Module 1: Topic 1: Scope of Clinical Biochemistry
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Reasons for Requesting Tests
to establish/confirm a diagnosis
to reassure a patient
to avoid litigation
to monitor disease state
monitor therapy progress
for population screening
Clinical Specimens: Bodily fluids/excreta
saliva e.g. micro, drugs
urine e.g. amylase
blood e.g. troponins, cholesterol
cerebrospinal fluid e.g. multiple sclerosis
faeces e.g. micro
Clinical Specimens: Tissue samples
biopsy e.g. surgery, needle biopsy
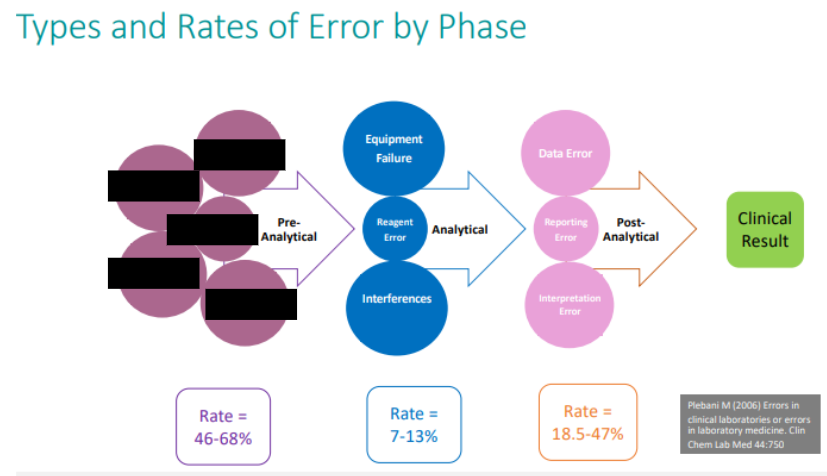
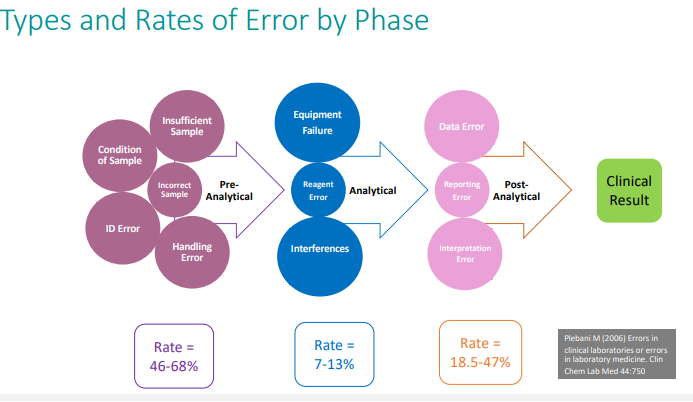
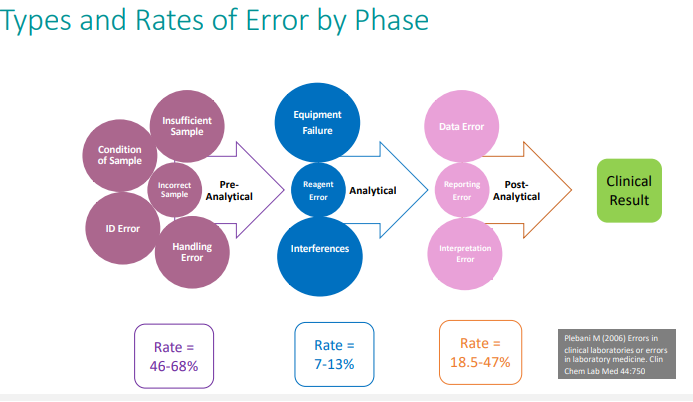
Approximately what % of diagnostic errors occur in which diagnostic testing cycle phase?
pre-analytical phase
Pre-analytical errors are detected in ____ phases
all three phases: pre-, analytical and post-
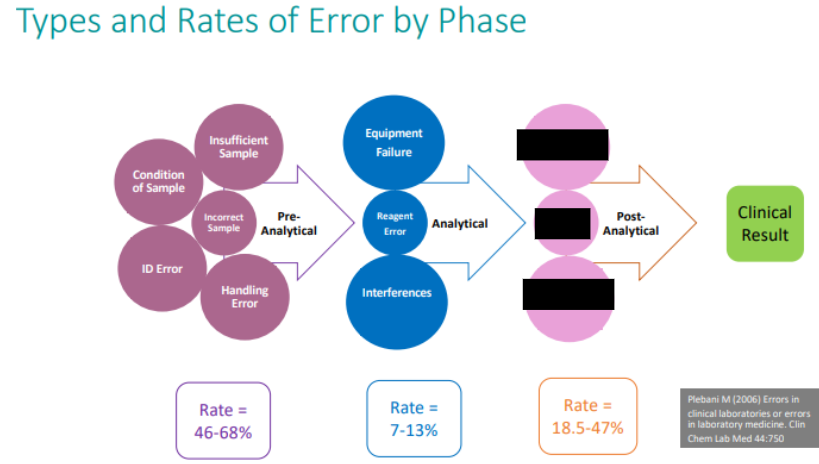
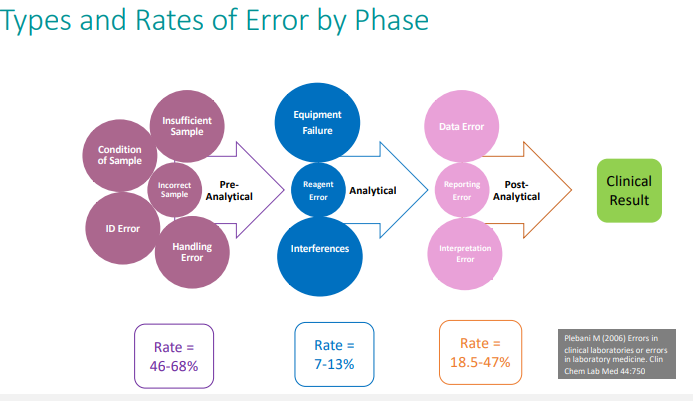
Types of Patient ID
critical and unambiguous patient ID
name
DOB
gender
UR or barcode
Location
name of medical prac
time, date + collectors signature on test request
Reducing Sample Variability in Pre-analytical Errors:
patient ID checks
quality management
Reducing Sample Variability in Reagents, instrumentation, use of standards?:
standards used to monitor performance regularly
Reducing Sample Variability in Labelling and data handling?:
appropriate protocols in place
Reducing Sample Variability in Lab accreditation:
comparison of standard samples between labs
What are some errors in Blood Sampling and Explain?
blood sampling technique
haemolysis w release of RBC Contents (K+, proteins, enzymes)
stasis during venipuncture
water diffuses away from plasma falsely increasing plasma content lvl
not enough specimen taken
insufficient test material
errors in timing
cholesterol measurement from unfasted patient
container not appropriate for specimen
anticoag use
inappropriate sampling site
downstream of intravenous line
incorrect specimen storage
prolonged blood storage at 4 degrees C or freezing of speciment harvested for blood count
What are some sources of variation prior to analysis?
Patient related:
- cyclical biological changes
- medication and smoking
- exercise
- stress
- posture
Collection:
- preservation
- anticoagulation
- haemolysis
- contamination
- Patient ID
After collection:
- sample transport and storage
Types of Testing Errors: random errors affecting Precision
What is the cause?
What type of distribution is seen?
unknown and unpredictable sources
Normal distribution
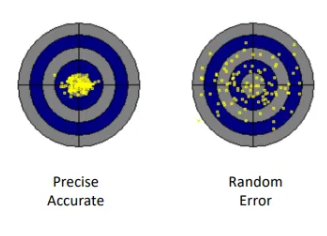
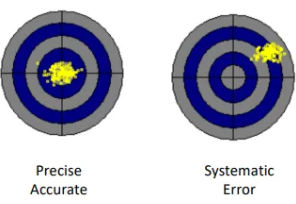
What is Precision and how is it determined?
a measure of how closely measurements cluster together and is limited by random errors.
determined by repeating measurements
Types of Testing Errors: systematic errors affecting Accuracy
What is the cause?
operator error or from measuring instruments
Systematic errors can show ____: alteration from standard values with pattern of divergence
Trend
Systematic errors can show _____: abrupt change in measurements
Shift
What is Accuracy and what reduces it?
Measure of how closely measurements is to the true value of the quantity being assayed and is often reduced by systematic errors
What type of systematic error is a constant error?
specific difference between new/test and reference methods
What type of systematic error is a proportional error?
variable difference between new/test and reference methods
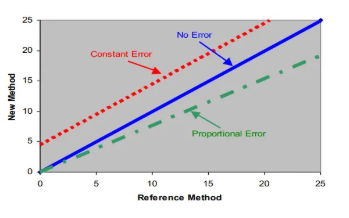
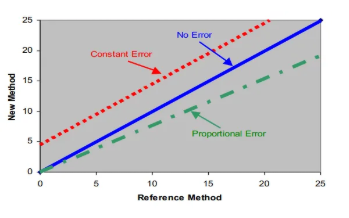
What are some causes of errors?
input data req - such as standards used, calibration values
instruments used - accuracy, repeatability
observer fallibility - reading errors, blunders, equipment selection, analysis and computation errors
environment - any external influences affecting measurement
what information is required to interpret results and what questions can we ask about the lab data and tests?
req info on N pop variability
what is the reproducibility of test results?
what is the test sensitivity/specificity?
what is the term for random changes that reduce agreement between replicate measurements?
imprecision
what type of imprecision defines the difference between results for the same specimen when assayed repeatedly at the same time?
Within-assay Imprecision
what type of imprecision defines the difference between results for the same specimen when assayed repeatedly at different times?
Day-to-day imprecision
What does coefficient of variation express?
expresses precision and should be as close to zero as possible
what is the coefficient of variation equation?
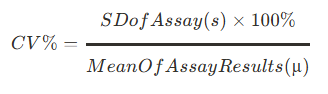
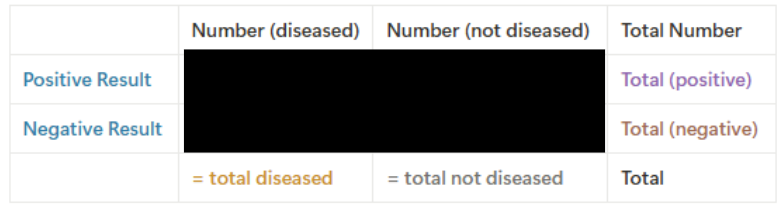
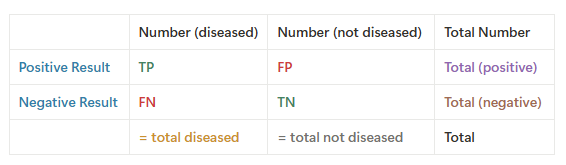
What is Sensitivity?
a measure of positive results
a measure of freq of a POSITIVE test result when a particular disease is present
sensitivity represents the percentage of TP results out of TP + FN results
What is Specificity?
a measure of negative results
a measure of freq of NEGATIVE test results when a particular disease is present
specificity represents the percentage of TN results out of TN + FP results
What is the equation for test sensitivity?
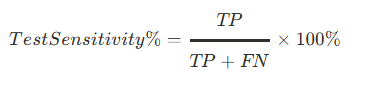
What is the equation for test specificity?
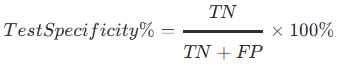
How is the usefulness of tests expressed visually?
as receiver operating chracteristic curves (ROC)
the greater the area under the curve = the more useful the test
What types of instruments are available for biochemical analysis?
Spectrophotometry
Atomic absorption
Nephelometry
Electrodes
Electrophoresis
Immunoassay
HPLC
What is spectrophotemtry? and what is it most used to measure?
the technique is defined as: “measurement of light by a specific molecule”
used most freq to measure the amount of purity of molecule in solution
What is the principle of atomic absorption spectroscopy?
principle: flame dissociates metal from chemical bonds > unexcited (ground) state
light from hollow cathode lamp (0.01 nm bandwidth) enters flame and is absorbed by ground state atoms > decreasing intensity
what does nephelometry measure?
measurement of precipitation of antibody:antigen complex from solution
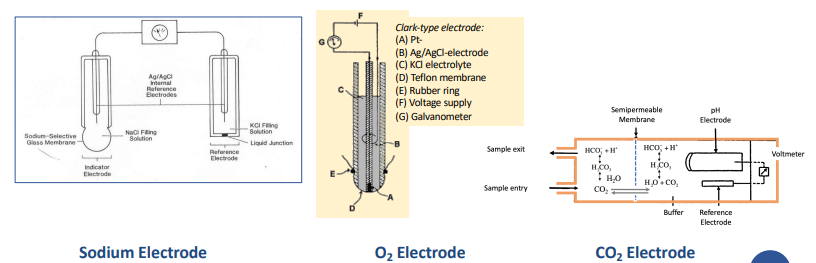
What are Ion-Selective electrodes used to measure?
measure the concentration of specific ions in a solution.
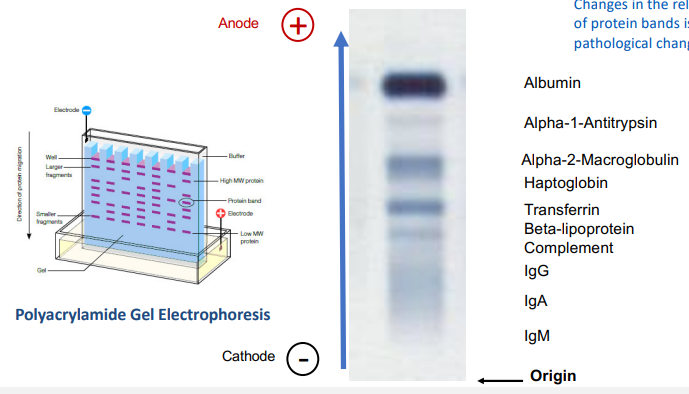
What is the principle of electrophoresis
principle: Zone electrophoresis is migration of charged particles in a support medium within an electric field
proteins are zwitterionic - can be negatively or positively charged depending on solution pH
What is migration dependent on in electrophoresis?
electric charge of molecule
size and shape of molecule
electric field strength
properties of support
temperature
what does changes in reletive band intensity represent in serum protein electrophoresis?
imformative of pathological changes
How do immunoassays work?
use antibodies to bind specific molecules:
selective purification of target molecules
highly sensitive detection
quantitation by measurement of signal intensity
What three types of immunoassays are mentioned? and how do these differ
Two-site immunometric assay
Antigen binds between two antibodies (solid phase and labeled antibody). The activity of the label bound is proportional to the amount of antigen.
Limited reagent or competitive immunoassay standard curve
Limited reagent: Labeled antigen competes with unlabeled antigen for a limited amount of antibody binding sites.
Immunolite automated immunoassay
What is HPLC
Application: Separating and quantifying a wide range of compounds.
Principle: Components in a sample are separated based on their interactions with a stationary phase and a mobile phase.