Cytogenetics
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Translocations, inversions and deletions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is a reciprocal translocation?
one part of a chromosome is exchanged with another
There’s no net loss of genetic material
Breakpoint
point of breakage event
Derivative chromosomes / der
rearranged chromosomes
centric segment
part that included the centromere
translocated segment
part that comes from another chromosome
What are the 2 types of effects of a translocation?
Balanced
Unbalanced
What is the effect of a balanced translocation?
(Usually) No effect
Unless a critical gene is affected
Efect can be on reproduction/ fertility due to meiosis
What is the effect of a balanced translocation?
some loss / gain
Quadrivalent
a structure that forms during meiosis when two normal chromosomes and two derivative chromosomes come together
What are the 3 modes of quadrivalent segregation?
2:2
3:1
4:0
What are the 3 types of 2:2 quadrivalent segregation?
alternate
adjacent-1
adjacent-2
What is the only form of quadrivalent segregation that results in balanced segregation?
alternate 2:2
What are the 2 possible gamete results of 4:0 segregation?
Doubly disomic
Nullisomic
What is the translocation pattern for 2:2 adjacent-1 translocation?
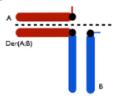
What is the translocation pattern for 2:2 adjacent-2 translocation?
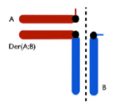
What is the translocation pattern for 2:2 alternate translocation?
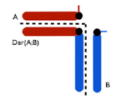
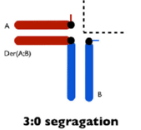
What is the translocation pattern for 3:0 translocation?
Robertsonian Translocations
a chromosomal abnormality where the long arms of two different chromosomes fuse together
What gametes can be formed as a result of Robertsonian translocations?
alternate
adjacent
What are the 3 possible effects of Robertsonian translocations?
Balanced
Trisomy
Monosomy
What is uniparental disomy?
2 copies of chromosomes from the same parent
Are monosomies of autosomes viable?
NO
Are monosomies of X chromosomes viable?
Yes
What is uniparental heterodisomy?
the two different chromosomes are inherited from one parent
How does uniparental heterodisomy occur?
Trisomy rescue
What is uniparental isodisomy?
two of the same chromosomes come from the same parent
How does uniparental isodisomy occur?
trisomy or monosomy resure
On what chromosomes can robertsonian translocations occur?
13,14,15,21,22
Why cam Robertsonian translocations only occur on certain chromosomes?
Chromosomes that are acrocentric
Acrocentric = ends of short arms have similar DNA seqs
Increased likelihood to fuse
What is the effect of robertsonian translocations in carriers?
45 chromosomes
fusion of 2 q arms
loss of two joint short arms
What are the 2 types of inversions?
Pericentric
Paracentric
What determines the type of inversion?
Position of the centromere
Where is the centromere in paracentric inversions?
Outside inverted regions
AWAY from centromere
Where is the centromere in pericentric inversions?
Centromere is within inverted regions
IN centromere
Which type of inversion leads to more likely imbalanced offspring?
PERICENTRIC
How is the ISCN written for inversions?
Number of Chromosomes
Sex Chromosomes
inv(x) - where x is chromosome number
(breakpoints) - with no ; between the breakpoint
e.g. 46,XY,inv(1)(p11q22)