blood. It ensures that the heart always has enough blood to pump.
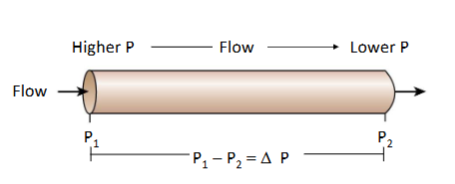
Driving Pressure
This is the force that makes the blood flow. It's created by the heart when it contracts, pushing the blood forward.
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle is like a heartbeat's rhythm, with the heart muscle contracting (systole) and relaxing (diastole) in a regular pattern.
Systole
This is when the heart muscle squeezes (contracts) to push blood out into the body.
Diastole
This is when the heart muscle relaxes, allowing the heart to fill with blood before the next contraction.
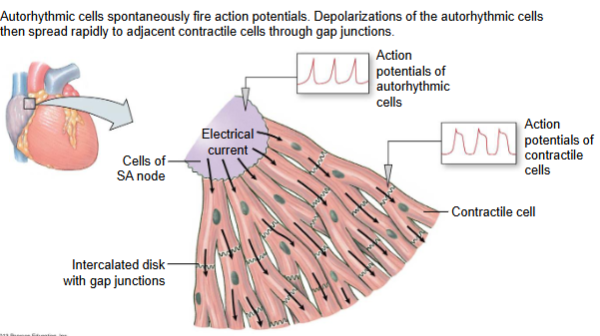
Sinoatrial Node (SA)
The SA node is the heart's natural pacemaker. It's a group of special cells that send out electrical signals to tell the heart when to contract and set the rhythm.
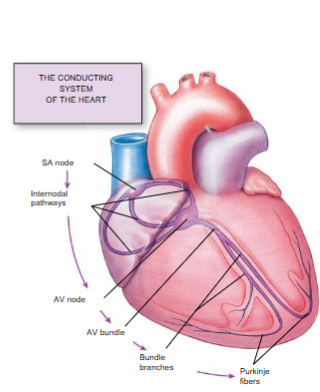
Atrioventricular Node (AV)
The AV node is like a pause button in the heart's electrical system. It's located between the upper and lower chambers of the heart and delays the electrical signal, giving the upper chambers time to finish contracting before the lower chambers start.
Bundle of His
This is a special pathway that carries the electrical signal from the AV node down into the lower chambers of the heart, helping to spread the signal quickly and evenly.
Purkinje Fibers
These fibers are like the branches of a tree, spreading throughout the lower chambers of the heart and carrying the electrical signal to all the muscle cells, ensuring they contract in a coordinated way.
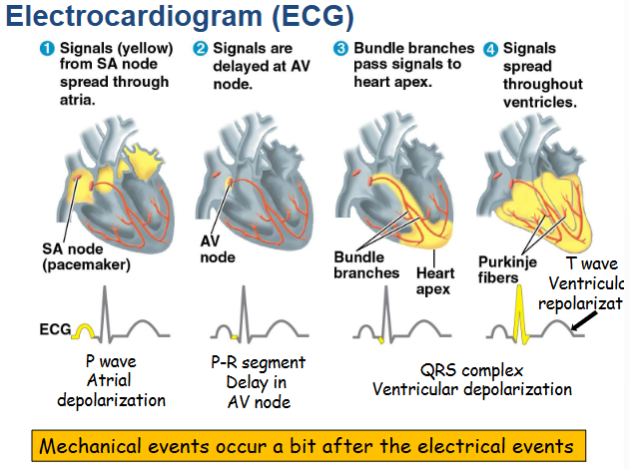
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An ECG is a special test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It can show how fast the heart is beating and whether the electrical signals are normal.
Cardiac Output
This is the amount of blood the heart pumps out into the body every minute. It depends on how fast the heart is beating and how much blood is pumped out with each beat.
Heart Rate
This is simply the number of times the heart beats in one minute.
Stroke Volume
This is the amount of blood that the heart pumps out with each single contraction or beat.
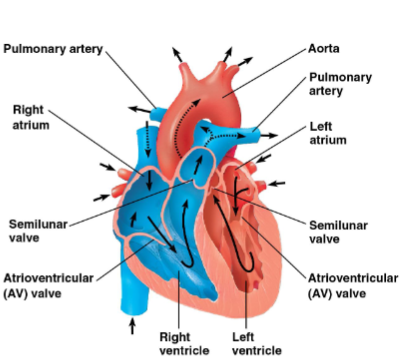
Blood Pathway
The blood pathway is the route that blood takes through the heart and lungs and back again. It follows this sequence: right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → mitral valve → left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta.
Venules
hese are small version of veins. Venules collect blood from the capillaries and then drain into the veins, kind of like small tributaries flowing into a larger river.
Arterioles
These are small vessels that branch from the arteries, leading to capillaries. They have an important role in regulating blood flow and pressure, ensuring that the right amount of blood reaches the capillaries.
spread of depolarization in myocardial calls
Autorhythmic cells spontaneously fire action potentials. Depolarizations of the autorhythmic cells then spread rapidly to adjacent contractile cells through gap junctions