Costs
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is meant by: Short run?
The short run is when at least one factor of production is fixed.
What is meant by: Long run?
The long run is when all factors are variable.
What is meant by: Fixed costs?
Costs which do not vary with output e.g. rent and salaries
What is meant by: Variable costs?
Costs which vary with output e.g. raw materials and wages
What is meant by: Total cost (TC)?
Total cost = Total Variable` Cost + Total Fixed Cost
TC = TVC + TFC
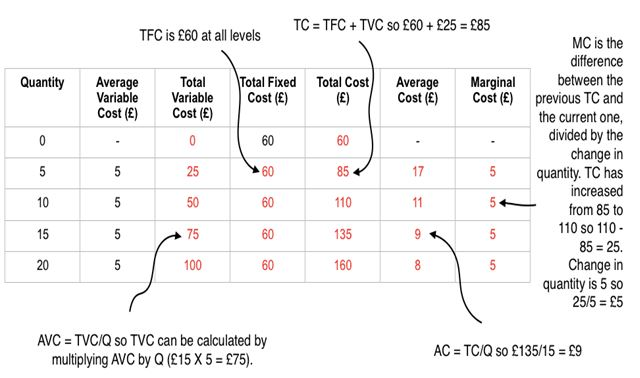
What is meant by: Total fixed cost (TFC) curve?
TFC does not vary with output because fixed costs are fixed!
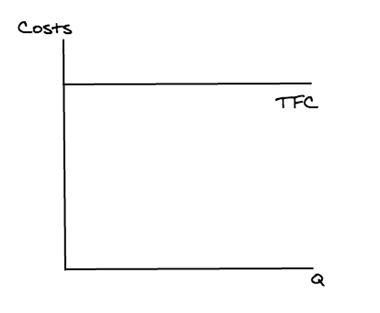
What is meant by: Marginal cost (MC)?
Marginal cost is the cost of selling an additional unit.
MC = ∆TC/∆Q
Diminishing marginal returns (or the law of diminishing marginal returns)
In the short run, as more factors are employed, the marginal returns from these factors will eventually decrease!
What is meant by: Marginal cost (MC) curve?
Explaining why the marginal cost (MC) curve goes down and then up
MC decreases because initially workers will specialise, increase productivity and decreasing marginal cost.
MC will then increase because diminishing marginal returns will set in, which will decrease productivity and increase marginal cost.
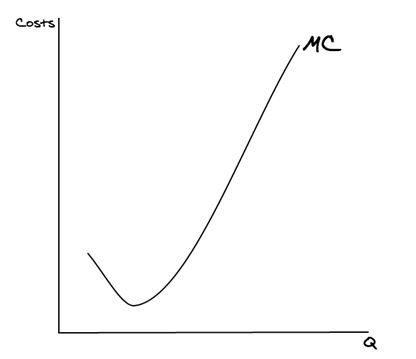
What is meant by: Internal economies of scale?
Internal economies of scale are when long run average costs fall as a firm’s quantity increases.
What is meant by: Types of internal economies of scale (RMFPTM)?
Richard’s Mum Flies Past The Moon
Risk-bearing economies
Managerial economies
Financial economies
Purchasing economies
Technical economies
Marketing economies
What is meant by: Risk-bearing economies?
Bigger firms can use their big profits to diversify into new areas, reducing the cost of failure in one sector.
E.g. Virgin have diversified into 400 different areas.
What is meant by: Managerial economies?
Bigger firms can afford to hire highly skilled specialist managers, increasing a firm’s productivity and decreasing their LR average costs!
E.g. Amazon hire specialist accounting, software and marketing managers.
What is meant by: Financial economies?
Bigger firms are less risky, so they can secure cheaper loans, reducing their long run average costs.
E.g. Alibaba.com borrowed £3bn at a tiny 2% interest rate.
What is meant by: Purchasing economies?
Bigger firms can bulk-buy and negotiate lower prices, reducing their long run average costs!
E.g. McDonald’s purchase thousands of tonnes of chicken breast at a very low average cost.
What is meant by: Technical economies?
Bigger firms can invest in specialist capital, to increase a firm’s productivity and decrease their long run average costs.
E.g. Amazon’s warehouse robots and Kameoka’s robot lettuce farmers have massively increased productivity.
What is meant by: Marketing economies?
Bigger firms can spread their marketing costs across many units, decreasing their long run average costs.
E.g. Guinness, Beats or Nike, who spend millions on marketing in total but just pennies on average, because their costs are so spread out.
What is meant by: External economies of scale?
External economies of scale will reduce long run average cost, as the industry expands.
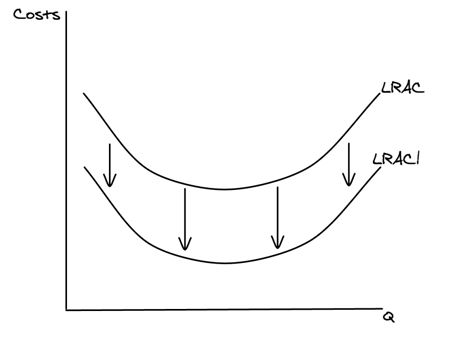
What is meant by: External economies of scale diagram?
External economies of scale will shift the entire long run average cost curve downwards, from LRAC to LRAC1
What is meant by: External economies of scale: lower recruitment costs?
When an industry expands, lots of specialist workers will be move to that area to find work. This makes it easier to recruit workers, reducing a firm’s recruitment costs, decreasing their LRAC.
E.g. In Silicon valley, there are 60,000+ coders which reduces tech firms’ recruitment costs.
What is meant by: External economies of scale: knowledge transfers?
When an industry expands, knowledge will be transferred between firms. This helps firms learn more effective new production techniques, decreasing their LRAC.
E.g. In LA’s film industry, the green screen technique was spread by knowledge transfer. Using green screens has reduced film producers’ long run average costs.
What is meant by: Internal diseconomies of scale?
Internal diseconomies of scale lead to a rise in long run average cost, as a firm expands.
What is meant by: Types of internal diseconomies of scale (ABC)?
Alienation
Bureaucracy
Communication
What is meant by: Alienation?
Workers feel alienated in very large firms, like they’re just another cog in the machine. This leads to demotivation, decreasing productivity, increase LRAC.
E.g. large call centres in India.
What is meant by: Bureaucracy?
Bureaucracy is all the paperwork, managers, filing and secretaries that a firm has to pay for when it expands, increasing LRAC.
What is meant by: Communication?
In big firms, employees may argue with each other and communication will be slow because big firms have so many layers. These factors will reduce productivity, increasing LRAC.
What is meant by: Average Variable Cost formula?
AVC = TVC/Q
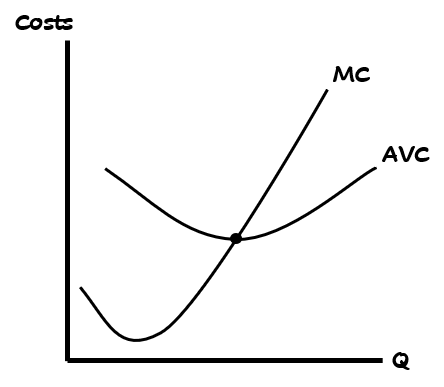
What is meant by: MC & AVC relationship?
When MC is below AVC, AVC will decrease
When MC is above AVC, AVC will increase
When MC = AVC, AVC is at its lowest
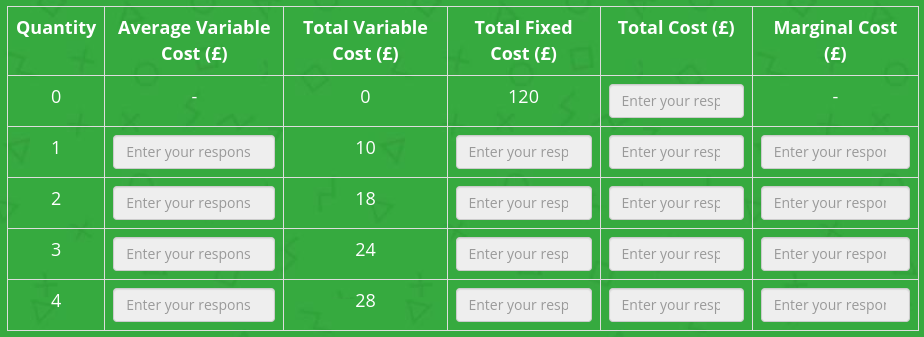
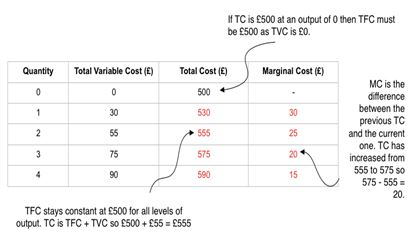
Complete the table.
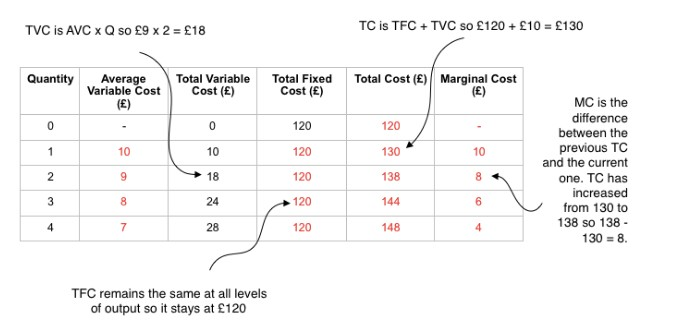
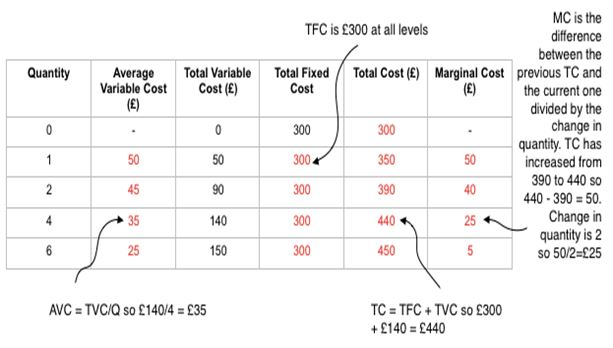
Model answer
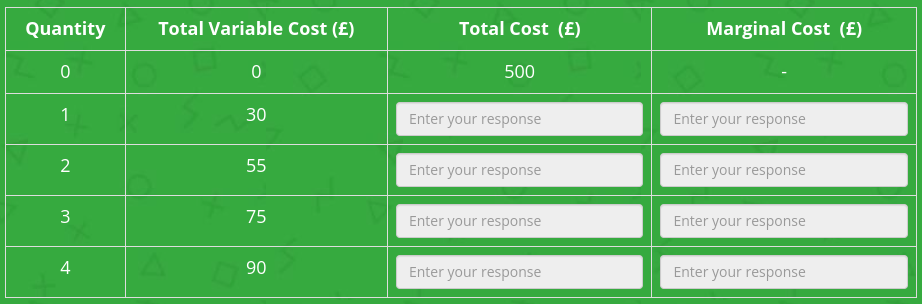
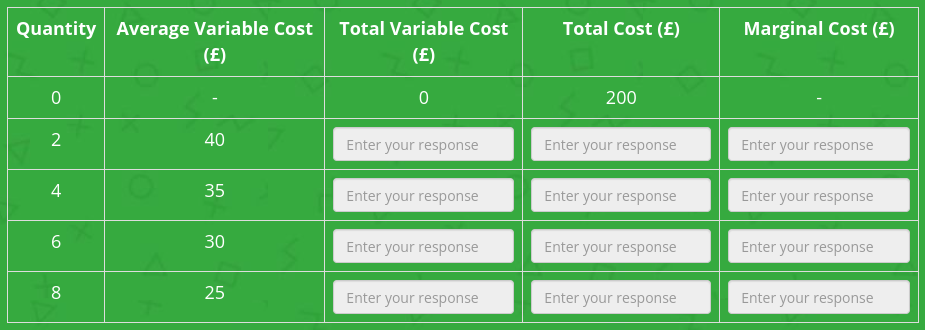
Complete the table.
Model answer
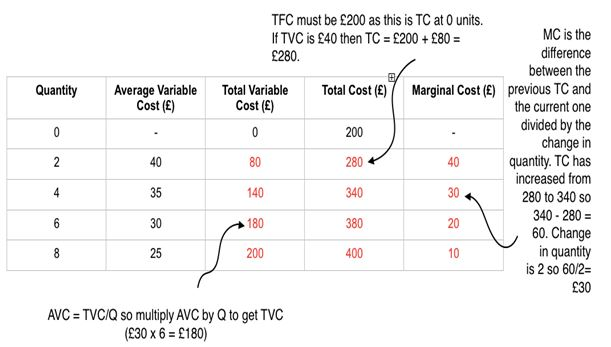
Complete the table.
Model answer
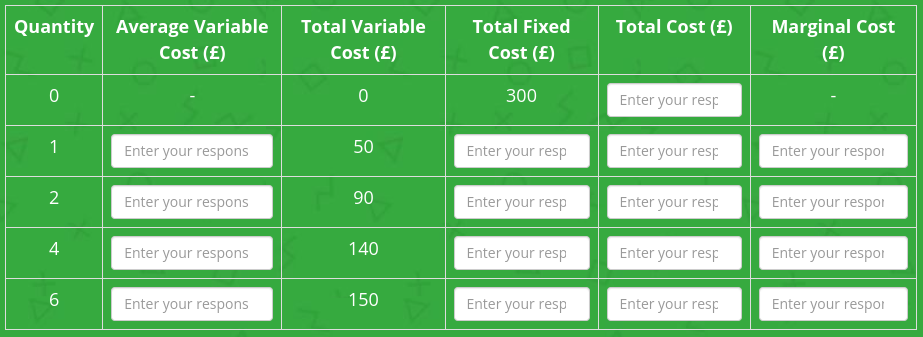
Complete the table.
Model answer
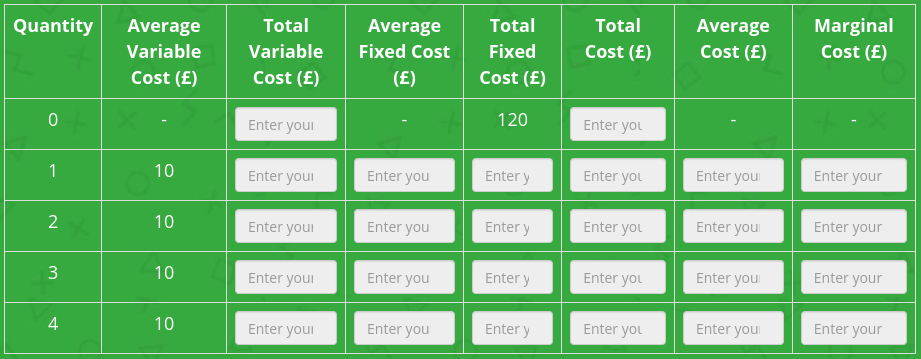
Complete the table
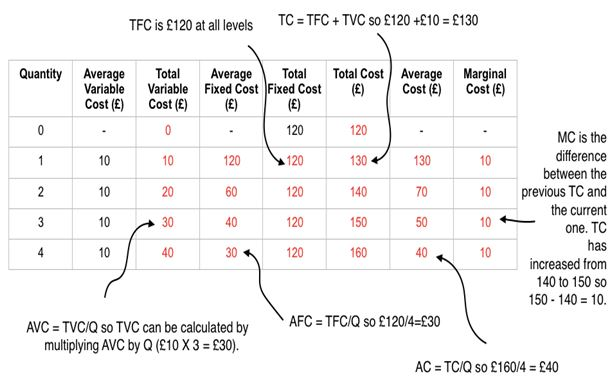
Model answer
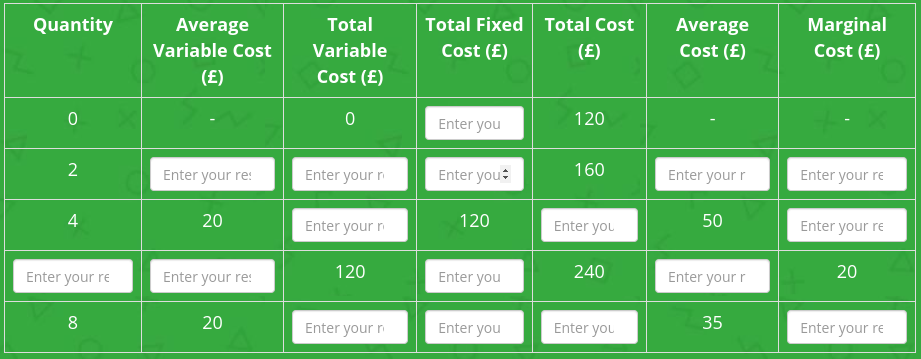
Complete the table
Model answer
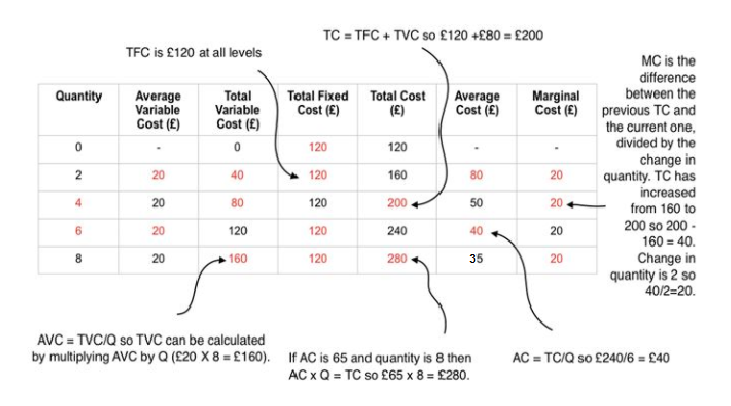
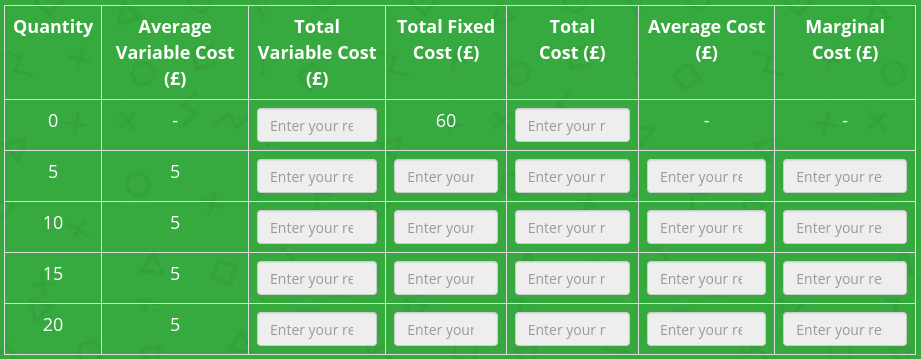
Complete the table
Model answer