Thermal Physics and Ideal Gases
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is the triple point of a substance?
One specific temperature and pressure where the 3 phases of matter (solid, liquid and gas) of that substance can exist in thermal equilibrium
There is no net transfer of energy (thermal) between the phases
What is the triple point of water? (Pressure and temperature)
0.01 °C
0.61 kPa
What is meant by thermal equilibrium?
There is no net flow of thermal energy between the objects of the same temperature
What is meant by temperature?
How does this work with a hot object being placed next to a cold object?
A measure of the hotness of an object
Net flow of thermal energy from the hotter object goes to to the colder object, lowering the temperature of the hotter object
What does the 0th law of thermodynamics mean?
If 2 objects are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, then all 3 objects are in thermal equilibrium with each other
What are the 2 fixed points on the Celsius temperature scale?
Why is the Celsius scale not perfect?
The Freezing point (0 °C) and Boiling point (100 °C) of pure water at 1 atmospheric pressure
The scale is not perfect as the points vary depending on the surrounding atmospheric pressure
What are the 2 fixed points in the absolute scale?
Triple point of pure water
Absolute zero (lowest possible temperature)
What is the SI unit of temperature on the absolute scale?
K (Kelvin)
What is meant by absolute zero?
The lowest possible temperature (internal energy is at a minimum, KE is 0 but there is still some electrostatic PE)
How would you calculate the absolute scale value of a temperature from the Celsius scale?
Temp (K) = θ(°C) + 273
What is meant by the kinetic model?
It describes how all substances are made up of atoms or molecules which are arranged differently depending on the phase of the substance
Describe a solid using the kinetic model?

Atoms or molecules are regularly arranged and packed closely together
They have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between them
They are in a fixed position, but they can vibrate as they have minimum kinetic energy
Describe a liquid using the kinetic model?

Atoms or molecules are still very closely together, but they have more kinetic energy than solids
They can change position and flow past each other
Describe a gas using the kinetic model?

Atoms or molecules have much more kinetic energy than liquids.
They are much farther apart and are free to move past each other as there are negligible electrostatic forces between them
They collide with each other or the walls of the container
They move with random speeds and directions
Brown recorded his observations of the random movements of fine pollen grains floating on water. He called it a term called Brownian motion
What is Brownian motion?
Showed that particles move in random/ haphazard, erratic movements
What did Einstein say about Brownian motion, and what did this provide evidence for?
The collisions were elastic and resulted in a transfer of momentum from the water molecules to the pollen grain, causing the grain to move in a haphazard way
Proved the Kinetic model as matter is made up of atoms and molecules and they have kinetic energy
How can Brownian motion be observed?
Use a diagram

Can be observed using a smoke cell
What is the relationship between density and phase?
The spacing between the particles in a substance in different phases affects the density of the substance
A substance is more dense when solid and least dense when in a gaseous phase (usually)
What is meant by internal energy?
The sum of the randomly distributed kinetic and potential energies of the atoms or molecules within a substance
What is meant by electrostatic potential energy and what does it mean if it has a negative value?
The energy stored between the particles
If it has a negative value, energy must be supplied to break the atomic/ molecular bonds
How does the internal energy of a substance change when its temperature is increased?
Increasing the temperature will increase the internal energy, this is because as temperature is increased, the average kinetic energy of the atoms/ molecules increase
The hotter an object, the faster its moving (higher internal energy)
How does the internal energy of a substance change when it changes phase?
The electrostatic potential energy increases significantly
When a substance reaches melting or boiling point, when it is changing phase, the energy transferred does NOT increase temperature, instead the electrostatic potential energy increases as the electrostatic forces between the molecules/atoms change
What is the difference in the electrostatic potential energy of a solid, liquid and gas?
Gas- electrostatic PE is 0, because there is negligible electrostatic forces between particles
Liquid- PE is a Negative value, as it requires energy to break the atomic/molecular bonds
Solid- electrostatic PE is a large negative number, because there are very large electrostatic forces holding the particles/ molecules together
What is the definition of specific heat capacity?
The energy required to increase 1 kg of a substance by 1 Kelvin (K) without a change in state
What are the units for specific heat capacity?
JKg^-1K^-1
What is the equation for specific heat capacity?
c (SHC) = E (energy) / m (mass) X Δ° (change in temperature)
Sketch the apparatus that can be used to determine the SHC of a solid?

E= IVt
I is the current in the heater, V is the p.d across the heater and t, is the time taken to increase the temperature
c= IVt/ mΔ°
Sketch the apparatus that can be used to determine the SHC of a liquid?
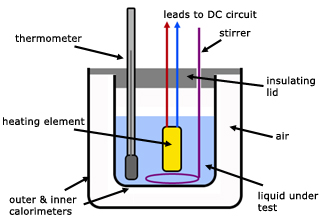
E= IVt
I is the current in the heater, V is the p.d across the heater and t, is the time taken to increase the temperature
c= IVt/ mΔ°
How can the “method of mixtures” be used?
Known masses of 2 substances at different temperatures are mixed together
Recording their final temperature at thermal equilibrium allows SHC of one of the substances to be determined if the SHC of the other is known
How is specific latent heat defined?
energy required to change the phase per unit mass while at a constant temperature
What is the equation for specific latent heat?
L (SLH) = E (energy supplied to change phase) / m (mass)
What is the difference between specific latent heat of fusion and specific latent heat of vaporisation?
Fusion (Lf) → A solid changing to a liquid
Vaporisation (Lv) → A liquid changing to a gas
Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to determine the SLH of fusion of water?
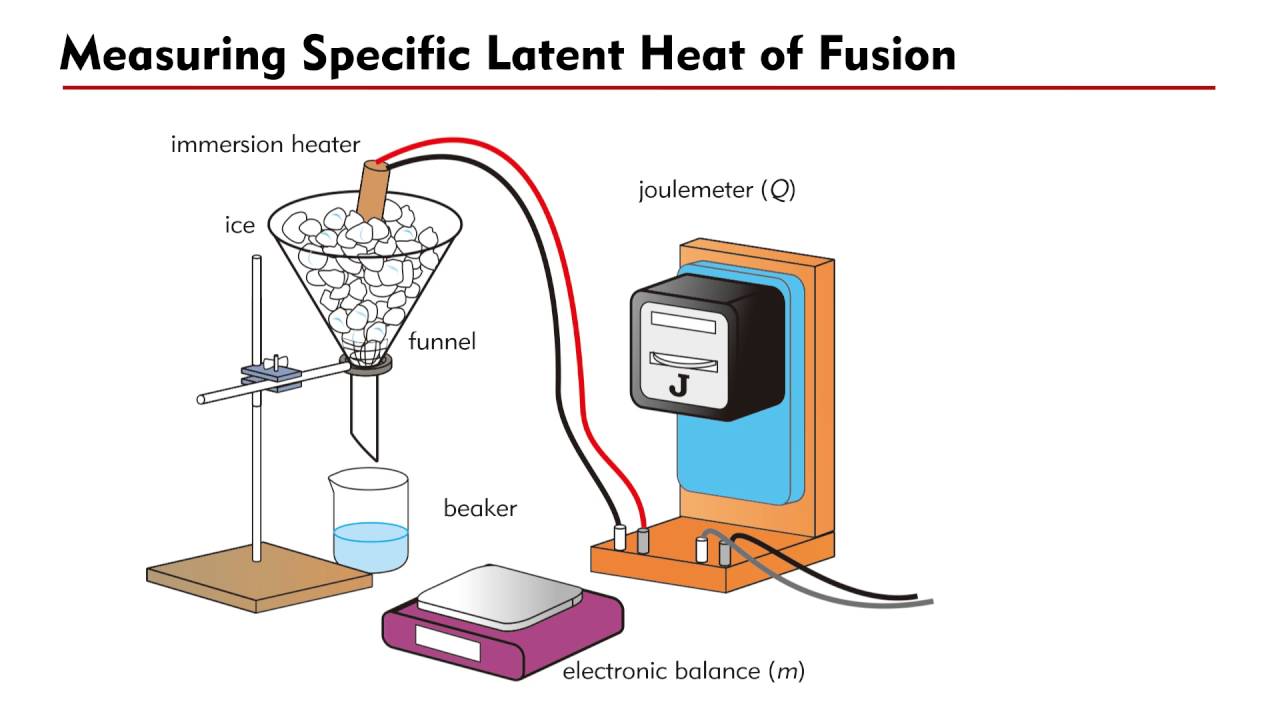
Lf= IVt/m
Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to determine the SLH of vaporisation of water?

Lv= VIt/m
Why is specific latent heat of vaporisation of a substance often much larger than the specific latent heat of fusion?
There is a much larger difference between the internal energy of a gas and liquid than between a liquid and a solid
Describe what happens (in terms of energy) when an object condenses or freezes?
It has less internal energy than the phase before
How does a temperature-time graph show specific latent heat and how do you calculate total energy from this graph
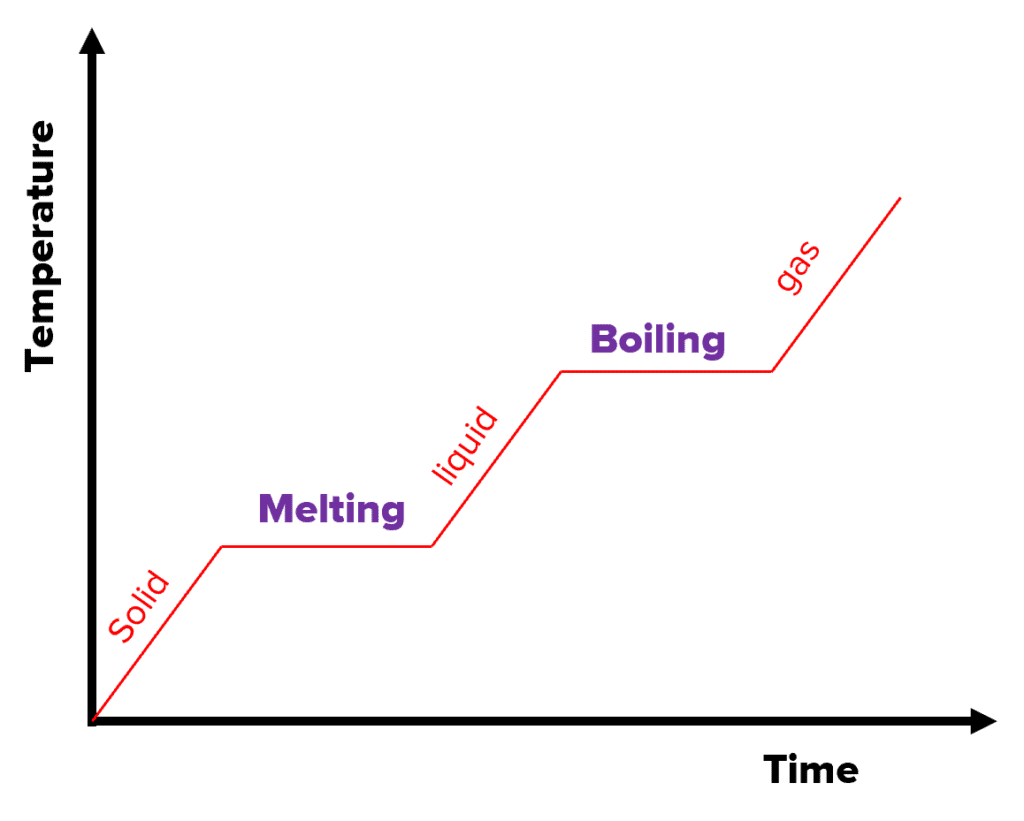
Add up the area under the graph to calculate total energy
How is one mole defined?
The amount of a substance (mol) that contains as many atoms/molecules as there are atoms in 12g of C-12
What is Avogadro’s Constant?
6.02×10^23
What is the equation that can be used to calculate the number of atoms in a substance?
N (no. atoms in a substance) = n (no. of moles) X Na (Alvogado constant)
What is Molar mass, M?
How can this be calculated?
The mass of one mole of a substance
m (mass of substance) = n (number of moles) X M (molar mass)
What are the 5 assumptions made in the kinetic model of an ideal gas?
the gas atoms/molecules move in random directions with random speeds
The volume occupied by atoms/molecules are negligible compared the volume occupied by the gas
The collisions of the atoms with each other and the container walls are elastic (Ke is conserved)
The time taken for the collisions of the atoms/molecules are negligible compared to the time between the collisions
Electrostatic forces between the atoms/molecules are negligible except during collisions
Why does a gas exert pressure on its container?
Gas particles move randomly and collide with the walls of the container, they exert a force on the walls due to the change in momentum.
The combined effect of many collisions per unit area results in the gas exerting pressure on the container.
What is the total change in momentum when a single molecule of gas collides with the wall of the container elastically?
-2mu
-2 X mass X initial speed
Use Newton’s 2nd and 3rd law to write an expression for the force exerted on the container wall of the container during a collision?
p= F/A
The momentum of each gas molecule changes in an elastic collision with the surface
Force on the molecule from the surface= rate of change of momentum (N2L)
Force on the surface is equal and opposite tot he force on the molecule (N3L)
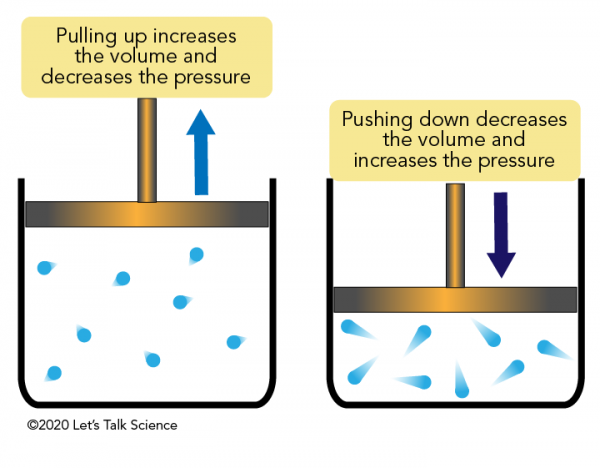
If the temperature and mass of an ideal gas remain constant, how are pressure and volume related (Boyle’s law)?
P (pressure) is indirectly proportional to volume
P is directly proportional to 1/V
Sketch the graph for the results of Boyle’s Law?
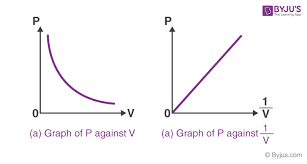
If the volume and mass of an ideal gas remain constant, how are pressure and temperature related?
Pressure is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, T in Kelvin
Sketch the graph that would show the relationship between pressure and temperature?


What expression can be used to create a constant using p, V and T?
pV/T = constant
What is the equation of state for an ideal gas to find the number of moles?
pV= nRT
R is molar gas constant
n is number of moles
What is the average velocity of particles in a gas?
The root mean squared speed, this because velocity is a vector, the average would be 0ms^-1 as the velocities of such a large number of particles would cancel out
How is root mean squared speed calculated?
Find the squares of the velocity
Find the mean of the squared velocities
Find the square root of the mean
How is the r.m.s speed of particles in an ideal gas related to pressure and volume?
pV=1/3 N m —c² (bar over c²)
Pressure X Volume = 1/3 X number of particles X mass of each particle X mean square speed
Sketch a graph to show the distribution of speed of particles in a gas at a given temperature (Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution)

How does the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution change if the temperature is increased?
The hotter the gas, the greater range of speeds
The most common (modal) speed and r.m.s speed increase as distribution is more spread out
What is the value of the Boltzmann constant (k)?
1.38X10^-23 JK^-1
k
How is the Boltzmann constant related to the molar gas constant?
k= R/ Na
Boltzmann constant= Molar gas constant / Avogadro constant
The equation of state is PV= nRt
How can this be expressed using the Boltzmann constant?
pV= (n X Na) X k X T
N= n X Na
pV= NkT
pV = 3/2 k T
What is the equation relating mean kinetic energy of the particles and the temperature of the gas, and what unit of temperature must be used?
½ m —c²
½ X mass X mean square speed
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to Temperature (Kelvin)
Kelvin
At a given temperature all molecules in a gas have the same mean kinetic energy.
Explain why different molecules in the gas have different r.m.s speeds?
They have different masses, therefore their r.m.s speeds will be different