theatres & amphitheaters
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
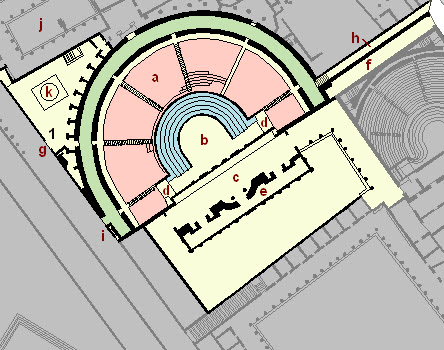
Pompeii Large Theatre
Pompeii, 2nd century BC by the Greeks
Layout: Semi-circular cavea w/ gladiatorial barracks
Construction: Built into a natural hillside.
Decoration: Painted stage buildings, segregated marble seating.
summa cavea
poor section
media cavea
well-off section
ima cavea
public official section

Odeon (Pompeii Small Theatre)
Pompeii, 80 BC next to its larger counterpart
Layout: functional roof to help with acoustics
Construction: Stone, multi-coloured marble sidings
Decoration: Mosaic floors

Amphitheatre (Pompeii, built 80 BC)
Layout: Oval arena, tiered seating, two main entrances
Construction: Sunk below ground with stone and earth embankment.
Function: to assert Roman authority in Pompeii and gain support of the citizens
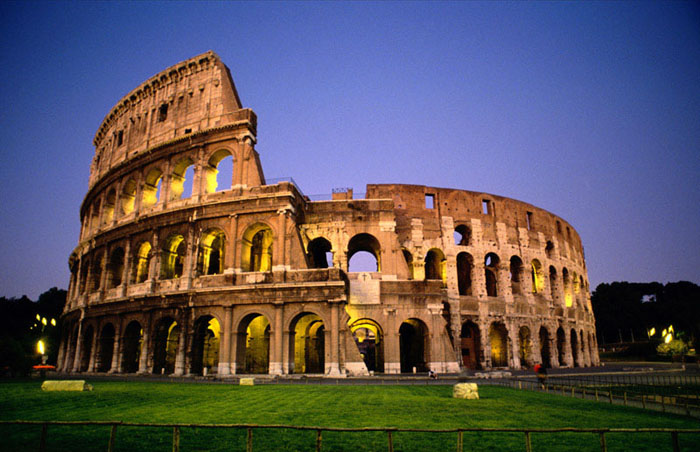

Colosseum - Flavian Amphitheatre (Rome, 70–80 AD)
Funded by the spoils of the Sack of Jerusalem - captives built
Layout: 80 entrance arches (76 - public, 4 - elite), hypogeum (animal underground), vomitoria.
Construction: Concrete, travertine, tufa.
Decoration: Marble seating, statues, different capitals for each storey
The stepped tiers of the Colosseum (cavea) presented a microcosm of the hierarchical Roman social structure. In ascending order, what are each of the levels called
podium (closest to arena) = the elite
maenianum primum = equestrians
maenianum secundum imum = general roman citizens
maenianum secundum summum = foreigners, slaves
maenianum summum in ligneis = women of all classes
Why were women in a separate seating area in the Colosseum?
To provide a visual symbol of the conception of woman as simultaneously part of Roman society, and also set apart from the structural divisions of Roman social order
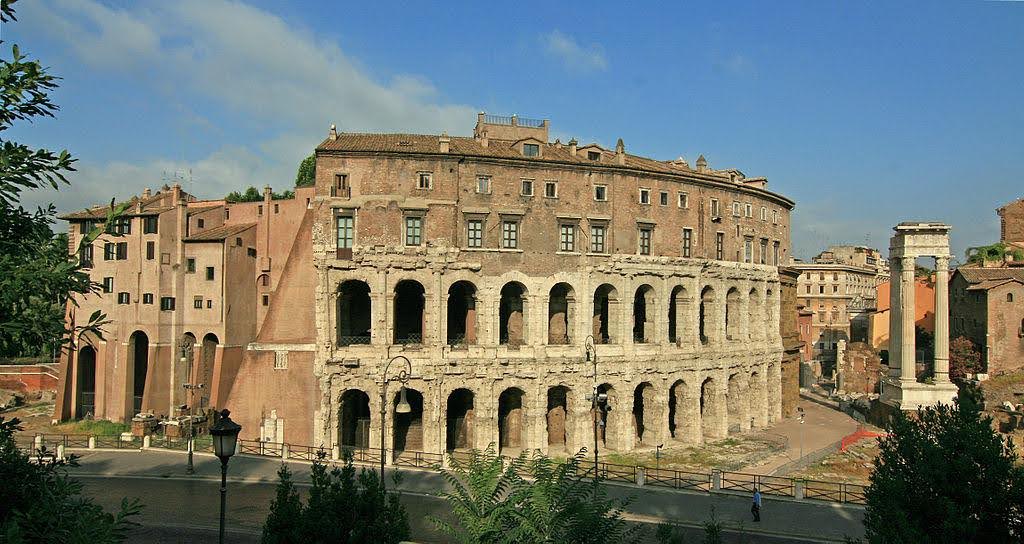

Theatre of Marcellus (Rome, completed 13 BC by Augustus dedicated to his nephew)
Layout: large cavea.
Construction: Concrete, stone, sheathed in white travertine
Decoration: lower tier - doric, middle - ionic, top-corinthian