Knowt - A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
I. THE EXPANSION OF INDUSTRY!
I. THE EXPANSION OF INDUSTRY!
OBJECTIVE: Discuss and explain how Americans used their natural resources and technological breakthroughs to begin building an industrial society.
OBJECTIVE: Discuss and explain how Americans used their natural resources and technological breakthroughs to begin building an industrial society.
NATURAL RESOURCES FUEL INDUSTRIALIZATION!
What were America's important natural resources?
NATURAL RESOURCES FUEL INDUSTRIALIZATION!
What were America's important natural resources?
1. natural resources
2. inventions
3. growing population
What three causes led the United States to the breakthroughs to begin building an industrial society?

kerosene
In 1840 a Canadian geologist discovered that THIS could be used to light lamps.

Edwin L. Drake
He used a steam engine to drill for oil in 1859.
This technological breakthrough helped to start the oil boom.

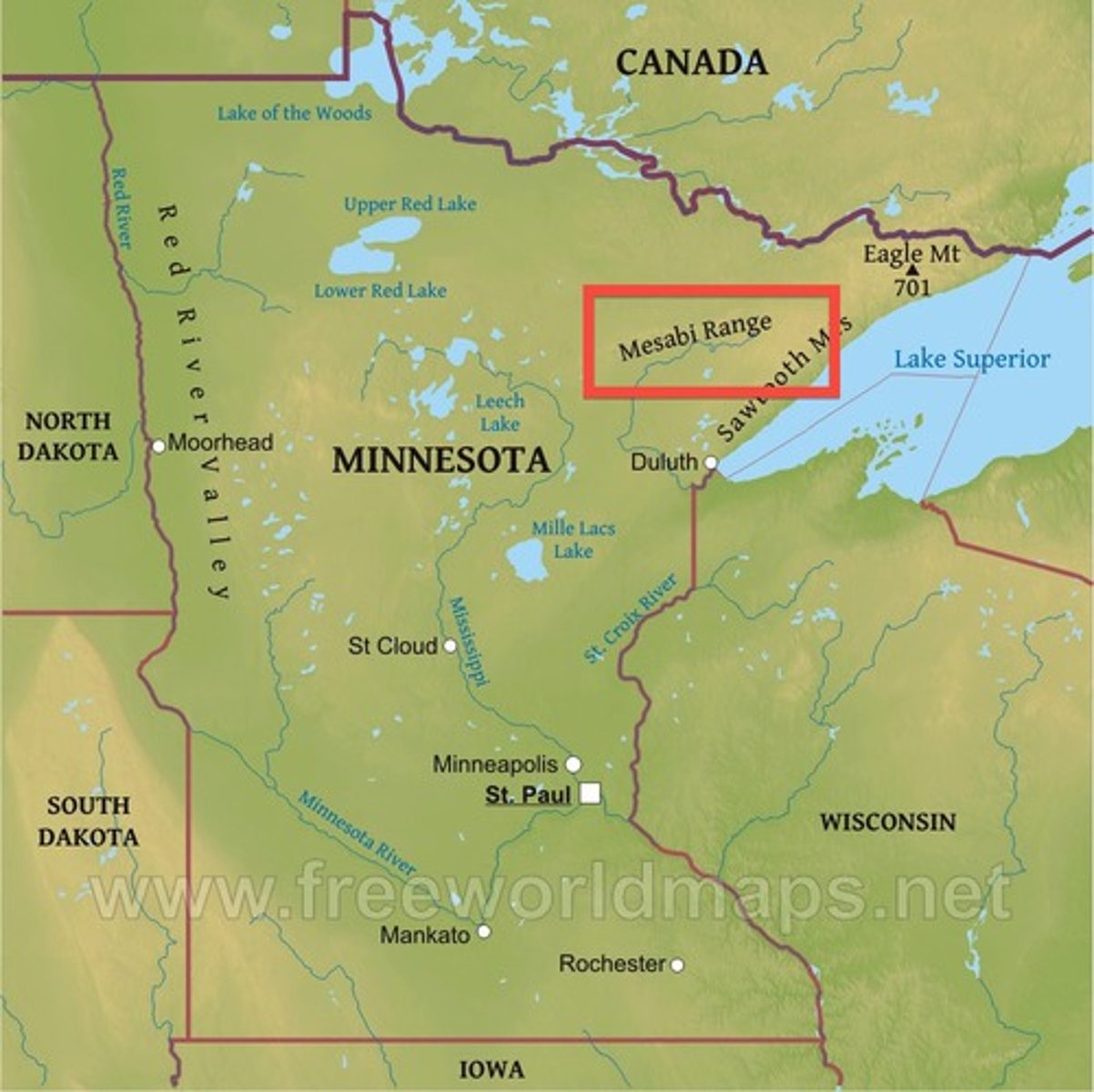
Minnesota
In 1887, explorers found large deposits of iron in THIS state. At the same time, coal production increased from 33 million tons in 1870 to more than 250 million tons in 1900.
Bessemer Process
First cheap and inefficient way to make steel, developed around 1850.

Henry Bessemer
The name of the man who invented the Bessemer process.
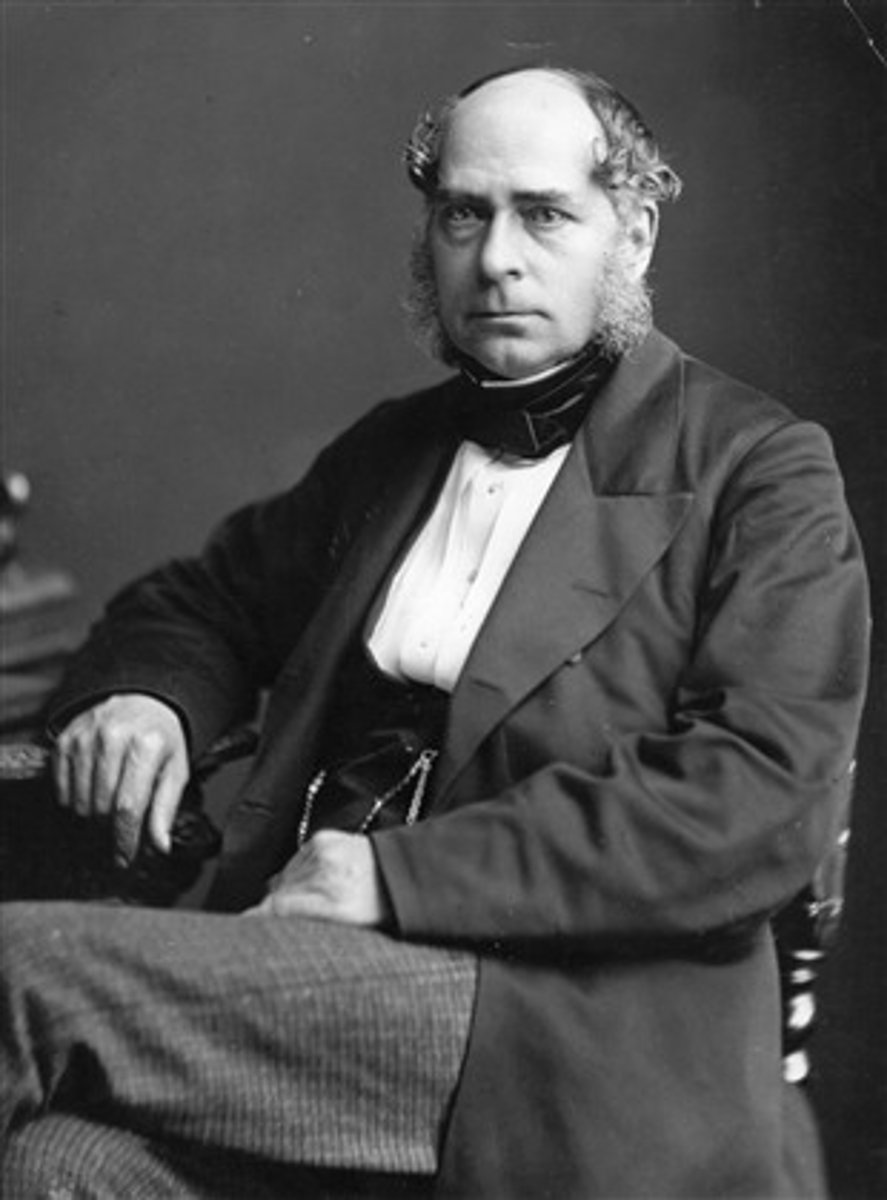

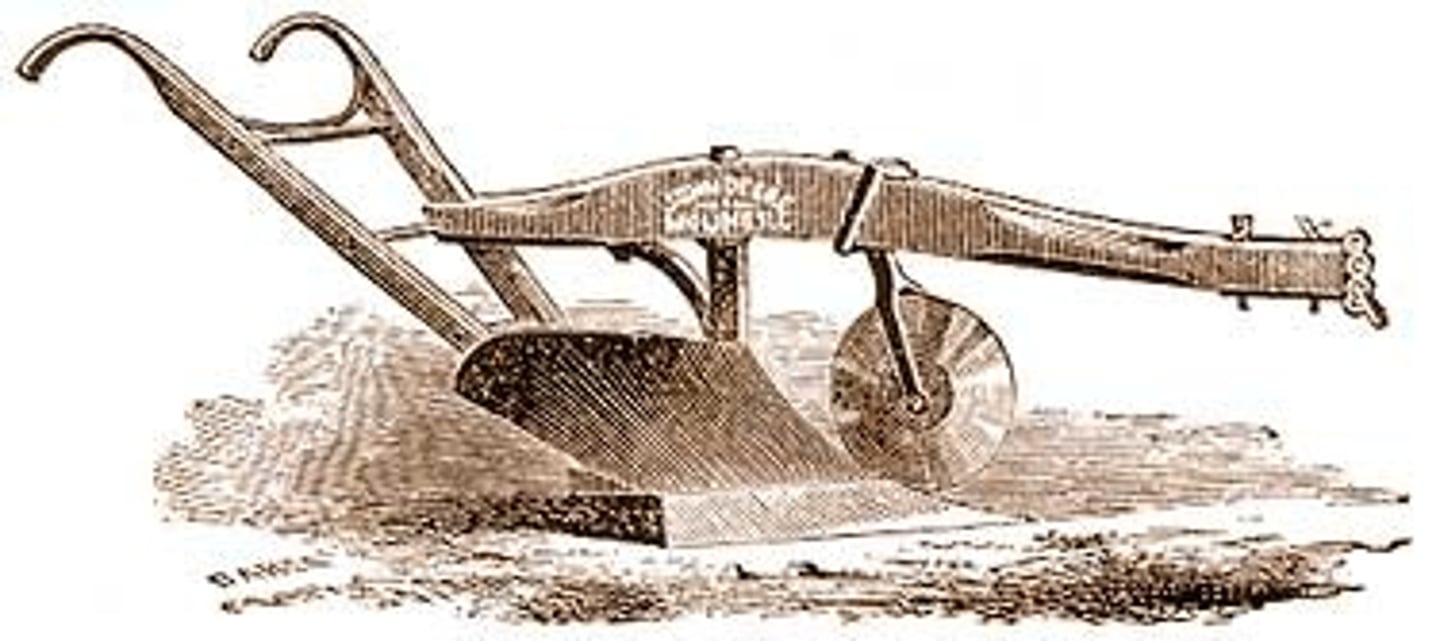
John Deere
Steel was used to improve the steel plow farming tool invented by HIM in 1837.

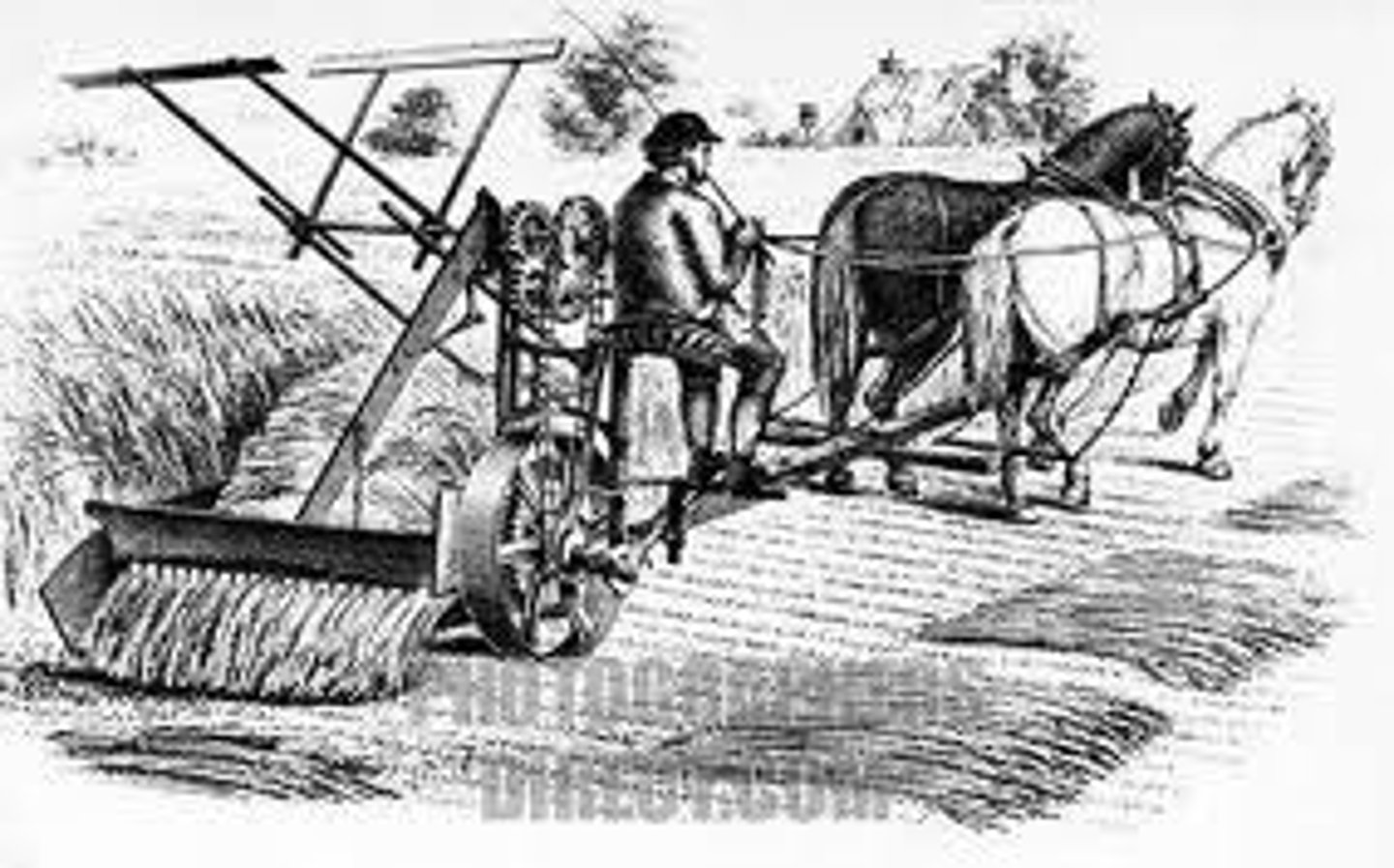
Cyrus McCormick
HE invented the mechanical reaper in 1831.
This machine, used by farmers, harvested crops mechanically.
For hundreds of years, farmers and field workers had to harvest crops by hand using a sickle or other methods, which was an arduous task at best.
HIS mechanical reaper replaced the manual cutting of the crop with scythes and sickles.
This new invention allowed wheat to be harvested quicker and with less labor force.

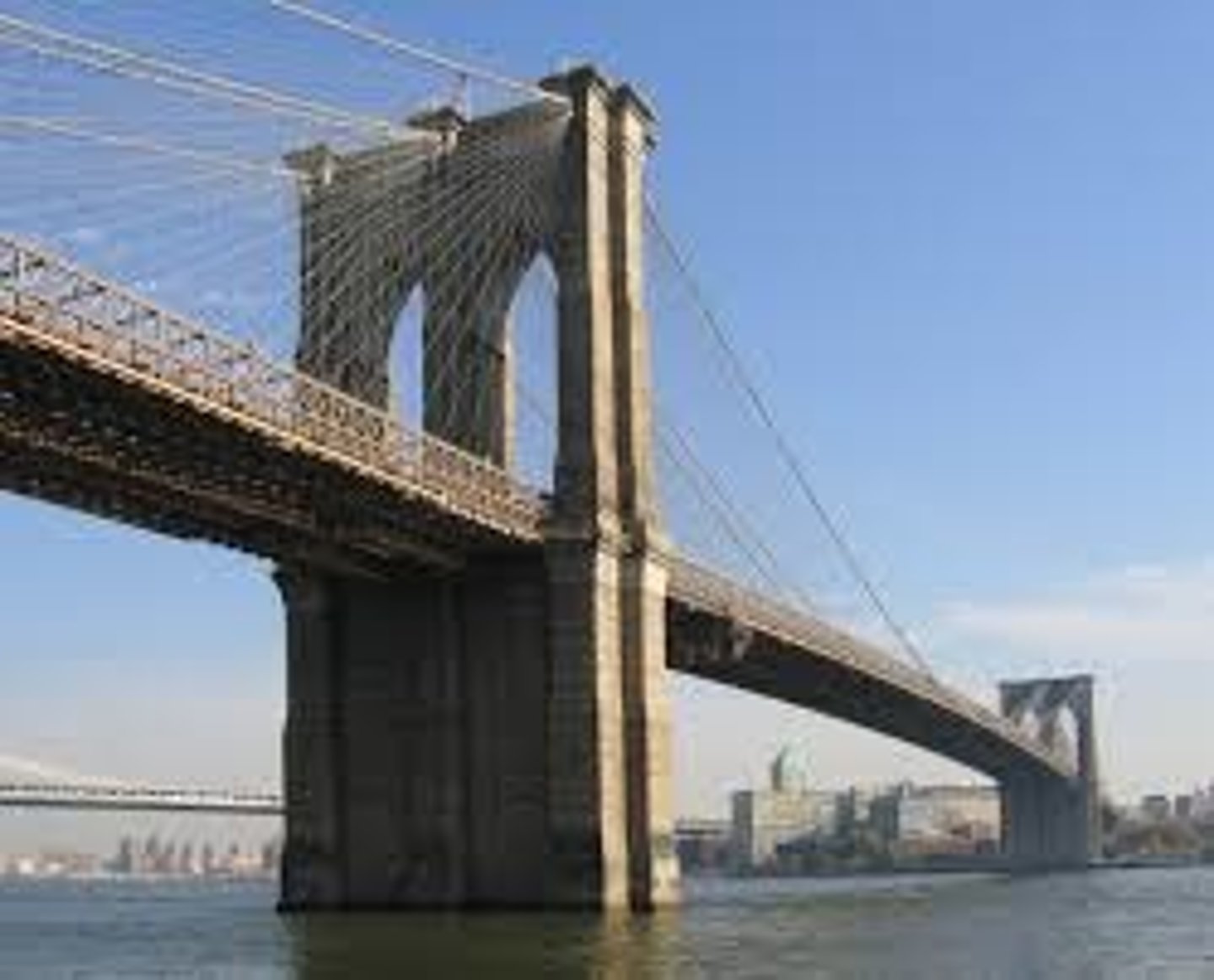
Brooklyn Bridge
THIS historical marvel opened in 1883 and connected New York City and Brooklyn.

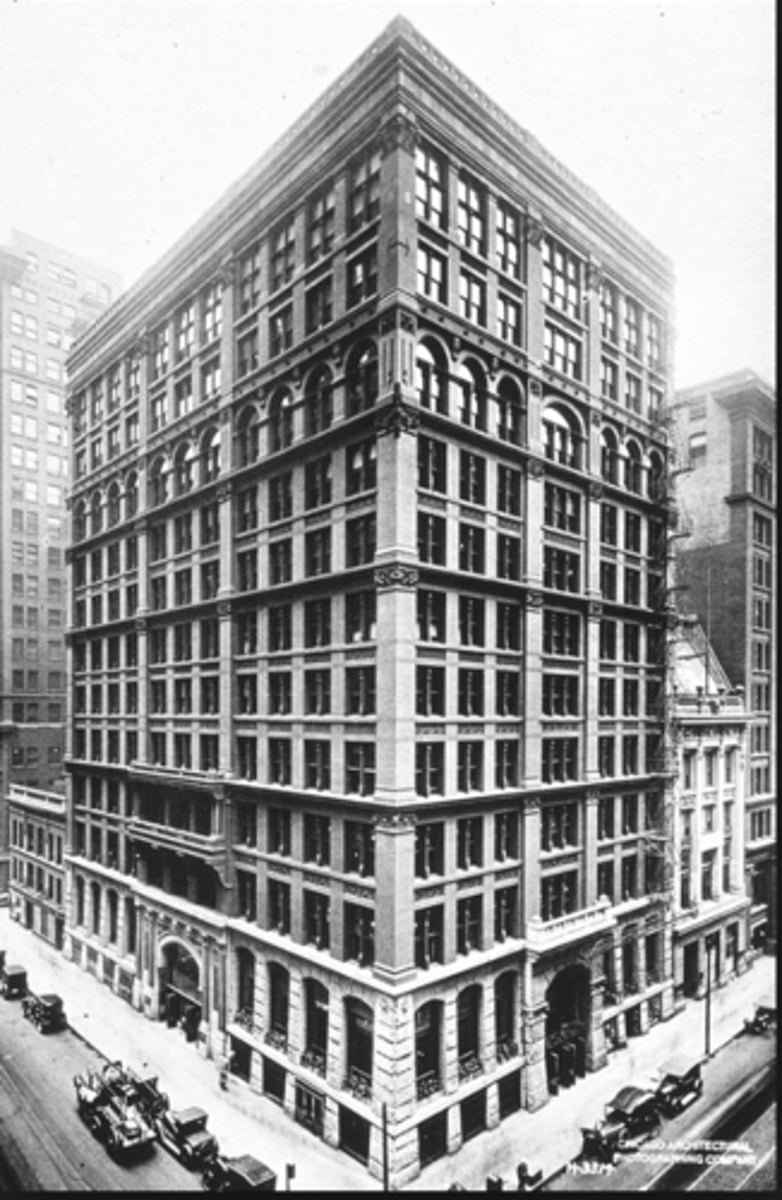
Chicago
Steel was also used to build skyscrapers, such as the Home insurance building in THIS city.

INVENTIONS PROMOTE CHANGE!
How did new inventions change Americans way of life?
INVENTIONS PROMOTE CHANGE!
How did new inventions change Americans way of life?
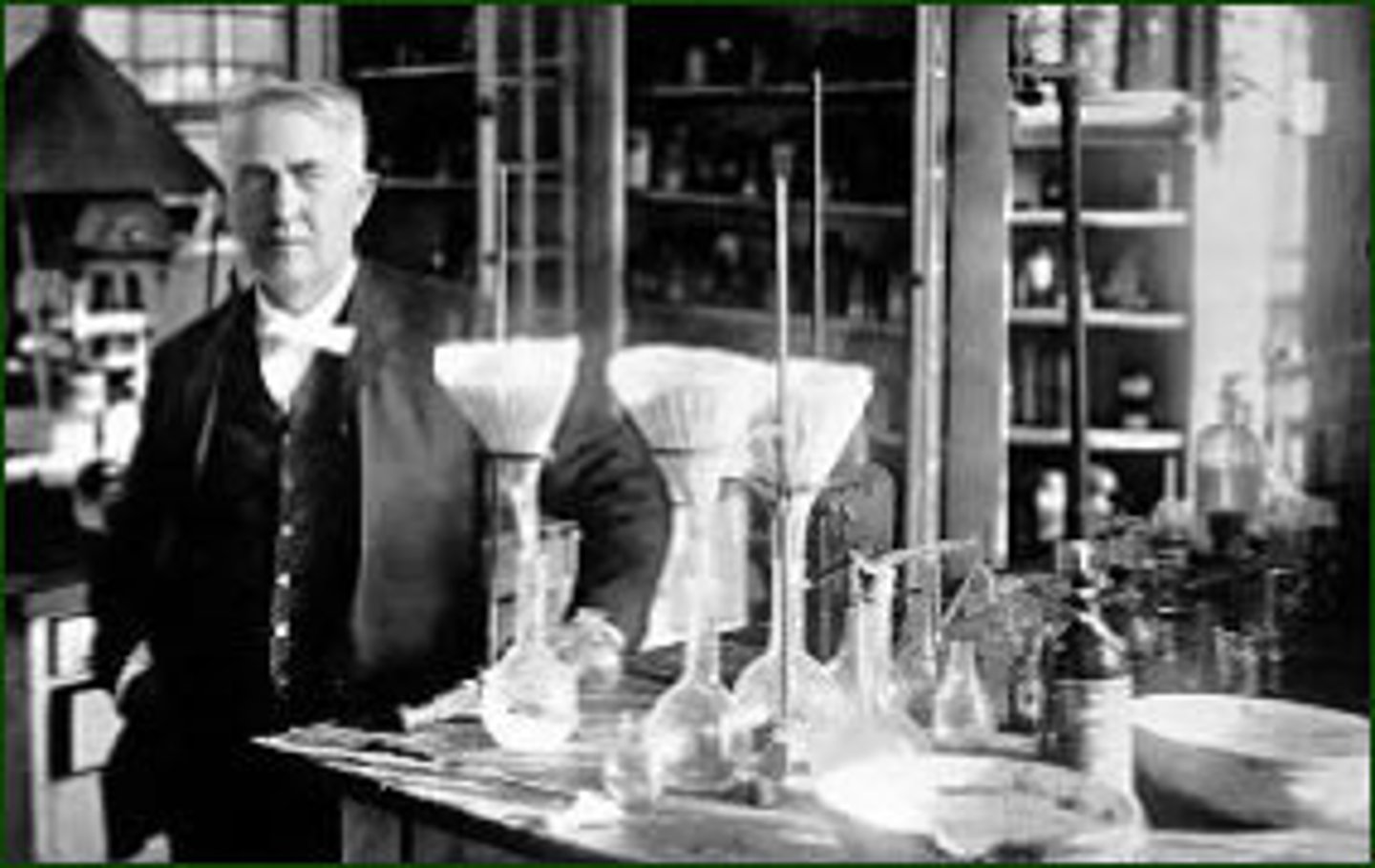
Thomas Elva Edison
In 1876 THIS inventor perfected the incandescent light bulb and created systems for producing and distributing electricity.

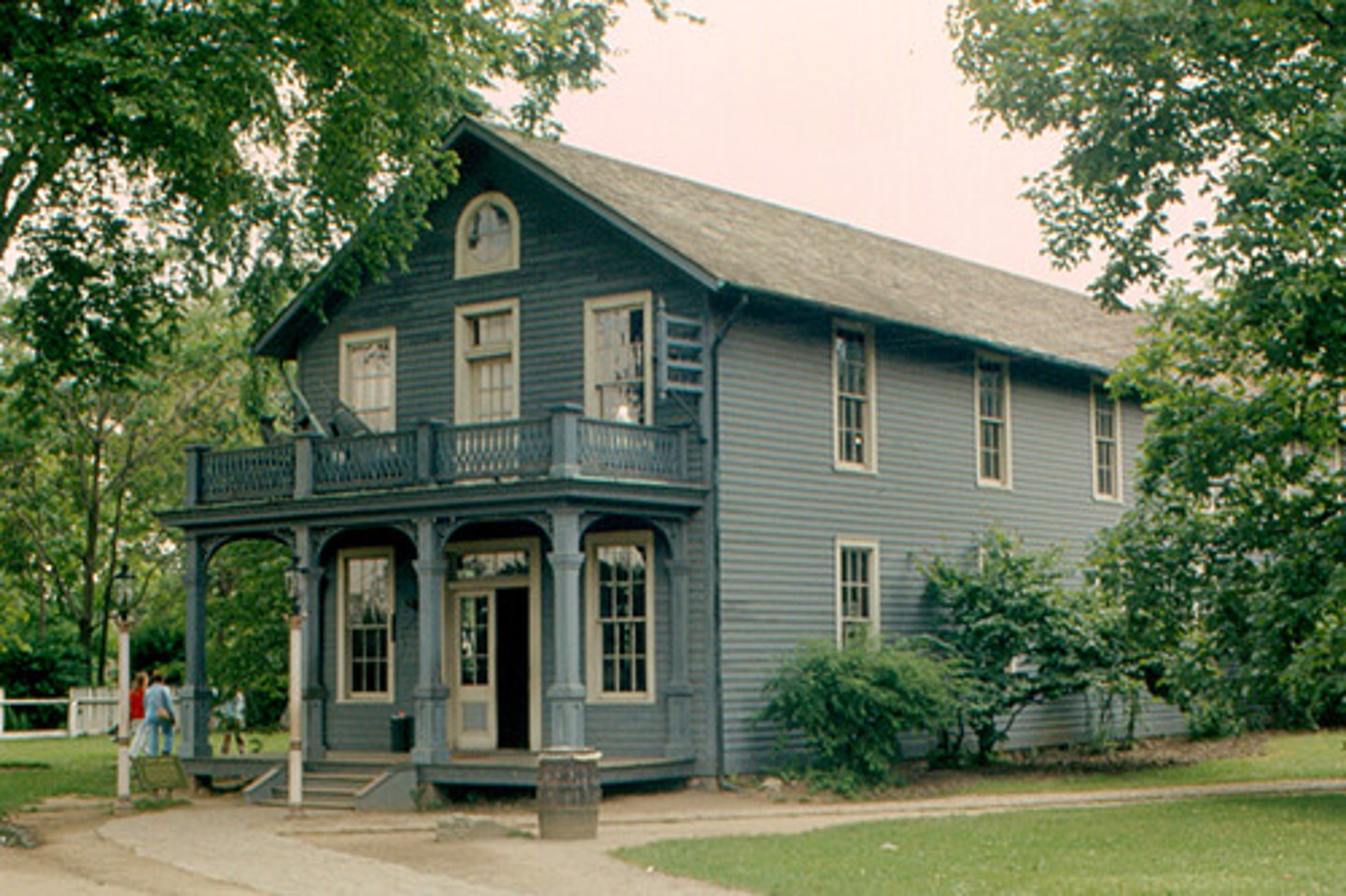
Menlo Park New Jersey
THIS is where Thomas Edison established the world's first research laboratory.

George Westinghouse
THIS inventor developed ways to make electricity safer and less expensive.

Typewriter
Office machine invented by Christopher Sholes in 1867 that changed the work world.

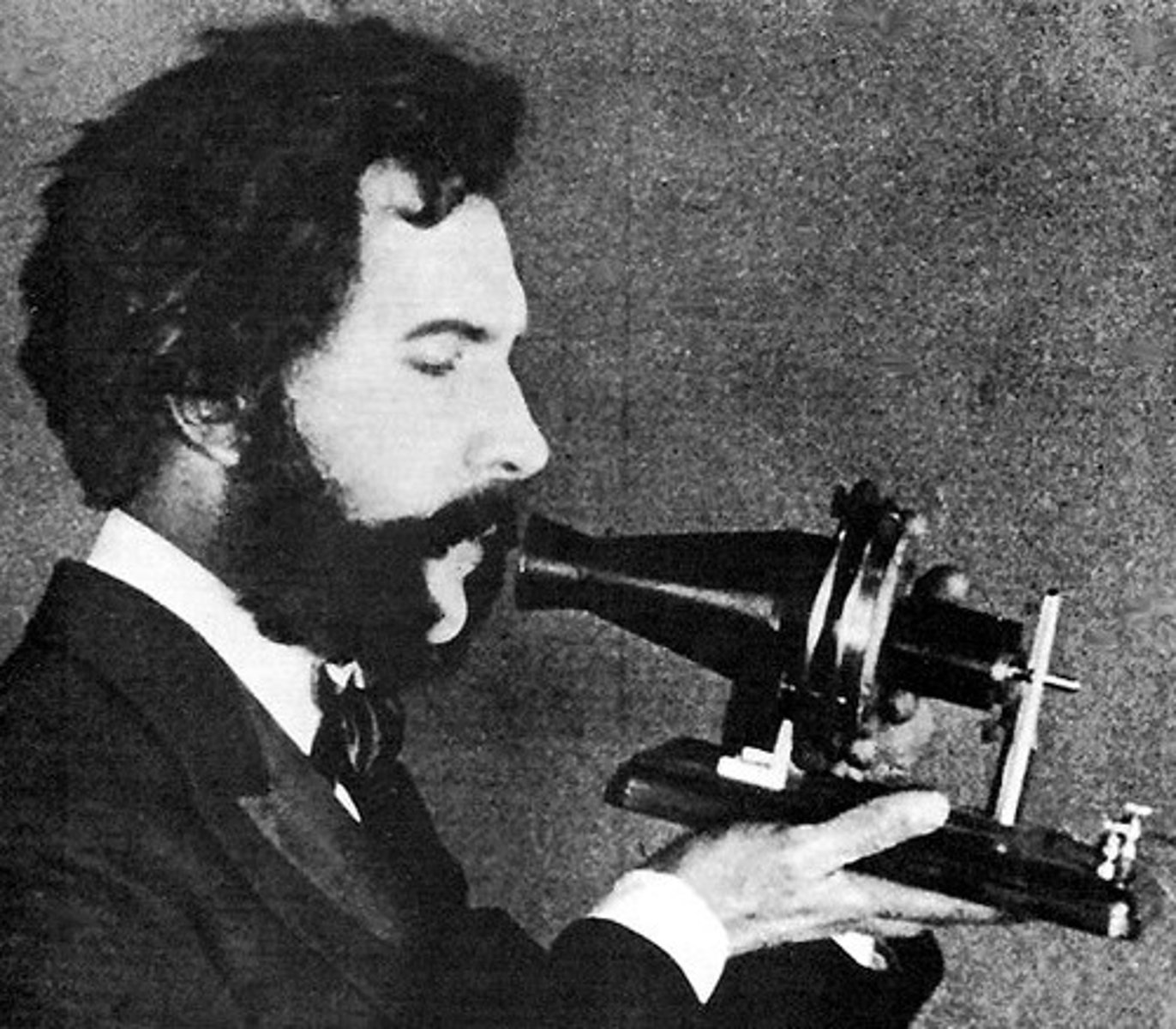
Alexander Graham Bell
along with
Thomas Watson
Almost 10 years later, the person most often credited with inventing the telephone.

II. THE AGE OF THE RAILROADS!
II. THE AGE OF THE RAILROADS!
OBJECTIVE: Discuss and explain the growth of the nation's railroad industry and its effect on the nation.
OBJECTIVE: Discuss and explain the growth of the nation's railroad industry and its effect on the nation.
Railroads Span Time and Place!
How did railroads change the way Americans told time?
Railroads Span Time and Place!
How did railroads change the way Americans told time?
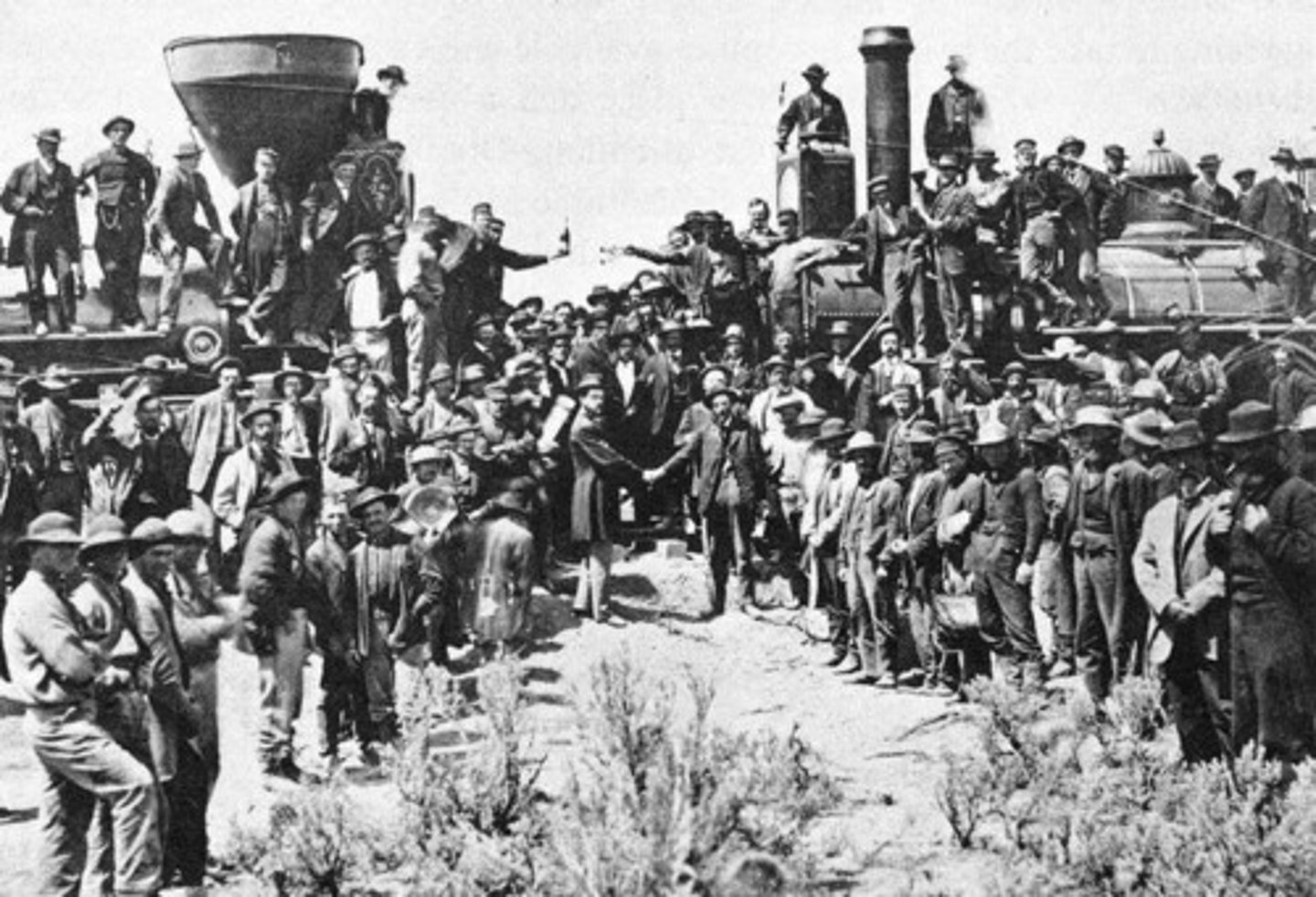
the transcontinental railroad
The transportation system that spanned the country from coast-to-coast by 1869.

Union Pacific
The railroad line that built tracks westward from Omaha, Nebraska.
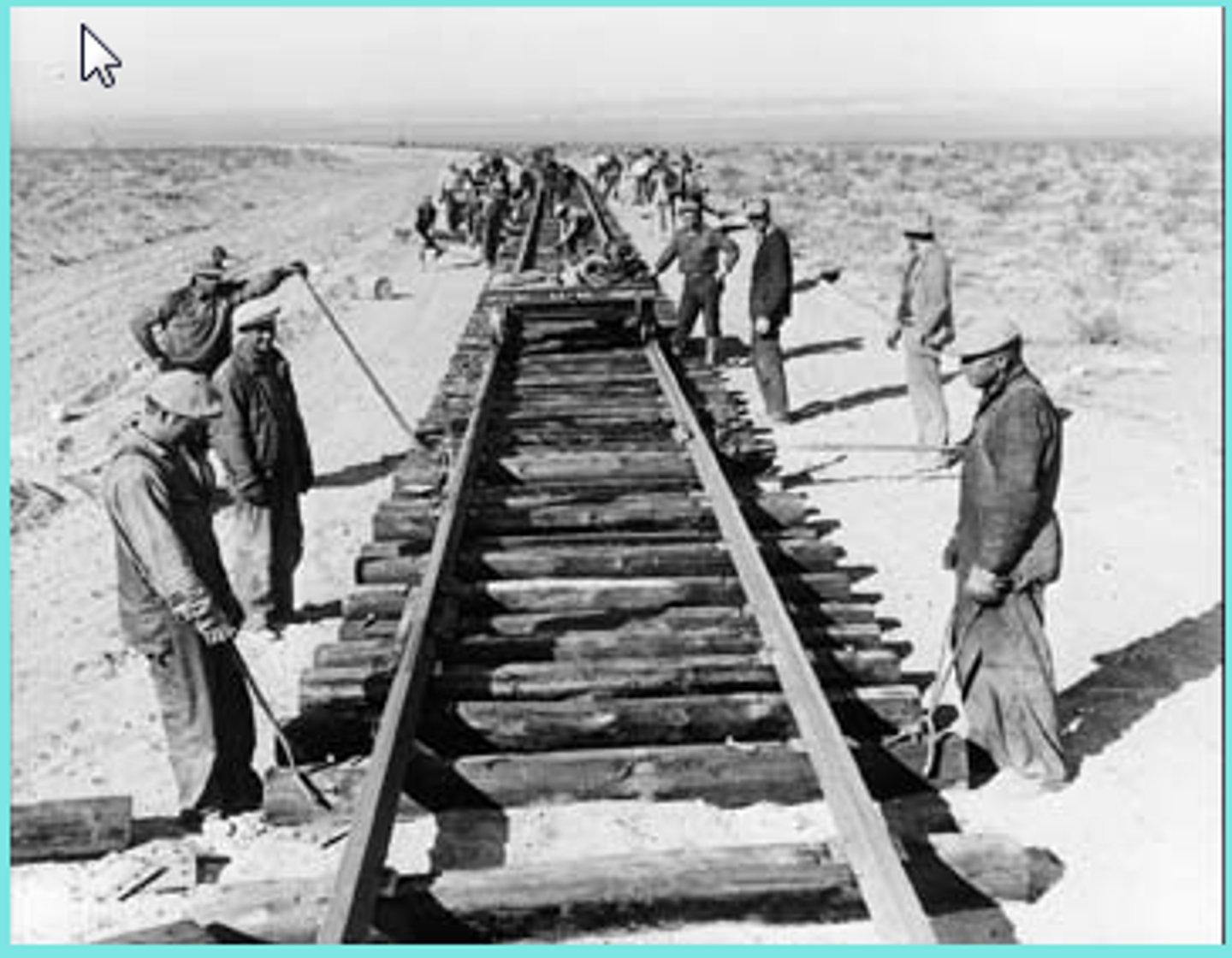

Central Pacific
The railroad line that built tracks eastward from Sacramento.
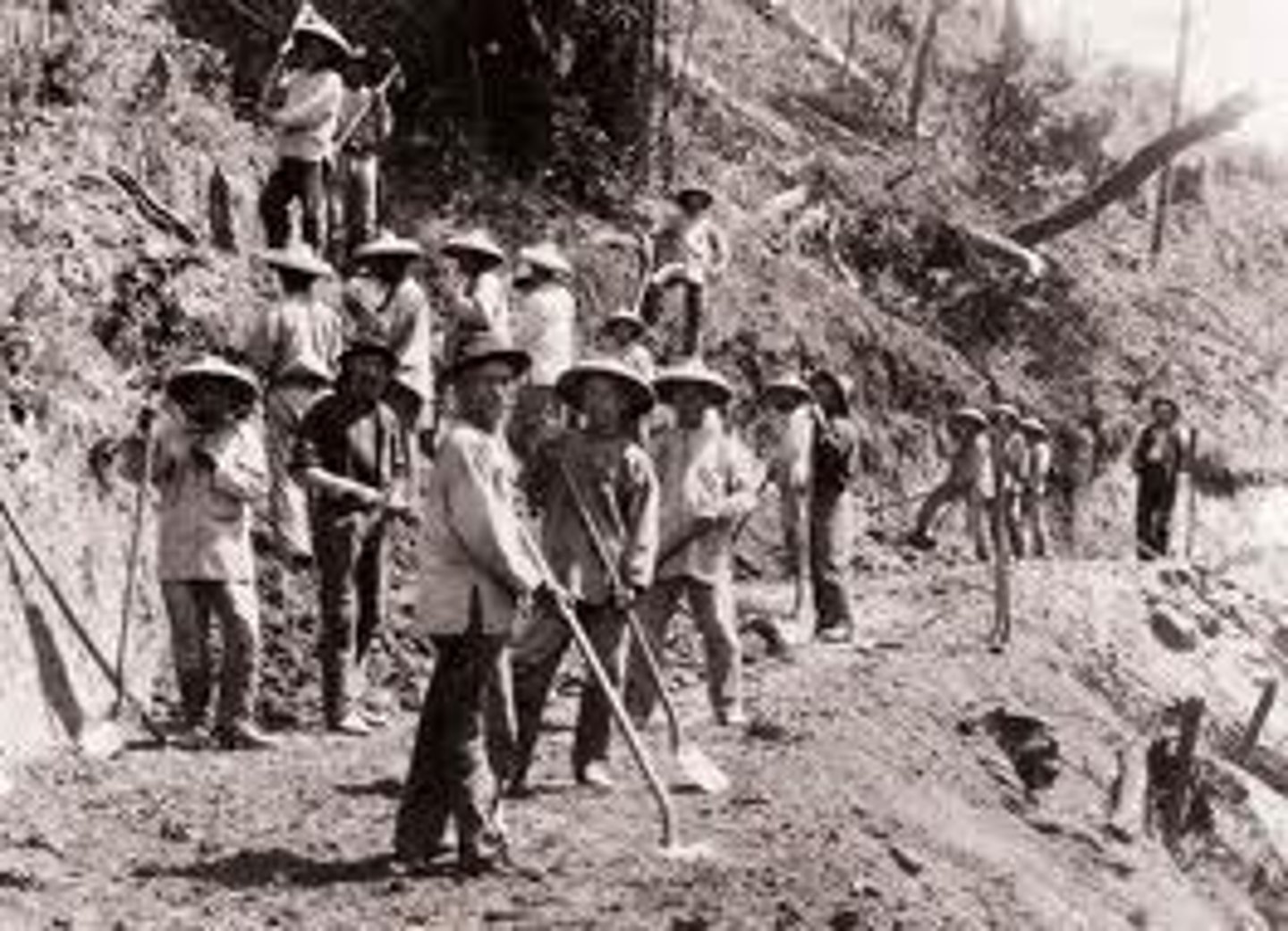

China
Many immigrants who worked on the Central Pacific were from this country.

Ireland
Many of the immigrants who worked on the Union Pacific were from this country.

C.F. Dowd
In 1870, HE invented time zones to simplify railroad schedules.
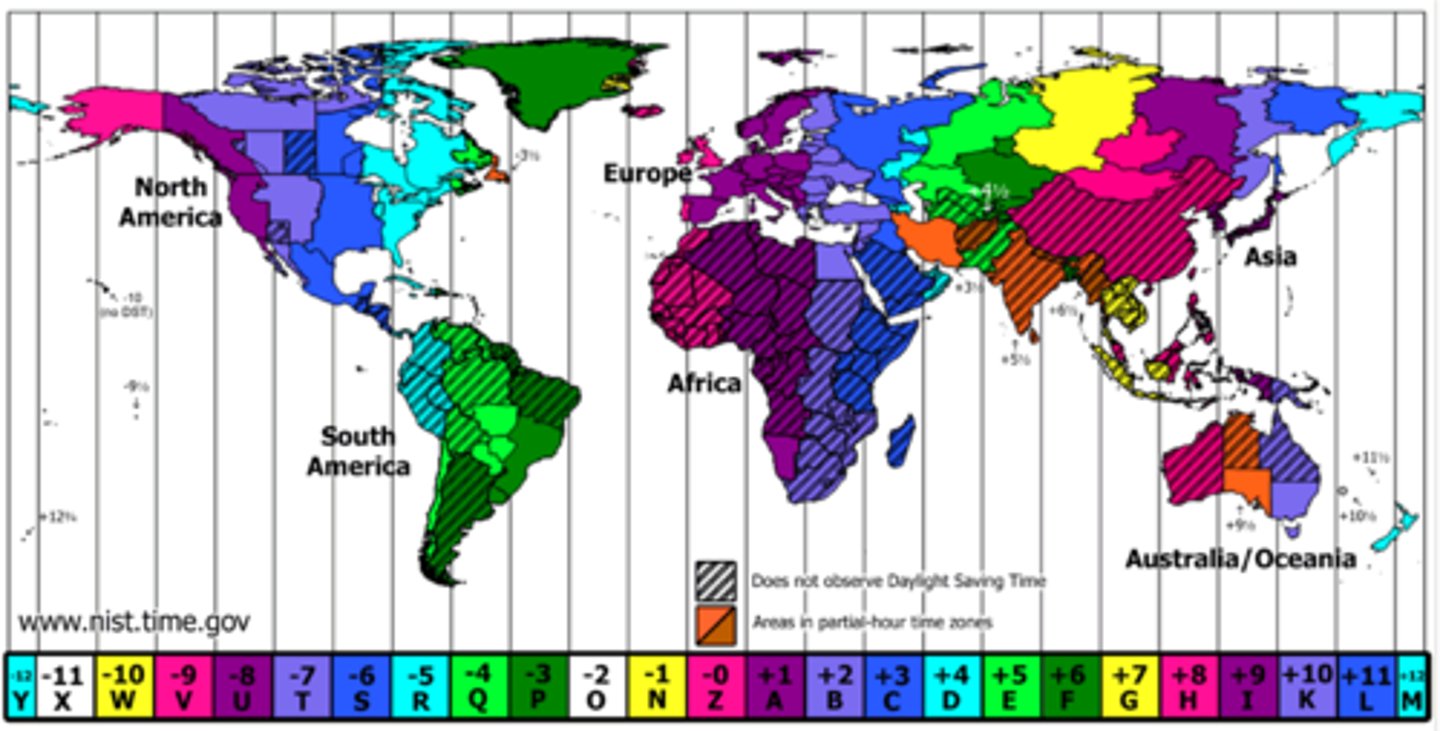
4
Number of time zones in the United States.

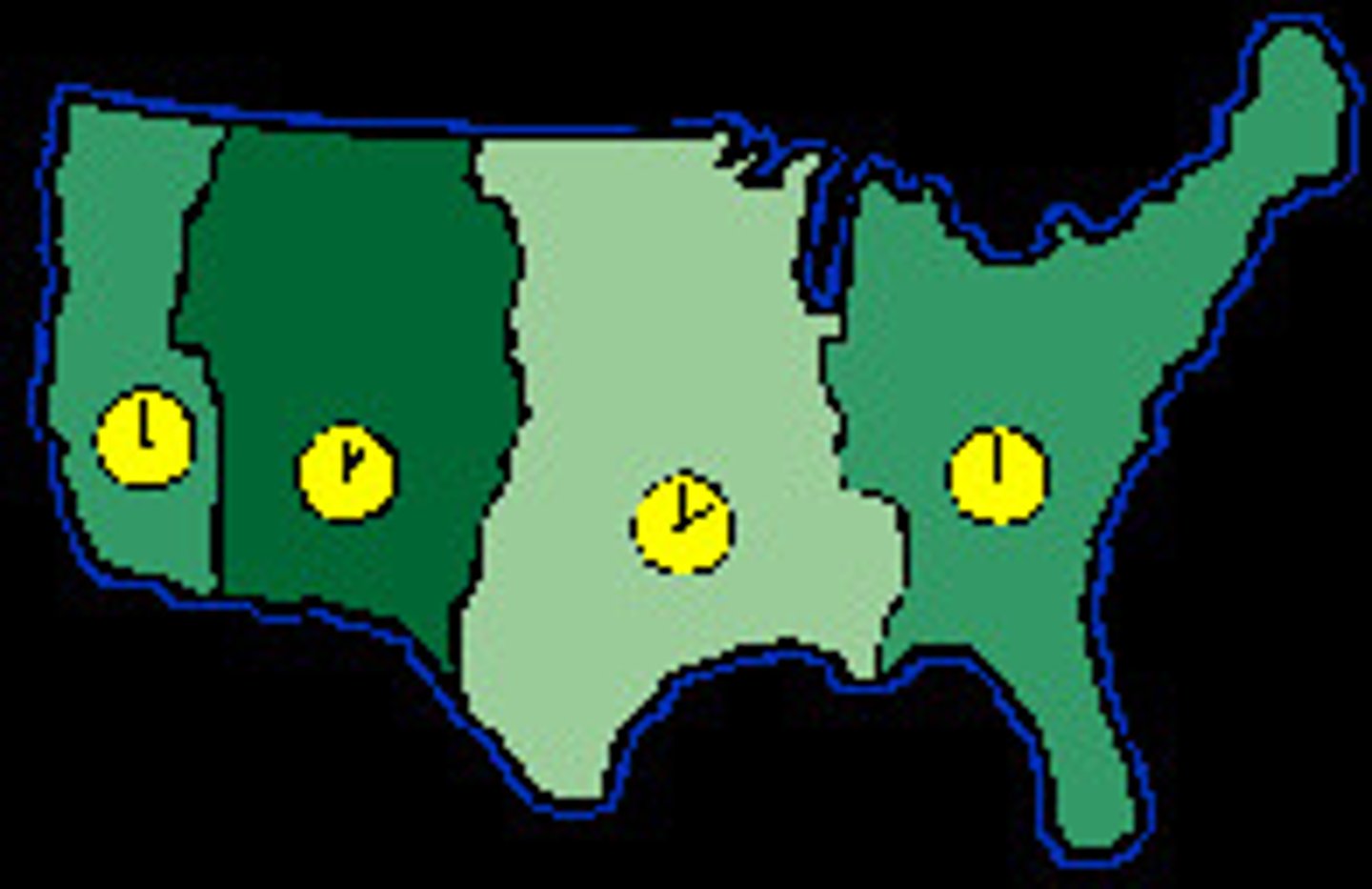
Pacific - Mountain - Central - Eastern
What are the names of the four time zones in the United States?
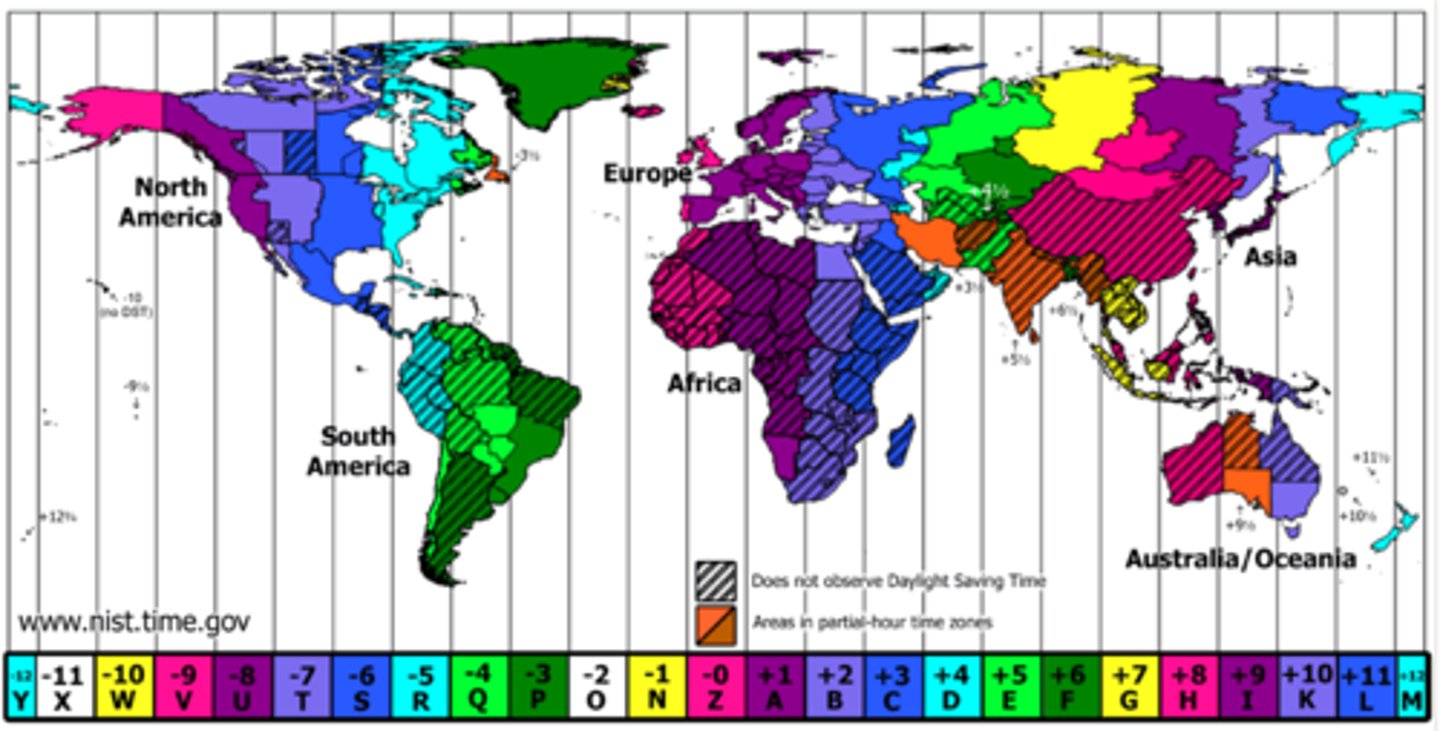
24
How many time zones span the Earth?
Opportunists and Opportunities!
How did the growth of railroads affect the nation?
Opportunists and Opportunities!
How did the growth of railroads affect the nation?
coal, iron, steel, lumber, glass
THESE five industries grew immensely due to the growth of the railroad industry.

George Pullman
Railroads led to the creation of news towns such as THIS Illinois railroad-car manufacturer who built a town for his employees.

stock holders
The railroad industry attracted many corrupt individuals including THIS group behind the Credit Mobilier scandal.

THE GRANGE AND THE RAILROADS!
Why did the farmers fight the railroads?
THE GRANGE AND THE RAILROADS!
Why did the farmers fight the railroads?
farmers
THIS group was angered because of high shipping prices and the selling of land grants to businesses.

Grangers
The group that took action and convinced some states to pass laws regulating railroads.

Munn v. Illinois
The battle reached the Supreme Court in THIS case of 1877 where states won the right to regulate the railroads.

Interstate Commerce Act
Law enacted in 1887 that reestablished the federal government's right to regulate the railroads.

Economic Depression of 1893
THIS affected numerous institutions in 1893 including the railroads as many failed and were taken over by 7 financial firms.

III. BIG BUSINESS AND LABOR!
III. BIG BUSINESS AND LABOR!
OBJECTIVE: Discuss and explain the growth and power of big business in America and how workers united to improve conditions in the nation's growing industries.
OBJECTIVE: Discuss and explain the growth and power of big business in America and how workers united to improve conditions in the nation's growing industries.
CARNEGIE'S INNOVATIONS, SOCIAL DARWINISM, AND BUSINESS!
CARNEGIE'S INNOVATIONS, SOCIAL DARWINISM, AND BUSINESS!
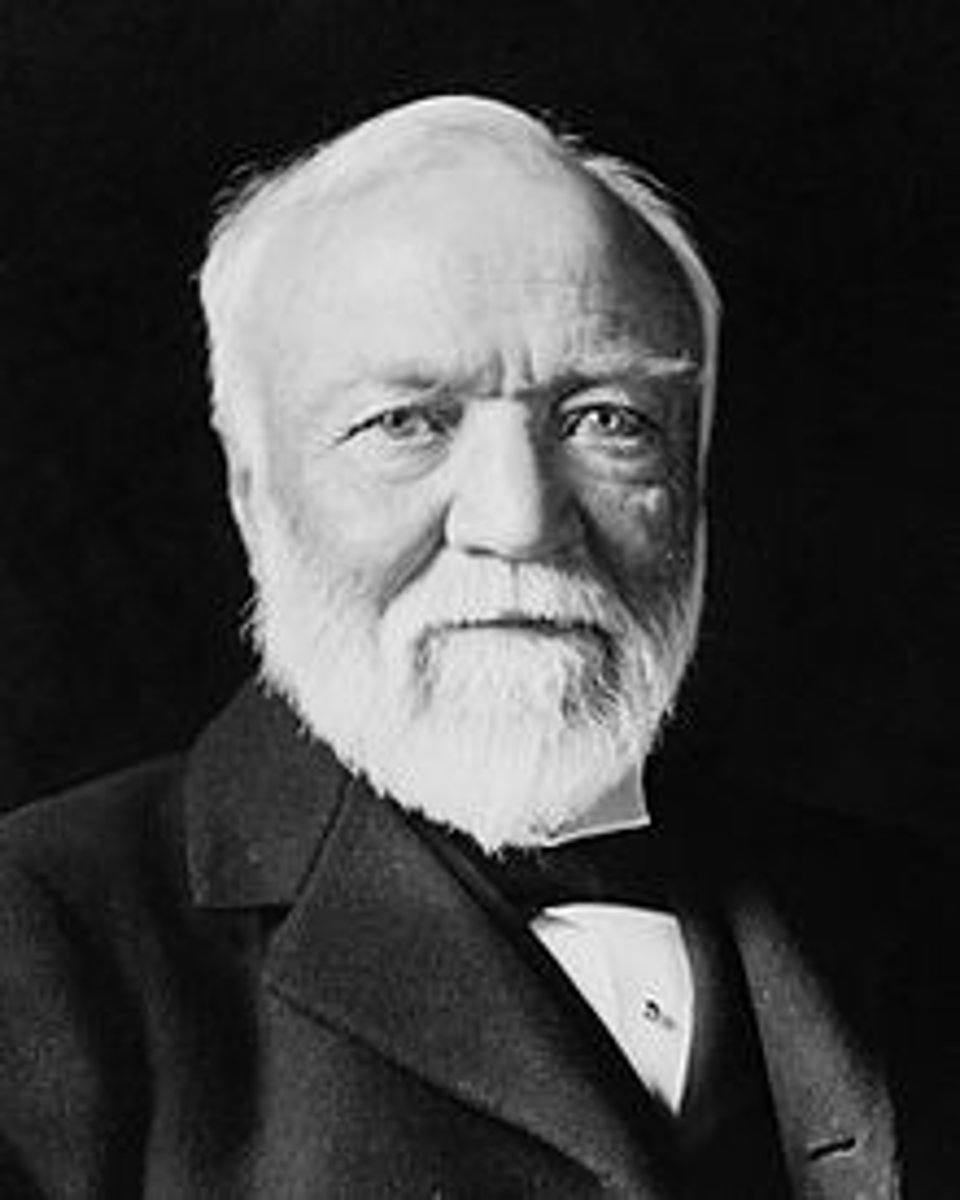
Andrew Carnegie
The rags to riches innovator and fierce competitor in the steel business.

horizontal integration
The merging of companies that make similar products.

vertical integration
Business strategy of buying out suppliers to gain control over the quality and costs of products (iron, coal, railroads).

Social Darwinism
Herbert Spencer's use of Darwin's theories to explain the evolution of human society. THIS theory justified the the efforts of millionaires and discouraged government interference in big business.

natural selection
Charles Darwin said that "THIS" enabled the best-suited people to survive and succeed.
FEWER CONTROL MORE; LABOR EMERGES!
FEWER CONTROL MORE; LABOR EMERGES!
John D. Rockefeller
The industrialist who created the Standard Oil Company of Ohio.

Holding Companies
A corporation that does nothing but buy out the stock of other companies.

Robber Barons
Tycoons like Rockefeller and Carnegie used ruthless business practices which earned them huge profits, but caused people to label them as THIS.

Sherman Antitrust Act 1890
The 1890 law that made it illegal to establish trusts that interfered with free trade.

the South
The business boom in the United States continued to bypass THIS region of the country which continued to suffer economic stagnation.

unions
Workers responded to business consolidation by Creating THESE.

National Labor Union (NLU)
They excluded African Americans
THIS union was an early labor union that that persuaded Congress to legalize an 8 hour workday for government workers in 1868.

the Colored National Labor Union (CNLU)
African Americans workers formed THIS union in 1869.
Knights of Labor
THIS union founded in 1869 and grew to one of the largest labor unions by the 1880s was led by Terrence Powderly but declined after a series of failed strikes.
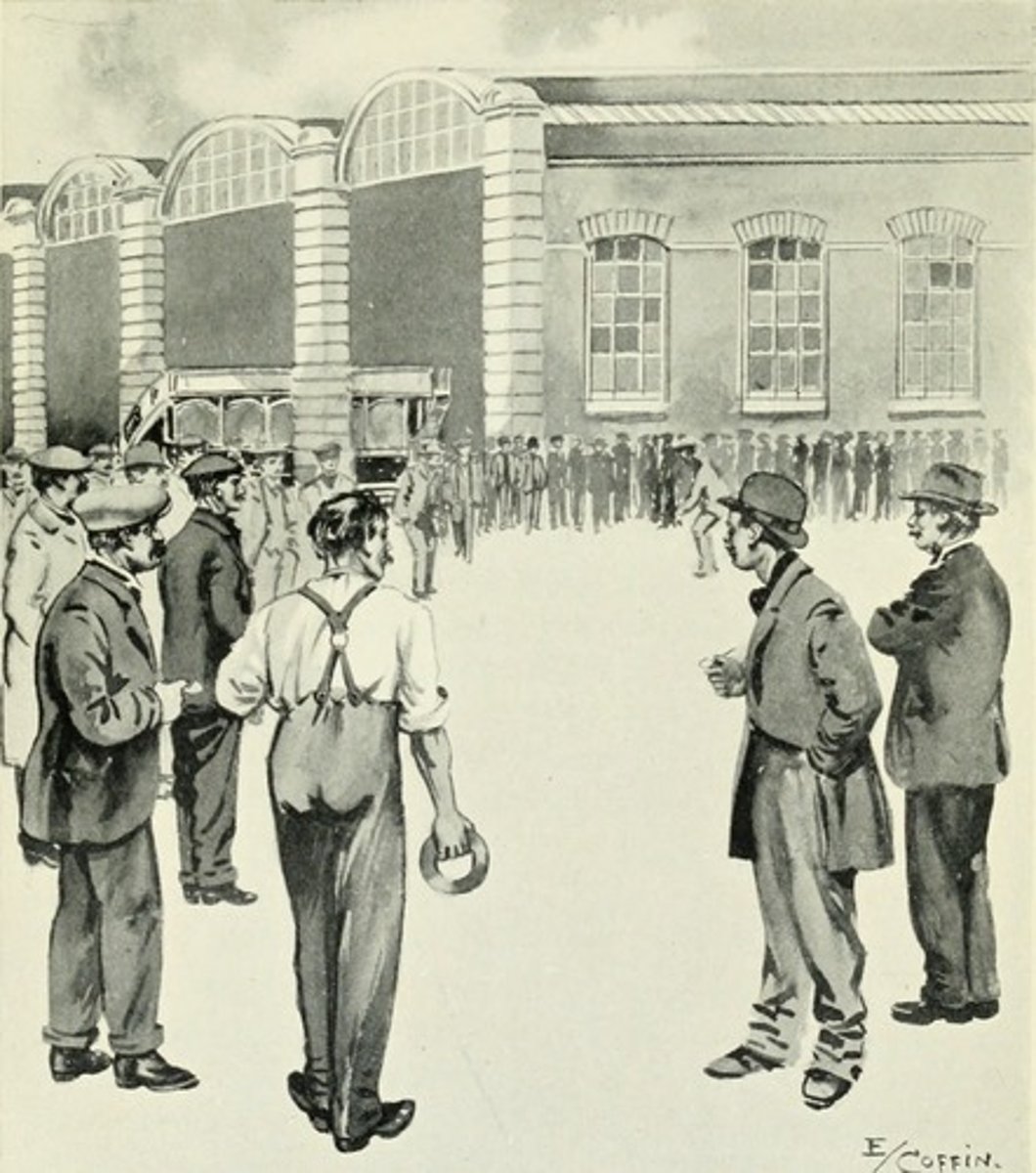

UNION MOVEMENTS DIVERGE; STRIKES TURN VIOLENT!
UNION MOVEMENTS DIVERGE; STRIKES TURN VIOLENT!
Samuel Gompers
The union organizer that helped create and then led the American Federation of Labor (AFL) 1886.
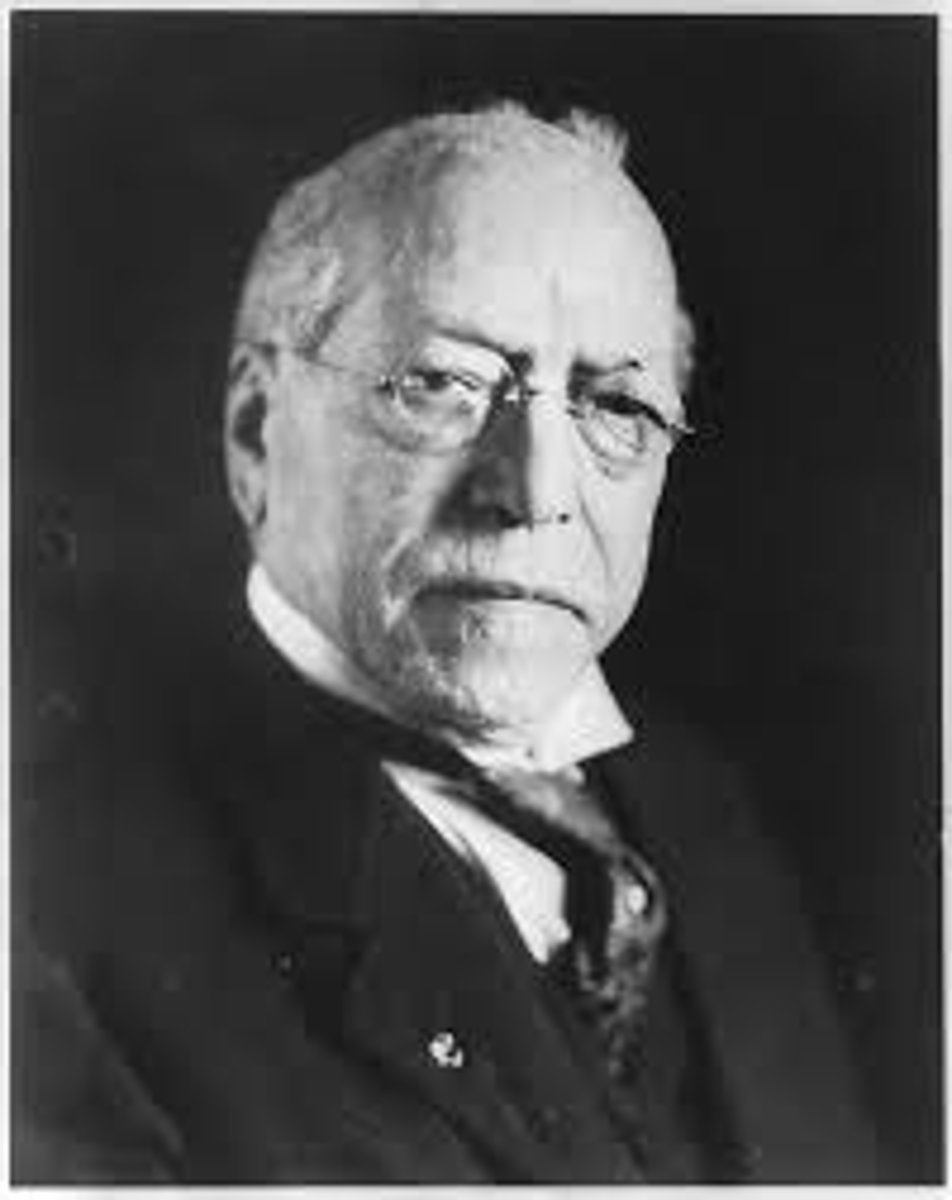

strikes and collective bargaining
Gompers used THESE two methods between labor and management to win higher wages and shorter workweeks.

Eugene V. Debs
Labor leader of the first union of skilled and unskilled workers in one industry; the American Railway Union.

Industrial Workers of the World (IWW)
Organized in Chicago in 1905, a group of radical unionists and socialists known as Wobblies.
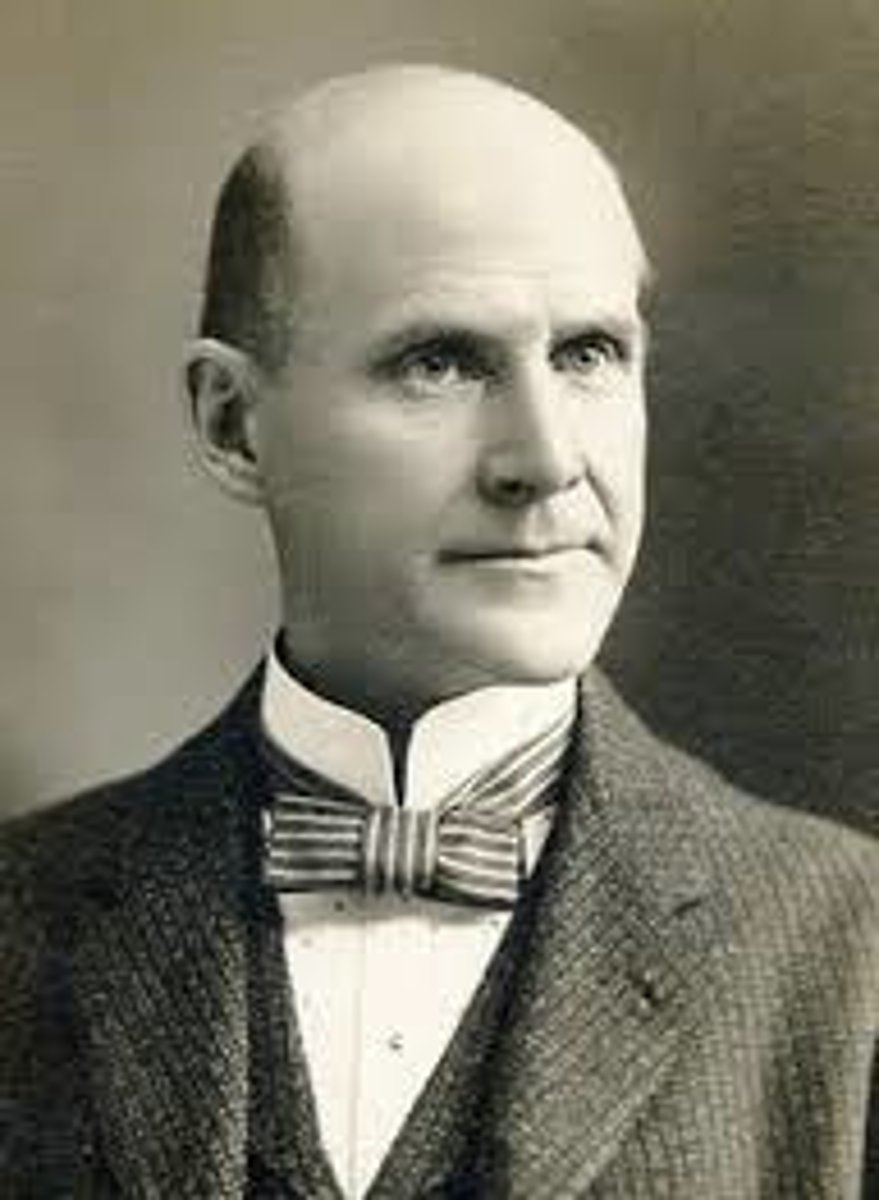

Rutherford B. Hayes
In 1877, workers for the Baltimore and Ohio railroad went out on strike. The strike was broken up when the railroad president persuaded HIM to bring in federal troops to end the strike.

Mary Harris Jones "Mother Jones"
Prominent organizer in the women's labor movement and the United Mine Workers of America, and a supporter of the Great Strike of 1877
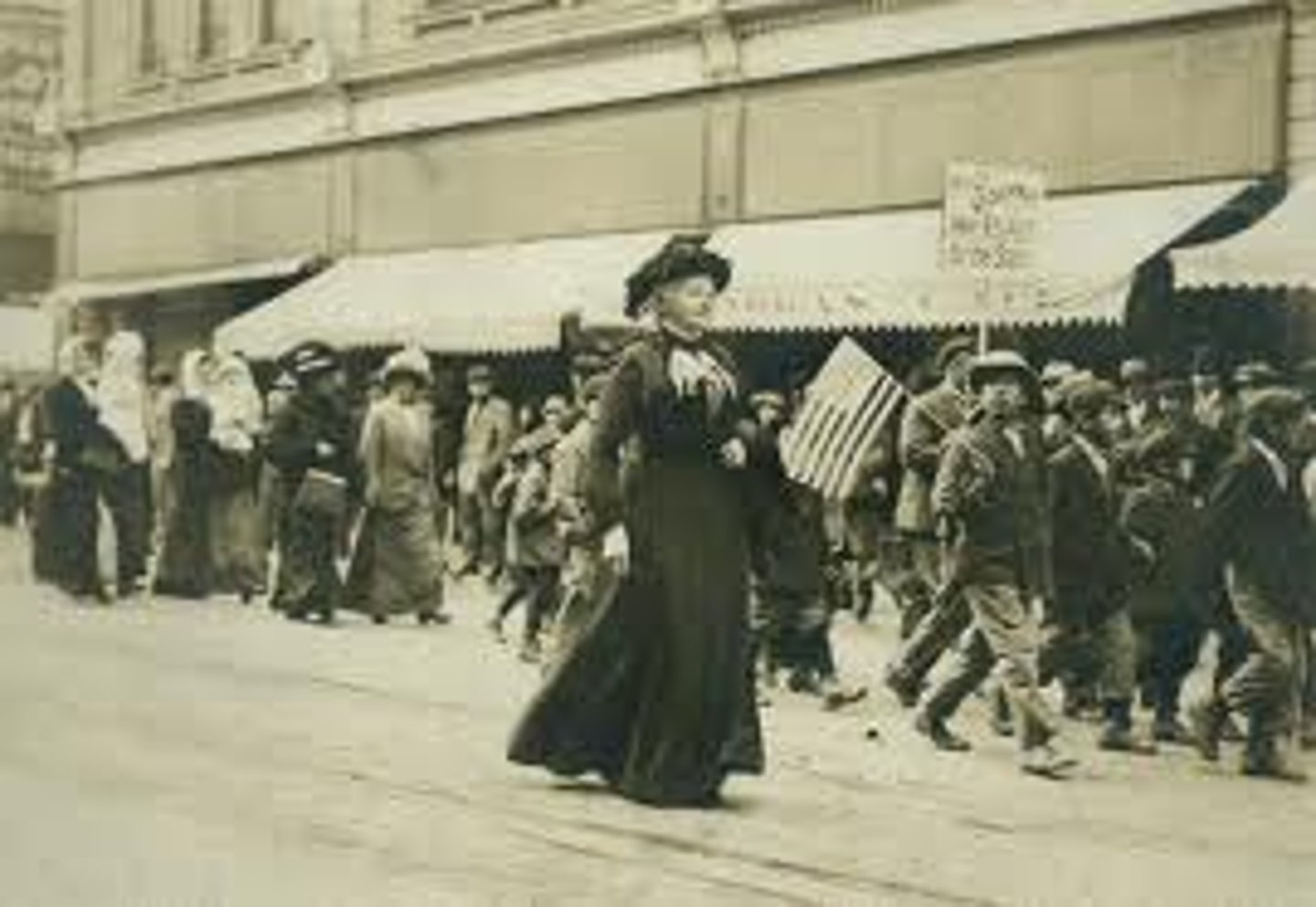

Haymarket Affair
Labor leaders were blamed when a bomb exploded at a demonstration in Chicago in 1886 killing several people. Four labor leaders were hanged even though no one knows who actually set off the bomb.
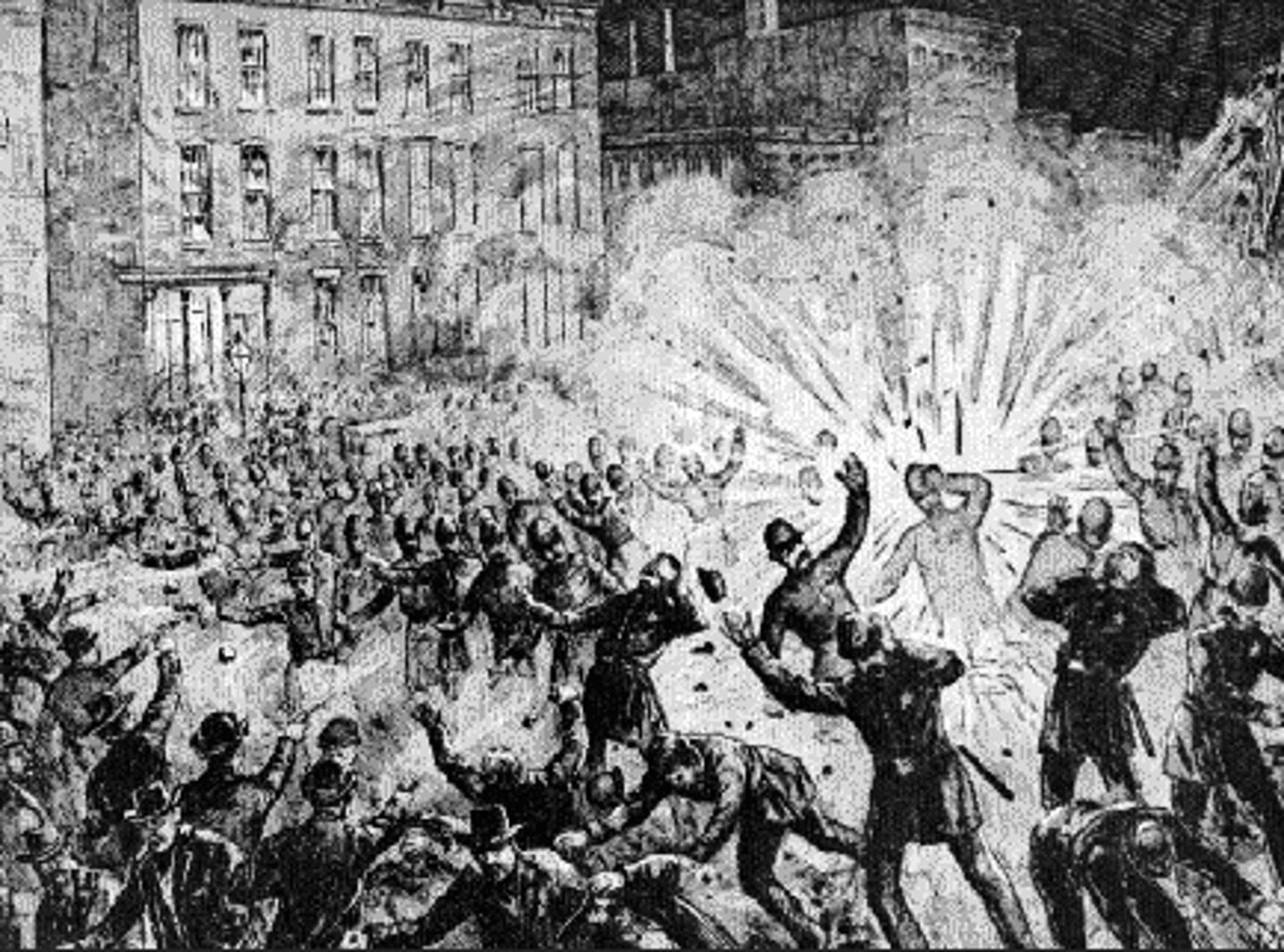

Homestead
In 1892, steel workers and Pinkerton Guards fought THIS battle near Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, that left dead on both sides.
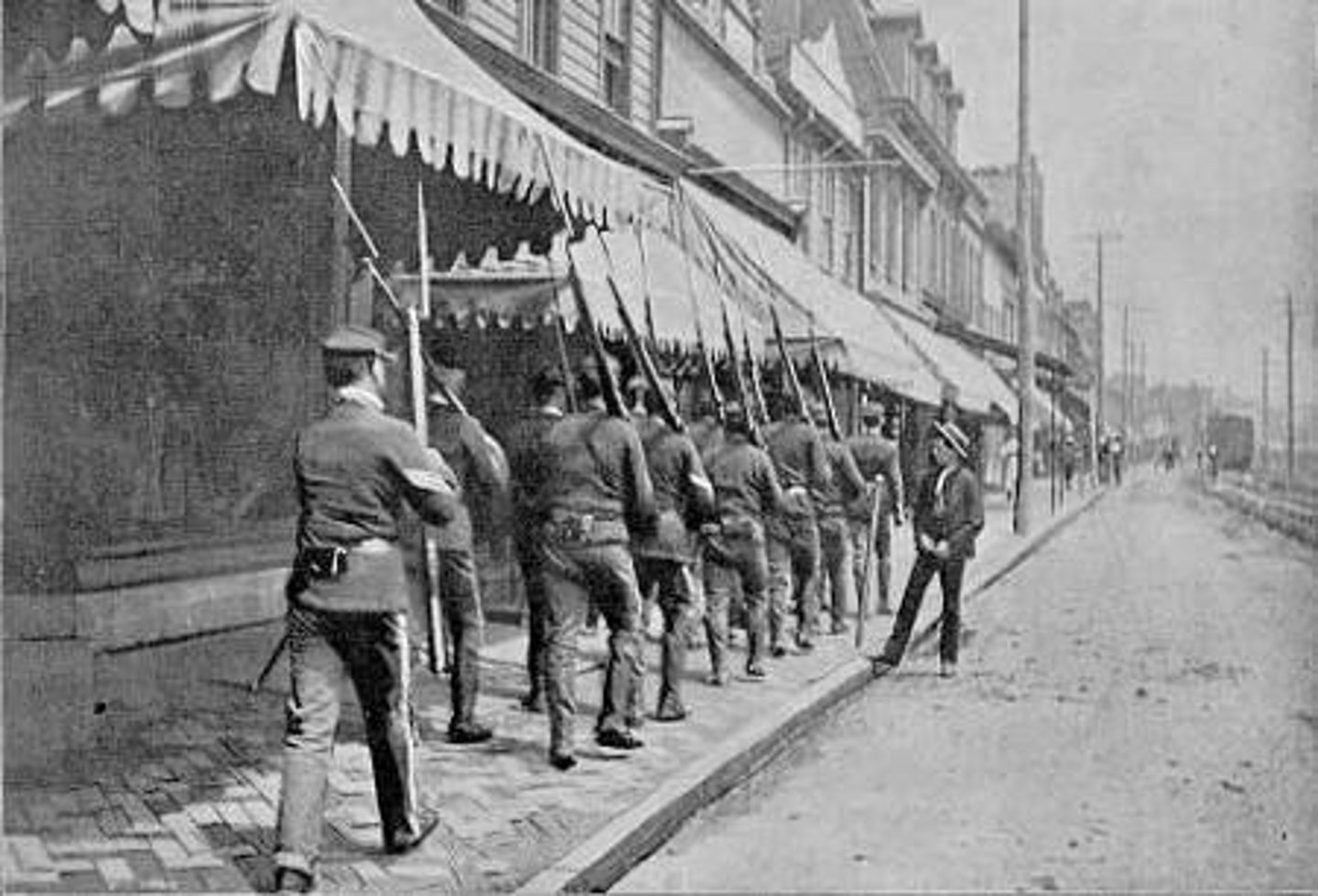

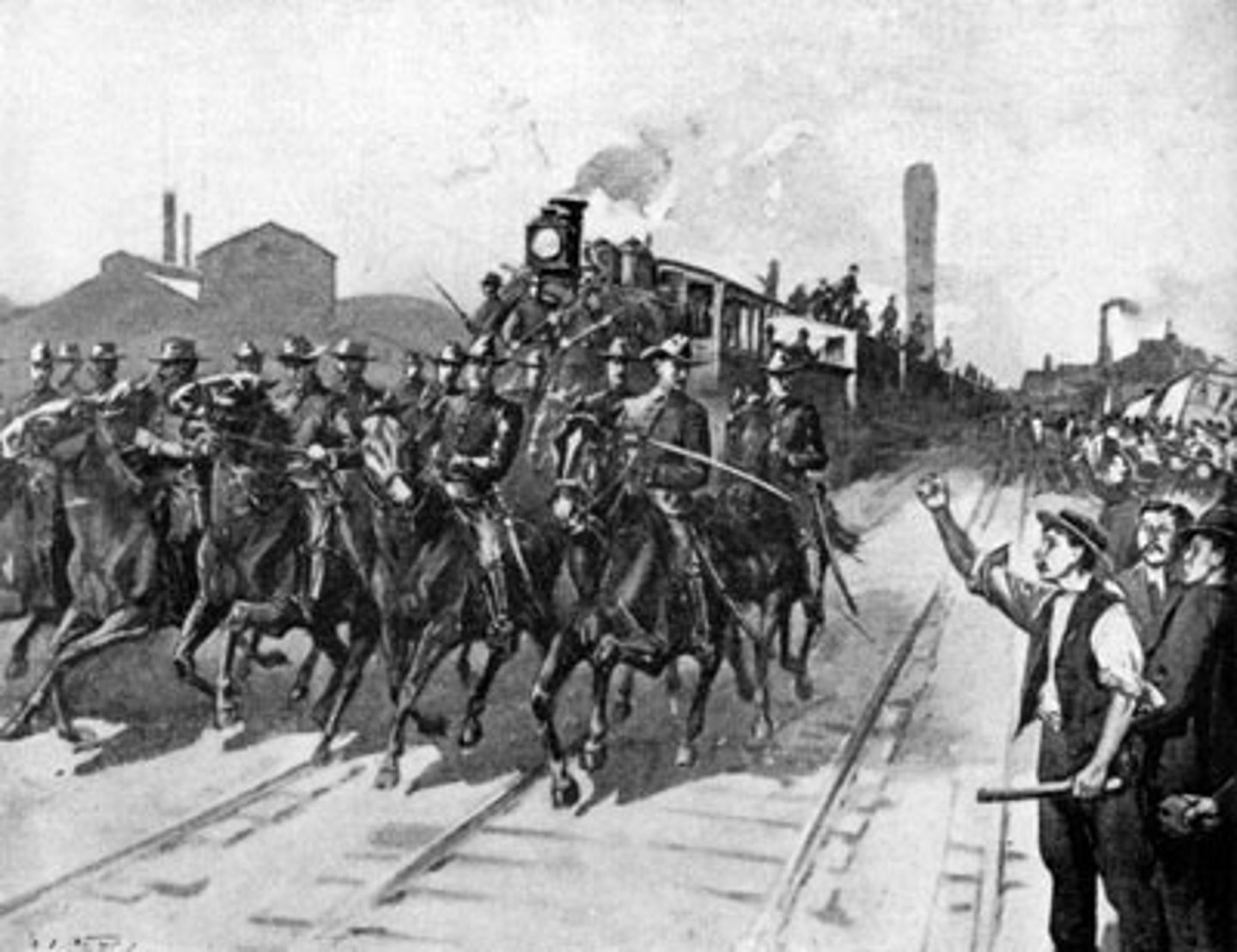
Pullman Company
A strike against THIS company in 1894, led by Eugene V. Debs and his American Railway Union turned violent where federal troops were called out to break the strike.

Sherman Antitrust Act
More often than not, the government sided with the owners and against the unions. Courts used THIS Act against the workers.
Despite the pressures of government action, unions continued to grow.

THE END!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
THE END!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!