TCP2 Terms/Questions
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
How many stars are visible on clear nights?
more than 2000 stars may be visible to the naked eye
Constellation
a region of the sky with well-defined borders; the familiar patterns of stars merely help us locate the constellations
(local sky) The boundary between Earth and sky defines the
horizon
(local sky) The point directly overhead is the
zenith
(local sky) an imaginary half circle stretching from the horizon due south, through the zenith, to the horizon due north.
Meridian
angular size
is the angle it appears to span in your field of view.
angular distance
is the angle that appears to separate them.
Stars near the north pole are
circumpolar meaning that they remain perpetually above the horizon, circling counterclockwise around the north celestial pole each day.
Latitude
measures north-south position on Earth
Longitude
measures east-west position
June solstice (summer)
occurs around June 21 and is the moment when the Northern Hemisphere is tipped most directly toward the Sun and receives the most direct sunlight.
December solstice (winter)
occurs around December 21 and is the moment when the Northern Hemisphere receives the least direct sunlight.
March equinox (spring)
occurs around March 21 and is the moment when the Northern Hemisphere goes from being tipped slightly away from the Sun to being tipped slightly toward the Sun.
September equinox
occurs around September 22 and is the moment when the Northern Hemisphere first starts to be tipped away from the Sun.
precession
a gradual wobble that alters the orientation of Earth’s axis in space.
As the Moon orbits Earth, it returns to the same position relative to the Sun in our sky (such as along the Earth-Sun line) about every
29.5 days.
A gibbous moon is essentially the opposite of a crescent moon—
a crescent moon has a small sliver of light while a gibbous moon has a small sliver of dark.
Lunar eclipse
occurs when Earth lies directly between the Sun and Moon, so Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon.
Solar eclipse
occurs when the Moon lies directly between the Sun and Earth, so the Moon’s shadow falls on Earth.
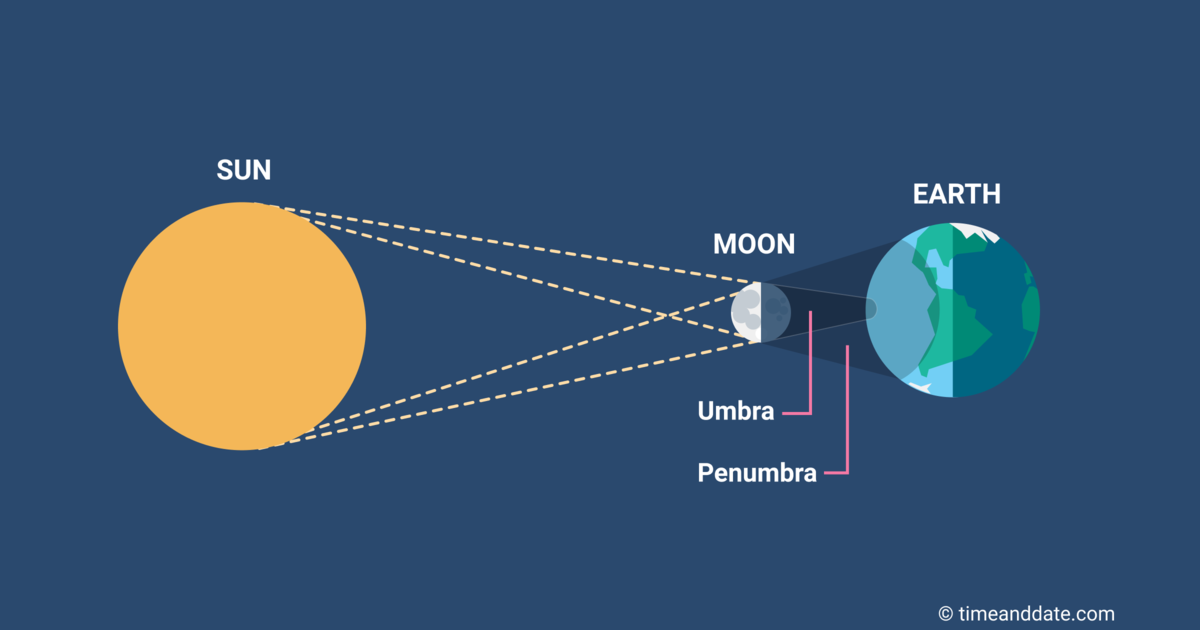
Umbra
sunlight is completely blocked
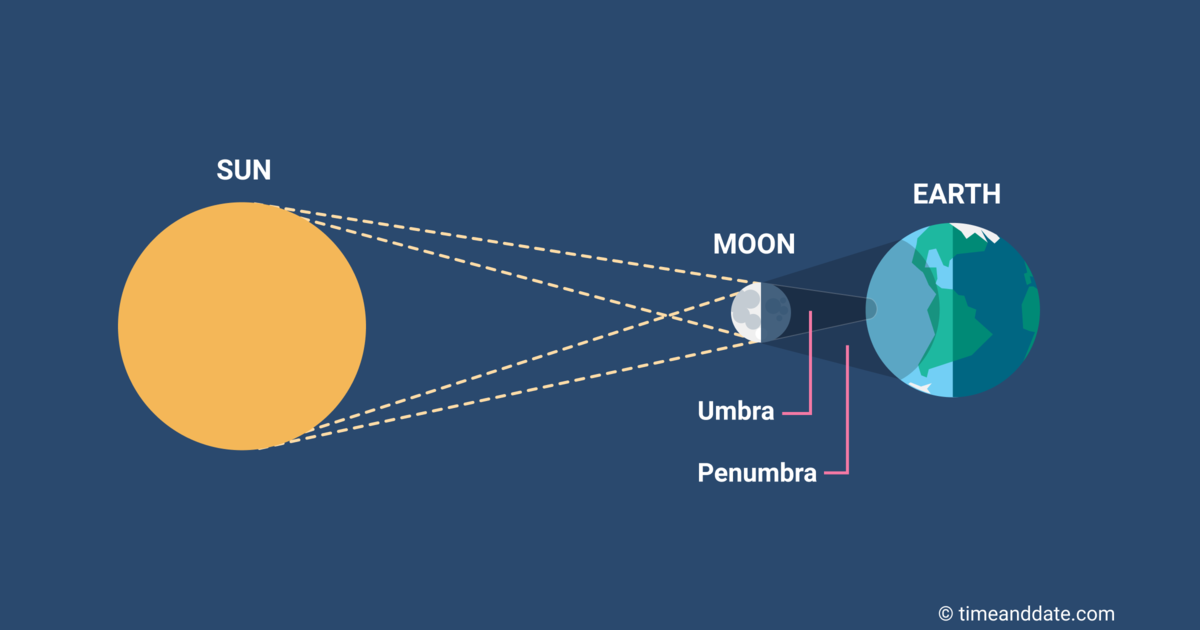
Penumbra
where sunlight is only partially blocked.
If the Sun, Earth, and Moon are nearly perfectly aligned, the Moon passes through Earth’s umbra and we see a
total lunar eclipse
If the alignment shows only part of the full moon passes through the umbra (with the rest in the penumbra) and we see a
partial lunar eclipse
If the Moon passes through only Earth’s penumbra, we see a
penumbral lunar eclipse