L4 Cardiac conduction system and ECG
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Learning objectives
list the pacemaker cells of the heart and understand its electric conduction system
Compare the action potentials in heart cells: pacemaker cells vs. non-pacemaker cells
Rationalise the regulation of heart rate
Understand the principles behind ECG
Describe the normal ECG trace and the corresponding electrical events in the heart
What are some shared characteristics between cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle?
Striated, tropononin-tropomyosin, length-tension relationship, T-tubules
What are some shared characteristics between cardiac muscle and smooth muscle?
Calcium enters from extracellular fluid (ECF) and sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), pacemaker activity, gap junctions
What are some unique characteristics of cardiac muscle?
Syncytium, long action potential (AP)
Pacemaker AP
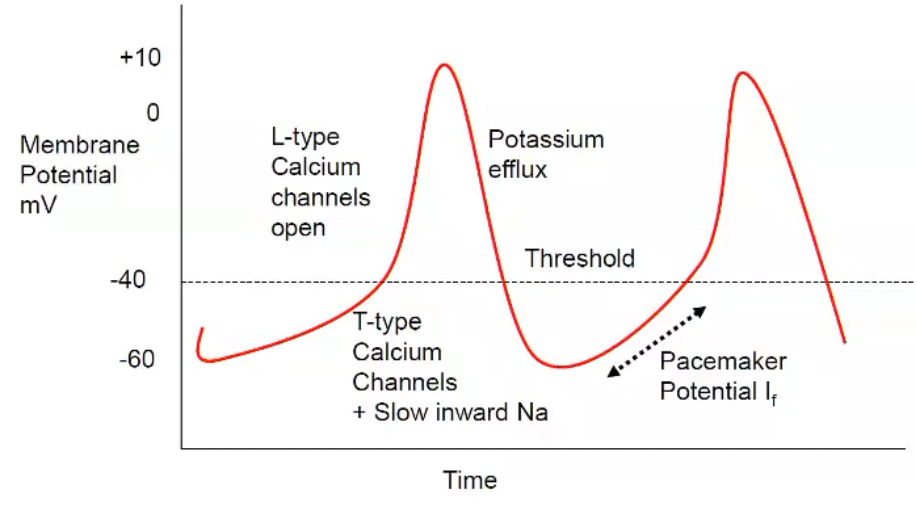
Non-pacemaker AP
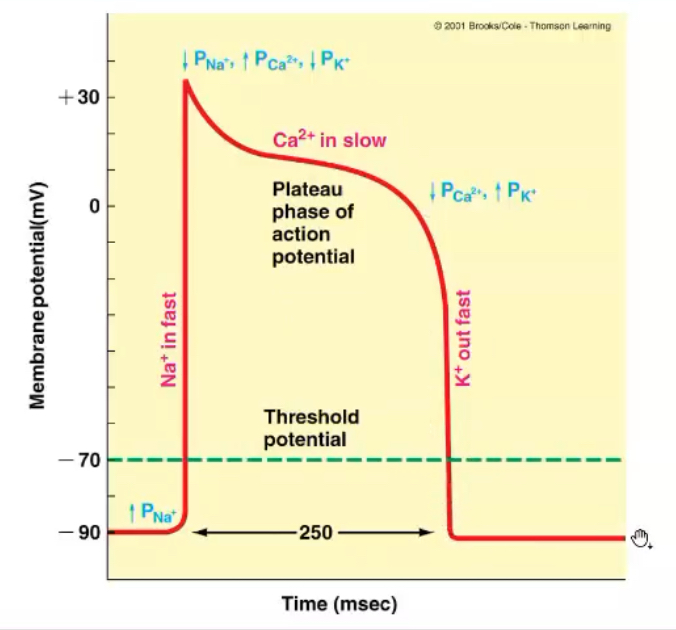
What are the pacemaker cells (4)?
Sinoatrial (sinus) node
Atrioventricular node
Bundle of His
Purkinje fibres
What nerve is activated by the PNS?
Vagus nerve → SA + AV node → acteylcholine → muscarinic receptors
What happens when PNS system is activated?
↓ HR
What is activated by SNS?
Noradrenaline → b1 receptors → SA node and myocardium
What happens when the SNS is activated?
↑ increase HR, ↑ contraction force
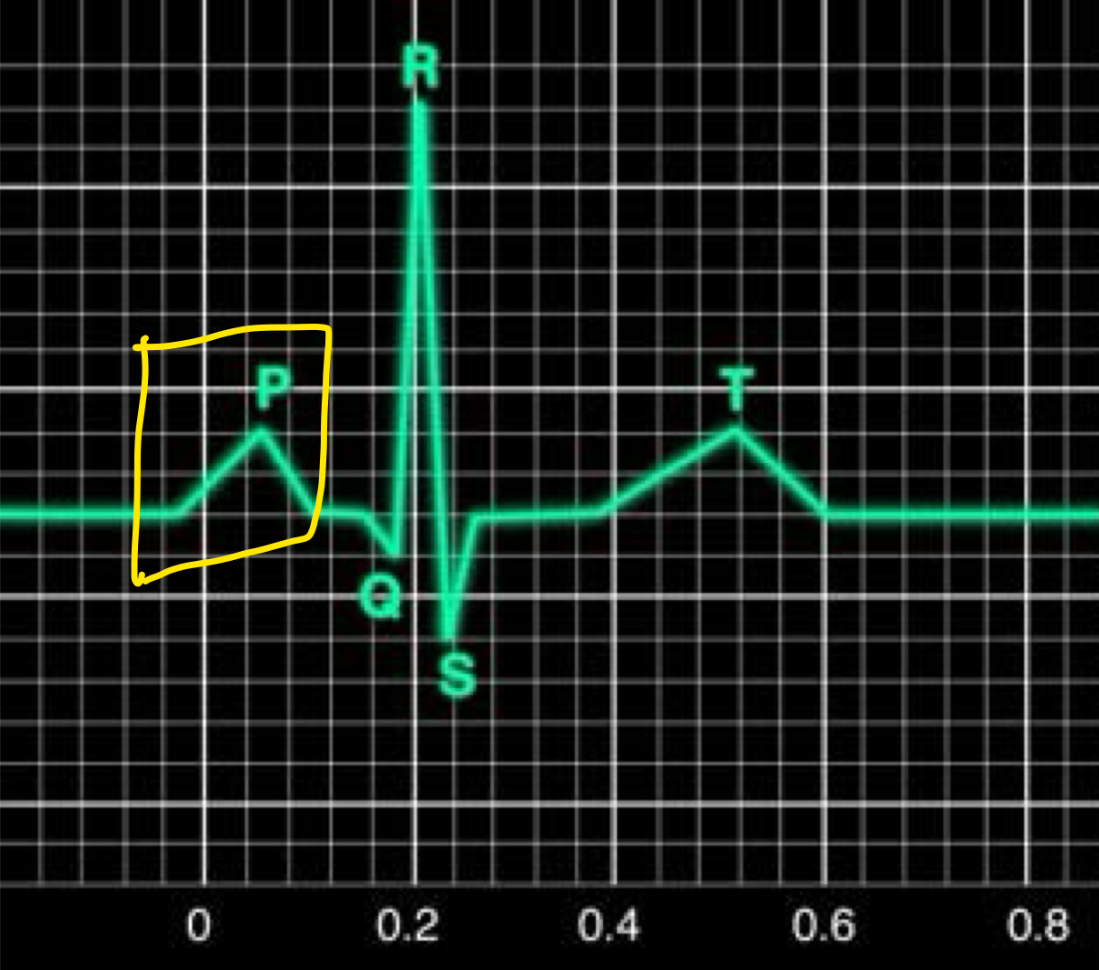
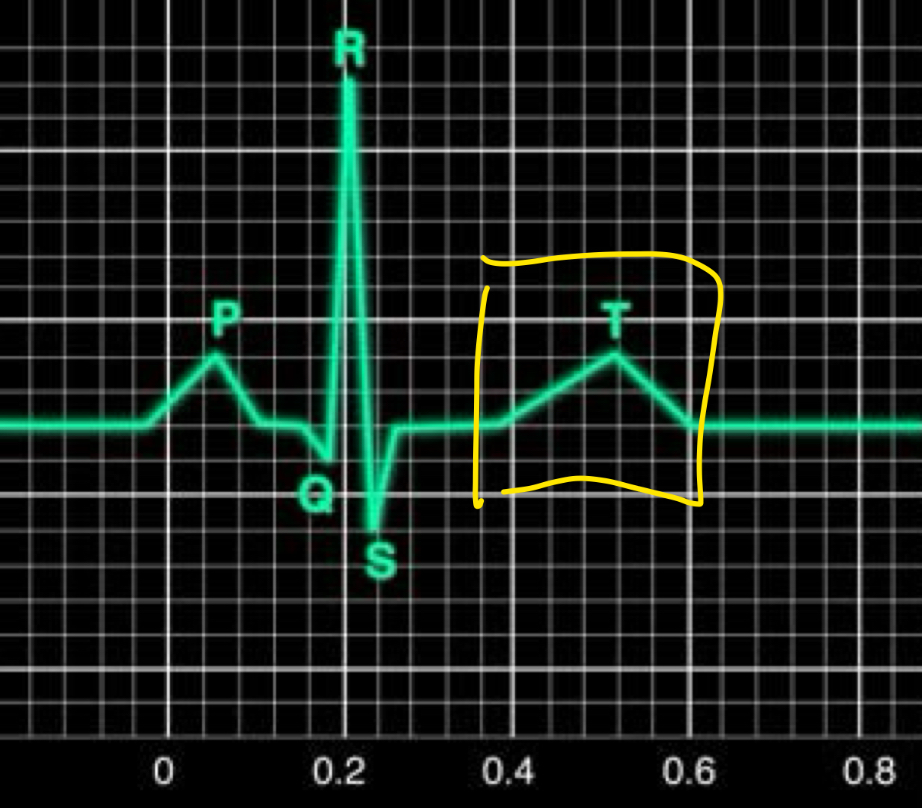
P wave
Atrial depolarisation
SA nodes undergo depolarisation
Message goes to AV node
Message went through interatrial pathway
Left/right atrium will contract soon
QRS complex
Ventricular depolarisation
bundle of His/purkinje fibres undergo depolarisation
2 ventricles will contract soon
Atrial repolarisation
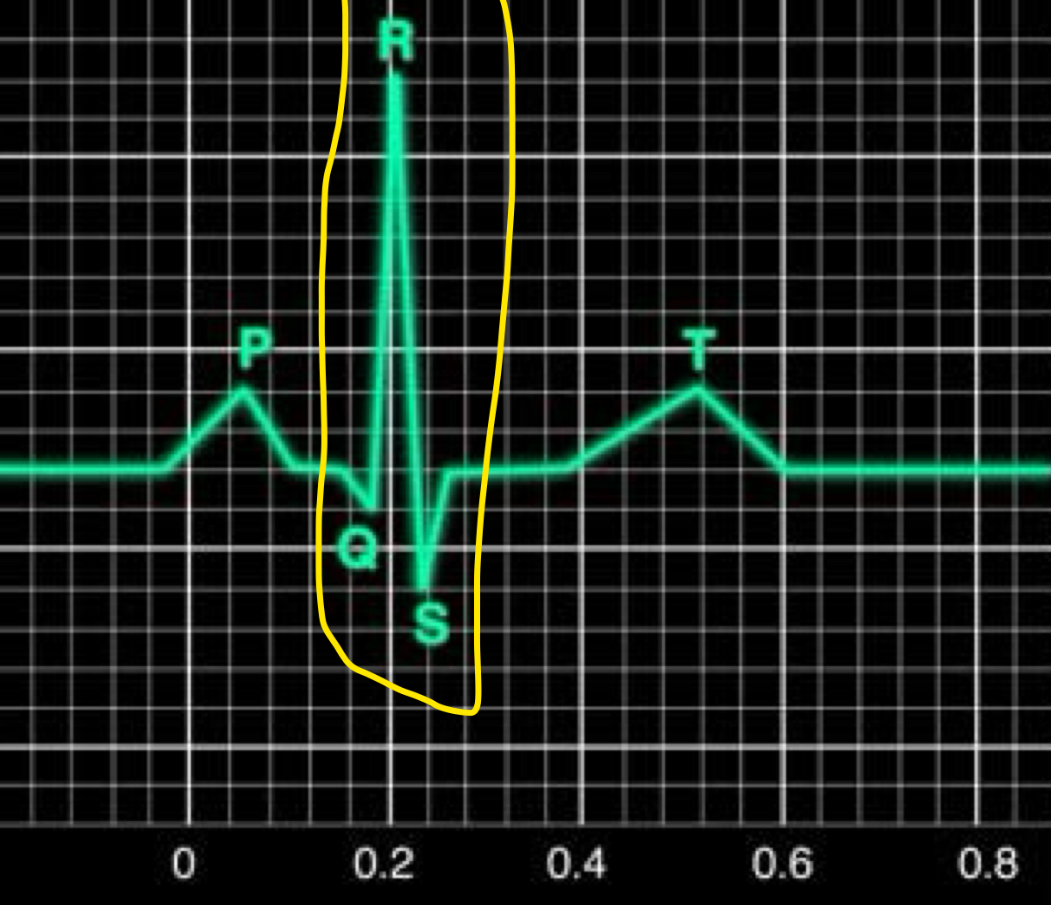
T wave
Ventricular repolarisation
ventricles will relax soon
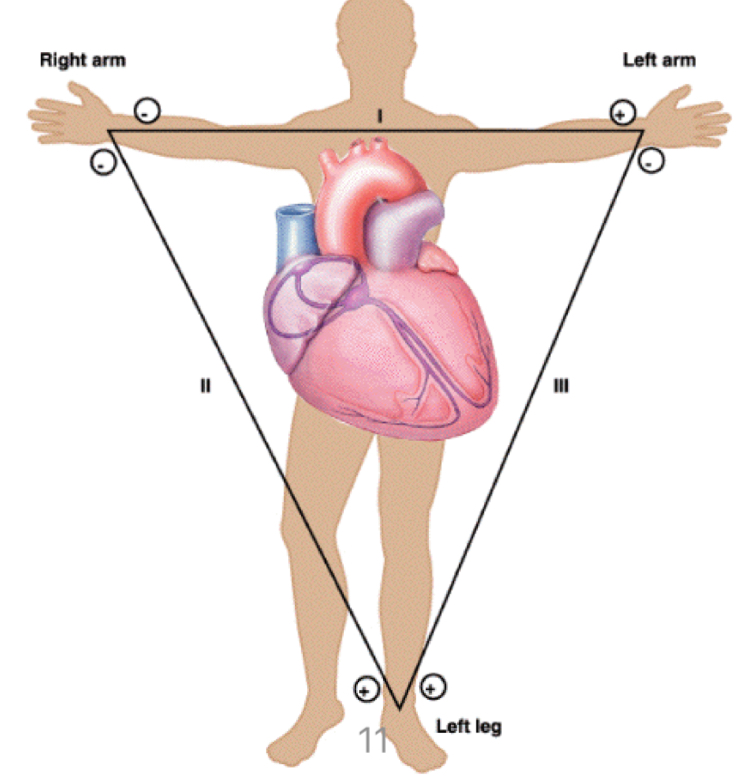
Bipolar limb leads
I,II,III → make up the Einthoven’s triangle
I
Measures from right arm to left arm
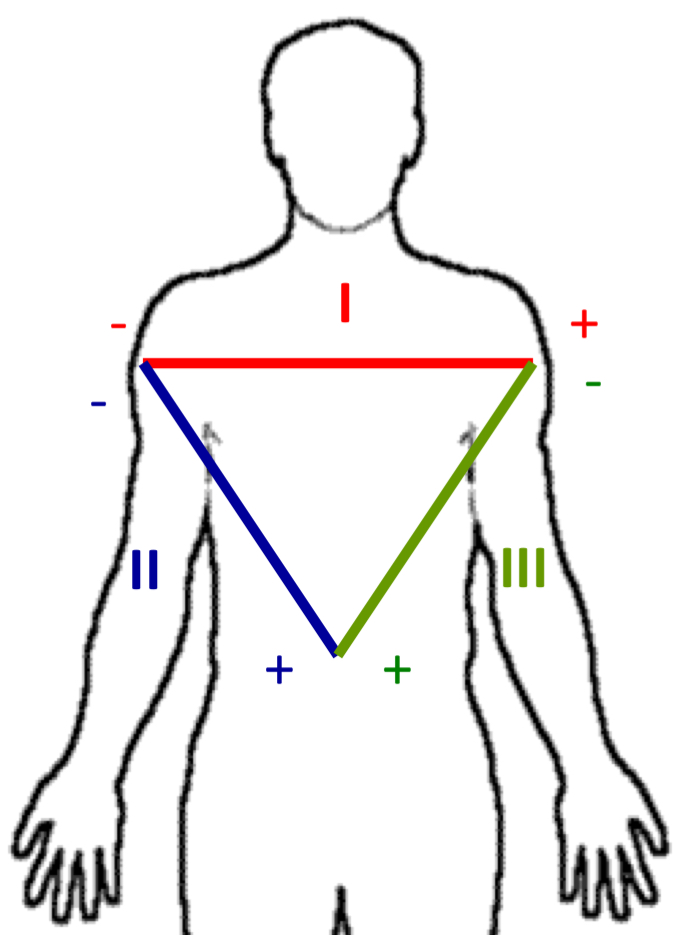
II
Measures between right arm and left leg
III
Measures from left arm to left leg
What happens if there is something wrong at I?
What happens if there is something wrong at II?
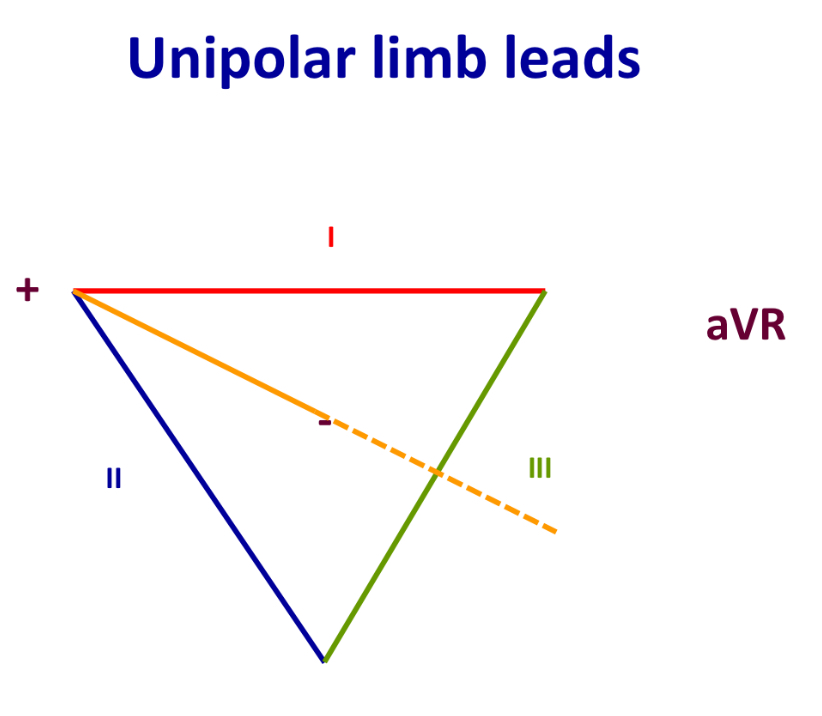
aVR (unipolar lead)
Between I and III
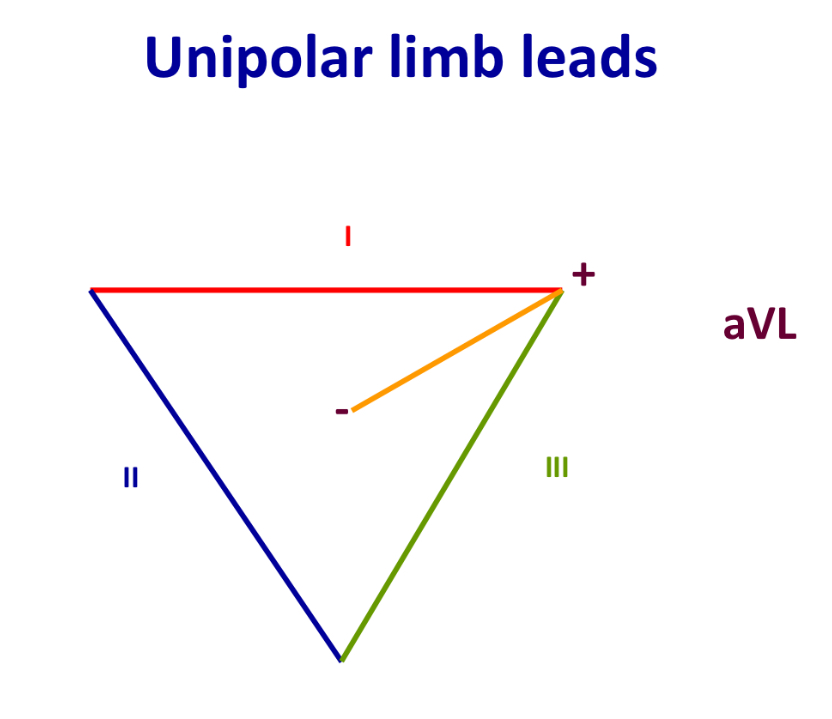
aVL (unipolar lead)
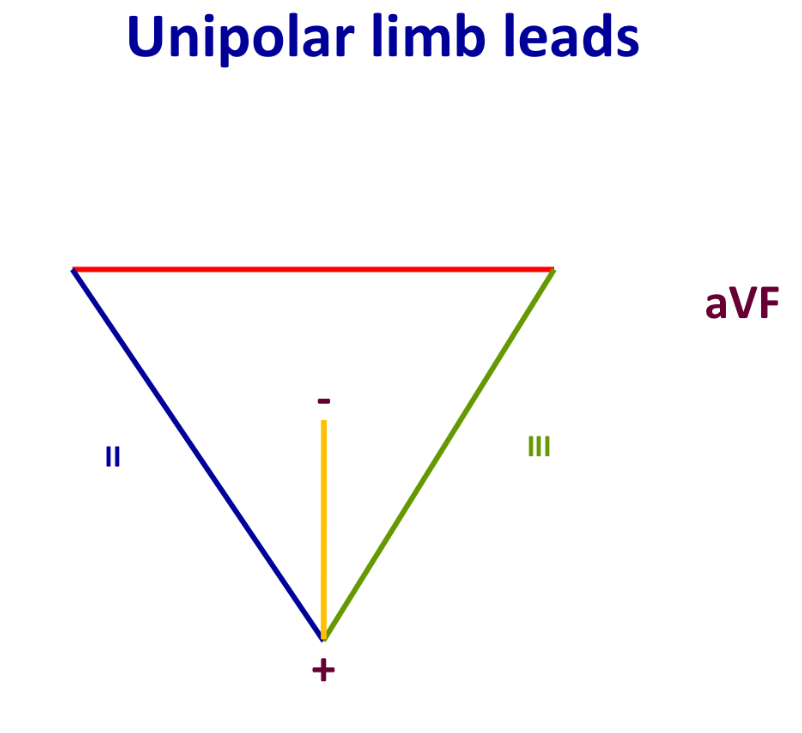
aVF (unipolar lead)
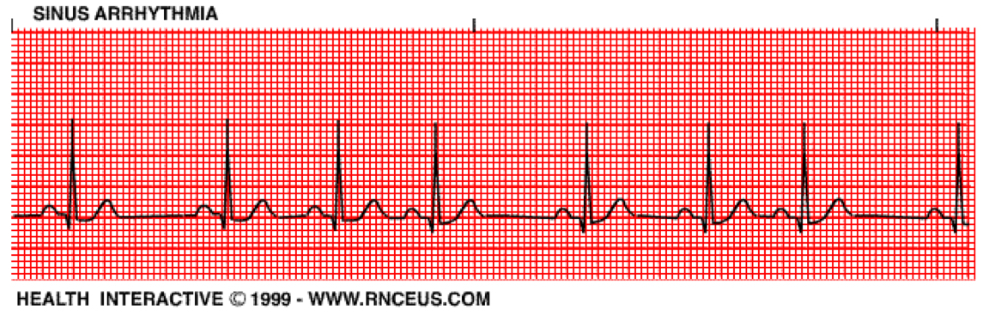
Sinus arrthymia
On inspiration: ↑ HR
On expiration: ↓ HR, cardioinhibitory centres in medulla via vagus nerve