material sciences
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
define medicine
formulated drug product that contains active drug substance
define ‘solid particle’
solid drug particles contain many drug molecules
drug molecules pack together to make particles
what 2 structures can solids take
amorphous
crystaline
what is the difference between amorphous and crystalline solids
amorphous means having no definite form or distinct shape - lacks structure
crystalline means solid has rigid, repeating structure
what are the characteristics of amorphous solids
fast dissolution
dissolves in any temp
stable without water
collapses in presence of water
has critical formation temp
what are the characteristics of crystalline solids
slow dissolution
in higher temps, it will dissolve faster
stable with or without water
has melting point
different arrangements
define crystalline solid
where molecules are arranged in repeating pattern aligned with each other
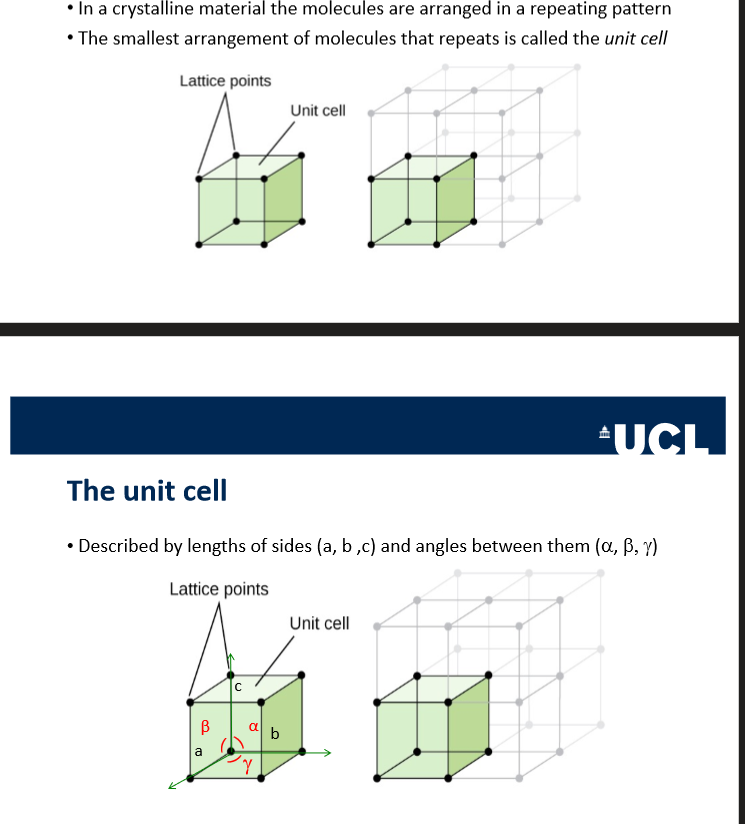
in crystalline structure, what is the name given to the smallest arrangement of molecules that repeats
unit cell
in crystalline structures, what is a ‘habit’
habit is the shape of the crystal
same unit cell can grow into different habits
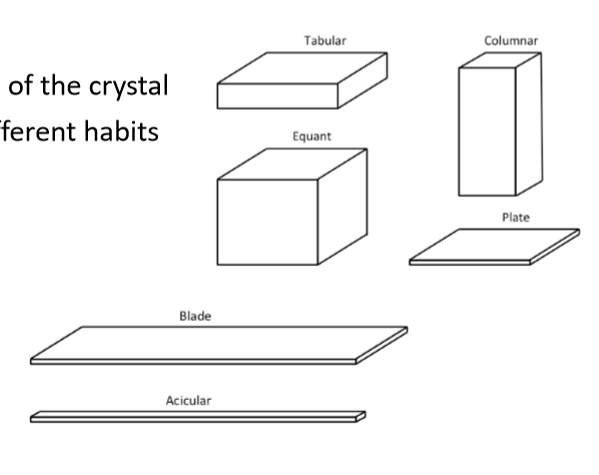
how many habits exist
6
why is habit (shape) important for crystalline structures
because shape affects powder flow, compaction and dissolution
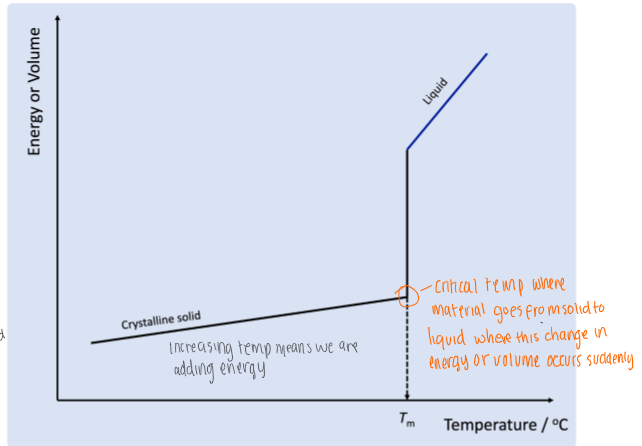
for a crystalline solid, this graph shows what happens to energy as temp increases - the crystal will melt at specific temp.
why are molecules with the lowest energy or volume the most stable
because:
the molecules are in the closest packed arrangement
it will have the highest crystal lattice energy which means it has the strongest bonds so the most energy is required to break the bonds
when creating these bonds, the most energy is required to form these bonds again - system loses the most energy
what makes a material polymorphic
polymorphism is when the molecules can arrange in more than one pattern

polymorphism true or false:
different molecule, same unit cell
strength of bonds between molecules are same
will affect melting point, enthalpy of fusion, dissolution rate, solubility and habit
false - same molecule, different unit cell
false - strength of bonds between molecules are different
true
how to determine which polymorphic form will be the most stable
form with the strongest intermolecular bonds and is the lowest energy form
true or false: each polymorph has different thermodynamic stability
true
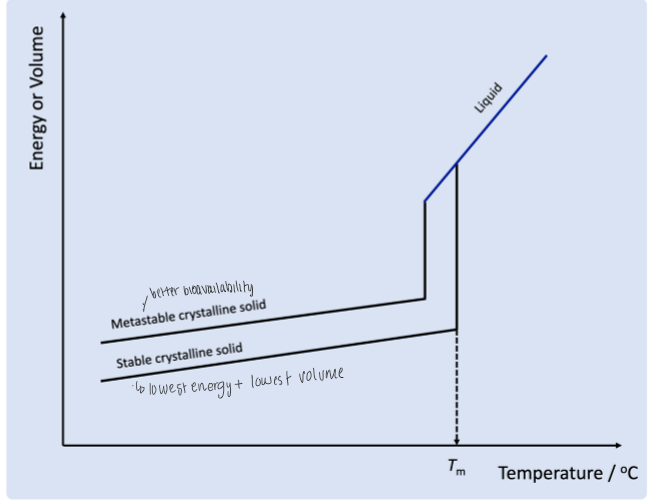
polymorphic graph
note that Tm means melting point temp
why are metastable crystalline solids at a higher energy/volume
because this form has weaker bonds and eventually will convert to stable form
why does metastable crystalline solid have higher bioavailability compared to stable crystalline solid (use graph in previous flashcard)
if you cool structure down too quickly, then the structure will not form as strongly packed structure so it is easier to dissolve
characteristics of polymorphs
each form has own melting point
each form has own enthalpy of fusion
if molecules are tightly packed together, bioavailability will be [lower/higher] because it is [easier/harder] to overcome bonds and dissolve
if molecules are tightly packed together, bioavailability will be [lower/higher] because it is [easier/harder] to overcome bonds and dissolve
there is a second component in unit cells which can either be solvents or water.
what is hydrate
what is solvate
if second component is water, material is hydrate
if second component is solvent, material is solvate
how to determine what type of hydrate material is (ie. monohydrate, dihydrate, hemihydrate)
dependent on drug: water ratio
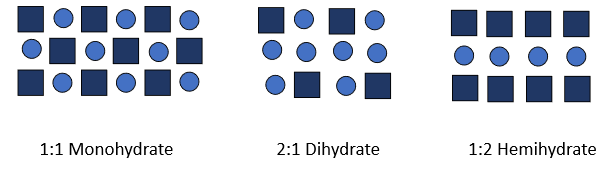
why is it harder to dissolve a hydrate and what impact does this have on bioavailability
because water forms strong hydrogen bonds to drug which can make it harder to dissolve. this results is lower bioavailability than anhydrous materials
cyrstalline materials have no water
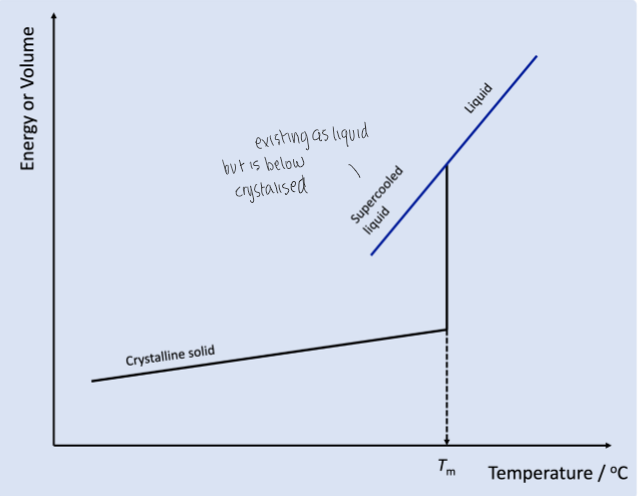
in simple terms, what is a amorphous material
material with molecular structure of liquid but viscosity of solid
high viscosity liquid - acts like a solid but particles are randomly arranged
e.g. glass - molecules are randomly arranged so some light goes through and it appears transparent or translucent vs crystalline structure has regular arrangement of molecules
what happens to a material if it is allowed to cool slowly
particles have time to arrange into regular structure so forms crystalised structure
viscosity is low when temp is high but upon cooling down, this thickens the material
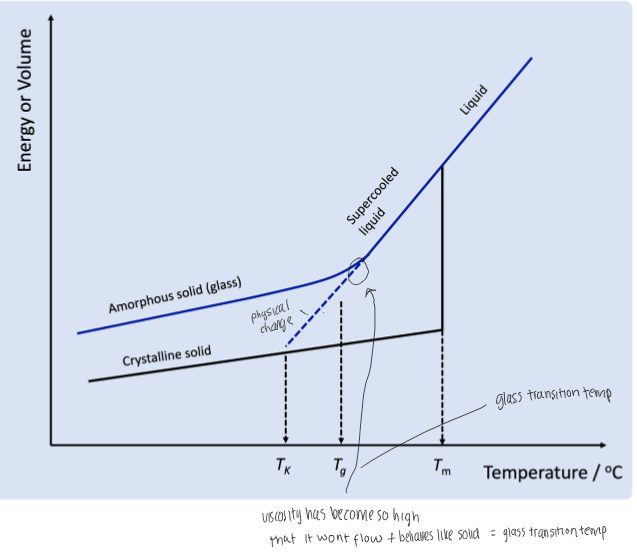
what is the glass transition temp
temp at which viscosity has become so high that it wont flow and behaves like a solid
true or false: amorphous materials will not melt on heating
true
why do amorphous materials have fast dissolution rates
because there is no crystal lattice energy to overcome
true or false: amorphous materials have higher solubilities
true
what is the disadvantage of having faster dissolution rates
material is more unstable
true or false: for amorphous materials, there is no melting point
true